Application Note. Tomoyoshi Soga
|
|
|
- Melvin Austin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
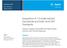
1 Simultaneous analysis of inorganic anions, organic acids, amino acids and carbohydrates using the Agilent Basic Anion Buffer Application Note Food Tomoyoshi Soga Absorbance [mau] Br 9 HPO 4 17 Ala 2 Phe 34 Glucose 2 Cl 10 Malate 18 Ser 26 Lys 3 Galactosamine 3 NO 2 11 Asp 19 Thr 27 Trp 36 Galactose 4 NO 3 12 Glu Pro 28 NGNA 37 Fucose SO 4 13 Acetate 21 Val 29 NANA 38 Sucrose 6 Oxalate 14 Tyr 22 Met 30 Ribose 39 Mannitol 7 F 1 Gly 23 His 31 Mannose 40 Sorbitol 8 Citrate 16 Lactate 24 Leu+Ile 32 Xylose 41 Xylitol 33 Glucosamine 42 Inositol Time [min] Introduction This application note describes extended applications of the Agilent Basic Anion Buffer. It facilitates the analysis of many anions including inorganic anions, organic acids, amino acids and carbohydrates. The method described here is useful for the screening analysis of anions in food and beverage samples. To separate these anions simultaneously, a highly alkaline ph condition is used to confer a negative charge not only on inorganic and organic anions but also on amino acids and carbohydrates, and promote their migration towards the anode. Electroosmotic flow (EOF) is reversed in the direction of the anode by adding quaternary ammonium salt to the electrolyte. This is necessary to have both anion migration and EOF in the same direction (towards the anode) and ensure anion migration past the detector. In this method, indirect UV detection is employed to visualize anions which have little or no chromophore. The Agilent Basic Anion Buffer is pre-made with the ph already adjusted, therefore no further preparation is required. Detailed method parameters and some typical electropherograms are shown.
2 Necessary supplies The following parts are necessary for the simultaneous analysis of anions: The following Agilent parts should be ordered separately when used with the Agilent CE system: Component Quantity Part No. Component Quantity Part No. Agilent Basic Anion 0 ml Buffer* Product literaure E * For this buffer, only 0-µm id straight capillaries are usable. Fused silica capillary 1 pk G (id = 0 µm, l=104 cm L=112. cm) CE buffer vials 100/pk ml (glass*) CE sample vials, 100 µl 1000/pk (polypropylene) CE caps (polyurethane) 100/pk CE water 00 ml * It is recommended to use glass vials rather than polypropylene vials. Procedures Buffer preparation The Basic Anion Buffer is premade and ready to use. Do not leave the solution uncapped since the buffer is a highly alkaline solution and will readily absorb gaseous carbonate from the atmosphere. This will cause its ph to drop immediately. Make certain the bottle is capped after use. Do not store opened bottles which are a third or less full. These should be discarded because gaseous carbonate in the bottle can be adsorbed and will reduce the ph of the residual buffer. The buffer should be stored at room temperature (not less than C, since some buffer components may crystallize at lower temperatures). Buffer and waste vials Prepare 3 vials (one flushing vial and two home vials). When using 2-ml glass vials (PN ), fill each vial with 1.4 ml of the buffer. Also prepare a waste vial (filled with 300-ml CE water or deionized water). Since buffers used for indirect UV detection have limited buffering capacity, the buffer should be replaced every 8 runs when using 2-ml glass vials (PN ). For this application, do not use the replenishment system for buffer replacement. The level of dissolved carbonate may increase due to pressurization of the buffer bottle, causing a ph drop. Also, crystallization of the buffer might block the tubes. Standard Preparation Individual stock solutions of inorganic and organic anions should be prepared from their sodium salts or free acids. Since carbohydrates are unstable, they should be prepared shortly before use. For amino acids, individual stock solution of Tyr, Cys-Cys, Asp, Trp, Leu, Ile and Phe should be prepared at a concentration of 10 g/l in 0.1 M NaOH. Other amino acids should be prepared in 0.01 M HCl. The working mixture standard should be prepared by diluting stock solutions with deionized water. If a commercially available amino acid standard mixture in 0.1 M HCl is used, Arg may not be detected since the pka value of Arg is Arg is positively charged in 0.1 M HCl and migrates
3 toward the opposite direction of the detector. In this case, the standard solution should be diluted with 0.01 M NaOH. The concentration of the standard mixture should be in the range of 0 to 1000 mg/l to obtain good peak shape and sensitivity. Sample Preparation For actual samples, dilution with deionized water is necessary in order to reduce the conductivity of the samples, for example, 1:0 dilution for soy sauce. If the sample contains proteins and the migration times increase from run to run, removal of the proteins is recommended by using centrifugal filtering through a 30-kDa cutoff filter. Capillary Only 0-µm id straight capillaries are suitable for this method. Baseline noise is markedly increased if a 7-µm id capillary is used due to the high UV absorptivity of the buffer. Neither bubble cell capillaries nor the High Sensitivity Detection Cell should be used. A 0-µm id capillary (L=112. cm, l=104 cm) is recommended. Capillary conditioning Avoid capillary conditioning with sodium hydroxide since this degrades the performance of this application. Prior to first use, a new capillary should be flushed only with the run buffer for 1 minutes. Between analyses it is recommended that the capillary be flushed for 4 minutes with buffer from the flushing vial. Capillary storage If the capillary is removed from the instrument it should be washed for 10 minutes with deionized water and then flushed with air for 10 minutes. When the capillary is to be reinstalled, it is necessary to flush with the run buffer for at least 1 minutes. Method summary The following method can be used to separate most inorganic anions, organic acids, amino acids and carbohydrates simultaneously. Below are the general analytical conditions. The method as it should be entered into the Agilent ChemStation is shown on the following page. Capillary Fused silica id = 0 µm, l=104 cm, L=112. cm (G ) Injection 1. Pressure: 0 mbar for 6 seconds from sample vial 2. Post-injection of buffer from InHome vial, 0 mbar for 4 s Applied voltage: - 30 kv Capillary temperature 1 C Detection wavelength Signal 30/ nm, reference 230/10 nm Preconditioning Buffer flush for 4 min at 1 bar prior to each run
4 Programming the method HPCE mode: CE Home values: Lift Offset 4 Cassette Temperature 1.00 C Inlet Home Vial 10 Place the buffer vials at position 10 and 11. Outlet Home Vial 11 Vial locations are exemplary only. Replenishment and Preconditioning: Serial processing Replenishment Entries: No Replenishment used Do not use replenishment. The level of dissolved carbonate might increase due to pressurization of the buffer bottle causing a ph drop. Preconditioning Entries: Function Parameter 1 Flush 4.00 min, I: 9, O:1 Place flushing vial at 9 and waste vial at 1. Remember to monitor the waste vial volume for overflow. Postcondition Entries: No Postconditioning used Injection Table Entries: Function Parameter 1 PRESSURE 0.0 mbar, 6.0 sec, I: InjectVial, O:OutHomeVial May be increased or decreased depending on sample concentration. 2 PRESSURE 0.0 mbar, 4.0 sec, I: InHomeVial, O:OutHomeVial The post injection plug helps to minimize sample loss upon application of voltage. A voltage ramp is used for the same purpose. Electric: Electric On Polarity Negative Negative polarity is used since EOF is reversed. Voltage 30.0 kv Current 10.0 ma A current limit is not necessary but may be used to prevent excessive current generation in case the wrong vial is used. Power System Limit Low Current Limit 2 µa Store Data: Collect voltage Yes Collect currentyes Collect power Collect pressure Collect temperature Time entries: Stop time Post time Time Table is empty. Diode array detector Settings: Stop Time Post Time Response Time 1.3 sec Peak width > Prerun Autobalance Postrun Autobalance Spectrum: Store It is recommended to store the current for every analysis. Current in this method shows from -30 to -40 µa. No No Yes min Adjust as needed when running actual sample. Off as HPCE: min Off This is recommended to reduce baseline noise. 0.1 min On Off None Signals: Store Reference Signal, Bw Reference, Bw [nm] A: Yes 30/ 230/10
5 Results and discussion Simultaneous analysis of inorganic anions, organic acids, amino acids and carbohydrates Figure 1 shows a typical electropherogram of a 43-component anion sample including seven inorganic anions, five organic acids, 16 amino acids and 1 carbohydrates using the standard method. If the results are not similar to these please refer to the section Troubleshooting in this note. In this method most inorganic anions and carbohydrates can be separated. However, migration times of several organic acids such as tartarate, succinate, malate and a-ketoglutarate are close. This separation can be improved by using the Organic Acids Analysis Kit from Agilent Technologies (PN ). With respect to amino acids, Leu and Ile cannot be resolved. Although Arg is not observed in figure 1, Arg can be detected at approximately 3 minutes if the sample is dissolved in an alkaline solution. Since Tyr and Trp have UV absorbance at 230 nm, they are recorded as negative peaks. Ser migrates just before a system peak. Electrophoretic mobilities at C The effective mobilities of 82 compounds including nine inorganic anions, 23 organic acids, 18 amino acids and 32 carbohydrates were determined by this method at C and are listed in table 1. If the mobilities of the compounds of interest are close, they are difficult to separate. In this case investigating a change of temperature or ph is recommended. Absorbance [mau] Br 9 HPO 4 17 Ala 2 Phe 34 Glucose 2 Cl 10 Malate 18 Ser 26 Lys 3 Galactosamine 3 NO 2 11 Asp 19 Thr 27 Trp 36 Galactose 4 NO 3 12 Glu Pro 28 NGNA 37 Fucose SO 4 13 Acetate 21 Val 29 NANA 38 Sucrose 6 Oxalate 14 Tyr 22 Met 30 Ribose 39 Mannitol 7 F 1 Gly 23 His 31 Mannose 40 Sorbitol 8 Citrate 16 Lactate 24 Leu+Ile 32 Xylose 41 Xylitol 33 Glucosamine 42 Inositol Buffer Agilent Basic Anion Buffer (PN ) Sample Cl 110 mg/l, carbohydrates 0 mg/l each, others 0 mg/l each Capillary fused silica, I=104 cm, L=112. cm, id= 0 µm Injection 300 mbar s Temperature 1 C Voltage -30 kv Detection signal 30/ nm, reference 230/10 nm Time [min] Figure 1 Analysis of 43-component anion standard mixture
6 Compound Mobility Compound ( X10-4 cm2/vs) Mobility Compound ( X10-4 cm2/vs) Mobility Compound ( X10-4 cm2/vs) Mobility ( X10-4 cm2/vs) Bromide Chloride Nitrite Nitrate Sulfate Oxalate Ascorbate Malonate Fluoride Formate Citrate Pyrophosphate Phosphate Tartarate Succinate Malate a-ketoglutarate Asp Glutarate Glu Adipate Acetate Pyruvate CysCys Glycolate Tyr Gly n-propionate Lactate Borate Ala Ser n-butyrate Levulinate Mannuronic Pyroglutamate n-pentanoate Thr Glucuronic Pro Val Met n-hexanoate Galacturonic His Leu Ile Phe n-heptanoate Gluconate Lys Trp NGNA n-octanoate NANA ManNAc Ribose Fructose GlcNAc Mannose Xylose GalNAc Rhamnose Glucosamine Mannosamine Lactose Arabinose Glucose Maltose Galactosamine Lactulose Galactose Fucose Sucrose Raffinose Mannitol Trehalose Sorbitol Galactitol Xylitol Erythritol Inositol Table 1 Electrophoretic mobilities of anions at C Applications Soy sauce analysis Figure 2 shows the analysis of a soy sauce. The sample was diluted 1:0 with CE water. Centrifugal filtering through a 30 kda cutoff filter was applied to remove proteins and peptides. A well-defined electropherogram was obtained without interference from other matrix compounds. Satisfactory reproducibilities were obtained for all compounds with RSD values (n=) for migration times better than 0.3 % and for peak areas between 0.6 and.4 %. Absorbance [mau] Cl 6 Glu 11 Ser 16 Leu+Ile 2 Citrate 7 Acetate 12 Thr 17 Phe 3 Succinate 8 Gly 13 Pro 18 Lys 4 Malate 9 Lactate 14 Val 19 Glucose Asp 10 Ala 1 Met Galactose Buffer Agilent Basic Anion Buffer (PN ) Sample soy sauce, 1:0 diluted with water, ultrafiltration with 30-kDa cutoff filter Preconditioning 4 min with run buffer Capillary fused silica, I=104 cm, L=112. cm, id= 0 µm Injection 300 mbar s Temperature 1 C Voltage -30 kv Detection signal 30/ nm, reference 230/10 nm Time [min] Figure 2 Analysis of soy sauce
7 Pineapple analysis Absorbance [mau] Citrate Malate This method was applied to the analysis of organic acids and carbohydrates in pineapple. In the agriculture industry, technical experts are trying to develop a new crossbreed of fruits. Since the content of organic acids and carbohydrates determines the taste of the pineapple juice, their analysis can help to characterize the product. If citrate and malate concentrations are high, the taste tends to be sour. If the carbohydrate concentration is high, the taste is Fructose Glucose Time [min] Figure 3 Analysis of pineapple Sucrose sweet. Determination of these compounds is traditionally performed using two HPLC methods. However, the method described here enables the simultaneous analysis of both organic acids and carbohydrates in a much shorter time (less than 18 min) and in a single run. In order to reduce the analysis time, a shorter length capillary was used for this sample. Squeezed pineapple juice was diluted 0-fold with CE water prior to injection. Figure 3 shows a result of the analysis. Buffer Agilent Basic Anion Buffer (PN ) Sample pineapple, 1:0 diluted with water, Capillary fused silica, I=72 cm, L=80. cm, id= 0 µm Injection 300 mbar s Temperature C Voltage -2 kv (reversed polarity) Detection signal 30/ nm, reference 27/10 nm Troubleshooting Problem Poor resolution or broad/split peaks Peak leading No signal Noisy baseline Poor reproducibility Unstable current Possible Cause Buffer is old Capillary damaged Sample overloaded Capillary too short Buffer absorbed carbonate Sample not injected Capillary damaged Wrong buffer used Wrong setting of power supply polarity Detection wavelength incorrect Wrong setting of response time Capillary window not adjusted Capillary window dirty Lamp is old Buffer ph higher than 12.3 Buffer overused Capillary broken Capillary not filled with buffer Solution Use new buffer Replace capillary Dilute sample Replace capillary Use new buffer Verify no air bubble trapped in bottom of sample vial Verify inlet capillary set correctly Replace capillary Verify buffer Check that polarity is negative Verify signal: 30/, reference: 230/10 nm Verify response time 1.3 sec DAD Examine capillary window Examine and clean with lint-free paper/meoh Replace lamp Verify buffer ph Replace buffer Replace capillary Increase flush time
8 References 1. Soga, T. and Ross, G. A. Capillary Electrophoretic Determination of Inorganic and Organic Anions using 2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid: Effect of Electrolyte's Complexing Ability, J. Chromatogr. A, 1997, 767, , Agilent publication number E. 2. Soga, T. and Heiger, D. N. Simultaneous Determination of Monosaccharides in Glycoproteins by Capillary Electrophoresis, Anal. Biochem., 1998, 261, 73-78, Agilent publication number E. 3. Soga, T. and Ross, G. A. Simultaneous Determination of Inorganic Anions, Organic Acids, Amino Acids and Carbohydrates by Capillary Electrophoresis J. Chromatogr., 1999, 837, , Agilent publication number E. Tomoyoshi Soga is application chemist at Yokogawa Analytical Systems, Japan. Agilent Technolgies recognizes his efforts in the development of this work. For more information on our products and services, visit our website at: Copyright 1999 Agilent Technologies All Rights Reserved. Reproduction, adaptation or translation without prior written permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright laws. Published in Germany 01/00 Publication Number E
columns CarboPac PA20 Column
 columns CarboPac PA Column Anion-exchange columns for the analysis of mono- and disaccharides in glycoprotein therapeutics, foods, and beverages: Simple, direct approach using pulsed electrochemical detection
columns CarboPac PA Column Anion-exchange columns for the analysis of mono- and disaccharides in glycoprotein therapeutics, foods, and beverages: Simple, direct approach using pulsed electrochemical detection
Carbohydrates in Food
 Application Note Food & Beverage The finest LC-EC Applications for Food & Beverage analysis Carbohydrates Phenols Bisphenol A Catechins Flavonoids Phenols Antioxidants Resveratrol Epicatechin Quercetin
Application Note Food & Beverage The finest LC-EC Applications for Food & Beverage analysis Carbohydrates Phenols Bisphenol A Catechins Flavonoids Phenols Antioxidants Resveratrol Epicatechin Quercetin
HC-75 Calcium Form. 305 x 7.8 mm HC-75 Calcium Form (P/N 79436)
 Page 1 of 5 U S A Example Applications HPLC Application Index Ordering Information Contact HPLC Support Polymeric cross-linked soft-gel columns for cation, ligand exchange separation of carbohydrates:
Page 1 of 5 U S A Example Applications HPLC Application Index Ordering Information Contact HPLC Support Polymeric cross-linked soft-gel columns for cation, ligand exchange separation of carbohydrates:
Unequalled durability against water elution. % tr
 Unequalled durability against water elution 2 Revolutionary aqueous durability for aminopropyl phase 1 3 4 1. fructose (2.5mg/mL) 3. sucrose (2.5mg/mL) 500 hr 2. glucose 400 hr Aqueous to non-aqueous Normal
Unequalled durability against water elution 2 Revolutionary aqueous durability for aminopropyl phase 1 3 4 1. fructose (2.5mg/mL) 3. sucrose (2.5mg/mL) 500 hr 2. glucose 400 hr Aqueous to non-aqueous Normal
ANTEC LEYDEN. Analysis of Carbohydrates in Food and Beverages using Anion-Exchange Chromatography and Pulsed Amperometric. Introduction.
 X Axis Title 220_002 #03 ANTEC LEYDEN System solutions from Antec Leyden... naturally! Analysis of Carbohydrates in Food and Beverages using Anion-Exchange Chromatography and Pulsed Amperometric Detection
X Axis Title 220_002 #03 ANTEC LEYDEN System solutions from Antec Leyden... naturally! Analysis of Carbohydrates in Food and Beverages using Anion-Exchange Chromatography and Pulsed Amperometric Detection
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM
 SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
Phases Available Description Applications Additional Notes RCM-Monosaccharide (L19 packing)*
 Carbohydrate and Organic Acid Analysis Excellent resolution Wide range of selectivities Excellent column-to-column reproducibility Recommended alternative to Bio-Rad, Supelco Supelcogel and Waters Sugar-Pak
Carbohydrate and Organic Acid Analysis Excellent resolution Wide range of selectivities Excellent column-to-column reproducibility Recommended alternative to Bio-Rad, Supelco Supelcogel and Waters Sugar-Pak
Detection and Quantification of Inorganic Arsenic in Fruit Juices by Capillary Ion Chromatography with Suppressed Conductivity Detection
 Detection and Quantification of Inorganic Arsenic in Fruit Juices by Capillary Ion Chromatography with Suppressed Conductivity Detection Hua Yang, Linda Lopez Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA
Detection and Quantification of Inorganic Arsenic in Fruit Juices by Capillary Ion Chromatography with Suppressed Conductivity Detection Hua Yang, Linda Lopez Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA
Application Note. Authors: C. Ledesma, M. Gibert, J.R. Gibert Ingenieria Analitica S.L. Extracts from various food products
 High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography coupled with Pulsed Electrochemical Detection as a powerful tool to evaluate lactose content in lactose-free labeled products Application Note Authors: C.
High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography coupled with Pulsed Electrochemical Detection as a powerful tool to evaluate lactose content in lactose-free labeled products Application Note Authors: C.
Mono- and Disaccharides
 Application Note Food/Beverage/Life Sciences The finest LC-EC Applications for Food & Beverage analysis Mono- and Phenols Bisphenol A Catechins Flavonoids Phenols Antioxidants Resveratrol Epicatechin Quercetin
Application Note Food/Beverage/Life Sciences The finest LC-EC Applications for Food & Beverage analysis Mono- and Phenols Bisphenol A Catechins Flavonoids Phenols Antioxidants Resveratrol Epicatechin Quercetin
Analysis - Carbohydrate analysis
 employ a technique called ligand exchange chromatography for the separation of monosaccharides, disaccharides and oligosaccharides up to 15 glucose units long. Ligand exchange resins are highly sulfonated
employ a technique called ligand exchange chromatography for the separation of monosaccharides, disaccharides and oligosaccharides up to 15 glucose units long. Ligand exchange resins are highly sulfonated
CE Columns and Accessories
 CE Columns and Accessories Complete Selection of Stationary Phases Sepax Nanofilm Capillary-Polyacrylamide Coatings Sepax Nanofilm Capillary-Poly(ethylene glycol) Coatings.. 4 Sepax Nanofilm Capillary-PEG/PAAm
CE Columns and Accessories Complete Selection of Stationary Phases Sepax Nanofilm Capillary-Polyacrylamide Coatings Sepax Nanofilm Capillary-Poly(ethylene glycol) Coatings.. 4 Sepax Nanofilm Capillary-PEG/PAAm
Sugar analysis according to the EU Regulation using amperometric detection and Metrosep Carb 2-150/4.0
 Sugar analysis according to the EU Regulation using amperometric detection and Metrosep Carb 2-150/4.0 Branch Food and beverages Bottle head 6.1602.200 Adsorber tube for Dosing Unit 6.1619.000 Keywords
Sugar analysis according to the EU Regulation using amperometric detection and Metrosep Carb 2-150/4.0 Branch Food and beverages Bottle head 6.1602.200 Adsorber tube for Dosing Unit 6.1619.000 Keywords
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications - Acids. Data No. Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection Data No.
 GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column
 Application Note Pharmaceutical and Food Testing Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column Author Lu Yufei Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract A liquid chromatographic
Application Note Pharmaceutical and Food Testing Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column Author Lu Yufei Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract A liquid chromatographic
Authors. Abstract. Introduction. Food
 Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening of additives in carbonated beverages with a robust organic acid column
 APPLICATION NOTE 21673 Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening of additives in carbonated beverages with a robust organic acid column Authors Aaron Lamb and Brian King, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, UK
APPLICATION NOTE 21673 Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening of additives in carbonated beverages with a robust organic acid column Authors Aaron Lamb and Brian King, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, UK
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2*
 Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Poster No. PT [ ANALYSIS OF ANION CONSTITUENTS OF URINE BY INORGANIC CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS
 Poster No. PT-56 94-[ ANALYSS OF ANON CONSTTUENTS OF URNE BY NORGANC CAPLLARY ELECTROPHORESS Presented by: Bill J.Wildman*, Peter E.Jackson, William R.Jones and Peter G.Alden Waters Division of Millipore
Poster No. PT-56 94-[ ANALYSS OF ANON CONSTTUENTS OF URNE BY NORGANC CAPLLARY ELECTROPHORESS Presented by: Bill J.Wildman*, Peter E.Jackson, William R.Jones and Peter G.Alden Waters Division of Millipore
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 4 Protein Sequence
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening for water soluble vitamins in sports beverages
 APPLICATION NOTE 21671 Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening for water soluble vitamins in sports beverages Authors Jon Bardsley, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, UK Keywords Vanquish Flex, Acclaim PolarAdvantage
APPLICATION NOTE 21671 Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening for water soluble vitamins in sports beverages Authors Jon Bardsley, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, UK Keywords Vanquish Flex, Acclaim PolarAdvantage
Separation of 15 Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards
 Application Note Raw Material & Media Analysis Separation of Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards Using an Agilent AdvanceBio MS Spent Media Column with TOF MS Detection Author Richard
Application Note Raw Material & Media Analysis Separation of Underivatized Saccharide and Sialic Acid USP Standards Using an Agilent AdvanceBio MS Spent Media Column with TOF MS Detection Author Richard
Determination of Organic Acids in Kombucha Using a High-Pressure Ion Chromatography System
 APPLICATION NOTE Determination of Organic Acids in Kombucha Using a High-Pressure Ion Chromatography System No. 1157 Beibei Huang, Jingli Hu, and Jeffrey Rohrer Keywords Dionex IonPac AS11-HC-4µm column,
APPLICATION NOTE Determination of Organic Acids in Kombucha Using a High-Pressure Ion Chromatography System No. 1157 Beibei Huang, Jingli Hu, and Jeffrey Rohrer Keywords Dionex IonPac AS11-HC-4µm column,
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Catalogue. Resins and Columns For High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Catalogue Resins and Columns For High Performance Liquid Chromatography Updated August 11, 2008 Contents Benson Polymeric provides premium polymeric column packing materials and prepacked columns for use
Catalogue Resins and Columns For High Performance Liquid Chromatography Updated August 11, 2008 Contents Benson Polymeric provides premium polymeric column packing materials and prepacked columns for use
Determination of Inorganic Ions and Organic Acids in Non-Alcoholic Carbonated Beverages
 Application Note Determination of Inorganic Ions and Organic Acids in Non-Alcoholic Carbonated Beverages INTRODUCTION The determination of inorganic anions and cations and organic acids in non-alcoholic
Application Note Determination of Inorganic Ions and Organic Acids in Non-Alcoholic Carbonated Beverages INTRODUCTION The determination of inorganic anions and cations and organic acids in non-alcoholic
Application Note. Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated OPA- Derivatization by the Autosampler. Summary. Fig. 1.
 Application Note Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated PA- Derivatization by the Autosampler Category Bio Analysis Matrix - Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic Amino acids, Canonical Amino
Application Note Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated PA- Derivatization by the Autosampler Category Bio Analysis Matrix - Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic Amino acids, Canonical Amino
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for Glycan Analysis
 Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for Glycan Analysis (Ludger Product Code: LS-R1-4.6x150) Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United Kingdom Tel: +44 1865 408 554 Fax: +44 870
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for Glycan Analysis (Ludger Product Code: LS-R1-4.6x150) Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United Kingdom Tel: +44 1865 408 554 Fax: +44 870
UPLC/MS Monitoring of Water-Soluble Vitamin Bs in Cell Culture Media in Minutes
 UPLC/MS Monitoring of Water-Soluble Vitamin Bs in Cell Culture Media in Minutes Catalin E. Doneanu, Weibin Chen, and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F
UPLC/MS Monitoring of Water-Soluble Vitamin Bs in Cell Culture Media in Minutes Catalin E. Doneanu, Weibin Chen, and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D
 LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
endopeptidases aminopeptidases carboxypeptidases hydrolyzes a peptide bond somewhere in the middle of the polypeptide
 1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
Rapid determination of phosphate and citrate in carbonated soft drinks using ion chromatography
 APPLICATION NOTE 7250 Rapid determination of phosphate and citrate in carbonated soft drinks using ion chromatography Authors Jingli Hu and Jeffrey Rohrer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA Keywords
APPLICATION NOTE 7250 Rapid determination of phosphate and citrate in carbonated soft drinks using ion chromatography Authors Jingli Hu and Jeffrey Rohrer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA Keywords
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM ur2 UHPLC Column for DMB Sialic Acid Analysis
 Product Guide for LudgerSep TM ur2 UHPLC Column for DMB Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-UR2-2.1x100 Ludger Document # LS-uR2-DMB-Guide-v2.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United Kingdom
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM ur2 UHPLC Column for DMB Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-UR2-2.1x100 Ludger Document # LS-uR2-DMB-Guide-v2.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United Kingdom
Mercury Speciation Determinations in Asian Dietary Supplements
 Mercury Speciation Determinations in Asian Dietary Supplements Terri Christison, Deepali Mohindra, Frank Hoefler, and Linda Lopez, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, California, USA Overview Purpose:
Mercury Speciation Determinations in Asian Dietary Supplements Terri Christison, Deepali Mohindra, Frank Hoefler, and Linda Lopez, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, California, USA Overview Purpose:
Application Note. Agilent Application Solution Analysis of ascorbic acid, citric acid and benzoic acid in orange juice. Author. Abstract.
 Agilent Application Solution Analysis of ascorbic acid, citric acid and benzoic acid in orange juice Application Note Author Food Syed Salman Lateef Agilent Technologies, Inc. Bangalore, India 8 6 4 2
Agilent Application Solution Analysis of ascorbic acid, citric acid and benzoic acid in orange juice Application Note Author Food Syed Salman Lateef Agilent Technologies, Inc. Bangalore, India 8 6 4 2
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis
 Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-R1-4.6x150 Ludger Document # LS-R1-DMB-Guide-v5.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-R1-4.6x150 Ludger Document # LS-R1-DMB-Guide-v5.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United
Glucose Oxidase Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 ab138884 Glucose Oxidase Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For quantifying Glucose oxidase in solution. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Table of
ab138884 Glucose Oxidase Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For quantifying Glucose oxidase in solution. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Table of
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Amino acids. Side chain. -Carbon atom. Carboxyl group. Amino group
 PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY/POLYMERS. 3. With respect to amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins, know:
 INTRDUCTIN T BICEMISTRY/PLYMERS A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. With respect to lipids, know: The characteristic common to members of the class (solubility in nonpolar solvents) The functional groups most
INTRDUCTIN T BICEMISTRY/PLYMERS A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. With respect to lipids, know: The characteristic common to members of the class (solubility in nonpolar solvents) The functional groups most
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム
 Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Hypersil BDS and Hypersil Classical HPLC Columns
 LC Columns and Accessories Hypersil BDS and Hypersil Classical HPLC Columns Exceptionally reliable and reproducible general purpose columns Exceptionally reliable robust columns that guarantee you have
LC Columns and Accessories Hypersil BDS and Hypersil Classical HPLC Columns Exceptionally reliable and reproducible general purpose columns Exceptionally reliable robust columns that guarantee you have
Organic molecules are molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen.
 Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry Introduction Organic molecules are molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen. All living things contain these organic molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry Introduction Organic molecules are molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen. All living things contain these organic molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid as the reductive thiol-containing reagent employed for the derivatization of amino acids with o-phthaldialdehyde analysis
 Acta Univ. Sapientiae, Alimentaria, 1 (2008) 49 60 Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid as the reductive thiol-containing reagent employed for the derivatization of amino acids with o-phthaldialdehyde analysis
Acta Univ. Sapientiae, Alimentaria, 1 (2008) 49 60 Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid as the reductive thiol-containing reagent employed for the derivatization of amino acids with o-phthaldialdehyde analysis
2. Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found on the outer surface of a properly folded protein?
 Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Thermo Scientific Dionex CarboPac MA1 Column
 CHROMATOGRAPHY Thermo Scientific Dionex CarboPac MA Column Product Specifications HPLC columns for the analysis of weakly ionizable carbohydrates. Simple methods with pulsed amperometric detection Reduced
CHROMATOGRAPHY Thermo Scientific Dionex CarboPac MA Column Product Specifications HPLC columns for the analysis of weakly ionizable carbohydrates. Simple methods with pulsed amperometric detection Reduced
Determination of Benzodiazepines in Urine by CE-MS/MS
 Determination of Benzodiazepines in Urine by CE-MS/MS Application ote Forensic Toxicology Authors audimir Lucio do Lago Department of Fundamental Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry University of São Paulo,
Determination of Benzodiazepines in Urine by CE-MS/MS Application ote Forensic Toxicology Authors audimir Lucio do Lago Department of Fundamental Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry University of São Paulo,
Determination of Tetracyclines in Chicken by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Determination of Tetracyclines in Chicken by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Application ote Food Safety Authors Chen-Hao Zhai and Yun Zou Agilent Technologies Co. Ltd.
Determination of Tetracyclines in Chicken by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Application ote Food Safety Authors Chen-Hao Zhai and Yun Zou Agilent Technologies Co. Ltd.
9/16/15. Properties of Water. Benefits of Water. More properties of water
 Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels. Supplementary Information
 Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular
 Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
BASIC SCIENCES & BIOCHEMISTRY FOR BETZPAENIC BRIMBLERS
 BASIC SCIENCES & BIOCHEMISTRY FOR BETZPAENIC BRIMBLERS Lymphatic Vessels One main lymph vessel receives lymph from the right upper arm and the right side of the head and the thorax and empties into the
BASIC SCIENCES & BIOCHEMISTRY FOR BETZPAENIC BRIMBLERS Lymphatic Vessels One main lymph vessel receives lymph from the right upper arm and the right side of the head and the thorax and empties into the
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds
 Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds Julie Kowalski, Michelle Misselwitz and Jack Cochran Restek
Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds Julie Kowalski, Michelle Misselwitz and Jack Cochran Restek
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
The Determination of Sugars in Molasses by High-Performance Anion Exchange with Pulsed Amperometric Detection
 Application Note 9 The Determination of Sugars in Molasses by High-Performance Anion Exchange with Pulsed Amperometric Detection INTRODUCTION The accurate measurement of the amount of sugar in final molasses
Application Note 9 The Determination of Sugars in Molasses by High-Performance Anion Exchange with Pulsed Amperometric Detection INTRODUCTION The accurate measurement of the amount of sugar in final molasses
Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon. Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011
 Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011 Contents Comparison with small molecule LC-MS/MS LC-MS/MS sensitivity of peptides detection Stability: neat vs. matrix solutions
Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011 Contents Comparison with small molecule LC-MS/MS LC-MS/MS sensitivity of peptides detection Stability: neat vs. matrix solutions
Implementing a Generic Methods Development Strategy for Enantiomer Analysis
 2 Chapman and Fu-Tai Chen Implementing a Generic Methods Development Strategy for Enantiomer Analysis Jeff Chapman and Fu-Tai A. Chen, Beckman Coulter Inc., Fullerton, California, USA. Introduction Whether
2 Chapman and Fu-Tai Chen Implementing a Generic Methods Development Strategy for Enantiomer Analysis Jeff Chapman and Fu-Tai A. Chen, Beckman Coulter Inc., Fullerton, California, USA. Introduction Whether
Analysis of several common. organic acids in tobacco leaf, snus, and moist snuff
 Analysis of several common organic acids in tobacco leaf, snus, and moist snuff S. C. Moldoveanu, W. A. Scott R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co. Background Among the organic acids commonly present in tobacco, are
Analysis of several common organic acids in tobacco leaf, snus, and moist snuff S. C. Moldoveanu, W. A. Scott R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co. Background Among the organic acids commonly present in tobacco, are
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam )ومن أحياها(
 Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Confident, lower-pressure analysis of carbohydrates, alcohols, and organic acids. Agilent Hi-Plex Ligand-Exchange HPLC Columns
 Confident, lower-pressure analysis of carbohydrates, alcohols, and organic acids Agilent Hi-Plex Ligand-Exchange HPLC Columns Agilent Hi-Plex Ligand-Exchange HPLC columns Satisfy your growing demands for
Confident, lower-pressure analysis of carbohydrates, alcohols, and organic acids Agilent Hi-Plex Ligand-Exchange HPLC Columns Agilent Hi-Plex Ligand-Exchange HPLC columns Satisfy your growing demands for
Determination of B-vitamins in Energy Drinks by CE/MS/MS
 Application ote Food Determination of B-vitamins in Energy Drinks by E/MS/MS Authors laudimir Lucio do Lago and Zuzana ieslarová Department of Fundamental hemistry, Institute of hemistry, University of
Application ote Food Determination of B-vitamins in Energy Drinks by E/MS/MS Authors laudimir Lucio do Lago and Zuzana ieslarová Department of Fundamental hemistry, Institute of hemistry, University of
Experiment 2 Introduction
 Characterization of Invertase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae Experiment 2 Introduction The method we used in A Manual for Biochemistry I Laboratory: Experiment 7 worked well to detect any created reducing
Characterization of Invertase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae Experiment 2 Introduction The method we used in A Manual for Biochemistry I Laboratory: Experiment 7 worked well to detect any created reducing
The Determination of Carbohydrates, Alcohols, and Glycols in Fermentation Broths
 The Determination of Carbohydrates, Alcohols, and Glycols in Fermentation Broths Valoran Hanko and Jeffrey S. Rohrer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA Application Note 122 Introduction Fermentation
The Determination of Carbohydrates, Alcohols, and Glycols in Fermentation Broths Valoran Hanko and Jeffrey S. Rohrer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA Application Note 122 Introduction Fermentation
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION A Robust and High Throughput Method for Anionic Metabolite Profiling: Preventing Polyimide Aminolysis and Capillary Breakage under Alkaline Conditions in CE-MS Mai Yamamoto, Ritchie
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION A Robust and High Throughput Method for Anionic Metabolite Profiling: Preventing Polyimide Aminolysis and Capillary Breakage under Alkaline Conditions in CE-MS Mai Yamamoto, Ritchie
Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents
 No. 079 SEPARATION REPORT Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Comparison
No. 079 SEPARATION REPORT Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High-performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Comparison
[ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector
![[ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector [ APPLICATION NOTE ] Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector](/thumbs/83/88757464.jpg) Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector Mark Benvenuti, Gareth Cleland, and Jennifer Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA
Profiling Mono and Disaccharides in Milk and Infant Formula Using the ACQUITY Arc System and ACQUITY QDa Detector Mark Benvenuti, Gareth Cleland, and Jennifer Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA
Fructose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 04. Intended for research use only.
 Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Rapid Gradient and Elevated Temperature UHPLC of Flavonoids in Citrus Fruit
 Rapid Gradient and Elevated Temperature UHPLC of Flavonoids in Citrus Fruit Application Note General Chromatography, Food Industry Authors John W. Henderson Jr., Judy Berry, Anne Mack, William Long Agilent
Rapid Gradient and Elevated Temperature UHPLC of Flavonoids in Citrus Fruit Application Note General Chromatography, Food Industry Authors John W. Henderson Jr., Judy Berry, Anne Mack, William Long Agilent
2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis
 2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis Direct Mass Selective Detection of a Pharmaceutical Peptide from an MS-Incompatible USP Method Application Note Biologics and Biosimilars Author Sonja
2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis Direct Mass Selective Detection of a Pharmaceutical Peptide from an MS-Incompatible USP Method Application Note Biologics and Biosimilars Author Sonja
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities by LC/MS. Application Note. Christine Miller Agilent Technologies.
 Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Biological Mass Spectrometry. April 30, 2014
 Biological Mass Spectrometry April 30, 2014 Mass Spectrometry Has become the method of choice for precise protein and nucleic acid mass determination in a very wide mass range peptide and nucleotide sequencing
Biological Mass Spectrometry April 30, 2014 Mass Spectrometry Has become the method of choice for precise protein and nucleic acid mass determination in a very wide mass range peptide and nucleotide sequencing
120. Paper Electrophoresis o f Hexosamines, N-Acetylhexosamines and N Acetylneuraminic Acid*l
 534 [Vol. 39, 120. Paper Electrophoresis o f Hexosamines, N-Acetylhexosamines and N Acetylneuraminic Acid*l By Seiichi OHKUMA and Toshiaki SHINOHARA Biochemical Laboratory, Scientific Police Research Institute,
534 [Vol. 39, 120. Paper Electrophoresis o f Hexosamines, N-Acetylhexosamines and N Acetylneuraminic Acid*l By Seiichi OHKUMA and Toshiaki SHINOHARA Biochemical Laboratory, Scientific Police Research Institute,
Fructose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 03. Intended for research use only.
 Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Operating Instructions
 Sequazyme C-Peptide Sequencing Kit Operating Instructions 1 Product Description The Sequazyme C-Peptide Sequencing Kit enables peptide digestion and the analysis of sequentially truncated peptides using
Sequazyme C-Peptide Sequencing Kit Operating Instructions 1 Product Description The Sequazyme C-Peptide Sequencing Kit enables peptide digestion and the analysis of sequentially truncated peptides using
Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High Performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2)*
 ANALYSIS S e p a r a t i o n R e p o r t N o. 7 9 Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High Performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2)* *Please refer to Separation
ANALYSIS S e p a r a t i o n R e p o r t N o. 7 9 Separation of Saccharides Using TSKgel Amide-80, a Packing Material for High Performance Normal Phase Partition Chromatography (2)* *Please refer to Separation
CE Pharm 2008, October 12-16, 2008, San Francisco, CA, USA
 Clinical Diagnostics by Capillary Electrophoresis: Determination of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin and lamotrigine in human serum under stringent quality control conditions CE Pharm 8, October 1-1,
Clinical Diagnostics by Capillary Electrophoresis: Determination of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin and lamotrigine in human serum under stringent quality control conditions CE Pharm 8, October 1-1,
HPLC Analysis of Sugars
 HPLC Analysis of Sugars Pre-Lab Exercise: 1) Read about HPLC, sugars and the experiment and its background. 2) Prepare a flowchart as appropriate for the lab exercise. 3) Note the various sugar concentrations
HPLC Analysis of Sugars Pre-Lab Exercise: 1) Read about HPLC, sugars and the experiment and its background. 2) Prepare a flowchart as appropriate for the lab exercise. 3) Note the various sugar concentrations
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Fructose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 02. Intended for research use only.
 Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM C3 anion exchange HPLC Column for Glycan Analysis
 Product Guide for LudgerSep TM C3 anion exchange HPLC Column for Glycan Analysis (Ludger Product Code: LS-C3-7.5x75) Ludger Document # LS-C3-Guide-v3.0 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM C3 anion exchange HPLC Column for Glycan Analysis (Ludger Product Code: LS-C3-7.5x75) Ludger Document # LS-C3-Guide-v3.0 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB
Analysis of Food Sugars in Various Matrices Using UPLC with Refractive Index (RI) Detection
 Analysis of Food Sugars in Various Matrices Using UPLC with Refractive Index (RI) Detection Mark E. Benvenuti Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS Using UPLC with RI detection enables
Analysis of Food Sugars in Various Matrices Using UPLC with Refractive Index (RI) Detection Mark E. Benvenuti Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS Using UPLC with RI detection enables
Electronic Supplementary Information. Table of Contents
 Electronic Supplementary Information Examination of native chemical ligation using peptidyl prolyl thioester Takahiro Nakamura, Akira Shigenaga, Kohei Sato, Yusuke Tsuda, Ken Sakamoto, and Akira Otaka*
Electronic Supplementary Information Examination of native chemical ligation using peptidyl prolyl thioester Takahiro Nakamura, Akira Shigenaga, Kohei Sato, Yusuke Tsuda, Ken Sakamoto, and Akira Otaka*
I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy
 Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Chem 306 Roper I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy 2. energy storage 3. structure 4. other functions!
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Chem 306 Roper I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy 2. energy storage 3. structure 4. other functions!
COLE-PARMER LABORATORY SURFACTANT ION ELECTRODE INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 COLE-PARMER LABORATORY SURFACTANT ION ELECTRODE INSTRUCTION MANUAL Cole-Parmer Instrument Company (800)323-4340 Fax:(847)247-2929 625 East Bunker Court, Vernon Hills, Illinois 60061 http://www.coleparmer.com
COLE-PARMER LABORATORY SURFACTANT ION ELECTRODE INSTRUCTION MANUAL Cole-Parmer Instrument Company (800)323-4340 Fax:(847)247-2929 625 East Bunker Court, Vernon Hills, Illinois 60061 http://www.coleparmer.com
Determination of Carbohydrates in Kombucha Using HPAE-PAD
 Determination of Carbohydrates in Kombucha Using HPAE-PAD Beibei Huang, Jingli Hu, and Jeffrey Rohrer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA USA Application Note 1152 Key Words Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose,
Determination of Carbohydrates in Kombucha Using HPAE-PAD Beibei Huang, Jingli Hu, and Jeffrey Rohrer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA USA Application Note 1152 Key Words Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose,
