A REVIEW OF IMAGE ANALYSIS BASED METHODS TO EVALUATE FIBER PROPERTIES
|
|
|
- Barnaby Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A REVIEW OF IMAGE ANALYSIS BASED METHODS TO EVALUATE FIBER PROPERTIES Ulrich Hirn and Wolfgang Bauer Institute for Paper, Pulp and Fiber Technology, Graz University of Technology Kopernikusgasse 24/II, 8010 Graz, Austria. Tel. +43/316/ , This review focuses on fiber analysis methods, where the fibers are carried in suspension. They are photographed in a flow cell and their properties are evaluated by digital image analysis. Three fields of fiber analysis are covered: Fiber morphology, pulp surface chemistry and chemically induced swelling respectively dissolving behaviour of pulp. For fiber morphology commercial analyzers were compared. On an absolute level the measurement differences between the analyzers varied from 15% to 40%, for some morphological parameters up to 70%. Still fiber length, width and curl results Introduction are highly correlated so relative comparison is possible. An increasing number of publications has has recently been devoted to image analysis based evaluation of surface chemistry respectively chemically induced fiber swelling and dissolving. Considering that research effort it can be expected, that numerous innovations in both fields, commercial fiber analyzers as well as new machine vision based fiber analysis techniques, can be expected in the next years. Keywords: fiber analysis, flow cell, fiber morphology, machine vision. The rapid development of digital image analysis technology within the last years has lead to a multitude of new applications in the field of fiber assessment. This paper gives a review of analysis methods with special emphasis put on the following: Flow cell based methods. That means that the fibers are measured in suspension, the fiber suspension is pumped through a transparent flow cell where the fibers are photographed. Application of image analysis. The review focuses on methods applying machine vision to characterize fibers. Only methods for fibers in a size range up to a few millimeters of length and 100 µm of width are considered. So the focus lies on pulp analysis, but some methods can also be used for other fiber types. A Flow cell combined with image analysis is an efficient concept for fiber characterization because the measurement can be carried out in a fully automated manner. Provided that hard- and software are stable enough, such analyzers can be used for online process control, e.g. in the pulp industry. This is the main motivation for the considerable research effort that has taken place in this area within the last years. In the following the focus has been set on three different aspects of fiber analysis: Fiber morphology Pulp surface chemistry Chemically induced pulp fiber swelling and dissolving
2 Fiber Morphology This section first gives an overview of the fiber properties which are commonly summarized under the term fiber morphology. Then six commercially available fiber morphology analyzers are discussed in detail. At the end of this section a quantitative comparison of measurements from the various analyzers as well as repeatability issues are treated. An overview of fiber morphology features The morphology, i.e. the structural appearance, of fibers is commonly described by five parameters: length, width, coarseness, kink and curl. Fiber length and width are common features which are fairly straightforward to implement for image analysis [8,14,27]. Fiber coarseness is defined as the fiber mass per unit length, usually in microgram per meter fiber length. It is closely related to the fiber wall thickness of tube shaped fibers like wood. Coarseness is normally determined by producing a fiber suspension with well defined solids content and measuring the cumulative fiber length in a defined volume of this suspension. Figure 1. Fibers with different curl but same curvature [11]. Please note, that the arithmetic mean may be a bad measure to characterize a population of fibers, especially when the multitude of elements is small (as it is the case for e.g. pulp). Then the mean value is merely determined by the amount of small particles in the sample. For that reason often the length weighted mean is recommended [3]. Fiber kink and fiber curl provide information about the bending of the fiber. Curl describes the degree of nonstraightness of a fiber, it gives no information if a fiber bends gradually or abruptly. A multitude of different mathematical definitions for curl is used [11,12,16,22,28]. The commercial pulp analyzers use varying definitions for curl. Figure 2 Fibers with different kink but the same curl [11]. Although it is reported that the various definitions for curl are correlated [22] the measurement results can usually not be compared. Figure 1 shows fibers with ascending curl, please note that the curl varies but fiber curvature remains unchanged. That is the case because curl, in contrast to curvature, is a size invariant descriptor. Fiber kink [13] denotes small regions of very high curvature, i.e. sharp bends, along the fiber. It indicates fiber deformations, mostly caused by mechanical damage. A fiber with high kink is shown in figure 1 on the right side, the fiber on the left side has the same curl (i.e. overall non straightness) but significantly lower kink. Further fiber characterization parameters are listed in figure 3. Fibrillation describes the number of fibrils, i.e. fiber wall fragments, sticking out of the surface of pulp fibers. Fines content denotes the
3 Figure 3. Fiber properties measured by six commercially available fiber analyzers. number of small fiber fragments. Unfortunately definitions below which size a particle is considered small vary largely between the examined analyzers [2,12,28,30]. Few analyzers evaluate number and size of hardwood vessel cells in the pulp, fiber flexibility or wall thickness. Finally shives are counted, they are bundles of fibers that were improperly disintegrated during the pulping process. Flow cell based fiber morphology Measurement Now six widely used commercial pulp analyzers from different manufacturers are reviewed. They are all based on a rear illumination flow cell and image analysis. The measurements obtainable, hardware concept and some aspects of image analysis are discussed for each analyzer. An overview of the fiber parameters measured by the devices gives figure 3, figure 4 summarizes some technical specifications. The Galai CIS-100 [2] is also sold under the name Pulp Fibre Analyzer. The flow cell light source is a pulsed flash, images are acquired by a CCD camera. Length, width and curl of roughly 2000 fibers are measured per pulp sample. The device also gives a value for fiber fibrillation, however neither a definition of this value, nor an empirical verification could be found in the literature. The Metso FiberLab has two light sources, it uses three optical detectors [30]. That enables it to perform a wide variety of fiber measurements. Images from a low resolution camera are evaluated for fiber length, coarseness, kink and curl. Fiber width, cell wall thickness and cross sectional area are measured by a separate high resolution camera. The fiberlab is the only device that offering measurement of these parameters. The third sensor is a light scatter detector used for measurement of smaller particles. The STFI Fibermaster [12] is a twocamera system providing fine and coarse resolution images. All image processing is hard wired as camera on-chip logic which makes measurements considerably faster than the other systems. The fiber measurement provides length, width, coarseness, kink and two shape factors for curl. Vessel cells are identified and counted, also shive content is evaluated. The Fibermaster is the only fiber analyzer that provides a measure for fiber flexibility [12]. It follows the principle that shear forces (and thus bending stress imposed on fibers) increase with flow speed in the flow cell channel. Therefore flexibility in Fibermaster measurements is defined as the change of fiber curl at different flow rates in the measurement cell. Large changes of fiber curl upon changes in flow speed indicate high fiber flexibility.
4 The OpTest Fiber quality analyzer (FQA) has a special flow cell design aimed to to prevent fouling and forming of deposits. Three currents are lead through the cell, only the middle current carries fibers, the currents flowing next to the wall consist of pure water [29]. Transmitted illumination is provided by a circular polarized laser flashlight, opposed to other flow cells which are using linear polarized light. The device measures length, width, coarseness, kink and curl. Fiber width measurement sensitivity is given as 1 μm although camera resolution is 36 μm/pixel, additional resolution is estimated by interpolation. The FQA also measures shives and vessel content. The Techpap MorFi fiber analyzer [28] has one high resolution camera. Fiber length, width, coarseness, kink and curl are analyzed. The system gives a measure for fiber fibrillation, it is defined as the length of all micro fibrils attached to the fibers in relation to total fiber length. However an empirical verification for this measure can not be found in the literature. Finally there is the Kajaani FS-200, which has been on the market since the 1980ies [34] and has been widely used since. Its working principle is totally different from the other devices: The sensor is a line camera aligned along the length axis of a capillary, this capillary carries the fiber suspension. The capillary is illuminated with transmitting polarized light, as the fibers are carried along in front of a sensor element, they induce changes in polarization which are detected by the sensor element [30]. So basically the 1- dimensional projection of a fiber is measured. For this reason only fiber length and coarseness can be measured. As the row sensor has a rather low resolution of 50µm/pixel fines measurement is only possible to a limited extent. Repeatability and comparison of results Repeatability of the above described fiber analyzers [2,5,8,24] is obviously closely related to processing speed and subsequent total number of fibers analyzed, see figure 4. Repeatability on a 95% confidence level according to Tappi standard T 1200 sp91 was between 2% and 5% for (length weighted) fiber length and fiber width. For curl and kink repeatability is not as good, it ranges between 6% and 11%. For Coarseness measurement, which additionally contains the error of determining the solids content of the suspension, repeatability is 10% or worse. No repeatability is given for other parameters. Comparing the results from measuring the same pulp fiber samples using the various pulp analyzers revealed large differences between the devices. For fiber length the Kajaani FS-200 has a totally different measurement principle than the other devices, mainly because it measures a 1-dimensional projection of the fibers whereas all other systems evaluate 2-dimensional projections. Consequently the FS-200 measures curled and kinked fibers too short. Apart from one publication [24], this result has repeatedly been confirmed in the literature [2,30,33] and was also found by our own investigations [8]. The MorFi system measures even shorter values for fiber length than the Kajaani [5,30] although it uses a 2D. That leads to the conclusion, that the MorFi system also measures fiber length too short. Deviations in (length weighted) mean fiber length between the systems was around 15% to 20%, so absolute comparison of results is impossible. However relative comparison of 17 different pulps measured in four analyzers [30] gave highly correlated results. The situation for fiber
5 Figure 4. Technical specifications of six commercially available flow cell based fiber analyzers. width was similar, differences in absolute values were up to 40%, still relative comparison is possible because the results are highly correlated. As mentioned above, different definitions for fiber curl are used by most of the reviewed pulp analyzers. Not surprisingly the curl values between MorFi, Fibermaster and Fiberlab differed strongly [30], absolute difference was up to 70%. Correlations were still fairly good, thus relative comparison is still possible to some extent. The analyzers do not recognize fine particles in the same way, which comes from two reasons. First there are great differences in optical resolution, from MorFi with 4 μm/pixel to Kajaani FS-200 with 50 μm/pixel. These differences become most relevant for recognition of small particles. Secondly different rules for classification of fines are implemented. As a consequence they measure different amount of fines, which in turn leads to strong differences in coarseness [30]. It does, however not lead to strong differences in average fiber length, because length weighted fiber length was compared, reducing the influence of fines content [8]. For coarseness not only absolute values differed, correlation was also bad [24, 30] thus the results of coarseness measurements from different pulp analyzers can not be compared. That is mainly due to the fact that for coarseness measurement, apart from the error of differing fines results, additional error for determining the (very low) measurement consistency of the suspension comes into effect. In conclusion quantitative comparison of the results displayed large differences between the fiber analyzers regarding several perspectives. Hardware concept, image resolution and illumination vary largely. It can be speculated that the implemented image analysis algorithms might also be very different. Most important however is the fact, that the measurement results are grossly differing, for some fiber properties they do not even reflect relative ranking. All these facts indicate, that developments in this field are far from being finished. Calibration and standardization of these measurements still needs to be accomplished. Surface chemistry of pulp fibers A multitude of dyeing or staining schemes exists for microscopic analysis of pulp fiber surface chemistry [3,16]. Some of them are directly observable [4,25], many apply fluorescence [23]. Apart from staining lignin exhibits strong autofluorescence, when it is excited with light in the wavelength range of 500 nm. This is often combined with Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy, for example
6 in order to measure lignin content profiles across the fiber wall [20]. The key point is, that many of these microscopic methods have the potential to be adapted for automated, image analysis based measurement in a flow cell. Several flow cells have been developed for measurement of pitch, i.e. colloids of hydrophobic substances, in pulp suspension. A measurement based on staining with fluorescent dye and laser light was described by [15]. They measure count and size of previously stained resin particles by pumping a colloidal particle suspension through a capillary and evaluating the scatter of laser light. An evaluation of the instrument [35] showed, that reproducible results are obtained, if influence parameters like for example solids concentration and flow speed are controlled. Flow cytometry of bacteria and wood resin particles is also discussed in [32] and [17]. Fluorescence scatter induced by staining of resin and bacteria is evaluated in a flow cytometer (i.e. a flow cell for cell counting). They find very good correlations between bacterial counts performed in a flow cell and counting of bacteria colonies grown on a laboratory nutrient media. Relations between resin agglomeration and bacteria count as well as interaction with carbonate particles are discussed. A particularly interesting approach to measure the uniformity of Kappa number on a single fiber basis describes [18]. This method stains the fibers with the metachromatic fluorescent dye Acridine Orange. It has been shown that at low lignin concentrations the stained fibers exhibit a green fluorescence, while at higher lignin content they exhibit a shift to red fluorescence. The ratio of red to green fluorescence correlates well with lignin content. Measurement of fluorescence is realized by picturing and subsequent image analysis of individual fibers in a flow cell. An interesting approach to combine a set of dyes to characterize different types of chemical fiber surfaces has been published quite recently [4]. They use basic dyes for identification of lignin on the surface, basic phthalocyanine dyes for detection of hemicellulosic surface regions and finally direct dyes, which have an affinity for alpha cellulose. Then they evaluate the effect of different laboratory bleaching sequences on the fiber light absorbancy caused by the varying dyes. Principal component analysis revealed two main components representing lignin content and polarity (hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity). Chemically induced fiber swelling and dissolving Since the 1960ies, the swelling and dissolving process of chemical pulp fibers dissolving in chemicals has been examined [10]. Fiber dissolution in chemicals like iron-sodium-tartrate (EWNN), lithiumchlorine/dimethylacetamide (LiCl/DiMAc) or cupriethylenediamine (CED) starts with intense swelling and proceeds to increasing disintegration of the fiber. These various stages of disintegration of the fiber have a very specific visual appearance [10], for example see figure 5. Fiber swelling starts with so called balloon swelling (I) where only limited parts of the fiber are swollen, it proceeds to volume swelling (II) where large parts of the fiber wall are already broken apart. Finally it reaches a phase called gel swelling (III), where the fiber has already widely disintegrated. It has been quite straightforward to observe, that the presence of specific swelling phenomena at lower chemical concentration is related to the ability to dissolve at higher concentration. So fiber swelling has been observed to assess the adequacy of chemical pulp for viscose production. A quantitative evaluation of swelling and dissolving of pulp fibers in EWNN and LiCl/DiMAc has been
7 implemented [31]. The authors record video images of single fibers dissolving and apply image analysis to evaluate changes in fiber thickness and fiber transparency. Finally they measure the time until the fiber breaks apart. These parameters, together with other laboratory results, are used to quantify swelling and dissolving behavior. On the other hand, the swelling behavior is largely related to the fiber wall structure [26]. The S2 layer of the wood fiber wall, due to its highly aligned fibril structure, is very prone to swelling, whereas the S1 wall layer with its crossed fibril structure restricts fiber swelling [26]. So chemically induced fiber swelling provides an indirect method to evaluate mechanical and chemical damage of the S1 wall, in fiber regions with heavy swelling the S1 is obviously damaged. Such methods use different chemical agents to promote strong fiber swelling. A CED based method [21] finds good correlations between beating degree and fiber swelling. This method was adapted at our institute, we evaluate fiber swelling using image analysis and a flow cell [5,6,8,33]. A different swelling chemical, iron-sodiumtartrate (EWNN) is used in [9]. The authors examined fiber swelling, fibrillation, nodes of damage and curl index by visual inspection of photographs taken at specified time intervals after addition of the swelling chemical. According to recent work [1], which compared fiber wall damage visualized by polarized light microscopy [7,19,22] to fiber wall damage indicated by chemically induced swelling, both methods indeed indicate cracks in the S1 fiber wall. Conclusions Figure 5. Characteristic types of pulp fiber swelling induced by a chemical agent: Balloon swelling (I), volume swelling (II), gel swelling (III). The present review shows, that considerable effort has been put on both, academic research as well as commercial development of image analysis based fiber characterization methods. In the field of fiber morphology, there are already several commercial devices available. The measurement results for basic features like fiber length or width show sizable differences in absolute values, still correlations are high. Thus comparison of the absolute values is not possible, relative comparison can be achieved. More complex fiber characteristics like curl or coarseness can not be compared well, neither in absolute nor in relative results. It will be the challenge for the following years to achieve standardization and comparability for these fiber analyzers. Even more advanced features like fiber wall thickness, fiber flexibility and fiber fibrillation are rarely offered yet, but without doubt these are under development by most of the fiber morphology flow cell manufacturers. For fiber surface chemistry respectively pulp swelling and resolving behavior no commercial analyzers are on the market yet. Still several research groups are working on such methods. To date the potential of these analytic approaches has not been fully tapped. It can be expected, that within the coming years on the one hand some existing microscopic fiber
8 analysis techniques will be adopted for automation. On the other hand, the fast growth of image analysis hardware and algorithmic capabilities will permit totally new methods and approaches to fiber analysis. For that reason fiber assessment has been a pronounced research focus at our institute during the last years [5,6,8,33]. Various flow cell prototypes with according image analysis software have been developed for pulp fiber quality research. References [1] P. Ander and D. Geoffrey. Morphology of spruce fibre dislocations as studied by balloon swelling and acid cleavage - light and electrone microscope observations. In U. Schmitt and P. Saränpää, editors, COST Action E20 - Wood Fibre Cell Walls: Methods to Study Their Formation, Strucure and Properties, Brussels, OPOCE. [2] M.G. Carvalho, P.J. Ferreira, A.A Martins, and M.M. Figueiredo. A comparative study of two automated techniques for measuring fiber length. Tappi J., 80(2):pp , [3] J. Clark. Pulp Technology and Treatment for Paper. Miller Freeman Publ., San Francisco, ISBN [4] T. Drnovsek and M. Perdih. Fibre surface characteristics evaluated by the method of selective staining. J. Wood Sc., 51(5): , [5] R. Eckhart. Beurteilung des Schädigungsgrades von Zellstofffasern anhand deren Quellverhalten in Kupferethylendiamin. Licentiate thesis, Graz Universtiy of Technology, [6] R. Eckhart, U. Hirn, and W. Bauer. Fiber wall damage in the refining process - accepted for publication. In Proceedings of the Progress in Paper Physics Seminar, Oxford (Ohio) - Oct , [7] O.L. Forgacs. Structural weakness in softwood pulp tracheids. Tappi J., 44(2):pp , [8] U. Hirn. New Methods in Paper Physics Based on Digital Image Analysis. PhD thesis, Graz University of Technology, [9] B. Hortling, T. Jousimaa, and H-K. Hyvärinen. Investigation of spruce pulp fibres by swelling experiments and light microscopy. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference CELLUCON 1998, pages Woodhead Publishing Ltd., [10] G. Jayme and M. Harders- Steinhäuser. Kinematografische Erfassung der bei der Auflösung von Cellulose auftretenden Querteilungsformen. Das Papier, 18(10a):pp , [11] B.D. Jordan and N.G. Nguyen. Curvature, kink and curl. Paperi ja Puu, 68(4):pp , [12] H. Karlsson, P.I. Fransson and U.B. Mohlin. STFI Fibermaster. In 1999 SPCI International Conference on New Available Technologies 1999, pages Swedish Association of Pulp and Paper (SPCI), [13] R.P. Kibblewhite. Effects of fiber kinking and pulp bleaching on wet web strength. Tappi J., 57(8):pp , [14] R. Klein and H. Droege. Image analysis of fibre morphology. In 3rd Symposion: Image Analysis for Pulp and Paper Research and Production. STFI, [15] T. Kroehl, P. Lorencak, A. Gierulski, H. Eipel, and D. Horn. A new laser-optical method for counting colloidally dispersed
9 pitch. Nordic Pulp and Paper R. J., 9(1):pp , [16] J.-E. Levlin and L. Söderhjelm, editors. Pulp and Paper Testing, volume 17 of Papermaking Science and Technology. Fapet Oy, ISBN [17] L. E. Lindberg, L.H. Vähäsalo, and B.R. Holmbom. Flow cytometry of bacteria and wood resin particles in paper production. Nordic Pulp and Paper R. J., 19(4):pp , [18] LY. Liu, R. Gustafson, and J.B. Callis. A novel method to measure fiber kappa number. Tappi J., 82(9):pp , also: /Forest/Flow Imager A-99.htm, download [19] C.-H. Ljungqvist, R. Lyng, and F. Thuvander. Influence of fibre damage in latewood spruce tracheids on strain to failure of wood fibres determined by weibull modelling. Nordic Pulp and Paper R. J., 19(2):pp , [20] P.A. Moss, I. Nyblom, A.M. Sneck, and H.K. Hyvärinen. The location and qualification of lignin in kraft pulps using clsm and image analysis. In PTS-COST E11 Workshop - Characterization Methods for Fibres and Paper, pages PTS, [21] H. Nisser and W. Brecht. Zwei neue Messkriterien von aufgeschwemmten Fasern zur Beurteilung der Blattfestigkeit. Svensk Papperstidning, 66(2):pp , [22] D. Page, R. Seth, B. Jordan, and M. Barbe. Curl, crimps, kinks and microcompressions in pulp fibers - their origin, measurement and significance. In Proceedings 8th Fundamental Reseach Symposium Oxford, pages , [23] M. Pluta. Advanced Light Microscopy - Specialized Methods (Vol. 2). Elsevier, ISBN [24] G. Robertson, J. Olson, and P. Allen. Measurement of fiber length, coarseness and shape with the fiber quality analyzer. Tappi J., 82(10):pp , [25] F.L. Simons. A stain for use in the microscopy of beaten fibers. Tappi J., 33(7):pp , [26] P. Stenius, editor. Forest Products Chemistry, volume 3 of Papermaking Science and Technology. Fapet Oy, ISBN [27] A. Tessadro, C. Voillot, and J. Silvy. Dynamic characterization of pulp fiber morphology. In Proceedings 2nd European Symposion Image Analysis for Pulp and Paper Research and Production, pages IFP Darmstadt, [28] G. E. P. Tourtollet. A new tool for pulp morphology analysis. In Proceedings Conference Measurement & Control of Papermaking, Edinburgh 2000, pages Pira, [29] R.J. Trepanier. Automatic fiber length and shape measurement by image analysis. Tappi J., 81(6):pp , [30] M. Turunen, C. LeNy, T. Tienvieri, and J. Niinimäki. Comparison of fibre morphology analysers. Appita J., 58(1):pp , [31] E.W. Unger, H.P. Fink, and B. Philipp. Morphometrische Untersuchungen des Quell- und Lösevorgangs von Celluslosefasern in EWNN und LiCl/Dimethylacetamid. Das Papier, 49(6): , [32] L. Vähäsalo, R. Degerth, and B. Holmbom. The use of flow cytometry in wet end research. Paper Technology, 44(1):pp. 45
10 49, [33] H. Widauer. Automatisierte bildanalytische Charakterisierung des Schädigungsgrades von Zellstofffasern. Licentiate thesis, Graz University of Technology, [34] S.C. Young. A Calibration and Maintenance Schedule for the Kajaani FS-200 Fibre Analyzer. Appita J., 46(6):pp , [35] L. Yu, L.H. Allen, and A. Esser. Evaluation of a laser-optical resin particle counter. Tappi J., 2(3):pp , 2003.
THE FIBER QUALITY ANALYZER
 PEER REVIEWED FIBER ANALYSIS Measurement of fiber length, coarseness, and shape with the fiber quality analyzer GORDON ROBERTSON, JAMES OLSON, PHILIP ALLEN, BEN CHAN, AND RAJINDER SETH THE FIBER QUALITY
PEER REVIEWED FIBER ANALYSIS Measurement of fiber length, coarseness, and shape with the fiber quality analyzer GORDON ROBERTSON, JAMES OLSON, PHILIP ALLEN, BEN CHAN, AND RAJINDER SETH THE FIBER QUALITY
PULP FIBER QUALITY AND THE RELATIONSHIP WITH PAPER TISSUE PROPERTIES. Roland J. Trepanier, PhD. OpTest Equipment Inc. Hawkesbury, ON K6A3S3, Canada
 PULP FIBER QUALITY AND THE RELATIONSHIP WITH PAPER TISSUE PROPERTIES Roland J. Trepanier, PhD OpTest Equipment Inc. Hawkesbury, ON K6A3S3, Canada Introduction Tissue papers include a wide range of products
PULP FIBER QUALITY AND THE RELATIONSHIP WITH PAPER TISSUE PROPERTIES Roland J. Trepanier, PhD OpTest Equipment Inc. Hawkesbury, ON K6A3S3, Canada Introduction Tissue papers include a wide range of products
Mid Sweden University
 Mid Sweden University This is a published version of a paper published in Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal. Citation for the published paper: Reyier Österling, S., Ferritsius, O., Ferritsius, R. (212)
Mid Sweden University This is a published version of a paper published in Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal. Citation for the published paper: Reyier Österling, S., Ferritsius, O., Ferritsius, R. (212)
Advances in Papermaking Wet End Chemistry Application Technologies
 Advances in Papermaking Wet End Chemistry Application Technologies Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Overview 1-1 Advances in Equipment Imply New Opportunities 1-2 Definitions, including Application Technologies
Advances in Papermaking Wet End Chemistry Application Technologies Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Overview 1-1 Advances in Equipment Imply New Opportunities 1-2 Definitions, including Application Technologies
Advanced characterization techniques to evaluate the structure of nanofibrillated cellulose
 Advanced characterization techniques to evaluate the structure of nanofibrillated cellulose Final Conference 19.6.2012 Asko Sneck, Atsushi Tanaka, VTT Valerie Meyer, CTP Jens Kretzschmar, PTS Aim Use advanced
Advanced characterization techniques to evaluate the structure of nanofibrillated cellulose Final Conference 19.6.2012 Asko Sneck, Atsushi Tanaka, VTT Valerie Meyer, CTP Jens Kretzschmar, PTS Aim Use advanced
AFM SURFACE ANALYSIS OF FUNGAL MODIFIED CTMP FIBERS
 CELLULOSE CHEMISTRY AND TECHNOLOGY AFM SURFACE ANALYSIS OF FUNGAL MODIFIED CTMP FIBERS CHONG-XING HUANG, QI-FENG YANG and SHUANG-FEI WANG College of Light Industry and Food Engineering, Guangxi University,
CELLULOSE CHEMISTRY AND TECHNOLOGY AFM SURFACE ANALYSIS OF FUNGAL MODIFIED CTMP FIBERS CHONG-XING HUANG, QI-FENG YANG and SHUANG-FEI WANG College of Light Industry and Food Engineering, Guangxi University,
Papermachine runnability of never dried, dried, and enzymatically treated dried pulp
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry: Advances in Applied and Fundamental Research Papermachine runnability of never dried, dried, and enzymatically
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry: Advances in Applied and Fundamental Research Papermachine runnability of never dried, dried, and enzymatically
IMPACT OF COOKING CONDITIONS ON PULP YIELD AND OTHER PARAMETERS
 IMPACT OF COOKING CONDITIONS ON PULP YIELD AND OTHER PARAMETERS Nam Hee Shin and Bertil Stromberg Andritz Inc 13 Pruyn s Island Drive Glens Falls, NY 12801 ABSTRACT Two laboratory studies using multiple
IMPACT OF COOKING CONDITIONS ON PULP YIELD AND OTHER PARAMETERS Nam Hee Shin and Bertil Stromberg Andritz Inc 13 Pruyn s Island Drive Glens Falls, NY 12801 ABSTRACT Two laboratory studies using multiple
Water Absorptiveness of Handsheets Produced with Various ph Levels of Pulp Suspension, AKD Dosages and Mixing Times
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 4-55 () Water Absorptiveness of Handsheets Produced with Various Levels of Pulp Suspension, AKD Dosages and Mixing Times Somwang Khantayanuwong*, Atipong Wattanayingyongkul
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 4-55 () Water Absorptiveness of Handsheets Produced with Various Levels of Pulp Suspension, AKD Dosages and Mixing Times Somwang Khantayanuwong*, Atipong Wattanayingyongkul
FIBER PROCESS CONTROL
 FIBER PROCESS CONTROL Pulmac International Introduction The Pulmac Z-Span System permits the real time characterization of the quality of the fibers in pulp anywhere from the brown stock washer to the
FIBER PROCESS CONTROL Pulmac International Introduction The Pulmac Z-Span System permits the real time characterization of the quality of the fibers in pulp anywhere from the brown stock washer to the
Influence of Processing Conditions on Melt Blown Web Structure: Part 2 Primary Airflow Rate
 ORIGINAL PAPER/PEER-REVIEWED Influence of Processing Conditions on Melt Blown Web Structure: Part 2 Primary Airflow Rate By Randall R. Bresee, Department of Materials Science & Engineering, The University
ORIGINAL PAPER/PEER-REVIEWED Influence of Processing Conditions on Melt Blown Web Structure: Part 2 Primary Airflow Rate By Randall R. Bresee, Department of Materials Science & Engineering, The University
Materials and NDT Applications in Aircraft Component Development Tests
 2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.4.B.2 Materials and NDT Applications in Aircraft Component Development Tests Sabine GOLDBACH, Rainer FRANKE, IMA Dresden Abstract. The concept
2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.4.B.2 Materials and NDT Applications in Aircraft Component Development Tests Sabine GOLDBACH, Rainer FRANKE, IMA Dresden Abstract. The concept
PENETRANT TESTING: ABILITY EXTENSION AND SENSITIVITY EVALUATION
 PENETRANT TESTING: ABILITY EXTENSION AND SENSITIVITY EVALUATION Migoun N. P. Institute of Applied Physics of National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, Minsk, Belarus Introduction. Several ways of the increasing
PENETRANT TESTING: ABILITY EXTENSION AND SENSITIVITY EVALUATION Migoun N. P. Institute of Applied Physics of National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, Minsk, Belarus Introduction. Several ways of the increasing
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TWO METHODS FOR EVALUATING FIVE-CARBON SUGARS IN EUCALYPTUS EXTRACTION LIQUOR
 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TWO METHODS FOR EVALUATING FIVE-CARBON SUGARS IN EUCALYPTUS EXTRACTION LIQUOR Congcong Chi, a,b* Zeng Zhang, a Weiwei Ge, a and Hasan Jameel b Alkaline pre-extraction and hydrothermal
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TWO METHODS FOR EVALUATING FIVE-CARBON SUGARS IN EUCALYPTUS EXTRACTION LIQUOR Congcong Chi, a,b* Zeng Zhang, a Weiwei Ge, a and Hasan Jameel b Alkaline pre-extraction and hydrothermal
Effect of fiber loading on paper properties
 PEERREVIEWED FIBER LOADING Effect of fiber loading on paper properties JOHN H. KLUNGNESS, MARGUERITE S. SYKES, FREYA TAN, SAID ABUBAKR, AND JACOB D. EISENWASSER P REVIOUS PUBLICATIONS REPORTED the benefits
PEERREVIEWED FIBER LOADING Effect of fiber loading on paper properties JOHN H. KLUNGNESS, MARGUERITE S. SYKES, FREYA TAN, SAID ABUBAKR, AND JACOB D. EISENWASSER P REVIOUS PUBLICATIONS REPORTED the benefits
Implementing Agencies: ACIRD, Yamuna Nagar CPPRI, Saharanpur
 Implementing Agencies: ACIRD, Yamuna Nagar CPPRI, Saharanpur February 20, 2014 Background Enzymatic pretreatment of chemical pulps before refining helps in fibrillation; this can reduce the energy requirement
Implementing Agencies: ACIRD, Yamuna Nagar CPPRI, Saharanpur February 20, 2014 Background Enzymatic pretreatment of chemical pulps before refining helps in fibrillation; this can reduce the energy requirement
Improving Black Liquor Processability and Combustibility
 Creating forest sector solutions www.fpinnovations.ca Improving Black Liquor Processability and Combustibility Pak Wong Steam & Steam Power Fall Meeting December 4, 2007 A mill can achieve significant
Creating forest sector solutions www.fpinnovations.ca Improving Black Liquor Processability and Combustibility Pak Wong Steam & Steam Power Fall Meeting December 4, 2007 A mill can achieve significant
bio-mof-1 DMASM Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM.
 bio-mof-1 Transmittance bio-mof-1 DMASM DMASMI 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM. Intensity (a.u.) bio-mof-1 DMASM as
bio-mof-1 Transmittance bio-mof-1 DMASM DMASMI 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM. Intensity (a.u.) bio-mof-1 DMASM as
APPLICATION AND DEPLOYMENT OF ADVANCED NDE TECHNIQUES IN HIGH PRESSURE VESSELS
 APPLICATION AND DEPLOYMENT OF ADVANCED NDE TECHNIQUES IN HIGH PRESSURE VESSELS Jeffrey P. Milligan, Daniel T. Peters, Structural Integrity Associates, Inc., USA Many advances in Non-Destructive Examination
APPLICATION AND DEPLOYMENT OF ADVANCED NDE TECHNIQUES IN HIGH PRESSURE VESSELS Jeffrey P. Milligan, Daniel T. Peters, Structural Integrity Associates, Inc., USA Many advances in Non-Destructive Examination
Copyright : 2005, Springer
 Deakin Research Online Deakin University s institutional research repository DDeakin Research Online Research Online This is the author s final peer reviewed version of the item published as: Wang, Huimin,
Deakin Research Online Deakin University s institutional research repository DDeakin Research Online Research Online This is the author s final peer reviewed version of the item published as: Wang, Huimin,
The scheduled dates for NDT Inspector Certification Examination are as below:
 This course gives a broad knowledge about In-Service Inspection of pressure vessel and prepares students for the NDT ( PT, MT, UT, RT ) Exam. The course is an intensive 208 Hrs(total). course with Special
This course gives a broad knowledge about In-Service Inspection of pressure vessel and prepares students for the NDT ( PT, MT, UT, RT ) Exam. The course is an intensive 208 Hrs(total). course with Special
NDT Challenges and Solutions for Metal Additive Manufactured (AM) Parts & Structures
 NDT Challenges and Solutions for Metal Additive Manufactured (AM) Parts & Structures Space Tech Expo Bremen, Germany, 24-26 October 2017 1 Everything starts with the Process Map 2 Process Chain - AM 1
NDT Challenges and Solutions for Metal Additive Manufactured (AM) Parts & Structures Space Tech Expo Bremen, Germany, 24-26 October 2017 1 Everything starts with the Process Map 2 Process Chain - AM 1
Introduction to Nondestructive Testing
 Introduction to Nondestructive Testing Outline Introduction to NDT Overview of Six Most Common NDT Methods Selected Applications Definition of NDT The use of noninvasive techniques to determine the integrity
Introduction to Nondestructive Testing Outline Introduction to NDT Overview of Six Most Common NDT Methods Selected Applications Definition of NDT The use of noninvasive techniques to determine the integrity
GAFCHROMIC MD-55 RADIOCHROMIC DOSIMETRY FILM FOR HIGH-ENERGY PHOTONS CONFIGURATION, SPECIFICATIONS AND PERFORMANCE DATA
 GAFCHROMIC MD-55 RADIOCHROMIC DOSIMETRY FILM FOR HIGH-ENERGY PHOTONS CONFIGURATION, SPECIFICATIONS AND PERFORMANCE DATA DESCRIPTION GAFCHROMIC MD-55 radiochromic dosimetry film is designed for the measurement
GAFCHROMIC MD-55 RADIOCHROMIC DOSIMETRY FILM FOR HIGH-ENERGY PHOTONS CONFIGURATION, SPECIFICATIONS AND PERFORMANCE DATA DESCRIPTION GAFCHROMIC MD-55 radiochromic dosimetry film is designed for the measurement
On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging. On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging. Wavelength Specific Imaging
 On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, FOPS, OCT-C Penn State Hershey Eye Center Hershey, PA On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Wavelengths
On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, FOPS, OCT-C Penn State Hershey Eye Center Hershey, PA On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Wavelengths
World Pulp & Paper THE INTERNATIONAL REVIEW FOR THE PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY
 World Pulp & Paper THE INTERNATIONAL REVIEW FOR THE PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY 2012 Maximyze your fibre basket By David R. Jones, Industry Specialist, Paper Technologies - Buckman Buckman GREEN. Our color.
World Pulp & Paper THE INTERNATIONAL REVIEW FOR THE PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY 2012 Maximyze your fibre basket By David R. Jones, Industry Specialist, Paper Technologies - Buckman Buckman GREEN. Our color.
AMENDMENTS TO THE SECOND REVISION OF THE FIRST EDITION OF THE MANUAL ON DEVELOPMENT AND USE OF FAO AND WHO SPECIFICATIONS FOR PESTICIDES
 AMENDMENTS TO THE SECOND REVISION OF THE FIRST EDITION OF THE MANUAL ON DEVELOPMENT AND USE OF FAO AND WHO SPECIFICATIONS FOR PESTICIDES Page Current text Revised text Notes P.21 A. 10.1. WHO classification
AMENDMENTS TO THE SECOND REVISION OF THE FIRST EDITION OF THE MANUAL ON DEVELOPMENT AND USE OF FAO AND WHO SPECIFICATIONS FOR PESTICIDES Page Current text Revised text Notes P.21 A. 10.1. WHO classification
The Chemistry of Bleaching and Post-Color Formation in Kraft Pulps. Göran Gellerstedt
 The Chemistry of Bleaching and Post-Color Formation in Kraft Pulps Göran Gellerstedt Content The structure of residual lignin The meaning of kappa number General aspects on bleaching The oxygen stage The
The Chemistry of Bleaching and Post-Color Formation in Kraft Pulps Göran Gellerstedt Content The structure of residual lignin The meaning of kappa number General aspects on bleaching The oxygen stage The
Straight Through Hole Drilling in Machinable Ceramics
 Technical Communication JLMN-Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering Vol. 10, No. 1, 2015 Straight Through Hole Drilling in Machinable Ceramics Susumu Nakamura *1, Takumi Miura *2 and Masaya Tsuta *2 *1
Technical Communication JLMN-Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering Vol. 10, No. 1, 2015 Straight Through Hole Drilling in Machinable Ceramics Susumu Nakamura *1, Takumi Miura *2 and Masaya Tsuta *2 *1
Cellulose swelling and dissolution as a tool to study the fiber structure
 Cellulose swelling and dissolution as a tool to study the fiber structure Patrick Navard, Céline Cuissinat To cite this version: Patrick Navard, Céline Cuissinat. Cellulose swelling and dissolution as
Cellulose swelling and dissolution as a tool to study the fiber structure Patrick Navard, Céline Cuissinat To cite this version: Patrick Navard, Céline Cuissinat. Cellulose swelling and dissolution as
VISUALIZATION OF TRANSDUCER-PRODUCED SOUND FIELDS IN SOLIDS
 VISUALIZATION OF TRANSDUCER-PRODUCED SOUND FIELDS IN SOLIDS Wolfgang Sachse* Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Cornell University, Ithaca, New York - 14853 ABSTRACT Broadband ultrasonic pulses
VISUALIZATION OF TRANSDUCER-PRODUCED SOUND FIELDS IN SOLIDS Wolfgang Sachse* Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Cornell University, Ithaca, New York - 14853 ABSTRACT Broadband ultrasonic pulses
ELECTROSPUN CELLULOSE ULTRA-FINE FIBERS FROM KRAFT PULP
 ELECTROSPUN CELLULOSE ULTRA-FINE FIBERS FROM KRAFT PULP S. J. Yeoh 1, W.Y. Hamad 2, F.K. Ko 1 1 University of British Columbia 2355, East Mall, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T1Z4 2 FPInnovations 3800, Wesbrook
ELECTROSPUN CELLULOSE ULTRA-FINE FIBERS FROM KRAFT PULP S. J. Yeoh 1, W.Y. Hamad 2, F.K. Ko 1 1 University of British Columbia 2355, East Mall, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T1Z4 2 FPInnovations 3800, Wesbrook
Three-Dimensional Quantitative Co-Mapping of Pulmonary Morphology and. Nanoparticle Distribution with Cellular Resolution in Nondissected Murine
 Three-Dimensional Quantitative Co-Mapping of Pulmonary Morphology and Nanoparticle Distribution with Cellular Resolution in Nondissected Murine Lungs Lin Yang,,, Annette Feuchtinger, Winfried Möller,,
Three-Dimensional Quantitative Co-Mapping of Pulmonary Morphology and Nanoparticle Distribution with Cellular Resolution in Nondissected Murine Lungs Lin Yang,,, Annette Feuchtinger, Winfried Möller,,
Improved Weatherability of Outdoor Wood Stains using Nanotechnology
 Improved Weatherability of Outdoor Wood Stains using Nanotechnology Roger Cayton, Patrick G. Murray, David Nelson, and Ryan Ostrowski Nanophase Technologies Corporation, US Introduction There is no question
Improved Weatherability of Outdoor Wood Stains using Nanotechnology Roger Cayton, Patrick G. Murray, David Nelson, and Ryan Ostrowski Nanophase Technologies Corporation, US Introduction There is no question
STATION 1 - Types of Blood Vessels
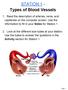 STATION 1 - Types of Blood Vessels 1. Read the description of arteries, veins, and capillaries on the computer screen. Use the information to fill in your Notes for Station 1 2. Look at the different size
STATION 1 - Types of Blood Vessels 1. Read the description of arteries, veins, and capillaries on the computer screen. Use the information to fill in your Notes for Station 1 2. Look at the different size
TissueSurgeon Hard Tissue Applications
 TissueSurgeon Hard Tissue Applications Laser Based Histology Hard Tissue with TissueSurgeon TissueSurgeon is an excellent tool for easy, fast and flexible sectioning of hard tissue. Native hard tissue
TissueSurgeon Hard Tissue Applications Laser Based Histology Hard Tissue with TissueSurgeon TissueSurgeon is an excellent tool for easy, fast and flexible sectioning of hard tissue. Native hard tissue
Introduction to Nondestructive Testing. Outline
 Introduction to Nondestructive Testing Outline Introduction to NDT Overview of Six Most Common NDT Methods Selected Applications Page 1 Definition of NDT The use of noninvasive techniques to determine
Introduction to Nondestructive Testing Outline Introduction to NDT Overview of Six Most Common NDT Methods Selected Applications Page 1 Definition of NDT The use of noninvasive techniques to determine
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa
 Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
In-Vitro Bioequivalence Studies for Oral Solid Dose products using the Morphologi G3-ID
 In-Vitro Bioequivalence Studies for Oral Solid Dose products using the Morphologi G3-ID PARTICLE SHAPE MOLECULAR SIZE CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION Introduction A generic drug is defined as being "identical
In-Vitro Bioequivalence Studies for Oral Solid Dose products using the Morphologi G3-ID PARTICLE SHAPE MOLECULAR SIZE CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION Introduction A generic drug is defined as being "identical
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(8): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 215, 7(8):257-261 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Pulping process for rice straw in basic ionic liquid
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 215, 7(8):257-261 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Pulping process for rice straw in basic ionic liquid
Underwater Acoustic Measurements in Megahertz Frequency Range.
 Underwater Acoustic Measurements in Megahertz Frequency Range. Current State and Prospects of Development in Russia Alexander M. Enyakov,, Many medical applications of underwater acoustic measurements
Underwater Acoustic Measurements in Megahertz Frequency Range. Current State and Prospects of Development in Russia Alexander M. Enyakov,, Many medical applications of underwater acoustic measurements
LIQUID PENETRANT EXAMINATION PROCEDURE
 Page 1 of 10 LIQUID PENETRANT EXAMINATION PROCEDURE Doc. No. KNS/PT/01.REV 0 Page: 8 of 8 Date: 15.09.2012 LIQUID PENETRANT EXAMINATION PROCEDURE (VISIBLE - SOLVENT REMOVABLE) PREPARED & APPROVED BY NDE-
Page 1 of 10 LIQUID PENETRANT EXAMINATION PROCEDURE Doc. No. KNS/PT/01.REV 0 Page: 8 of 8 Date: 15.09.2012 LIQUID PENETRANT EXAMINATION PROCEDURE (VISIBLE - SOLVENT REMOVABLE) PREPARED & APPROVED BY NDE-
Exceptional versatility without compromise
 Introducing the VICTUS femtosecond laser platform Exceptional versatility without compromise FEMTOSECOND TECHNOLOGY that empowers Introducing VICTUS the first femtosecond laser capable of exceptional performance
Introducing the VICTUS femtosecond laser platform Exceptional versatility without compromise FEMTOSECOND TECHNOLOGY that empowers Introducing VICTUS the first femtosecond laser capable of exceptional performance
New Core Alignment Fusion Splicer FSM-50S
 New Core Alignment Fusion Splicer FSM-50S Shigeru Saito, Katsumi Sasaki, Kenji Takahashi, Koji Ohzawa, Taku Otani and Srachate Chumpol For many years, most fiber optic splicing in the core and edges of
New Core Alignment Fusion Splicer FSM-50S Shigeru Saito, Katsumi Sasaki, Kenji Takahashi, Koji Ohzawa, Taku Otani and Srachate Chumpol For many years, most fiber optic splicing in the core and edges of
Precise defect detection with sensor data fusion
 Precise defect detection with sensor data fusion Composite Europe 2016 Dipl.-Ing. Philipp Nienheysen Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering (WZL) of RWTH Aachen University, Germany Chair
Precise defect detection with sensor data fusion Composite Europe 2016 Dipl.-Ing. Philipp Nienheysen Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering (WZL) of RWTH Aachen University, Germany Chair
Keywords: TEMPO-mediated oxidation; Thermomechanical pulp; Carboxylic group; Lignin; Paper strength
 Selective TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation of Thermomechanical Pulp Pu Ma and Huamin Zhai * Carboxylic acid groups were introduced onto thermomechanical pulp (TMP) long fiber surfaces by 2,2,6,6,- tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl
Selective TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation of Thermomechanical Pulp Pu Ma and Huamin Zhai * Carboxylic acid groups were introduced onto thermomechanical pulp (TMP) long fiber surfaces by 2,2,6,6,- tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl
Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
A novel approach to determining the contribution of the fiber and fines fraction to the water retention value (WRV) of chemical and mechanical pulps
 Cellulose (2017) 24:3029 3036 DOI 10.1007/s10570-017-1298-6 ORIGINAL PAPER A novel approach to determining the contribution of the fiber and fines fraction to the water retention value (WRV) of chemical
Cellulose (2017) 24:3029 3036 DOI 10.1007/s10570-017-1298-6 ORIGINAL PAPER A novel approach to determining the contribution of the fiber and fines fraction to the water retention value (WRV) of chemical
Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
Defining Cutting Edge Quality. Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC BIMO-FSC
 Defining Cutting Edge Quality Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC BIMO-FSC Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC for Flexible Flat Sheet Cutting The use of fibre lasers for cutting applications is growing steadily. The
Defining Cutting Edge Quality Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC BIMO-FSC Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC for Flexible Flat Sheet Cutting The use of fibre lasers for cutting applications is growing steadily. The
Structure and Function of Cells, Organs and Organ Systems 1
 I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics
 Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics Dr Liz Meehan, Pharmaceutical Development, Macclesfield UK 1 Excipients Definition
Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics Dr Liz Meehan, Pharmaceutical Development, Macclesfield UK 1 Excipients Definition
Evolution of analytical techniques for extractives
 Evolution of analytical techniques for extractives A personal review Bjarne Holmbom Final Seminar on COST Action FP 0901, Turku/Åbo, September 17, 2013 State-of-the-art in 1966 Perkin-Elmer F11 Pyrolyzer
Evolution of analytical techniques for extractives A personal review Bjarne Holmbom Final Seminar on COST Action FP 0901, Turku/Åbo, September 17, 2013 State-of-the-art in 1966 Perkin-Elmer F11 Pyrolyzer
Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
 Proceedings of the 215 2nd International Symposium on Physics and Technology of Sensors, 8-1th March, 215, Pune, India Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
Proceedings of the 215 2nd International Symposium on Physics and Technology of Sensors, 8-1th March, 215, Pune, India Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x
 J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
FORMULATION CHOICE. How and why they are chosen. Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group
 FORMULATION CHOICE How and why they are chosen Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group Topics Why formulate? How to identify formulation options Drivers Principle formulation type overview
FORMULATION CHOICE How and why they are chosen Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group Topics Why formulate? How to identify formulation options Drivers Principle formulation type overview
Measurement of Mechanical Properties of Coronary Stents according to the European Standard pren
 February 1999 45 Measurement of Mechanical Properties of Coronary Stents according to the European Standard pren 12006-3 W. SCHMIDT, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND, K.-P. SCHMITZ Institute for Biomedical Engineering,
February 1999 45 Measurement of Mechanical Properties of Coronary Stents according to the European Standard pren 12006-3 W. SCHMIDT, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND, K.-P. SCHMITZ Institute for Biomedical Engineering,
Cell Boundaries. Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h
 Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Lignin Isolation from Pulp
 Lignin Isolation from Pulp Several different enzymatic, chemical and mechanical methods have been developed for the isolation of lignin from wood and pulp. However, due to the heterogeneous nature of wood
Lignin Isolation from Pulp Several different enzymatic, chemical and mechanical methods have been developed for the isolation of lignin from wood and pulp. However, due to the heterogeneous nature of wood
Nanostructured ZnO as a solution-processable transparent electrode material for low-cost photovoltaics
 Nanostructured ZnO as a solution-processable transparent electrode material for low-cost photovoltaics Investigators P.I: Alberto Salleo, Assistant Professor, Materials Science and Engineering Dr. Ludwig
Nanostructured ZnO as a solution-processable transparent electrode material for low-cost photovoltaics Investigators P.I: Alberto Salleo, Assistant Professor, Materials Science and Engineering Dr. Ludwig
Research on Digital Testing System of Evaluating Characteristics for Ultrasonic Transducer
 Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Research on Digital Testing System of Evaluating Characteristics for Ultrasonic Transducer Qin Yin, * Liang Heng, Peng-Fei
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Research on Digital Testing System of Evaluating Characteristics for Ultrasonic Transducer Qin Yin, * Liang Heng, Peng-Fei
CPGAN #002. FTIR Quantification of Absorbed Radiation Dose in Polyethylene
 1.1 Introduction Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is the current material of choice for bearing surface applications in total joint arthroplasty. In an effort to enhance the wear properties
1.1 Introduction Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is the current material of choice for bearing surface applications in total joint arthroplasty. In an effort to enhance the wear properties
Defining Cutting Edge Quality. Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC BIMO-FSC
 Defining Cutting Edge Quality Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC BIMO-FSC Modules 40 Laser light cable receiver Cover slide in front of collimation 9 46,5 0,2 86,5 64,4 2,5 131,2 Collimation module with manual
Defining Cutting Edge Quality Laser Cutting Head BIMO-FSC BIMO-FSC Modules 40 Laser light cable receiver Cover slide in front of collimation 9 46,5 0,2 86,5 64,4 2,5 131,2 Collimation module with manual
An Information Theory-Based Thermometer to Uncover Brid... Bridge Defects. Research January 17, 2017
 Research January 17, 2017 An Information Theory-Based Thermometer to Uncover Bridge Defects By Lakshmi Chandrasekaran (https://sinews.siam.org/aboutthe-author/lakshmi-chandrasekaran) Aging roadway infrastructure
Research January 17, 2017 An Information Theory-Based Thermometer to Uncover Bridge Defects By Lakshmi Chandrasekaran (https://sinews.siam.org/aboutthe-author/lakshmi-chandrasekaran) Aging roadway infrastructure
Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects
 7 th Asia-Pacific Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring November 12-15, 2018 Hong Kong SAR, P.R. China Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects Zhenggan Zhou 1,2,3
7 th Asia-Pacific Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring November 12-15, 2018 Hong Kong SAR, P.R. China Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects Zhenggan Zhou 1,2,3
GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3
 GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3 WARNING: Store below 25ºC Store away from radiation sources Avoid exposure of film to sunlight Handle film carefully, creasing may cause damage Do not expose to temperatures
GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3 WARNING: Store below 25ºC Store away from radiation sources Avoid exposure of film to sunlight Handle film carefully, creasing may cause damage Do not expose to temperatures
Dispersants and Related Oil Spill Technologies at the Nanoscale!
 vj@tulane.edu Dispersants and Related Oil Spill Technologies at the Nanoscale! Vijay T. John Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Tulane University Funding: Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative
vj@tulane.edu Dispersants and Related Oil Spill Technologies at the Nanoscale! Vijay T. John Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Tulane University Funding: Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative
MUSCLE STRUCTURE AND WATER RETENTION IN FRESH AND COOKED MEAT PRODUCTS
 MUSCLE STRUCTURE AND WATER RETENTION IN FRESH AND COOKED MEAT PRODUCTS Project Report Reference: 2013-5009 Date: 14 November 2017 Project Description Raw meat is cooked to achieve a palatable and safe
MUSCLE STRUCTURE AND WATER RETENTION IN FRESH AND COOKED MEAT PRODUCTS Project Report Reference: 2013-5009 Date: 14 November 2017 Project Description Raw meat is cooked to achieve a palatable and safe
O. Repeat the measurement in all relevant modes used in your experiments (e.g. settings for orbital averaging).
 Before You Begin Read through this entire protocol sheet carefully before you start your experiment and prepare any materials you may need. This year, in order to improve reproducibility, we are requiring
Before You Begin Read through this entire protocol sheet carefully before you start your experiment and prepare any materials you may need. This year, in order to improve reproducibility, we are requiring
The Benefits of Enzymes in Pulp & Paper Processes
 The Benefits of Enzymes in Pulp & Paper Processes Tom Woodward Director of Technology EnzKem Associates EnzKem Associates Tom Woodward, Jack Turner and John Gurganious Over 30 years experience each in
The Benefits of Enzymes in Pulp & Paper Processes Tom Woodward Director of Technology EnzKem Associates EnzKem Associates Tom Woodward, Jack Turner and John Gurganious Over 30 years experience each in
Enzyme Applications in Pulp and Paper Manufacturing
 Enzyme Applications in Pulp and Paper Manufacturing Mike Paice Lakehead University Symposium September 27, 2005 2005 Paprican 1 utline Background on status of biotech in P&P Enzymes in Kraft pulping Enzymes
Enzyme Applications in Pulp and Paper Manufacturing Mike Paice Lakehead University Symposium September 27, 2005 2005 Paprican 1 utline Background on status of biotech in P&P Enzymes in Kraft pulping Enzymes
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion
 Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
A Hierarchical Artificial Neural Network Model for Giemsa-Stained Human Chromosome Classification
 A Hierarchical Artificial Neural Network Model for Giemsa-Stained Human Chromosome Classification JONGMAN CHO 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Inje University, Gimhae, 621-749, KOREA minerva@ieeeorg
A Hierarchical Artificial Neural Network Model for Giemsa-Stained Human Chromosome Classification JONGMAN CHO 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Inje University, Gimhae, 621-749, KOREA minerva@ieeeorg
Portable Retina Eye Scanning Device
 Portable Retina Eye Scanning Device Engineering Science Department Sonoma State University Students: Cristin Faria & Diego A. Espinosa Faculty Advisor: Dr. Sudhir Shrestha Industry Advisor: Ben Valvodinos
Portable Retina Eye Scanning Device Engineering Science Department Sonoma State University Students: Cristin Faria & Diego A. Espinosa Faculty Advisor: Dr. Sudhir Shrestha Industry Advisor: Ben Valvodinos
Chapter 2. Palmyra Fiber Separation Process And Properties Of Fiber And. Polyester Resin
 Chapter 2 Palmyra Fiber Separation Process And Properties Of Fiber And Polyester Resin 1.1 Introduction Fibers of lightweight and high strength are embedded in the week matrix to get high strength composites
Chapter 2 Palmyra Fiber Separation Process And Properties Of Fiber And Polyester Resin 1.1 Introduction Fibers of lightweight and high strength are embedded in the week matrix to get high strength composites
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation
 Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
THE OPHTHALMOLOGIST S NEEDS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF THE RETINA
 biophotonics end-users needs THE OPHTHALMOLOGIST S NEEDS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF THE RETINA Dr Matonti Frédéric CHU Nord / INT AMU Marseille ANATOMY OF THE RETINA ANATOMY OF THE RETINA ANATOMY OF THE RETINA
biophotonics end-users needs THE OPHTHALMOLOGIST S NEEDS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF THE RETINA Dr Matonti Frédéric CHU Nord / INT AMU Marseille ANATOMY OF THE RETINA ANATOMY OF THE RETINA ANATOMY OF THE RETINA
Engineering the Growth of TiO 2 Nanotube Arrays on Flexible Carbon Fibre Sheets
 Engineering the Growth of TiO 2 Nanotube Arrays on Flexible Carbon Fibre Sheets Peng Chen, a Li Gu, b Xiudong Xue, a Mingjuan Li a and Xuebo Cao* a a Key Lab of Organic Synthesis of Jiangsu Province and
Engineering the Growth of TiO 2 Nanotube Arrays on Flexible Carbon Fibre Sheets Peng Chen, a Li Gu, b Xiudong Xue, a Mingjuan Li a and Xuebo Cao* a a Key Lab of Organic Synthesis of Jiangsu Province and
Dry fractionation for sustainable production
 Dry fractionation for sustainable production of functional legume pea ingredients Pascalle Pelgrom, Remko Boom, Maarten Schutyser Wageningen University Laboratory of Food Process Engineering Maarten.Schutyser@wur.nl
Dry fractionation for sustainable production of functional legume pea ingredients Pascalle Pelgrom, Remko Boom, Maarten Schutyser Wageningen University Laboratory of Food Process Engineering Maarten.Schutyser@wur.nl
Level 1/2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Unit 01 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness
 Level /2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Sample 207 Unit 0 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness Mark Scheme v0. All the material in this publication
Level /2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Sample 207 Unit 0 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness Mark Scheme v0. All the material in this publication
Technologies and Methods for Visualizing the Retina
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/revealing-retina/technologies-and-methods-for-visualizing-theretina/3663/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/revealing-retina/technologies-and-methods-for-visualizing-theretina/3663/
RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY. L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
 IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation
 Laboratory Hematology 8:85-90 2002 Carden Jennings Publishing Co.. Ltd. Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation T. SCHISANO, L. VAN HOVE Abbott
Laboratory Hematology 8:85-90 2002 Carden Jennings Publishing Co.. Ltd. Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation T. SCHISANO, L. VAN HOVE Abbott
Flaw Assessment Using Shear wave Phased array Ultrasonic Transducer
 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Flaw Assessment Using Shear wave Phased array Ultrasonic Transducer Byungsik YOON AUTHOR 1, Hee-Jong LEE CO-AUTHOR
18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Flaw Assessment Using Shear wave Phased array Ultrasonic Transducer Byungsik YOON AUTHOR 1, Hee-Jong LEE CO-AUTHOR
Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors
 Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors Guoying Zhao, Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, P. O. Box
Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors Guoying Zhao, Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, P. O. Box
QUANTIFICATION OF PROGRESSION OF RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER ATROPHY IN FUNDUS PHOTOGRAPH
 QUANTIFICATION OF PROGRESSION OF RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER ATROPHY IN FUNDUS PHOTOGRAPH Hyoun-Joong Kong *, Jong-Mo Seo **, Seung-Yeop Lee *, Hum Chung **, Dong Myung Kim **, Jeong Min Hwang **, Kwang
QUANTIFICATION OF PROGRESSION OF RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER ATROPHY IN FUNDUS PHOTOGRAPH Hyoun-Joong Kong *, Jong-Mo Seo **, Seung-Yeop Lee *, Hum Chung **, Dong Myung Kim **, Jeong Min Hwang **, Kwang
THE EFFECT OF OFFSET PRINTING INK ON LASER TONER INK AGGLOMERATION UNDER NEUTRAL PULPING CONDITIONS
 THE EFFECT OF OFFSET PRINTING INK ON LASER TONER INK AGGLOMERATION UNDER NEUTRAL PULPING CONDITIONS Sujin Xie, a Guolin Tong, a, * and Yungchang F. Chin b 1-octadecanol is known to be a highly effective
THE EFFECT OF OFFSET PRINTING INK ON LASER TONER INK AGGLOMERATION UNDER NEUTRAL PULPING CONDITIONS Sujin Xie, a Guolin Tong, a, * and Yungchang F. Chin b 1-octadecanol is known to be a highly effective
Nautilus Bulletin # 1
 Nautilus Bulletin # 1 ArthurJonesExercise.com 2 Basic Physics of Conventional Exercise Methods Almost all conventional exercises are based upon resistance provided by gravity; but even when springs are
Nautilus Bulletin # 1 ArthurJonesExercise.com 2 Basic Physics of Conventional Exercise Methods Almost all conventional exercises are based upon resistance provided by gravity; but even when springs are
The Relevance of Science for Innovations
 Bjarne Holmbom Christer Eckerman Åbo, Finland Recipients of the 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Prize The Relevance of Science for Innovations Is science really relevant? Bjarne Holmbom Christer Eckerman The Marcus
Bjarne Holmbom Christer Eckerman Åbo, Finland Recipients of the 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Prize The Relevance of Science for Innovations Is science really relevant? Bjarne Holmbom Christer Eckerman The Marcus
Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System
 Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System R. K. Saha, S. Karmakar, S. Saha, M. Roy, S. Sarkar and S.K. Sen Microelectronics Division, Saha Institute of
Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System R. K. Saha, S. Karmakar, S. Saha, M. Roy, S. Sarkar and S.K. Sen Microelectronics Division, Saha Institute of
Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. Abstract
 Progress Report No. 2-3, March 31, 1999 The Home Automation and Healthcare Consortium Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Kamal Youcef-Toumi Principal Investigator
Progress Report No. 2-3, March 31, 1999 The Home Automation and Healthcare Consortium Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Kamal Youcef-Toumi Principal Investigator
2. Which is likely to be a nonpolar solvent? A. B. B shows a carboxyl group, while A is only carbons and hydrogens.
 An organic chemistry lab uses thin layer chromatography to determine the relative polarity of different molecules. The molecules are added to the bottom of a glass plate covered with polar silicone gel
An organic chemistry lab uses thin layer chromatography to determine the relative polarity of different molecules. The molecules are added to the bottom of a glass plate covered with polar silicone gel
Diffusers Beam Splitters Refractive Microlens Arrays
 Stock Products Diffusers Beam Splitters Refractive Microlens Arrays For Custom Designs, Prototypes, or Production Quantities Contact Us Directly: MEMS Optical, Inc. 205 Import Circle Huntsville, AL 35806
Stock Products Diffusers Beam Splitters Refractive Microlens Arrays For Custom Designs, Prototypes, or Production Quantities Contact Us Directly: MEMS Optical, Inc. 205 Import Circle Huntsville, AL 35806
8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture
 8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture 8.1 Introduction In the foregoing parts of this thesis, a model membrane system of SC lipids has been developed and characterized.
8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture 8.1 Introduction In the foregoing parts of this thesis, a model membrane system of SC lipids has been developed and characterized.
MicroNIR: soluzioni QbD e PAT
 MicroNIR: soluzioni QbD e PAT Milano, 8 Maggio 2018 Emiliano Genorini MicroNIR EMEA & India Account Manager +39 039 9300225 (office) +39 337 1362987 (mobile) Via Torri Bianche, 10 20871, Vimercate (MB)
MicroNIR: soluzioni QbD e PAT Milano, 8 Maggio 2018 Emiliano Genorini MicroNIR EMEA & India Account Manager +39 039 9300225 (office) +39 337 1362987 (mobile) Via Torri Bianche, 10 20871, Vimercate (MB)
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
Application of high-power ultrasound in fibre suspensions to increase the strength of paper
 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Wood and Paper Technologies, Professorship of Paper Technology International meeting of Slovenian papermakers DITP, November 20-21, 2013 Dipl.-Ing. Tobias
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Wood and Paper Technologies, Professorship of Paper Technology International meeting of Slovenian papermakers DITP, November 20-21, 2013 Dipl.-Ing. Tobias
CHAPTER I From Biological to Artificial Neuron Model
 CHAPTER I From Biological to Artificial Neuron Model EE543 - ANN - CHAPTER 1 1 What you see in the picture? EE543 - ANN - CHAPTER 1 2 Is there any conventional computer at present with the capability of
CHAPTER I From Biological to Artificial Neuron Model EE543 - ANN - CHAPTER 1 1 What you see in the picture? EE543 - ANN - CHAPTER 1 2 Is there any conventional computer at present with the capability of
A reliable, practical and easy-to-use Determination of Soil Conductivity and Salt Content with TRIME Probes
 A reliable, practical and easy-to-use Determination of Soil Conductivity and Salt Content with TRIME Probes IMKO s TRIME TDR-probes can now report soil EC as standard simultaneously with soil moisture
A reliable, practical and easy-to-use Determination of Soil Conductivity and Salt Content with TRIME Probes IMKO s TRIME TDR-probes can now report soil EC as standard simultaneously with soil moisture
