Tanimoto et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
|
|
|
- Ethel Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of aster centration dynamics, and effects of various inhibitors on MTs and actin organization. (A and B) Method for 3D aster tracking. (A) Sperm pronuclei are imaged at each time point by acquiring 15 confocal z-slices spaced by an interval of 3 µm. The mid z-position is then automatically selected by finding the plane with maximal Hoechst signal. (B) The high Z resolution tracking confirms that asters migrate straight in 3D. Time is color coded. (C) Probability density function of T 1, T 2, and T 1 T 2 (period of phase 2) obtained from n = 13 cells. Note that the PDF of T 2 T 1 is narrower than that of T 1 and T 2, suggesting the duration of the centering phases is rather constant between cells though the time when it starts may vary more. (D) Probability density function of aster instantaneous in-plane velocity vectors for the migration three phases. The coordinates were defined so that the x axis connects sperm entry point and cell center. (E) Mean square displacement (MSD) of asters in normal conditions and in the presence of 20 µm nocodazole and 50 µm ciliobrevin D (see Materials and methods). The MSDs are the mean of n = 13 (control), n = 7 (nocodazole), and n = 6 (ciliobrevin D) cells. Broken lines indicate linear (blue) and quadratic (red) fits. The control data were well fitted by a quadratic function indicating a uniform centration with constant speed. In contrast, nocodazole data were fitted well by linear function indicating random diffusion. The MSD of ciliobrevin D treated asters was not well fitted by a linear or quadratic function, suggesting a weakly biased random motion. The speed of normal centration computed from this MSD analysis (MSD(τ) = Aτ 2, V = A) is 5.2 µm/min, similar to the speed determined from a linear fitting of the traveling distance curve (5.3 µm/min). (F) MT aster immunostaining performed in the presence of DMSO (control), latrunculin B, nocodazole, and ciliobrevin D. Drug assays are performed as in Fig. 1 (F I) and cells are fixed 3 min after drug addition. (G) F-Actin staining in the presence/absence of latrunculin B. The same image intensity range is used for phalloidin staining in control and latrunculin B treated cells. (H) Effects of ciliobrevin D on mitotic spindle bipolarity. DMSO (control) and ciliobrevin D were added 60 min postinsemination (between prophase and metaphase), and cells were imaged 10 min after. Control cells exhibit a normal spindle bipolar organization and chromosome plate alignment, whereas ciliobrevin D treated cells display disorganized chromosomes. S13
2 Figure S2. Effects of ciliobrevin D on vesicle trafficking, growth of sperm MT asters, dose-dependent effects of ciliobrevin D on aster speed, and influence of the female pronucleus on sperm aster speed and trajectories. (A and B) Lysosome movements. (A) Lysosome vesicles stained with LysoTracker are imaged every 1 s during a whole centration process. (B) Kymograph highlighting a rapid centripetal lysosome motion toward the aster center along a length of more than 10 µm, at a speed of 0.5 µm/s. The vesicle tracked is highlighted by the white arrowhead in A. (C F) Quantification of lysosome movement. (C and E) Superimposition of all tracked trajectories of lysosomes during a 10 min movie after fertilization in eggs treated with DMSO (C) or with 50 µm ciliobrevin D (E). Red trajectories correspond to lysosome movements within ±20 toward the aster center. (D and F) Scatterplot of lysosome motion orientation plotted as a function of their traveled distance. Ciliobrevin D treatment abolishes most persistent centripetal vesicle motion within the plane of focus. (G) Time-dependent immunostaining of growing and centering sperm MT asters (MTs are in green and aster centers are indicated with white arrowheads). The indicated time is taken in reference with sperm entry by accounting for a mean 3-min delay between sperm addition and sperm entry into the egg. Note the absence of MT cortex contact at timings before 7 min (H) Aster growth rate estimation. Mean aster size is computed from immunostaining images of several eggs fixed at different time points after sperm entry. Both front and rear radius growth rate are estimated from the slope of the linear fit indicated by the dotted lines, which yields an estimate of 3.8 µm/min. (I) Aster shape asymmetry is computed by comparing front and rear radii of asters images obtained from 21 individual stained eggs at various times. More than 10 individual astral MTs (or bundles) are analyzed for each aster front to compute front radius, and the rear radius is defined as the distance between the aster center and the nearest cell cortex. The dotted line marks the symmetry axis for aster shapes. The plot suggests that the shape asymmetry is 5 to 10 µm and mostly independent of aster absolute size. Immunostaining used for both H and I was performed in PDMS channel, which flattens slightly the eggs in Z, to maintain centration in the plane. (J) Sperm MT aster in a rectangular-shaped egg visualized by in situ immunostaining. (K) Dose-dependent effects of ciliobrevin D concentration on aster speed. The assay and quantification is performed as in Fig. 1 (F I). Note that for 10 µm, asters show a transient slow down followed by a speed recovery (Fig. 4, G I). (L and M) Effects of female pronucleus (marked with large red dots) movement on aster centration (small dots) dynamics. The female pronucleus starts migrating toward aster center presumably when contacting astral MTs. (L) The small black dots mark the aster center before or after female pronucleus movement; the small red dots correspond to the period when the female pronucleus in moving. In rare cases, the female pronucleus position is initially close to the sperm entry point and begins migration soon after fertilization, when the sperm aster is small and bends the aster trajectory (L, top). In most cases, the female pronucleus position is initially far from sperm entry point, and the female starts moving when the sperm aster is already large enough and does neither influence sperm aster trajectory and speed (L, bottom; and M). Error bars represent SD. Bars, 50 µm. S14 JCB 2016
3 Figure S3. 3D numerical simulations testing the influence of scaling exponents and cell shape on aster speed. (A) Simulations of aster distance time plots for α = 1, 2, 3 and α = β + 1 were performed for a spherical boundary condition. Colors in distance time plots indicate the amplitude of the force parameter a/b. The white dotted line in the left (α = 1) correspond to the result of the analytical solution of the 1D model with adjusting a/b (Eq. 11). (B) Simulations of aster distance-time plots for α = 1, 2, 3 and α = β; colors in distance time plots indicate the amplitude of the force parameter a/b. (C) Density plots of aster instantaneous speed against L front L rear and L front /L rear obtained for α = 1 and β = 0 and relatively small values of the force parameter a/b. Note that this density plot was produced from a single simulation run containing more than 9,000 data points (the same for D, G, and H). (D) Density plots of aster instantaneous speed against L front L rear and L front /L rear obtained for α = 1 and β = 1 and relatively small values of the force parameter a/b. (E H) 3D numerical simulations using the same parameter assays as in A D, but in a 3D rectangular shape. (I) Trajectories of sperm asters obtained from 3D numerical simulation obtained using different values of scaling exponents, as indicated. S15
4 Video 1. Sperm MT aster centration in a normal spherical shape cell. Male pronucleus of fertilized sea urchin egg was visualized using DNA dye Hoechst. DIC (gray) and Hoechst (cyan) images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every 10 s (shown every 2 frames) for 15 min. Video 2. Aster centration in the presence of various inhibitors. Aster centration in the presences of 1% DMSO (top left), 20 µm Latrunculin B (top right), 20 µm Nocodazole (bottom left), 50 µm Ciliobrevin D (bottom right). DIC (gray) and Hoechst (cyan) images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every 30 s for 20 min. Video 3. Lysosome dynamics during aster centration. Lysosome vesicle trafficking during pronuclear migration in the presence of 1% DMSO was visualized with LysoTracker dye. Images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every second (shown every six frames) for 10 min. Video 4. Lysosome dynamics in the presence of 50 µm ciliobrevin D. Lysosome vesicle trafficking during pronuclear migration visualized with LysoTracker dye. Addition of 50 µm ciliobrevin D in the course of the time lapse is indicated with the red text. Images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every second (shown every six frames) for 10 min. Video 5. Laser ablation of a centering MT aster 1: side ablation. Sperm aster motion is monitored before and after photoablation along the red dotted line. DIC (left) and Hoechst (right) images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every 30 s for 17 min. Video 6. Laser ablation of a centering MT aster 2: front ablation. Sperm aster motion is monitored before and after photo-ablation along the red dotted line. DIC (left) and Hoechst (right) images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every 10 s for 17 min. S16 JCB 2016
5 Video 7. Live MT aster dynamics visualized with injected fluorescent tubulin. The MT aster was visualized by injecting fluorescent tubulin solution. Images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every 30 s for 17 min. Video 8. Aster centration in a rectangular-shaped egg. Aster centration in a rectangular-shaped egg was visualized using DNA dye Hoechst. Images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every 10 s for 15 min. Video 9. 3D Numerical simulation of an aster centering in normal spherical and rectangular geometries. Numerical simulations of a 3D model for normal spherical cell geometry (left) and for a rectangular cell geometry (right). The spherical cell has a radius of 45 µm. The rectangular-shaped cell dimensions are [width, depth, height] = [144, 48, 55] in μm. In the rectangular geometry simulation, the aster starts at the corner in the midplane. 1/50 of total MTs are shown. Frames were taken every 10 s (100 simulation steps) for 25 min. Video 10. Aster centration in the presence of 10 µm ciliobrevin D. Sperm aster motion is filmed before and after treatment with 10 µm ciliobrevin D using DNA dye Hoechst. Images were obtained by time-lapse spinning-disk confocal microscopy (Ti-Eclipse [Nikon] combined with CSU-X1 spinning head [Yokogawa]). Frames were taken every 30 s for 17 min. S17
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Dunsch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201202112/dc1 Figure S1. Characterization of HMMR and CHICA antibodies. (A) HeLa
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Dunsch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201202112/dc1 Figure S1. Characterization of HMMR and CHICA antibodies. (A) HeLa
d e f Spatiotemporal quantification of subcellular ATP levels in a single HeLa cell during changes in morphology Supplementary Information
 Ca 2+ level (a. u.) Area (a. u.) Normalized distance Normalized distance Center Edge Center Edge Relative ATP level Relative ATP level Supplementary Information Spatiotemporal quantification of subcellular
Ca 2+ level (a. u.) Area (a. u.) Normalized distance Normalized distance Center Edge Center Edge Relative ATP level Relative ATP level Supplementary Information Spatiotemporal quantification of subcellular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
Microtubule Teardrop Patterns
 Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma.
 Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Karen L.P. McNally, Amy S. Fabritius, Marina L. Ellefson, Jonathan R. Flynn, Jennifer A. Milan, and Francis J. McNally
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Kinesin-1 Prevents Capture of the Oocyte Meiotic Spindle by the Sperm Aster Karen L.P. McNally, Amy S. Fabritius, Marina L. Ellefson, Jonathan R.
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Kinesin-1 Prevents Capture of the Oocyte Meiotic Spindle by the Sperm Aster Karen L.P. McNally, Amy S. Fabritius, Marina L. Ellefson, Jonathan R.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Courtheoux et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200902093/dc1 S1 Figure S2. Visualization of multiple merotelic attachments.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Courtheoux et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200902093/dc1 S1 Figure S2. Visualization of multiple merotelic attachments.
El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach
![klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach](/thumbs/91/104639484.jpg) DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm
 Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment
 Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
J. Cell Sci. 129: doi: /jcs : Supplementary information
 Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
Supplementary information. The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic. Spindle Orientation
 Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of CerTN-L15 expressed in Arabidopsis roots. a. Ratiometric images of CerTN-L15 in roots under osmotic stress Ratiometric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of CerTN-L15 expressed in Arabidopsis roots. a. Ratiometric images of CerTN-L15 in roots under osmotic stress Ratiometric
JCB. Supplemental material. Gu et al.,
 Supplemental material Gu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201010075/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. S1P directly induces actin assembly. Actin assembly at the
Supplemental material Gu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201010075/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. S1P directly induces actin assembly. Actin assembly at the
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Dynamic Partitioning of a GPI-Anchored Protein in Glycosphingolipid-Rich Microdomains Imaged by Single-Quantum Dot Tracking
 Additional data for Dynamic Partitioning of a GPI-Anchored Protein in Glycosphingolipid-Rich Microdomains Imaged by Single-Quantum Dot Tracking Fabien Pinaud 1,3, Xavier Michalet 1,3, Gopal Iyer 1, Emmanuel
Additional data for Dynamic Partitioning of a GPI-Anchored Protein in Glycosphingolipid-Rich Microdomains Imaged by Single-Quantum Dot Tracking Fabien Pinaud 1,3, Xavier Michalet 1,3, Gopal Iyer 1, Emmanuel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
 a Control IgG Intestine c Testis b Thymus 1 3 2 S S 2 1 3 4 4 Figure S1 The wild-type mouse (C57BL/6J) organs (intestine, thymus and testis) were frozen in liquid nitrogen and sectioned at 5 µm on a cryostat.
a Control IgG Intestine c Testis b Thymus 1 3 2 S S 2 1 3 4 4 Figure S1 The wild-type mouse (C57BL/6J) organs (intestine, thymus and testis) were frozen in liquid nitrogen and sectioned at 5 µm on a cryostat.
Supplementary Figure 1. Mother centrioles can reduplicate while in the close association
 C1-GFP distance (nm) C1-GFP distance (nm) a arrested HeLa cell expressing C1-GFP and Plk1TD-RFP -3 s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 26 27 28 29 3 b 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 arrested HeLa
C1-GFP distance (nm) C1-GFP distance (nm) a arrested HeLa cell expressing C1-GFP and Plk1TD-RFP -3 s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 26 27 28 29 3 b 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 arrested HeLa
Figure S1. HP1α localizes to centromeres in mitosis and interacts with INCENP. (A&B) HeLa
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. HP1α localizes to centromeres in mitosis and interacts with INCENP. (A&B) HeLa tet-on cells that stably express HP1α-CFP, HP1β-CFP, or HP1γ-CFP were monitored with livecell
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. HP1α localizes to centromeres in mitosis and interacts with INCENP. (A&B) HeLa tet-on cells that stably express HP1α-CFP, HP1β-CFP, or HP1γ-CFP were monitored with livecell
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
McWilliams et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Posch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912046/dc1 Figure S1. Biochemical characterization of the interaction between
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Posch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912046/dc1 Figure S1. Biochemical characterization of the interaction between
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
Chromosomes Can Congress To The Metaphase Plate Prior. To Bi-Orientation
 Chromosomes Can Congress To The Metaphase Plate Prior To Bi-Orientation Tarun M. Kapoor 1,2, Michael Lampson 1, Polla Hergert 3, Lisa Cameron 2,4, Daniela Cimini 4, E.D. Salmon 2,4, Bruce F. McEwen 3,
Chromosomes Can Congress To The Metaphase Plate Prior To Bi-Orientation Tarun M. Kapoor 1,2, Michael Lampson 1, Polla Hergert 3, Lisa Cameron 2,4, Daniela Cimini 4, E.D. Salmon 2,4, Bruce F. McEwen 3,
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Changing expectations about speed alters perceived motion direction
 Current Biology, in press Supplemental Information: Changing expectations about speed alters perceived motion direction Grigorios Sotiropoulos, Aaron R. Seitz, and Peggy Seriès Supplemental Data Detailed
Current Biology, in press Supplemental Information: Changing expectations about speed alters perceived motion direction Grigorios Sotiropoulos, Aaron R. Seitz, and Peggy Seriès Supplemental Data Detailed
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Self-Organization of Dynein Motors Generates Meiotic Nuclear Oscillations
 Generates Meiotic Nuclear Oscillations PLoS BIOLOGY Sven K. Vogel 1[, Nenad Pavin 2,3[, Nicola Maghelli 1, Frank Jülicher 2, Iva M. Tolić-Nørrelykke 1* 1 Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology
Generates Meiotic Nuclear Oscillations PLoS BIOLOGY Sven K. Vogel 1[, Nenad Pavin 2,3[, Nicola Maghelli 1, Frank Jülicher 2, Iva M. Tolić-Nørrelykke 1* 1 Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology
7 Grip aperture and target shape
 7 Grip aperture and target shape Based on: Verheij R, Brenner E, Smeets JBJ. The influence of target object shape on maximum grip aperture in human grasping movements. Exp Brain Res, In revision 103 Introduction
7 Grip aperture and target shape Based on: Verheij R, Brenner E, Smeets JBJ. The influence of target object shape on maximum grip aperture in human grasping movements. Exp Brain Res, In revision 103 Introduction
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Comparison of a Persistent Random Walk to 3D Chemo taxis in. MDA-MB-231 Cancer Cells
 Comparison of a Persistent Random Walk to 3D Chemo taxis in MDA-MB-231 Cancer Cells Cameron Thayer-Freeman Advisor: Dr. Bo Sun 2015 Abstract This research specifically examines the collective motion of
Comparison of a Persistent Random Walk to 3D Chemo taxis in MDA-MB-231 Cancer Cells Cameron Thayer-Freeman Advisor: Dr. Bo Sun 2015 Abstract This research specifically examines the collective motion of
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a
 Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a expression in GFP-expressing HEp3 cells. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a expression in GFP-expressing HEp3 cells. (b) Representative
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Simulation of Chemotractant Gradients in Microfluidic Channels to Study Cell Migration Mechanism in silico
 Simulation of Chemotractant Gradients in Microfluidic Channels to Study Cell Migration Mechanism in silico P. Wallin 1*, E. Bernson 1, and J. Gold 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Applied Physics,
Simulation of Chemotractant Gradients in Microfluidic Channels to Study Cell Migration Mechanism in silico P. Wallin 1*, E. Bernson 1, and J. Gold 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Applied Physics,
M Cells. Why parallel pathways? P Cells. Where from the retina? Cortical visual processing. Announcements. Main visual pathway from retina to V1
 Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
Introduction to the High Jump The high jump is a track and field event that requires athletes to jump over a heightened horizontal bar by jumping off
 1 Introduction to the High Jump The high jump is a track and field event that requires athletes to jump over a heightened horizontal bar by jumping off of only one foot. The high jump can be broken into
1 Introduction to the High Jump The high jump is a track and field event that requires athletes to jump over a heightened horizontal bar by jumping off of only one foot. The high jump can be broken into
BIOLOGY 4/6/2015. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
DAPI ASY1 DAPI/ASY1 DAPI RAD51 DAPI/RAD51. Supplementary Figure 1. Additional information on meiosis in R. pubera. a) The
 a % 10 Number of crossover per bivalent b 0 1 c DAPI/telomere 80 1 60 40 1 2 20 d 0 0 1 2 >=3 DAPI ASY1 DAPI/ASY1 e DAPI RAD51 DAPI/RAD51 Supplementary Figure 1. Additional information on meiosis in R.
a % 10 Number of crossover per bivalent b 0 1 c DAPI/telomere 80 1 60 40 1 2 20 d 0 0 1 2 >=3 DAPI ASY1 DAPI/ASY1 e DAPI RAD51 DAPI/RAD51 Supplementary Figure 1. Additional information on meiosis in R.
SDS-Assisted Protein Transport Through Solid-State Nanopores
 Supplementary Information for: SDS-Assisted Protein Transport Through Solid-State Nanopores Laura Restrepo-Pérez 1, Shalini John 2, Aleksei Aksimentiev 2 *, Chirlmin Joo 1 *, Cees Dekker 1 * 1 Department
Supplementary Information for: SDS-Assisted Protein Transport Through Solid-State Nanopores Laura Restrepo-Pérez 1, Shalini John 2, Aleksei Aksimentiev 2 *, Chirlmin Joo 1 *, Cees Dekker 1 * 1 Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Visualization of the Self Assembly of Silica Nanochannels reveals growth mechanism Christophe Jung, Peter Schwaderer, Mark Dethlefsen, Ralf Köhn, Jens Michaelis * and Christoph
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Visualization of the Self Assembly of Silica Nanochannels reveals growth mechanism Christophe Jung, Peter Schwaderer, Mark Dethlefsen, Ralf Köhn, Jens Michaelis * and Christoph
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
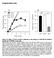 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/334/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapidly rendering cells phagocytic through a cell surface display technique and concurrent Rac activation Hiroki Onuma,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/334/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapidly rendering cells phagocytic through a cell surface display technique and concurrent Rac activation Hiroki Onuma,
Learning to Control Collisions: The Role of Perceptual Attunement and Action Boundaries
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2006, Vol. 32, No. 2, 300 313 Copyright 2006 by the American Psychological Association 0096-1523/06/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0096-1523.32.2.300
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2006, Vol. 32, No. 2, 300 313 Copyright 2006 by the American Psychological Association 0096-1523/06/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0096-1523.32.2.300
Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A)
 Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
1 Fundamentals. Basic Definitions and Physics Principles. Fundamentals
 1 To become versed in the language of ultrasonography, it is necessary to review some of the basic principles of physics. The wave physics principles of ordinary (i.e., audible) sound apply to ultrasound
1 To become versed in the language of ultrasonography, it is necessary to review some of the basic principles of physics. The wave physics principles of ordinary (i.e., audible) sound apply to ultrasound
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
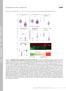 Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
BIOLOGY. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Mitosis in polarized MDCK cells after 14 days of culture. (a) Confocal microscopy image of polarized MDCK cells expressing actin- mcherry and H2B- egfp
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Mitosis in polarized MDCK cells after 14 days of culture. (a) Confocal microscopy image of polarized MDCK cells expressing actin- mcherry and H2B- egfp
Simplifying Microfluidic Separation Devices towards Field-Detection of Blood Parasites
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods Simplifying Microfluidic Separation Devices towards Field-Detection of Blood Parasites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods Simplifying Microfluidic Separation Devices towards Field-Detection of Blood Parasites
Pac-man motility of kinetochores unleashed by laser microsurgery
 MBoC ARTICLE Pac-man motility of kinetochores unleashed by laser microsurgery James R. LaFountain, Jr. a, Christopher S. Cohan b, and Rudolf Oldenbourg c,d a Department of Biological Sciences, University
MBoC ARTICLE Pac-man motility of kinetochores unleashed by laser microsurgery James R. LaFountain, Jr. a, Christopher S. Cohan b, and Rudolf Oldenbourg c,d a Department of Biological Sciences, University
CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplementary Figure 1
 S U P P L E M E N TA R Y I N F O R M AT I O N DOI: 10.1038/ncb2896 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sequence alignment of TERB1 homologs in vertebrates. M. musculus TERB1 was derived from
S U P P L E M E N TA R Y I N F O R M AT I O N DOI: 10.1038/ncb2896 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sequence alignment of TERB1 homologs in vertebrates. M. musculus TERB1 was derived from
Supplemental Information. 3D-CLEM Reveals that a Major Portion. of Mitotic Chromosomes Is Not Chromatin
 Molecular Cell, Volume 64 Supplemental Information 3D-CLEM Reveals that a Major Portion of Mitotic Chromosomes Is Not Chromatin Daniel G. Booth, Alison J. Beckett, Oscar Molina, Itaru Samejima, Hiroshi
Molecular Cell, Volume 64 Supplemental Information 3D-CLEM Reveals that a Major Portion of Mitotic Chromosomes Is Not Chromatin Daniel G. Booth, Alison J. Beckett, Oscar Molina, Itaru Samejima, Hiroshi
Alterations of the cytoskeleton and polyploidy induced by cryopreservation of metaphase II mouse oocytes
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 69, NO. 5, MAY 1998 Copyright 1998 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Alterations of the cytoskeleton
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 69, NO. 5, MAY 1998 Copyright 1998 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Alterations of the cytoskeleton
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
2 INSERM U280, Lyon, France
 Natural movies evoke responses in the primary visual cortex of anesthetized cat that are not well modeled by Poisson processes Jonathan L. Baker 1, Shih-Cheng Yen 1, Jean-Philippe Lachaux 2, Charles M.
Natural movies evoke responses in the primary visual cortex of anesthetized cat that are not well modeled by Poisson processes Jonathan L. Baker 1, Shih-Cheng Yen 1, Jean-Philippe Lachaux 2, Charles M.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Supplemental Information. Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes. Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain. and Regulates Ventricular Development
 Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep
 Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep Microtubules are a Dynamic Scaffold Microtubules in red, XMA215 family MT polymerase protein in green Some Microtubule Functions Cell Structure Polarized Motor Track (kinesins
Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep Microtubules are a Dynamic Scaffold Microtubules in red, XMA215 family MT polymerase protein in green Some Microtubule Functions Cell Structure Polarized Motor Track (kinesins
Ultrasound. Principles of Medical Imaging. Contents. Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin. MIAC, University of Basel. Oct 17th, 2016
 Ultrasound Principles of Medical Imaging Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents Abstract 1 Image Generation Echography A-Mode B-Mode M-Mode 2.5D Ultrasound 3D Ultrasound 4D Ultrasound
Ultrasound Principles of Medical Imaging Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents Abstract 1 Image Generation Echography A-Mode B-Mode M-Mode 2.5D Ultrasound 3D Ultrasound 4D Ultrasound
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM
 J. exp. Biol. 192, 73 81 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 73 RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM II. ASYMMETRY OF THE CILIARY
J. exp. Biol. 192, 73 81 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 73 RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM II. ASYMMETRY OF THE CILIARY
Supplemental Information. Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras. Promotes Basal Extrusion. of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P. Current Biology, Volume 24
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras Promotes Basal Extrusion of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P Gloria Slattum, Yapeng Gu, Roger Sabbadini, and Jody Rosenblatt
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras Promotes Basal Extrusion of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P Gloria Slattum, Yapeng Gu, Roger Sabbadini, and Jody Rosenblatt
Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh
 Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Descriptions of NDT Projects Fall 2004 October 31, 2004
 Descriptions of NDT Projects Fall 2004 October 31, 2004 Introduction There are two separate NDT labs in Magister: ULTRA for ultrasound and EDDY for eddy current. Both labs are equipped with mechanical
Descriptions of NDT Projects Fall 2004 October 31, 2004 Introduction There are two separate NDT labs in Magister: ULTRA for ultrasound and EDDY for eddy current. Both labs are equipped with mechanical
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Key Concepts in Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Video: Sea Urchin Embryonic Development (time-lapse)
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Loss of Ena/VASP proteins inhibits filopodia and neuritogenesis. (a) Bar graph of filopodia number per stage 1 control and mmvvee (Mena/ VASP/EVL-null) neurons at 40hrs in culture. Loss of all
Figure S1. Loss of Ena/VASP proteins inhibits filopodia and neuritogenesis. (a) Bar graph of filopodia number per stage 1 control and mmvvee (Mena/ VASP/EVL-null) neurons at 40hrs in culture. Loss of all
Supplementary Figures for
 mirns regulate s Supplementary igures for MicroRNs Reprogram Normal ibroblasts into Cancer ssociated ibroblasts in Ovarian Cancer nirban K. Mitra, Marion Zillhardt, Youjia Hua, Payal iwari, ndrea E. Murmann,
mirns regulate s Supplementary igures for MicroRNs Reprogram Normal ibroblasts into Cancer ssociated ibroblasts in Ovarian Cancer nirban K. Mitra, Marion Zillhardt, Youjia Hua, Payal iwari, ndrea E. Murmann,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Fluorescence Microscopy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
JCB. Myosin and the PAR proteins polarize microfilament-dependent forces that shape and position mitotic spindles in Caenorhabditis elegans
 JCB Published Online: 14 April, 2003 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200210171 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on January 15, 2019 Report Myosin and the PAR proteins polarize microfilament-dependent
JCB Published Online: 14 April, 2003 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200210171 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on January 15, 2019 Report Myosin and the PAR proteins polarize microfilament-dependent
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering
 nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
bio-mof-1 DMASM Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM.
 bio-mof-1 Transmittance bio-mof-1 DMASM DMASMI 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM. Intensity (a.u.) bio-mof-1 DMASM as
bio-mof-1 Transmittance bio-mof-1 DMASM DMASMI 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM. Intensity (a.u.) bio-mof-1 DMASM as
