INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND CHEMICAL SCIENCES
|
|
|
- Clyde Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: Research Article Marine natural Products with a Special Reference to Aplidine as a ew Bioactive Compound in Anti-Cancer Class Dilipkumar Pal 1 *, Tanmoy De 2 and Arijit Baral 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guru Ghasidash Vishwavidyalya (A Central University) Koni, Bilashpur , Chattisgarh, India 2 School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, IFTM University, Lodhipur, Rajput, Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, , India. ABSTRACT The marine environment has proven to be a very rich source of extremely potent compounds that have demonstrated significant activities in antitumor, anti-parasitic, anti-microbial, anti-coagulants, antiviral, cytotoxic compounds, anti-inflammatory, proteins. Aplidine is a promosing anti-tumor agent that is derived from the diterranean tunicate Aplidum albicans. We have found that aplidine at nm concentrations ( nm) induced apoptosis in human leukemic cell lines and in primary leukemic cell culture from leukemic patients. Aplidine induced a rapid and sustained c jun 2 terminal kinase activation and apoptosis. Thus, Aplidine is an extremely potent and rapid apoptic inducer on leukemic cells that triggers Fas/CD 95- and mitochondrial mediated apoptotic singling routes, and shows a rather selective apoptotic action on cancer cells and activated T- cells. Keywords: Anti-parasitic, anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory activity; anticoagulant, Aplidine. ITRDUCTI In compansion to land plants and animals, the use of marine natural products is restricted. Several marine products are still are used as cod liver oil, spermaceti, protamine sulphate and some polysaccharide as agar, carrageenan and alginic acid. 1. Cod liver oil Cod liver oil is obtained from fresh liver of the cod i.e Gadus collorias, family Gadidae with enriched vitamin A & D. Two types of oil are found that are - i. Type A (Prone to oxidation) ii.type B (Commerical product) 1 2. Spermaceti Spermaceti are obtained from the sperms of whole Physeter macrocephalus Linn 2, family Physeteridae. Spermaceti is oil contains- -Cetyl palmitate -Free cetyl alcohol -Ester of lauric acid Myristic acid 3. Protamine sulphate Protamine sulphate is obtained from the sperms of fish belonging to family Salmonidae. It contains various proteins and is used as a heparin antagonist Agar Agar is a dried gelatinous substance obtained from Gelidium amansii, belonging to family Geladiaceae. Also some species of Gracilaria (Gracilariaceae) are a source of agar, which contains Agarose and agaropectin Agarose is responsible for gel strength and composed of D-galactose and 3,6 anhydrogalactose unit. Agaropectin is responsible for viscosity of agar solution and is used as gelling agent and in formulations etc Carrageenan It is obtained from see weeds called carrageenan or Irishmoss i.e red algae- Chondrus crispus, family-rhodophyceae. It is used as emulsifying agent, stabilizing agent, viscosity builder etc. In tooth paste, cream, lotions and other products. Constituents- Depending upon position of sulphate and presence or absence of anhydrogaloctose, two types are therei.kappa (k) ii.lambda (α) K-carrageenan contains D-galactose, 3,6 anhydrous D-galactose and ester sulphate group. α-carrageenan contains D-galactose and mono, disulphate ester 5. Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
2 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: Algenic acid Algenic acid 6 is composed of reduced manuuronic and glucoronic acid which are obtained from algal growth species- Laminaria degitata, Laminaria hyperborean. It is soluble in water forming viscous colloidal solution, insoluble in alcohol and ethers etc. 7. ccurrence of red tide caused by Karenia mikimotoi (toxic dinoflagellate) in the Southwest coast of India Red tides are common especially in the coastal waters that threaten marine living resources and local economy. At times, red tides are dominated by harmful algal bloom 7 (AB), species that adversely affect aquatic ecosystem by releasing toxic substances. So far several phytoplankton blooms were frequently reported from the west coast of india. Among them, blooms of ictiluca miliaris (dinoflagellate) and Trichodesmium erythraeum (blue green algae) are frequently occurring red tides. Even through these two blooms are recurrent and sometimes cause fish kill 8 due to oxygen depletion, both of them are not accounted to be toxic yet. Few years back (September-ctober 2004) an unusual stench event observed in the coastal waters off Trivandrum and Kollam had created some health problems (nausea, chest pain and breathlessness) to the local people in the region Juvenile abundance and post-larval incursion of mud crabs (Scylla spp.) in chilika lagoon The mud crabs Scylla spp., represents a valuable component of small-scale coastal fisheries in many countries of tropical and subtropical Asia and African coast. Through the mud crabs are marine dwellers, they immigrate into brackish water system during their postlarval stages, grow fast attain maturity and form alucrative fishery in estuaries, backwaters and lagoons. With great demand for live export and increased price, fishery and aquaculture of mud crabs have gained importance in India and abroad. The two mud crab species (S. serrata and S. tranquebarica) are coexisting in the lagoon 10. The lagoon was in a degraded state during the last few decades tending towards a freshwater ecosystem due to the natural changes coupled with anthropogenic pressure 11, 12. Present study consists of the details which is related to the nature of coral disease in nine locations from Vethalai to Rameswaram north in the Palk Bay. Among the overall corals 21% were affected by diseases. Six disease types were till now recorded. Black Band Disease (BBD) is high with 9.8% folled by white band (5.5%), white spot (2.2%), pink spot (1.9%), white plague (1.15%) and yellow band (0.6%). Eight coral genera were found to be affected, wherein Acropora and Porites showed severe damage and the high prevalence of diseases. The coral genus, Porites was found to be affected by four different types of diseases. BBD affected colonies were tagged and photographed at regular intervals to quantify the progression rate in two coral genera, Acropora and platygyra and the disease progression rate was 3 cm per month. White band disease was widespread and was found to affect exclusively Acropora sp. Corals like Symphylia sp. and Cyphastrea sp. in the Palk Bay were comparatively not affected by diseases. Classes of active compounds: 1. Anti-parasitic compounds i. Red algae, Digenia simplex 14 has been used as vermifuge since hundreds of years. Many companies are marketing it as broad spectrum antihelmintic. Effective against round worm, tape worm and in which kainic acid 15 is the active constituent. C 2 Kainic acid C C ii. Red algae Chondria armata and Alsidium corallium also used as antihelmintic properties. Constitute- Domoic acid Coral disease prevalence in the Palk Bay, South-eastern India with special emphasis to black band 13 Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
3 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: C 2 C 2 C Domoic acid C 2. Anti-microbial agent Generally marine micro-organisms are Isolated and characterized posse s anti-microbial activity. e.g.fungus- cephalosporium acremonium, from which cephalosporin C 17 is isolated i.e. semi synthetic derivatives as cephalosporium sodium. S CC( 2 C) 3 C 2 C Cephalosporin c ther marine anti-microbial compounds isolated from marine micro-organism are 18, 19 istamycins-a and B produced by fermentation of marine streptomycete, Streptomyces tenyimariens. It is effective against gram (+) and gram (-). C 2 CC 3 3. Anti-coagulants Generally polysaccharides collected from marine algae are considered as good source of anti-coagulants. Sulphated galactum of Iridaea laminarioides 14 is responsible for anti-coagulant effect. Carrageenans isolated from Chondrus crispus, Euchema spinosum, Polyides rotundus are known for anti-coagulant activity and were reported to cause inactivation of thrombin. 4. Anti-viral Anti-viral agents which are against human virus are in great demand because of AIDS epidemic. Ara-A 20 is semi synthetic substance (arabinosyl nucleosides) that is isolated from marine sponge-tethya crypta. Ara-A Several compounds which are isolated from the marine are reported for its anti-viral action invitro but didemnins (cyclic depesipeptide) shows an anti-viral activity in vivo as well as anti-tumour activity. Eudistomins (β-carbolines) which are isolated from the Udistoma olivaceum 21 (family polycytoridae) are known for its potent antiviral activity. Br Eudistomin A Avarol and Avarone which are extracted from sponge Disidea avara 22 are known to inhibit immunodeficiency virus and cross bbb. Thus used as a potent anti-viral agent for AIDS treatment. Avarone Avarol Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
4 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: Cytotoxic Compounds Cytotoxic compounds are a group of macrolides known as bryostatins isolated from bryozoon Bugula neritina. 23 Some macrolides were also collected from sponges and tunicates. Bryostatins also stimulates human haemopoietic cells and are thus useful for treating neoplastic bone marrow failure. Bryostatins activates and differentiate peripheral blood cells of lymphocytic leukemia patients and also activates protein kinase and arachidonic acid metabolite release. Bryostatin-1 is under phase-2 clinical trial. Alkaloid-niphatesine is isolated from iphates species, 24 and epinardins is isolated from Stelleta globostellata are cytotoxic agents from marine sponges. iphatesine Epinardin A Sesquiterpenes- Suberosenone extracted from Subergorgia suberosa, 25,26 Diterpene sarcoglane from sarcophyton glaucum are examples of cytotoxic agent from coelenterates Sarcoglane Dolastatins are peptides derived from Dolabella aericularia, a mollusc found in the Indian ocean. Dolastatin 10 and the dolastatin 15 are included in dolastatin family. Structurally dolastatin is a pentapeptide with four of the residues being unique (dolavaline, dolaisoleucine, dolaproline and dolaphenine, in addition to valine). Dolastatin 10 has phase 1clinical trials as anticancer agent and it is for used for the treatment of breast and liver cancers, solid tumours and leukaemia. Dolastatin 10 and 15 are small peptides. It blocks microtubule assembly, there by causing cells to accumulate in metaphase and is extremely potent in vitro. The side effects of dolastatin 10 are bone marrow toxicity in initial clinical trials, as well as local irritation at the injection site and mild peripheral neuropathy. Dolastatin 15, a seven subunit depsipeptide and it is derived from Dolabella auricularia, a potent antmitotic agent structurally related to the antitubulin agent dolastatin 10, a five subunit peptide isolated from extracts of the Indian ocean sea hare D. Auricularia. Indeed, numerous dolastatin 15- related peptides have been isolated from diverse marine cyanobacteria. Its linear depsipeptide sequence is composed of seven amino acid or hydroxyl acid residues 28. Suberosenone Dolastatin Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
5 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: Anti-inflamatory compounds Sesquiterpene Palaulol from sponge Fascaplysinopsis sps 29 and Sesquiterpene furan 30 from coelenterates- Sinularia species are synthesized. Palaulol cyclopentane ring and these are now available as synthetic products. owever, prior to synthetic compounds being available, research on prostaglandins was restricted by inadequate supplies of the two active compounds, PGE 2 and PGF 2a. This discovery that the soft coral, Plexaura homomalla, was a rich source of 15-epi-PGA 2 and its acetate, methyl ester derivative, was a major breakthrough as the Upjohn Company developed a synthetic pathway to convert these inactive compounds into the required active ones. Prostaglandins have also been isolated from red algae belonging to the genus Gracilaria. 7. Proteins 31, 32 The group of proteins known as Lectins has received a good idea of attention in recent years. Lectins are carbohydrates binding proteins and are found in a wide variety of life forms, including marine organisims. Probably the best known Lectins from a marine source are the potent haemagglutinins obtained from the haemolymph of L. polyphemus. ne of the lectins, limulin, has that been isolated and shown to be a large, 18-subunit protein with a molecular mass of 350 kda. Limulin shows specificity for binding to sialic acid, although other structures are recognized. Another lecithin that shows specificity to sialic acid is that obtained from the haemolymphn of the lobster and omarus americanus. 8. Argochemical usage The marine annelid, Lumbriconeris heteropoda, 14 has long been known to be toxic to insects. This activity was shown to be due to nereistoxin, which has rapid anaesthetic properties on insects and is toxic to fish and mammals, affecting the nervous system and heart. Studies on this compound led to the introduction of the synthetic pesticide Padan. the most widely used species in the preparation of the product are Ascophyllum nodosum, Ecklonia maxima and Durvillaea patatorum. 12. Prostaglandins 33 Prostaglandins constitute a group of biologically potent substances of wide spectrum activity. Although first recognized in the 1930s, they remained of little interest until the structures of two of them were determined in Structurally, all the compounds are based on prostanoic acid, which is it inactive. Six series (A-E) arise by modification of the Prostaglandins E 2 Prostaglandin F 2α C C 13. Aplidine Its others name: Aplidin, Dihydrodidemnin B, plitidepsin; source: The tinucate Aplidium albicans (CRDTA) 34, 35. Activity:Anti-cancer agent via apoptosis; status:phase II clinical trials Properties Molecular formula C Molar mass g mol _1 Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
6 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: Aplidium albicans 3 C 3 C C 3 C 3 3 C C 3 C 3 C 3 3 C C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 Chemical structure of aplidine Aplidine is a new marine natural products isolated from Aplidium albicans. It is a member of the class of compounds known as didemnins. It is a cyclic depsipeptide in which there is one or more ester bond in place of one or more of a peptide bond. It shows strong anti-tumour activity against different human cancer cells growing in vitro and in vivo It was first reported in a 1991 patent applications. The chemical structure of aplidine is very close to didemnin B, the only difference being that the lactate residue in didemnin B is present in the oxidized pyruvate version. It has completed phase 1 trials and is under phase 2 development. The exact mechanism of action of aplidine is still unknown. It induces cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in the human leukemia cell line MLT-4 at G-1 phase in the cell cycle. This cell line has the ability to secrete VEGF ( vascular endothelial growth factor) which is present on the surface of VEGF receptor -1 (VEGFR-1). A change in gene expression induced by aplidine in MLT-4 cells is also seen and it also decreases the expression of VEGFR-1 which is bind to the angiogenic factor VEGF 36. Increasing suggests, however, Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
7 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: that certain cancer cells of different origin, including leukemic cells, also express VEGF receptors on their surface. n the other hand, VEGF is secreted by virtually all cancer cells as a homodimeric glycoprotein which is able to bind VEGFR-1 and other components of the VEGF receptors family with high affinity 37. The simultaneous presence of a receptor and the ability to secrete the ligand for it, suggests the possible presence of an autocrine loop important for the growth of cancer cells expressing these receptors. Aplidine has the ability to block the VEGF/VEGFR-1 loop thereby decreasing the production of VEGF and VEGFR-1. This reviews gives the evidence that aplidine has strong effect on the VEGF/VEGFR-1 autocrine loop regulating the growth of the human leukemic cell line MLT In vitro characterization of Aplidine biotransformation- [3S,4R,5S-lst] The in vitro biotransformation of aplidine was characterized by using incubations with liver preparations, human plasma, cytochrome P450 (CYP) and uridine diphosphoglucuronosyl transferase (UGT) supersomes in combination with PLC analysis and cytotoxicity assays with cell lines. Carboxyl esterases is an enzyme which metabolised aplidine in human plasma. It was shown that aplidine was metabolised mainly by CYP3A4 and also by CYP2A6, 2E1 and 4A11. Aplidine formed four metabolites after incubation with human liver microsomes, one formed by CYP2A6 (C-demethylation) and three by CYP3A4 (hydroxylation and/or C- dealkylation). This metabolites were further conjugated by the phase II enzymes UGT, GST and SULT. The human cancer cell lines ep G2 and IGRV-1 were used to study the cytotoxicity of aplidine and its metabolites. The enzyme CYP3A4 has a major role in metabolising aplidine in vitro with additional involvement of CYP2A6, 2E1, and 4A11 39,40. [2S,4S-hip] [IS,2R-Thr] [(R)()-Leu] [(S)-Leu] [(S)- Pro] [(S)-Pro] [(S)--Tyr] xidation and conjugation ydroxylation Conjugation Chemical structure of aplidine. The different squares and ovals indicate potential sites for biotransformation.in addition all the ester and amide bonds are potential sites for hydrolysis. iphydroxyisovalerylpropionyl, Ist-isostatine, Leu-leucine, -methyl, Pro-proline, pyr-pyruvoyl, Thrthreonine, Tyr-tyrosine. Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
8 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: CCLUSI It has been demonstrated in this review; the potential for marine natural products as sources and/or leads to drugs that cover a very wide range of pharmacological effects (i.e., cancer, anti-infective, analgesia, Alzheimer s disease, inflammation, immunomodulation) is only now being realized. It is probable that within the next two years at least one marine-derived novel agent will enter commerce as an anticancer or analgesia drug following governmental approval. Perhaps the most important current discovery, however, is the proof with Aplidine that, as suspected by many investigators over the years. The effects of aplidine were evaluated in experimental models. At the time of submission of the application for orphan designation, no clinical trials in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia were initiated. Aplidine was not marketed anywhere worldwide for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia or designated as orphan medicinal product elsewhere for this condition, at the time of submission. REFERECES 1. Rajakumar K. Vitamin D, Cod-Liver il, Sunlight, and Rickets: A istorical Perspective. Paediatrics. 2003; 112: David RC, Stephen MD and Jason. The face that sank the Essex: potential function of the spermaceti organ in aggression. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 2002; 205: Sie P, Cremers B, Dupouy D, Caranobe C, Dol F and Boneu B. eutralization of Dermatan Sulfate in Vitro and in vivo by protamine sulphate and polybrene thromb. Research. 1989;54: Davidson Alan and Tom Jaine. The xford Companion to Food. xford university Press, USA. 2006; Yiu. ui. andbook of Food Science, Technology, and Engineering. CRC Press. 2006; Raymond CR, Paul JS, Marine EQ, editors. Adipic acid, andbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients (Rowe, andbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients), Pharmaceutical Press, 2009; Smayda TJ. Reflections on the ballast water dispersal harmful algal bloom paradigm. armful Algae. 2007; 6: aqvi SWA, George MD, arvekar PV, Jayakumar DA, Shailaja MS, Rajesh G, Sudhir AK and Binu MS. Severe fish mortality associated with red tide observed in the sea of Cochin. Current Science. 1998; 6: Bhat SR and Matondkar SGP. Algal blooms in the seas around India etworking for research and outreach. Current Science. 2004; 8: Bhatta KS. Report on chilika environmental monitoring, Chilika Development Authority. 2001; Devassy VP and Sreekumaran. Discolouration of water and its effects on fisheries along the Goa coast. Mahasagar 1987; 2: Mohanty SK, Mohaptra A, Mohanty RK, Bhatta KS and Pattanaik AK. ccurrence and biological outlines of two species in the genus Scylla (De aan) in Chilika lagoon, India. Indian Journal of Fish. 2006; 53: Sutherland K, Porter J & Torres C. Disease and immunity in Caribbean and Indo-pacific zooxanthellate corals. Marine Ecology Progressive Series. 2004; 266: Evans W.C. Trease and Evans pharmacognosy. 15 th edition. W.B. Saunders publication, 1995; Kitagawa I and Kobayashi M. Antitumour natural products isolated from marine organisms; Gan to kagaku Ryoho. 1989; 16: Fenical W. Marine biodiversity and the medicine cabinate, the status of new drugs from marine organisms ceanography. 1996; 9: Leonard Engle. The sea; young readers Library (ed). Time-life international (ederland).v P 9; Leonard E. The sea; young readers Library (ed). Time-life international (ederland).v P 16; Bergman W and Feeney RJ. ucleosides of sponges. Journal of rganic Chemistry. 1952; 16: Clark AM. atural products as resources for new drugs. Pharmaceutical Research. 1996; 13: Rinehart KL, Shield LS and Cohenparsons M. Anti-viral substances. In Marine Biotechonology, vol-1. Pharmaceutical and Bioactive natural products, Attaway Dh, Zaborsky R Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
9 ITERATIAL JURAL F PARMACEUTICAL AD CEMICAL SCIECES ISS: (eds). Plenum Pres: ew York and London; 1993; Sarin PS, Sun D, Thornton A and Muller WEG. Inhibition of replication of the etiologic agent of acquired immune deficiency Syndrome(human T- lymphotropic retrovirus/lymphadenopathyassociated virus) by avarol and avarone. ational cancer Institute: 1987; 78: Pettit GR, Boyd MR and Doubck DL. The search for antiviral and anticancer compounds from marine organisms. Journal of American Chemical Society. 1987; 109: Garson MJ. The biosynthesis of sponge secondary metabolites, why it is important; Van Soest RWM, Kempen TMG, Brackman JC, (Eds). Spongy in time and space. Balkma, Rotterdem 1994; Munro MG, Blunt JW, Dun dei EJ, ick ford SJ, Liu E, Lis,Bttershill C and Duckworth AR. The discovery and development of marine compounds with pharmaceutical potential. Journal of Biotechnology.1999;70: Boksech R, Mckee CT, Cardelline J and Boyd MR. Suberosenone, a new cytotoxin from Subergorgia suberase, Tetrehedron Letter.1996; 37: Poncet J. The dolastatins, a family of promising antineoplastic agents. Current Pharmaceutical Research. 1999; 5: Suenaga K, Kigoshi and Yamade K. Auripyrones A and B, Cytotoxic Polyprapionates from the seattare Doledalla auricularia Tetrahedron letter.1996;37: Brit J. In vitro activity of aplidine, a new marine-derived anti-cancer compound on freshly explanted clonogenic human tumour cells and haematopoietic precursor cells Cancer. 1998;78(6): Schmidt WE and Faulkner DJ. Paluaolol, a new Anti-inflamatory sesterpene from the sponge Fascaplysinopsis sp. from Palau, Tetrehedron Letter.1996; 37: Ferrer FA, Miller Lj, Lindquist R, Kowalczykp, Laundona VP, Albrtsen PC and Kreutzer Dl. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in human prostate cancer. Urology 1999; 54: Gabius J. Animal lectins, European Journal of Biochemistry, 1997; 243: Komoto J, Yamada T, Watanabe K and Takusagawa F. Crystal structure of human prostaglandin-f synthase (AKR1C3). Biochemistry. 2004;43(8): Fairelath JG, Rinehart K, unez De castro I, Jimeno J. Dihrodidemnin B a new marine derived antitumor agent with activity against experimental tumor models. An ncology. 1996; 7: Depenbrock, Peter R, Fairecloth GT, Manzaneres I, Jimono J and anauske AR. In vitro activituyof aplidine, a new marine derived anticancer compound, a freshly explanted clonogenic humqan tumor cells and haematopoietic Precursor cells. Brazil Journal of Cancer.1998; 78: Marchini S, Contegno F, D Incalci M, Broggini M and Faircloth GT. Gene expression profile in human leukemic MLT-4 cells treated with the marine compound aplidine. Proceedings of American Association of Cancer Research. 2000; 41: Watanable Y, Lee SW, Detemar M, Ajioka T and Dvorak F. Vascular permeability factor /vascular endothelial growth factor (DVPF/VEGF) delays and induces escape from senescence in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. ncogene 1997;14: Gerber P, Dixit V and Ferrara. Vascular endothelial growth factor indues expression of the antiapoptoptic proteins Bcl-2 and A1 in vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in heaptopoietic malignancies. Cancer Research. 1999; 59: Curry S. Drug disposition and pharmacokinetics with a consideration of pharmacological and clinical relationships. Blackwell Scientific Publications (xford, UK).1974; Gibson GG and Skett P. Introduction to Drug tabolism. Blackie Academic and Professional (London, UK), Second edition. 1994;1-34. Vol. 2 (2) Apr-Jun
OH H CH 2 OH. 3,6-Anhydro-L-Galactose
 C 2 X C 2 3 β 4 1 α C 2 C 2 X 3 3 β β D-Galactose 3,6-Anhydro-L-Galactose n X = or S 3 n Fig. 2: opectin CAS NUMBER: 9002-18-0 SYNNYMS: -agar; Gum agar; Bacto-agar; Bengal gelatin; Bengal ising glass;
C 2 X C 2 3 β 4 1 α C 2 C 2 X 3 3 β β D-Galactose 3,6-Anhydro-L-Galactose n X = or S 3 n Fig. 2: opectin CAS NUMBER: 9002-18-0 SYNNYMS: -agar; Gum agar; Bacto-agar; Bengal gelatin; Bengal ising glass;
AGAR CH 2 X O OH H. H β H O O H. X = OH or OSO 3 n. Fig. 2: Agaropectin
 C 2 β 4 1 α C 2 3 D-Galactose 3,6-Anhydro-L-Galactose n C 2 X 3 C 2 X 3 β β X = or S 3 n Fig. 1: ose Fig. 2: opectin CAS NUMBER: 9002-18-0 SYNNYMS: -agar; Gum agar; Bacto-agar; Bengal gelatin; Bengal ising
C 2 β 4 1 α C 2 3 D-Galactose 3,6-Anhydro-L-Galactose n C 2 X 3 C 2 X 3 β β X = or S 3 n Fig. 1: ose Fig. 2: opectin CAS NUMBER: 9002-18-0 SYNNYMS: -agar; Gum agar; Bacto-agar; Bengal gelatin; Bengal ising
Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products
 Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products Presented by Akram Najafi Marine actinobacteria Actinobacteria are a group of Gram positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial (soil)
Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products Presented by Akram Najafi Marine actinobacteria Actinobacteria are a group of Gram positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial (soil)
Marine natural products. in clinical trials and on the market. By: Z. Janahmadi
 Marine natural products in clinical trials and on the market By: Z. Janahmadi Presentation outline Marine natural products that are under clinical trials, or that have been approved as drugs: Antitumor
Marine natural products in clinical trials and on the market By: Z. Janahmadi Presentation outline Marine natural products that are under clinical trials, or that have been approved as drugs: Antitumor
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
ISSN Volume 1 (2015) The 1st International Symposium on Aquatic Product Processing 2013
 ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 1 (2015) The 1st International Symposium on Aquatic Product Processing 2013 PHYSIC AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF NATA DE SEAWEED FROM Eucheuma cottonii and Gracilaria sp. Max R.
ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 1 (2015) The 1st International Symposium on Aquatic Product Processing 2013 PHYSIC AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF NATA DE SEAWEED FROM Eucheuma cottonii and Gracilaria sp. Max R.
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Non-fuel Products from Algae An Overview
 List of Contents Non-fuel Products from Algae An Overview Introduction Non-fuel Products from Algae o Pharmaceuticals & Nutraceuticals o Food & Feed o Specialty Chemicals o Personal Care Products o Natural
List of Contents Non-fuel Products from Algae An Overview Introduction Non-fuel Products from Algae o Pharmaceuticals & Nutraceuticals o Food & Feed o Specialty Chemicals o Personal Care Products o Natural
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
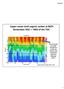 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Author to whom correspondence should be addressed;
 Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 73-82 Marine Drugs ISS 1660-3397 www.mdpi.net/marinedrugs/ Review Drugs and Cosmetics from the Sea Anake Kijjoa 1,* and Pichan Sawangwong 2 1 ICBAS-Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas
Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 73-82 Marine Drugs ISS 1660-3397 www.mdpi.net/marinedrugs/ Review Drugs and Cosmetics from the Sea Anake Kijjoa 1,* and Pichan Sawangwong 2 1 ICBAS-Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas
Productos naturales marinos como fuente de agentes anticáncer
 Productos naturales marinos como fuente de agentes anticáncer Marcelino Gutiérrez G. Centro de Biodiversidad y Descubrimiento de Drogas, IDICASAT, Panamá Primer Simposio Iberoamericano de Investigación
Productos naturales marinos como fuente de agentes anticáncer Marcelino Gutiérrez G. Centro de Biodiversidad y Descubrimiento de Drogas, IDICASAT, Panamá Primer Simposio Iberoamericano de Investigación
189,311, , ,561, ,639, ,679, Ch13; , Carbohydrates
 Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Spirulin BOTANY V 03-10/ ,
 Spirulin BOTANY Spirulina spp. Spirulina is a blue green micro-alga. These tiny green spiral coils harvest the energy of the sun, growing a treasure of bioavailable nutrients. This first photosynthetic
Spirulin BOTANY Spirulina spp. Spirulina is a blue green micro-alga. These tiny green spiral coils harvest the energy of the sun, growing a treasure of bioavailable nutrients. This first photosynthetic
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
FIRST BIOCHEMISTRY EXAM Tuesday 25/10/ MCQs. Location : 102, 105, 106, 301, 302
 FIRST BIOCHEMISTRY EXAM Tuesday 25/10/2016 10-11 40 MCQs. Location : 102, 105, 106, 301, 302 The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and Control General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis
FIRST BIOCHEMISTRY EXAM Tuesday 25/10/2016 10-11 40 MCQs. Location : 102, 105, 106, 301, 302 The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and Control General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis
MODULE No.26: Drug Metabolism
 SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag PAPER No. 9: Drugs of Abuse MODULE No. 26: Drug Metabolism FSC_P9_M26 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Sites of Drug
SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag PAPER No. 9: Drugs of Abuse MODULE No. 26: Drug Metabolism FSC_P9_M26 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Sites of Drug
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES. Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr.
 BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 6(5): September-October 2016
 International Standard Serial umber (ISS): 2249-6807 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 6(5): September-ctober 2016 ITERATIAL JURAL F ISTITUTIAL PARMACY AD LIFE SCIECES Pharmaceutical
International Standard Serial umber (ISS): 2249-6807 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 6(5): September-ctober 2016 ITERATIAL JURAL F ISTITUTIAL PARMACY AD LIFE SCIECES Pharmaceutical
Contents. Contributors...xi. Preface...xv. 1 Configurations, Structures and Morphologies of Cellulose... 1
 Contents Contributors...xi Preface...xv 1 Configurations, Structures and Morphologies of Cellulose... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure... 2 1.2.1 Molecular Structure... 2 1.2.2 Hydrogen Bonding...
Contents Contributors...xi Preface...xv 1 Configurations, Structures and Morphologies of Cellulose... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure... 2 1.2.1 Molecular Structure... 2 1.2.2 Hydrogen Bonding...
Oncology Program. Chlorotoxin Technology Platform. Corporate Partnering Opportunities
 TransMolecular, Inc. A Neuroscience Biotechnology Company Oncology Program Chlorotoxin Technology Platform Corporate Partnering Opportunities Background TransMolecular, Inc. (TMI) is a neuroscience biotechnology
TransMolecular, Inc. A Neuroscience Biotechnology Company Oncology Program Chlorotoxin Technology Platform Corporate Partnering Opportunities Background TransMolecular, Inc. (TMI) is a neuroscience biotechnology
1. Denaturation changes which of the following protein structure(s)?
 Chem 11 Fall 2008 Examination #5 ASWER KEY MULTIPLE CICE (20 pts. total; 2 pts. each) 1. Denaturation changes which of the following protein structure(s)? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. both b
Chem 11 Fall 2008 Examination #5 ASWER KEY MULTIPLE CICE (20 pts. total; 2 pts. each) 1. Denaturation changes which of the following protein structure(s)? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. both b
Fucoreverse. An anti-ageing glyconutrient for sensitive skin 100 % ISO for natural cosmetic. natural. origin
 Fucoreverse An anti-ageing glyconutrient for sensitive skin IS 16128 for natural cosmetic 100 % natural origin TE UNIQUE CMPSITIN Fucose - An anti-ageing glyconutrient The unique composition of Fucoreverse
Fucoreverse An anti-ageing glyconutrient for sensitive skin IS 16128 for natural cosmetic 100 % natural origin TE UNIQUE CMPSITIN Fucose - An anti-ageing glyconutrient The unique composition of Fucoreverse
Bioactive compounds from coral reef invertebrates*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 589 593, 2001. 2001 IUPAC Bioactive compounds from coral reef invertebrates* Tatsuo Higa, Junichi Tanaka, Ikuko I. Ohtani, Musri Musman, Michael C. Roy, and Ikuma
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 589 593, 2001. 2001 IUPAC Bioactive compounds from coral reef invertebrates* Tatsuo Higa, Junichi Tanaka, Ikuko I. Ohtani, Musri Musman, Michael C. Roy, and Ikuma
Lipids are broadly classified in to simple, complex and derived, which are further subdivided into different groups.
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Lipids. Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals. Storage Lipids: derivatives of fatty acids. 11/21/10
 1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
Chapter 4. Drug Biotransformation
 Chapter 4 Drug Biotransformation Drug Biotransformation 1 Why is drug biotransformation necessary 2 The role of biotransformation in drug disposition 3 Where do drug biotransformation occur 4 The enzymes
Chapter 4 Drug Biotransformation Drug Biotransformation 1 Why is drug biotransformation necessary 2 The role of biotransformation in drug disposition 3 Where do drug biotransformation occur 4 The enzymes
Pharmacognosy- 1 PHG 222. Prof. Dr. Amani S. Awaad
 Pharmacognosy- 1 PHG 222 Prof. Dr. Amani S. Awaad Professor of Pharmacognosy Pharmacognosy Department, College of Pharmacy Salman Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj. KSA. Email: amaniawaad@hotmail.com
Pharmacognosy- 1 PHG 222 Prof. Dr. Amani S. Awaad Professor of Pharmacognosy Pharmacognosy Department, College of Pharmacy Salman Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj. KSA. Email: amaniawaad@hotmail.com
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Round Table: Chemogenomics and Drug Discovery
 Round Table: Chemogenomics and Drug Discovery Weisenheim am Sand, Germany E-Mail kubinyi@t-online.de omepage 32nd Annual FEBS Congress Vienna, Austria, July 07-12, 2007 Drug Discovery - The Ancient Times
Round Table: Chemogenomics and Drug Discovery Weisenheim am Sand, Germany E-Mail kubinyi@t-online.de omepage 32nd Annual FEBS Congress Vienna, Austria, July 07-12, 2007 Drug Discovery - The Ancient Times
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units
 Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
In steady state, new production = carbon export
 In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
La Biodiversidad marina como fuente de nuevos agentes anticáncer
 La Biodiversidad marina como fuente de nuevos agentes anticáncer Marcelino Gutiérrez G. Centro de Biodiversidad y Descubrimiento de Drogas, IDICASAT, Panamá Segundo Simposio Iberoamericano de Investigación
La Biodiversidad marina como fuente de nuevos agentes anticáncer Marcelino Gutiérrez G. Centro de Biodiversidad y Descubrimiento de Drogas, IDICASAT, Panamá Segundo Simposio Iberoamericano de Investigación
Lesson: Plankton. We will use each of these three categories in our investigations of plankton.
 Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
Receptor Sites and Drug Design
 Receptor Sites and Drug Design Case Study: piates use for Anesthesia & analgesia 1 PAI 2 The functional groups and their placement in three-dimensional space determines to a large degree a molecule s biological
Receptor Sites and Drug Design Case Study: piates use for Anesthesia & analgesia 1 PAI 2 The functional groups and their placement in three-dimensional space determines to a large degree a molecule s biological
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Controlling ADME through Chemical Design. Marty Mulvihill Chris Vulpe
 Controlling ADME through Chemical Design Marty Mulvihill Chris Vulpe ADME Chemical Processes in ADME Wang and Skolnik, Chemistry and Biodiversity, 2009, 1887. Controlling toxicity through ADME Toward molecular
Controlling ADME through Chemical Design Marty Mulvihill Chris Vulpe ADME Chemical Processes in ADME Wang and Skolnik, Chemistry and Biodiversity, 2009, 1887. Controlling toxicity through ADME Toward molecular
Acremostrictin, a Highly Oxygenated Metabolite from the marine-derived fungus Acremonium strictum. Elin Julianti, PhD. Sekolah Farmasi ITB
 Acremostrictin, a ighly xygenated Metabolite from the marine-derived fungus Acremonium strictum Elin Julianti, PhD. Sekolah Farmasi ITB Introduction The oceans cover 70% of our planet s surface and as
Acremostrictin, a ighly xygenated Metabolite from the marine-derived fungus Acremonium strictum Elin Julianti, PhD. Sekolah Farmasi ITB Introduction The oceans cover 70% of our planet s surface and as
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
2. Aim and Objectives
 AIM AND OBJECTIVES 2. Plants represent unlimited sources of natural products. Biologically active compounds are accumulated in plants especially as secondary metabolites that have been used as a source
AIM AND OBJECTIVES 2. Plants represent unlimited sources of natural products. Biologically active compounds are accumulated in plants especially as secondary metabolites that have been used as a source
Marine Drugs ISSN
 Mar. Drugs 211, 9, 514-525; doi:1.339/md94514 Article OPEN ACCESS Marine Drugs ISSN 166-3397 www.mdpi.com/journal/marinedrugs Statistical Research on Marine Natural Products Based on Data Obtained between
Mar. Drugs 211, 9, 514-525; doi:1.339/md94514 Article OPEN ACCESS Marine Drugs ISSN 166-3397 www.mdpi.com/journal/marinedrugs Statistical Research on Marine Natural Products Based on Data Obtained between
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Market
 May 2017 Report Id : REP-GB-3292 Status : Ongoing Category : Healthcare, Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices 2015 Future Market Insights, All Rights Reserved About Future Market Insights Future Market Insights
May 2017 Report Id : REP-GB-3292 Status : Ongoing Category : Healthcare, Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices 2015 Future Market Insights, All Rights Reserved About Future Market Insights Future Market Insights
Chemical Composition of the Cell. B. Balen
 Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
Effects of alkyl chain length and degree of unsaturation at the α-anomeric position of D- galactose on gel formation and small molecule solubility
 Effects of alkyl chain length and degree of unsaturation at the α-anomeric position of D- galactose on gel formation and small molecule solubility Narrative 1. Goals and Objectives Nicholas Toupin and
Effects of alkyl chain length and degree of unsaturation at the α-anomeric position of D- galactose on gel formation and small molecule solubility Narrative 1. Goals and Objectives Nicholas Toupin and
CHITOSAN PRODUCTION LINE OFFER
 CHITOSAN PODUCTION LINE OFFE CHITOSAN PODUCTION - INTODUCTION is a deacetylated derivative of chitin. It is polysaccharide found in nature with an amino group, contained in the shells of Crustacea such
CHITOSAN PODUCTION LINE OFFE CHITOSAN PODUCTION - INTODUCTION is a deacetylated derivative of chitin. It is polysaccharide found in nature with an amino group, contained in the shells of Crustacea such
Life Science 1A Final Exam. January 19, 2006
 ame: TF: Section Time Life Science 1A Final Exam January 19, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use non-erasable
ame: TF: Section Time Life Science 1A Final Exam January 19, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use non-erasable
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Purification of agar from Gracilaria - heteroclada alga by means of ion-exchange chromatography
 Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 41, No. 3, P. 111-116, 2003 Purification of agar from Gracilaria - heteroclada alga by means of ion-exchange chromatography Received 5-8-2002 Le Dinh Hung, Ngo Quoc Buu, Bui
Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 41, No. 3, P. 111-116, 2003 Purification of agar from Gracilaria - heteroclada alga by means of ion-exchange chromatography Received 5-8-2002 Le Dinh Hung, Ngo Quoc Buu, Bui
Case Study: Opiates use for Anesthesia & analgesia
 rganic Lecture Series Receptor Sites and Drug Design Case Study: piates use for Anesthesia & analgesia 52 rganic Lecture Series PAI 53 Drug interactions at the cellular level rganic Lecture Series The
rganic Lecture Series Receptor Sites and Drug Design Case Study: piates use for Anesthesia & analgesia 52 rganic Lecture Series PAI 53 Drug interactions at the cellular level rganic Lecture Series The
Algal ingredients for health and potential for use in abatement of GHG emissions
 Algal ingredients for health and potential for use in abatement of GHG emissions Dr Maria Hayes Scientific Research Officer, Teagasc Food Research Centre, Ashtown, Dublin 15, Ireland. Email: Maria.Hayes@teagasc.ie
Algal ingredients for health and potential for use in abatement of GHG emissions Dr Maria Hayes Scientific Research Officer, Teagasc Food Research Centre, Ashtown, Dublin 15, Ireland. Email: Maria.Hayes@teagasc.ie
STANDARD FOR CREAM AND PREPARED CREAMS
 1 Codex Standard 288-1976 STANDARD FOR CREAM AND PREPARED CREAMS CODEX STAN 288-1976 1. SCOPE This Standard applies to cream and prepared creams for direct consumption or further processing as defined
1 Codex Standard 288-1976 STANDARD FOR CREAM AND PREPARED CREAMS CODEX STAN 288-1976 1. SCOPE This Standard applies to cream and prepared creams for direct consumption or further processing as defined
Lipids. Lipids. Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague
 Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY/POLYMERS. 3. With respect to amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins, know:
 INTRDUCTIN T BICEMISTRY/PLYMERS A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. With respect to lipids, know: The characteristic common to members of the class (solubility in nonpolar solvents) The functional groups most
INTRDUCTIN T BICEMISTRY/PLYMERS A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. With respect to lipids, know: The characteristic common to members of the class (solubility in nonpolar solvents) The functional groups most
Chemistry 5.07 Problem Set
 Chemistry 5.07 Problem Set 8 2013 Problem 1. All oxidation steps in the pathway from glucose to CO 2 result in the production of NADH, except the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) step in the TCA cycle, which
Chemistry 5.07 Problem Set 8 2013 Problem 1. All oxidation steps in the pathway from glucose to CO 2 result in the production of NADH, except the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) step in the TCA cycle, which
Seaweed and seaweed components as novel protein sources in animal diets
 Seaweed and seaweed components as novel protein sources in animal diets EAAP 2013 Paul Bikker, Marinus van Krimpen, Arjan Palstra, Willem Brandenburg, Ana López-Contreras, Sander van den Burg Background
Seaweed and seaweed components as novel protein sources in animal diets EAAP 2013 Paul Bikker, Marinus van Krimpen, Arjan Palstra, Willem Brandenburg, Ana López-Contreras, Sander van den Burg Background
The four levels of protein structure are: primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure.
 Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
elucidate the role of trace metals in the ecology of the oceans and the
 CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
I) Choose the best answer: 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine.
 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
 entre Number andidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF AMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General ertificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/02 Paper 2 Structured Questions
entre Number andidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF AMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General ertificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/02 Paper 2 Structured Questions
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
CELLULAR METABOLISM. Metabolic pathways can be linear, branched, cyclic or spiral
 CHM333 LECTURE 24 & 25: 3/27 29/13 SPRING 2013 Professor Christine Hrycyna CELLULAR METABOLISM What is metabolism? - How cells acquire, transform, store and use energy - Study reactions in a cell and how
CHM333 LECTURE 24 & 25: 3/27 29/13 SPRING 2013 Professor Christine Hrycyna CELLULAR METABOLISM What is metabolism? - How cells acquire, transform, store and use energy - Study reactions in a cell and how
2. Which of the following is NOT true about carbohydrates
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Examination #5 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response questions
Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Examination #5 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response questions
through the cell cycle. However, how we administer drugs also depends on the combinations that we give and the doses that we give.
 Hello and welcome to this lecture. My name is Hillary Prescott. I am a Clinical Pharmacy Specialist at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. My colleague, Jeff Bryan and I have prepared this
Hello and welcome to this lecture. My name is Hillary Prescott. I am a Clinical Pharmacy Specialist at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. My colleague, Jeff Bryan and I have prepared this
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2016, 7(2): 49-53 ISSN: 2088 0197 Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin Laeli
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2016, 7(2): 49-53 ISSN: 2088 0197 Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin Laeli
It the process by which a drug reversibly leaves blood and enter interstitium (extracellular fluid) and/ or cells of tissues.
 It the process by which a drug reversibly leaves blood and enter interstitium (extracellular fluid) and/ or cells of tissues. Primarily depends on: 1.Regional blood flow. 2.Capillary permeability. 3.Protein
It the process by which a drug reversibly leaves blood and enter interstitium (extracellular fluid) and/ or cells of tissues. Primarily depends on: 1.Regional blood flow. 2.Capillary permeability. 3.Protein
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O
 BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
Biochemical constituents of Gracilaria edulis cultured from spores
 Seaweed Res. Utiln., 27 (1 & 2) : 39-44, 2005 Biochemical constituents of Gracilaria edulis cultured from spores REETA JAYASANKAR 1, REMYA RAMAKRISHNAN, K. NIRMALA AND C. SEEMA 1 Central Marine Fisheries
Seaweed Res. Utiln., 27 (1 & 2) : 39-44, 2005 Biochemical constituents of Gracilaria edulis cultured from spores REETA JAYASANKAR 1, REMYA RAMAKRISHNAN, K. NIRMALA AND C. SEEMA 1 Central Marine Fisheries
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(12): Research Article. Amino acids and fatty acids in Turbinaria conoides
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(12):5093-5097 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Amino acids and fatty acids in Turbinaria conoides
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(12):5093-5097 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Amino acids and fatty acids in Turbinaria conoides
AGRESSIVE LYMPHOMAS - FUTURE. Dr Stéphane Doucet CHUM
 AGRESSIVE LYMPHOMAS - FUTURE Dr Stéphane Doucet CHUM What are clinical trials? Clinical trials are carefully planned research studies where the most-promising discoveries and results from laboratory studies
AGRESSIVE LYMPHOMAS - FUTURE Dr Stéphane Doucet CHUM What are clinical trials? Clinical trials are carefully planned research studies where the most-promising discoveries and results from laboratory studies
Extraction of carotenoids from crustacean waste using organic solvents
 Extraction of carotenoids from crustacean waste using organic solvents Hanif Houshmand Kouchi 1, Marzieh Moosavi-Nasab 2, Bahareh Shabanpour 1 1 Department of Fishery, Gorgan University of Agricultural
Extraction of carotenoids from crustacean waste using organic solvents Hanif Houshmand Kouchi 1, Marzieh Moosavi-Nasab 2, Bahareh Shabanpour 1 1 Department of Fishery, Gorgan University of Agricultural
Mangrove ecology: application of fatty acid biomarkers as trophic tracers in the ecosystem
 Kaiho Super Science High School Mangrove ecology: application of fatty acid biomarkers as trophic tracers in the ecosystem Prosper Mfilinge Advisor: Prof. Makoto Tsuchiya JSPS Self Introduction What are
Kaiho Super Science High School Mangrove ecology: application of fatty acid biomarkers as trophic tracers in the ecosystem Prosper Mfilinge Advisor: Prof. Makoto Tsuchiya JSPS Self Introduction What are
Principles of Biotechnology INDUSTRIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY WEEKS 8+9
 Principles of Biotechnology INDUSTRIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY WEEKS 8+9 Industrial Microbiology Industrial Microorganisms and Product formation involved: 1- Use microorganisms to produce valuable commercial product
Principles of Biotechnology INDUSTRIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY WEEKS 8+9 Industrial Microbiology Industrial Microorganisms and Product formation involved: 1- Use microorganisms to produce valuable commercial product
Inhibitors of Methionine Aminopeptidase-2 2 in the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin
 Inhibitors of Methionine Aminopeptidase-2 2 in the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin Hodgkin s s Lymphoma Targeted Cancer Therapies William Westlin, Ph.D. Vice President, Preclinical Research Discovery of Fumagillin
Inhibitors of Methionine Aminopeptidase-2 2 in the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin Hodgkin s s Lymphoma Targeted Cancer Therapies William Westlin, Ph.D. Vice President, Preclinical Research Discovery of Fumagillin
TISSUES, CELLS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 Inorganic Compounds: Water (2H: 1O) Minerals (Na, P, I, Ca, Fe, K, nitrates, phosphates) functions and deficiencies Fertilizers Organic molecules are made up of C, H, O and some contain other elements
Inorganic Compounds: Water (2H: 1O) Minerals (Na, P, I, Ca, Fe, K, nitrates, phosphates) functions and deficiencies Fertilizers Organic molecules are made up of C, H, O and some contain other elements
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
CODEX STANDARD FOR CREAM AND PREPARED CREAMS
 CODEX STANDARD FOR CREAM AND PREPARED CREAMS CODEX STAN 288-1976 1. SCOPE This Standard applies to cream and prepared creams for direct consumption or further processing as defined in Section 2 of this
CODEX STANDARD FOR CREAM AND PREPARED CREAMS CODEX STAN 288-1976 1. SCOPE This Standard applies to cream and prepared creams for direct consumption or further processing as defined in Section 2 of this
Chapter 1: Curcumin is excellent compound for various medicinal usages
 Super-Curcumin Story Chapter 1: Curcumin is excellent compound for various medicinal usages Chapter 2: Discovery of Super-Curcumin analog Chapter 3: Anti-tumor activities of Super-Curcumin analog Chapter
Super-Curcumin Story Chapter 1: Curcumin is excellent compound for various medicinal usages Chapter 2: Discovery of Super-Curcumin analog Chapter 3: Anti-tumor activities of Super-Curcumin analog Chapter
Advances in Fish Processing Technology
 SUB Hamburg A/516614 Advances in Fish Processing Technology D.P. Sen ALLIED PUBLISHERS PRIVATE LIMITED New Delhi Mumbai Kolkata Lucknow * Chjennai Nagpur Bangalore Hyderabad Ahmedabad Contents Dedication
SUB Hamburg A/516614 Advances in Fish Processing Technology D.P. Sen ALLIED PUBLISHERS PRIVATE LIMITED New Delhi Mumbai Kolkata Lucknow * Chjennai Nagpur Bangalore Hyderabad Ahmedabad Contents Dedication
What are the 6 Nutrients. Carbohydrates Proteins Fats/Oils (Lipids) Vitamins Minerals Water
 Nutrients AG 240 What are the 6 Nutrients Carbohydrates Proteins Fats/Oils (Lipids) Vitamins Minerals Water Carbohydrates (CHO) Primary component of livestock feed Referred to as energy CHO Characteristics
Nutrients AG 240 What are the 6 Nutrients Carbohydrates Proteins Fats/Oils (Lipids) Vitamins Minerals Water Carbohydrates (CHO) Primary component of livestock feed Referred to as energy CHO Characteristics
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
3.9 Carbohydrates. Provide building materials and energy storage. Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
 3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
MPS Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course. Fall Semester Lecture 22. Alkaloids IV
 MPS 587 - Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course Fall Semester 2011 Lecture 22 Alkaloids IV 14. Alkaloids derived from strictosidine 14a. Indole alkaloids 14b. Quinoline alkaloids Disclaimer As part of the
MPS 587 - Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course Fall Semester 2011 Lecture 22 Alkaloids IV 14. Alkaloids derived from strictosidine 14a. Indole alkaloids 14b. Quinoline alkaloids Disclaimer As part of the
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits)
 Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
WHY TARGETTING SIGNALLING PATHWAYS?
 WHY TARGETTING SIGNALLING PATHWAYS? Cancer cells are particularly sensitive to stress therefore sensitive to inhibition of their hyper activated signaling proteins the re instatement of lost tumor suppressors.
WHY TARGETTING SIGNALLING PATHWAYS? Cancer cells are particularly sensitive to stress therefore sensitive to inhibition of their hyper activated signaling proteins the re instatement of lost tumor suppressors.
Distribution Ecology attempts to explain the restricted and generally patchy distribution of species
 Marine Mammal Ecology Ecology : An attempt to describe and explain the patterns of distribution and abundance of organisms. These patterns reflect the history of complex interactions with other organisms
Marine Mammal Ecology Ecology : An attempt to describe and explain the patterns of distribution and abundance of organisms. These patterns reflect the history of complex interactions with other organisms
PRO G max Probiotic fermented soybean meal Benefits of PRO G max
 PRO G max Probiotic fermented soybean meal Benefits of PRO G max Probiotic bacteria > 10 10 CFU/kg High protein with low molecular weight protein approaching small peptides enhancing digestion and absorption
PRO G max Probiotic fermented soybean meal Benefits of PRO G max Probiotic bacteria > 10 10 CFU/kg High protein with low molecular weight protein approaching small peptides enhancing digestion and absorption
METABOLISM. Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. Office: 2B 84
 METABOLISM Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Metabolism By the end of this lecture, you should: Recognize the importance of biotransformation Know the different sites for
METABOLISM Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Metabolism By the end of this lecture, you should: Recognize the importance of biotransformation Know the different sites for
SPRIN Protease Kit. Content Code Description Application. Covalently immobilised preparation of Subtilisin. Epoxy Acrylic Resin
 SPRIN Protease Kit SPRIN Protease Kit Normal (5 g each) Product code: SPKN SPRIN Protease Kit Large (20 g each) Product code: SPKL The kit contains four different covalently immobilised protease preparations,
SPRIN Protease Kit SPRIN Protease Kit Normal (5 g each) Product code: SPKN SPRIN Protease Kit Large (20 g each) Product code: SPKL The kit contains four different covalently immobilised protease preparations,
Figure 2. Figure 1. Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules
 Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
