Fracture Mechanics Analysis of Fourth Lumbar Vertebra in Method of Finite Element Analysis
|
|
|
- Jessica Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2217 Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), IJABBR eissn: International Journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Journal homepage: Research Article Fracture Mechanics Analysis of Fourth Lumbar Vertebra in Method of Finite Element Analysis Majid Ghadiri *, Abbas Khanmohammadi, Hamid Reza Mahdavi, Marzieh Ahmadi, Tahereh Mirzaei, Hossein Easy 1 Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanics, Imam Khomeini International University, Qazvin, Iran A R T I C L E I N F O Article history: Received: 1 May, 2014 Revised: 17 May, 2014 Accepted: 11 June, 2014 epublished: 30 July, 2014 Key words: Maximum stress Finite element analysis Fourth lumbar vertebrae Fracture toughness Stress intensity factor A B S T R A C T Objective: In this paper, finite element model of the L4 vertebra subjected to combination of compression and flexion loading in isotropic and anisotropic cases is investigated. Methods: In both cases, the vertebra is considered homogeneous. Also, the body of vertebra is divided to cancellous and cortical sections in anisotropic model, but the process is assumed isotropic such as isotropic model. The maximum Von Mises stress on the fourth lumbar vertebrae is obtained. Also, the stress intensity factor is analyzed with placing a small crack on the critical region of the model from view point of fracture mechanics. Furthermore, the required force for the fracture of fourth lumbar vertebrae is obtained through increasing the applied force for assumed model. Results: The results show that the highest stress value and its position is 7.237MPa in the upper pedicle region for anisotropic property of vertebrae. At the end of this article, stress intensity factors in different aspect ratios of crack for anisotropic vertebrae under combination of flexion and compression loading are plotted. INTRODUCTION It is always assumed in fracture mechanics that each piece has some flaw and small cracks. In fact, since no phenomenon in nature is ideal, this assumption can always be true and the used equations in strength of materials can be replaced with equations of fracture mechanics. In this way, the stress intensity factor can be considered as a basis criterion for analysis in both real and critical state. Because of the body weight and daily activities such as sitting, standing, walking, etc, forces and moments will be applied to all vertebras of spine. Lumbar spine as a strong support always plays an important role in tolerating daily life pressures, such as static and dynamic activities. These activities can be a little impact due to sliding, running, or sudden lifting a heavy weight. So regardless of the disc hernia ion or swelling, fracture in vertebrae due to unwanted cracks should also be taken into consideration. Nowadays with progression of technology, laboratories and experimental stations in field of Biomechanics, try to produce exact and nearly true models for simulating behaviors and analyzing forces acting on human body parts such as the sensitive part of lumbar spine. This section consists of five vertebrae, inter vertebral discs, muscles, etc., which are connected to thoracic spine from the top side and to sacrum from the bottom side. Recognizing the critical failure position can be performed clinically or experimentally that this is the approach of orthopedic specialists, But another way to distinguish the critical failure position, is analytical and engineering approach that has more variety and lower cost than the previous method. Finite element analysis is one of the most advanced simulation techniques and has been used in orthopedic *Corresponding Author: Majid Ghadiri, Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanics, Imam Khomeini International University, Qazvin, Iran, ghadiri@eng.ikiu.ac.ir, Tel.: ; Fax:
2 2218 Ghadiri et al/ Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), biomechanics for many decades (Kayabasi and Ekici 2008). Up to now, many finite element (FE) simulations both in vivo and in vitro studies have been conducted for biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine (Kuo et al., 2010). They can also be successfully applied for the simulation of biomechanical systems (Odin et al., 2010). FE methods have become an important tool to evaluate mechanical stresses and strains in bone (Hernandez et al., 2001) and have been widely used to investigate the mechanical behavior of bone tissue (Herrera et al., 2007). Finite element analysis of the three-dimensional model of the forth vertebrae was developed to clarify the mechanical causes of low back pain. The stresses in a modeled lumbar structure were then analyzed as solid cortical bone, as a hollow shell of cortical bone and with its inner cancellous bone structure. In all cases, material properties have been supposed as isotropic. The results show large stress concentrations were found in the superior and inferior facet region and on the central surfaces of the vertebral body. Higher stress concentrations were also found in the cortical shell of the vertebrae (Nabhani and Wake, 2002). Zulkifli and Ariffin (2012) have studied lumbar vertebrae under compression load with isotropic properties. They have been obtained the maximum stress at the upper region of the pedicle with value of 4.5 MPa. Also the value of stress intensity factor was obtained 0.525MPa m at their research, and the fracture toughness has been presented 1.46MPa m. Various values of K c and G c for bone has been found from different orientations and sizing conditions (Isaac and Graham, 2011). In this study fourth lumbar vertebra with regard to statically activities is investigated. For simplicity, the effect of inter vertebral disc, another lumbar vertebras, muscles and ligaments are not included. The purpose of this paper is to determine the maximum Von Mises stress and stress intensity factor (SIF) and the required force for fracture of the fourth lumbar vertebra due to the combined loading in two cases. In the first case, material properties of vertebrae are supposed as isotropic and in the other case, true model of the vertebrae is considered as the different anisotropic properties for the cortical and cancellous and isotropic property for the process. Also using finite element analysis, stress distribution and the stress intensity factors have been studied in two cases at the fourth lumbar vertebrae, under combination of flexion and compression loads, i.e. isotropic and anisotropic properties for vertebrae materials. In all states of body position, these two kinds of loading are always applied to the lumbar spine. Because if we consider the weight of the trunk, we should not forget the moment caused by the body's gravity center. The gravity center of the body lies in the mid-sagittal plane (due to anatomic symmetry) and somehow upside the sacral spine. It is reported to be 4 cm in front of the first sacral vertebra in the standing anatomic position (White and Panjabi, 1990). Results of a survey showed that the pedicle is a critical region (Nabhani and Wake, 2002). So, we put the considered crack in this region (Zulkifli and Ariffin, 2012). Certainly, current study contributes to orthopedic specialists in the detecting failing potential region in fourth lumbar vertebrae with an analytical and engineering point of view. 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS A vertebra is composed of six components which are: vertebral body, spinous process, transverse process, lamina, pedicle, and facet joints. Point cloud model of vertebra has been provided from biomechanics department of BRNO University. Then, the three dimensional model of vertebrae was constructed in Catia and Inventor software s and was imported by Abaqus 6.12 software for the analysis. Figure 1 shows the anatomy of the fourth lumbar vertebrae. The vertebrae's body has two layers, consist of cortical and cancellous bone, and each of these two sections have different properties. In fact, the surface of the lumbar vertebra is not smooth. Figure 1: Anatomy of the fourth lumbar vertebrae 2.1. Loading and boundary conditions To evaluate the effect of the compression condition, a simple compressive loading is applied to the vertebral model. At first, to obtain the critical region of the fourth lumbar vertebrae, a force of 578 N including head weight,
3 2219 Ghadiri et al/ Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), trunk weight, arms weight and a box weight that, person picks it up, was applied to the lumbar vertebrae. According to Figure 2, we can determine pressure and moments which have been exerted on vertebrae by weight of the box, head, trunk, hands, and calculating the distance between each of them from the vertebra (Kurtz and Edidin, 2006). Figure 2: View of forces and the distances from each part to L4 (Kurtz and Edidin, 2006) Table 1 shows the weight of each segment and its distance from the vertebrae. The load is divided to 70% on the upper vertebral body and 30% on the facets joint (Ahmad and Arifin, 2010). Table 1: Head weight )N( distance )cm( Trunk Arms weight )N( distance )cm( weight )N( distance )cm( Box weight )N( distance )cm( Also, 70% of load bearing surface has been assigned to the body and 30% to the facet joints and the loading conditions is assumed uniform. For considering the flexion effects, a concentrated moment of 108 N.m is applied to reference point which is located on the geometric center of the upper part of the vertebral body by kinematic coupling (Weisse et al., 2012). For applying the boundary conditions, the lower vertebral body is fully constrained in all degrees of freedom (Ahmad and Arifin, 2010). Figure 3 shows applied loads and boundary conditions. Areas which are measured in Catia software have been presented in Table 2.
4 2220 Ghadiri et al/ Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), Table 2: Area of surfaces on body and facet joints Body Facet joints (mm 2 ) 248 (mm 2 ) Figure 3: View of the loading and boundary conditions 2.2. Mechanical properties Human vertebra is a non-linear, inhomogeneous and anisotropic material and varies in the boundary regions between cortical and cancellous bone (Xia et al., 2006). In this paper, for loading conditions, two cases are considered by using the finite element analysis. In the first case, for simplicity, the vertebra is considered as isotropic material and in the second case; true material properties of vertebrae are considered. For applying appropriate material properties to different parts of vertebrae, the vertebra has been separated from pedicles. Thus, we can choose each part of vertebrae as a separate cell. Assigned properties to the fourth lumbar vertebrae in the two cases are presented in tables 3 and 4 (Chena et al., 2009). Table 3: Material properties of isotropic vertebrae (Ahmad and Arifin, 2010) E)GPa( 12 ν 0.3 Table 4: Material properties of anisotropic vertebrae (Chena et al., 2009) cortical cancellous process Ex (MPa) E (MPa) υ Ey (MPa) Ez (MPa) Gx(MPa) Gy (MPa) Gz (MPa) υxy υyz υxz Applying finite element mesh to the model Applying the finite element mesh to the geometry, the vertebra is divided into a grid of elements which form the finite element model. Once the finite element model has been created, the next step is to identify the type of element that will be used for meshing various partitioned volumes. The model can use more than one element type. Generally, the simplest element type should be used for
5 2221 Ghadiri et al/ Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), modeling the problem. In this study, it was decided to use three-dimensional, solid, linear, tetrahedral elements for all parts. This decision was based on the complexity of model shape and this type of element was able to give a good accurate rendition of the surface geometry. Also, the approximate size of each element has been altered to get an optimum converge in a specific stress value. 4. Results and Discussion As previously mentioned, in this study, critical region of vertebra, in conjunction with the value of Von Mises stress and stress intensity factor were found, unlike other papers. At continuing this discussion, the results and the relating points will express in two models of anisotropic and isotropic. Figure 4 shows the stress distribution of the fourth lumbar spine for evaluating the Combination of compression and flexion forces in anisotropic case. It was found that the highest stress concentration points were at the upper pedicle region, with Von Mises stress value MPa. So, this area is a critical region of the fourth lumbar vertebrae. Figure 4. Von Mises stress distribution in anisotropic vertebrae under combination of flexion and compression loadings (in uncracked model) As mentioned in the introduction part, due to the criticality of the pedicle and opening mode, crack has been put at the upper part of the pedicle (Zulkifli and Ariffin, 2012). According to the mathematical theory of fracture mechanics, the shape of crack growth is an ellipse, even though the first shape of crack is not an ellipse (Parker, 1981). So the crack has been modeled in a shape of ideal half- ellipse, respectively, with 3 and 2 millimeters in length and width. Fig. 5 shows stress distribution and crack opening in isotropic vertebrae under flexion and compression forces and the contours represent the level of Von Mises stress. Figure 5: Von Mises stress distribution and crack opening in isotropic vertebrae under combination of flexion and compression loadings
6 2222 Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), We could see that the highest stress concentrations are at the top of the pedicle and around the crack, with Von Mises stress value MPa. This suggests that pedicle is a high potential region for the failure. This critical region of the pedicle tends to act as a pivot when another load is applied to the facet joints and creates a bending effect. A longer distance between the facet joints and the vertebral body causes an increase in the bending moment, and also a stress concentration region. The value of stress intensity factor (K I) at deepest point of crack is MPa m. It should be noted that the number of contours around the crack tip is considered 5. Figure 6 shows Von Mises stress distribution and crack opening in anisotropic vertebrae under combination of flexion and compression forces. It is found that like the pervious case, the highest stress concentration is at the upper pedicle region, but with Von Mises stress value of MPa. The value of stress intensity factor (K I) at deepest point of the crack is MPa m. Figure 6: Von Mises stress distribution and crack opening in anisotropic vertebrae under combination of flexion and compression loadings For obtaining the required force for the fracture of lumbar vertebrae, we increased the value of applied force and then computed the corresponding stress intensity factors and compared them with the reported fracture toughness by literatures and a force of 2250 N obtained as a critical force. Figure 7 shows the stress distribution of the fourth lumbar vertebrae under the mentioned load. It's been found that similar to previous cases, the highest stress concentration is around the crack, but with Von Mises stress value of MPa. Figure 7: Von Mises stress distribution in anisotropic vertebrae under a load of 2250N In Fig. 8, the crack opening is visible. The value of stress intensity factor (K I) at deepest point of crack is MPa m.
7 2223 Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), It is important that real properties and actual loading conditions have been considered for analysis purpose. We are looking at this subject that whether the crack has been extended or not during a static loading. Therefore, the stress intensity factor and fracture toughness values have been required to compare with each other. In the first two cases, cracks are still far from reaching a critical Figure 8: Crack opening in anisotropic vertebrae under a load of 2250N Table 5: Summary of stress and stress intensity factor values stage. But in case with larger load, we ve been very close to the critical region. This fact shows that it must be avoided to lift loads with a large amount. Table 5 compares these mentioned cases in summary. Stress intensity factor values obtained in the first two cases show that the vertebrae tolerated under applied load, because the stress intensity factor values is lower than fracture toughness. Table 6 shows fracture toughness limits K c and the thicknesses used for the biomechanical testing of the some specimens. isotropic with a load of 111N anisotropic with a load of 111N anisotropic with a load of 2250N stress intensity factor (MPa m) (MPa m) (MPa m) maximum stress (MPa) (MPa) (MPa) Table 6: Summary of Fracture toughness limits K c and the thicknesses used for the biomechanical testing of the specimens (Isaac and Graham, 2011) Study Direction Thickness (mm) Kc MPa m Norman et al., 1994 Longitudinal ±.65 Longitudinal ±.89 Bonfield et al., 1978 Longitudinal According to the above discussion, two cases arise for rupturing: the length of crack should be larger with same load value, or a bigger load is needed for failing with same size of crack. Actually, when value of SIF reach to value of fracture toughness, the vertebra will fail and the crack will spread in critical region. This is what leads to the movement modification. After the crack detection by X-ray photos, Orthopedics specialists based on amount damage, prescribe instructions to help to modify daily actions and prevent increasing damage. Also, Figure 9 shows stress intensity factors in some aspect ratio of crack under second loading case (flexion and compression loadings) for anisotropic vertebra. It's been observed that with increasing aspect ratio ( a b), the stress intensity factor increases.
8 2224 Ghadiri et al/ Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res, 2014; 2 (7), Figure 9: Stress intensity factors in some aspect ratio of crack for anisotropic vertebrae under combination of flexion and compression loadings. (a=crack length, b=crack depth) 3. Conclusion This paper has studied the use of the finite element model to determine the maximum stress and stress intensity factor and the required force for the fracture of fourth lumbar vertebrae under combination of compression and flexion forces in isotropic and anisotropic cases, regardless of inter vertebral discs, References Ahmad, Z., Arifin A.K., Probabilistic stress analysis of the Human lumbar spine extended finite element method. The 11th Asia Pacific Industrial Engineering and Management Systems Conference. Melaka, 7-10 December Bonfield, W., Grynpas, M.D., Young, R.J., Crack velocity and the fracture of bone. J. Biomechanics. 1, Chena, S.H., Zhongb, Z.C., Chenc, C.S., Biomechanical comparison between lumbar disc arthroplasty and fusion. J. Medical Engineering & Physics. 31, Hernandez, C.J., Beaupre, G.S., Keller, T.S., The influence of bone volume fraction and ash fraction on bone strength and modulus. J. Bone. 29, Herrera, A., Panisello, J.J, Ibarz, E., Long-term study of bone remodeling after femoral stem: A comparison between dexa and finite element simulation. J. Biomechanics. 40, Isaac, M., Graham, A., probabilistic assessment of vertebral cortical bone fracture of intraosteonal structures. MSc Thesis, University of Wright State. USA. Kayabasi, O., Ekici, B., Probabilistic design of a newly designed cemented hip prosthesis using finite element method. J. Materials and Design. 29, Kuo, C.S., Hu, H.T., Lin, R.M., Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine on facet joint force an intradiscal pressure-a finite element study. J. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 11, muscles and other vertebras. The results indicated that the maximum Von Mises stress value was in anisotropic case and at the upper pedicle region, with Von Mises stress value of MPa. Hence, placed assumed crack on this region and computed corresponding value of SIF. Also, according to above condition, it was observed that the value of stress intensity factor in this region was MPa m. Kurtz, S.M., Edidin, A.A., Spine Technology Handbook. Elsevier. Nabhani, F., Wake, M., Computer modeling and stress analysis of the lumbar spine. J. Materials Processing Technology. 127, Norman, T.L., Vashishth, D., Burr, D. B., Fracture toughness of human bone under tension. J. Biomechanics. 28, Odin, G., Savoldelli, C., Bouchard, P.O., Determination of young s modulus of mandibular bone using inverse analysis. J. Medical Engineering & Physics. 32, Parker, A.P., The mechanics of fracture and fatigue: an introduction. Newyork. Weisse, B., Aiyangar, A.K., Affolter, C., Determination of the translational and rotational stiffnesses of an L4 L5 functional spinal unit using a specimen-specific finite element model. J. Mechanical behavior of biomedical materials. 13, White, A., Panjabi, M., Clinical biomechanics of the spine. Second ed. J.B. Lippincott Company Xia, Q.T., Tan, K.W., Lee, V.S., Investigation of Thoracolumbar T12-L1 burst fracture mechanism using finite element method. J. Medical Engineering & Physics. 28, Zulkifli, A., Ariffin, A.K., Monte Carlo analysis of the human vertebra based on compressive loading. J. Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering. 12,
A Finite Element Study of the Stress Redistribution of the Lumbar Spine after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery
 A Finite Element Study of the Stress Redistribution of the Lumbar Spine after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery Hsuan-Teh Hu 1, Kuo-Yuan Huang 2,3, Che-Jung Liu 1, Ching-Sung Kuo 1,4 1 Department
A Finite Element Study of the Stress Redistribution of the Lumbar Spine after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery Hsuan-Teh Hu 1, Kuo-Yuan Huang 2,3, Che-Jung Liu 1, Ching-Sung Kuo 1,4 1 Department
KINEMATIC RESPONSE OF THE L4-L5 FUNCTIONAL SPINAL UNIT AFTER A LATERAL LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY
 Proceedings of the 1 st Iberic Conference on Theoretical and Experimental Mechanics and Materials / 11 th National Congress on Experimental Mechanics. Porto/Portugal 4-7 November 2018. Ed. J.F. Silva Gomes.
Proceedings of the 1 st Iberic Conference on Theoretical and Experimental Mechanics and Materials / 11 th National Congress on Experimental Mechanics. Porto/Portugal 4-7 November 2018. Ed. J.F. Silva Gomes.
Lumbo-sacral destruction fixation biomechanics
 Lumbo-sacral destruction fixation biomechanics Amin Joukhar MSc * Jwalant S. Mehta FRCS Orth ^ David Marks FRCS Orth ^ Prof Vijay Goel PhD * ^ Birmingham Spine Centre, England *Engineering Centre for Orthopaedic
Lumbo-sacral destruction fixation biomechanics Amin Joukhar MSc * Jwalant S. Mehta FRCS Orth ^ David Marks FRCS Orth ^ Prof Vijay Goel PhD * ^ Birmingham Spine Centre, England *Engineering Centre for Orthopaedic
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Lumbar Spine for Snatch Action in Weight Lifting Based on Finite Element Method
 ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 04 (2010) No. 01, pp. 048-052 Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Lumbar Spine for Snatch Action in Weight Lifting
ISSN 1750-9823 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 04 (2010) No. 01, pp. 048-052 Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Lumbar Spine for Snatch Action in Weight Lifting
Kinematic Analysis of Lumbar Spine Undergoing Extension and Dynamic Neural Foramina Cross Section Measurement
 Copyright c 2008 ICCES ICCES, vol.7, no.2, pp.57-62 Kinematic Analysis of Lumbar Spine Undergoing Extension and Dynamic Neural Foramina Cross Section Measurement Yongjie Zhang 1, Boyle C. Cheng 2, Changho
Copyright c 2008 ICCES ICCES, vol.7, no.2, pp.57-62 Kinematic Analysis of Lumbar Spine Undergoing Extension and Dynamic Neural Foramina Cross Section Measurement Yongjie Zhang 1, Boyle C. Cheng 2, Changho
Topology optimisation of hip prosthesis to reduce stress shielding
 Computer Aided Optimum Design in Engineering IX 257 Topology optimisation of hip prosthesis to reduce stress shielding S. Shuib 1, M. I. Z. Ridzwan 1, A. Y. Hassan 1 & M. N. M. Ibrahim 2 1 School of Mechanical
Computer Aided Optimum Design in Engineering IX 257 Topology optimisation of hip prosthesis to reduce stress shielding S. Shuib 1, M. I. Z. Ridzwan 1, A. Y. Hassan 1 & M. N. M. Ibrahim 2 1 School of Mechanical
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Biomechanics of compensatory mechanisms in spinal-pelvic complex
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Biomechanics of compensatory mechanisms in spinal-pelvic complex To cite this article: D V Ivanov et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 991 012036 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Biomechanics of compensatory mechanisms in spinal-pelvic complex To cite this article: D V Ivanov et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 991 012036 View
Raymond Wiegand, D.C. Spine Rehabilitation Institute of Missouri
 2D Pattern matching of frontal plane radiograph to 3D model identifies structural and functional deficiencies of the spinal pelvic system in consideration of mechanical spine pain (AKA Spine distortion
2D Pattern matching of frontal plane radiograph to 3D model identifies structural and functional deficiencies of the spinal pelvic system in consideration of mechanical spine pain (AKA Spine distortion
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
А тация 69, 47, Ц Д - ( Д). -,. - ANSYS. И,,.,,.,.
 А тация 69, 47, 18 31. Ц Д - ( Д). -,. - ANSYS. И,,.,,.,. Abstract Master's dissertation was set out on 69 pages with 47 figures, 18 tables and 31 literature sources. The purpose of this work was to investigate
А тация 69, 47, 18 31. Ц Д - ( Д). -,. - ANSYS. И,,.,,.,. Abstract Master's dissertation was set out on 69 pages with 47 figures, 18 tables and 31 literature sources. The purpose of this work was to investigate
DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING OF A SLIDING TABLE FOR A SIX AXIS SPINE TESTING MACHINE
 Volume 118 No. 20 2018, 815-819 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING OF A SLIDING TABLE FOR A SIX AXIS SPINE TESTING
Volume 118 No. 20 2018, 815-819 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING OF A SLIDING TABLE FOR A SIX AXIS SPINE TESTING
Illustrative exercises for the lectures
 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
Simulation of bone indentation
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 113 Simulation of bone indentation S. Kasiri 1, G. Reilly 1,2 & D. Taylor 1 1 Trinity Centre for Bioengineering, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland 2 Institute of Technology
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 113 Simulation of bone indentation S. Kasiri 1, G. Reilly 1,2 & D. Taylor 1 1 Trinity Centre for Bioengineering, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland 2 Institute of Technology
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 8, No. 1, 2006 Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis MARTINA FRIOVÁ, ZDENK HORÁK, SVATAVA KONVIKOVÁ Laboratory of Biomechanics, Department of
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 8, No. 1, 2006 Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis MARTINA FRIOVÁ, ZDENK HORÁK, SVATAVA KONVIKOVÁ Laboratory of Biomechanics, Department of
The Influence of Muscle Forces on the Stress Distribution in the Lumbar Spine
 The Open Spine Journal, 2011, 3, 21-26 21 Open Access The Influence of Muscle Forces on the Stress Distribution in the Lumbar Spine Christian Wong *,1, John Rasmussen 2, Erik Simonsen 3, Lone Hansen 4,
The Open Spine Journal, 2011, 3, 21-26 21 Open Access The Influence of Muscle Forces on the Stress Distribution in the Lumbar Spine Christian Wong *,1, John Rasmussen 2, Erik Simonsen 3, Lone Hansen 4,
Effects of Moment Arms on the Internal Spinal Loads during Manual Material Handling
 Effects of Moment Arms on the Internal Spinal Loads during Manual Material Handling Murali Subramaniyam 1&2, Se Jin Park 1, Sangho Park 2 1 Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, Daejeon, 305-340,
Effects of Moment Arms on the Internal Spinal Loads during Manual Material Handling Murali Subramaniyam 1&2, Se Jin Park 1, Sangho Park 2 1 Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, Daejeon, 305-340,
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
(c) B. Ravi, IIT Bombay 1
 Collaborative Engineering Evaluation, Testing TKP Safety, TKP System Mechanism FEA Physical testing Fatigue Wear What How Evaluate Testing Judgement Criteria's Testing Conditions Parameters Measured OrthoCAD
Collaborative Engineering Evaluation, Testing TKP Safety, TKP System Mechanism FEA Physical testing Fatigue Wear What How Evaluate Testing Judgement Criteria's Testing Conditions Parameters Measured OrthoCAD
The Effects of L4/5 Fusion on the Adjacent. Segments in the Lumbar Spine
 The Effects of L4/5 Fusion on the Adjacent Segments in the Lumbar Spine A Thesis submitted to The University of Manchester for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Engineering and Physical
The Effects of L4/5 Fusion on the Adjacent Segments in the Lumbar Spine A Thesis submitted to The University of Manchester for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Engineering and Physical
Spinologics.com. Scoliosis Surgery Simulation
 Scoliosis Surgery Simulation Finite Element (FE) Models Finite element model: mathematical method widely used in traditional engineering fields (aeronautics, car industry, civil engineering). Principle:
Scoliosis Surgery Simulation Finite Element (FE) Models Finite element model: mathematical method widely used in traditional engineering fields (aeronautics, car industry, civil engineering). Principle:
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
Experimental and Numerical Comparison of Stresses Level between Titanium and Novel Composite Single Tooth Implant
 International Journal of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering IJMME-IJENS Vol:15 No:06 84 Experimental and Numerical Comparison of Stresses Level between Titanium and Novel Composite Single Tooth Implant
International Journal of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering IJMME-IJENS Vol:15 No:06 84 Experimental and Numerical Comparison of Stresses Level between Titanium and Novel Composite Single Tooth Implant
Effect of the femoral stem size on femur bone quality towards THR
 Original article: Effect of the femoral stem size on femur bone quality towards THR Palash Kumar Maji a,*, Amit Roy Chowdhury b, Debasis Datta b, S Karmakar a, Subhomoy Chatterjee b and A K Prasad a a
Original article: Effect of the femoral stem size on femur bone quality towards THR Palash Kumar Maji a,*, Amit Roy Chowdhury b, Debasis Datta b, S Karmakar a, Subhomoy Chatterjee b and A K Prasad a a
LEARN * DREAM * AWAKEN* DISCOVER * ENLIGHTEN * INVESTIGATE * QUESTION * EXPLORE
 S C I E N C E H U M A N Spine & Vertebrate The Spine & Vertebrate in Focus This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of the spine and vertebrate. In this e-guide you will: Human Body Spine/Vertebrate
S C I E N C E H U M A N Spine & Vertebrate The Spine & Vertebrate in Focus This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of the spine and vertebrate. In this e-guide you will: Human Body Spine/Vertebrate
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Freedom. Lumbar Disc Polymer-Metal Bond Integrity. CAUTION: Investigational device. Limited by Federal law to investigational use.
 Freedom Lumbar Disc Polymer-Metal Bond Integrity CAUTION: Investigational device. Limited by Federal law to investigational use. 1 White Paper Freedom Lumbar Disc Polymer-Metal Bond Integrity Abstract
Freedom Lumbar Disc Polymer-Metal Bond Integrity CAUTION: Investigational device. Limited by Federal law to investigational use. 1 White Paper Freedom Lumbar Disc Polymer-Metal Bond Integrity Abstract
DEVELOPMENT OF L1 TO L5 FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF LUMBAR SPINE: A BIOMECHANICAL STUDY
 Volume 118 No. 20 2018, 829-838 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu DEVELOPMENT OF L1 TO L5 FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF LUMBAR SPINE: A BIOMECHANICAL
Volume 118 No. 20 2018, 829-838 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu DEVELOPMENT OF L1 TO L5 FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF LUMBAR SPINE: A BIOMECHANICAL
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist. Concept ENGSTRÖM
 FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
An effort is made to analyse the stresses experienced by the human femur. In order
 Finite Element Analysis of Human Femur Bone U N Mughal 1, H A Khawaja 2*, M Moatamedi 1, M Souli 3 1. Narvik University College, Norway 2. UiT-The Arctic University of Norway, Norway 3. University of Lille,
Finite Element Analysis of Human Femur Bone U N Mughal 1, H A Khawaja 2*, M Moatamedi 1, M Souli 3 1. Narvik University College, Norway 2. UiT-The Arctic University of Norway, Norway 3. University of Lille,
Chiro-Tech IV Midterm Questions
 hiro-tech IV Midterm Questions 1. What is NOT a factor in shaping the Lumbar lordosis?. Wedge shaped L-S IV.. L5 vertebral body is wedge-shaped.. The size of the Sacrum.. Inclination of the vertebrae above
hiro-tech IV Midterm Questions 1. What is NOT a factor in shaping the Lumbar lordosis?. Wedge shaped L-S IV.. L5 vertebral body is wedge-shaped.. The size of the Sacrum.. Inclination of the vertebrae above
The Nucleus Pulpous of Intervertebral Disc Effect on Finite Element Modeling of Spine
 Original Article The Nucleus Pulpous of Intervertebral Disc Effect on Finite Element Modeling of Spine Midiya Khademi 1, Yousef Mohammadi 2, Seifollah Gholampour 3, Nasser Fatouraee 4 1 M.Sc. Department
Original Article The Nucleus Pulpous of Intervertebral Disc Effect on Finite Element Modeling of Spine Midiya Khademi 1, Yousef Mohammadi 2, Seifollah Gholampour 3, Nasser Fatouraee 4 1 M.Sc. Department
APPLICATION OF COMPOSITE FRACTURE MECHANICS TO BONE FRACTURE ANALYSIS USING ABAQUS XFEM
 APPLICATION OF COMPOSITE FRACTURE MECHANICS TO BONE FRACTURE ANALYSIS USING ABAQUS XFEM Presenter: David Reid Dassault Systemes UK Ltd SIMULIA david.reid@3ds.com 01925 885971 07825 308031 Work by: Xiaoliang
APPLICATION OF COMPOSITE FRACTURE MECHANICS TO BONE FRACTURE ANALYSIS USING ABAQUS XFEM Presenter: David Reid Dassault Systemes UK Ltd SIMULIA david.reid@3ds.com 01925 885971 07825 308031 Work by: Xiaoliang
Spinal Correction FRA Spacers. Angled and parallel spacers designed for a lateral approach.
 Processed by MTF, designed and available through Synthes Spine Spinal Correction FRA Spacers. Angled and parallel spacers designed for a lateral approach. Spinal Correction FRA Spacers Two varieties of
Processed by MTF, designed and available through Synthes Spine Spinal Correction FRA Spacers. Angled and parallel spacers designed for a lateral approach. Spinal Correction FRA Spacers Two varieties of
The Most Reliable Spinal Solution
 MFG : 09.02.20 REV : 1 4CIS VANE introduces you the reliable pedicle screw The Most Reliable Spinal Solution Non-slip threaded joint Ergonomic design Wedged trapezoid thread Superior locking mechanism
MFG : 09.02.20 REV : 1 4CIS VANE introduces you the reliable pedicle screw The Most Reliable Spinal Solution Non-slip threaded joint Ergonomic design Wedged trapezoid thread Superior locking mechanism
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
The Biomechanics of the Human Spine. Basic Biomechanics, 6 th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
 Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Finite Element Analysis of Radius and Ulna. Eli Pavlatos April 24, 2013
 Finite Element Analysis of Radius and Ulna Eli Pavlatos April 24, 2013 Outline Review bone biomechanics bone behavior during fracture Stress analysis concepts properties of bone for models Fracture simulations
Finite Element Analysis of Radius and Ulna Eli Pavlatos April 24, 2013 Outline Review bone biomechanics bone behavior during fracture Stress analysis concepts properties of bone for models Fracture simulations
Numerical predicting of contact and pressure sore of lower extremity parts caused by prosthetic and orthotic
 MACROJOURNALS The Journal of MacroTrends in Health and Medicine Numerical predicting of contact and pressure sore of lower extremity parts caused by prosthetic and orthotic Reza Fakhrai, Bahram Saadatfar,
MACROJOURNALS The Journal of MacroTrends in Health and Medicine Numerical predicting of contact and pressure sore of lower extremity parts caused by prosthetic and orthotic Reza Fakhrai, Bahram Saadatfar,
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Posture. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
An Advanced 3D Multi-Body System Model for the Human Lumbar Spine
 An Advanced 3D Multi-Body System Model for the Human Lumbar Spine Sousa, S. 1 and Claro, J. C. P. 2 1 University of Minho, Portugal, e-mail: sofia_sts@hotmail.com 2 University of Minho, Portugal, e-mail:
An Advanced 3D Multi-Body System Model for the Human Lumbar Spine Sousa, S. 1 and Claro, J. C. P. 2 1 University of Minho, Portugal, e-mail: sofia_sts@hotmail.com 2 University of Minho, Portugal, e-mail:
HERNIATED DISCS AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
Introduction to Biomedical Engineering: Basic concepts and Bone Biomechanics
 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering: Basic concepts and Bone Biomechanics Fall 2016, AKUT G. Rouhi Biomechanics The field of biomechanics applies principles of mechanics to study the structure and function
Introduction to Biomedical Engineering: Basic concepts and Bone Biomechanics Fall 2016, AKUT G. Rouhi Biomechanics The field of biomechanics applies principles of mechanics to study the structure and function
Advanced ACF Spacer. An allograft spacer with demineralized surfaces for anterior cervical interbody fusion.
 Processed by MTF, designed and available through Synthes Spine Advanced. An allograft spacer with demineralized surfaces for anterior cervical interbody fusion. Advanced The Advanced has been engineered
Processed by MTF, designed and available through Synthes Spine Advanced. An allograft spacer with demineralized surfaces for anterior cervical interbody fusion. Advanced The Advanced has been engineered
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
Stress and Displacement Analysis of Dental Implant Threads Using Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis
 1 Research Article Stress and Displacement Analysis of Dental Implant Threads Using Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Aswin Yodrux* Department of Materials Handling and Logistics for Engineering,
1 Research Article Stress and Displacement Analysis of Dental Implant Threads Using Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Aswin Yodrux* Department of Materials Handling and Logistics for Engineering,
Biomechanical Study of the Effects of Balloon Kyphoplasty on the Adjacent Vertebrae
 J. Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2016, 9, 478-487 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbise ISSN Online: 1937-688X ISSN Print: 1937-6871 Biomechanical Study of the Effects of Balloon Kyphoplasty on the
J. Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2016, 9, 478-487 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbise ISSN Online: 1937-688X ISSN Print: 1937-6871 Biomechanical Study of the Effects of Balloon Kyphoplasty on the
Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs
 Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs Chapter Five: Movement Examination of the Lumbar Spine Time) (45 minutes
Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs Chapter Five: Movement Examination of the Lumbar Spine Time) (45 minutes
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
Idiopathic scoliosis Scoliosis Deformities I 06
 What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
Biomechanical Implications of Lumbar Spinal Ligament TransectionA Finite Element Study
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2012-01-09 Biomechanical Implications of Lumbar Spinal Ligament TransectionA Finite Element Study Gregory Allen Von Forell Brigham
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2012-01-09 Biomechanical Implications of Lumbar Spinal Ligament TransectionA Finite Element Study Gregory Allen Von Forell Brigham
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of Swanson Flexible Hinge Toe Implant
 Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of Swanson Flexible Hinge Toe Implant Xiao (Cathy) Zhou (1), Agustín Vidal Lesso (2) 1 Candidate for Bachelors of Science in Mechanical Engineering, Massachusetts Institute
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of Swanson Flexible Hinge Toe Implant Xiao (Cathy) Zhou (1), Agustín Vidal Lesso (2) 1 Candidate for Bachelors of Science in Mechanical Engineering, Massachusetts Institute
Traction. Process of drawing or pulling apart. May involve distraction and gliding. Pulling 2 articulating surfaces away from each other
 Traction Process of drawing or pulling apart May involve distraction and gliding Pulling 2 articulating surfaces away from each other Axis Traction in line with the long axis of a part Types of Traction
Traction Process of drawing or pulling apart May involve distraction and gliding Pulling 2 articulating surfaces away from each other Axis Traction in line with the long axis of a part Types of Traction
FORCES AND MOMENTS AT THE L41L5 VERTEBRAL LEVEL WHILE FORWARD BENDING IN A SUPPORTED POSTURE
 FORCES AND MOMENTS AT THE L41L5 VERTEBRAL LEVEL WHILE FORWARD BENDING IN A SUPPORTED POSTURE Daniel J. Wilson, Jennie L. Gorham, and Kimberly M. Hickey University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO, 65212
FORCES AND MOMENTS AT THE L41L5 VERTEBRAL LEVEL WHILE FORWARD BENDING IN A SUPPORTED POSTURE Daniel J. Wilson, Jennie L. Gorham, and Kimberly M. Hickey University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO, 65212
Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
NECK AND BACK PAIN AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NECK AND BACK PAIN This booklet provides general information on neck and back pain. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician
AN INTRODUCTION TO NECK AND BACK PAIN This booklet provides general information on neck and back pain. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician
A Biomechanical Evaluation of Lumbar Facet Replacement Systems
 A Thesis Entitled A Biomechanical Evaluation of Lumbar Facet Replacement Systems By Miranda N. Shaw Submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Master of Science in Bioengineering Adviser:
A Thesis Entitled A Biomechanical Evaluation of Lumbar Facet Replacement Systems By Miranda N. Shaw Submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Master of Science in Bioengineering Adviser:
Study on Structural Behaviour of Human Vertebral Column Using Staad.Pro
 Study on Structural Behaviour of Human Vertebral Column Using Staad.Pro Healtheephan alexis. S Post graduate student, Government College of Technology, Coimbatore-641 013 healtheephan@yahoo.com doi:10.6088/ijcser.00202010001
Study on Structural Behaviour of Human Vertebral Column Using Staad.Pro Healtheephan alexis. S Post graduate student, Government College of Technology, Coimbatore-641 013 healtheephan@yahoo.com doi:10.6088/ijcser.00202010001
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF EMBEDDING
 EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF EMBEDDING THICKNESS IN COMPRESSIVE MECHANICAL TESTING OF VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION AND SPINAL INTERBODY FUSION Márta Kurutz 1, Péter Nédli 1, Péter
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF EMBEDDING THICKNESS IN COMPRESSIVE MECHANICAL TESTING OF VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION AND SPINAL INTERBODY FUSION Márta Kurutz 1, Péter Nédli 1, Péter
Influence of clavicle midshaft fracture pattern on the superior plate stabilization
 Influence of clavicle midshaft fracture pattern on the superior plate stabilization PD Dr.med. Carsten Englert* Dr.-Ing. Sebastian Dendorfer** *Department of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, University
Influence of clavicle midshaft fracture pattern on the superior plate stabilization PD Dr.med. Carsten Englert* Dr.-Ing. Sebastian Dendorfer** *Department of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, University
Numerical Simulation of the Cervical Spine in a Normal Subject and a Patient with Intervertebral Cage under Various Loadings and in Various Positions
 Original Article Numerical Simulation of the Cervical Spine in a Normal Subject and a Patient with Intervertebral Cage under Various Loadings and in Various Positions Seifollah Gholampour 1, Nikoo Soleimani
Original Article Numerical Simulation of the Cervical Spine in a Normal Subject and a Patient with Intervertebral Cage under Various Loadings and in Various Positions Seifollah Gholampour 1, Nikoo Soleimani
Implementation of facet joints in a detailed musculoskeletal lumbar spine model based on
 Implementation of facet joints in a detailed musculoskeletal lumbar spine model based on inverse dynamics The web cast will start t in a few minutes. Why not spend the time checking these points: Does
Implementation of facet joints in a detailed musculoskeletal lumbar spine model based on inverse dynamics The web cast will start t in a few minutes. Why not spend the time checking these points: Does
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy.
 Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities
 Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities Iryna Havenko Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities Iryna Havenko Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
Quality of Life. Quality of Motion.
 Quality of Life. Quality of Motion. Lateral Bend Vertical Translation Flexion Extension Lateral Translation Axial Rotation Anterior Posterior Translation Motion in all Directions Kinematics is the study
Quality of Life. Quality of Motion. Lateral Bend Vertical Translation Flexion Extension Lateral Translation Axial Rotation Anterior Posterior Translation Motion in all Directions Kinematics is the study
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions
 Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES
 AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland
 Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical Terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical Terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJMET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJMET) International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET), ISSN 0976 6340(Print), ISSN 0976 6340 (Print) ISSN 0976 6359
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJMET) International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET), ISSN 0976 6340(Print), ISSN 0976 6340 (Print) ISSN 0976 6359
Preliminary measurements of lumbar spine kinematics and stiffness
 5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 2007 10-12 December 2007, Brisbane, Australia Preliminary measurements of lumbar spine kinematics and stiffness L. Jirková 1, Z. Horák 1, R. Sedláek
5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 2007 10-12 December 2007, Brisbane, Australia Preliminary measurements of lumbar spine kinematics and stiffness L. Jirková 1, Z. Horák 1, R. Sedláek
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The University of Sydney Slide 1
 The University of Sydney Slide 1 SIMULATION DRIVEN BIOMEDICAL DESIGN Lecture 4 Presented by Dr Paul Wong AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 2 Simulation Types There is more to
The University of Sydney Slide 1 SIMULATION DRIVEN BIOMEDICAL DESIGN Lecture 4 Presented by Dr Paul Wong AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 2 Simulation Types There is more to
IN VIVO CERVICAL SPINE KINEMATICS, ARTHROKINEMATICS AND DISC LOADING IN ASYMPTOMATIC CONTROL SUBJECTS AND ANTERIOR FUSION PATIENTS.
 IN VIVO CERVICAL SPINE KINEMATICS, ARTHROKINEMATICS AND DISC LOADING IN ASYMPTOMATIC CONTROL SUBJECTS AND ANTERIOR FUSION PATIENTS by William Anderst BS in Mechanical Engineering, University of Notre Dame,
IN VIVO CERVICAL SPINE KINEMATICS, ARTHROKINEMATICS AND DISC LOADING IN ASYMPTOMATIC CONTROL SUBJECTS AND ANTERIOR FUSION PATIENTS by William Anderst BS in Mechanical Engineering, University of Notre Dame,
A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING
 A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING M. Mengoni 1 and J.-P. Ponthot 2 1. ABSTRACT Tooth movements obtained through orthodontic appliances result from a complex biochemical process of bone
A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING M. Mengoni 1 and J.-P. Ponthot 2 1. ABSTRACT Tooth movements obtained through orthodontic appliances result from a complex biochemical process of bone
Comparison of in Vitro Young and Old Lumbar Vertebrae of Ewes Related to Bone Density and Compression Strength
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 11, No. 4; 2017 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Comparison of in Vitro Young and Old Lumbar Vertebrae of Ewes Related
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 11, No. 4; 2017 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Comparison of in Vitro Young and Old Lumbar Vertebrae of Ewes Related
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor
![[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor [ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/88/117546298.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
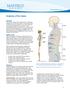 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
KINEMATIC RESPONSE OF THE L4-L5 FUNCTIONAL SPINAL UNIT AFTER A LATERAL LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY
 Revista da Associação Portuguesa de Análise Experimental de Tensões ISSN 1646-7078 KINEMATIC RESPONSE OF THE L4-L5 FUNCTIONAL SPINAL UNIT AFTER A LATERAL LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY RESPOSTA CINEMÁTICA DA UNIDADE
Revista da Associação Portuguesa de Análise Experimental de Tensões ISSN 1646-7078 KINEMATIC RESPONSE OF THE L4-L5 FUNCTIONAL SPINAL UNIT AFTER A LATERAL LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY RESPOSTA CINEMÁTICA DA UNIDADE
Summer Workshop of Applied Mechanics. Theoretical Analysis of Total Hip Joint Replacement of Sandwich design by FEM
 Summer Workshop of Applied Mechanics June 2002 Department of Mechanics Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague Theoretical Analysis of Total Hip Joint Replacement of Sandwich
Summer Workshop of Applied Mechanics June 2002 Department of Mechanics Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague Theoretical Analysis of Total Hip Joint Replacement of Sandwich
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Initiation and Progression of Lumbar Disc Degeneration under Cyclic Loading: A Finite Element Study
 Initiation and Progression of Lumbar Disc Degeneration under Cyclic Loading: A Finite Element Study By Muhammad Qasim BSc. Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan,
Initiation and Progression of Lumbar Disc Degeneration under Cyclic Loading: A Finite Element Study By Muhammad Qasim BSc. Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan,
Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion
 ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 13, No. 1, 2018, pp.044-048 Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion Bao Chunyu 1,3,Meng
ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 13, No. 1, 2018, pp.044-048 Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion Bao Chunyu 1,3,Meng
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity
 Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Why do I perform PFP? Fernando Fonseca, MD PhD Head of Department Orthopaedics
 Why do I perform PFP? Fernando Fonseca, MD PhD Head of Department Orthopaedics Acknowledges to António Completo Paulo Flores Susana Meireles André Castro Disclosures: None ... Knee is one of the most complex
Why do I perform PFP? Fernando Fonseca, MD PhD Head of Department Orthopaedics Acknowledges to António Completo Paulo Flores Susana Meireles André Castro Disclosures: None ... Knee is one of the most complex
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF STRESSES IN REAL (PRESERVED) INTACT PROXIMAL HUMAN FEMUR (THIGH) BONE UNDER STATIC LOAD
 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF STRESSES IN REAL (PRESERVED) INTACT PROXIMAL HUMAN FEMUR (THIGH) BONE UNDER STATIC LOAD Maheshkumar V.Jadhav 1, V.R.Gambhire 2, G.S.Kamble 3 1 P.G. Student, 2 Professor, 3 Assistant
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF STRESSES IN REAL (PRESERVED) INTACT PROXIMAL HUMAN FEMUR (THIGH) BONE UNDER STATIC LOAD Maheshkumar V.Jadhav 1, V.R.Gambhire 2, G.S.Kamble 3 1 P.G. Student, 2 Professor, 3 Assistant
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
Detailed Finite Element Modeling of the Human Ligamentous Cervical Spine. Faisal Agah
 Detailed Finite Element Modeling of the Human Ligamentous Cervical Spine by Faisal Agah A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Structural Engineering
Detailed Finite Element Modeling of the Human Ligamentous Cervical Spine by Faisal Agah A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Structural Engineering
BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES
 63 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES Rafael F. Escamilla, Tracy M. Lowry, Daryl C. Osbahr, and
63 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES Rafael F. Escamilla, Tracy M. Lowry, Daryl C. Osbahr, and
