Design of a Novel Total Knee Prosthesis Using TRIZ
|
|
|
- Sophie Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Author: Yeh-Liang Hsu, Yung-Chieh Hung, Ju-Zhong Yin ( ); recommended: Yeh-Liang Hsu ( ). Note: This paper is published in Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, Vol. 26, No. 4, December 2006, p Design of a Novel Total Knee Prosthesis Using TRIZ Abstract The ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) type of knee implant usually has high contact stress, often higher than the yield point of UHMWPE tibial platform, which results in wear. As wear progresses, the polyethylene meniscus component becomes successively thinner, and the wear debris or particles will accumulate on the dished surface of the meniscus. In this study, a novel design concept of using a convex meniscus shape is generated using theory of inventive problem-solving (TRIZ), so that the wear debris or particles will not accumulate on the surface of the meniscus. In the meantime, the geometry of the sliding surface of the meniscus remains concave in the A-P direction to conform to the shape of the femoral component. The contact surface between the femoral component and the meniscus are designed as double enveloping surfaces to provide a smooth sliding interface with a large contact area. After the novel design concept is generated, the detailed dimensions and the interface surfaces between the components are then carefully designed. The motion of the new knee 1
2 prosthesis is simulated using a kinematics computer simulation software and compared with that of a four-bar linkage system replicating the polycentric motion of the true knee joint. Keyword: total knee prosthesis, TRIZ 1. Introduction Disease and trauma affecting the articular surfaces of the knee joint are commonly treated by replacing surgically the articulating ends of the femur and tibia with prosthetic femoral and tibial implants, referred to as total knee replacement (TKR). These knee implants are made of materials that exhibit a low coefficient of friction as they articulate against one another so as to restore normal pain-free knee function. A TKP (total knee prosthesis) generally comprises a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces, a tibial component having a tibial platform fixed to the resected tibia, and a bearing component usually of low friction plastic material interposed between the condylar surfaces and the tibial platform. The bearing component generally has dished surfaces for receiving the condylar surfaces of the femoral component. The bearing component can be made to be fixed onto the tibial platform or be rotatable and/or slidable in the anterior/posterior direction. During the motion of TKP, the tibia-femoral interface bears loading several times larger than its body weight. In normal functions, the applied forces are uniformly distributed on the polyethylene (PE) cushion at the tibiofemoral cavity. Owing to long-term compression on the polyethylene part, wear at the polyethylene-bearing surface is one of the critical factors limiting the long-term success of the prosthesis [Blunn et al., 1992; Landy and Walker, 1988; Jordan et al., 2002]. Today, TKP failures are caused by wear and consequences of wear such as osteolysis [Cadami et al., 1994; Ingram et al., 2004]. Polyethylene wear of the articular surface is a well-known complication of total knee prosthesis [Feng et al., 1994; Huang et al., 1999; Kennedy et al., 2003]. Factors that play a role in the accelerated wear of the tibial polyethylene component, include tibiofemoral 2
3 articular geometry, polyethylene thickness, extremity and implant alignment, and the quality of the polyethylene [Feng et al., 1994]. The so-called third particle problem is often discussed among surgeons as a typical reason for the accelerated wear of the tibial polyethylene component. Figure 1 shows a TKP that is widely used, which consists of a shiny Co-Cr femoral component, a white ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) bearing, and a metal tibial tray. UHMWPE wear particles are generated around the joint region due to the articulation motion between the metal parts and UHMWPE components. It is observed that various wear particles are embedded among the peri-prosthetic tissues or synovial fluid around the failed artificial joints. Several studies have isolated UHMWPE particles from the tissues retrieved from the revision surgery [Campbell et al., 1995; Hirakawa et al., 1996; Minoda et al., 2003]. Figure 1. Total knee prosthesis Wear removes polyethylene material from the UHMWPE components. As wear progresses, not only does the function of the bearing deteriorate with plastic loss, the debris generated in the wear process can also evoke inflammatory reactions within the joint [Schmalzried et al., 1992; Kadoya et al., 1997; DeHeer et al., 2001]. Attempts made to solve this problem include elaborate and often costly locking systems to minimize relative motion at the interface between the bearing insert and the metal tibial tray. For example, the mobile meniscal bearing allows more physiological movement and replaces the A-P translation of the femoral component on the tibial polyethylene surface with the A-P 3
4 gliding of the femoral metal component in articulation with the congruent surfaces of the platform on the tibial tray. This concept therefore alleviates the wear rate of the polyethylene, improves the kinematics and helps the fixation to the bone by reducing the stress at the interface [Goodfellow et al., 1978; Psychoyios et al., 1998]. One of the problems encountered when using mobile meniscal bearing systems is the constant wear that occurs between the meniscus (UHMWPE) and the femoral component (Co-Cr materials) due to articulation. The typical femoral component has two lower convex surfaces, which are compatible with the concave surfaces of the meniscus component. The meniscus is not constrained, so that it can move in the anterior-posterior direction and/or the medial-lateral direction, which often creates small wear particles or debris and accumulates on the upper surfaces of the meniscus component. In vivo the generation of submicron-sized polyethylene wear debris (PWD) can cause adverse cellular reactions in the surrounding tissues, resulting in macrophage activity and necrosis of the bone-prosthesis interface [Schmalzried et al., 1994; Morawski et al., 1995; Horowitz et al., 1998]. To deal with the problems discussed above, TRIZ is used as the concept generator for proposing a novel knee prosthesis design in this study. TRIZ (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving) was put forward by a former Soviet Union scientist Altshuller, who after studying almost 400,000 patents, deemed that it is possible to turn this theory into a systematic method [Terninko et al., 1998; Shulyak et al., 1997]. TRIZ is an available tool for design engineers to handle conflict conditions during the innovation design problem solving process [Savransky, 2000]. In this study, a novel design concept of using a convex meniscus shape is generated using TRIZ, as shown in Figure 2, so that the wear debris or particles will not accumulate on the surface of the meniscus. In the meantime, the geometry of the sliding surface of the meniscus remains concave in the A-P direction to conform to the shape of the femoral component. The contact surface between the femoral component and the meniscus are designed as double enveloping surfaces to provide a smooth sliding interface with a large contact area. The guide surface on the tibial platform is also carefully designed to provide proper guidance during flexion-extension by the interaction of femoral cam and tibial guide 4
5 curve. The interface between the meniscus and tibial platform is designed to allow certain amount of A-P translation and internal-external rotation between the two components. femur convex meniscus shape guide surface meniscus tibia double enveloping surface Figure 2. A novel design concept of total knee prosthesis The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents how the novel design concept of the new total knee prosthesis was generated using TRIZ. Section 3 describes the interface surface design of each component of the new total knee prosthesis. The motion of the knee prosthesis model is also simulated by a kinematics simulation software. Then the motion of the new knee prosthesis is compared with that of a four-bar linkage system replicating the polycentric motion of the true knee joint in Section 4. At last, Section 5 concludes this paper. 2. Generating a novel design concept of the new total knee prosthesis using TRIZ As shown in Figure 3, the conceptual framework in this study comprises of five main stages which basically follows the classical TRIZ problem solving process [Domb, 1998]. The initial input to the entire process is a list of identified problems from existing product or design. At stage one and two, these original problems are defined with the language of TRIZ in order to provide insightful information for the further problem solving. After problem definition, the problems are structured into typical TRIZ contradictions by using contradiction analysis. At stage four, some TRIZ problem resolution tools are employed to eliminate the 5
6 formulated contradictions. At stage five, the feasibilities of the solutions are then evaluated. If solutions are still not found after contradiction elimination, or some other new problems occur after solution evaluation, the problem solving process must be iterated back to the first stage to redefine the original situation. These five stages will be described in details below. Figure 3. The design process using TRIZ (1) Preliminary problem analysis The objective of this stage is to identify and collect existing problems in existing products or designs. As mentioned earlier, a typical knee prosthesis comprises a femoral component, a tibial, and a bearing component. The bearing component generally has dished 6
7 surfaces for receiving the condylar surfaces of the femoral component. Some problems occur after long-term usage: (a) The polyethylene meniscus bearing surfaces of the total knee suffer wear damages. Wear removes the polyethylene material from the polyethylene meniscus component. As wear progresses, the polyethylene meniscus component becomes successively thinner, and the wear debris or particles will accumulate on the dished surface of the meniscus. (b) TKP usually has high contact stress, often higher than the yield point of UHMWPE tibial platform, resulting in wear. (2) Problem modelling and formulation Based on the analysis of the problem situation above, further problem modeling and formulation can be done by using the TRIZ technique of Problem Formulator (PF)[Zlotin et al., 2001]. The purpose of problem modeling is to build a function model by using function analysis, while problem formulation is to formulate an exhaustive set of problem statements on the basis of the function diagram. In this research, commercial software TechOptimizer 4.0 from Invention Machine Corporation is used in the following TRIZ process. It is used to model product functions and provide assistance in understanding what aspects of a product need improvement, and which of the inventive principles are most applicable. Figure 4 shows the function model of the knee prosthesis design problem, built in TechOptimizer 4.0. In Figure 4, a rectangle represents a system component, the solid line represents a useful function, the dotted line represents a harmful function, and the cross-solid line represents an excessive useful function. All components of the knee prosthesis are built into the function model showing useful, harmful and excessive actions linking the various components. 7
8 Figure 4. Function model for typical knee prosthesis In Figure 4, there are two major harmful functions to be solved by TRIZ: The femoral condylar abrades the meniscus. The meniscus bears a large contact stress from the femoral condylar. (3) Contradiction analysis From the TRIZ viewpoint, these two problems are translated into the following contradictions expressed by the 39 design parameters of TRIZ. The two problems can be reorganized and stated as, I want to prevent wear debris or particles accumulated on the surface of the meniscus by changing the structure of the meniscuc, which leads to a problem of shortage of stability in knee prosthesis. 8
9 I want to reduce contact stress between the femoral component and the tibial platform by changing the combination of the femoral and the tibial platform, which leads to a problem of increasing component numbers. (4) Contradiction elimination To eliminate formulated contradictions effectively, TRIZ provides a set of powerful tools and principles, such as ARIZ, substance-field analysis, 40 inventive principles and contradiction table, etc. Among them, the 40 inventive principles and contradiction table are considered one of the most accessible and useful TRIZ problem resolution techniques. The contradiction table in the TRIZ theory contains 39 design parameters and 40 generic principles for solving the contradictions. As shown in Table 1, to solve the first problem described above, the parameter to be improved is No. 15 duration of a moved object, and the major parameter not to deteriorate is No. 13 stability of the object s composition. The three generic principles in the corresponding brackets is Principle 13 (the other way around), Principle 3 (local quality), and Principle 35 (parameter changes). 9
10 Table 1. The contradiction table for the first problem Characteristic to be improved Characteristics 1 Weight of a moving object 2 Weight of stationary object 15 Durability of a moved object Characteristic that is getting worse Weight of a moving object 39 Productivity 35, 26, 24, 37 Weight of stationary object Stability of the object s composition 1, 35, 19, 39 26, 39, 1, 40 Productivity 35, 3, 24, 37 1, 28, 15, 35 19, 5, 34, 31 13, 3, 35 35, 17, 14, 19 28, 27, 15, 3 35, 3, 22, 39 In TRIZ, Principle 13 has three explanations: (1) invert the action(s) used to solve the problem (e.g. instead of cooling an object, heat it), (2) make movable parts (or the external environment) fixed, and fixed parts movable, and (3) turn the object (or process) upside down. As shown in Table 2, to solve the second problem described above, the parameter to be improved is No. 11 stress or pressure, and the major parameter not to deteriorate is No. 26 quantity of substance. The three generic principles in the corresponding brackets is Principle 10 (preliminary action), Principle 14 (curvature increase), and Principle 36 (phase transitions). 10
11 Table 2. The contradiction table for the second problem Characteristic to be improved Characteristics Characteristic that is getting worse Weight of a moving object 1 Weight of a moving object 2 Weight of stationary object 11 Stress or pressure 10, 36, 37, Productivity 35, 26, 24, 37 Weight of stationary object Quantity of substance 3, 26, 18, 31 19, 6, 18, 26 Productivity 35, 3, 24, 37 1, 28, 15, 35 13, 29, 10, 18 10, 14, 36 10, 14, 35, 37 28, 27, 15, 3 35, 38 In TRIZ, Principle 14 has three explanations: (1) instead of using rectilinear parts, surfaces, or forms, use curvilinear ones, move from flat surfaces to spherical ones, from cubical (parallelepiped) parts to ball-shaped structures, (2) use rollers, balls, spirals, and domes, and (3) go from linear to rotary motion, use centrifugal forces. (5) Solution evaluation Principles 13 and 14 are utilized to generate the new concept in our novel knee prosthesis design. Principle 13 proposes to invert the actions, and to turn the object upside down. The analogical thinking on these two principles generates the new concept of using a convex meniscus shape, as opposed to the typical dished shape, so that the wear debris or particles will not accumulate on the surface of the meniscus. However, the shape of the femoral condylar is also convex. Using a convex meniscus shape will further increase the contact stress between the femoral condylar and the meniscus. Figure 5 shows a solution example of Principle 14 provided by TechOptimizer 4.0: the worm and worm gear wheel are made in the form of globoids (in the form of the inner surface of an 11
12 open torus). This design increases contact area and reduces contact zone stresses. This concept can be employed to solve the problem of high contact stress. Worm gear-wheel worm Globoid surfaces Figure 5. A solution example provided by TechOptimizer (6) New concept of the knee prosthesis design Finally, a novel design concept of using a convex meniscus shape and a double enveloping contact surface for the femoral condylar is shown in Figure 6. The upper surface of the meniscus is designed as a plurality of convex surfaces for engagement with concave surfaces on the inferior side of the femoral component, so that the wear debris or particles will not accumulate on the surface of the meniscus. In the meantime, the geometry of the sliding surface of the meniscus remains concave in the A-P direction to conform to the shape of the femoral component, as shown in Figure 7. The double enveloping contact surface of the femoral condylar provides a smooth sliding interface with a large contact area. 12
13 Figure 6. A convex meniscus shape and a double enveloping contact surface for femoral condylar Figure 7. The flexion-extension contact surfaces 3. Interface surface design and simulation After the design concept is generated, the detailed designs of the interface surfaces are carried out with the aid of kinematics simulation software Working Model. There are three major interface surfaces: the flexion-extension contact surface between the meniscus and the femoral component, the flexion-extension guide surface, and the meniscal-sliding surface. (1) Flexion-extension contact surface In the new design concept, the contact surface between the femoral and meniscus are designed into double enveloping surfaces to provide a smooth sliding interface with a large contact area. As shown in Figure 8, the sagittal condylar profile was constructed from curves of radii 15, 40, and 32 mm for the posterior, distal and anterior sections, respectively. The 13
14 anterior-posterior length of meniscus was 42 mm. The minimum thickness of the femoral condylar is 8.64 mm. The bearing surface of the meniscus includes an anterior radius 40 mm to conform to the femoral condylar surface when the femoral condylar is sitting on the meniscus. When the femoral condylar flexes, the posterior radius (15 mm) comes into contact with the meniscus, as shown in Figure 8. This conformed curvature design, as well as the double enveloping contact surface design described in the previous section, should be able to distribute the pressure and reduce contact stress when standing or in the flexion-extension. Sagittal Profiles r=32mm r=15mm r=40mm 8.64mm 42mm Figure 8. The 3-D model of the novel knee prosthesisflexion-extension guide surface As shown in Figure 9, a guide surface is designed as an integral part of the tibial platform to guide the A-P displacement of the femoral condylar during flexion. The guidepost is located at the extreme posterior end of the femoral condylar sections. The tibial guide surface interacts with the post to imitate natural posterior femoral rollback by limiting and defining the pivot between the femoral component posterior post and the tibial component. 14
15 guide surface guide post tibial platform Figure 9. Flexion-extension guide surface To design the profile of the guide surface, the trajectory of the guidepost in Working Model simulation when the femoral condylar flexes from 0 to 150 is plotted, as shown in Figure 10. The outer edge of the trajectory is used as the profile of the guide surface, so that the guide post will always be in contact with the guide surface in flexion. Figure 10. Outer edge of the trajectory 15
16 (2) Meniscal-sliding surface As shown in Figure 11, a meniscal post component is designed to be implanted in the upper portion of the tibia. The post may serve to guide the meniscal component in the A-P direction and allows rotation with respect to the tibial plateau component as the femur and tibia move from a position of full extension to a position of flexion. In our simulation using Working Model, there is a 4.05 mm sliding distance in the A-P direction when the femoral condylar flexes from 0 to 150. Therefore, the radius of the meniscal post is set to be 9 mm and that of the tibial plate hole is set to be 12 mm to allow this sliding. r=9 r=12 meniscal post Figure 11. Meniscal-sliding surface 4. Comparison between knee prosthesis and true knee joint After the novel design concept and the detailed dimensions are generated, the motion of the new knee prosthesis is simulated using a kinematics computer simulation software. Then the motion of the new knee prosthesis is compared with that of a four-bar linkage system replicating the polycentric motion of the true knee joint. A three-dimensional tibiofemoral joint model of the new knee prosthesis was constructed as shown in Figure 12. The orthogonal coordinate system XYZ was attached to the centroid of femoral condylar. The Y-axis coincided with the long axis of the tibia, the X-axis was in the anterior direction, and the Z-axis was in the medial direction. 16
17 Figure D model of tibiofemoral joint Figure 13 to Figure 16 show the simulation results of the new TKP. In the simulation, the new TKP flexes from 0 to 150. When the new TKP flexes close to 150, the posterior direction displacement of femur center is 8.98mm (Figure 13), the amount of axial rotation is (Figure 14), the A-P displacement is 4.05mm (Figure 15), and the M-L displacement is 4mm (Figure 16). Figure 13. Movement of A-P contact position of the centroid of femoral condylar 17
18 Figure 14. Axial rotation 4.05 Figure 15. Anterior-Posterior displacement 18
19 Figure 16. Medial-Lateral displacement A four-bar linkage system was proposed to replicate the polycentric motion of the knee that occurs during passive knee flexion-extension [Goodfellow and O Connor, 1994]. As shown in Figure 17, it is assumed that the ligaments are straight inextensible line elements attached to the bones, each one at a single point and having no strength in bending. Since the movements allowed to the bones at the human knee occur mainly in the sagittal plane, it is adequate to identify the knee as a two-dimensional single degree of freedom linkage. The cruciate ligaments are represented as two inextensible fibers, which, together with the femur and the tibia, are analyzed as a crossed four-bar linkage. The ligaments together with the two bones from the cruciate linkage ABCD. AD is called the tibial link, the line joining the attachment points of the two ligaments to the tibia, and it is regarded as the fixed bar of the knee mechanism. BC is the femoral link. 19
20 Femur Femoral link Posterior cruciate Ligament (PCL) B C Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) A Tibial link Tibia D Figure 17. Elements of the knee model The motion of the knee prosthesis developed in this research and simulated by Working Model is compared with the motion generated by the four-bar linkage model. Figure 18 shows the trajectories of points B and C when the femoral condylar flexes from 0 to 150. The motion of the new knee prosthesis developed in this research exhibits similar trends as the motion replicated by the four-bar linkage system. Point B trajectory by four-bar linkage Point C trajectory by four-bar linkage Point B trajectory by knee prosthesis Point C trajectory by knee prosthesis y direction(mm) x direction(mm) Figure 18. Movement of Point B and C during flexion from 0 to
21 Finally Figure 19 shows the prototype of the new knee prosthesis fabricated by CNC (computer numerical control) machining. Note that the interfaces between the new TKP and femoral condylar and tibial condylar are the same as traditional TKP. Figure 19. The prototype of our new knee prosthesis 5. Conclusion In this paper, TRIZ is applied to the design of a novel total knee prosthesis to solve the problems of high contact stress and the wear debris accumulation. This new design concept uses a convex meniscus shape so that the wear debris or particles will not accumulate on the surface of the meniscus. In the meantime, the geometry of the sliding surface of the meniscus remains concave in the A-P direction to conform to the shape of the femoral component. The contact surface between the femoral component and the meniscus are designed as double enveloping surfaces to provide a smooth sliding interface with a large contact area. The motion of the new knee prosthesis is simulated by kinematics computer simulation software, and a prototype is produced using CNC machining. This paper demonstrates how the conceptual design method TRIZ is applied to the biomedical engineering field. The new TKP design generated in this research also received two patents, ROC and ROC To further develop the design concept into real a 21
22 commercial product, intensive physical tests considering various factors, such as the real lubrication occurs in the implant, are needed in the future. Acknowledgement The authors wish to thank Professor H.C. Liu and Professor T.W. Lu of Institute of Biomedical Engineering, National Taiwan University, for their valuable input during the process of this research. This research is sponsor by the National Science Council, Taiwan, grants No. NSC E This support is gratefully acknowledged. Reference Blunn, G.W., Joshi, A.B., Polyethylene wear in unicondylar knee prostheses, Acta Orthop Scand, v.63, p , Cadami, A., Engh, G.A., Dwyer, K.A., Osteolysis of the distal femur after total knee arthroplasty, Journal of Arthroplasty, v.9, p , Campbell, P.A., Ma, S., Yeom, B., McKellop, H., Schmalzried, T.P., Amstutz, H.C., Isolation of predominantly submicron-sized UHMWPE wear particles from periprosthetic tissues, J Biomed Mater Res, v.29, p , DeHeer, D. H., Engels, J. A., DeVries, A. S., Knapp, R. H., Beebe, J. D., In situ complement activation by polyethylene wear debris, J Biomed Master Res, v.54, p.12-19, Domb, E., The 39 features of Altshuller contradiction matrix, TRIZ Journal, 1998, November. Feng, E.L., Stulberg, S.D., Wixson, R.L., Progressive subluxation and polyethylene wear in total knee replacements with flat articular surfaces, Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research, v.299, p.60-71, Goodfellow, J., O Connor, J., The mechanics of the knee and prosthesis design, J Bone Joint Surg, v.60, p.358, Goodfellow, J., and O Connor, J., The Knee, W. Norman Scott Mosby-Year Book, Inc
23 Hirakawa, K., Bauer, T. W., Stulberg, B. N., Wilde, A. H., Comparison and quantification of wear debris of failed total hip and total knee arthroplasty, J Biomed Master Res, v.31, p , Horowitz, S. M., Luchetti, W. T., Gonzales, J. B., Ritchie, C. K., The effects of cobalt chromium upon macrophages, J Biomed Master Res, v.41, p , Huang, C.H., Yang, C.Y., Cheng, C.K., Fracture of the femoral component associated with polyethylene wear and osteolysis after total knee arthroplasty- a case report, Journal of Arthroplasty, v.14, p , Ingram, J. H., Stone, M., Fisher, J., Ingram, E., The influence of molecular weight, crosslinking and counterface roughness on TNF-Alpha production by macrophages in response to ultra high molecular weight polyethylene particles, Biomaterials, v.25, p , Invention Machine Corporation, Jordan, L. R., Olivio, J. L., Aseptic loosening in the LCS total knee arthroplasty, LCS: Mobile Bearing Knee Arthroplasty, K. J. Hamelynck, ed., Springer, New York, p Kadoya, Y., Revell, P. A., Kobayashi, A., al-saffar, N., Scott, G., Freeman, M. A., Wear particulate species and bone loss in failed total knee arthroplasty, Clinical Orthopaedics, v.340, p , Kennedy, F. E., Currier, B. H., Van Citters, D. W., Currier, J. H., Collier, J. P., Mayor, M. B., Oxidation of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene and its influence on contact fatigue and pitting of knee bearings, Tribol. Trans., v.46, p , Kocmond, J. M., Stability and Range of Motion of Insall-Burstein Condylar Prostheses, Journal of Arthroplasty, v.10, p , Landy, M. M., Walker, P.S., Wear on ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene components of 90 retrieved knee prostheses, Journal of Arthroplasty, v.8, p.73-85, Minoda, Y., Kobayashi, A., Iwaki, H., Miyaguchi, M., Kadoya, Y., Ohashi, H., Yamano, Y., Takaoka, k., Polyethylene wear particles in synovial fluid after total knee arthroplasty, Clinical Orthopaedics, v.410, p , Morawski, D.R., Coutts, R.D., Handal, E.G., Luibel, F.J., Santore, R.F., Ricci, J.L., Polyethylene debris in lymph nodes after a total hip arthroplasty. A report of two cases, J Bone Joint Surg, v.77, p ,
24 Psychoyios, V., Crawford, R.W., O Connor, J., Murray, D.W., Wear of congruent meniscal bearings in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, J Bone Joint Surg, v.80, p.976, Savransky, S. D., Engineering of creativity, Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, Schmalzried, T.P., Jasty, M., Harris, W.H., Periprosthetic bone loss in total hip arthroplasty: polyethylene wear debris and the concept of the effective joint space, J Bone Joint Surg, v.74, p , Schmalzried, T.P., Guttmann, D., Grecula, M., Amstutz, H.C., The relationship between the design, position, and articular wear of acetabular components inserted without cement and the development of pelvic osteolysis, J Bone Joint Surg, v.76, p , Shulyak, L., Rodman, S., 40 Principles TRIZ Keys to Technical Innovation, Technical Innovation Center, Worcester, MA, Terninko, J., Zusman, A., Zlotin, B., Systematic Innovation- An introduction to TRIZ, St. Lucie Press, New York, Zlotin, B., Zusman, A., Directed Evolution: Philosophy, Theory and Practice, Ideation International Inc., Southfield, MI,
Improved design of sagittal femoral condylar geometry using TRIZ
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Improved design of sagittal femoral condylar geometry using TRIZ Guo Liang Zhang 1, Fu Xing Pei 2, Zong
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Improved design of sagittal femoral condylar geometry using TRIZ Guo Liang Zhang 1, Fu Xing Pei 2, Zong
Evolution. Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee. Key Aspects
 Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement
 ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement Chadd Clary, PhD Staff Engineer DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Young and active total knee replacement (TKR) patients demand a knee that feels
ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement Chadd Clary, PhD Staff Engineer DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Young and active total knee replacement (TKR) patients demand a knee that feels
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT
 ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Knee Replacement Implants
 Knee Replacement Implants During knee replacement surgery, an orthopaedic surgeon will resurface your damaged knee with artificial components, called implants. There are many different types of implants.
Knee Replacement Implants During knee replacement surgery, an orthopaedic surgeon will resurface your damaged knee with artificial components, called implants. There are many different types of implants.
Biomechanics of. Knee Replacement. Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm
 Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Gold standard of a TKA. Conflicting goals? POLYETHYLENE WEAR THE SOLUTION: MOBILE BEARING KNEES. MOBILE BEARING A totally new approach (1977)
 Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
Zimmer FuZion Instruments. Surgical Technique (Beta Version)
 Zimmer FuZion Surgical Technique (Beta Version) INTRO Surgical Technique Introduction Surgical goals during total knee arthroplasty (TKA) include establishment of normal leg alignment, secure implant fixation,
Zimmer FuZion Surgical Technique (Beta Version) INTRO Surgical Technique Introduction Surgical goals during total knee arthroplasty (TKA) include establishment of normal leg alignment, secure implant fixation,
EMPOWERING LIFE THROUGH NATURAL MOTION
 EMPOWERING LIFE THROUGH NATURAL MOTION em pow r əm pou(ə)r/ verb make (someone) stronger and more confident, especially in controlling their life and claiming their rights. WHY NATURAL MOTION? Today s
EMPOWERING LIFE THROUGH NATURAL MOTION em pow r əm pou(ə)r/ verb make (someone) stronger and more confident, especially in controlling their life and claiming their rights. WHY NATURAL MOTION? Today s
Intramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Ten-year in vivo wear measurement of a fully congruent mobile bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
 Ten-year in vivo wear measurement of a fully congruent mobile bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty A. J. Price, A. Short, C. Kellett, D. Beard, H. Gill, H. Pandit, C. A. F. Dodd, D. W. Murray From
Ten-year in vivo wear measurement of a fully congruent mobile bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty A. J. Price, A. Short, C. Kellett, D. Beard, H. Gill, H. Pandit, C. A. F. Dodd, D. W. Murray From
[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor
![[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor [ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/88/117546298.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF DEGREE OF FREEDOM OF MOVEMENTS OF AN NOVEL HIGH FLEXION KNEE FOR ITS SUITABILITY IN EASTERN LIFESTYLES
 International Journal on Applied Bioengineering, Vol.4, No.2, July 2009 5 BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF DEGREE OF FREEDOM OF MOVEMENTS OF AN NOVEL HIGH FLEXION KNEE FOR ITS SUITABILITY IN EASTERN LIFESTYLES
International Journal on Applied Bioengineering, Vol.4, No.2, July 2009 5 BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION OF DEGREE OF FREEDOM OF MOVEMENTS OF AN NOVEL HIGH FLEXION KNEE FOR ITS SUITABILITY IN EASTERN LIFESTYLES
CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEARING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTRAINT
 CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEAING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTAINT Orthopaedic esearch Laboratories Lutheran Hospital Cleveland Clinic Health System Christine S. Heim, B.Sc. Paul. D. Postak, B.Sc. Nicholas
CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEAING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTAINT Orthopaedic esearch Laboratories Lutheran Hospital Cleveland Clinic Health System Christine S. Heim, B.Sc. Paul. D. Postak, B.Sc. Nicholas
Uniglide. Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique. The mobile bearing is not commercially available in the USA
 Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique The mobile bearing is not commercially available in the USA Uniglide Contents Introduction 4 Compatibility chart 7 Operative summary
Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique The mobile bearing is not commercially available in the USA Uniglide Contents Introduction 4 Compatibility chart 7 Operative summary
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval
 Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot
 Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot Total Knee Replacement Patient Brochure Does your knee prevent you from performing and enjoying everyday activities? Osteoarthritis affects nearly 350 million people
Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot Total Knee Replacement Patient Brochure Does your knee prevent you from performing and enjoying everyday activities? Osteoarthritis affects nearly 350 million people
Section of total knee replacement. Total Knee Replacement System. Knieendoprothesen System. Système de prothèse totale de genou
 Section of total knee replacement Total Knee Replacement System Knieendoprothesen System Système de prothèse totale de genou Introduction: This knee system features great versality with its modular component
Section of total knee replacement Total Knee Replacement System Knieendoprothesen System Système de prothèse totale de genou Introduction: This knee system features great versality with its modular component
Luminus Flex Total Knee System (Fixed Type) The Innovative Technology for Knee Replacement
 Luminus Flex Total Knee System (Fixed Type) The Innovative Technology for Knee Replacement Intro The Luminus-Flex Total Knee system takes its name from the English word "Luminous" An adjective meaning
Luminus Flex Total Knee System (Fixed Type) The Innovative Technology for Knee Replacement Intro The Luminus-Flex Total Knee system takes its name from the English word "Luminous" An adjective meaning
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Saiph Knee System. Technical Dossier
 Saiph Knee System Technical Dossier Developed in collaboration with an international surgical team Professor Justin P Cobb Chair in Orthopaedic Surgery Imperial College Hospital, London Professor Fares
Saiph Knee System Technical Dossier Developed in collaboration with an international surgical team Professor Justin P Cobb Chair in Orthopaedic Surgery Imperial College Hospital, London Professor Fares
Biomechanics of the Knee. Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital
 Biomechanics of the Knee Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital Knee Biomechanics Kinematics Range of Motion Joint Motion Kinetics Knee Stabilisers Joint Forces Axes The Mechanical Stresses to which
Biomechanics of the Knee Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital Knee Biomechanics Kinematics Range of Motion Joint Motion Kinetics Knee Stabilisers Joint Forces Axes The Mechanical Stresses to which
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS KNEE SYSTEM
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS KNEE SYSTEM IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR WITH THE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE.
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS KNEE SYSTEM IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR WITH THE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE.
Zimmer Segmental System
 Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC. Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Frontal Plane Kinematics After Mobile- Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 392, pp. 56 61 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Frontal Plane Kinematics After Mobile- Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty James B. Stiehl, MD*; Richard
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 392, pp. 56 61 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Frontal Plane Kinematics After Mobile- Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty James B. Stiehl, MD*; Richard
Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA
 Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA MBBS, MS, FCPS, DIP SICOT. Arthroplasty fellow- USA, Germany, Aus Joint replacement surgeon COLUMBIA ASIA HOSPITAL, GZB. Fresh
Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA MBBS, MS, FCPS, DIP SICOT. Arthroplasty fellow- USA, Germany, Aus Joint replacement surgeon COLUMBIA ASIA HOSPITAL, GZB. Fresh
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
Aesculap Orthopaedics univation
 Aesculap Orthopaedics univation Knee Endoprosthesis System one system two knees Secure alignment and implantation with OrthoPilot UNIVATION one system two knees The univation System provides implant precision,
Aesculap Orthopaedics univation Knee Endoprosthesis System one system two knees Secure alignment and implantation with OrthoPilot UNIVATION one system two knees The univation System provides implant precision,
Consistency in U2 Knee System over Time
 U2 TM Knee System Consistency in U2 Knee System over Time Share the same femoral profile of all types allow inter-changibility Uniform AP/ML dimensions in all tibial components enhance intraoperative flexibility
U2 TM Knee System Consistency in U2 Knee System over Time Share the same femoral profile of all types allow inter-changibility Uniform AP/ML dimensions in all tibial components enhance intraoperative flexibility
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success. Zimmer Natural-Knee II System
 Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Rotating Platform System. Product Rationale
 References 1. Meftah M, Ranawat A, Ranawat C. Ten-Year Follow-up of a Rotating-Platform, Posterior-Stabilised Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:426-32 2. Dalury D, Gonzales R, Adams
References 1. Meftah M, Ranawat A, Ranawat C. Ten-Year Follow-up of a Rotating-Platform, Posterior-Stabilised Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:426-32 2. Dalury D, Gonzales R, Adams
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll
 (12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
(12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
Observations on retrieved articular surfaces of total knee prostheses. Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden University Medical Center, The Netherlands
 Chapter 11 Observations on retrieved articular surfaces of total knee prostheses Eric H. Garling 1, Henk K. Koerten 2, Edward R. Valstar 1,3, Rob G.H.H. Nelissen 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
Chapter 11 Observations on retrieved articular surfaces of total knee prostheses Eric H. Garling 1, Henk K. Koerten 2, Edward R. Valstar 1,3, Rob G.H.H. Nelissen 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
Think isometry Feel balance
 Think isometry Feel balance Learning from the experience of over 40 years of total knee development, Unity Knee is the latest evolution in total knee arthroplasty, unifying key design technologies with
Think isometry Feel balance Learning from the experience of over 40 years of total knee development, Unity Knee is the latest evolution in total knee arthroplasty, unifying key design technologies with
Finite element analysis of prosthetic knee joint using ANSYS
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 5 Finite element analysis of prosthetic knee joint using ANSYS C. Shashishekar & C. S. Ramesh Siddaganga Institute of Technology, India P.E.S. Institute of Technology,
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 5 Finite element analysis of prosthetic knee joint using ANSYS C. Shashishekar & C. S. Ramesh Siddaganga Institute of Technology, India P.E.S. Institute of Technology,
Surgical Technique. Hinge Disassembly and Rebuild Technique
 Surgical Technique Hinge Disassembly and Rebuild Technique Revision Knee Arthroplasty Surgical Technique LEGION HK Hinge Knee System Introduction The LEGION HK Hinge Knee System has been designed as an
Surgical Technique Hinge Disassembly and Rebuild Technique Revision Knee Arthroplasty Surgical Technique LEGION HK Hinge Knee System Introduction The LEGION HK Hinge Knee System has been designed as an
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
I want that next-generation knee
 I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
Rotaglide+ TM. Total Knee System Product overview
 Rotaglide+ TM Total Knee System Product overview Rotaglide+ TM Originality Stability History Originally implanted in 1988, Rotaglide+ was the first total knee design to adopt a true mobile bearing philosophy.
Rotaglide+ TM Total Knee System Product overview Rotaglide+ TM Originality Stability History Originally implanted in 1988, Rotaglide+ was the first total knee design to adopt a true mobile bearing philosophy.
YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT
 Knee pain? YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT Introduction If you re reading this brochure, you or a loved one is likely suffering from a severe knee problem. Serious knee joint conditions can cause pain,
Knee pain? YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT Introduction If you re reading this brochure, you or a loved one is likely suffering from a severe knee problem. Serious knee joint conditions can cause pain,
Cement Polished Tapered Stems of 12/14 Taper. 96 mm 98 mm 104 mm 110 mm 116 mm 122 mm 128 mm. Ceramic Femoral Head. Outer Diameter
 Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
A Strain-Energy Model of Passive Knee Kinematics for the Study of Surgical Implantation Strategies
 IN:Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1935 A Strain-Energy Model of Passive Knee Kinematics for the Study of Surgical Implantation Strategies E. Chen R. E. Ellis J. T. Bryant Computing and Information
IN:Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1935 A Strain-Energy Model of Passive Knee Kinematics for the Study of Surgical Implantation Strategies E. Chen R. E. Ellis J. T. Bryant Computing and Information
Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
(c) B. Ravi, IIT Bombay 1
 Collaborative Engineering Evaluation, Testing TKP Safety, TKP System Mechanism FEA Physical testing Fatigue Wear What How Evaluate Testing Judgement Criteria's Testing Conditions Parameters Measured OrthoCAD
Collaborative Engineering Evaluation, Testing TKP Safety, TKP System Mechanism FEA Physical testing Fatigue Wear What How Evaluate Testing Judgement Criteria's Testing Conditions Parameters Measured OrthoCAD
Knee Revision. Portfolio
 Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
Product Information & Procedure Wall Chart
 Partial Knee System Product Information & Procedure Wall Chart Reproducible, balanced approach to partial knee replacement Developed by Dr. Gerard A. Engh Dr. Engh is renowned for his expertise in developing
Partial Knee System Product Information & Procedure Wall Chart Reproducible, balanced approach to partial knee replacement Developed by Dr. Gerard A. Engh Dr. Engh is renowned for his expertise in developing
The Cruciate Ligaments in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 5 2000 The Cruciate Ligaments in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Kinematic Analysis of 2 Total Knee Arthroplasties James B. Stiehl, MD,* Richard D. Komistek, PhD, Jean-Marie
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 5 2000 The Cruciate Ligaments in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Kinematic Analysis of 2 Total Knee Arthroplasties James B. Stiehl, MD,* Richard D. Komistek, PhD, Jean-Marie
HIGH FLEXION IN CONTEMPORARY TOTAL KNEE DESIGN: A PRECURSOR OF UHMWPE DAMAGE? A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY
 HIGH FLEXION IN CONTEMPORARY TOTAL KNEE DESIGN: A PRECURSOR OF UHMWPE DAMAGE? A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY Orthopaedic Research Laboratories Cleveland, Ohio Edward A. Morra, M.S.M.E. A. Seth Greenwald, D.Phil.(Oxon)
HIGH FLEXION IN CONTEMPORARY TOTAL KNEE DESIGN: A PRECURSOR OF UHMWPE DAMAGE? A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY Orthopaedic Research Laboratories Cleveland, Ohio Edward A. Morra, M.S.M.E. A. Seth Greenwald, D.Phil.(Oxon)
National Joint Replacement Registry. Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement
 National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
Medial Rotation Knee. Technical Dossier
 Medial Rotation Knee Technical Dossier Manufactured by MatOrtho Limited 13 Mole Business Park Randalls Road Leatherhead Surrey KT22 7BA United Kingdom. T: +44 (0)1372 224200 info@matortho.com For more
Medial Rotation Knee Technical Dossier Manufactured by MatOrtho Limited 13 Mole Business Park Randalls Road Leatherhead Surrey KT22 7BA United Kingdom. T: +44 (0)1372 224200 info@matortho.com For more
TOTAL KNEE SYSTEM WHEN INNOVATION AND INTUITION ALIGN.
 TOTAL KNEE SYSTEM WHEN INNOVATION AND INTUITION ALIGN. Exactech has made history with our highly evolved Optetrak comprehensive knee system a system that has three decades of clinical success and proven
TOTAL KNEE SYSTEM WHEN INNOVATION AND INTUITION ALIGN. Exactech has made history with our highly evolved Optetrak comprehensive knee system a system that has three decades of clinical success and proven
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Analysis of an Early Intervention Tibial Component for Medial Osteoarthritis
 Analysis of an Early Intervention Tibial Component for Medial Osteoarthritis Miriam Chaudhary, M.Sc. 1, Peter S. Walker, PhD 2. 1 NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York City, NY, USA, 2 NYU-Hospital
Analysis of an Early Intervention Tibial Component for Medial Osteoarthritis Miriam Chaudhary, M.Sc. 1, Peter S. Walker, PhD 2. 1 NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York City, NY, USA, 2 NYU-Hospital
Regenerex Porous Titanium Construct. Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology
 Regenerex Porous Titanium Construct Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized
Regenerex Porous Titanium Construct Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized
Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil
 Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil M.M.Souza 1, R.M. Trommer 2, M.M.Maru 2, C.R.M.Roesler 3, W.S.Barros 1, M.S. Dutra 3 1 Dimensional Metrology Laboratory, Inmetro. Brazil;
Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil M.M.Souza 1, R.M. Trommer 2, M.M.Maru 2, C.R.M.Roesler 3, W.S.Barros 1, M.S. Dutra 3 1 Dimensional Metrology Laboratory, Inmetro. Brazil;
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
BULLETIN. Medial Rotation Knee Technical Dossier. Derek R Cooper Director of Sales & Marketing. 14th January 2004
 14th January 2004 Medial Rotation Knee Technical Dossier BULLETIN Bulletin No. 011 The attached document is now readily available to support your sales and marketing activities. The dossier plots the development
14th January 2004 Medial Rotation Knee Technical Dossier BULLETIN Bulletin No. 011 The attached document is now readily available to support your sales and marketing activities. The dossier plots the development
The challenge. Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery
 The challenge Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery THA 52% Post-op TKA 42% Preop 36% Preop 34% Post-op Total
The challenge Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery THA 52% Post-op TKA 42% Preop 36% Preop 34% Post-op Total
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
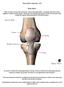 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
Masterclass. Tips and tricks for a successful outcome. E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter. September 15th, 2012, Brussels
 Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Retrospective Study of Patellar Tracking in an Anatomical, Motion Guided Total Knee Design. Adam I. Harris, M.D. & Michelle Ammerman
 Retrospective Study of Patellar Tracking in an Anatomical, Motion Guided Total Knee Design Adam I. Harris, M.D. & Michelle Ammerman History: The Total Condylar knee represented a significant advance in
Retrospective Study of Patellar Tracking in an Anatomical, Motion Guided Total Knee Design Adam I. Harris, M.D. & Michelle Ammerman History: The Total Condylar knee represented a significant advance in
BIOTECH FUTURE KNEE Minimal Invasive (and classic) Surgical Technique
 BIOTECH FUTURE KNEE Minimal Invasive (and classic) Surgical Technique Page No. Product description 2. Pre-operational planning 3. 1st step Femoral resection 4. P/S Femoral component 7. 2nd step Proximal
BIOTECH FUTURE KNEE Minimal Invasive (and classic) Surgical Technique Page No. Product description 2. Pre-operational planning 3. 1st step Femoral resection 4. P/S Femoral component 7. 2nd step Proximal
Uniglide. Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique
 Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique Uniglide Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative assessment 6 Preparation 7 Incision 7 Approach 7 Medial procedure 8 Tibial preparation
Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique Uniglide Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative assessment 6 Preparation 7 Incision 7 Approach 7 Medial procedure 8 Tibial preparation
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD
 UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
With over 40 years clinical experience, the Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used, 1 clinically proven 2 partial knee system in the world.
 Oxford Partial Knee A Definitive Implant With over 40 years clinical experience, the Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used, 1 clinically proven 2 partial knee system in the world. Compared with total
Oxford Partial Knee A Definitive Implant With over 40 years clinical experience, the Oxford Partial Knee is the most widely used, 1 clinically proven 2 partial knee system in the world. Compared with total
Knee arthroplasty: What radiologists should know.
 Knee arthroplasty: What radiologists should know. Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Araújo 1, J. Pires 2, J. Oliveira 3, C. Macedo 1, S. Magalhães 1, I. Ferreira
Knee arthroplasty: What radiologists should know. Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Araújo 1, J. Pires 2, J. Oliveira 3, C. Macedo 1, S. Magalhães 1, I. Ferreira
ATTUNE Knee System: Cruciate Sacrificing Fixed Bearing
 ATTUNE Knee System: Cruciate Sacrificing Fixed Bearing Christel Wagner Knee Development Manager DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction INTRODUCTION: The purpose of a well functioning posterior cruciate ligament
ATTUNE Knee System: Cruciate Sacrificing Fixed Bearing Christel Wagner Knee Development Manager DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction INTRODUCTION: The purpose of a well functioning posterior cruciate ligament
EXPERIENCE GPS FOR TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY DETERMINE YOUR OWN COURSE.
 EXPERIENCE GPS FOR TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY DETERMINE YOUR OWN COURSE. The year 2010 marked Exactech s silver aiversary and 25 years of mobility. As a company founded by an orthopaedic surgeon and a biomedical
EXPERIENCE GPS FOR TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY DETERMINE YOUR OWN COURSE. The year 2010 marked Exactech s silver aiversary and 25 years of mobility. As a company founded by an orthopaedic surgeon and a biomedical
The Evolution of Modern Total Knee Prostheses
 Chapter 9 The Evolution of Modern Total Knee Prostheses Eun-Kyoo Song, Jong-Keun Seon, Jae-Young Moon and Yim Ji-Hyoun Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/54343
Chapter 9 The Evolution of Modern Total Knee Prostheses Eun-Kyoo Song, Jong-Keun Seon, Jae-Young Moon and Yim Ji-Hyoun Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/54343
Instrumentation Options
 Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
 Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
20 Kinematics of Mobile Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty
 2 2 Kinematics of Mobile Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty D. A. Dennis, R. D. Komistek Summary Review of the kinematic patterns of fixed- vs. mobile TKA has not demonstrated major differences, with the
2 2 Kinematics of Mobile Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty D. A. Dennis, R. D. Komistek Summary Review of the kinematic patterns of fixed- vs. mobile TKA has not demonstrated major differences, with the
Continuing the Tradition. VerSys Heritage Hip System
 Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect. Two classification methods are used to categorize joints:
 Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 410 417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis C. Catier, M.
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 410 417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis C. Catier, M.
Fixed Bearing Knees Function with Wear Resistance
 Fixed Bearing Knees Function with Wear Resistance Sigma Knee System Today s surgeons demand a knee system that can react to the needs of the individual patient. The Sigma Knee System brings together function
Fixed Bearing Knees Function with Wear Resistance Sigma Knee System Today s surgeons demand a knee system that can react to the needs of the individual patient. The Sigma Knee System brings together function
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE and LEGION Disposable instrument technique* Note: All disposable instruments are interchangeable with the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE and LEGION Disposable instrument technique* Note: All disposable instruments are interchangeable with the
