Neurologic injuries after primary total ankle arthroplasty: prevalence and effect on outcomes
|
|
|
- Dylan Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 DOI /s JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Neurologic injuries after primary total ankle arthroplasty: prevalence and effect on outcomes Andri Primadi 2, He-Xing Xu 1, Taek-Rim Yoon 1, Je-Hwang Ryu 3 and Keun-Bae Lee 1* Abstract Background: Neurologic injuries are complications that can arise after total joint arthroplasty. However, no comprehensive study has been conducted on peripheral nerve injuries after total ankle arthroplasty. The purpose of the present study was to identify the prevalence of neurologic injury following primary total ankle arthroplasty, the predisposing factors, and evaluate the effect on clinical outcomes. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 150 consecutive primary total ankle arthroplasty using the mobile-bearing prosthesis between January 2005 and December 2011, in 150 patients with symptomatic ankle end-stage arthritis. All the patients were divided into groups according to whether they had postoperative peripheral neuropathy (23 patients) or not (127 patients). We investigated the prevalence, predisposing factors, and effect on clinical outcomes of neurologic injuries. The mean age was 61.3 years, and the mean follow-up period was 41.8 months. Results: There were 23 nerve injuries (15.3 %), including nine in posterior tibial nerves, six superficial peroneal nerves, six deep peroneal nerves, one saphenous nerve, and one sural nerve. Neurologic injury was significantly associated with the development of posttraumatic osteoarthritis, but it was not significantly associated with other predisposing factors, such as age, gender, body mass index, and symptom duration. Of the 23 nerve injuries, 13 (56.5 %) presented a complete, spontaneous recovery, 9 (39.1 %) presented an incomplete recovery, and 1 (4.3 %) presented no recovery. The patients with neurologic injury had significantly lower American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society scores and lower levels of patient satisfaction. Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that the prevalence of neurologic injury after total ankle arthroplasty is considerable, and that neurologic injury is associated with low levels of patient satisfaction and poor clinical outcomes at mean of 3 years, postoperatively. Care is needed to reduce the occurrence of neurologic injuries. Keywords: Neurologic injury, Total ankle arthroplasty, Prevalence, Outcomes Background Peripheral neurologic injury is an important complication following ankle arthroplasty, but its incidence is thought to be uncommon [1 7]. For lower limb arthroplasty, the common mechanisms related to neurologic injuries include traction, compression, entrapment, direct laceration, and indirect trauma [8 12]. Many studies have investigated the incidence of peripheral nerve injury following arthroplasty [9 12], and the prevalence of such injuries has been reported to range between 0.17 and 1 % after * Correspondence: kbleeos@chonnam.ac.kr Equal contributors 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, 42 Jebongro, Donggu, Gwangju , Republic of Korea Full list of author information is available at the end of the article total hip arthroplasty [11, 13 16] and between 0.3 and 1.28 % after total knee arthroplasty [12, 17, 18]. Studies of neurologic injuries after total hip arthroplasty have identified the contributing factors to be traction injuries during positioning, prolonged traction, and traumatic compression as well as for the patient to be a female gender and for a less experienced surgeon to have carried out the procedure [14 16]. In total knee arthroplasty, the association between preoperative flexion contracture or valgus deformity and peroneal nerve injury has been established, but the effects of the application of a pneumatic tourniquet have yet to be conclusively determined [11]. In recent years, total ankle arthroplasty has become a viable option for patients with osteoarthritis of the 2015 Primadi et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
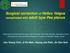
2 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 Page 2 of 8 ankle and has achieved favorable clinical results as it provides reliable pain relief, preserves motion, and facilitates recovery. Some studies reported the incidence of peripheral neurologic injuries in patients who underwent total ankle arthroplasty to be between 1.8 and 21 % of all cases, and these were found to be related to several causes [1, 10, 19 23]. Lee at al. [20] argued that the majority of nerve injuries were due to either excessive stretching during retraction or to improper release and improper protection distally in the incisional wound. However, no comprehensive study has been conducted on peripheral nerve injuries after primary total ankle arthroplasty. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the prevalence of neurologic injury following primary total ankle arthroplasty, identify predisposing factors (preoperative diagnosis, laterality and body mass index) for neurologic injury sustained during surgery, and evaluate effect of neurologic injury on clinical outcomes of American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hind foot score, and patient satisfaction. Methods We retrospectively analyzed 158 consecutive primary total ankle arthroplasty procedures, performed by a single surgeon between January 2005 and December 2011, in 158 patients with symptomatic ankle end-stage arthritis using the HINTEGRA prosthesis (Integra, Plainsboro, NJ, USA). We did not operate on patients with combined pathologies, such as charcot arthropathy, infectious arthropathy, and severe musculoskeletal injuries, since all of these can affect outcomes assessment. We excluded eight patients with preexisting sensoryor motor deficits (e.g., five diabetic peripheral neuropathy, three posttraumatic peripheral neuropathy). The remaining 150 patients were included in this study cohort. All the patients were divided into groups according to whether they had postoperative neuropathy (23 patients) or not (127 patients). This study was approved by the institutional review board of our hospital, and informed consent was provided to all patients. There were 13 men (56.5 %) and 10 women (43.5 %), and the mean age was 54 years (33 to 70) in patients with a neurologic injury. And there were 78 men (61.4 %) and 49 women (38.6 %), and the mean age was 53 years (24 to 71) in patients without a neurologic injury. The average body mass index (BMI) was 24.5 kg/m 2 in patients with neurologic injury and 25.6 kg/m 2 in patients without a neurologic injury. Eightytwo patients had posttraumatic osteoarthritis, 65 presented primary osteoarthritis, and three patients had rheumatoid arthritis. We also checked the patient s laterality and the symptom duration. The mean duration of the follow-up was 39 months (24 to 54) in patients with neurologic injury and 38 months (24 to 52) in patients without a neurologic injury (Table 1). To identify predisposing factors to nerve injury sustained during surgery, patients with and without neurologic injury were compared with regard to sex, age, BMI, preoperative diagnosis, operation laterality, symptom duration, and the preoperative AOFAS score [24]. Neurologic injuries that occurred as a complication from surgery were obtained by examining patients during their hospital stay or follow-up period, as written in their medical records. All patients were followed at one, three, six, and 12 months postoperatively, and annually thereafter. The data of clinical assessment included injured nerves, injury types, and recovery status. We used the clinical assessment to evaluate neurologic injuries according to cutaneous innervation of the foot (Fig. 1). For the patients in this study, electromyography studies were not routinely assigned. Injury types of nerve were classified as described by Asp and Randas complete or partial, sensory or motor, or a combination Table 1 Demographics of total ankle arthroplasty patients with and without neurologic Injuries With neurologic injury (N = 23) Without neurologic injury (N = 127) p-value * RR (95 % CI) Sex, male/female, n 13/10 78/ Age, y 62.7 ± ± BMI *, kg/m ± ± Preoperative diagnosis, n Primary osteoarthritis Posttraumatic osteoarthritis Rheumatoid arthritis 1 2 Side of operation, Rt/Lt, n 14/9 77/ Duration of ankle pain, m 38.7 ± ± Follow-up duration, m 44.7 ± ± BMI body mass index, RR releative risk, 95 % CI 95 % confidence Values are expressed as mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated * Independent t-test or Chi-square test. The p-values are of inter-group comparisons. Significance was accepted for p-values less than 0.05
3 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 Page 3 of 8 on a four-point Likert scale [26]. The response categories consisting of very satisfied (100 points), somewhat satisfied (75 points), somewhat dissatisfied (50 points), and very dissatisfied (25points). The scale score is the un-weighted mean of the scores from the individual items, ranging from 25 to 100 per item (with 100 being most satisfied). Fig. 1 Cutaneous innervation of the foot. a Dorsal surface b Plantar surface. a. Saphenous nerve; b. Deep peroneal nerve; c. Superficial peroneal nerve; d. Sural nerve; e. Medial plantar nerve; f. Lateral plantar nerve; g. Medial calcaneal nerve of these [9]. Any weakness in toe or ankle dorsiflexion was recorded as a motor deficit. Complete motor deficiency was defined to be when no contraction of innervated musculature occurred during examination, and partial motor deficit was defined to be when any muscle movement was retained. A profound loss of sensation was defined as a complete sensory deficit, and a less than complete loss was defined as a partial sensory deficit [9]. Patient recovery was graded as none, incomplete, or complete and was further evaluated in relationship to the baseline characteristics and perioperative conditions, such as the underlying diagnosis and additional procedures performed. Recovery of nerve injury is defined as aoccurance of skin sensation and muscle function. To avoid examiner bias, neurologic injury and clinical scoring were evaluated by two independent observers who were not involved in the surgical treatment of the patients. For evaluating the effect of neurologic injury on clinical outcomes, the AOFAS score and patient satisfaction were used. The 100-point AOFAS scoring system combines subjective and objective data to evaluate clinical parameters; pain (40 points), function (45 points), and alignment (15 points). The AOFASscore is the most commonly reported outcome assessment after total ankle arthroplasty, but evidence of its validity and reliability is limited [25]. Furthermore, questionnaires were administered postoperatively to record patient satisfaction that was scored Statistical analysis Descriptive statistics (arithmetic means, averages, and ranges) were calculated using standard formulas, to determine the significances of intergroup differences, univariable analysis was used to assess whether gender, age, preoperative diagnosis, BMI, operation laterality, duration of ankle pain and preoperative AOFAS score were predisposing factor for nerve injury. Multivariable linear regression analysis was used to assess the relationship between postoperative AOFAS score and above independent variables. The Paired t-test wasused to analyze AOFAS score intergroup and intragroup differences before and after surgery. And the Pearson s Chi-square test or Fisher s exact test was used to compare patient satisfaction between two groups. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered to indicate significance, and all aspects of the statistical analysis were reviewed by a statistician. Results Prevalence and typesof nerve injuries The overall prevalence of nerve injuries was 15.3 % (23 patients) in 150 patients. Nine (39 %) of the 23 patients suffered from neurologic injuries that involved the posterior tibial nerve or one of its branches. There were six (26 %) cases where there was an isolated injury to superficial peroneal nerve, and in six (26 %) cases the injury was in the deep peroneal nerve. Sural nerve and saphenous nerve injuries were found in one (4 %) patient each. Almost all of them (19 out of 23, 82.6 %) presented partialsensory deficiency, two had both partial motor and sensory and two had complete sensory injuries (Table 2). Neurologic symptom was occurred at mean 2.1 months (range, 0.4 to 6.0 month) postoperatively. The cause for neurologic injury was estimated to be prolonged retraction or excessive nerve stretching, improper nerve release during surgery in 18 (78.2 %) cases. Tarsal tunnel syndrome was found in three patients who presented neurology at mean 4.3 month (1.0 to 6.0 month) postoperatively and posterior tibial nerve lacerations were observed in two patients who presented neurology at mean 3.2 month (0.9 to 6.0 month) postoperatively. Tarsal tunnel syndrome was confirmed by nerve conduction velocity and electromyography. Tarsal tunnel release and neurolysis were performed after failed conservative treatment including medication and physical therapy. Posterior tibial nerve lacerations were occurred by the saw blade
4 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 Page 4 of 8 Table 2 Summary of nerve injuries after primary total ankle arthroplasty Injured Nerve Number (%) Recovery Status Treatment Patient Satisfaction Posterior tibial 9 (39.1) Complete : 3 Tarsal tunnel release: 3 Very satisfied: 3 Incomplete : 5 Neurorrhapy: 2 Somewhat satisfied: 1 None : 1 Observation: 4 Somewhat dissatisfied: 3 Superficial peroneal 6 (26.1) Complete : 4 Observation: 6 Very dissatisfied: 2 Incomplete : 2 Very satisfied: 4 Somewhat satisfied: 2 Deep peroneal 6 (26.1) Complete: 4 Observation: 6 Very satisfied: 4 Incomplete: 2 Somewhat satisfied: 2 Sural 1 (4.3) Complete: 1 Observation: 1 Very satisfied: 1 Saphenous 1 (4.3) Complete: 1 Observation: 1 Very satisfied: 1 during bone cuts at the posteromedial corner of the ankle without appropriate protection. The above five patients who had severe pain enough to interfere with the daily life or had obvious cause of pain underwent reoperation to treat neurologic injuries. Three patients with tarsal tunnel syndrome presented a partial sensory injury, and after decompression,1 recovered completely and two showed incomplete recovery. Two patients with posterior tibial nerve lacerations presented complete sensory injuries and underwent neurorrhaphy, but 1 showed incomplete recovery and 1 no improvement insymptoms. Predisposing factors Neurologic injury had a significantly twice higher risk in patients with preoperative diagnosis of posttraumatic osteoarthritis (19.5 %) than patients with primary osteoarthritis (9.23 %) (p = 0.004) (Table 1, univariable analysis), but it was not significantly associated with other risk factors, such as age (p = 0.48), gender (p = 0.495), BMI (p = 0.13), laterality (p = 0.771), and duration of ankle pain (p = 0.167). Rheumatoid arthritis could not be considered during the analysis due to the lack of patients (0.02 %, 3 of 150). To identify factors affecting postoperative AOFAS scores, patients were analyzed with multivariable regression analysis (Table 3). The preoperative diagnosis (p = 0.007) and nerve injury (p = 0.008) did present significant correlation to the postoperative AOFAS scores in both group, whereas gender (p = 0.508), age (p = 0.399), BMI (p = 0.917), laterality (p = 0.502), duration of ankle pain (p = 0.634) and follow-up duration (p = 0.604) did not. This study showed that the preoperative posttraumatic osteoarthritis and nerve injury may affect clinical outcomes on AOFAS score. Therefore, this study showed that preoperative diagnosis of posttraumatic osteoarthritis was considered to be the only significant predisposing factor for nerve injury among variables (Table 1, 3). Recovery and clinical outcomes At the final follow-up evaluation, 13 (56.5 %) patients presented a complete, spontaneous clinical recovery, nine (39.1 %) presented an incomplete recovery, and one (4.3 %) did not show any recovery. Most of the patients (18 of 23 patients, 78.2 %) recovered spontaneously. Five of 23 (21.8 %) patients underwent reoperation, and one (4.3 %) showed complete recovery, three (17.3 %) showed incomplete recovery, but 1 (4.3 %) had no recovery (Table 4). The mean AOFAS score improved from 48.9 points (range, 22 to 58 points) preoperatively to 81.2 points (range, 66 to 90 points) at the final follow-up in the group with neurologic injuries (p = 0.002). In the neurologically intact group,the score improved from 47.9 points(range,20to66points)preoperativelyto88.4 points (range, 71 to 100 points) at the final follow-up (p = 0.001). There was a significant difference in the AOFAS score between the two groups at the final follow-up (p = 0.03).In particular, the two patients with a laceration of the posterior tibial nerve showed Table 3 Influence of individual factors on postoperative AOFAS in total ankle arthroplasty patients Estimate (95 % CI) p-value * Sex, female ( 1.936, 3.888) Age, y ( 0.165, 0.066) BMI, kg/m ( 0.489, 0.441) Preoperative diagnosis Posttraumatic osteoarthritis ( 1.768, 4.546) Side of operation, Rt ( 3.791, 1.870) Duration of ankle pain, m ( 4.165, 1.189) Follow-up duration, m ( 0.048, 0.082) Nerve injury ( 9.421, 1.416) BMD body mass index, 95 % CI 95 % confidence intervals * Multivariable linear regression test. The p-values are of inter-group comparisons. Significance was accepted for p-values less than 0.05
5 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 Page 5 of 8 Table 4 Literature review of neurologic injuries after total ankle arthroplasty Study Implant Case (n) Neurologic Injury, n (%) Injured Nerve (n) Recovery Rate Risk Factors Myerson et al. [21] Agility 50 2 (4 %) Deep peroneal (1) 0 (0 %) Excessive stretching Superficial peroneal (1) Improper release Improper protection Knecht et al. [19] Agility (21 %) Superficial peroneal (6) N/A a N/A Deep peroneal (3) Common peroneal (6) Lee et al. [20] Hintegra 50 3 (6 %) Deep peroneal (3) N/A a Excessive stretching, Improper release Improper protection Krause et al. [1] Agility (1.8 %) Deep peroneal (2) 1 (50 %) N/A- Mobility STAR Hintegra Current study Hintegra (15.3 %) Posterior tibial (9) 22 (95.6 %) Excessive stretching, Deep peroneal (6) Improper release Superficial peroneal (6) Improper protection Sural (1) Laceration Saphenous (1) a N/A, data not available a poor AOFAS score (66 and 70 points in each) (paired t-test, p <0.05). With respect to the levels of patient satisfaction in the neurologically intact group, 115 patients (90.5 %) responded that they were either Very satisfied or Somewhat satisfied, three patients (7.8 %) responded to be Somewhat dissatisfied, and two patients (1.5 %) responded to be Very dissatisfied. In the neurologically injured group,18 patients (78.2 %) reported to be Very satisfied or Somewhat satisfied, three patients (13 %) reported to be Somewhat dissatisfied, and two patients (8.7 %) reported to be Very dissatisfied. There was a significant difference in the levels of patient satisfaction between the two groups at the final follow-up (fisher exact test, p = 0.017). The patients with neurologic injuries had a lower reported satisfaction levels than those of the group without neurologic injury. Additional procedures Eighteen additional procedures were carried out before or at the time of the total ankle arthroplasty to correct accompanying malalignment, joint contractures, or instabilities in three ankles (2.1 %) in the neurologically injured group and in 15 ankles (10.5 %) in neurologically intact group. Intraoperatively, percutaneous Achilles tendon lengthening was performed in one ankle in the neurologically injured group and in three ankles in the neurologically intact group. Deltoid release was performed in seven ankles only in the neurologically intact group. However, no significant difference with respect to these additional procedures was found between these two groups (Pearson s Chi-square test, p = 0.934). Discussion The most important finding of this study is that there were 23 nerve injuries (16 %), including nine posterior tibial nerves, six superficial peroneal nerves, and six deep peroneal nerves. Of the 23 patients, 13 (56.5 %) presented a complete recovery, nine (39.1 %) presented an incomplete recovery, and one (4.3 %) showed no recovery. The prevalence of a neurologic injury after primary total ankle arthroplasty was found to be considerable, and the neurologic injury is associated with low levels of patient satisfaction and poor clinical outcomes at a mean time of three years postoperatively. In this study, overall rate (15.3 %)of peripheral neurologic injury was relatively higher than average rate (10.4 %)of the literature (Table 4). There was no report about any specific relation between the HINTEGRA prosthesis and prevalence of peripheral neurologic injuries. We supposed that was because we did accurate investigation interested in neurologic injury, including mild numbness which was often not reported in previous studies, at the time of every follow-up. Generally, the precise etiology of a neurologic injury is rarely identified with absolute certainty. We found that posttraumatic osteoarthritis had a relationship with
6 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 Page 6 of 8 neurologic injuries sustained during surgery, and this might be logically explained by local scarring in the soft tissue that could tether the nerve, making it less able to tolerate even minor amounts of change [11]. A longer operation time is needed in such situations to ensure that a more cautious approach is taken, securing the operation field from more osteophytes, performing additional proceduresto correct deformities, and releasing scar tissue. Such conditions might be important causes of prolonged retraction of the nerve. Our study did not find age, gender, BMI, symptom duration, or laterality to be significant risk factors for the development of nerve injury following total ankle arthroplasty. These findings were consistent with those presented by Rose et al. [27] who mentioned that patient age and gender were of no predictive value for the development of peripheral neuropathy after total knee arthroplasty. However some authors also postulated that female gender was a risk factors for neurologic complications, without presenting well established reasons [14]. Many authors have mentioned that, without appropriate release and protection, superficial and deep peroneal nerves are at risk of being injured by the saw during bone cuts, especially during cuts made at the dome of the talus [22]. We were very careful when the talus was cut to avoid injury of the superficial peroneal nerve, so there seems to have been no direct injury resulting from sawing the bone in our series. Direct pressure from a tight dressing, compression of the vascular supply to the nerve by the fascia, pressure from postoperative hematoma, and use of a tourniquet have been proposed to be possible cause as well [12]. In our institute, to avoid those kind of risk factors during and after operationthe adequate time for the tourniquet and meticulous hemostasis after release are kept, suction drainage is performed for 2 days after operation until there is only minimal drainage, and direct compression of the nerve under the swollen soft tissue is prevented by dressing the site with a cotton bandage. In our study, 5 (21.7 %) patients out of 23 underwent reoperation to treat a nerve injury. The diagnosis consisted of three tarsal tunnel syndromes and two posterior tibial nerve lacerations. The other patients were each treated conservatively without surgical intervention. Ankle-foot orthosis and physical therapy involving range-of-motion exercises were used as required to further patient recovery. Generally, while minor stretch injuries may present spontaneous recovery, prolonged traction or traumatic compression of the nerve may show a less favorable prognosis, accounting for the higher percentage of permanent neurologic injuries in reoperation procedures that often require repeated manipulation of soft tissue [14]. We found three cases of tarsal tunnel syndrome following the surgery. Previous studies have described how traumatic injuries in the region of the tarsal tunnel can cause stenosis and scarring, leading to symptoms of the condition [4, 20, 21]. Entrapment resulting from spaceoccupying lesions has also been described. Bejjanki et al. [10] reported an unusual case that where the condition resulted from post-surgical entrapment and impingement from a displaced osteophyte rather than as a result of scarring. Extensive tibiotalar osteophytes are commonly seen and excised from patients undergoing ankle arthroplasty. It is difficult to ensure that all bony debris are removed from the surrounding soft tissue at the time of surgery. Proper soft tissue release and familiarity with the surgical technique allowed us to avoid neurologic injuries [19, 20, 22]. In our series, the anterior approach was used in all cases. The anterior approach to the ankle is known to have a proximity to the deep peroneal nerve and to the branch of the superficial peroneal nerve, making them prone to injury. However, our results did not show any established relationship between this approach and an injury to the superficial/deep peroneal nerve. By handling the soft tissue carefully, an adequate incision can be made, and self-retaining retractors should be avoided because they carry the risk for uncontrolled retraction. Therefore, hand-retained retractors must be released intermittently during operation. After a mean follow-up period of 41.8 months, 13 (56.5 %) of the patients showed a complete recovery of their symptoms, but nine (43.4 %) patients showed an incomplete clinical recovery, with 1 (4.3 %) showing no recovery. The potential for recovery often varies with the severity of the initial symptoms, and the patients comorbidities, peripheral vascular disease, and preexisting neuropathy should be assessed on a patient-by-patient basis [17]. This study has some limitations. First, the sample size and the number of patients who were discovered to have neurologic injuries were relatively small. This limits our ability to investigate the influence of baseline and perioperative characteristics to the outcome of interests. Second, we used a retrospective methodology. In the process of gathering analytical data of patients, even though author chose sample patients arbitrarily, a possible bias could occur. Moreover, we canonly presume for the cause of the neurologic injury to be excessive stretching, improper release and improper protection if there is no other identified cause, such as a laceration or tarsal tunnel syndrome. Third, operations for the present study were performed by a single surgeon in the same institute using the same prosthesis. This can be regarded as limitations on the interpretation of results for nerve injuries. Further investigation for multicenter trial is required. Finally, we did not routinely perform electrodiagnostic testing or nerve exploration. Instead,we used various clinical assessments of nerve injury, which have
7 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 Page 7 of 8 not yet been reported for their reliability and validity. Some authors have recommended routine electrodiagnostic testing for patients who are considered to be at high risk for sustaining a nerve injury during surgery. At our institution, we did not routinely monitor each patient. Currently, the indications for postoperative electromyography for the diagnosis and treatment of nerve injuries following total ankle arthroplasty have not been well established, and many patients recovered before electromyography was considered in a clinical situation. Despitethelimitationsnoted,thisisthefirstcomprehensive study evaluating the prevalence and types of neurologic injury following total ankle arthroplasty, and this is the largest series of nerve injuries following total ankle arthroplastyreported to date. As shown in this present study, patients with posttraumatic osteoarthritis are prone to nerve injuries after total ankle arthroplasty and showed low level of patient satisfaction and poor clinical outcomes. Therefore, surgery should be performed with care to avoid any nerve injuries. Conclusions The conclusion of this study suggests that the prevalence of neurologic injury after primary total ankle arthroplasty is considerable, and that neurologic injury is associated with low patient satisfaction and poor clinical outcomes at a mean time of 3 years postoperatively. Therefore, care during surgery should be taken to reduce the occurrence of neurologic injuries. Abbreviations AOFAS: American orthopedic foot and ankle society. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interest. Authors contributions AP participated in its design and collected the data and wrote the article. KBL conceived of the study and participated in its design and coordination, carried out the operations and helped to write the manuscript. TRY involved in the interpretation of the data and helped to write the article. JHR carried out statistical analysis and involved in the interpretation of the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgement The authors thank all patients and clinical researchers involved in this study we included in our article. This study was supported by a grant (CRI ,22 and CRI ) from the Chonnam National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute. Author details 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, 42 Jebongro, Donggu, Gwangju , Republic of Korea. 2 Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Universitas Padjadjaran Medical School/Hasan Sadikin Hospital, Bandung, Indonesia. 3 Department of Pharmacology and Dental Therapeutics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. Received: 10 March 2015 Accepted: 23 September 2015 References 1. Krause FG, Windolf M, Bora B, Penner MJ, Wing KJ, Younger AS. Impact of complication in total ankle replacement and ankle arthrodesis analyzed with a validated outcome measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: Lädermann A, Stimec BV, Denard PJ, Cunningham G, Collin P, Fasel JH. Injury to the axillary nerve after reverse shoulder arthroplasty: an anatomical study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100: Morrey BF, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Zarkadas PC, Throckmorton TW. Radial nerve palsy after humeral revision in total elbow arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20: Schmalzried T, Amstutz H, Dorey F. Nerve palsy associated with total hip replacement. risk factors and prognosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73: Christofilopoulos P, Bacle G, Stern R, Melis B, Lubbeke A, Ladermann A, et al. Prevalence of neurologic lesion after total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: Yuan HF, Yang MY, Xu WD. Late sciatic nerve palsy caused by recurrent hematoma after primary total hiparthroplasty: a case report. Orthop Surg. 2013;5: May O, Girard J, Hurtevent J, Delayed H, Miqaud F. Transient sciatic nerve palsy after primary cementless hip arthroplasty: a report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90: Saidha S, Spillane J, Mullins G, McNamara B. Spectrum of peripheral neuropathies associated with surgical interventions; A neurophysiological assessment. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2010;5:9. 9. Asp JP, Rand JA. Peroneal nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;261: Bejjanki NK, Moulder E, Al-Nammari S, Budgen A. Tarsal tunnel syndrome as a complication of total ankle arthroplasty: a case report. Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29: Farrell CM, Springer BD, Haidukewych GJ, Morrey BF. Motor nerve palsy following primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87: Idusuyi O, Morrey B. Peroneal nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty: assessment of predisposing and prognostic factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78: Johanson NA, Pellicci PM, Tsairis P, Salvati EA. Nerve injury in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;179: Nercessian OA, Macaulay W, Stinchfield FE. Peripheral neuropathies following total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1994;9: Dietze S, Perka C, Baecker H. Blood vessel and nerve damage in total hip arthroplasty. Orthopade. 2014;43: Park JH, Hozack B, Kim P, Norton R, Mandel S, Restropo C. Common peroneal nerve palsy following total hip arthroplasty: prognostic factors for recovery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95: Nercessian OA, Kiernan H, Parks ML, Parks ML, Schinsky MF, Macaulay W. Nerve injury after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16: Park JH, Restrepo C, Norton R, Mandel S, Sharkey PF, Parvizi J. Common peroneal nerve palsy following total knee arthroplasty: prognostic factors and course of recovery. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28: Knecht SI, Estin M, Callaghan JJ, Zimmerman MB, Alliman KJ, Alvine FG. The Agility total ankle arthroplasty:seven to sixteen-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86: Lee KB, Cho SG, Hur CI, Yoon TR. Perioperative complication of HINTEGRA total ankle replacement: our initial 50 cases. Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29: Myerson MS, Mroczek K. Perioperative complications of total ankle arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2003;24: Rippstein P, Huber M, Coetzee C, Naal FD. Total ankle replacement with Use of a three-component implant. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: Zaidi R, Cro S, Gurusamy K, Siva N, Macgregor A, Henricson A. The outcome of total ankle replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Joint J. 2013;95(B): Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 1994;15(7): Naal FD, Impellizzeri FM, Rippstein PF. Which are the most frequently used outcome instruments in studies on total ankle arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:
8 Primadi et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:55 Page 8 of Mahomed N, Gandhi R, Daltroy L, Katz JN. The self-administered patient satisfaction scale for primary hip and knee arthroplasty. Arthritis. 2011;2011:6. doi: /2011/ Rose HA, Hood RW, Otis JC, Ranawat CS, Insall JN. Peroneal-nerve palsy following total knee arthroplasty. A review of the Hosapital for Special Surgery experience. The self-administered patient satisfaction scale for primary hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(3): Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Effect of anterior translation of the talus on outcomes of three-component total ankle arthroplasty
 Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:260 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effect of anterior translation of the talus on outcomes of three-component total ankle arthroplasty Keun-Bae Lee 1*, Myung-Sun
Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:260 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effect of anterior translation of the talus on outcomes of three-component total ankle arthroplasty Keun-Bae Lee 1*, Myung-Sun
Surgical Decompression Improves Symptoms of Late Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction After TKA
 Surgical Decompression Improves Symptoms of Late Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction After TKA Joseph P. Ward, MD; Lynda J.-S. Yang, MD; Andrew G. Urquhart, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
Surgical Decompression Improves Symptoms of Late Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction After TKA Joseph P. Ward, MD; Lynda J.-S. Yang, MD; Andrew G. Urquhart, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion
 Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion W I L L I A M P. H U N T I N G T O N, M. D. W. H O D G E S D A V I S, M. D. R O B E R T B. A N D E R S O N,
Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion W I L L I A M P. H U N T I N G T O N, M. D. W. H O D G E S D A V I S, M. D. R O B E R T B. A N D E R S O N,
Common peroneal nerve palsy following total knee arthroplasty: prognostic factors and course of recovery.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 10-1-2013 Common peroneal nerve palsy following total knee arthroplasty:
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 10-1-2013 Common peroneal nerve palsy following total knee arthroplasty:
The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis in Total Ankle Arthroplasty
 The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis in Total Ankle Arthroplasty Robert Flavin, MD, Scott Coleman, James Brodsky, MD Baylor University Medical Center The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis
The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis in Total Ankle Arthroplasty Robert Flavin, MD, Scott Coleman, James Brodsky, MD Baylor University Medical Center The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature D Reichner, G Evans Citation D Reichner,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature D Reichner, G Evans Citation D Reichner,
Salto Talaris total ankle arthroplasty: Early clinical results from eighty-one consecutive patients by a single surgeon
 Salto Talaris total ankle arthroplasty: Early clinical results from eighty-one consecutive patients by a single surgeon Kurt Hofmann, MD, Zabrina Shabin, MD, Eric Ferkel, MD, Jeffrey Jockel, MD, Mark Slovenkai,
Salto Talaris total ankle arthroplasty: Early clinical results from eighty-one consecutive patients by a single surgeon Kurt Hofmann, MD, Zabrina Shabin, MD, Eric Ferkel, MD, Jeffrey Jockel, MD, Mark Slovenkai,
Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure)
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 306-310 ORIGINAL STUDIES Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure) Bart VINGERHOEDS, Ilse DEGREEF, Luc DE SMET From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 306-310 ORIGINAL STUDIES Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure) Bart VINGERHOEDS, Ilse DEGREEF, Luc DE SMET From the University
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries. First Global Conflict Medicine Congress
 Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Long-term sequel of posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow: a case report
 CASE REPORT Open Access Long-term sequel of posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow: a case report Chun-Ying Cheng * Abstract The natural course of untreated posterior lateral rotatory instability
CASE REPORT Open Access Long-term sequel of posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow: a case report Chun-Ying Cheng * Abstract The natural course of untreated posterior lateral rotatory instability
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
What variables influence final range of motion following Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Kevin T. Grosshans MD Mark S. Myerson MD
 What variables influence final range of motion following Total Ankle Arthroplasty Kevin T. Grosshans MD Mark S. Myerson MD Disclosures My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Mobile App I have no potential
What variables influence final range of motion following Total Ankle Arthroplasty Kevin T. Grosshans MD Mark S. Myerson MD Disclosures My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Mobile App I have no potential
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total ankle arthroplasty Total ankle arthroplasty in Western France: Influence of volume on complications and clinical outcome
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, S26 S30 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com WORKSHOPS OF THE SOO (2011, LA BAULE). ORIGINAL ARTICLE Total ankle arthroplasty Total ankle
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, S26 S30 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com WORKSHOPS OF THE SOO (2011, LA BAULE). ORIGINAL ARTICLE Total ankle arthroplasty Total ankle
Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Schedule Of Anaesthetic Rates Applicable To Podiatric Surgery. Procedure List. As Of.
 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2016 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2016/03/22 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2016/04/01 07 PHYSICAL MEDICINE, REHABILITATION,
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2016 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2016/03/22 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2016/04/01 07 PHYSICAL MEDICINE, REHABILITATION,
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 Introduction Compartment Syndromes of the Leg Related to Athletic Activity Mark M. Casillas, M.D. Consequences of a misdiagnosis persistence of a performance limitation loss of function/compartment loss
Introduction Compartment Syndromes of the Leg Related to Athletic Activity Mark M. Casillas, M.D. Consequences of a misdiagnosis persistence of a performance limitation loss of function/compartment loss
DOJ ABSTRACT. MATERIALS AND METHODS Following approval by our Institutional Review Board, we performed a search of our institution s perioperative
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1038 ORIGINAL Restoration RESEARCH of Shoulder Abduction after Radial to Axillary Nerve Transfer following Trauma or Shoulder Arthroplasty Restoration of Shoulder Abduction after
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1038 ORIGINAL Restoration RESEARCH of Shoulder Abduction after Radial to Axillary Nerve Transfer following Trauma or Shoulder Arthroplasty Restoration of Shoulder Abduction after
The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction
 The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, South Korea
The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, South Korea
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Accuracy assessment of measuring component position after total ankle arthroplasty using a conventional method
 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0611-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Accuracy assessment of measuring component position after total ankle arthroplasty
Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0611-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Accuracy assessment of measuring component position after total ankle arthroplasty
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW?
 ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW? Christian Veillette M.D., M.Sc., FRCSC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Shoulder & Elbow Reconstructive Surgery Toronto Western Hospital @ University Health
ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW? Christian Veillette M.D., M.Sc., FRCSC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Shoulder & Elbow Reconstructive Surgery Toronto Western Hospital @ University Health
Patients Expectations of Foot and Ankle Surgery: Variations by Diagnosis
 Patients Expectations of Foot and Ankle Surgery: Variations by Diagnosis Elizabeth A Cody, MD; Jayme C. B. Koltsov, PhD; Anca Marinescu; Carol A. Mancuso, MD; Scott J Ellis, MD; HSS Orthopaedic Foot and
Patients Expectations of Foot and Ankle Surgery: Variations by Diagnosis Elizabeth A Cody, MD; Jayme C. B. Koltsov, PhD; Anca Marinescu; Carol A. Mancuso, MD; Scott J Ellis, MD; HSS Orthopaedic Foot and
A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es
 A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es Stephen A. Brigido, DPM, FACFAS Director, Fellowship for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Coordinated
A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es Stephen A. Brigido, DPM, FACFAS Director, Fellowship for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Coordinated
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Schedule Of Anaesthetic Rates Applicable To Podiatry. Procedure List. As Of. 01 April Government of Alberta
 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle
 Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, Y. S. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Our study describes the clinical
Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, Y. S. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Our study describes the clinical
Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review. Key words: Pantalar fusion, non-union and total ankle replacement
 The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review Author: Bryan Williams DPM 1 and Jonathan Sharpe
The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review Author: Bryan Williams DPM 1 and Jonathan Sharpe
2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME
 2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME THURSDAY, MAY 25 07h45 07h55: WELCOME & INTRODUCTIONS Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes (08h00-10h00 Lectures) 08h00 08h30: Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Rippstein,
2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME THURSDAY, MAY 25 07h45 07h55: WELCOME & INTRODUCTIONS Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes (08h00-10h00 Lectures) 08h00 08h30: Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Rippstein,
Dr. Ashish Shah MD Dr. John Kirchner MD Dr. Sameer Naranje MD
 Dr. Ashish Shah MD Dr. John Kirchner MD Dr. Sameer Naranje MD Assistant Professor, UAB Orthopaedic Surgery, Foot & Ankle Section, 1313 13th Street South, Birmingham, AL 35205 Clinical Instructor Fellow,
Dr. Ashish Shah MD Dr. John Kirchner MD Dr. Sameer Naranje MD Assistant Professor, UAB Orthopaedic Surgery, Foot & Ankle Section, 1313 13th Street South, Birmingham, AL 35205 Clinical Instructor Fellow,
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical?
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
NON-CONSTRAINED TITANIUM-POLYETHYLENE TOTAL ENDOPROSTHESIS IN THE TREATMENT OF HALLUX RIGIDUS A prospective clinical 2-year follow-up study
 Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 91: 202 207, 2002 NON-CONSTRAINED TITANIUM-POLYETHYLENE TOTAL ENDOPROSTHESIS IN THE TREATMENT OF HALLUX RIGIDUS A prospective clinical 2-year follow-up study P. Ess, M.
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 91: 202 207, 2002 NON-CONSTRAINED TITANIUM-POLYETHYLENE TOTAL ENDOPROSTHESIS IN THE TREATMENT OF HALLUX RIGIDUS A prospective clinical 2-year follow-up study P. Ess, M.
A National Comparison of Total Ankle Replacement Versus Arthrodesis. Is There a Paradigm Shift?
 A National Comparison of Total Ankle Replacement Versus Arthrodesis. Is There a Paradigm Shift? Andrew F. Sabour, BS R. Kiran Alluri, MD Eric W. Tan, MD Keck School of Medicine of USC Los Angeles, CA Disclosures
A National Comparison of Total Ankle Replacement Versus Arthrodesis. Is There a Paradigm Shift? Andrew F. Sabour, BS R. Kiran Alluri, MD Eric W. Tan, MD Keck School of Medicine of USC Los Angeles, CA Disclosures
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle AOFAS Resident Review Course September 28, 2013
 Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Toe walking gives rise to parental concern. Therefore, toe-walkers are often referred at the 3 years of age.
 IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
Foot and ankle update
 Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS
 RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
Surgical Off-loading. Reiber et al Goals of Diabetic Foot Surgery 4/28/2012. The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration
 Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
 Xu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0655-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
Xu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0655-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
Disclosures. The authors disclosures are in the Final AOFAS Mobile App. The authors may have a potential conflict with this presentation due to:
 COFAS Multicenter Study Comparing Ankle Replacement and Ankle Fusion: The effect of Ipsilateral peri-articular deformity and arthritis on Mid-term outcome Murray J. Penner, MD, FRCSC Kevin J. Wing, MD,
COFAS Multicenter Study Comparing Ankle Replacement and Ankle Fusion: The effect of Ipsilateral peri-articular deformity and arthritis on Mid-term outcome Murray J. Penner, MD, FRCSC Kevin J. Wing, MD,
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia
 220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
Knee Disarticulation Amputation
 Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Chronic Lymphedema of the Lower Limb: A Rare Cause of Dislocation of Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.579 Chronic Lymphedema of the Lower Limb: A Rare Cause of Dislocation of Total Hip Arthroplasty Raju Vaishya 1, Amit Kumar Agarwal 1, Nishint Gupta 2, Vipul
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.579 Chronic Lymphedema of the Lower Limb: A Rare Cause of Dislocation of Total Hip Arthroplasty Raju Vaishya 1, Amit Kumar Agarwal 1, Nishint Gupta 2, Vipul
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Jeannie Huh, MD Christopher Gross, MD Alex Lampley, MD Samuel B. Adams, MD James K. DeOrio, MD James A. Nunley II, MD Mark E.
 Jeannie Huh, MD Christopher Gross, MD Alex Lampley, MD Samuel B. Adams, MD James K. DeOrio, MD James A. Nunley II, MD Mark E. Easley, MD Duke University Medical Center Durham, NC Disclosures Predictors
Jeannie Huh, MD Christopher Gross, MD Alex Lampley, MD Samuel B. Adams, MD James K. DeOrio, MD James A. Nunley II, MD Mark E. Easley, MD Duke University Medical Center Durham, NC Disclosures Predictors
Medincenter GlavUpDK by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, Moscow.
 Medincenter GlavUpDK by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, Moscow. Berezhnoy Sergey. Percutaneous First Metatarsocuneiform Joint Arthrodesis in a Treatment of Metatarsus Primus Varus: a Prospective
Medincenter GlavUpDK by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, Moscow. Berezhnoy Sergey. Percutaneous First Metatarsocuneiform Joint Arthrodesis in a Treatment of Metatarsus Primus Varus: a Prospective
Claw toes after tibial fracture in children
 J Child Orthop (2009) 3:339 343 DOI 10.1007/s11832-009-0200-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Claw toes after tibial fracture in children Frank Fitoussi Æ Brice Ilharreborde Æ Florent Guerin Æ Philippe Souchet
J Child Orthop (2009) 3:339 343 DOI 10.1007/s11832-009-0200-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Claw toes after tibial fracture in children Frank Fitoussi Æ Brice Ilharreborde Æ Florent Guerin Æ Philippe Souchet
Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched
 Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Continuing Education Conference Gregory P Witkowski, MD Orthopaedic Trauma and Foot/Ankle Surgery Disclosures I have nothing
Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Continuing Education Conference Gregory P Witkowski, MD Orthopaedic Trauma and Foot/Ankle Surgery Disclosures I have nothing
Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora
 Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora 8 ICD-9 CODE 838.03 Lisfranc (Tarsometatarsal) Fracture-Dislocation Key Concepts The Lisfranc joint represents
Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora 8 ICD-9 CODE 838.03 Lisfranc (Tarsometatarsal) Fracture-Dislocation Key Concepts The Lisfranc joint represents
Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014
 Total Ankle Arthroplasty Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014 Ankle Anatomy The ankle is a hinge or ginglymus joint Made up of the tibia, fibula, & talus
Total Ankle Arthroplasty Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014 Ankle Anatomy The ankle is a hinge or ginglymus joint Made up of the tibia, fibula, & talus
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries. Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital
 A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
Index. orthopedic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
Trainer vs Trainee: Clinical outcome of primary total ankle replacement. Can learning curve be included during training?
 Trainer vs Trainee: Clinical outcome of primary total ankle replacement. Can learning curve be included during training? Kailash Devalia, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Jayasree Ramaskandhan, BPhT, MPT, MSc Malik Siddique,
Trainer vs Trainee: Clinical outcome of primary total ankle replacement. Can learning curve be included during training? Kailash Devalia, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Jayasree Ramaskandhan, BPhT, MPT, MSc Malik Siddique,
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates
 Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Research New York University / Hospital for Joint Diseases, NY, NY Director Orthopaedic
Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Research New York University / Hospital for Joint Diseases, NY, NY Director Orthopaedic
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
Too young for an ankle replacement? Does patient age affect outcomes following total ankle replacement -5 year results
 Too young for an ankle replacement? Does patient age affect outcomes following total ankle replacement -5 year results Ruth Varrall, Jayasree Ramas, Anjani Singh and Malik Siddique AOFAS 2015 NO CONFLICT
Too young for an ankle replacement? Does patient age affect outcomes following total ankle replacement -5 year results Ruth Varrall, Jayasree Ramas, Anjani Singh and Malik Siddique AOFAS 2015 NO CONFLICT
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
John G Anderson MD 1 Donald R Bohay MD 1 John D Maskill MD 1 Paul D Butler MD 2
 John G Anderson MD 1 Donald R Bohay MD 1 John D Maskill MD 1 Paul D Butler MD 2 Jessica Hooper MD 3 Derek Axibal MD 3 Michelle A Padley BS 1 Lindsey Behrend BS 1 1 Orthopedic Associates of Michigan 2 Grand
John G Anderson MD 1 Donald R Bohay MD 1 John D Maskill MD 1 Paul D Butler MD 2 Jessica Hooper MD 3 Derek Axibal MD 3 Michelle A Padley BS 1 Lindsey Behrend BS 1 1 Orthopedic Associates of Michigan 2 Grand
Neglected synovial osteochondromatosis of the elbow: a rare case
 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY Neglected synovial osteochondromatosis of the elbow: a rare case Giannetti et al. Giannetti et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:233 Giannetti et al. World
WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY Neglected synovial osteochondromatosis of the elbow: a rare case Giannetti et al. Giannetti et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:233 Giannetti et al. World
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
RECURRENT INTERMETATARSAL NEUROMA
 4 th Foot & Ankle Symposium RECURRENT INTERMETATARSAL NEUROMA Martin Berli, MD Department of Prosthetics and Orthotics Uniklinik Balgrist, Zurich martin.berli@balgrist.ch Recurrence: General Topics Pain
4 th Foot & Ankle Symposium RECURRENT INTERMETATARSAL NEUROMA Martin Berli, MD Department of Prosthetics and Orthotics Uniklinik Balgrist, Zurich martin.berli@balgrist.ch Recurrence: General Topics Pain
5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE
 5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA IN A NUTSHELL ~ ALL ANATOMY & BIOMECHANICS >90% OF CONDITIONS IN FOOT & ANKLE DIAGNISED FROM GOOD
5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA IN A NUTSHELL ~ ALL ANATOMY & BIOMECHANICS >90% OF CONDITIONS IN FOOT & ANKLE DIAGNISED FROM GOOD
Management of arthritis of the shoulder. Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
The Lapidus Procedure as Salvage After Failed Surgical Treatment of Hallux Valgus A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY
 60 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Lapidus Procedure as Salvage After Failed Surgical Treatment of Hallux Valgus A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY BY J. CHRIS COETZEE,
60 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Lapidus Procedure as Salvage After Failed Surgical Treatment of Hallux Valgus A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY BY J. CHRIS COETZEE,
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Surgical Technique Guide
 Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Comparison of complications in one-stage bilateral total knee arthroplasty with and without drainage
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:3 DOI 10.1186/s13018-014-0140-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of complications in one-stage bilateral total knee arthroplasty with
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:3 DOI 10.1186/s13018-014-0140-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of complications in one-stage bilateral total knee arthroplasty with
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Investigation performed at the Department of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow, United Kingdom
 748 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Long-Term Results of the Modified Hoffman Procedure in the Rheumatoid Forefoot BY S. THOMAS, MBCHB, BSC, MRCS, A.W.G. KINNINMONTH,
748 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Long-Term Results of the Modified Hoffman Procedure in the Rheumatoid Forefoot BY S. THOMAS, MBCHB, BSC, MRCS, A.W.G. KINNINMONTH,
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture
 Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture Robert W. Mendicino, DPM, FACFAS, 1 Lara J. Murphy, DPM, 2 Michael P. Maskill, DPM, 3 Alan R. Catanzariti,
Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture Robert W. Mendicino, DPM, FACFAS, 1 Lara J. Murphy, DPM, 2 Michael P. Maskill, DPM, 3 Alan R. Catanzariti,
Surgical correction of Hallux Valgus
 Surgical correction of Hallux Valgus complicated with adult type Pes planus Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang-si, Korea * W Institute for Foot and Ankle Diseases
Surgical correction of Hallux Valgus complicated with adult type Pes planus Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang-si, Korea * W Institute for Foot and Ankle Diseases
Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
 Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
Rippstein, Trnka, Saragas, Narramore
 THURS 25th MAY 07:45 07:55 Welcome and Introductions Paulo Ferrao Lecture 1: 08:00 10:20 Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes Mark Easley 30 mins 08:00 08:30 Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Saragas,
THURS 25th MAY 07:45 07:55 Welcome and Introductions Paulo Ferrao Lecture 1: 08:00 10:20 Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes Mark Easley 30 mins 08:00 08:30 Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Saragas,
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF PERIPHERAL NERVE ENTRAPMENTS AND NEUROPATHY
 DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF PERIPHERAL NERVE ENTRAPMENTS AND NEUROPATHY Foreword Vincent J. Mandracchia xi Preface Babak Baravarian xv From There to Here: A Personal Viewpoint after Three Decades of Neuropathy
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF PERIPHERAL NERVE ENTRAPMENTS AND NEUROPATHY Foreword Vincent J. Mandracchia xi Preface Babak Baravarian xv From There to Here: A Personal Viewpoint after Three Decades of Neuropathy
Sciatic Nerve Injury in Total Hip Resurfacing
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 8 2010 Sciatic Nerve Injury in Total Hip Resurfacing A Biomechanical Analysis Dustin P. Gay, MD, Dana R. Desser, MD, Brent G. Parks, MSc, and Henry R. Boucher, MD
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 8 2010 Sciatic Nerve Injury in Total Hip Resurfacing A Biomechanical Analysis Dustin P. Gay, MD, Dana R. Desser, MD, Brent G. Parks, MSc, and Henry R. Boucher, MD
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Heterotopic ossification after total ankle arthroplasty
 FOOT AND ANKLE after total ankle arthroplasty W. J. Choi, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea We evaluated the incidence of heterotopic ossification following total ankle
FOOT AND ANKLE after total ankle arthroplasty W. J. Choi, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea We evaluated the incidence of heterotopic ossification following total ankle
The Influence of Patient Activation, Pain Self-Efficacy, and Resilience on Patient-Reported Pain and Function in Patients with Hip and Knee Arthritis
 The Influence of Patient Activation, Pain Self-Efficacy, and Resilience on Patient-Reported Pain and Function in Patients with Hip and Knee Arthritis Tiffany C. Liu BA, Tom Crijns BSc, Kevin J. Bozic MD
The Influence of Patient Activation, Pain Self-Efficacy, and Resilience on Patient-Reported Pain and Function in Patients with Hip and Knee Arthritis Tiffany C. Liu BA, Tom Crijns BSc, Kevin J. Bozic MD
2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY. Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois)
 2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois) John S. Reach, Jr, M.Sc., MD (New Haven, Connecticut) 133 2:00 2:15 pm SESSION 6: Varus, Valgus Whatever!
2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois) John S. Reach, Jr, M.Sc., MD (New Haven, Connecticut) 133 2:00 2:15 pm SESSION 6: Varus, Valgus Whatever!
Chamnanni Rungprai, M.D.
 Comparison Outcomes of Total Ankle Replacement with and without Achilles tendon lengthening 1,2 Chamnanni Rungprai, M.D. Co-authors 1 Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. 1 John E. Femino M.D. 1 Annunziato Amendola,
Comparison Outcomes of Total Ankle Replacement with and without Achilles tendon lengthening 1,2 Chamnanni Rungprai, M.D. Co-authors 1 Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. 1 John E. Femino M.D. 1 Annunziato Amendola,
2013/10/18 GANGLION CYSTS ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY ARTHROSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OPEN GANGLIONECTOMY COMPARED TO FOOT AND ANKLE
 GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Lower Extremity Conditions
 Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Lower Extremity Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Lower Extremity Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from
Endoscopic Soft Tissue Release System. SafeViewTM 360 Panoramic Visualization Sterile Packaged Fully Disposable
 L O W E R E X T R E M I T Y T E C H N I Q U E G U I D E Endoscopic Soft Tissue Release System SafeViewTM 360 Panoramic Visualization Sterile Packaged Fully Disposable Versatility and Control SafeView is
L O W E R E X T R E M I T Y T E C H N I Q U E G U I D E Endoscopic Soft Tissue Release System SafeViewTM 360 Panoramic Visualization Sterile Packaged Fully Disposable Versatility and Control SafeView is
Lateral Ankle Instability Surgical Treatment: A Comparison between Primary Repair and Revision Surgery
 Lateral Ankle Instability Surgical Treatment: A Comparison between Primary Repair and Revision Surgery B. Sahranavard, MD; C. de Cesar Netto, MD, PhD; C. Jones, BS; I. Araoye, MS; P. Hudson, BS; S. Lee,
Lateral Ankle Instability Surgical Treatment: A Comparison between Primary Repair and Revision Surgery B. Sahranavard, MD; C. de Cesar Netto, MD, PhD; C. Jones, BS; I. Araoye, MS; P. Hudson, BS; S. Lee,
Compartment Syndrome
 Compartment Syndrome Andrew H. Schmidt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery, Univ. of Minnesota Chief, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hennepin County Medical Center April 2016 Disclosure Information
Compartment Syndrome Andrew H. Schmidt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery, Univ. of Minnesota Chief, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hennepin County Medical Center April 2016 Disclosure Information
