Pattern of Fractures in Non-Accidental Injuries in the Pediatric Population in Singapore
|
|
|
- Roderick Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6: Pattern of Fractures in Non-Accidental Injuries in the Pediatric Population in Singapore Sumanth Kumar Gera, MBBS, Rakesh Raveendran, MBBS, Arjandas Mahadev, MBBS Department of Orthopaedics Surgery, KK Women s and Children s Hospital, Singapore Background: Fractures as a result of non-accidental injuries (NAI) are not uncommon among children. The purpose of our study was to describe the incidence, demographic characteristics, and associated risk factors in patients with NAI in a multiethnic Asian cohort. Methods: A retrospective record review of patients admitted to our hospital between September 2007 and 2009 with the diagnosis of NAI was conducted. Results: A total of 978 children were reported with suspicion of NAI. Among them, 570 patients (58.28%) were diagnosed with NAI. Fractures were observed in 35 children (6.14%). NAI fractures were highest among female infants (73.3%). The biological father was the most common known perpetrator of NAI (n = 155, 29.0%). The most common perpetrator sadly remained unknown (n = 14, 40%). All NAI fractures were closed (n = 35, 6.14%), and the most commonly affected bone was the humeral shaft (n = 10, 28.57%) with an oblique configuration. Age < 1 year and parental divorce were significant risk factors associated with these fractures. Conclusions: The skeletal injury pattern and risk factors highlighted in our study will help treating physicians identify patients susceptible to NAI, as many of these patients are young and vulnerable. Protective measures can be initiated early by recognizing these injuries and preventing further physical and psychological harm to the child. Keywords: Child abuse, Bone fractures, Risk factors, Etiology Child abuse is a global problem with multiple causes 1) and is responsible for 11% 55% of children with physical trauma. 2) Non-accidental injuries (NAI) not only indicate serious assault but also signify child abuse in infants, toddlers, and non-communicative children. Recognizing fracture characteristics caused by NAI are important, as it helps clinicians initiate the timely process of child protection, which prevents further harm to the child. 3) Racial differences exist in the evaluation and reporting of pediatric fractures in cases of child abuse. 4) Studies in Western populations report higher rates of NAI frac- Received February 7, 2014; Accepted April 28, 2014 Correspondence to: Sumanth Kumar Gera, MBBS Department of Orthopaedics Surgery, KK Women s and Children s Hospital, Level 4, Children s Tower, Singapore Tel: , Fax: Sumanth.Kumar@kkh.com.sg tures among non-caucasian children compared to those in Caucasian children. 5) It is difficult to compare prevalence across ethnicities due to different cultural practices, laws, and reporting mechanisms. 2) Additionally, international definitions and thresholds for NAI vary greatly among communities and may account for these ethnic differences. 4) Existing data indicate that approximately one-third of children with NAI eventually consult an orthopedic surgeon for suspected fractures. 6) The incidence and characteristics of fractures among Asian children with NAI provide valuable information not only for orthopedic surgeons but also for pediatricians and other healthcare providers for holistic management. 7) The purpose of this study was to describe the incidence, clinical features, risk factors, and fracture patterns in children with NAI among a large multiethnic Asian cohort. Copyright 2014 by The Korean Orthopaedic Association This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery pissn X eissn
2 433 METHODS A retrospective study of patients diagnosed with NAI was conducted at KK Women s and Children s Hospital from January 2007 to October Risk factors were assessed with respect to type of abuse, likely perpetrators, and social status. Radiological data such as X-rays, skeletal surveys, and bone scans were reviewed to determine fracture characteristics. The children were stratified by age into four groups: infants (< 1 year), toddlers (1 to < 2 years), school children (2 to 13 years), and teenagers (13 to < 18 years) to allow for a comparative analysis among the groups. This study adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki, and ethics approval was obtained from the KK Women s and Children s Hospital Institutional Review Board. Statistical Analysis Descriptive statistics and univariate analyses were generated using chi-square tests to compare discrete outcomes, and t-tests were used to compare means across conditions, except when skewed distributions warranted use of the Kruskal-Wallis equality-of-populations rank test. Mean with standard deviation and median with 25th and 75th percentiles are displayed where appropriate. Collinearity (r > 0.8), the number of missing values, and missing data patterns were checked. Binary logistic regression modeling was applied in multivariate analyses. The covariables adjusted in the multivariate analysis were those found to be univariately associated with outcome (absence and presence of fractures) and included major confounding factors, such as age, inpatient stay, perpetrators, need for an investigation, and parental divorce. A p < 0.05 was considered significant. All analyses were performed using STATA/SE ver (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA). RESULTS Study Population A total of 978 children were suspected to have NAI. Among them, 570 (58.28%) were diagnosed with NAI. Fractures were observed in 35 children (6.14%), and 304 children (53.3%) had soft tissue injuries. Table 1 shows the demographic data of the 570 children with NAI stratified by the presence or absence of fracture. Of the 535 patients (94.0%) with non-fracture related injuries, the majority were of Chinese ethnicity (n = 286, 53.5%). A total of 270 children from the NAI cohort (48.4%) required hospital admission. Those with fractures had a longer duration inpatient stay (6.6 days vs. 3.4 days, p < 0.001). All 35 children with NAI fractures needed investigating, such as a skeletal survey and bone scan (p < 0.001). Boys were affected more frequently than girls in both the fracture and non-fracture groups. Although NAI was most commonly noted among school children (n = 359, 67.1%), fractures were noted in infants (n = 19, 54.3%) and toddlers (n = 9, 25.7%) (p < 0.05). Biological fathers were the main perpetrators (n = 155, 29%) in the NAI without fractures cohort. The perpetrators remained unknown (n = 14, 40%) in the largest subset of NAI with fractures group. Approximately 94.0% (n = 536) of abuse was physical and was responsible for 97.1% (n = 34) of the fractures compared to psychological or sexual abuse. The presence of fracture tended to have a higher chance of the abuse being reported (94.3% vs. 86%), though this was not significant. A significantly higher rate of parental divorce (n = 166, 29.2%) was noted among the study patients in the NAI cohort (n = 570) than those without fracture. Seventy-seven children (13.5%) reported repeated abuse. About 5.6% of children (n = 32) had a pre-existing illness, behavioral problems, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (each, n = 8, 25%). Autism (n = 5, 15.6%), nephrotic syndrome (n = 2, 6.25%), and developmental delay (n = 2, 6.25%) were the other diseases noted in the study children. Fracture Characteristics Table 2 shows the characteristics of the 35 of 570 children diagnosed with a fracture secondary to NAI stratified by sex. The largest number of fractures was noted among female infants (73.3%). All fractures in the study population (n = 35, 6.14%) were closed, and multiple fractures were documented in three cases (8.5%). A total of 40% of the children (n = 228) needed X-rays, of which 106 (46.5%) underwent a skeletal survey to establish a diagnosis. X-rays were most commonly performed on the skull (n = 42, 18.4%) followed by the humerus (n = 19, 8.3%), facial skeleton (n = 13, 5.7%), and spine (n = 11, 4.8%). The humerus was the most common site of fracture and was noted in 10 children (28.57%). Seven children (20%) each had femoral shaft and skull (parietal bone) fractures, whereas four (11.4%) had distal radius fractures as a result of NAI. The majority of the fractures were oblique (n = 13, 37.14%), followed by transverse fracture (n = 10, 28.57%). Details of the NAI fractures are depicted in Figs. 1 and 2. Boys sustaining fractures underwent more physical abuse, and they had more pre-existing illness. Parental divorce and repeat abuse were noted equally in male and female children. However, none of these variables showed statistical significance. Multivariate logistic regression models were conducted for the risk factor assessment, as demonstrated in
3 434 Table 1. Characteristics of Children with Non-Accidental Injury Stratified by the Presence and Absence of Fractures Characteristic Without fracture (n = 535) With fracture (n = 35) p-value* Age (yr) < Infants (< 1) 30 (5.6) 19 (54.3) Toddlers (1 to < 2) 60 (11.2) 9 (25.7) School children (2 to < 13) 359 (67.1) 7 (20.0) Teenagers (13 to < 18) 86 (16.1) 0 Gender (male) 346 (64.7) 20 (57.1) Race 0.11 Chinese 286 (53.5) 16 (45.7) Malay 137 (25.6) 15 (42.9) Indian 91 (17.0) 4 (11.4) Other 21 (3.9) 0 No. of inpatient days 3.4 ± ± 9.3 < Perpetrator < Father 155 (29.0) 4 (11.4) Mother 98 (18.3) 3 (8.6) Other relatives/one parent and another non-parent 133 (24.9) 4 (11.4) Non-family members 96 (18.0) 10 (28.6) Unknown 53 (9.9) 14 (40.0) Type of abuse 0.72 Physical 502 (93.8) 34 (97.1) Physical + either psychological/neglect/sexual 32 (6.0) 1 (2.9) Sexual only 1 (0.2) 0 Required investigation 180 (33.6) 35 (100) < Pre-existing illness 0.27 Unknown 358 (66.9) 19 (54.3) No 147 (27.5) 14 (40.0) Yes 30 (5.6) 2 (5.7) Parental divorce Unknown 265 (49.5) 17 (48.6) No 108 (20.2) 14 (40.0) Yes 162 (30.2) 4 (11.4) Abuse reported 460 (86.0) 33 (94.3) Medical social worker assessment Unknown 171 (32.0) 17 (48.6) No 262 (49.0) 13 (37.1) Yes 102 (19.1) 5 (14.3) Resulted in death 3.0 (0.6) 0 Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation or number (%). *p < 0.05 for differences in characteristics by the presence and absence of fracture based on the chi-square or Student t-test.
4 435 Table 2. Characteristics of Patients with Non-Accidental Injuries and Fractures Stratified by Sex Characteristic Males (n = 20) Females (n = 15) p-value Age (yr) Infants (< 1) 8 (40.0) 11 (73.3) Toddlers (1 to < 2) 6 (30.0) 3 (20.0) School children (2 to < 13) 6 (30.0) 1 (6.7) Teenagers (13 to < 18) 0 0 Race Chinese 10 (50.0) 6 (40.0) Malay 10 (50.0) 5 (33.3) Indian 0 4 (26.7) Other 0 0 No. of inpatient days 3 (0 4.5) 4 (0 12) Perpetrators Father 1 (5.0) 3 (20.0) Mother 2 (10.0) 1 (6.7) Other relatives/one parent and another non-parent 4 (20.0) 0 Non-family members 7 (35.0) 3 (20.0) Unknown 6 (30.0) 8 (53.3) Type of abuse Physical 20 (10.0) 14 (93.3) Physical + psychological 0 1 (6.7) Sexual only 0 0 Multiple injuries 1 (5.0) 2 (13.3) Soft tissue injury 19 (95.0) 15 (100) Mechanism of injury Not applicable 4 (20.0) 2 (13.3) Fall 14 (70.0) 12 (80.0) Direct impact 2 (10.0) 1 (6.7) Abuse reported 19 (95.0) 14 (93.3) Pre-existing illness Unknown 11 (55.0) 8 (53.3) No 9 (45.0) 5 (33.3) Yes 0 2 (13.3) Parental divorce 2 (10.0) 2 (13.3) Medical social worker assessment Unknown 10 (50.0) 7 (46.7) No 0 0 Yes 3 (15.0) 2 (13.3) Feature Buckle 0 1 (6.7) Comminuted 0 2 (13.3) Lateral condyle 1 (10.0) 0 Oblique 8 (40.0) 5 (33.3) Transverse 7 (35.0) 3 (20.0) Site Upper limb 11 (55.0) 7 (53.3) Lower limb 4 (30.0) 3 (20.0) Skull 2 (15.0) 4 (26.7) Mean with standard deviation, median with 25th and 75th percentiles, and numbers with percentages are presented where appropriate based on the chi-square/ Student t-test/kruskal-wallis equality-of-populations rank test.
5 436 Fig. 1. Fracture sites secondary to non-accidental injuries noted among 35 children. Fig. 2. Types of fractures secondary to non-accidental injuries noted among 35 children. Table 3. Risk Factors for Fractures in Children with Non-Accidental Injuries Age (yr) Sex Variable Model 1 Model 2 OR (95% CI) p-value OR (95% CI) p-value School children (2 13) 1 1 Toddlers (1 to < 2) ( ) ( ) Infants (< 1) ( ) < ( ) < Male 1 1 Female ( ) ( ) Abuse Physical 1 1 Non-physical ( ) ( ) Pre-existing illness No 1 1 Yes ( ) ( ) Parental divorce No 1 1 Yes ( ) ( ) Inpatient days ( ) ( ) Perpetrator Father 0.92 ( ) ( ) Mother 0.74 ( ) ( ) Non-family members 1.77 ( ) ( ) Unknown 5.11 ( ) ( ) Hospital admission No 1 1 Yes ( ) ( ) Model 1: adjusted for age and sex, Model 2: adjusted for age, sex, inpatient stay duration, perpetrator, and parental divorce. OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval.
6 437 Table 3. After adjusting for variables that were univariately significant such as age, sex, inpatient stay duration, perpetrator, and parental divorce, infants (odds ratio [OR], 0.10; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03 to 0.11; p < 0.001) and higher rate of parental divorce (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.04 to 0.94) were associated with an increased risk of sustaining a fracture. Additionally, fractures were associated with longer duration of hospitalization (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.07 to 1.33). Moreover, there was a five-fold increase in the incidence of fracture when the perpetrator remained unknown (OR, 4.89; 95% CI, 1.21 to 19.8; p = 0.026). DISCUSSION The results show that NAI was common among male school children in our multiethnic Asian cohort. However, NAI fractures were more common in female infants (31.4%), which required them to be hospitalized for a longer duration for further investigation. Humerus fractures with an oblique configuration were the most common in this group. Age < 1 year, unknown perpetrator, and parental divorce were significantly associated with NAI fractures. Our results further support existing data that fractures resulting from NAI are most commonly seen in infants and toddlers. 8-13) However, the presence of multiple fractures consistent with NAI, as observed in other studies, was not detected in our study. 10,11,14,15) Additionally, our results show that the humerus was the most common fracture site as opposed to other studies reporting classic metaphyseal lesions, rib, 3,15) and skull fractures 9,10) to have the highest risk of NAI. The parietal bone was the most commonly involved skull fracture in patients suffering NAI, which was found in other studies. 3,10,14) Among the humerus fractures associated with NAI, the oblique fracture configuration is the most common, 14-16) and was confirmed in our study. These data emphasize that NAI should to be excluded in infants and toddlers with a humerus fracture. Parental divorce and unknown perpetrators as factors associated with NAI fractures is new information. The difference in results noted in our multiethnic Asian cohort pediatric population with those in Caucasian populations could be attributed to lifestyle variations. Definitions of NAI vary between Asian and Western communities and this could account for the findings in our study. 2) The fracture trend noted among the Asian cohort, which was quite different from that in Caucasians, can be used to predict the NAI pattern in our community. Although our sample size was large, the prevalence of fractures was rather low compared to that in other studies. 2,3) This could either be due to underreporting or improved lifestyle and better childcare in this part of Asia. Our data provide new and interesting findings among our multiethnic cohort of Chinese, Indian, and Malay children, which will certainly help with the diagnosis and management of NAI. As our study was retrospective, a prospective study in an Asian pediatric population with NAI is needed. Our study was also limited by the lack of a control group with fractures due to causes other than NAI. The results of our large retrospective study involving multiethnic Asian children with NAI show that age < 1 year and parental divorce were risk factors associated with fractures, whereas an unknown perpetrator was a related factor. These findings are not only helpful to identify doubtful cases of NAI fracture in our community but also will help with timely and multidisciplinary management of these children. CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. REFERENCES 1. Matschke J, Herrmann B, Sperhake J, Korber F, Bajanowski T, Glatzel M. Shaken baby syndrome: a common variant of non-accidental head injury in infants. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009;106(13): Mok JY. Non-accidental injury in children: an update. Injury. 2008;39(9): Kemp AM, Dunstan F, Harrison S, et al. Patterns of skeletal fractures in child abuse: systematic review. BMJ. 2008;337: a Lane WG, Rubin DM, Monteith R, Christian CW. Racial differences in the evaluation of pediatric fractures for physical abuse. JAMA. 2002;288(13): Hampton RL, Newberger EH. Child abuse incidence and reporting by hospitals: significance of severity, class, and race. Am J Public Health. 1985;75(1): Kocher MS, Kasser JR. Orthopaedic aspects of child abuse. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000;8(1): Fong CM, Cheung HM, Lau PY. Fractures associated with non-accidental injury: an orthopaedic perspective in a local regional hospital. Hong Kong Med J. 2005;11(6):
7 Feldman KW, Brewer DK. Child abuse, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and rib fractures. Pediatrics. 1984;73(3): Belfer RA, Klein BL, Orr L. Use of the skeletal survey in the evaluation of child maltreatment. Am J Emerg Med. 2001; 19(2): Day F, Clegg S, McPhillips M, Mok J. A retrospective case series of skeletal surveys in children with suspected nonaccidental injury. J Clin Forensic Med. 2006;13(2): Rennie L, Court-Brown CM, Mok JY, Beattie TF. The epidemiology of fractures in children. Injury. 2007;38(8): Bishop N, Sprigg A, Dalton A. Unexplained fractures in infancy: looking for fragile bones. Arch Dis Child. 2007;92(3): King J, Diefendorf D, Apthorp J, Negrete VF, Carlson M. Analysis of 429 fractures in 189 battered children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1988;8(5): Merten DF, Radkowski MA, Leonidas JC. The abused child: a radiological reappraisal. Radiology. 1983;146(2): Worlock P, Stower M, Barbor P. Patterns of fractures in accidental and non-accidental injury in children: a comparative study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;293(6539): Kleinman PK, Marks SC Jr. A regional approach to the classic metaphyseal lesion in abused infants: the proximal humerus. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(6):
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries
 Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures
 Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical?
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Upper extremity open fractures in hospitalized road traffic accident patients: adult versus pediatric cases
 Rubin et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:157 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0657-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upper extremity in hospitalized road traffic accident : adult versus pediatric
Rubin et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:157 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0657-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upper extremity in hospitalized road traffic accident : adult versus pediatric
CORE-INFO: fractures in children
 CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
Radiological investigations
 Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS CHILD ABUSE. A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non-
 ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS OF CHILD ABUSE A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non- Accidental Injury with specific references to both the perpetrator and victim
ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS OF CHILD ABUSE A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non- Accidental Injury with specific references to both the perpetrator and victim
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics
 Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
High Specificity Features on Plain Film of Non-Accidental Injury
 High Specificity Features on Plain Film of Non-Accidental Injury Adam A Dmytriw 1,2, Kota Talla 1, Munire Gündogan 2 1 Department of Medical Imaging, University of Toronto 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology,
High Specificity Features on Plain Film of Non-Accidental Injury Adam A Dmytriw 1,2, Kota Talla 1, Munire Gündogan 2 1 Department of Medical Imaging, University of Toronto 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology,
Incidence and Mortality after Proximal Humerus Fractures Over 50 Years of Age in South Korea: National Claim Data from 2008 to 2012
 J Bone Metab 2015;22:17-21 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.1.17 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Incidence and Mortality after Proximal Humerus Fractures Over 50 s of Age in South
J Bone Metab 2015;22:17-21 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.1.17 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Incidence and Mortality after Proximal Humerus Fractures Over 50 s of Age in South
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Bilateral rib fractures 2 on right and 1 on left In different stages of healing, with left fracture older than right fractures
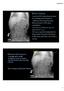 More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
Monkey Bars are for Monkeys: A Study on Playground Equipment Related Extremity Fractures in Singapore
 Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(1) : 9-13 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Monkey Bars are for Monkeys: A Study on Playground Equipment Related Extremity Fractures in Singapore A Mahadev, M Y H Soon, K S Lam
Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(1) : 9-13 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Monkey Bars are for Monkeys: A Study on Playground Equipment Related Extremity Fractures in Singapore A Mahadev, M Y H Soon, K S Lam
Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient
 September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
ASJ. Magnification Error in Digital Radiographs of the Cervical Spine Against Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
ARTICLE. Intracranial Hemorrhage in Children Younger Than 3 Years
 Intracranial Hemorrhage in Children Younger Than 3 Years Prediction of Intent ARTICLE Robert G. Wells, MD; Christine Vetter, MD; Prakash Laud, PhD Objective: To determine whether certain computed tomographic
Intracranial Hemorrhage in Children Younger Than 3 Years Prediction of Intent ARTICLE Robert G. Wells, MD; Christine Vetter, MD; Prakash Laud, PhD Objective: To determine whether certain computed tomographic
10/8/17. I have no disclosures. What are they? Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma
 I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation **
 PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation ** I. RECOGNITION A. History 1. Unexplained or un-witnessed injury 2.
PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation ** I. RECOGNITION A. History 1. Unexplained or un-witnessed injury 2.
Stair falls: caregiver s missed step as a source of childhood fractures
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0551-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Stair falls: caregiver s missed step as a source of childhood fractures Andrew T. Pennock George D. Gantsoudes Jennifer
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0551-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Stair falls: caregiver s missed step as a source of childhood fractures Andrew T. Pennock George D. Gantsoudes Jennifer
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications
 MWSUG 2017 - Paper DG02 Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications ABSTRACT Deanna Naomi Schreiber-Gregory, Henry M Jackson
MWSUG 2017 - Paper DG02 Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications ABSTRACT Deanna Naomi Schreiber-Gregory, Henry M Jackson
Are Gap and Cast Indices Predictors of Efficacy of Reduction in Fractures of Both Bones of the Leg? A Cohort Study
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.003 Are Gap and Cast Indices Predictors of Efficacy of Reduction in Fractures of Both Bones of the Leg? A Cohort Study Shalabh K, MS, Ajai S, MS, Vineet K, MS, Sabir
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.003 Are Gap and Cast Indices Predictors of Efficacy of Reduction in Fractures of Both Bones of the Leg? A Cohort Study Shalabh K, MS, Ajai S, MS, Vineet K, MS, Sabir
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHYSEAL FEMUR FRACTURE WITH INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL AND K. NAIL
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
Epidemiology of Venous Thromboembolism in the East. Heng Joo NG Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital Singapore
 Epidemiology of Venous Thromboembolism in the East Heng Joo NG Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital Singapore Early Literature Tinckler LF Br Med J 1964;1:502 Propagating a notion.. Hwang
Epidemiology of Venous Thromboembolism in the East Heng Joo NG Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital Singapore Early Literature Tinckler LF Br Med J 1964;1:502 Propagating a notion.. Hwang
The Role of Skeletal Survey in Identifying Non- Accidental Trauma in Pediatric Trauma Patients
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms GSBS Dissertations and Theses Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 6-13-2017 The Role of Skeletal Survey in Identifying Non- Accidental Trauma
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms GSBS Dissertations and Theses Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 6-13-2017 The Role of Skeletal Survey in Identifying Non- Accidental Trauma
Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis
 pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.422 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis Kyung Ho
pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.422 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis Kyung Ho
Is Hospital Admission Useful for Syncope Patients? Preliminary Results of a Multicenter Cohort
 Is Hospital Admission Useful for Syncope Patients? Preliminary Results of a Multicenter Cohort F. Dipaola, E. Pivetta, G. Costantino, G. Casazza, M.J. Reed, B. Sun, M. Solbiati, F. Barbic, D. Shiffer,
Is Hospital Admission Useful for Syncope Patients? Preliminary Results of a Multicenter Cohort F. Dipaola, E. Pivetta, G. Costantino, G. Casazza, M.J. Reed, B. Sun, M. Solbiati, F. Barbic, D. Shiffer,
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Interethnic variation in the prevalence of claustrophobia during MRI at Singapore General Hospital: does a wider bore MR scanner help?
 695819PSH0010.1177/2010105817695819Proceedings of Singapore HealthcareKoh et al. research-article2017 Original Article PROCEEDINGS OF SINGAPORE HEALTHCARE Interethnic variation in the prevalence of claustrophobia
695819PSH0010.1177/2010105817695819Proceedings of Singapore HealthcareKoh et al. research-article2017 Original Article PROCEEDINGS OF SINGAPORE HEALTHCARE Interethnic variation in the prevalence of claustrophobia
Predictors of Severity of Alcohol Withdrawal in Hospitalized Patients
 Elmer Original Article ress Predictors of Severity of Alcohol Withdrawal in Hospitalized Patients Radhames Ramos a, Thierry Mallet b, Anthony DiVittis c b, d, e, Ronny Cohen Abstract Background: Alcohol
Elmer Original Article ress Predictors of Severity of Alcohol Withdrawal in Hospitalized Patients Radhames Ramos a, Thierry Mallet b, Anthony DiVittis c b, d, e, Ronny Cohen Abstract Background: Alcohol
A record based study of frequency and pattern of medico-legal cases reported at a tertiary care hospital in Miraj
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Brahmankar TR et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Apr;4(4):1348-1352 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Brahmankar TR et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Apr;4(4):1348-1352 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Late diagnosis of influenza in adult patients during a seasonal outbreak
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2018;33:391-396 Late diagnosis of influenza in adult patients during a seasonal outbreak Seong-Ho Choi 1, Jin-Won Chung 1, Tark Kim 2, Ki-Ho Park 3, Mi Suk Lee 3, and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2018;33:391-396 Late diagnosis of influenza in adult patients during a seasonal outbreak Seong-Ho Choi 1, Jin-Won Chung 1, Tark Kim 2, Ki-Ho Park 3, Mi Suk Lee 3, and
A Probable Case of Child Abuse from Historic Gloucester
 A Probable Case of Child Abuse from Historic Gloucester Bernadette M Manifold Department of Archaeology, School of Human and Environmental Sciences, University of Reading, Whiteknights, Reading Address
A Probable Case of Child Abuse from Historic Gloucester Bernadette M Manifold Department of Archaeology, School of Human and Environmental Sciences, University of Reading, Whiteknights, Reading Address
6/23/2017. What do you see? skull fracture
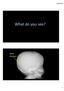 What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Public Health Sciences
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Public Health Sciences THE LENGTH OF STAY AND READMISSIONS IN MASTECTOMY PATIENTS A Thesis in Public Health Sciences by Susie Sun 2015
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Public Health Sciences THE LENGTH OF STAY AND READMISSIONS IN MASTECTOMY PATIENTS A Thesis in Public Health Sciences by Susie Sun 2015
Parental Attitudes toward Human Papilloma Virus Vaccine Participation of Adolescent Daughters in a Rural Population
 Diversity and Equality in Health and Care (2018) 15(4): 164-168 2018 Insight Medical Publishing Group Research Article Parental Attitudes toward Human Papilloma Virus Vaccine Participation of Adolescent
Diversity and Equality in Health and Care (2018) 15(4): 164-168 2018 Insight Medical Publishing Group Research Article Parental Attitudes toward Human Papilloma Virus Vaccine Participation of Adolescent
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic Spinal Compression Fractures
 J Bone Metab 2013;20:11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2013.20.1.11 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic
J Bone Metab 2013;20:11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2013.20.1.11 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic
Ankle fractures in patients with diabetes mellitus
 Lower limb Ankle fractures in patients with diabetes mellitus K. B. Jones, K. A. Maiers-Yelden, J. L. Marsh, M. B. Zimmerman, M. Estin, C. L. Saltzman From the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics,
Lower limb Ankle fractures in patients with diabetes mellitus K. B. Jones, K. A. Maiers-Yelden, J. L. Marsh, M. B. Zimmerman, M. Estin, C. L. Saltzman From the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics,
Statistical Reasoning in Public Health Biostatistics 612, 2009, HW#3
 Statistical Reasoning in Public Health Biostatistics 612, 2009, HW#3 1. A random sample of 200 patients admitted to an adult intensive care unit (ICU) was collected to examine factors associated with death
Statistical Reasoning in Public Health Biostatistics 612, 2009, HW#3 1. A random sample of 200 patients admitted to an adult intensive care unit (ICU) was collected to examine factors associated with death
Downloaded from by on 12/24/17 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
 Pediatric Imaging Prosser et al. Radiologic Dating of Pediatric Fractures Ingrid Prosser 1 Sabine Maguire 1 Sara K. Harrison 2 Mala Mann 3 Jonathan R. Sibert 1 Alison M. Kemp 1 Welsh Child Protection Systematic
Pediatric Imaging Prosser et al. Radiologic Dating of Pediatric Fractures Ingrid Prosser 1 Sabine Maguire 1 Sara K. Harrison 2 Mala Mann 3 Jonathan R. Sibert 1 Alison M. Kemp 1 Welsh Child Protection Systematic
Multicentre study of physical abuse and limb fractures in young children in the East Anglia Region, UK
 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough City Hospital, Peterborough, UK 2 Department of Paediatrics, Peterborough City Hospital, Peterborough, UK 3 Statistical Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge,
1 Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough City Hospital, Peterborough, UK 2 Department of Paediatrics, Peterborough City Hospital, Peterborough, UK 3 Statistical Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge,
Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin configuration
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:473 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0624-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:473 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0624-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin
Unplanned 30-Day Readmissions in Orthopaedic Trauma
 Unplanned 30-Day Readmissions in Orthopaedic Trauma Introduction: 30-day readmission is increasingly used as a hospital quality metric. The objective of this study was to describe the patient factors associated
Unplanned 30-Day Readmissions in Orthopaedic Trauma Introduction: 30-day readmission is increasingly used as a hospital quality metric. The objective of this study was to describe the patient factors associated
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Materials for Suicidal Behavior During Lithium and Valproate Medication: A Withinindividual Eight Year Prospective Study of 50,000 Patients With Bipolar Disorder Supplementary Methods We
Supplementary Materials for Suicidal Behavior During Lithium and Valproate Medication: A Withinindividual Eight Year Prospective Study of 50,000 Patients With Bipolar Disorder Supplementary Methods We
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript World J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 February 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
Shiu YK(1), Shek CC(1), Sin NC(2)
 Outcomes of 6 year Follow up of a Cohort of Infants of Substance Abusing Mothers Showed that The New Community Paediatric Service Model Achieved All the Objectives of Comprehensive Child Development Service
Outcomes of 6 year Follow up of a Cohort of Infants of Substance Abusing Mothers Showed that The New Community Paediatric Service Model Achieved All the Objectives of Comprehensive Child Development Service
Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in Appendicitis
 Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in Appendicitis Steven L. Lee, MD Chief of Pediatric Surgery, Harbor-UCLA Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics David Geffen School of Medicine at
Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in Appendicitis Steven L. Lee, MD Chief of Pediatric Surgery, Harbor-UCLA Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics David Geffen School of Medicine at
The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression between FBSS or Not
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
A new classification system of nasal contractures
 Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Epidemiology of adolescent and young adult hospital utilization for alcohol and drug use, poisoning, and suicide attempts in the United States
 Journal of Adolescent and Family Health Volume 6 Issue 2 Article 4 November 2014 Epidemiology of adolescent and young adult hospital utilization for alcohol and drug use, poisoning, and suicide attempts
Journal of Adolescent and Family Health Volume 6 Issue 2 Article 4 November 2014 Epidemiology of adolescent and young adult hospital utilization for alcohol and drug use, poisoning, and suicide attempts
Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Surveys
 J Bone Metab 2016;23:243-247 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.243 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the
J Bone Metab 2016;23:243-247 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.243 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the
ASJ. How Many High Risk Korean Patients with Osteopenia Could Overlook Treatment Eligibility? Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2014;8(6):729-734 High http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.729 risk patients with osteopenia How Many High Risk Korean Patients with
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2014;8(6):729-734 High http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.729 risk patients with osteopenia How Many High Risk Korean Patients with
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast
 The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
NICE guideline Published: 17 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng38
 Fractures (non-complex): assessment and management NICE guideline Published: 17 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng38 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Fractures (non-complex): assessment and management NICE guideline Published: 17 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng38 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
A Pair-Matched Case Control Study of Family-Environmental Factors Associated with ADHD in Chinese Children
 A Pair-Matched Case Control Study of Family-Environmental Factors Associated with ADHD in Chinese Children Xianming Carroll September 14 th 2016 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) A persistent
A Pair-Matched Case Control Study of Family-Environmental Factors Associated with ADHD in Chinese Children Xianming Carroll September 14 th 2016 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) A persistent
Management of Hip Fractures
 Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.008 Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures Pundkare GT, DNB Orthopaedics, Deshpande
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.008 Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures Pundkare GT, DNB Orthopaedics, Deshpande
Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures
 July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
Normal Value of Skull Base Angle. Using the Modified Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique in Thai Population
 Open Access Journal of Oral Health and Craniofacial Science Research Article Normal Value of Skull Base Angle ISSN 2573-6191 Using the Modified Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique in Thai Population Siriporn
Open Access Journal of Oral Health and Craniofacial Science Research Article Normal Value of Skull Base Angle ISSN 2573-6191 Using the Modified Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique in Thai Population Siriporn
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis
 Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Pitfalls in Paediatric Appendicitis: Highlighting Common Clinical Features of Missed Cases
 Original Article Pitfalls in Paediatric Appendicitis: Highlighting Common Clinical Features of Missed Cases Melanie D.W. Seah and Kee-Chong Ng, Department of Emergency Medicine, KK Women s and Children
Original Article Pitfalls in Paediatric Appendicitis: Highlighting Common Clinical Features of Missed Cases Melanie D.W. Seah and Kee-Chong Ng, Department of Emergency Medicine, KK Women s and Children
Massive Transfusion in Pediatric Trauma: Analysis of the National Trauma Databank
 Massive Transfusion in Pediatric Trauma: Analysis of the National Trauma Databank Michelle Shroyer, MPH, Russell Griffin, PhD, Vincent Mortellaro, MD, and Rob Russell MD, MPH Introduction Hemorrhage is
Massive Transfusion in Pediatric Trauma: Analysis of the National Trauma Databank Michelle Shroyer, MPH, Russell Griffin, PhD, Vincent Mortellaro, MD, and Rob Russell MD, MPH Introduction Hemorrhage is
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection
 Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Intake Form. Date: Referred By: Name: Phone Number: Religious Affiliation: Where are you currently staying? City?
 Intake Form Date: Referred By: Name: Phone Number: Email: Religious Affiliation: Where are you currently staying? City?: Birthdate: Age: Place of Birth: Citizenship: Race: Social Security Number: Marital
Intake Form Date: Referred By: Name: Phone Number: Email: Religious Affiliation: Where are you currently staying? City?: Birthdate: Age: Place of Birth: Citizenship: Race: Social Security Number: Marital
A study of the radiographic morphometry of the distal radius in a south Indian population
 Original Article Hand Microsurg 2018;7:9-15 doi:10.5455/handmicrosurg.285986 A study of the radiographic morphometry of the distal radius in a south Indian population Supreeth Nekkanti, Jacqueline Shah,
Original Article Hand Microsurg 2018;7:9-15 doi:10.5455/handmicrosurg.285986 A study of the radiographic morphometry of the distal radius in a south Indian population Supreeth Nekkanti, Jacqueline Shah,
Patterns of ADRs and Risk Factors Involved: Study In Cardiology Unit Of An Indian Tertiary Care Center
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pharmacology Volume 8 Number 1 Patterns of ADRs and Risk Factors Involved: Study In Cardiology Unit Of An Indian Tertiary Care Center S Kaur, V Kapoor, R Mahajan, M Lal,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pharmacology Volume 8 Number 1 Patterns of ADRs and Risk Factors Involved: Study In Cardiology Unit Of An Indian Tertiary Care Center S Kaur, V Kapoor, R Mahajan, M Lal,
Obesity and Control. Body Mass Index (BMI) and Sedentary Time in Adults
 Obesity and Control Received: May 14, 2015 Accepted: Jun 15, 2015 Open Access Published: Jun 18, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.14437/2378-7805-2-106 Research Peter D Hart, Obes Control Open Access 2015, 2:1
Obesity and Control Received: May 14, 2015 Accepted: Jun 15, 2015 Open Access Published: Jun 18, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.14437/2378-7805-2-106 Research Peter D Hart, Obes Control Open Access 2015, 2:1
RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES. It is far more common in adults than in children, (who more commonly fracture their neck of radius).
 RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the head of the radius are relatively common. The injury can be subtle unless specifically looked for. It is far more common in adults than in children,
RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the head of the radius are relatively common. The injury can be subtle unless specifically looked for. It is far more common in adults than in children,
 Geographia Napocensis Anul VI, Nr. 2, 2012 GEOCODING OF TRAUMA IN CHILDREN AS A MODELING OF CITY RISK ASSESSMENT AREAS (GIS BASED METHOD) DAMIAN ABSALON 1, BARBARA ŚLESAK 2, RYSZARD TOMASZEWSKI 2 Abstract:
Geographia Napocensis Anul VI, Nr. 2, 2012 GEOCODING OF TRAUMA IN CHILDREN AS A MODELING OF CITY RISK ASSESSMENT AREAS (GIS BASED METHOD) DAMIAN ABSALON 1, BARBARA ŚLESAK 2, RYSZARD TOMASZEWSKI 2 Abstract:
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline
 Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
BIOSTATISTICAL METHODS
 BIOSTATISTICAL METHODS FOR TRANSLATIONAL & CLINICAL RESEARCH PROPENSITY SCORE Confounding Definition: A situation in which the effect or association between an exposure (a predictor or risk factor) and
BIOSTATISTICAL METHODS FOR TRANSLATIONAL & CLINICAL RESEARCH PROPENSITY SCORE Confounding Definition: A situation in which the effect or association between an exposure (a predictor or risk factor) and
Fri., 10/17/14 Polytrauma, PAPER #74, 4:00 pm OTA 2014
 Fri., 10/17/14 Polytrauma, PAPER #74, 4:00 pm OTA 2014 Clinical Indications for CT Angiography in Lower Extremity Trauma Joseph T. Patterson, MD 1 ; Thomas Fishler, MD 2 ; Daniel D. Bohl, MPH 3 ; Michael
Fri., 10/17/14 Polytrauma, PAPER #74, 4:00 pm OTA 2014 Clinical Indications for CT Angiography in Lower Extremity Trauma Joseph T. Patterson, MD 1 ; Thomas Fishler, MD 2 ; Daniel D. Bohl, MPH 3 ; Michael
Interpersonal Conflict & Role Transitions Predict Poor Adherence to Aspirin after Acute Coronary Syndromes
 Interpersonal Conflict & Role Transitions Predict Poor Adherence to Aspirin after Acute Coronary Syndromes Ian M. Kronish, MD, MPH 1, Nina Rieckmann, PhD 2, Matthew M. Burg, PhD 1,3, Carmela Alcantara,
Interpersonal Conflict & Role Transitions Predict Poor Adherence to Aspirin after Acute Coronary Syndromes Ian M. Kronish, MD, MPH 1, Nina Rieckmann, PhD 2, Matthew M. Burg, PhD 1,3, Carmela Alcantara,
Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
12/13/16. Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016
 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
Prevalence of vertebral fractures on chest radiographs of elderly African American and Caucasian women
 Osteoporos Int (2011) 22:2365 2371 DOI 10.1007/s00198-010-1452-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of vertebral fractures on chest radiographs of elderly African American and Caucasian women D. Lansdown & B.
Osteoporos Int (2011) 22:2365 2371 DOI 10.1007/s00198-010-1452-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of vertebral fractures on chest radiographs of elderly African American and Caucasian women D. Lansdown & B.
OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE
 2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean university hospital pediatric dental clinic
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Guidelines to standards. Orthogeriatrics How The UK Care For Fragility Fractures
 Guidelines to standards Orthogeriatrics How The UK Care For Fragility Fractures Karen Hertz-SOTN Advanced Nurse Practitioner The NHFD Project - jointly led by BOA and BGS with the involvement of the RCN
Guidelines to standards Orthogeriatrics How The UK Care For Fragility Fractures Karen Hertz-SOTN Advanced Nurse Practitioner The NHFD Project - jointly led by BOA and BGS with the involvement of the RCN
A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the Little Finger
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
FATHER ABSENCE AND DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN ADOLESCENT GIRLS FROM A UK COHORT
 FATHER ABSENCE AND DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN ADOLESCENT GIRLS FROM A UK COHORT Iryna Culpin, Roberto Melotti, Ricardo Araya, Carol Joinson School of Social and Community Medicine Avon Longitudinal Study of
FATHER ABSENCE AND DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN ADOLESCENT GIRLS FROM A UK COHORT Iryna Culpin, Roberto Melotti, Ricardo Araya, Carol Joinson School of Social and Community Medicine Avon Longitudinal Study of
PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND
 JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Hue University, N 0 61, 2010 PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND Pornnapa
JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Hue University, N 0 61, 2010 PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND Pornnapa
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD
 Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
TITLE: A Data-Driven Approach to Patient Risk Stratification for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
 TITLE: A Data-Driven Approach to Patient Risk Stratification for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) AUTHORS: Tejas Prahlad INTRODUCTION Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a condition
TITLE: A Data-Driven Approach to Patient Risk Stratification for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) AUTHORS: Tejas Prahlad INTRODUCTION Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a condition
SURGERY OF THE HAND. Basosquamous Carcinoma of the Hand in a Radiologist with Prolonged Radiation Exposure INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT CASE REPORT
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2016;21(3):162-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.3.162 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Basosquamous
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2016;21(3):162-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.3.162 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Basosquamous
Attention Deficit Disorder. Evaluation Scale-Home Version 16. The Attention Deficit Disorders. Evaluation Scale-School Version 17
 The Development of an Educational and Screening Instrument for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in a Pediatric Residency Program Stephen P. Amos, Ph.D., Robert Wittler, M.D., Corrie Nevil, M.D.,
The Development of an Educational and Screening Instrument for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in a Pediatric Residency Program Stephen P. Amos, Ph.D., Robert Wittler, M.D., Corrie Nevil, M.D.,
Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation
 Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation Seung Woo Lee, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae General
Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation Seung Woo Lee, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae General
2/13/13. Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University
 Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Open Access Case Report DOI: /cureus.599. Ashok K. Rathod 1, Rakesh P. Dhake 1, Aditya Pawaskar 1
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.599 Minimally Invasive Treatment of a Complex Tibial Plateau Fracture with Diaphyseal Extension in a Patient with Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.599 Minimally Invasive Treatment of a Complex Tibial Plateau Fracture with Diaphyseal Extension in a Patient with Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report
Ammonia level at admission predicts in-hospital mortality for patients with alcoholic hepatitis
 Gastroenterology Report, 5(3), 2017, 232 236 doi: 10.1093/gastro/gow010 Advance Access Publication Date: 1 May 2016 Original article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ammonia level at admission predicts in-hospital mortality
Gastroenterology Report, 5(3), 2017, 232 236 doi: 10.1093/gastro/gow010 Advance Access Publication Date: 1 May 2016 Original article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ammonia level at admission predicts in-hospital mortality
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
CORE STANDARDS STANDARDS USED IN TARN REPORTS
 CORE STANDARDS Time to CT Scan BEST PRACTICE TARIFF SECTION 4.10 MAJOR TRAUMA 7 If the patient is admitted directly to the MTC or transferred as an emergency, the patient must be received by a trauma team
CORE STANDARDS Time to CT Scan BEST PRACTICE TARIFF SECTION 4.10 MAJOR TRAUMA 7 If the patient is admitted directly to the MTC or transferred as an emergency, the patient must be received by a trauma team
Neurologic improvement after thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar spinal cord (conus medullaris) injuries
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 1-2011 Neurologic improvement after thoracic, thoracolumbar, and
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 1-2011 Neurologic improvement after thoracic, thoracolumbar, and
