COMPLICATIONS OF BRACHYMETATARSIA REPAIR WITH CALLUS DISTRACTION
|
|
|
- Magnus Turner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C H A P T E R 4 1 COMPLICATIONS OF BRACHYMETATARSIA REPAIR WITH CALLUS DISTRACTION Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Brachymetatarsia represents one of the best and most useful indications for callus distraction in the foot. 1 The author believes callus distraction offers many advantages over other techniques for surgical correction of brachymetatarsia. Technically, the procedure is easier than procurement and placement of bone graft or complex lengthening osteotomies. Also, correction is closely monitored and achieved over time. The surgeon slowly obtains correction through a gradual process as opposed to being restricted to the degree of correction achieved at the time of surgery. Therefore, he or she can modify the amount of correction needed by lengthening more and possibly shortening slightly if over lengthened. This gradual lengthening process provides sufficient time for the soft tissues to slowly adapt; therefore, the chances of vascular insult are greatly decreased for callus distraction when compared with other procedures, since immediate, abrupt lengthening of the vasculature is avoided. It is because of these advantages and many other aspects unique to callus distraction that the author favors this surgical technique for brachymetatarsia repair. Although callus distraction has many advantages over other techniques for brachymetatarsia repair, it is not without its limitations. The postoperative course is rigorous and demanding on both the surgeon and the patient. Also, the success of this procedure is highly dependent upon patient compliance and the patient understanding the importance of their compliance. Due to the intense patient involvement postoperatively, this is not the procedure of choice for a potentially noncompliant patient. Careful patient selection is of the utmost importance when choosing this procedure for repair of brachymetatarsia. Patient education is one of the keys to a successful surgical result for brachymetatarsia repair with callus distraction. All relevant deformities, the amount of correction that can be obtained, the possible complications, and the intense postoperative course with which the patient will be intimately involved should be thoroughly discussed with the patient preoperatively. If the patient does not seem to comprehend the extent of their involvement postoperatively or understand that a postoperative complication can occur and is not uncommon, they should not proceed with the procedure. Also, even though this deformity has many cosmetic and psychological components, the author does not advocate this procedure strictly for cosmetic purposes. This surgical technique has many possible complications including scarring and persistent digital deformity, which can often be cosmetically displeasing and require further surgical intervention. The patient must weigh the benefits and risks of the surgical procedure and make an educated decision understanding all potential complications unique to this deformity prior to surgical intervention. COMPLICATIONS Although this surgical procedure is technically not that difficult to employ, there are many possible complications. Potential complications for brachymetatarsia repair with callus distraction include but are not limited to hypertrophic scarring, pin loosening, pin tract infections, flexion deformities or deviation of the digit, temporary malalignment, angulation of the metatarsal or malunion, decreased range of motion and stiffness at the metatarsophalangeal joint with or without subsequent arthritis, dislocation or subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joint, premature consolidation resulting in under-correction, prolonged consolidation time or non-union, over lengthening of the metatarsal, fracture through the bone callous, infection of the bone and or joint, and neurovascular injury. Although the list of potential complications for brachymetatarsia repair by callus distraction appears quite lengthy, fortunately, many of them are minor and resolve uneventfully when appropriate treatment is instilled. When complications are encountered, expedient identification of the problem and development of a treatment plan are paramount for overall success. The biggest pitfall for a surgeon can be avoiding the realization of a complication. The surgeon must be honest with the patient when a complication is present. Most complications can be treated effectively and successfully even though additional surgery may be warranted. If they are avoided however, they will only worsen and failure is sure to ensue.
2 230 CHAPTER 41 Surgeon Dependent Complications Complications may be surgeon dependent or iatrogenic, or they may be due to patient noncompliance, or they may just be inherent to the procedure itself. Although this is technically not a very difficult procedure to perform, proper execution is necessary to obtain a successful result and minimize potential complications. First, the surgeon has to be meticulous in the soft tissue dissection. There should be minimal periosteal reflection around the osteotomy site; in fact, the author chooses to leave the periosteum intact and perform the osteotomy through the periosteum. This helps maintain vascularity to the site and aids in osteogenesis during the distraction process. The osteotomy should be made in the proximal metaphysis of the metatarsal because it is a stable area filled with good cancellous bone. This again increases vascularity of the site and helps ensure new bone formation throughout the distraction process. Also, the osteotomy must be perpendicular to the long axis of the bone. If the osteotomy is not made properly, either because of the placement or the design, many possible complications, including malalignment, can result. Proper pin placement and alignment are also paramount for a successful outcome. The pins must be placed perpendicular to the metatarsal and should be parallel to one another. The external fixator frame should always be used as a guide for all pin placement. This helps ensure accurate distance between each pin and the osteotomy and also helps maintain alignment. If the pins are not placed properly, the pins will be placed under tension when trying to apply the external fixator increasing the risk of complications, such as malalignment and malunion, which can ultimately lead to metatarsophalangeal joint subluxation. Finally, the surgeon must closely monitor the patient during the postoperative course and supply a clear and concise postoperative regimen for the patient. The surgeon must give the patient detailed instructions about how much to turn, when to turn, and in which direction to turn the device. The author has found it helpful to distribute diagrams and specific, detailed instructions to the patient including a turning check-off sheet. The patient brings this check-off sheet to every appointment and it is dated and copied and placed in their chart. If the patient is honest in their documentation, this could aid the surgeon in determining if the turning increments are appropriate and are yielding the desired results. If it appears as if the distraction process is too slow, the increments can be increased and if it is too fast, they can be decreased. Close, weekly monitoring during the distraction process allows the surgeon to make modifications easily and effectively to produce a successful surgical result. Patient Dependent Complications Due to the significant involvement of the patient postoperatively, the success of callus distraction for brachymetatarsia repair is highly dependent on patient compliance. It is of the utmost importance that the patient understands the significance of their compliance in order to obtain a successful outcome. Proper patient selection, therefore, is critical for the surgeon when utilizing callus distraction for the repair of brachymetatarsia. Proper timing of the distraction is critical for a successful result. The patient is responsible for actually performing the distraction process and they must comply with the surgeons instructions at all times. For lesser metatarsals, a 1-week latency period is recommended before distraction is begun when the osteotomy is performed in the proximal metaphysis. Latency allows for an increase in vascularity and potential for bone formation. The author has found that the ideal rate of distraction for lesser metatarsals is 5/8 mm (0.625 mm) per day. This coincides with other recent surgeons recommending between 0.5 mm a day 2 to 0.7 mm a day. 3 The patient turns 1/8 of a turn 5 times a day. Smaller, more frequent turning intervals results in efficient osteogenesis and yields the best results. For patient compliance and comprehension however, ¼ turns may be easier for the patient to understand and have been effective as well. The surgeon can adjust the distraction rate as deemed necessary according to length obtained and callus formation visualized on radiographs. The patient must turn the device exactly the amount instructed by the surgeon. If they do not turn the device enough, the distraction will be too slow, and the area can begin to consolidate making further distraction impossible resulting in a continued shortened metatarsal. If they turn the device too much, the distraction will be too fast, and the gap may widen too quickly and a nonunion could result. Also, if the patient continues to turn the device, even after the surgeon has instructed them not to, the metatarsal will be over lengthened. One of the most common reasons for an unhappy or displeased patient postoperatively is that the toe is still shorter than they would like it to be. Many times the phalanx in the toe will be short as well as the metatarsal. When the metatarsal has reached its optimal length, the toe will probably still be short. The patient must understand that the metatarsal cannot be over lengthened and they should not try to make the toe longer because significant complications will most likely result. Over lengthening of the metatarsal
3 CHAPTER usually leads to subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joint and deviation of the digit. Unfortunately, when over lengthening of the metatarsal results, surgery is usually necessary to obtain full correction. If the patient does not understand that if their toe is short preoperatively, their toe may still be short even after adequate metatarsal length has been obtained, the procedure is doomed to failure. Finally, the patient should be kept nonweight bearing during the entire postoperative course until osseous consolidation has been achieved. Excessive weight-bearing forces on the metatarsal during the distraction process or ossification period could result in plastic deformation of the immature bone substance and a sagittal plane deformity. When weight bearing is initiated, the external fixator and pins should be left in place. It is felt that this provides some measure of protection against weight-bearing forces on the newly lengthened areas of bone. A gradual disassembly of the frame should then ensue allowing the osseous tissues to adapt to weightbearing stress over time. POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS In order to have a more organized approach during preoperative discussions with the patient concerning potential complications, they can be divided into 2 categories, minor and major. Minor complications commonly occur with this technique; fortunately however, these complications are typically treated with conservative measures and they usually resolve without any significant sequelae. If clinical symptoms persist from these minor complications, despite conservative therapies, additional surgery can be performed. This subsequent surgery typically involves more basic types of techniques such as soft tissue balancing, digital realignment, and scar excision. Major complications fortunately are less common; however, when they occur they typically require additional surgery for successful structural correction and relief of clinical symptoms. This additional surgery is usually more involved than those of minor complications and typically involves osseous reconstruction as well as soft tissue balancing. As with any other surgical procedure, a complication may begin as minor and progress to major sequelae if proper treatment is not instilled or the patient is noncompliant. The more commonly encountered complications will be reviewed in greater detail including treatment options. Minor Complications Hypertrophic scarring is a common complication that can result with callus distraction since the skin and all surrounding soft tissues are lengthened in addition to the bone with this procedure. Conservative measures can help reduce the thickened scar but if clinical symptoms persist surgical excision of the scar can be attempted. It is imperative that the surgeon discuss the possible complication of a thickened scar preoperatively with the patient when undergoing the callus distraction technique. If the patient is pursuing the surgery primarily for cosmesis, they must understand complications may result which may not be cosmetically pleasing. Pin loosening may also be encountered. When it occurs, it is typically the frame or hinge loosening around the pin, which can be easily fixed by tightening the device. Pin loosening within the bone typically does not occur. If the pin is placed appropriately intraoperatively, through two cortices, and there is no creation of stress risers, typically the pin does not loosen in the bone. If it appears that the pin is loosened in the bone then the surgeon should evaluate the patient for infection, possible trauma the patient could have experienced postoperatively, or noncompliance of the patient causing possible fracturing or displacement. Most pin tract infections that occur with this technique are minor complications and usually resolve with local pin and wound care and oral antibiotics. They may however, progress into major complications with significant sequelae; therefore, close monitoring during the postoperative course is essential. It is imperative that treatment be initiated immediately once a pin tract infection is suspected. A delay in treatment could end in disastrous results. Temporary malalignment of the osteotomy can also occur. If there is mild displacement or malalignment seen on immediate postoperative radiographs prior to the start of the distraction process, typically this malalignment resolves as the metatarsal is lengthened. This displacement can occur for various reasons. There may be excessive manipulation at the osteotomy secondary to the surgeon trying to ensure that the osteotomy is indeed through and through. There could also be excessive soft tissue reflection during the procedure destabilizing the osteotomy site. The osteotomy may be over compressed once the surgeon replaces the external fixator or instability at the osteotomy site may result during the actual frame application. Sometimes the pins have to be manipulated into the frame to fit appropriately and this can cause some displacement of the osteotomy. Typically, as the bone is distracted the soft tissues direct the bone back into a fully corrected position. If the malalignment occurs during the distraction process itself however, this is a different entity and usually it does not correct itself but worsens as the distraction
4 232 CHAPTER 41 process proceeds. This malalignment can result in subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joint and digital deviation and is typically the result of inaccurate osteotomy design or poor pin alignment. There may however, be an angulation deformity in the metatarsal itself seen on radiographs preoperatively that becomes exaggerated as the metatarsal is lengthened. If malalignment occurs, the distraction process should still be continued until optimal metatarsal length is obtained. Many times, the metatarsal malalignment that is visualized on radiographs is clinically asymptomatic and a good postoperative result ensues. If the malalignment ultimately results in persistent postoperative pain or deformity, additional surgery can be performed to obtain proper alignment of the metatarsal and respective metatarsophalangeal joint and digit. Probably the most common complication with this procedure is subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joint and deviation of the toe. This is usually a definite consequence when the metatarsal is over lengthened but it can also occur even when optimal metatarsal length is obtained (Figure 1). When the metatarsal is lengthened, all of the soft tissues including the extensor and flexor tendons are also lengthened. If the tendons do not adapt adequately, despite the gradual lengthening process, tension is placed on the tendons and the metatarsophalangeal joint can sublux and the toe can deviate and rub on an adjacent toe. Sometimes these deformities are minor and resolve with temporary taping and/or strapping during the distraction process. If the subluxation and digital deformity persist and are clinically symptomatic however, additional surgery may be needed. Typically this subsequent surgery consists of metatarsophalangeal joint release with extensor tendon lengthening and temporary Kirschner wire (K-wire) fixation to help maintain joint alignment. Major Complications Over lengthening is one of the most difficult complications to deal with and is usually due to patient noncompliance (Figure 2). The distraction process should be discontinued when the metatarsal has reached optimal length to produce a normal metatarsal parabola. It is recommended that the amount of lengthening achieved should not exceed 40% of the original length of the metatarsal. 4 When the metatarsal is lengthened greater than 40% of its preoperative length, complications such as decreased range of motion and joint stiffness of the metatarsophalangeal joint, subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joint with digital deviation, and neurovascular compromise can result. It is critical that once the appropriate metatarsal parabola is obtained, the distraction process must stop; even if the toe still appears short. This can be a very difficult concept for the patient to understand. Many times, as was stated previously, the phalanges in the toe are short as well as the metatarsal so once the metatarsal has reached the ideal length, the toe will still probably be short compared with the adjacent digits. Patients will visually see that their toe is still short and may try to lengthen the Figure 1A. Postoperative radiograph at 4 months displays complete consolidation and good metatarsal length. Despite the ideal metatarsal length however, metatarsophalangeal joint subluxation and digital deviation occurred requiring additional surgery. Figure 1B. Extensor tendon lengthening with metatarsophalangeal joint release and temporary K- wire fixation was performed to gain full correction.
5 CHAPTER Figure 2A. At 5 weeks postoperative, optimal metatarsal length was obtained and the patient was instructed to discontinue the distraction process. Figure 2B. The patient continued to turn the device to try to lengthen her toe further despite instructions from the surgeon. At 8 weeks postoperative, the metatarsal is over-lengthened and there is subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joint. Figure 2C. At 6 months postoperative, significant subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joint is noted and the fourth toe is deviated laterally onto the fifth toe. Additional surgery was performed at this point to shorten the metatarsal and realign the digit and metatarsophalangeal joint. Figure 2D. A shortening metatarsal osteotomy was performed and the metatarsophalangeal joint and fourth toe were realigned and maintained with temporary K-wire fixation. This radiograph reveals complete healing and patient satisfaction at 10 months postoperatively from the original callus distraction. Although the fourth metatarsal is still somewhat longer than ideally desired, good clinical results and patient satisfaction was achieved.
6 234 CHAPTER 41 metatarsal more in an attempt to make their toe longer. It is critical for the surgeon to identify this deformity preoperatively if it exists and have a thorough discussion with the patient concerning its effect on the clinical results. If it is not discussed preoperatively, the patient will not understand why their toe still appears short because they believe the surgery should have corrected their short toe. Sometimes, if the metatarsal is over lengthened the reverse of the distraction process can be employed and the metatarsal can be shortened back to its appropriate length as previously described. Unfortunately, when the metatarsal is over lengthened, the toe usually dislocates at the metatarsophalangeal joint and additional surgery is required for structural correction and proper realignment. This surgery typically consists of shortening the metatarsal back to its appropriate length, releasing the metatarsophalangeal joint, and maintaining alignment with temporary K-wire fixation. It must be stressed that if the metatarsal is over lengthened, it must be shortened in order to release tension from within the joint and surrounding soft tissues or persistent subluxation and reoccurrence will most likely ensue. Premature consolidation and nonunion are rare with the authors chosen technique. The rate of distraction is the key to avoiding these potential complications. Smaller, more frequent intervals for distraction are recommended. The turning rate preferred by the author for lesser metatarsals is 1/8 mm 5 times a day. This rate has been shown to favor a more gradual relaxation of the surrounding soft tissues producing a more stable neurovascular environment and more efficient osteogenesis. This rate can be modified and increased if premature consolidation is of a concern. Likewise, the rate can be decreased if the distraction appears to be progressing too quickly. Monitoring the distraction process closely and making modifications as necessary will ensure an efficient remodeling process. The author has never experienced fracture through the bone callus. The osteotomy is made in the proximal metaphyseal bone, which is a stable area of bone. Authors that have encountered fracture through the bone callus as a complication of this procedure have typically performed the osteotomy through the diaphysis. 5 Also, the author begins weight bearing prior to the removal of the external fixator. This allows the bone to slowly adapt to the weightbearing stresses over time and helps avoid fracturing through the newly consolidated bone. Fortunately, the author has never experienced a vascular injury with the callus distraction technique. Since the lengthening is obtained gradually over several weeks, the vascular structures have time to adapt and abrupt vasospasms of the vasculature are avoided. Although neuritis has been encountered by the author, it has always resolved with conservative measures and the author has not experienced any significant or permanent nerve damage with this procedure. CONCLUSION Brachymetatarsia repair with callus distraction is a demanding procedure postoperatively on both the surgeon and the patient but it can be a very rewarding surgery with limited complications if the surgeon is diligent in the surgical execution and the patient is compliant with the postoperative regimen. If the patient is educated preoperatively about the deformity itself, the vigorous postoperative course, and all potential complications, they are more likely to have a successful result even if complications arise. Unfortunately, there are a fair amount of complications associated with this procedure and although many of them are minor, the patient must be adequately informed. Many patients are eager to pursue this surgery to improve cosmesis and they can be discouraged postoperatively if their toe is still shorter than they think it should be or if they have a thickened scar. A well-educated patient should understand the potential complications of the procedure and be able to weigh the risks and benefits of the surgery. If they then choose to pursue the surgery, this knowledge should help them have realistic expectations and will usually result in a happier postoperative patient and a higher surgical success. REFERENCES 1. Banks AS, Downey MS, Martin DE, Miller SJ. McGlamry s Comprehensive Textbook of Foot Surgery, 3rd Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p Song HR, Oh CW, Kyung HS. Fourth brachymetatarsia treated with distraction osteogenesis. Foot Ankle Int 2003;24: Wada A, Bensahel H, Takamura K, et al. Metatarsal lengthening by callus distraction for brachymetatarsia. J Pediatr Orthop 2004;13: Masada K, Fujita S, Fuji T, Ohno H. Complications following metatarsal lengthening by callus distraction for brachymetatarsia. J Pediatr Orthop 1999;19: Wilusz PM, Van P, Pupp GR. Complications associated with distraction osteogenesis for the correction of brachymetatarsia: a review of five procedures. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2007;97:
Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 1014 1019 CASE REPORT Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia Naoto Yamada*, Yoshihiro Yasuda, Nobuko Hashimoto,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 1014 1019 CASE REPORT Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia Naoto Yamada*, Yoshihiro Yasuda, Nobuko Hashimoto,
RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF END-TO-END DIGITAL ARTHRODESIS
 C H A P T E R 1 7 RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF END-TO-END DIGITAL ARTHRODESIS Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM Michael S. Downey, DPM Digital deformities are one of the most common entities we face as foot and
C H A P T E R 1 7 RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF END-TO-END DIGITAL ARTHRODESIS Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM Michael S. Downey, DPM Digital deformities are one of the most common entities we face as foot and
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia
 220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL
 C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia. Case Report and Review of the Literature
 The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy
 METATARSAL BONES LENGTHENING WITH LAKI MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy alexander@kirienko.com Alexander KIRIENKO, MD
METATARSAL BONES LENGTHENING WITH LAKI MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy alexander@kirienko.com Alexander KIRIENKO, MD
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Digital Surgery Complications
 Annual Surgical Conference 2018 Digital Surgery Complications Zeeshan S. Husain, DPM, FACFAS, FASPS Great Lakes Foot and Ankle Institute September 21, 2018 None Disclosures Presentation Outline Differentials
Annual Surgical Conference 2018 Digital Surgery Complications Zeeshan S. Husain, DPM, FACFAS, FASPS Great Lakes Foot and Ankle Institute September 21, 2018 None Disclosures Presentation Outline Differentials
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. MiniRail System. Part B: Foot Applications. By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ALWAYS INNOVATING
 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ALWAYS INNOVATING ORDERING INFORMATION Sterilization box, empty M190 Can accommodate: M101 Standard MiniRail
14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ALWAYS INNOVATING ORDERING INFORMATION Sterilization box, empty M190 Can accommodate: M101 Standard MiniRail
Lengthening of fourth brachymetatarsia by three different surgical techniques
 Lengthening of fourth brachymetatarsia by three different surgical techniques W.-C. Lee, J. H. Yoo, J.-S. Moon From Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea W.-C. Lee, Md, PhD, Professor J.-S. Moon, MD, Orthopaedic
Lengthening of fourth brachymetatarsia by three different surgical techniques W.-C. Lee, J. H. Yoo, J.-S. Moon From Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea W.-C. Lee, Md, PhD, Professor J.-S. Moon, MD, Orthopaedic
MiniRail System. Part B: Foot Applications. By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito
 Q U I C K R E F E R E N C E G U I D E 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ORDERING INFORMATION MiniRail System Kit, M190C Contents: M 101 Standard
Q U I C K R E F E R E N C E G U I D E 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ORDERING INFORMATION MiniRail System Kit, M190C Contents: M 101 Standard
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Minimally Invasive Bunionectomy: The Lam Modification of the Traditional Distal First Metatarsal Osteotomy Bunionectomy
 CHAPTER 2 Minimally Invasive Bunionectomy: The Lam Modification of the Traditional Distal First Metatarsal Osteotomy Bunionectomy Kevin Lam, DPM Rikhil Patel, DPM Thomas Merrill, DPM Hallux abducto valgus
CHAPTER 2 Minimally Invasive Bunionectomy: The Lam Modification of the Traditional Distal First Metatarsal Osteotomy Bunionectomy Kevin Lam, DPM Rikhil Patel, DPM Thomas Merrill, DPM Hallux abducto valgus
HEMI IMPLANT ARTHROPLASTY FOR THE SECOND METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINT
 C H A P T E R 1 5 HEMI IMPLANT ARTHROPLASTY FOR THE SECOND METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINT Joe T. Southerland, DPM Mickey D. Stapp, DPM INTRODUCTION Hemi-implant arthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal
C H A P T E R 1 5 HEMI IMPLANT ARTHROPLASTY FOR THE SECOND METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINT Joe T. Southerland, DPM Mickey D. Stapp, DPM INTRODUCTION Hemi-implant arthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal
Section 6: Preoperative Planning
 Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity
 REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures
 FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
CORRECTING HAMMERTOE DEFORMITIES UTILIZING AN INTRAMEDULLARY DEVICE: Case Reports
 C H A P T E R 1 1 CORRECTING HAMMERTOE DEFORMITIES UTILIZING AN INTRAMEDULLARY DEVICE: Case Reports B. Cory Brown, DPM Robert K. Cohen, DPM Jason R. Miller, DPM Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most
C H A P T E R 1 1 CORRECTING HAMMERTOE DEFORMITIES UTILIZING AN INTRAMEDULLARY DEVICE: Case Reports B. Cory Brown, DPM Robert K. Cohen, DPM Jason R. Miller, DPM Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most
COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION
 C H A P T E R 3 0 COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most common fixation for proximal interphalangeal fusion
C H A P T E R 3 0 COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most common fixation for proximal interphalangeal fusion
REPAIR OF THE DISPLACED AUSTIN OSTEOTOMY
 C H A P T E R 2 1 REPAIR OF THE DISPLACED AUSTIN OSTEOTOMY John V. Vanore, DPM INTRODUCTION Bunion surgery is frequently performed by foot and ankle surgeons. Generally, bunion surgery is quite predictable,
C H A P T E R 2 1 REPAIR OF THE DISPLACED AUSTIN OSTEOTOMY John V. Vanore, DPM INTRODUCTION Bunion surgery is frequently performed by foot and ankle surgeons. Generally, bunion surgery is quite predictable,
Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction
 Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction VOLUME: 23 PUBLICATION DATE: Apr 01 2010 Issue Number: 4 April 2010 Author(s): Lawrence DiDomenico, DPM, FACFAS While tendon transfers have
Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction VOLUME: 23 PUBLICATION DATE: Apr 01 2010 Issue Number: 4 April 2010 Author(s): Lawrence DiDomenico, DPM, FACFAS While tendon transfers have
ANATOMIC APPROACH TO PREPARATION AND FUSION OF THE INTERPHALANGEAL JOINT
 C H A P T E R 1 2 ANATOMIC APPROACH TO PREPARATION AND FUSION OF THE INTERPHALANGEAL JOINT Robert B. Weinstein, DPM INTRODUCTION The complex combination of deformities grouped under the umbrella hammertoes
C H A P T E R 1 2 ANATOMIC APPROACH TO PREPARATION AND FUSION OF THE INTERPHALANGEAL JOINT Robert B. Weinstein, DPM INTRODUCTION The complex combination of deformities grouped under the umbrella hammertoes
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
DARCO. Bow 2 Plate SURGIC AL TECHNIQUE
 DARCO Bow 2 Plate SURGIC AL TECHNIQUE Contents 2 Preface 3 Chapter 1 4 Chapter 2 5 6 7 8 9 Appendix 10 10 11 Intended Use Indications/Contraindications Design Rationale Preoperative Planning Surgical Technique
DARCO Bow 2 Plate SURGIC AL TECHNIQUE Contents 2 Preface 3 Chapter 1 4 Chapter 2 5 6 7 8 9 Appendix 10 10 11 Intended Use Indications/Contraindications Design Rationale Preoperative Planning Surgical Technique
Increased pressures at
 Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna with Distraction Osteogenesis: Three Cases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures:
 Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE. Limb Reconstruction System. Part B: Correction of Deformities. By Dr. S. Nayagam
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
Operative Technique. by PROF. NAYAGAM. LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities
 Operative Technique by PROF. NAYAGAM LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities 11 Quick Reference Guide CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part A: General Principles Page N o I Introduction
Operative Technique by PROF. NAYAGAM LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities 11 Quick Reference Guide CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part A: General Principles Page N o I Introduction
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Workshop Outline. Pre-operative planning
 Workshop Objective To build and apply the True/Lok TM circular external fixator frame for correction of the Charcot forefoot deformity (Lisfranc fracture dislocation) Workshop Outline Pre-operative planning
Workshop Objective To build and apply the True/Lok TM circular external fixator frame for correction of the Charcot forefoot deformity (Lisfranc fracture dislocation) Workshop Outline Pre-operative planning
Lesser Toe Correction
 Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Lesser Toe Correction Lesser toe deformities are classified
Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Lesser Toe Correction Lesser toe deformities are classified
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
PHALANGEAL BASE AUTOGRAFT FOR THE CORRECTION OF THE SUBLUXED HAMMERTOE
 C H A P T E R 5 PHALANGEAL BASE AUTOGRAFT FOR THE CORRECTION OF THE SUBLUXED HAMMERTOE Raymond G. Cavaliere, DPM INTRODUCTION Hammertoes can be classified as simple, moderate, and severe. The deformities
C H A P T E R 5 PHALANGEAL BASE AUTOGRAFT FOR THE CORRECTION OF THE SUBLUXED HAMMERTOE Raymond G. Cavaliere, DPM INTRODUCTION Hammertoes can be classified as simple, moderate, and severe. The deformities
Distraction osteogenesis for brachymetatarsia: Clinical results and implications on the metatarsophalangeal joint
 Original Article Distraction osteogenesis for brachymetatarsia: Clinical results and implications on the metatarsophalangeal joint Amgad M. Haleem 1,2, Angela Balagadde 4, Eugene Wilson Borst 3, Huong
Original Article Distraction osteogenesis for brachymetatarsia: Clinical results and implications on the metatarsophalangeal joint Amgad M. Haleem 1,2, Angela Balagadde 4, Eugene Wilson Borst 3, Huong
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity
 Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
Stretch Beyond Your Expectations.
 CLINICIAN INSTRUCTIONS Dynasplint Toe Metatarsophalangeal Extension System Type III Corporate Headquarters: 800.638.6771 toll-free 800.380.3784 fax Canada: 800.668.9139 toll-free 905.851.3494 fax Europe:
CLINICIAN INSTRUCTIONS Dynasplint Toe Metatarsophalangeal Extension System Type III Corporate Headquarters: 800.638.6771 toll-free 800.380.3784 fax Canada: 800.668.9139 toll-free 905.851.3494 fax Europe:
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Joint Preserving Surgery in Severe Forefoot Disorders
 Joint Preserving Surgery in Severe Forefoot Disorders J ORTHOP TRAUMA SURG REL RES 4 (12) 2008 Review article LOUIS S. BAROUK*, PIERRE BAROUK** * 39, Chemin de la Roche, 33370, Yvrac, France ** Clinique
Joint Preserving Surgery in Severe Forefoot Disorders J ORTHOP TRAUMA SURG REL RES 4 (12) 2008 Review article LOUIS S. BAROUK*, PIERRE BAROUK** * 39, Chemin de la Roche, 33370, Yvrac, France ** Clinique
Hallux Malleus develops after Flexible Hallux Varus correction with Tensioned Suture Device: A Case Report
 The Foot and nkle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & nkle Foundation Hallux Malleus develops after Flexible Hallux Varus correction with Tensioned Suture Device: Case Report
The Foot and nkle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & nkle Foundation Hallux Malleus develops after Flexible Hallux Varus correction with Tensioned Suture Device: Case Report
Fracture and Dislocation of the Carpus ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Small-wire circular fixators and hybrid external fixation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
A New Incisional Approach to the Rheumatoid Foot
 A New Incisional Approach to the Rheumatoid Foot The authors introduce a new incisional approach to surgery of the rheumatoid foot. Advantages and disadvantages are presented. Historical comparisons are
A New Incisional Approach to the Rheumatoid Foot The authors introduce a new incisional approach to surgery of the rheumatoid foot. Advantages and disadvantages are presented. Historical comparisons are
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016
 SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
Dorsiflexory Wedge Osteotomy to Treat Freiberg s Infraction of the Second Metatarsal Head: A case report
 Open Access Publication Dorsiflexory Wedge Osteotomy to Treat Freiberg s Infraction of the Second Metatarsal Head: A case report 1 2 by Georgeanne Botek, DPM, FACFAS, Martha A. Anderson, DPM, George Balis,
Open Access Publication Dorsiflexory Wedge Osteotomy to Treat Freiberg s Infraction of the Second Metatarsal Head: A case report 1 2 by Georgeanne Botek, DPM, FACFAS, Martha A. Anderson, DPM, George Balis,
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Introduction Basics MIS Screw 2 System Characteristics 2 Indication 2
 Clinical Advisor M. Walther. M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Head of Department Centre for Foot and Ankle Surgery Schön Klinik München Harlaching FIFA Medical Centre Table of Contents Introduction
Clinical Advisor M. Walther. M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Head of Department Centre for Foot and Ankle Surgery Schön Klinik München Harlaching FIFA Medical Centre Table of Contents Introduction
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
THE FIBULAR SESAMOID ELEVATOR: A New Instrument to Aid the Lateral Release in Hallux Valgus Surgery
 C H A P T E R 1 4 THE FIBULAR SESAMOID ELEVATOR: A New Instrument to Aid the Lateral Release in Hallux Valgus Surgery Thomas F. Smith, DPM Lopa Dalmia, DPM INTRODUCTION Hallux valgus surgery is a complex
C H A P T E R 1 4 THE FIBULAR SESAMOID ELEVATOR: A New Instrument to Aid the Lateral Release in Hallux Valgus Surgery Thomas F. Smith, DPM Lopa Dalmia, DPM INTRODUCTION Hallux valgus surgery is a complex
A pictorial review of reconstructive foot and ankle surgery: elective lesser forefoot procedures
 A pictorial review of reconstructive foot and ankle surgery: elective lesser forefoot procedures Andrew J Meyr 1*, Laura Sansosti 1, Sayed Ali 2 1. Department of Podiatric Surgery, Temple University School
A pictorial review of reconstructive foot and ankle surgery: elective lesser forefoot procedures Andrew J Meyr 1*, Laura Sansosti 1, Sayed Ali 2 1. Department of Podiatric Surgery, Temple University School
SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT
 C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture
 Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture Robert W. Mendicino, DPM, FACFAS, 1 Lara J. Murphy, DPM, 2 Michael P. Maskill, DPM, 3 Alan R. Catanzariti,
Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture Robert W. Mendicino, DPM, FACFAS, 1 Lara J. Murphy, DPM, 2 Michael P. Maskill, DPM, 3 Alan R. Catanzariti,
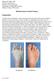
Lesser MPJ Hemi Implant
 Lesser MPJ Hemi Implant Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Lesser MPJ Hemi Implant is a simple, durable, metallic hemiarthroplasty resurfacing prosthesis for the treatment of arthritis, Freiberg
Lesser MPJ Hemi Implant Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Lesser MPJ Hemi Implant is a simple, durable, metallic hemiarthroplasty resurfacing prosthesis for the treatment of arthritis, Freiberg
PROXIMAL TIBIAL PLATE
 SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
Implantable K-wire SURGIC A L T ECHNIQUE
 Implantable K-wire SURGIC A L T ECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Product Information 4 Device Description 4 Indications 4 Contraindications Chapter 2 5 Surgical Technique 5 Hammertoe Correction 6 MTP Joint
Implantable K-wire SURGIC A L T ECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Product Information 4 Device Description 4 Indications 4 Contraindications Chapter 2 5 Surgical Technique 5 Hammertoe Correction 6 MTP Joint
Soft Tissue Rebalancing Procedures for the Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformities
 Soft Tissue Rebalancing Procedures for the Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformities NO DISCLOSURES Objectives The main objectives of any procedure in hallux abducto valgus surgery are to correct the deformity,
Soft Tissue Rebalancing Procedures for the Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformities NO DISCLOSURES Objectives The main objectives of any procedure in hallux abducto valgus surgery are to correct the deformity,
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
Weil osteotomy and flexor to extensor transfer for irreparable plantar plate tear: prospective study
 Weil osteotomy and flexor to extensor transfer for irreparable plantar plate tear: prospective study Daniel Baumfeld, MD Fernando Raduan, MD Fernanda Catena, MD Tania Mann, MD Caio Nery, MD Disclosure
Weil osteotomy and flexor to extensor transfer for irreparable plantar plate tear: prospective study Daniel Baumfeld, MD Fernando Raduan, MD Fernanda Catena, MD Tania Mann, MD Caio Nery, MD Disclosure
Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement: Case Series
 737481FAIXXX10.1177/1071100717737481Foot & Ankle InternationalDa Cunha et al research-article2017 Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement:
737481FAIXXX10.1177/1071100717737481Foot & Ankle InternationalDa Cunha et al research-article2017 Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement:
DuaFit. Proximal Interphal angeal Impl ant
 DuaFit Proximal Interphal angeal Impl ant DUAFIT - TABLE OF CONTENTS PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3 INDICATIONS 6 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE #1 7 Without guide wire (DuaFit 0 10 17 ) SURGICAL TECHNIQUE #2 14 With guide
DuaFit Proximal Interphal angeal Impl ant DUAFIT - TABLE OF CONTENTS PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3 INDICATIONS 6 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE #1 7 Without guide wire (DuaFit 0 10 17 ) SURGICAL TECHNIQUE #2 14 With guide
Bunion Surgery. This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155).
 Bunion Surgery This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155). Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments
Bunion Surgery This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155). Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments
A Patient information guide to. Bunion Correction. Foot and Ankle Unit. Mr Amit Amin Mr Ali Abbasian BUNION CORRECTION (SCARF/AKIN) JAN
 A Patient information guide to Bunion Correction Foot and Ankle Unit Mr Amit Amin Mr Ali Abbasian BUNION CORRECTION (SCARF/AKIN) JAN 2016 1 What does surgery involve? Surgery to correct a bunion is not
A Patient information guide to Bunion Correction Foot and Ankle Unit Mr Amit Amin Mr Ali Abbasian BUNION CORRECTION (SCARF/AKIN) JAN 2016 1 What does surgery involve? Surgery to correct a bunion is not
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months.
 Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children
 PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
Guidance for the Physiotherapy Management of Patients Undergoing Limb Reconstruction with a Circular Frame External Fixator.
 Guidance for the Physiotherapy Management of Patients Undergoing Limb Reconstruction with a Circular Frame External Fixator. Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 TARGET AUDIENCE... 2 KEY CHANGES FROM PREVIOUS
Guidance for the Physiotherapy Management of Patients Undergoing Limb Reconstruction with a Circular Frame External Fixator. Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 TARGET AUDIENCE... 2 KEY CHANGES FROM PREVIOUS
Other Upper Extremity Trauma. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin
 Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot
 168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
pedcat Clinical Case Studies
 pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Goals. Initial management skeletal trauma. Physical Exam ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT 12/4/2010
 ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
Kocaoglu, Mehmet MD; Eralp, Levent MD; Sen, Cengiz MD; Cakmak, Mehmet MD; Dincyürek, Hakan MD; Göksan, S. Bora MD
 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion
 Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Thumbs Up! A Novel Use of the Acutrak Screw Fixation System for the Management of Triphalangeal Thumb
 Thumbs Up! A Novel Use of the Acutrak Screw Fixation System for the Management of Triphalangeal Thumb Z. Ahmad, BSc(Hons), MBBS, MRCS, and C. N. McGuiness, MBBS, FRCS(Plast) Odstock Centre for Burns and
Thumbs Up! A Novel Use of the Acutrak Screw Fixation System for the Management of Triphalangeal Thumb Z. Ahmad, BSc(Hons), MBBS, MRCS, and C. N. McGuiness, MBBS, FRCS(Plast) Odstock Centre for Burns and
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE
 DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
Minimally Invasive Bunion Surgery: Methods and Outcomes
 Minimally Invasive Bunion Surgery: Methods and Outcomes Hummira H. Abawi, DPM Diplomate ABPM, AACFAS Instructor of Orthopedics, University of Maryland Medical Center Director of Education, Maryland VA
Minimally Invasive Bunion Surgery: Methods and Outcomes Hummira H. Abawi, DPM Diplomate ABPM, AACFAS Instructor of Orthopedics, University of Maryland Medical Center Director of Education, Maryland VA
Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery
 Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
19 Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsocuneiform Joint
 19 Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsocuneiform Joint CHARLES GUDAS Abduction of the first metatarsal to correct metatarsus primus varus and hallux valgus was first described by Albrecht in 1911. 1 Lapidus
19 Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsocuneiform Joint CHARLES GUDAS Abduction of the first metatarsal to correct metatarsus primus varus and hallux valgus was first described by Albrecht in 1911. 1 Lapidus
Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery
 Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery A bunion (also called hallux
Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery A bunion (also called hallux
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
TABLE E-1 Complications and Clinical Remarks for Pediatric Humeral Lengthening Procedures Study Complications (No.) Clinical Remarks*
 Page 1 TABLE E-1 Complications and Clinical Remarks for Pediatric Humeral Lengthening Procedures Study Complications (No.) Clinical Remarks* Janovec 12 Infection (4), radial nerve palsy (1), radial and
Page 1 TABLE E-1 Complications and Clinical Remarks for Pediatric Humeral Lengthening Procedures Study Complications (No.) Clinical Remarks* Janovec 12 Infection (4), radial nerve palsy (1), radial and
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Functional Evaluation after the Treatment of Brachymetatarsia through Bone Lengthening With Callotaxis by One Year of Follow-Up in Adult Patients
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Functional Evaluation after the Treatment of Brachymetatarsia through Bone Lengthening With Callotaxis by One Parra Tellez Patricia 1 *, Lezama Peniche
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Functional Evaluation after the Treatment of Brachymetatarsia through Bone Lengthening With Callotaxis by One Parra Tellez Patricia 1 *, Lezama Peniche
Long Oblique Distal Osteotomy of the Fifth Metatarsal for Correction of Tailor s Bunion: A Retrospective Review
 Long Oblique Distal Osteotomy of the Fifth Metatarsal for Correction of Tailor s Bunion: A Retrospective Review Barry P. London, DPM, 1 Stephen F. Stern, DPM, 2 Mark A. Quist, DPM, 3 Robert K. Lee, DPM,
Long Oblique Distal Osteotomy of the Fifth Metatarsal for Correction of Tailor s Bunion: A Retrospective Review Barry P. London, DPM, 1 Stephen F. Stern, DPM, 2 Mark A. Quist, DPM, 3 Robert K. Lee, DPM,
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS
 RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE: JONES FRACTURE USING THE PRECISION JONES FRACTURE SCREW SYSTEM
 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The PRECISION Jones Fracture Screw System offers extensive options of Type II Anodized Titanium screws. System-specific instrumentation is designed to address procedural challenges
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The PRECISION Jones Fracture Screw System offers extensive options of Type II Anodized Titanium screws. System-specific instrumentation is designed to address procedural challenges
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Metacarpal Lengthening in Adults With Brachymetacarpia
 736859HANXXX10.1177/1558944717736859HANDLam et al research-article2017 Surgery Article Metacarpal Lengthening in Adults With Brachymetacarpia HAND 1 7 The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
736859HANXXX10.1177/1558944717736859HANDLam et al research-article2017 Surgery Article Metacarpal Lengthening in Adults With Brachymetacarpia HAND 1 7 The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
