Indirect MR Arthrographic Findings of Adhesive Capsulitis
|
|
|
- Amber McDonald
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Song et al. MR Arthrography of Adhesive Capsulitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kyoung Doo Song 1 Jong Won Kwon Young Cheol Yoon Sang-Hee Choi Song KD, Kwon JW, Yoon YC, Choi SH Keywords: adhesive capsulitis, arthrography, MRI, shoulder, sports medicine DOI: /AJR Received November 8, 2010; accepted after revision May 18, All authors: Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 50, Ilwon-Dong, Kangnam-Ku, Seoul , Korea. Address correspondence to J. W. Kwon (jwjwkwon@gmail.com). WEB This is a Web exclusive article. AJR 2011; 197:W1105 W X/11/1976 W1105 American Roentgen Ray Society Indirect MR Arthrographic Findings of Adhesive Capsulitis OBJECTIVE. The objective of our study was to compare the indirect MR arthrographic findings of patients with adhesive capsulitis and patients without adhesive capsulitis. MATERIALS AND METHODS. Indirect MR arthrograms of 35 patients (21 women, 14 men; mean age, 50.1 years) diagnosed with adhesive capsulitis clinically were compared with indirect MR arthrograms of 45 patients (23 women, 22 men; mean age, 48.9 years) without adhesive capsulitis. Joint capsule thickness in the axillary recess and the thicknesses of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess and the rotator interval were, respectively, evaluated on coronal T2-weighted images and coronal and sagittal fat-suppressed enhanced T1-weighted images by two radiologists independently. Reliability was studied using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were compared. RESULTS. Patients with adhesive capsulitis had significantly thickened joint capsules in the axillary recess and a thickened enhancing portion in the axillary recess and in the rotator interval. The difference in the thicknesses of the enhancing portion in the axillary recess and in the rotator interval were significantly greater than the difference in joint capsule thicknesses in the axillary recess between the adhesive capsulitis group and the control group (p < 0.001). Interobserver reliability was good for all three indexes (ICC 0.80). The area under the ROC curve for the thickness of the joint capsule in the axillary recess and the thicknesses of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess and the rotator interval were 0.797, 0.861, and 0.847, respectively. CONCLUSION. An abundance of enhancing tissue in the rotator interval and thickening and enhancement of the axillary recess are signs suggestive of adhesive capsulitis on indirect MR arthrography. A dhesive capsulitis, or frozen shoulder, is a disabling and sometimes severely painful condition that is commonly managed in the primary care setting [1 5]. This clinical entity is characterized by gradual worsening of pain and loss of active and passive glenohumeral movement. The term frozen shoulder was first introduced by Codman in 1934 [6]. In 1945, Naviesar [7] coined the term adhesive capsulitis in recognition of the pathologic changes in the capsule. Today, the two terms are commonly interchangeable. Although the cause of adhesive capsulitis remains unclear, abnormalities in the synovium and joint capsule have been reported in several histologic studies. Arthroscopy shows small joint capacity with the loss of the axillary fold and a tight anterior capsule, synovial changes in the glenohumeral joint such as villous hypertrophy, fibrinous reaction, increased vascularity, and thickening of the synovium [8, 9]. These results suggest that adhesive capsulitis is associated with inflammatory or degenerative change of the glenohumeral joint capsule with subsequent reactive capsular fibrosis. Adhesive capsulitis is essentially a clinical diagnosis [1]. There are few laboratory tests or radiologic markers specific for frozen shoulder. Arthrography has been the advocated imaging test of choice to assess for adhesive capsulitis. It shows characteristic findings, such as limited shoulder joint capacity and a small or nonexistent dependent axillary fold [1]. However, arthrography is invasive and cannot explore changes in the synovial and capsular membranes [10]. Therefore, in most institutions, this modality is not used routinely to diagnose adhesive W1105
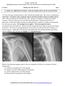
2 Song et al. capsulitis. On the other hand, MRI is a noninvasive modality. It can identify changes in the synovium and the joint capsule and can exclude other causes of shoulder pain that mimic adhesive capsulitis such as rotator cuff tear, tendinitis, osteoarthritis, subacromial impingement, and occult fracture [10 12]. In several studies, investigators reported unenhanced MRI, contrast-enhanced MRI, or direct MR arthrography imaging findings suggestive of adhesive capsulitis and assessed the usefulness of these modalities in diagnosing the condition [10, 11, 13 15]. To our knowledge, no study has investigated the indirect MR arthrographic findings of adhesive capsulitis and the usefulness of indirect MR arthrography in diagnosing adhesive capsulitis. The purpose of this study was to compare the indirect MR arthrographic findings of patients with adhesive capsulitis and patients without adhesive capsulitis. Materials and Methods Patients and Control Subjects Between January 2008 and December 2009, 194 patients underwent indirect MR arthrography at our institution; of those patients, 80 were enrolled in the study. Thirty-five patients (21 women, 14 men; mean age, 50.1 years) were clinically diagnosed with adhesive capsulitis on the basis of the following criteria [16 20]: painful stiff shoulder for at least 4 weeks, severe shoulder pain that interfered with successful performance of activities of daily living or work activities, nocturnal pain, painful restriction of both active and passive elevation to less than 100, 50% restriction of external rotation, normal radiologic appearance, and A no secondary causes. The control group consisted of 45 subjects (23 women, 22 men; mean age, 48.9 years) with shoulder discomfort who underwent indirect MR arthrography for evaluation. However, they did not have limited range of motion in the shoulder joint in all directions. Of the 114 excluded patients, 27 had a clinical history and clinical evidence of rotator cuff tear. Twenty-eight had calcium deposition on radiography suggestive of calcific tendinitis. Five had bony abnormalities, such as fracture of the clavicle, fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus, and bony Bankart lesion. One had a history of shoulder surgery. The remaining 53 patients were excluded because they did not meet the criteria for limited range of motion. MRI Protocol MRI was performed using a 3-T whole-body MR imager (Gyroscan Intera Achieva, Philips Healthcare) with a dedicated receive-only shoulder coil. Indirect MR arthrography was initiated after IV injection of gadobutrol (Gadovist, Schering; 0.1 mmol/kg body weight) into an antecubital vein. Immediately after the injection of contrast material, patients were instructed to move their shoulder for 15 minutes. Patients were positioned for imaging with the humerus in a neutral position and the thumb pointing upward [21]. Indirect MR arthrography was performed using the following imaging sequences: Fat-suppressed T1-weighted turbo spin-echo sequences were performed in the axial and coronal oblique planes (TR range/te range, /18 24; section thickness, 3 mm; FOV, 15 cm; matrix size, ), parallel to the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon and in the sagittal oblique plane Fig. 1 Indirect MR arthrography of 50-year-old man with adhesive capsulitis. A, Oblique coronal T2-weighted image shows thickened joint capsule in axillary recess (arrows). B, Oblique coronal gadolinium chelate enhanced T1-weighted image shows enhancing portion of axillary recess (arrows). C, Oblique sagittal gadolinium chelate enhanced T1-weighted image shows enhancing portion of rotator interval (arrows). B ( /20 24; section thickness, 3 mm; FOV, 15 cm; matrix size, ), and perpendicular to the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon ( /18 24; section thickness, 4 mm; FOV, 15 cm; matrix size, ). T2-weighted turbo spinecho sequences were performed in the axial plane (TR range/te, /80; section thickness, 3 mm; FOV, 15 cm; matrix size, ; echo-train length [ETL], 16), the coronal oblique plane ( /80; section thickness, 3 mm; FOV, 15 cm; matrix size, ; ETL, 16), and the sagittal oblique plane ( /80; section thickness, 4 mm; FOV, 15 cm; matrix size, ; ETL, 16). Analysis of MR Images Analysis was performed by a musculoskeletal radiologist with 5 years of experience in the interpretation of shoulder MRI and by a radiology resident; both were blinded to the diagnoses. A PACS (Centricity 2.0, GE Healthcare) was used. The thickness of the joint capsule in the axillary recess and the thicknesses of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess and the rotator interval were independently measured by the two radiologists. The subacromial bursa, acromioclavicular joint, and glenohumeral joint effusion were evaluated by consensus of the two radiologists. Joint capsule thickness and the thickness of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess were measured at the widest portion of the humeral and glenoid aspects of the axillary recess on oblique coronal T2-weighted (Fig. 1A) and oblique coronal fat-suppressed enhanced T1-weighted (Fig. 1B) images, respectively [10]. In the rotator interval, the thickness of the enhancing portion was measured by the widest portion of the capsule and the synovium between the superior aspect of C W1106
3 MR Arthrography of Adhesive Capsulitis the subscapularis tendon and the anterior aspect of the supraspinatus tendon perpendicular to the adjacent humeral head cortex on oblique sagittal fat-suppressed enhanced T1-weighted images [10] (Fig. 1C). The images were also evaluated for evidence of subacromial bursitis and osteoarthritis of the acromioclavicular joint. The criteria for these entities were the presence of a fluid collection and enhancement in the subacromial bursa and acromioclavicular joint on oblique coronal T2-weighted images and oblique coronal fat-suppressed enhanced T1-weighted images. The glenohumeral joint effusion was evaluated. It was scored on oblique coronal T2-weighted images using a modified MRI classification scheme developed by Schweitzer et al. [22] as follows by consensus of the two radiologists: 0, no joint fluid; 1, mild loculated fluid signal; or 2, extensive fluid signal [23]. Statistical Analysis Interobserver reliability was assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) (3,1 method) under the mixed-effects model. In an analysis using a mixed model, raters corresponded to fixed effect and subjects corresponded to random effect. The ICC (3,1 method) was determined as follows: Each subject was measured by a rater involved in the study who then selected the two-way mixed-effects model. Reliability was calculated from a single measurement. The two-tailed Student t test was used to compare the mean thickness of the joint capsule in the axillary recess and the mean thicknesses of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess and the rotator interval between the adhesive capsulitis group and control group. Subacromial bursitis, osteoarthritis of the acromioclavicular joint, and glenohumeral joint effusion were compared using a chi-square test. A p value of < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference. In addition, to determine the diagnostic performance of joint capsule thickness in the axillary recess and the thicknesses of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess and the rotator interval for the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was calculated. The constructed ROC curves were compared, and p values were constructed using the methodology of DeLong et al. [24], which is a nonparametric approach using generalized U statistics, to compare the areas under three correlated ROC curves in the prediction of adhesive capsulitis. To calculate the corresponding sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value, the variables were dichotomized at the most optimal cutoff point determined by maximizing the Youden index (defined as sensitivity plus specificity minus 1). TABLE 1: Joint Capsule Thickness in the Axillary Recess and Enhancing Portion of the Axillary Recess and the Rotator Interval in Patients With Adhesive Capsulitis and Control Group Mean Thickness ± SD (mm) Intraclass Correlation Structure Adhesive Capsulitis Control Group p Coefficient (95% CI) Axillary recess Joint capsule 5.9 ± ± 1.7 < ( ) Enhancing portion 6.5 ± ± 3.0 < ( ) Rotator interval Enhancing portion 8.3 ± ± 3.6 < ( ) Results The patient group had a significantly thicker joint capsule in the axillary recess and significantly thicker enhancing portion of the axillary recess and the rotator interval than the control group (p < 0.001) (Table 1 and Figs. 1 and 2). The differences in the thicknesses of the enhancing portion in the axillary recess and in the rotator interval were significantly greater than the difference in joint capsule thickness in the axillary recess between the adhesive capsulitis group and the control group (p < 0.001). Interobserver reliability, as measured by the ICC, was good (Table 1). The AUCs for joint capsule thickness in the axillary recess and for the thicknesses of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess and of the rotator interval were 0.797, 0.861, and 0.847, respectively (Fig. 3). However, the AUC between these thicknesses was not significantly different (p = 0.189). The optimal cutoff values of joint capsule thickness in the axillary recess and the thicknesses of the enhancing portion of the axillary recess and of Fig. 2 Indirect MR arthrography of 21-year-old man without adhesive capsulitis who presented with shoulder pain but did not show restricted range of motion. There is no visible enhancing portion in axillary recess on oblique coronal gadolinium chelate enhanced T1-weighted image. the rotator interval were 4.8, 3, and 4.6 mm, respectively. The corresponding sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis were 69% and 78%, 91% and 78%, and 89% and 80%, respectively. Five patients with adhesive capsulitis (14%) and seven control subjects (16%) had subacromial bursitis (p = 1.0). Three patients with adhesive capsulitis (9%) and seven control subjects (16%) had osteoarthritis of the acromioclavicular joint (p = 0.5). No glenohumeral joint effusion was observed in 29 of 35 patients with adhesive capsulitis (83%) and mild loculated fluid signal in six (17%). No glenohumeral joint effusion was observed in 41 of the 45 control subjects (91%), mild loculated fluid signal in three (7%), and extensive fluid signal in one (2%). There was no statistical difference between the two groups in the amount of glenohumeral joint effusion (p = 0.223). Discussion Although the results of many studies have suggested that synovial inflammation with subsequent reactive capsular fibrosis is the underlying pathologic process of adhesive capsulitis based on arthroscopic and pathologic findings and biochemical studies [8, 25 28], the exact cause of adhesive capsulitis remains unclear. Furthermore, there are few laboratory tests or radiologic markers specific for frozen shoulder, so the diagnosis is essentially clinical [1]. However, many studies using various imaging modalities have been performed to determine findings specific for adhesive capsulitis. One of the modalities is MRI. Emig et al. [14] reported imaging findings suggestive of adhesive capsulitis using unenhanced MR images. Several groups of researchers have performed studies with enhanced MR images [10, 13, 29, 30], and Mengiardi et al. [31] and Lee et al. [15] used direct MR arthrography. However, to our knowledge, no study on the imaging findings of adhesive capsulitis has been performed using indirect MR arthrography. W1107
4 Song et al. Sensitivity Specificity Indirect MR arthrography is based on the concept that IV injected contrast material diffuses into the joint space over time, so direct arthrography like images can be obtained [32]. Several advantages of indirect MR arthrography are that intraarticular injection is not needed and the timing of MRI after contrast injection does not have to be exact. In addition, both the joint space and extraarticular vascularized structures will be enhanced on indirect MR arthrography [33]. Hyperemia related to the pathologic process will cause enhancement of extraarticular structures more quickly and intensely. Therefore, the presence and extent of enhancement can be used to detect the pathologic processes. In addition, indirect MR arthrography of the shoulder includes the process of active joint movement after IV gadolinium injection. This process may increase blood supply to the inflamed tissue in the joint. As a result, indirect MR arthrography may increase enhancement in the inflamed tissue in the joint compared with conventional enhanced MR images. There has been disagreement about the usefulness of joint capsule thickness measurements in the axillary recess for the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis. Emig et al. [14] reported that capsular thickening of more than 4 mm in the axillary recess was a useful criterion for the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis. On the other hand, there was no significant thickening of the joint capsule in the axillary recess in adhesive capsulitis patients according to Mengiardi et al. [31]. In our Fig. 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve and area under curve (AUC) for diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis using joint capsule thickness in axillary recess evaluated on coronal T2- weighted images (thick black line; AUC = 0.797), thickness of enhancing portion in axillary recess on coronal fatsuppressed enhanced T1-weighted images (thin black line; AUC = 0.861), and thickness of enhancing portion of the rotator interval on sagittal fat-suppressed enhanced T1-weighted images (dashed line; AUC = 0.847). study, joint capsule thickness in the axillary recess was statistically different between the patient group and the control group. However, the mean thickness of the joint capsule in the axillary recess on coronal T2-weighted images was 4.2 ± 1.7 mm in the control group and 5.9 ± 1.7 mm in patients with adhesive capsulitis. The difference between the groups is not substantial. On the other hand, the mean thicknesses of the enhancing portion in the axillary recess and in the rotator interval were, respectively, 2.1 ± 3.0 mm and 3.0 ± 3.6 mm in the control group and 6.5 ± 2.5 mm and 8.3 ± 3.4 mm in the adhesive capsulitis group. The differences in the thicknesses of the enhancing portion in the axillary recess and in the rotator interval were significantly greater than the difference in joint capsule thickness in the axillary recess between the adhesive capsulitis group and the control group. These results may be explained by the possible pathologic process of adhesive capsulitis, such as inflammation and fibrosis, which were mentioned at the beginning of this discussion. Joint capsule inflammation may cause hyperemia in the surrounding soft tissue, which can be enhanced. In other words, enhancement can reflect abnormalities of the joint capsule as well as secondary change of the surrounding soft tissue. On the other hand, joint capsule thickness reflects only joint capsule abnormalities. For this reason, the differences in the thicknesses of the enhancing portion may be greater than the difference of joint capsule thickness between the adhesive capsulitis group and control group. Our study has several potential limitations. We used a set of clinical and radiographic criteria as the reference standard for the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis. In previous studies, arthrographic or arthroscopic findings were treated as the gold standard for the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis. However, diagnostic criteria for adhesive capsulitis have not been fully established in arthrography and arthroscopy. In addition, these modalities are invasive. Adhesive capsulitis is usually managed with medical and physical therapies [3 5]. Surgical treatment is applied only to severe cases. Therefore, if arthroscopy findings are treated as the gold standard, selection bias may be increased. The criteria that we used are not a gold standard for the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis. However, the criteria based on the patient s history, physical examination findings, and radiographic findings are a second-best method considering real clinical situations. Nevertheless, our criteria might not be exactly the same as the criteria used at other institutions. Therefore, our results might not be generalized to populations of patients in other practices using different criteria. Another limitation of our study was that the control group was not age- and sex-matched with the adhesive capsulitis group. There was no significant difference in the mean age. However, subjects in the control group tended to be men. It remains unclear whether matching the control group to the patient group would have had any impact on the results. A final limitation of our study was the exclusion criteria. We excluded patients who had limited shoulder joint motion but did not fulfill the inclusion criteria (i.e., painful restriction of both active and passive elevation to less than 100 and 50% restriction of external rotation). Patients with early-stage adhesive capsulitis may have been excluded. As a result, patients with relatively severe adhesive capsulitis were included in our study and the difference in the thicknesses between the patient and control groups could be exaggerated. In conclusion, an abundance of enhancing tissue in the rotator interval and thickening and enhancement of the axillary recess are signs suggestive of adhesive capsulitis on indirect MR arthrography. References 1. Dias R, Cutts S, Massoud S. Frozen shoulder. BMJ 2005; 331: W1108
5 MR Arthrography of Adhesive Capsulitis 2. Diercks RL, Stevens M. Gentle thawing of the adhesive capsulitis: correlation with clinical stag- Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulders frozen shoulder: a prospective study of supervised ing. HSS J 2008; 4: with idiopathic adhesive capsulitis: reliability of neglect versus intensive physical therapy in seven- 13. Connell D, Padmanabhan R, Buchbinder R. Ad- measures. Eur Radiol 2005; 15: ty-seven patients with frozen shoulder syndrome hesive capsulitis: role of MR imaging in differen- 24. DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. followed up for two years. J Shoulder Elbow Surg tial diagnosis. Eur Radiol 2002; 12: Comparing the areas under two or more corre- 2004; 13: Griggs SM, Ahn A, Green A. Idiopathic adhesive capsulitis: a prospective functional outcome study of nonoperative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000; 82: Mitchell C, Adebajo A, Hay E, Carr A. Shoulder pain: diagnosis and management in primary care. BMJ 2005; 331: van der Windt DA, Koes BW, Deville W, Boeke AJ, de Jong BA, Bouter LM. Effectiveness of corticosteroid injections versus physiotherapy for treatment of painful stiff shoulder in primary care: randomised trial. BMJ 1998; 317: Codman EA. Tendinitis of the short rotators in the shoulder: rupture of the supraspinatus tendon and other lesions in or about the subacromial bursa. Boston, MA: Thomas Todd and Company, Naviesar JS. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg 1945; 27: Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Wiley AM. Arthroscopic surgery of the shoulder: a general appraisal. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1986; 68: Wiley AM. Arthroscopic appearance of frozen shoulder. Arthroscopy 1991; 7: Lefevre-Colau MM, Drapé JL, Fayad F, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of shoulders with idiopathic adhesive capsulitis: reliability of measures. Eur Radiol 2005; 15: Jung JY, Jee WH, Chun HJ, Kim YS, Chung YG, Kim JM. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: evaluation with MR arthrography. Eur Radiol 2006; 16: Sofka CM, Ciavarra GA, Hannafin JA, Cordasco FA, Potter HG. Magnetic resonance imaging of 14. Emig EW, Schweitzer ME, Karasick D, Lubowitz J. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: MR diagnosis. AJR 1995; 164: Lee MH, Ahn JM, Muhle C, et al. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: diagnosis using magnetic resonance arthrography, with arthroscopic findings as the standard. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2003; 27: Kim KC, Rhee KJ, Shin HD. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: dimensions of the rotator interval measured with magnetic resonance arthrography. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2009; 18: Warner JJ. Frozen shoulder: diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 1997; 5: Shaffer B, Tibone JE, Kerlan RK. Frozen shoulder: a long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1992; 74: Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1987; 214: Omari A, Bunker TD. Open surgical release for frozen shoulder: surgical findings and results of the release. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2001; 10: Oh DK, Yoon YC, Kwon JW, et al. Comparison of indirect isotropic MR arthrography and conventional MR arthrography of labral lesions and rotator cuff tears: a prospective study. AJR 2009; 192: Schweitzer ME, Magbalon MJ, Fenlin JM, Frieman BG, Ehrlich S, Epstein RE. Effusion criteria and clinical importance of glenohumeral joint fluid: MR imaging evaluation. Radiology 1995; 194: Lefevre-Colau MM, Drapé JL, Favad F, et al. lated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988; 44: Bunker TD, Anthony PP. The pathology of frozen shoulder: a Dupuytren-like disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1995; 77: Bunker TD, Reilly J, Baird KS, Hamblen DL. Expression of growth factors, cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in frozen shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2000; 82: Ha eri GB, Maitland A. Arthroscopic findings in the frozen shoulder. J Rheumatol 1981; 8: Rodeo SA, Hannafin JA, Tom J, Warren RF, Wickiewicz TL. Immunolocalization of cytokines and their receptors in adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Orthop Res 1997; 15: Carrillon Y, Noel E, Fantino O, Perrin-Fayolle O, Tran-Minh VA. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in idiopathic adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. Rev Rhum Engl Ed 1999; 66: Tamai K, Yamato M. Abnormal synovium in the frozen shoulder: a preliminary report with dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 1997; 6: Mengiardi B, Pfirrmann CW, Gerber C, Hodler J, Zanetti M. Frozen shoulder: MR arthrographic findings. Radiology 2004; 233: Steinbach LS, Palmer WE, Schweitzer ME. Special focus session: MR arthrography. Radio- Graphics 2002; 22: Burstein D, Velyvis J, Scott KT, et al. Protocol issues for delayed Gd(DTPA)(2-)-enhanced MRI (dgemric) for clinical evaluation of articular cartilage. Magn Reson Med 2001; 45:36 41 W1109
Ultrasonographic measurement of the axillary recess thickness in an asymptomatic shoulder
 Ultrasonographic measurement of the axillary recess thickness in an asymptomatic shoulder Gi-Young Park, Jin Hoon Lee, Dae Gil Kwon Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School
Ultrasonographic measurement of the axillary recess thickness in an asymptomatic shoulder Gi-Young Park, Jin Hoon Lee, Dae Gil Kwon Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
An MRI Study of Symptomatic Adhesive Capsulitis
 An MRI Study of Symptomatic Adhesive Capsulitis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
An MRI Study of Symptomatic Adhesive Capsulitis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal Derangement of Shoulder
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
Intramuscular Rotator Cuff Cysts: Association with Tendon Tears on MRI and Arthroscopy
 Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Diagnostic Accuracy Using Indirect MR Arthrography
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative MRI
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology
 Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
imri 2018;22:
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology & Nuc. Med., Vol. 36, No.3, (September): , 2005
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology & Nuc. Med., Vol. 36, No.3, (September): 633-643, 2005 FROZEN SHOULDER: RELIABILITY OF SHOULDER MR ARTHROGRAPHY BY AHMAD MOHAMMAD GHANDOUR MD*, HESHAM Y. ALGAZZAR MD**,
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology & Nuc. Med., Vol. 36, No.3, (September): 633-643, 2005 FROZEN SHOULDER: RELIABILITY OF SHOULDER MR ARTHROGRAPHY BY AHMAD MOHAMMAD GHANDOUR MD*, HESHAM Y. ALGAZZAR MD**,
Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder: Value of Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament Signal Changes on T2-Weighted Fat- Saturated Images
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gondim Teixeira et al. MRI of dhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Pedro. Gondim Teixeira 1 Clémence Balaj nne Chanson
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gondim Teixeira et al. MRI of dhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Pedro. Gondim Teixeira 1 Clémence Balaj nne Chanson
Imaging the shoulder - Adhesive capsulitis
 Imaging the shoulder - Adhesive capsulitis Poster No.: C-1452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit I. Martins 1, R. D. G. P. de Carvalho 2, M. Pimenta 1 ; 1 Porto/PT, 2 Santarém, Sa/PT
Imaging the shoulder - Adhesive capsulitis Poster No.: C-1452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit I. Martins 1, R. D. G. P. de Carvalho 2, M. Pimenta 1 ; 1 Porto/PT, 2 Santarém, Sa/PT
Comparison of Three-dimensional Isotropic T1-weighted Fast Spin-Echo MR Arthrography with Two-dimensional MR Arthrography of the Shoulder 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Is ultrasonographic evaluation of rotator interval useful in diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis of shoulder?
 Is ultrasonographic evaluation rotator interval useful in diagnosis adhesive capsulitis shoulder? Poster No.: C-2230 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: Y. C. Yoon, J. M. Seo, H. S. Kim,
Is ultrasonographic evaluation rotator interval useful in diagnosis adhesive capsulitis shoulder? Poster No.: C-2230 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: Y. C. Yoon, J. M. Seo, H. S. Kim,
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Technical Guidelines SHOULDER
 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Calcific Tendinitis of the Long Head of the Biceps Brachii Distal to the Glenohumeral Joint: Plain Film
 1011 Calcific Tendinitis of the Long Head of the Biceps Brachii Distal to the Glenohumeral Joint: Plain Film Radiographic Findings Amy Beth Goldman1 Calcific tendinitis is a painful condition related to
1011 Calcific Tendinitis of the Long Head of the Biceps Brachii Distal to the Glenohumeral Joint: Plain Film Radiographic Findings Amy Beth Goldman1 Calcific tendinitis is a painful condition related to
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
Correlation of MR Arthrographic Findings and Range of Shoulder Motions in Patients With Frozen Shoulder
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MR rthrography in Patients With Frozen Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research So-Yeon Lee 1,2 Jeongmi Park 1 Seok-Whan Song 3 Lee SY, Park
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MR rthrography in Patients With Frozen Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research So-Yeon Lee 1,2 Jeongmi Park 1 Seok-Whan Song 3 Lee SY, Park
Degenerative joint disease of the shoulder, while
 Arthroscopic Debridement of the Shoulder for Osteoarthritis David M. Weinstein, M.D., John S. Bucchieri, M.D., Roger G. Pollock, M.D., Evan L. Flatow, M.D., and Louis U. Bigliani, M.D. Summary: Twenty-five
Arthroscopic Debridement of the Shoulder for Osteoarthritis David M. Weinstein, M.D., John S. Bucchieri, M.D., Roger G. Pollock, M.D., Evan L. Flatow, M.D., and Louis U. Bigliani, M.D. Summary: Twenty-five
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
The Shoulder. By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson
 The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:229 235 (2009) Technical Note Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration Yao Shang, MD, Zhuo-zhao Zheng, MD,* and
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:229 235 (2009) Technical Note Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration Yao Shang, MD, Zhuo-zhao Zheng, MD,* and
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review
 Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA
 Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA Consultant, OEHN (Occupational and Environmental Network)
Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA Consultant, OEHN (Occupational and Environmental Network)
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Shoulder Problems Fractures Instability Impingement Miscellaneous Anatomy Bones Joints / Ligaments Muscles Neurovascular Anatomy Anatomy Supraspinatus Anterior Posterior Anatomy
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Shoulder Problems Fractures Instability Impingement Miscellaneous Anatomy Bones Joints / Ligaments Muscles Neurovascular Anatomy Anatomy Supraspinatus Anterior Posterior Anatomy
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff Tears. University of Medical Sciences, Iran. Medical Sciences, Iran.
 Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Introduction & Question 1
 Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.63 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(1):63-71 The Association between the Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.63 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(1):63-71 The Association between the Magnetic Resonance Imaging
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기
 US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
21 year-old collegiate rower: R/O labral tear
 Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders
 Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty
 Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty John W. Sperling, MD, MS, a Hollis G. Potter, MD, b Edward V. Craig, MD, a Evan Flatow, MD, c and Russell F. Warren, MD, a New York, NY Specialized
Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty John W. Sperling, MD, MS, a Hollis G. Potter, MD, b Edward V. Craig, MD, a Evan Flatow, MD, c and Russell F. Warren, MD, a New York, NY Specialized
Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP MR arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion
 1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
Rotator Cable: MRI Study of Its Appearance in the Intact Rotator Cuff With Anatomic and Histologic Correlation
 Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
ADHESIVE CAPSULITIS (FROZEN SHOULDER)
 ADHESIVE CAPSULITIS (FROZEN SHOULDER) Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis is a condition that generally begins with the gradual onset of pain followed by a limitation of shoulder motion. The discomfort
ADHESIVE CAPSULITIS (FROZEN SHOULDER) Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis is a condition that generally begins with the gradual onset of pain followed by a limitation of shoulder motion. The discomfort
Shoulder MR arthrography
 Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Primary frozen shoulder: brief review of pathology and imaging abnormalities
 J Orthop Sci (2014) 19:1 5 DOI 10.1007/s00776-013-0495-x REVIEW ARTICLE Primary frozen shoulder: brief review of pathology and imaging abnormalities Kazuya Tamai Miwa Akutsu Yuichiro Yano Received: 23
J Orthop Sci (2014) 19:1 5 DOI 10.1007/s00776-013-0495-x REVIEW ARTICLE Primary frozen shoulder: brief review of pathology and imaging abnormalities Kazuya Tamai Miwa Akutsu Yuichiro Yano Received: 23
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Arthroscopic Evaluation of Subluxation of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon and Its Relationship with Subscapularis Tears
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:332-339 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.3.332 Arthroscopic Evaluation of Subluxation of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon and Its Relationship
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:332-339 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.3.332 Arthroscopic Evaluation of Subluxation of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon and Its Relationship
MRI Shoulder - Slap tear
 MRI Shoulder - Slap tear Poster No.: C-1149 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, R. Ravi; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal soft tissue,
MRI Shoulder - Slap tear Poster No.: C-1149 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, R. Ravi; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal soft tissue,
Bilateral Shoulder Pain
 HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
CiSE. Clinical Outcome after Arthroscopic Capsular Release for Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 21, No. 3, September, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5397/cise.2018.21.3.127 CiSE Clinical Outcome after Arthroscopic Capsular Release for Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder Jae Chul Yoo,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 21, No. 3, September, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5397/cise.2018.21.3.127 CiSE Clinical Outcome after Arthroscopic Capsular Release for Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder Jae Chul Yoo,
Does hydrodilatation help avoid the need for surgical intervention in adhesive capsulitis?
 Does hydrodilatation help avoid the need for surgical intervention in adhesive capsulitis? Poster No.: P-0122 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Rajesparan, S. Molathoti, T. Sikdar,
Does hydrodilatation help avoid the need for surgical intervention in adhesive capsulitis? Poster No.: P-0122 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Rajesparan, S. Molathoti, T. Sikdar,
What can Imaging tell us?
 What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective randomized comparison study
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Sensitivity of MR Arthrography in the Evaluation of Acetabular Labral Tears
 MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
Evaluation of the Effusion within Biceps Long Head Tendon Sheath Using Ultrasonography
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:351-358 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.351 Evaluation of the Effusion within Biceps Long Head Tendon Sheath Using Ultrasonography In Park,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:351-358 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.351 Evaluation of the Effusion within Biceps Long Head Tendon Sheath Using Ultrasonography In Park,
MRI evaluation of the shoulder: Beyond rotator cuff
 MRI evaluation of the shoulder: Beyond rotator cuff Poster No.: C-2447 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Rumie, A. Vasquez, J. A. Abreu, A. P. Guarnizo, O. Rivero, 1 1 2 3 1 1 1
MRI evaluation of the shoulder: Beyond rotator cuff Poster No.: C-2447 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Rumie, A. Vasquez, J. A. Abreu, A. P. Guarnizo, O. Rivero, 1 1 2 3 1 1 1
Impingement syndrome. Clinical features. Management. Rotator cuff tear diagnosed. Go to rotator cuff tear
 Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology
 Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
MRI and Sonography of the Shoulder
 Clinical Radiology (1991) 43, 323-327 and of the Shoulder J. HODLER, B. TERRIER*, G. K. yon SCHULTHESS and W. A. FUCHS Departments of Medical Radiology and *Rheumatology, University Hospital, Zurich, Switzerland
Clinical Radiology (1991) 43, 323-327 and of the Shoulder J. HODLER, B. TERRIER*, G. K. yon SCHULTHESS and W. A. FUCHS Departments of Medical Radiology and *Rheumatology, University Hospital, Zurich, Switzerland
Adhesive capsulitis of the knee
 DOI 10.1007/s00256-013-1582-y CASE REPORT Adhesive capsulitis of the knee Marcelo Rodrigues de Abreu & Mateus Falcão & Clarice Sprinz & Roque Furian & Luis Roberto Marczyk Received: 4 July 2012 /Revised:
DOI 10.1007/s00256-013-1582-y CASE REPORT Adhesive capsulitis of the knee Marcelo Rodrigues de Abreu & Mateus Falcão & Clarice Sprinz & Roque Furian & Luis Roberto Marczyk Received: 4 July 2012 /Revised:
The Upper Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012
 Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings
 C A S E R E P O R T Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings Amelia Bargiela*, Esther Rodriguez, Rafaela Soler The present study describes the ultrasound findings of
C A S E R E P O R T Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings Amelia Bargiela*, Esther Rodriguez, Rafaela Soler The present study describes the ultrasound findings of
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections
 Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
Shoulder vs Neck Pathology. Goal: Simplify Evaluation of the Painful Shoulder. Shoulder: Bony Anatomy Three major bones. Shoulder Disorders: Overview
 Goal: Simplify Evaluation of the Painful Shoulder Can be challenging Overlapping diagnoses Multiple complaints - Neck - Shoulder - Back - Arm Shoulder vs Neck Pathology Very common to have neck pain with
Goal: Simplify Evaluation of the Painful Shoulder Can be challenging Overlapping diagnoses Multiple complaints - Neck - Shoulder - Back - Arm Shoulder vs Neck Pathology Very common to have neck pain with
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods )
 Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography. Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears
 Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
ABSTRACT. Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 S ORIGINAL ARTICLE A prospective randomized trial comparing manipulation under anaesthesia and capsular distension for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 S ORIGINAL ARTICLE A prospective randomized trial comparing manipulation under anaesthesia and capsular distension for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder
Original Article pissn / eissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2016;75(6): https://doi.org/ /jksr
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
Since the description of the superior labral lesions. Biceps Load Test II: A Clinical Test for SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder
 Biceps Load Test II: A Clinical Test for SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Seung-Ho Kim, M.D., Ph.D., Kwon-Ick Ha, M.D., Ph.D., Jin-Hwan Ahn, M.D., Ph.D., Sang-Hyun Kim, M.D., and Hee-Joon Choi, M.D. Purpose:
Biceps Load Test II: A Clinical Test for SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Seung-Ho Kim, M.D., Ph.D., Kwon-Ick Ha, M.D., Ph.D., Jin-Hwan Ahn, M.D., Ph.D., Sang-Hyun Kim, M.D., and Hee-Joon Choi, M.D. Purpose:
MRI Evaluation of Bipolar Bone Loss Using the On-Track Off-Track Method: A Feasibility Study
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
Chronic Shoulder Disorders
 Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
Case Report A Thickened Coracohumeral Ligament and Superomedial Capsule Limit Internal Rotation of the Shoulder Joint: Report of Three Cases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 9384974, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9384974 Case Report A Thickened Coracohumeral Ligament and Superomedial
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 9384974, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9384974 Case Report A Thickened Coracohumeral Ligament and Superomedial
Management of arthritis of the shoulder. Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Case 61. Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative.
 Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
Hugo C. van der Veen James P. M. Collins Paul C. Rijk
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
Intraarticular Local Anesthesia: Can It Reduce Pain Related to MR or CT Arthrography of the Shoulder?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Dong Wook Kim 1 Seok Jin Choi 1 In Sook Lee 2 Choo HJ, Lee SJ, Kim DW, Choi
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Dong Wook Kim 1 Seok Jin Choi 1 In Sook Lee 2 Choo HJ, Lee SJ, Kim DW, Choi
Joint mobilization versus self-exercises for limited glenohumeral joint mobility: randomized controlled study of management of rehabilitation
 Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1439 1444 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1525-0 BRIEF REPORT Joint mobilization versus self-exercises for limited glenohumeral joint mobility: randomized controlled study of management
Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1439 1444 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1525-0 BRIEF REPORT Joint mobilization versus self-exercises for limited glenohumeral joint mobility: randomized controlled study of management
Imaging Modalities: Clinical Reasoning and Key Instructional Elements: Radiography
 Imaging Modalities: Clinical Reasoning and Key Instructional Elements: Radiography Michael D. Ross, PT, DHSc, OCS mross@daemen.edu Disclosure No relevant financial relationship exists Objectives Determine
Imaging Modalities: Clinical Reasoning and Key Instructional Elements: Radiography Michael D. Ross, PT, DHSc, OCS mross@daemen.edu Disclosure No relevant financial relationship exists Objectives Determine
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR Arthrography and Arthroscopic Correlation
 Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
