Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration
|
|
|
- Meredith McCormick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30: (2009) Technical Note Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration Yao Shang, MD, Zhuo-zhao Zheng, MD,* and Xuan Li, MD Purpose: To determine the optimal concentration of gadopentetate dimeglumine for direct shoulder MR arthrography at 3T in vivo. Materials and Methods: Sixty-eight consecutive shoulder MR arthrograms were obtained with 1 mmolgd/l (n 12), 2 mmolgd/l (n 12), 4 mmolgd/l (n 12), 6 mmolgd/l (n 12), 9 mmolgd/l (n 10) and 12 mmolgd/l (n 10). All postinjection fat-suppressed T1-weighted and T2- weighted images were analyzed retrospectively. For qualitative evaluation, image contrast was graded on a subjective three-level scale (excellent, moderate, and poor). For quantitative analysis, the contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) of intra-articular fluid to muscle was measured. Results: All postinjection T1-weighted images and T2- weighted images with 1 mmolgd/l, 2 mmolgd/l, 4 mmolgd/l, and 6 mmolgd/l were qualitatively evaluated as excellent or moderate. Two of the ten 9-mmolGd/L images and seven of the ten 12-mmolGd/L images were rated as poor with regard to the T2 image contrast. On the T1- weighted images, no significant difference existed between the CNRs of the six concentrations, but a peak CNR was seen at the concentration of 6 mmolgd/l. On the T2- weighted images, CNRs at concentrations of 1 mmolgd/l, 2 mmolgd/l, 4 mmolgd/l, 6 mmolgd/l, and 9 mmolgd/l showed no statistical difference, but were all significantly higher than that with 12 mmolgd/l. Conclusion: The acceptable concentration of gadopentetate dimeglumine for shoulder MR arthrography at 3T was found to be in the range of 1 mmolgd/l to 6 mmolgd/l. 6 mmolgd/l may be the optimal concentration. Key Words: magnetic resonance imaging; shoulder; arthrography; gadopentetate dimeglumine J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009;30: Wiley-Liss, Inc. DIRECT MR ARTHROGRAPHY with gadopentetate dimeglumine has been proven to be an effective method in assessing internal derangements of the major joints, Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Haidian District, Beijing, China. *Address reprint requests to: Z.-z.Z., Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, 49 North Garden Road, Haidian District, Beijing , P.R. China. zzhuozhao@yahoo.com.cn Received November 3, 2008; Accepted April 14, DOI /jmri Published online in Wiley InterScience ( particularly for partial-thickness rotator cuff tears, glenoid labral tears, re-tear of the meniscus postoperation, acetabular labrum tears, injuries of the triangular fibrocartilage complex, and osteochondral lesions (1 4). The optimized concentration of gadopentetate dimeglumine for MR arthrography at 1.5T has been suggested to be 2 mmolgd/l (5 8). However, optimization studies for gadopentetate dimeglumine concentrations at 3T in vivo have not previously been performed in depth. In several recent in vitro studies, the optimal concentrations for direct MR arthrograms at 3T were reported (9 11), but results of phantom studies may differ from those obtained in vivo. In addition, direct MR arthrograms with gadolinium may be performed without preceding conventional MR examinations in clinical practice. Under these circumstances, supplemental T2-weighted images are indispensable because these images aid in the identification of extra-articular fluid collections, periarticular masses, bone marrow lesions, and certain specific injuries. For example, in the shoulder, the bursal-sided or intrasubstance partial-thickness tears of the rotator cuff can only be well-assessed by T2-weighted images. Therefore, during MR arthrography, it is advisable to consider the influence of intra-articular gadopentetate dimeglumine on T2-weighted images as well. This influence, however, has not been fully evaluated in vivo. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the influence of intra-articular gadopentetate dimeglumine qualitatively and quantitatively on both postinjection T1-weighted and T2-weighted images to determine the optimum concentration of gadolinium for the shoulder at 3T in vivo. MATERIAL AND METHODS Patients Sixty-eight consecutive patients (21 female, 47 male; age range, years; mean age, 34 years) referred for MR arthrography of the glenohumeral joint were included in this prospective study. The only exclusion criterion was in the patient had prior shoulder surgery or arthroscopy. These patients were examined for suspected labrum disorders (n 36), suspected rotator cuff disorders (n 24), or shoulder pain with unknown cause (n 8). This project was approved by the investigational review board of our hospital, and informed consent was obtained from all patients Wiley-Liss, Inc. 229
2 230 Shang et al. MR Arthrography Joint puncture was performed with fluoroscopic guidance by a musculoskeletal radiologist with 10 years of experience in arthrography. A 21-gauge needle was placed into the glenohumeral joint by means of a rotator interval approach. This was used to inject ml of prepared contrast material into the shoulder after aspiration of any joint fluid. On the basis of our previous experience, this procedure was performed with only minor pain or discomfort of the patient, so local anesthesia was not necessary. The contrast material injected was a mixture of diluted Magnevist solution(schering, GuangZhou, China), iodine-based contrast (Omnipaque 300 mg I/mL; AnSheng, ShangHai, China), and lidocaine hydrochloride injection. The admixture was prepared as follows: first, a variable amount of Magnevist was added to 250 ml of normal saline, then 5 ml of this solution was mixed with 5 ml of iodinated contrast and 5 ml of lidocaine using a 20-mL syringe before injection (12). The final gadolinium concentration of the contrast material was adjusted to 1 mmolgd/l (n 12), 2 mmolgd/l (n 12), 4 mmolgd/l (n 12), 6 mmolgd/ L(n 12), 9 mmolgd/l(n 10), and 12 mmolgd/l(n 10). All patients underwent MR imaging of the shoulder on a 3.0 Tesla (T) scanner (Magnetom Trio with TIM system, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) with a maximum gradient amplitude of 45 mt/m and a maximum slew rate of 200 mt/m/s. The time interval between joint injection and initiation of imaging was strictly controlled to be within 30 min (13). The patient was placed in a supine position, with the affected shoulder wrapped by a dedicated flexible surface coil (4-Channel Flex Coil, Large) supplied by the MR manufacturer. The arm position was standardized, with the thumb pointing upward. Fat saturation T1-weighted turbo spinecho images were obtained in the transverse plane and in the coronal oblique plane, parallel to the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon (700 ms / 12 ms [repetition time / echo time], 3.5 mm section thickness, 160 mm 160 mm field of view, 2 turbo factors). Fat saturation T2-weighted turbo spin-echo images (3200/78, 4 mm section thickness, 160 mm 160 mm field of view, 11 turbo factors) were obtained routinely in the coronal oblique plane. T1-weighted turbo spin-echo images were also obtained in the sagittal oblique plane, perpendicular to the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon (650/11, 4-mm section thickness, 160 mm 160 mm field of view). The total MR examination time was approximately 13 minutes long. Qualitative Assessment of Images Two musculoskeletal radiologists, blinded to the exact gadolinium concentration used, reviewed all MR images independently by an image processing workstation (Leonardo, Siemens Medical Systems). Qualitative evaluation of image contrast between intra-articular fluid and adjacent structures on fat-suppressed T1-weighted sequence and fat-suppressed T2-weighted sequence was graded on a subjective three-level scale: excellent meant a homogenous high signal of the intra-articular fluid, distinct contrast between the intra-articular fluid and other relevant structures, and completely satisfactory for diagnostic purposes; moderate meant a nonhomogenous high signal of the intra-articular fluid with vague low signal intensity regionally, but contrast still sufficient for diagnosis; poor meant a nonhomogenous signal of the intra-articular fluid with obvious low signal intensity regionally or a homogenous low signal of the intra-articular fluid, and diagnosis may be confused. Quantitative Assessment of Images On the axial fat-suppressed T1-weighted images through the middle-lower part of the glenohumeral joint, the contrast-to-noise ratios (CNRs) between the intra-articular contrast material and the teres minor muscle were calculated. Signal intensities were measured by region of interest (ROI) using the same image processing workstation mentioned above. All ROI measurements were performed by the same analyst. Oval ROIs were drawn in the areas of the contrast-enhanced posterior joint cavity and the muscle belly of the teres minor behind the glenoid neck, as large as possible without including adjacent structures. The standard deviation (SD) of the background signal intensity was obtained by placing a ROI no less than 100 mm 2 in the air anterior to the body along the phase-encoding direction. CNRs were then calculated by dividing the difference in mean signal intensity of intra-articular contrast material and the muscle belly by the SD of the air (14). On the coronal oblique fat-suppressed T2-weighted image through the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon, oval ROIs were drawn in the areas of the axillary recess, the musculotendinous junction of the supraspinatus, and the air lateral to the body. The ROI sizes in the axillary recess and supraspinatus were made as large as possible without including adjacent structures. The ROI in the air was no less than 100 mm 2. CNRs of the intra-articular fluid to the supraspinatus were then calculated by the method described earlier. Statistics Evaluation One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare the CNRs of the six concentrations on both the T1-weighted images and the T2-weighted images. If the difference was determined to be significant, least-significance-difference (LSD) method was then used to compare each two concentrations. Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS 11.5 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL), and a P value less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS Qualitative Assessment Table 1 gives an overview of the frequency distribution of the different quality ratings made by the two readers. When examining the T1-weighted sequence, all MR arthrograms obtained with 1 mmolgd/l to 6 mmolgd/l were graded as excellent by both readers. A few discrepancies between the readers existed in the grading of MR
3 Shoulder MR Arthrography at 3T 231 Table 1 Overview of Frequency Distribution of Image Contrast Ratings FS T1-Weighted FS T2-Weighted Excellent Moderate Poor Excellent Moderate Poor 1 mmolgd/l 12 (12) 0 (0) 0 (0) 12 (12) 0 (0) 0 (0) 2 mmolgd/l 12 (12) 0 (0) 0 (0) 12 (12) 0 (0) 0 (0) 4 mmolgd/l 12 (12) 0 (0) 0 (0) 12 (12) 0 (0) 0 (0) 6 mmolgd/l 12 (12) 0 (0) 0 (0) 12 (10) 0 (2) 0 (0) 9 mmolgd/l 10 (9) 0 (1) 0 (0) 6 (4) 4 (4) 0 (2) 12 mmolgd/l 6 (7) 4 (3) 0 (0) 0 (1) 3 (2) 7 (7) The numbers outside the parentheses are the grading results of reader 1, and the numbers within the parentheses are the grading results of reader 2. arthrograms obtained with 9 mmolgd/l and 12 mmolgd/l, but all of them were still rated as sufficient for diagnosis (excellent or moderate) (Fig. 1). Both readers agreed on the fat suppressed T2- weighted images with 1 mmolgd/l, 2 mmolgd/l, and 4 mmolgd/l, which were all rated as excellent. A few discrepancies were noted for T2-weighted images with a concentration of 6 mmolgd/l, but were still rated as sufficient for diagnostic purposes. Two patients with 9 mmolgd/l were graded as poor by reader 2, but not by reader 1, and seven with 12 mmolgd/l were graded as poor by both readers (Fig. 2). Quantitative Assessment With the fat suppressed T1-weighted MR arthrograms, there was no statistically significant difference of CNRs among the six concentrations (F 2.26; P 0.064). The highest mean CNR was obtained with 6 mmolgd/l (Fig. 3). With the fat suppressed T2-weighted images, a statistically significant difference of CNRs was seen among the six different concentrations (F 8.11; P 0.001). Further analysis by LSD revealed that the CNRs for concentrations of 1 mmolgd/l, 2 mmolgd/l, 4 mmolgd/l, 6 mmolgd/l, and 9 mmolgd/l showed no significant difference for each two concentrations, but were all statistically higher than the CNR with a concentration of 12 mmolgd/l (Fig. 4). DISCUSSION When performing direct MR arthrography of the shoulder at 3T in vivo, this study found that the acceptable concentration of gadopentetate dimeglumine could range from 1 mmolgd/l to 12 mmolgd/l if only postinjection T1-weighted images were taken into account. All MR arthrograms with these concentrations were sufficient for diagnosis with regard to image contrast and had similar CNRs of intra-articular contrast material to the surrounding muscles. In addition, the concentrations from 1 mmolgd/l to 6 mmolgd/l were found to be superior, due to the possibility of a slightly deteriorated image contrast with higher gadolinium concentrations. However, when fat suppressed T2-weighed images were integrated to the consideration concomitantly, this study indicated that 12 mmolgd/l and 9 mmolgd/l should not be used for direct MR arthrography. These two concentrations may lead to a severe loss of signal intensity of the intra-articular fluid on postinjection T2-weighed images in several cases, and a concentration of 12 mmolgd/l will also result in a significantly lower CNR of the intra-articular fluid to the supraspinatus. Fat suppressed T2-weighed images obtained using the other concentrations (1 mmolgd/l to 6 mmolgd/l) were found to be acceptable both qualitatively and quantitatively, despite a few cases using a concentration of 6 mmolgd/l might show a suboptimal T2 contrast. Therefore, with consideration for both T1-weighted and T2-weighted images, the concentrations ranging from 1 mmolgd/l to 6 mmolgd/l were all found to be acceptable for direct shoulder MR arthrography at 3T. But which one would be the optimal concentration within this range? Due to the general concept of MR arthrography emphasizing the T1 contrast and the fact that concentration of 6 mmolgd/l provided the highest mean CNR on T1-weighed images, we consider 6 mmolgd/l to be the optimal concentration. The acceptable range of gadolinium concentration defined by present study was not conflicted with values suggested by previous studies with lower scanner field strength, in which gadolinium concentrations ranging from 1 mmolgd/l to 10 mmolgd/l had been recommended for direct MR arthrography, with a concentration of 2 mmolgd/l being the most frequently used. For instance, 1 mmolgd/l was recommended by Hajek et al (15), 2 mmolgd/l by Palmer and Caslowitz (12), 2.5 mmolgd/l by Jacobson et al (16), 4 mmolgd/l by Czerny et al (17), 5 mmolgd/l by Brenner et al (13), and 10 mmolgd/l by Kopka et al (18). However, the optimal concentration of 6 mmolgd/l, with a peak CNR for the T1-weighed images in this study, was unexpectedly higher than the concentrations recommended by previous phantom studies. For example, Montgomery et al (19) found that peak signal of gadolinium contrast diluted in saline for T1-weighted images was observed at mmolgd/l at 0.2T and 2.5 mmolgd/l at 1.5T. Masi et al (9) and Andreisek et al (10) recommended the optimum gadolinium concentration in the range of mmolgd/l and mmolgd/l, respectively, in later phantom studies at 3T, based on the results of signal to noise ratio on T1-weighted sequences. The discrepancy of results between our study in vivo and those studies in vitro may be ascribed to many factors, such as interaction of
4 Figure 1. Coronal oblique fat-suppressed T1-weighted MR arthrograms obtained with different concentrations of gadopentetate dimeglumine. The panels a e have excellent image contrast, however, f is graded moderate due to inhomogeneous signal intensity of the contrast material.
5 Figure 2. Coronal oblique fat-suppressed T2-weighted MR arthrograms obtained with different concentrations of gadopentetate dimeglumine. The panels a d have excellent image contrast, however, e is sorted moderate due to inhomogeneous signal intensity of the fluid, and f is graded poor due to marked low signal intensity of the fluid.
6 234 Shang et al. Figure 3. Graph of contrast-to-noise ratios on fat-suppressed T1-weighted MR arthrograms (mean value standard deviation) obtained with six concentrations (1 mmolgd/l, 2 mmolgd/l, 4 mmolgd/l, 6 mmolgd/l, 9 mmolgd/l, and 12 mmolgd/l). contrast material with articular synovium, higher body temperatures than the ambient conditions, delay time between injection and imaging, and dilution by preexisting joint effusion. In addition, this discordance also suggested that results in vitro needed to be further verified before being applied in vivo. In this study, mixtures of diluted gadopentetate dimeglumine, Omnipaque, and lidocaine, each accounting for one-third volume of the injection admixture, was used for MR arthrography. Premixing these types of materials has been previously proved safe in vitro (20) and this mixing proportion was based on a previous study (12). The clinical experience of the study team has also demonstrated the amount of iodinated contrast used here was sufficient to verify correct needle placement under fluoroscopy and to guarantee the quality of conventional x-ray arthrography or CT arthrography. The administration of lidocaine was an effective way to relieve pain and improve the compliance of patients during the MR scanning. The effect of adding iodinated contrast into gadolinium solution had been thoroughly investigated in phantom studies (9,10,19). In general, additional iodinated contrast decreased signal intensity of the gadolinium solution on all pulse sequences, and this decline was more obvious at 3T than at 1.5T and found to be more intensive on the T2-weighted images rather than on the T1-weighted images. In addition, it was found that if gadolinium was diluted in iodinated contrast, a lower concentration should be used due to the left shift of signal peak. Due to this, a minimal iodinated contrast during MR arthrography was advocated by these authors (9,19). Nevertheless, this view point was not unified in in vivo studies, where the use of high concentrations of iodinated contrast agents could be found frequently, such as 10 ml recommended by Jacobson et al (16), 5 ml by Palmer and Caslowitz (12), etc. The advantages of mixing high amount of iodine into gadolinium solution consists of ease of handling (not required to change syringe) and convenience in acquiring conventional x-ray arthrography or CT arthrography. This study focused on the glenohumeral joint, because the shoulder MR arthrography is most frequently used in clinic. However, it does require the consideration of whether the results are applicable for the other major joints. When compared with other joints (such as a knee joint), at least one difference should be kept in mind, in the case of the shoulder, the pre-existing joint effusion is usually far less, and has a correspondingly smaller effect of dilution of the gadolinium-based contrast material on MR arthography. Therefore, a minute increase may be considered to further optimize gadolinium concentration during the performance of direct MR arthrography of other joints. This study had several limitations. First, imaging of the shoulder did not take place directly after injection due to transportation and scheduling delays, so the injected gadolinium may have been partially resorbed by the synovium. Second, there was some variability in the time delay from shoulder injection to MR imaging, which might have different influence on the capsular resorption rate. However, all patients underwent imaging within 30 minutes of injection, and this time delay was considered reasonable for in clinic considerations. Third, turbo spin-echo T1-weighted sequence recommended by the manufacturer at 3T was used in this study, which may result in a mild difference of image contrast compared with spin-echo T1-weighted sequence or gradient echo sequence used in other studies. Finally, the injected contrast material was prepared on-site by the performing radiologist, so a little imprecision with the gadolinium concentration might exist in comparison to the level of precision that might be expected in a purely laboratory setting. Figure 4. Graph of contrast-to-noise ratios on fat-suppressed T2-weighted MR arthrograms (mean value standard deviation) obtained with six concentrations (1 mmolgd/l, 2 mmolgd/l, 4 mmolgd/l, 6 mmolgd/l, 9 mmolgd/l, and 12 mmolgd/l).
7 Shoulder MR Arthrography at 3T 235 In conclusion, with a focus on both T1-weighted and T2-weighted images, the acceptable concentration of gadopentetate dimeglumine for direct shoulder MR arthrography at 3T in vivo was found to be in the range of 1 6 mmolgd/l. The optimal concentration was determined to be 6 mmolgd/l. REFERENCES 1. Magee T, Williams D, Mani N. Shoulder MR arthrography: which patient group benefits most? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004;183: Toms AP, White LM, Marshall TJ, Donell ST. Imaging the postoperative meniscus. Eur J Radiol 2005;54: Petersilge CA. From the RSNA Refresher Courses. Radiological Society of North America. Chronic adult hip pain: MR arthrography of the hip. Radiographics 2000;20:S43 S Steinbach LS, Palmer WE, Schweitzer ME. Special focus session. MR arthrography. Radiographics 2002;22: Schulte-Altedorneburg G, Gebhard M, Wohlgemuth WA, et al. MR arthrography: pharmacology, efficacy and safety in clinical trials. Skeletal Radiol 2003;32: Helgason JW, Chandnani VP, Yu JS. MR arthrography: a review of current technique and applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1997; 168: Rafii M, Minkoff J. Advanced arthrography of the shoulder with CT and MR imaging. Radiol Clin North Am 1998;36: Mengiardi B, Pfirrmann CW, Gerber C, Hodler J, Zanetti M. Frozen shoulder: MR arthrographic findings. Radiology 2004;233: Masi JN, Newitt D, Sell CA, et al. Optimization of gadodiamide concentration for MR arthrography at 3 T. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184: Andreisek G, Froehlich JM, Hodler J, et al. Direct MR arthrography at 1.5 and 3.0 T: signal dependence on gadolinium and iodine concentrations phantom study. Radiology 2008;247: Stecco A, Brambilla M, Puppi AM, Lovisolo M, Boldorini R, Carriero A. Shoulder MR arthrography: in vitro determination of optimal gadolinium dilution as a function of field strength. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007;25: Palmer WE, Caslowitz PL. Anterior shoulder instability: diagnostic criteria determined from prospective analysis of 121 MR arthrograms. Radiology 1995;197: Brenner ML, Morrison WB, Carrino JA, et al. Direct MR arthrography of the shoulder: is exercise prior to imaging beneficial or detrimental? Radiology 2000;215: Binkert CA, Zanetti M, Gerber C, Hodler J. MR arthrography of the glenohumeral joint: two concentrations of gadoteridol versus Ringer solution as the intraarticular contrast material. Radiology 2001;220: Hajek PC, Sartoris DJ, Neumann CH, Resnick D. Potential contrast agents for MR arthrography: in vitro evaluation and practical observations. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1987;149: Jacobson JA, Lin J, Jamadar DA, Hayes CW. Aids to successful shoulder arthrography performed with a fluoroscopically guided anterior approach. Radiographics 2003;23: Czerny C, Hofmann S, Urban M, et al. MR arthrography of the adult acetabular capsular-labral complex: correlation with surgery and anatomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999;173: Kopka L, Funke M, Fischer U, Keating D, Oestmann J, Grabbe E. MR arthrography of the shoulder with gadopentetate dimeglumine: influence of concentration, iodinated contrast material, and time on signal intensity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994;163: Montgomery DD, Morrison WB, Schweitzer ME, Weishaupt D, Dougherty L. Effects of iodinated contrast and field strength on gadolinium enhancement: implications for direct MR arthrography. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002;15: Brown RR, Clarke DW, Daffner RH. Is a mixture of gadolinium and iodinated contrast material safe during MR arthrography? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;175:
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1
 A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP MR arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Intramuscular Rotator Cuff Cysts: Association with Tendon Tears on MRI and Arthroscopy
 Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
Comparison of radiation doses of various approaches of MR arthrograms with fluoroscopic guided contrast injection
 Comparison of radiation doses of various approaches of MR arthrograms with fluoroscopic guided contrast injection Poster No.: C-1294 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. M. Cheng, C.
Comparison of radiation doses of various approaches of MR arthrograms with fluoroscopic guided contrast injection Poster No.: C-1294 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. M. Cheng, C.
Comparison of Three-dimensional Isotropic T1-weighted Fast Spin-Echo MR Arthrography with Two-dimensional MR Arthrography of the Shoulder 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
MR Arthrography of Shoulder
 MR Arthrography of UNIT A22.2 The glenohumeral joint boasts the greatest range of motion of any peripheral joint in the body, but not without cost; it is also the most frequently dislocated joint in the
MR Arthrography of UNIT A22.2 The glenohumeral joint boasts the greatest range of motion of any peripheral joint in the body, but not without cost; it is also the most frequently dislocated joint in the
4 MR and MR Arthrography
 MR and MR Arthrography 35 4 MR and MR Arthrography J. Hodler CONTENTS 4.1 Introduction 35 4.2 Hardware Requirements 35 4.2.1 Field Strength 35 4.2.2 Coil Selection 36 4.3 The Patient 36 4.3.1 Patient Screening
MR and MR Arthrography 35 4 MR and MR Arthrography J. Hodler CONTENTS 4.1 Introduction 35 4.2 Hardware Requirements 35 4.2.1 Field Strength 35 4.2.2 Coil Selection 36 4.3 The Patient 36 4.3.1 Patient Screening
Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography
 Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-1016 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit Z. Maras Ozdemir 1, F. B. Ergen 2, U. Aydingoz
Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-1016 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit Z. Maras Ozdemir 1, F. B. Ergen 2, U. Aydingoz
Shoulder MR arthrography
 Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Original Article pissn / eissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2016;75(6): https://doi.org/ /jksr
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal Derangement of Shoulder
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine
 Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
Diagnosis of SLAP lesions with Grashey-view arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2003) 32:388 395 DOI 10.1007/s00256-003-0642-0 ARTICLE J. H. Edmund Lee Vanessa van Raalte Vartan Malian Diagnosis of SLAP lesions with Grashey-view arthrography Received: 19 November
Skeletal Radiol (2003) 32:388 395 DOI 10.1007/s00256-003-0642-0 ARTICLE J. H. Edmund Lee Vanessa van Raalte Vartan Malian Diagnosis of SLAP lesions with Grashey-view arthrography Received: 19 November
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast Necessary?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Original Effective Date:
 Subject: Upper Extremity Joint MRI 73221, 73222, 73223 Upper Extremity Non-Joint MRI 73218, 73219, 73220 Policy Number: MCR: 629 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: Review Date: DISCLAIMER This
Subject: Upper Extremity Joint MRI 73221, 73222, 73223 Upper Extremity Non-Joint MRI 73218, 73219, 73220 Policy Number: MCR: 629 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: Review Date: DISCLAIMER This
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Intraarticular Local Anesthesia: Can It Reduce Pain Related to MR or CT Arthrography of the Shoulder?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Dong Wook Kim 1 Seok Jin Choi 1 In Sook Lee 2 Choo HJ, Lee SJ, Kim DW, Choi
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Dong Wook Kim 1 Seok Jin Choi 1 In Sook Lee 2 Choo HJ, Lee SJ, Kim DW, Choi
Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:669 674 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0677-y SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff Jan E. Vandevenne & Filip Vanhoenacker & Jestinah
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:669 674 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0677-y SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff Jan E. Vandevenne & Filip Vanhoenacker & Jestinah
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
imri 2018;22:
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
MRI Shoulder - Slap tear
 MRI Shoulder - Slap tear Poster No.: C-1149 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, R. Ravi; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal soft tissue,
MRI Shoulder - Slap tear Poster No.: C-1149 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, R. Ravi; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal soft tissue,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
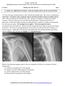 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
MR measurements of subcoracoid impingement using a new method and its relationship to rotator cuff pathology at MR arthrography
 MR measurements of subcoracoid impingement using a new method and its relationship to rotator cuff pathology at MR arthrography Poster No.: P-0055 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
MR measurements of subcoracoid impingement using a new method and its relationship to rotator cuff pathology at MR arthrography Poster No.: P-0055 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the
 CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology
 Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
Wrist Ligament Tears: Evaluation of MRI and Combined MDCT and MR Arthrography
 MR and MDCT Arthrography of Wrist Ligament Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas Moser 1 Jean-Claude Dosch Akli Moussaoui Jean-Louis Dietemann Moser T, Dosch J-C, Moussaoui A, Dietemann
MR and MDCT Arthrography of Wrist Ligament Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas Moser 1 Jean-Claude Dosch Akli Moussaoui Jean-Louis Dietemann Moser T, Dosch J-C, Moussaoui A, Dietemann
Received: 27 April 2015 /Revised: 9 July 2015 /Accepted: 23 July 2015 /Published online: 8 August 2015 # European Society of Radiology 2015
 Eur Radiol (2016) 26:1221 1225 DOI 10.1007/s00330-015-3945-3 MUSCULOSKELETAL Ultrasound guidance to perform intra-articular injection of gadolinium-based contrast material for magnetic resonance arthrography
Eur Radiol (2016) 26:1221 1225 DOI 10.1007/s00330-015-3945-3 MUSCULOSKELETAL Ultrasound guidance to perform intra-articular injection of gadolinium-based contrast material for magnetic resonance arthrography
Sensitivity of MR Arthrography in the Evaluation of Acetabular Labral Tears
 MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
Service Line: Rapid Response Service Version: 1.0 Publication Date: August 31, 2018 Report Length: 10 Pages
 CADTH RAPID RESPONSE REPORT: SUMMARY OF ABSTRACTS Magnetic Resonance Imaging Arthrograms for Labral Tear Diagnosis: Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines Service Line: Rapid Response Service
CADTH RAPID RESPONSE REPORT: SUMMARY OF ABSTRACTS Magnetic Resonance Imaging Arthrograms for Labral Tear Diagnosis: Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines Service Line: Rapid Response Service
Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative MRI
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22: (2005)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
Sonography of the Acetabular Labrum
 Case Series Visualization of Labral Injuries During Intra-Articular Injections Carolyn M. Sofka, MD, Ronald S. Adler, PhD, MD, Martha A. Danon, MD Objective. The purpose of this series was to describe
Case Series Visualization of Labral Injuries During Intra-Articular Injections Carolyn M. Sofka, MD, Ronald S. Adler, PhD, MD, Martha A. Danon, MD Objective. The purpose of this series was to describe
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Technical Guidelines SHOULDER
 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Post-procedure pain following direct MR arthrography
 Post-procedure pain following direct MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2310 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Musculoskeletal J. Giaconi, T. Link, R. Hong, R. Singh,
Post-procedure pain following direct MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2310 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Musculoskeletal J. Giaconi, T. Link, R. Hong, R. Singh,
Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
Indirect MR Arthrographic Findings of Adhesive Capsulitis
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Song et al. MR Arthrography of Adhesive Capsulitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kyoung Doo Song 1 Jong Won Kwon Young Cheol Yoon Sang-Hee Choi Song
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Song et al. MR Arthrography of Adhesive Capsulitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kyoung Doo Song 1 Jong Won Kwon Young Cheol Yoon Sang-Hee Choi Song
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology
 Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology & Nuc. Med., Vol. 36, No.3, (September): , 2005
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology & Nuc. Med., Vol. 36, No.3, (September): 633-643, 2005 FROZEN SHOULDER: RELIABILITY OF SHOULDER MR ARTHROGRAPHY BY AHMAD MOHAMMAD GHANDOUR MD*, HESHAM Y. ALGAZZAR MD**,
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology & Nuc. Med., Vol. 36, No.3, (September): 633-643, 2005 FROZEN SHOULDER: RELIABILITY OF SHOULDER MR ARTHROGRAPHY BY AHMAD MOHAMMAD GHANDOUR MD*, HESHAM Y. ALGAZZAR MD**,
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 44 S3 (2013) S26 S32. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Injury
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 44 S3 (213) S26 S32 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Injury journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/injury Diagnostic value of US, MR and MR arthrography
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 44 S3 (213) S26 S32 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Injury journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/injury Diagnostic value of US, MR and MR arthrography
Glenoid Articular Surface on Magnetic Resonance Arthrography of the Shoulder
 Glenoid Articular Surface on Magnetic Resonance Arthrography of the Shoulder Poster No.: P-0054 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. Jackson; Manchester/UK Bones, Musculoskeletal
Glenoid Articular Surface on Magnetic Resonance Arthrography of the Shoulder Poster No.: P-0054 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. Jackson; Manchester/UK Bones, Musculoskeletal
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR Arthrography and Arthroscopic Correlation
 Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder
 MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
ULTRASOUND- GUIDED INJECTIONS A TECHNICAL REVIEW
 PRACTICAL ADVICE ULTRASOUND- GUIDED INJECTIONS A TECHNICAL REVIEW Written by Akira M. Murakami, USA Ultrasound is a powerful modality for guiding the intra-articular injection of both therapeutic medication
PRACTICAL ADVICE ULTRASOUND- GUIDED INJECTIONS A TECHNICAL REVIEW Written by Akira M. Murakami, USA Ultrasound is a powerful modality for guiding the intra-articular injection of both therapeutic medication
Imaging of the Elbow. Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich
 Imaging of the Elbow Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich Elbow Case 1 Case 8 Case 2 Case 9 Case 3 Case 10 Case 4 Case 11 Case 5 Case 12 Case 6 Case 13 Case 7 Case 14 Elbow Imaging
Imaging of the Elbow Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich Elbow Case 1 Case 8 Case 2 Case 9 Case 3 Case 10 Case 4 Case 11 Case 5 Case 12 Case 6 Case 13 Case 7 Case 14 Elbow Imaging
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Postoperative Evaluation of the Pectoralis Major Transfer for the Rotator Cuff Tear in Shoulder: Focusing on MR and US
 Postoperative Evaluation of the Pectoralis Major Transfer for the Rotator Cuff Tear in Shoulder: Focusing on MR and US Poster No.: C-2337 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. T. Kwon,
Postoperative Evaluation of the Pectoralis Major Transfer for the Rotator Cuff Tear in Shoulder: Focusing on MR and US Poster No.: C-2337 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. T. Kwon,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software For evaluation only. Tishreen University Journal. Med.
 Tishreen University Journal. Med. Sciences Series Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software Tishreen University Journal for Research and Scientific Studies - Medical Sciences Series Vol. (30) No. (
Tishreen University Journal. Med. Sciences Series Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software Tishreen University Journal for Research and Scientific Studies - Medical Sciences Series Vol. (30) No. (
Imaging the shoulder - Adhesive capsulitis
 Imaging the shoulder - Adhesive capsulitis Poster No.: C-1452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit I. Martins 1, R. D. G. P. de Carvalho 2, M. Pimenta 1 ; 1 Porto/PT, 2 Santarém, Sa/PT
Imaging the shoulder - Adhesive capsulitis Poster No.: C-1452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit I. Martins 1, R. D. G. P. de Carvalho 2, M. Pimenta 1 ; 1 Porto/PT, 2 Santarém, Sa/PT
Hugo C. van der Veen James P. M. Collins Paul C. Rijk
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
Rotator Cable: MRI Study of Its Appearance in the Intact Rotator Cuff With Anatomic and Histologic Correlation
 Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Lawrence Gulotta Gillian Lieberman, MD October Gillian Lieberman, MD. Shoulder Imaging. Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02
 October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities
 Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD
 Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
MRI of the long head of the biceps tendon: a pictorial review.
 MRI of the long head of the biceps tendon: a pictorial review. Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Dewachter, L. Dewachter, A. P. Parkar ; Lier/BE, Bergen/ NO Keywords:
MRI of the long head of the biceps tendon: a pictorial review. Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Dewachter, L. Dewachter, A. P. Parkar ; Lier/BE, Bergen/ NO Keywords:
Elbow Synovial Fold Syndrome: MR Imaging Findings
 Hitomi Awaya 1,2 Mark E. Schweitzer 1 Sunah A. Feng 3 Tamotsu Kamishima 1 Phillip J. Marone 4 Shella Farooki 3 Debra J. Trudell 3 Parviz Haghighi 5 Donald L. Resnick 3 Received February 7, 2001; accepted
Hitomi Awaya 1,2 Mark E. Schweitzer 1 Sunah A. Feng 3 Tamotsu Kamishima 1 Phillip J. Marone 4 Shella Farooki 3 Debra J. Trudell 3 Parviz Haghighi 5 Donald L. Resnick 3 Received February 7, 2001; accepted
Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation
 Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
MR Arthrography of the Labral Capsular Ligamentous Complex in the Shoulder: Imaging Variations and Pitfalls
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.194.143 on 12/31/17 from IP address 37.44.194.143. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Yang Hee Park 1 Ji Yeon Lee 2 Sung Hee Moon 1 Jong
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.194.143 on 12/31/17 from IP address 37.44.194.143. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Yang Hee Park 1 Ji Yeon Lee 2 Sung Hee Moon 1 Jong
Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder instability
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0027-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0027-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
EVALUATION OF THE ACETABULAR LABRUM BY MR ARTHROGRAPHY
 EVALUATION OF THE ACETABULAR LABRUM BY MR ARTHROGRAPHY M. LEUNIG, S. WERLEN, A. UNGERSBÖCK, K. ITO, R. GANZ From the University of Berne and the Sonnenhof Clinic, Berne, and the AO/ASIF Research Institute,
EVALUATION OF THE ACETABULAR LABRUM BY MR ARTHROGRAPHY M. LEUNIG, S. WERLEN, A. UNGERSBÖCK, K. ITO, R. GANZ From the University of Berne and the Sonnenhof Clinic, Berne, and the AO/ASIF Research Institute,
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography. Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears
 Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
12/13/17. Policy Number: MCR: 627 Revision Date(s): 12/11/18. Review Date: 12/13/17, 12/19/18 DISCLAIMER
 Subject: Upper Extremity CT, (73200, 73201, 73202) Policy Number: MCR: 627 Revision Date(s): 12/11/18 Original Effective Date: 12/13/17 Review Date: 12/13/17, 12/19/18 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review
Subject: Upper Extremity CT, (73200, 73201, 73202) Policy Number: MCR: 627 Revision Date(s): 12/11/18 Original Effective Date: 12/13/17 Review Date: 12/13/17, 12/19/18 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review
 Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Obturator Externus Bursa: Anatomic Origin and MR Imaging Features of Pathologic Involvement 1
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Philip Robinson, MB, ChB 2 Lawrence M. White, MD Anne Agur, MD Jay Wunder, MD Robert S. Bell, MD Index terms: Hip, abnormalities, 44.4843 Hip, anatomy, Hip, arthrography,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Philip Robinson, MB, ChB 2 Lawrence M. White, MD Anne Agur, MD Jay Wunder, MD Robert S. Bell, MD Index terms: Hip, abnormalities, 44.4843 Hip, anatomy, Hip, arthrography,
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI
 Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Anastasia Fotiadou & Antonios Drevelegas & Michelangelo Nasuto & Giuseppe Guglielmi
 Insights Imaging (2013) 4:157 162 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0225-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance arthrography of the shoulder in the evaluation of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities:
Insights Imaging (2013) 4:157 162 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0225-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance arthrography of the shoulder in the evaluation of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities:
Lateral Mortise Approach for Therapeutic Ankle Injection: An Alternative to the Anteromedial Approach
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Fox et al. Therapeutic Ankle Injection Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Michael G. Fox 1 Philip R. Wright 2 Bennett Alford 1 James T. Patrie 3 Mark W.
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Fox et al. Therapeutic Ankle Injection Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Michael G. Fox 1 Philip R. Wright 2 Bennett Alford 1 James T. Patrie 3 Mark W.
MRI Features of the Acromioclavicular Joint That Predict Pain Relief from Intraarticular Injection
 Klaus Strobel 1 Christian W. A. Pfirrmann 1 Marco Zanetti 1 Ladislav Nagy 2 Juerg Hodler 1 Received November 20, 2002; accepted after revision February 28, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Orthopedic University
Klaus Strobel 1 Christian W. A. Pfirrmann 1 Marco Zanetti 1 Ladislav Nagy 2 Juerg Hodler 1 Received November 20, 2002; accepted after revision February 28, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Orthopedic University
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography.
 Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Diagnostic Accuracy Using Indirect MR Arthrography
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
The Upper Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
