Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
|
|
|
- Owen Nichols
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, Department of Radiology, Cliniques Universitaires St. Luc, Université Catholique de Louvain, 10 Ave. Hippocrate, 1200 Brussels, Belgium. Address correspondence to B. C. Vande Berg. 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Cliniques Universitaires St. Luc, Université Catholique de Louvain, 1200 Brussels, Belgium. AJR 2001;176: X/01/ American Roentgen Ray Society s of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable s OBJECTIVE. This study aimed to determine the value of four MR imaging criteria for evaluating unstable meniscal lesions. MATERIALS AND METHODS. Criteria for unstable meniscal lesions were the presence of a displaced meniscal fragment, visibility on more than three 3-mm-thick coronal and two 4- mm-thick sagittal images, having more than one orientation plane or more than one pattern (contour irregularity, peripheral separation, tear), and having intrameniscal high signal intensity on T2-weighted spin-echo images. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for recognition of instability among all meniscal lesions were determined for the presence of each individual criterion and for the presence of at least one criterion in 50 consecutive patients (mean age, 46 years) who underwent MR imaging and subsequent arthroscopy. RESULTS. Sensitivities and specificities of these four criteria ranged between 18% and 54% and between 94% and 100%, respectively. Positive and negative predictive values ranged between 92% and 100% and between 39% and 52%, respectively. The presence of at least one criterion enabled recognition of unstable lesions with a sensitivity and specificity of 82% and with positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 70%, respectively. CONCLUSION. The four MR imaging criteria have high specificities and positive predictive values and low sensitivities and negative predictive values when evaluating unstable meniscal lesions. M anagement of meniscal lesions of the knee encompasses nonoperative care, partial or total meniscectomy, and meniscus repair or grafting [1, 2]. stability is an important criterion in deciding whether to resect, repair, or leave alone a meniscal lesion [3, 4] and is best determined by direct visualization and palpation at arthroscopy [2, 5, 6]. Unstable lesions are lesions in which the meniscus or a fragment of it can be inappropriately displaced by a probe into the femorotibial joint. The ability of MR imaging to detect meniscal lesions has been extensively studied. Little attention has been given to the preoperative determination of meniscal lesion stability using MR imaging. A high positive predictive value of MR imaging to recognize unstable meniscal lesions would mean that MR imaging could help recognize patients who are most likely to benefit from surgery. To the best of our knowledge, no established MR imaging criteria for unstable meniscal lesions exist. Theoretically, these criteria should be based on the presence of a displaced meniscal fragment and on lesion shape, size, and signal, as proposed by Carpenter et al. [7]. The purpose of our study was to define and assess the value of four MR imaging criteria for recognizing unstable meniscal lesions. Materials and Methods Patients The study population consisted of 50 consecutive patients who underwent MR imaging of the knee between January and November 1999 and subsequent arthroscopy at our institution but without prior arthroscopy on that knee. The 36 male and the 14 female patients of the study population had a mean age of 46 years (range, years). All patients were referred by two orthopedic surgeons from our institution for MR imaging of the right (n = 24) or left (n = 26) knee because of a clinical suspicion of a meniscal lesion. Twentyfive patients had a history of knee trauma that had occurred 4 weeks to 5 years before the MR imaging (mean delay, 10.9 months). Twenty-five patients had a history of spontaneous knee pain without a recognizable triggering event. AJR:176, March
2 Vande Berg et al. MR Imaging Thirty-four MR imaging studies were performed using a 0.5-T magnet (.5 NT; Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands), and 16 MR imaging studies were performed using a 1.5-T magnet (Signa; General Electric Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI) with dedicated phased array quadrature knee coils. The imaging system used was randomly selected depending on the examination schedule. Patients were imaged in the conventional supine position. With the 0.5-T magnet, the following protocols were used: coronal spin-echo T1-weighted (TR/TE, 509/20) and gradient-echo T2*-weighted (800/28, 45 flip angle) sequences; parasagittal dual-echo spin-echo intermediate- and T2- weighted (TR/first-echo TE, second-echo TE, 2670/ 14,120) sequences; and axial gradient-echo T2- weighted (1000/28, 45 flip angle) sequences. Fields of view were 140 mm for coronal sequences and 160 mm for sagittal and axial sequences. Matrix size was Numbers of signal acquisitions were four for coronal T1-weighted sequences, two for gradientecho sequences, and one for parasagittal dual-echo sequences. Slice thickness was 3 mm for coronal and axial images and 4 mm for parasagittal images, with a 0.1 slice thickness interval. With the 1.5-T magnet, the following protocols were used: coronal spin-echo T1-weighted (520/15) and gradient-echo T2*-weighted (800/25, 30 flip angle) sequences; parasagittal fast spin-echo intermediate-weighted (3000/ 25) and T2-weighted (3000/120) sequences; and axial gradient-echo T2*-weighted (800/25, 30 flip angle) sequences. Slice thickness was 3 mm for coronal and axial images and 4 mm for parasagittal images, with a 0.1 slice thickness interval. Fields of view were 180 mm for parasagittal sequences and 160 mm for coronal and axial sequences. Matrix size was Two acquisitions were used for all sequences. Image Analysis A musculoskeletal radiologist with 9 years experience who was unaware of the arthroscopic findings reviewed the 50 MR imaging studies to determine the presence or absence of meniscal lesions, including contour irregularity, peripheral separation, and tear. Contour irregularity was defined as an altered meniscus shape with truncation, blunting, flattening, or rounding of the inner borders on coronal T1- or T2*- weighted or sagittal intermediate- or T2-weighted MR images. Peripheral meniscus separation was defined by the presence of high signal intensity on T2- weighted images between the meniscus and the capsule. Meniscal tear was defined as an abnormal intrameniscal signal that extended to the articulating surface of the meniscus on more than one coronal T2*-weighted or sagittal intermediate- or T2- weighted MR image. Questionable extension of abnormal signal to the free meniscal surface when viewed on only a single image was not reported as a tear [8, 9]. Meniscal lesions were identified as involving the medial or lateral menisci. The same musculoskeletal radiologist determined the presence or absence of each of the following four MR imaging criteria that were adapted from the initial proposal of Carpenter et al. [7]. Criteria for unstable meniscal lesions were the presence of a displaced meniscal fragment; visibility on more than three 3-mm-thick coronal and two 4- mm-thick sagittal images; having more than one orientation plane or more than one pattern (contour irregularity, peripheral separation, tear); and having intrameniscal high signal intensity on T2-weighted spin-echo images. A displaced meniscal fragment consisted of a fragment that had lost its anatomic location and was found in the intercondylar notch or in a meniscal recess [2, 10, 11]. The presence of a displaced meniscal fragment was considered to indicate an unstable lesion. size was determined by counting the number of contiguous coronal gradient-echo T2*- weighted or sagittal intermediate-weighted MR images on which contour abnormality, peripheral separation, or tear were seen at the meniscal surface. s that were visible on more than two 4-mm-thick sagittal and more than three 3-mmthick coronal images were considered unstable. shape was determined by noting the presence of one or more of the three lesion patterns just described (contour irregularity, peripheral meniscus separation, and meniscal tear) and the different cleavage plane orientations within the meniscus on coronal T2*-weighted or sagittal intermediate-weighted MR images. s that included more than one lesion pattern or more than one cleavage plane orientation in the same meniscal area were considered unstable. The presence of more than one lesion pattern or more than one cleavage plane orientation that were not in continuity with one another was not considered to indicate an unstable lesion. signal intensity was determined on spinecho T2-weighted MR images. The presence of high signal intensity identical to that of joint fluid in the meniscus on T2-weighted images was considered to indicate an unstable lesion. High signal intensity adjacent to the meniscus caused by a meniscal cyst was not considered indicative of instability. Size, shape, and signal intensity of the meniscal lesions were determined within the meniscus, and the presence of a displaced meniscal fragment was not taken into account for determination of these parameters. Arthroscopy All knee arthroscopy was performed by two orthopedic surgeons of our institution after a mean delay of 11.8 weeks (range, 1 30 weeks) after MR imaging. MR studies were available to surgeons on films. Original reports made by three radiologists, including the one who retrospectively reviewed the MR studies of the knees that underwent surgery, included descriptions of meniscal lesions and of displaced meniscal fragments. Initial reports by the three radiologists did not mention the precise extent, shape, or signal of the lesions and did not determine whether lesions were considered stable or unstable. At the time of arthroscopy, meniscal lesion patterns, including contour irregularities, peripheral separations, and tears, were noted on charts. Drawings that showed the location and configuration of all meniscal abnormalities were made. Meniscal lesions were considered unstable if they were displaced or if mobile meniscal fragments were found at inspection and palpation during arthroscopy, according to standard criteria [2]. Meniscal lesions without flaps or displaced fragments were considered stable. Statistics Operative notes and drawings were used as the gold standard for determining meniscal integrity and meniscal lesion stability. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values with 95% confidence intervals for the detection of meniscal lesions were calculated. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for detecting unstable lesions among all lesions were calculated for each of the four MR imaging criteria. Finally, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for detecting unstable lesions among all lesions were calculated for the presence of at least one of the four criteria. s that were missed at MR imaging were considered stable. Results Meniscal s At arthroscopy, 23 unstable and seven stable medial meniscal lesions and 10 stable and 10 unstable lateral meniscal lesions were found. Twenty-nine of 30 medial and 19 of 20 lateral meniscal lesions found at arthroscopy were observed on MR images. Among the 20 medial and 30 lateral menisci that were normal at arthroscopy, 18 medial and 27 lateral menisci were found to be normal on MR images. One medial and one lateral meniscal abnormality at arthroscopy were missed on MR images. These two lesions were stable at arthroscopy. Two normal medial and three normal lateral menisci at arthroscopy were considered abnormal and stable in MR imaging (Table 1). Sensitivity and specificity of MR imaging for the detection of meniscal abnormality were 96% and 90%, respectively (Table 2). Displaced Meniscal Fragment Seven medial and five lateral meniscal fragments were observed in the intercondylar space (n = 9) or in the medial inframeniscal recess (n = 3) (Fig. 1). The presence of a displaced meniscal fragment had sensitivity and specificity for the detection of an unstable tear of 36% and 94%, respectively, with positive and negative predictive values of 92% and 43%, respectively. Size Fifteen medial and three lateral meniscal lesions were visible on more than three T2*- 772 AJR:176, March 2001
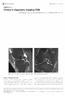
3 MR Imaging of Knee Meniscus s weighted coronal and two intermediateweighted sagittal MR images. The presence of lesion visibility on more than three T2*- weighted coronal and two intermediateweighted sagittal MR images had a sensitivity and specificity for the detection of an unstable lesion of 54% and 94%, respectively, with positive and negative predictive values of 95% and 52%, respectively. Shape Fourteen medial and one lateral meniscal lesions consisted of more than one lesion pattern or more than one cleavage plane (Figs. 1 and 2). The presence of more than one lesion pattern or more than one cleavage plane in the same meniscal area had a sensitivity and a specificity for the detection of an unstable lesion of 45% and 94%, respectively, with positive and negative predictive values of 94% and 47%, respectively. Signal Intensity Six medial and no lateral meniscal lesions displayed intrameniscal high signal intensity on T2-weighted images (Fig. 3). The presence of high signal intensity in the medial or lateral meniscus had a sensitivity and specificity for the detection of an unstable lesion of 18% and 100%, respectively, with positive and negative predictive values of 100% and 39%. TABLE 1 Arthroscopy Presence of Any MR Imaging Criterion Twenty-one of 23 medial and six of 10 lateral menisci had at least one MR imaging crite- Distribution of Normal Menisci and Stable and Unstable s of the Medial and Lateral Menisci Found at Arthroscopy and at MR Imaging Normal Medial Meniscus Stable Unstable MR Imaging Normal Lateral Meniscus Stable Unstable Normal Stable lesion Unstable lesion Note. Stable lesions on MR imaging presented none of the four MR imaging criteria for unstable lesions. Unstable lesions presented at least one of the four criteria. TABLE 2 Fig year-old man with chronic right knee pain. A, Parasagittal intermediate-weighted spin-echo MR image shows horizontal tear (white arrow ) in posterior horn of medial meniscus. Note contour irregularity (black arrow ) of inner margin. B, MR image medial to A shows radial tear (arrow ) of meniscal body. Note meniscal fragment (arrowheads) flipped anteriorly and inferiorly. C, Coronal gradient-echo T2*-weighted MR image shows meniscal fragment (arrowheads) displaced in inferior recess. Unstable meniscal lesion with displaced fragment was found at arthroscopy. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Positive and Negative Predictive Values for Detection of Meniscal Abnormalities on Knee MR Imaging Compared with Knee Arthroscopy in 50 Patients Parameter Medial Meniscus Lateral Meniscus Medial and Lateral Menisci Sensitivity (%) 97 (87 99) 95 (85 98) 96 (90 98) Specificity (%) 90 (79 96) 90 (79 96) 90 (82 94) PPV (%) 93 (83 98) 86 (74 93) 90 (83 95) NPV (%) 95 (85 98) 96 (87 99) 96 (90 98) Note. Numbers in parentheses are 95% confidence intervals. PPV = positive predictive value, NPV = negative predictive value. A B C AJR:176, March
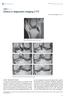
4 Vande Berg et al. rion indicative of instability and corresponded to an unstable tear at arthroscopy. Two medial and four lateral menisci without MR imaging criteria for instability were found to be unstable at arthroscopy. Sensitivity and specificity of the presence of at least one MR imaging criterion indicative of instability in medial and lateral menisci were both 82%, with positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 70%, respectively (Table 3). C A Fig year-old man with left knee pain. A, Parasagittal intermediate-weighted spin-echo MR image shows contour irregularity (arrow ) of apex of posterior horn of medial meniscus. B, MR image medial to A shows vertical tear (arrow ). C, MR image medial to B shows horizontal tear (arrow ). D, Coronal gradient-echo T2*-weighted MR image of posterior horn of medial meniscus shows focal substance loss (arrow ) and horizontal cleavage plane (arrowhead ) that extends to posteromedial aspect of medial meniscus. Presence of two lesion patterns and two cleavage planes, along with visibility of lesion on six coronal and five sagittal contiguous sections (not shown) suggests unstable tear, which was confirmed at arthroscopy. TABLE 3 Sensitivity, Specificity, and Positive and Negative Predictive Values of the Presence of At Least One of the Four MR Imaging Criteria for Detecting Unstable s on MR Imaging Compared with Knee Arthroscopy Parameter Medial Meniscus Lateral Meniscus Medial and Lateral Menisci Sensitivity (%) 91 (76 97) 60 (39 78) 82 (69 90) Specificity (%) 71 (53 84) 90 (70 97) 82 (70 90) PPV (%) 91 (76 97) 86 (65 95) 90 (79 96) NPV (%) 71 (53 84) 69 (47 85) 70 (56 81) Note. Numbers in parentheses are 95% confidence intervals. PPV = positive predictive value, NPV = negative predictive value. Discussion Our study shows that each of the proposed MR imaging criteria had high specificity but low sensitivity for the recognition of instability among all meniscal lesions when used retrospectively in a series of 50 patients in whom knee arthroscopy was performed. Moreover, when the presence of at least one of the four MR imaging criteria was considered, MR imaging was found to have sensitivity and specificity of 82% and positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 70%, respectively, for the determination of meniscal lesion stability. The high negative predictive value of MR imaging in recognizing meniscal lesions has taken on an important clinical significance with the possibility of conservative management of patients with clinically suspected meniscal lesions and negative results on MR imaging [12 14]. The positive predictive value of 90% for MR imaging in recognizing instability among all meniscal lesions that was shown in our study further increases the clinical role of MR imaging because it implies that MR imaging could help select patients with meniscal abnormalities who have B D 774 AJR:176, March 2001
5 MR Imaging of Knee Meniscus s Fig year-old man with right knee pain. Sagittal T2-weighted fast spin-echo MR image shows tear of posterior horn of medial meniscus with high signal intensity (arrow ) equivalent to that of joint fluid in meniscus. was found unstable at arthroscopy, with large meniscal flap of posterior horn of medial meniscus. unstable lesions that are more likely to benefit from surgery. Our study aimed at validating MR imaging criteria for unstable meniscal lesions. First, the presence of a displaced meniscal fragment at MR imaging was considered direct evidence of an unstable lesion. In the literature, sensitivity in the detection of displaced meniscal fragments on MR imaging was initially low [10, 15] and increased progressively with experience [7, 11, 16]. The fact that one fragment observed at MR imaging was associated with a stable lesion at arthroscopy could result from false-positive or false-negative findings at MR imaging or at arthroscopy, respectively. Second, lesion visibility on more than two 4- mm-thick sagittal and three 3-mm-thick coronal images corresponded to a lesion extent greater than 10 mm. This value was selected in agreement with the initial proposal of Carpenter et al. [7] and corresponded to the cutoff value used at arthroscopy to characterize unstable lesions [4, 17]. Third, lesion number was taken into account instead of lesion shape because exact fissure plane orientation was difficult to recognize. instability was recognized if more than one cleavage plane or more than one lesion pattern, including contour irregularity, peripheral meniscal separation, and meniscal tear, was found in the same meniscal area. Actually, oblique or parrot-beak tears that are the most frequent unstable meniscal lesions can be decomposed into focal contour irregularity because of meniscal substance loss or a radial or oblique tear at the meniscus free edge and longitudinal tear [5, 10]. A nondisplaced meniscal flap can be difficult to recognize on MR images. However, parrot-beak tears with a nondisplaced meniscal flap probably cause a lesion with multiple lesion patterns or plane orientations. Finally, the presence of fluidlike signal intensity in the meniscus on T2-weighted images also indicated unstable meniscal lesions. The presence of high signal intensity on T2- weighted images is a highly specific but poorly sensitive sign for a meniscal lesion [18]. The presence of intrameniscal high signal intensity on T2-weighted images likely occurred only in meniscal lesions in which torn edges were moderately separated and thus unstable, with subsequent accumulation of articular fluid in the large cleavage plane. Our study concluded that arthroscopy should not be performed in knees with meniscal lesions that lack MR imaging criteria for an unstable tear because the sensitivity and negative predictive value of the MR imaging criteria are relatively low. These criteria need to be refined to increase their sensitivity. Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility also need to be determined. Our purpose was not to determine with MR imaging whether the meniscal lesions were repairable because no lesions in this series were sutured. Neither did we correlate the meniscal lesion patterns on MR imaging with the arthroscopic findings because this correlation needs precise surgical data that were not available. The results of our study are limited by the imaging technique and the study design. First, coronal and sagittal imaging planes were used for lesion analysis. The performance of submillimetric axial imaging could have enhanced the results by providing better delineation of radial or oblique lesion components with subsequent direct visualization of parrot-beak tears and meniscal flaps, as previously shown [10, 19 21]. Second, we analyzed the MR studies that were obtained using mid (0.5-T) or high field strength (1.5- T) without taking into account field strength difference because of its lack of influence on MR imaging accuracy for meniscal tear detection [10, 22]. The influence of field strength cannot be excluded in assessing meniscal lesion stability. Third, selection bias existed in our study because only MR imaging studies from patients who underwent arthroscopy were retrospectively reviewed by a radiologist who knew that these patients had undergone surgery. Patients with negative findings on MR imaging or with subtle lesions probably did not undergo surgery and could be a group of potential false-negative findings on MR imaging. However, the two false-negative results on MR imaging were stable lesions at arthroscopy, and the five false-positive results at MR imaging showed no MR criteria for instability. Finally, other criteria independent of meniscal MR imaging appearance, including age of the patient and associated ligament lesions that could influence lesion stability [1, 3 6, 23], were not taken into account. In conclusion, MR imaging criteria for unstable meniscal lesions that are based on the presence of a displaced meniscal fragment and on determination of meniscal lesion extent, shape, and signal intensity have a high specificity and a high positive predictive value for the recognition of instability among all meniscal lesions. These criteria remain to be assessed in prospective clinical studies. References 1. Awbrey BJ. Arthroscopic management of meniscal injuries. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1993;5: Metcalf RW, Burks RT, Metcalf MS, et al. Arthroscopic menisectomy. In: McGinty JB, ed. Operative arthroscopy, 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1996: DeHaven KE. Decision-making factors in the treatment of meniscus lesions. Clin Orthop 1990;252: Weiss CB, Lundberg M, Hamberg P, DeHaven KE, Gillquist J. Non-operative treatment of meniscal tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1989;71-A: Dandy DJ. The arthroscopic anatomy of symptomatic meniscal lesions. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1990;72-B: Newman AP, Daniels AU, Burks RT. Principles and decision making in meniscal surgery. Arthroscopy 1993;9: Carpenter JS, Rubin DA, Harner CD, et al. Assessment of meniscal tear stability with MR imaging. (abstr) Radiology 1996;201(P): Kaplan PA, Nelson NL, Garvin KL, Brown DE. MR of the knee: the significance of high signal in AJR:176, March
6 Vande Berg et al. the meniscus that does not clearly extend to the surface. AJR 1991;156: De Smet AA, Norris MA, Yandow DR, Quintana FA, Graf BK, Keene JS. MR diagnosis of meniscal tears of the knee: importance of high signal in the meniscus that extends to the surface. AJR 1993;161: Rubin DA. MR imaging of the knee menisci. Radiol Clin North Am 1997;35: Lecas LK, Helms CA, Kosarek FJ, Garret WE. Inferiorly displaced flap tears of the medial meniscus: MR appearance and clinical significance. AJR 2000;174: Coumas JM, Palmer WE. Knee arthrography: evolution and current status. Radiol Clin North Am 1998;36: Ruwe PA, Wright J, Randall RL, Lynch JK, Jokl P, McCarthy S. Can MR imaging effectively replace diagnostic arthroscopy? Radiology 1992; 183: Spiers ASD, Meagher T, Ostlere SJ, Wilson DJ, Dodd CAF. Can MRI of the knee affect arthroscopic practice? J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75- B: Wright DH, De Smet AA, Norris M. Bucket-handle tears of the medial and lateral menisci of the knee: value of MR imaging in detecting displaced fragments. AJR 1995;165: Magee TH, Hinson GW. MRI of meniscal buckethandle tears. Skeletal Radiol 1998;27: Matava MJ, Eck K, Totty W, Wright RW, Shively RA. Magnetic resonance imaging as a tool to predict meniscal reparability. Am J Sports Med 1999;27: Mink JH, Levy T, Crues JV 3d. Tears of the anterior cruciate ligament and menisci of the knee: MR imaging evaluation. Radiology 1988;167: Araki Y, Ootani F, Tsukaguchi I, et al. MR diagnosis of meniscal tears of the knee: value of axial three-dimensional Fourier transformation GRASS images. AJR 1992;158: Tuckman GA, Miller WJ, Remo JW, Fritts HM, Rozansky MI. Radial tears of the menisci: MR findings. AJR 1994;163: Disler DG, Kattapuram SV, Chew FS, Rosenthal DI, Patel D. Meniscal tears of the knee: preliminary comparison of three-dimensional MR reconstruction with two-dimensional MR imaging and arthroscopy. AJR 1993;160: Barnett MJ. MR diagnosis of internal derangements of the knee: effects of field strength on efficacy. AJR 1993;161: De Smet AA, Graf BK. Meniscal tears missed on MR imaging: relationship to meniscal tear patterns and anterior cruciate ligament tears. AJR 1994;162: AJR:176, March 2001
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics
 Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee
 Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and
 MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
a - CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) CASE PRESENTATION
 !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
!Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
Key words: arthroscopy, orthopaedic examination, magnetic resonance imaging, knee injury.
 Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Resection of bucket-handle tears is one of the most
 Technical Note Arthroscopic Resection of Bucket-Handle Tears With the Help of a Suture Punch: A Simple Technique to Shorten Operating Time Mehmet S. Bı nnet, M.D., İlksen Gürkan, M.D., and Cem Çetı n,
Technical Note Arthroscopic Resection of Bucket-Handle Tears With the Help of a Suture Punch: A Simple Technique to Shorten Operating Time Mehmet S. Bı nnet, M.D., İlksen Gürkan, M.D., and Cem Çetı n,
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas
 Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. A. M. R. Tinto, J. Raposo,
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. A. M. R. Tinto, J. Raposo,
ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE
 MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
MRI Characteristics of Healed and Unhealed Peripheral Vertical Meniscal Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas
 Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. Tinto, J. Raposo, T. Bilhim, A.
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. Tinto, J. Raposo, T. Bilhim, A.
Original Research Article. Atul Bucha 1, Sunita Dashottar 2 *, Surabhi Sharma 2, Preeth Pany 2, Rushabh Bhikhanhai Suthar 2
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
Original Research Article
 ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
T HE clinical history and findings at physical examination in patients with abnormalities of the knee are known to be nonspecific in the determination
 Patrick A. Ruwe, MD #{149} James Wright, MD, MPH, FRCSC #{149}R. Lawr Randall, BA J. Kevin Lynch, MD #{149}Peter Joki, MD #{149}Shirley McCarthy, MD, PhD Can MR Imaging Effectively Replace Diagnostic Arthroscopy?
Patrick A. Ruwe, MD #{149} James Wright, MD, MPH, FRCSC #{149}R. Lawr Randall, BA J. Kevin Lynch, MD #{149}Peter Joki, MD #{149}Shirley McCarthy, MD, PhD Can MR Imaging Effectively Replace Diagnostic Arthroscopy?
A comparative study of MRI versus arthroscopic findings in ACL and meniscal injuries of the knee
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 0, pp. 000 000 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery Peleg Ben-Galim, MD*; Ely
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 0, pp. 000 000 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery Peleg Ben-Galim, MD*; Ely
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears ABSTRACT
 1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
Ultrasound assessment of internal derangement of the knee
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 72-76 ORIGINAL STUDY sound assessment of internal derangement of the knee Zaka KHAN, Zia FARUQUI, Olajide OGYUNBIYI, Guy ROSSET, Javaid IQBAL From Armed Forces Hospital, Southern
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 72-76 ORIGINAL STUDY sound assessment of internal derangement of the knee Zaka KHAN, Zia FARUQUI, Olajide OGYUNBIYI, Guy ROSSET, Javaid IQBAL From Armed Forces Hospital, Southern
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age
 DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1028-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age Jung-Ryul Kim Byung-Guk Kim Jin-Woo Kim Jin-Hyun
DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1028-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age Jung-Ryul Kim Byung-Guk Kim Jin-Woo Kim Jin-Hyun
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy
 Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
Arthroscopic Resection of Bucket- Handle Tears With the Help of a Suture Punch: A Simple Technique to Shorten Operating Time
 Arthroscopic Resection of Bucket- Handle Tears With the Help of a Suture Punch: A Simple Technique to Shorten Operating Time Mehmet S. Binnet, M.D., İlksen Gürkan, M.D., and Cem Çetin, M.D. Resection of
Arthroscopic Resection of Bucket- Handle Tears With the Help of a Suture Punch: A Simple Technique to Shorten Operating Time Mehmet S. Binnet, M.D., İlksen Gürkan, M.D., and Cem Çetin, M.D. Resection of
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears
 Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177)
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
The role of magnetic resonance imaging in routine decision making for meniscal surgery
 Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (1999) 7 :278 283 KNEE Springer-Verlag 1999 T. Muellner A. Nikolic H. Kubiena F. Kainberger M. Mittlboeck V. Vécsei The role of magnetic resonance imaging in routine
Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (1999) 7 :278 283 KNEE Springer-Verlag 1999 T. Muellner A. Nikolic H. Kubiena F. Kainberger M. Mittlboeck V. Vécsei The role of magnetic resonance imaging in routine
Role of Mri in Meniscal Tearsdr
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. III (March. 2017), PP 111-117 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Mri in Meniscal Tearsdr Jeevika
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. III (March. 2017), PP 111-117 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Mri in Meniscal Tearsdr Jeevika
Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Prospective evaluation of the McMurray test PETER J. EVANS,* MD, PhD, G. DOUGLAS BELL, MD, FRCS(C), AND CY FRANK, MD, FRCS(C)
 Prospective evaluation of the McMurray test PETER J. EVANS,* MD, PhD, G. DOUGLAS BELL, MD, FRCS(C), AND CY FRANK, MD, FRCS(C) From the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sport Medicine Centre, University
Prospective evaluation of the McMurray test PETER J. EVANS,* MD, PhD, G. DOUGLAS BELL, MD, FRCS(C), AND CY FRANK, MD, FRCS(C) From the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sport Medicine Centre, University
The Meniscus. History. Anatomy. Anatomy. Blood Supply. Attachments
 History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
COMMON KNEE AND SHOULDER INJURIES IN THE YOUNG ATHLETE. Outline 5/11/2017
 COMMON KNEE AND SHOULDER INJURIES IN THE YOUNG ATHLETE IRVING RAPHAEL MD Syracuse Orthopedic Specialists Former S.U. Head Team Physician May 19, 2017 Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries
COMMON KNEE AND SHOULDER INJURIES IN THE YOUNG ATHLETE IRVING RAPHAEL MD Syracuse Orthopedic Specialists Former S.U. Head Team Physician May 19, 2017 Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries
Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Validity of flounce sign to rule out medial meniscus tear in knee arthroscopy
 Gupta et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:337 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0800-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Validity of flounce sign to rule out medial meniscus tear in knee arthroscopy Yogendra
Gupta et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:337 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0800-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Validity of flounce sign to rule out medial meniscus tear in knee arthroscopy Yogendra
Original Report MR Imaging of Infrapatellar Plica Injury OBJECTIVE. CONCLUSION. Materials and Methods
 R. Lee Cothran 1 Philip M. McGuire 1,2 Clyde A. Helms 1 Nancy M. Major 1 David E. Attarian 3 Received October 25, 2001; accepted after revision October 11, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Box 3808, Duke
R. Lee Cothran 1 Philip M. McGuire 1,2 Clyde A. Helms 1 Nancy M. Major 1 David E. Attarian 3 Received October 25, 2001; accepted after revision October 11, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Box 3808, Duke
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation
 A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
Sensitivity of MR Arthrography in the Evaluation of Acetabular Labral Tears
 MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Meniscectomy Curriculum
 Meniscectomy Curriculum ARTHRO Mentor Meniscectomy Curriculum 1 Description The following curriculum is focused on the Meniscectomy procedure: relevant pathologies and their classification, instrumentation
Meniscectomy Curriculum ARTHRO Mentor Meniscectomy Curriculum 1 Description The following curriculum is focused on the Meniscectomy procedure: relevant pathologies and their classification, instrumentation
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
MRI of Acute Meniscal Injury Associated with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Prevalence, Type, and Location
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Mustonen et al. MRI of Meniscal Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ntti O. T. Mustonen 1 Mika P. Koivikko 1 Jan Lindahl 2 Seppo K. Koskinen 1 Mustonen
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Mustonen et al. MRI of Meniscal Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ntti O. T. Mustonen 1 Mika P. Koivikko 1 Jan Lindahl 2 Seppo K. Koskinen 1 Mustonen
Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
 Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy Mustafa Koplay 1, Elif Aksakallı 2, Serdar Toker 3, Seda Özbek 1, Ali Sami
Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy Mustafa Koplay 1, Elif Aksakallı 2, Serdar Toker 3, Seda Özbek 1, Ali Sami
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak 1, Andrew Arjun Sayampanathan 2, Thean-Howe Bryan Koh 2, Hwee-Chye Andrew Tan 1. Original Article.
 Original Article Page 1 of 6 Diagnosis of ligamentous and meniscal pathologies in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic findings Hamid
Original Article Page 1 of 6 Diagnosis of ligamentous and meniscal pathologies in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic findings Hamid
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Diagnostic Accuracy Using Indirect MR Arthrography
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions
 Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
Epidemiology. Meniscal Injury & Repair. Meniscus Anatomy. Meniscus Anatomy
 Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
The Meniscal Roots: Gross Anatomic Correlation with 3-T MRI Findings
 rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
ARTHROSCOPY OF THE KNEE
 Acta orthop. scand. 54, 2428, 983 ARTHROSCOPY OF THE KNEE An Analysis of 588 Consecutive Knee Arthroscopies HENNING HANSEN, PER B. THOMSEN & EBBE DYREBORG Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 0, Odense University
Acta orthop. scand. 54, 2428, 983 ARTHROSCOPY OF THE KNEE An Analysis of 588 Consecutive Knee Arthroscopies HENNING HANSEN, PER B. THOMSEN & EBBE DYREBORG Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 0, Odense University
Causation Review - Meniscal Tears.
 Causation Review - Meniscal Tears. Classification Of Meniscal Tears Of The Knee And The Evidence That Certain Tears Are Degenerative In Origin; Including The Relationship Of Meniscal Tears To Knee Osteoarthritis.
Causation Review - Meniscal Tears. Classification Of Meniscal Tears Of The Knee And The Evidence That Certain Tears Are Degenerative In Origin; Including The Relationship Of Meniscal Tears To Knee Osteoarthritis.
doi: /j.knee
 doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2013.04.016 Title page (a) title: Oblique coronal and oblique sagittal MRI for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears and evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament remnant tissue
doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2013.04.016 Title page (a) title: Oblique coronal and oblique sagittal MRI for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears and evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament remnant tissue
MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast Necessary?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological
 The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears
 Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Can discoid lateral meniscus be returned to the correct anatomic position and size of the native lateral meniscus after surgery?
 Can discoid lateral meniscus be returned to the correct anatomic position and size of the native lateral meniscus after surgery? Seong Hwan Kim,*M.D. 1, Joong Won Lee M.D. 2, and Sang Hak Lee, M.D. 2 From
Can discoid lateral meniscus be returned to the correct anatomic position and size of the native lateral meniscus after surgery? Seong Hwan Kim,*M.D. 1, Joong Won Lee M.D. 2, and Sang Hak Lee, M.D. 2 From
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
The diagnostic value of 0.2 Tesla low-field imaging in the detection of meniscal tears
 Merit Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences (ISSN: 2354-3238) Vol. 2(1) pp. 019-028, January, 2014 Available online http://www.meritresearchjournals.org/mms/index.htm Copyright 2014 Merit Research
Merit Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences (ISSN: 2354-3238) Vol. 2(1) pp. 019-028, January, 2014 Available online http://www.meritresearchjournals.org/mms/index.htm Copyright 2014 Merit Research
Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis?
 Skeletal Radiol (2012) 41:273 280 DOI 10.1007/s00256-011-1169-4 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis? Pieter Van Dyck & Jan L. Gielen
Skeletal Radiol (2012) 41:273 280 DOI 10.1007/s00256-011-1169-4 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis? Pieter Van Dyck & Jan L. Gielen
Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride. Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT
 Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT Disclosure Consultant Mitek Smith and Nephew-biologic patch Good
Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT Disclosure Consultant Mitek Smith and Nephew-biologic patch Good
Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair?
 Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair? Jack M. Bert, MD Adjunct Clinical Professor University of Minnesota Minnesota Bone & Joint Specialists, Ltd St. Paul, Minnesota Disclosures
Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair? Jack M. Bert, MD Adjunct Clinical Professor University of Minnesota Minnesota Bone & Joint Specialists, Ltd St. Paul, Minnesota Disclosures
Unlocking the locked Knee
 Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Correspondence should be addressed to Min Jung; and Kun-Bo Park;
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 5941057, 9 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5941057 Research Article Preoperative Diagnosis and Treatment Outcomes of Incarcerated Inferiorly Displaced Flap
BioMed Research International, Article ID 5941057, 9 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5941057 Research Article Preoperative Diagnosis and Treatment Outcomes of Incarcerated Inferiorly Displaced Flap
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping
 Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes
 Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes William M Weiss, MD MSc FRCSC Orthopedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy & Extremity Reconstruction
Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes William M Weiss, MD MSc FRCSC Orthopedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy & Extremity Reconstruction
Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
Management of neglected ACL avulsion fractures: a case series and systematic review
 Management of neglected ACL avulsion fractures: a case series and systematic review Presenter Dr. Devendra K chouhan Additional Professor PGIMER, Chandigarh India Co-Author Prof. Mandeep S Dhillon Department
Management of neglected ACL avulsion fractures: a case series and systematic review Presenter Dr. Devendra K chouhan Additional Professor PGIMER, Chandigarh India Co-Author Prof. Mandeep S Dhillon Department
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional
 MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography. Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears
 Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
