Original Research Article
|
|
|
- Brenda Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Research Article Study of Rotator Cuff Disorders by Ultrasound with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Hemanth Purigali Naganna 1, Shashikumar Mysore Rangaswamy 2, Jaganathan 3, Nanjaraj Chakenalli Puttaraju 2, Rajendra Kumar Narasipura Lingaiah 2, Pradeep Hagalahalli Nagarajegowda 4 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Professor, 3 Senior Resident, 4 Associate Professor, Mysore Medical College and Research Institute, India Corresponding author: Dr Shashikumar Mysore Rangaswamy Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, KR Hospital, Mmcri, Mysore, , India How to cite this article: Hemanth Purigali Naganna, Shashikumar Mysore Rangaswamy, Jaganathan, Nanjaraj Chakenalli Puttaraju, Rajendra Kumar Narasipura Lingaiah, Pradeep Hagalahalli Nagarajegowda. Study of Correlation. International Journal of Contemporary Medicine Surgery and Radiology. 2018;3(1): A B S T R A C T Introduction: Shoulder pain is one of the most common complaints encountered in orthopedic department. Rotator cuff pathologies are the cause of most common problems at the shoulder joint. Accurate diagnosis of these pathologies is essential for appropriate management. In addition to history and physical examination, evaluation of a patient with shoulder pain often involves assessment of the rotator cuff with a diagnostic test such as high resolution ultrasonography or MRI. This study aimed to assess the accuracy of high resolution ultrasonography in detecting the rotator cuff disorders by correlating with Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings. Material and methods: The study included thirty patients who presented with shoulder joint pain, restriction of movements or clinically suspected rotator cuff disorders. Patients were subjected to both High resolution USG and MRI investigations. USG findings were then correlated with MRI findings. Results: USG detected 18 cases of supraspinatous pathologies out of the 24 MRI detected abnormal supraspinatous tendons, with a sensitivity of 75%. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy for supraspinatus tendon pathologies were found to be 75%, 66.7%, 90%, 40% and 73.7% respectively and that for subscapularis tendon were 66.7%, 95.8%, 80%, 92% and 90% respectively. USG had 58.3% sensitivity in identifying partial thickness tears, 100% specificity and PPV. For full thickness tear, USG had 100% sensitivity, 96.4% specificity, 75% PPV, 100% NPV and an accuracy of 100%. Conclusion: USG is comparable to MRI in evaluation of disorders of the rotator cuff disorders, particularly more accurate in full thickness tear of rotator cuff tendons. USG can be used as the first line investigation, MRI can be used in situations where the diagnosis is equivocal on USG or in patients in whom USG examination is difficult to perform or patient is not cooperative. Ultrasonography being non-invasive, non-ionizing, combined with low cost with advantage of dynamic real time assessment, may serve as the most cost effective imaging method for screening of rotator cuff disorders. Key words: Ultrasonography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Rotator Cuff Tears INTRODUCTION Shoulder pain is one of the most common complaints encountered in orthopedic department and often leads to considerable disability 1. Pathologies of the rotator cuff are the cause of most common problems at the shoulder joint and accurate diagnosis is essential for appropriate management 2. Cuff strain, impingement syndrome and rotator cuff tears make up a group of lesions that produce shoulder pain. It is clinically difficult to differentiate between these conditions and distinguish them from other conditions like glenohumeral instability. In addition to history and physical examination, evaluation of a patient with shoulder pain often involves assessment of the rotator cuff with a diagnostic test such as high resolution ultrasonography or MRI 3. High resolution ultrasound being non invasive, less expensive and non-ionizing modality with added advantage of real time assessment has good sensitivity in detecting rotator cuff disorders. It can be used as a focused examination providing rapid, real-time diagnosis in many clinical situations 4. The reported accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of high resolution ultrasound in detecting any tear, whether partial or full thickness are all greater than 90% 5. It serves as a complementary role to MRI in shoulder imaging. High resolution ultrasound can also reveal the presence of other abnormalities that may mimic rotator cuff tear at clinical examination including tenosynovitis, tendinosis, calcific tendinitis, subacromial-subdeltoid bursitis, greater tuberosity fracture, etc., MRI has become the gold standard for detecting both subtle and obvious internal derangement assessing overall joint structure. MRI is an excellent modality because of its multiplanar capability. MRI can provide information about rotator cuff disorders such as tendinosis, calcific tendinitis, tears, muscle atrophy and involvement of adjacent structures such as rotator interval, long head of biceps brachii tendon, all of which have implications for rotator cuff treatment and prognosis 6. 70
2 Magnetic resonance arthrography is commonly used for instability 7. Arthrography appears to be more accurate in diagnosing rotator cuff injuries than either MRI or ultrasound but that benefit must be set against the invasiveness and potential discomfort to patients. MRI and ultrasonography have replaced arthrography for evaluating the integrity of the rotator cuff. Ultrasonography is as accurate as MRI, these combined with low cost for ultrasound suggests that ultrasound may be the most cost effective imaging method of screening for rotator cuff disorders. Sonography has the advantage of dynamic real time assessment 8. This study aimed to assess the accuracy of high resolution ultrasonography in detecting the rotator cuff disorders by correlating with Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings. MATERIAL AND METHODS A structured pre-prepared case proforma was used to enter the patient details, clinical history and imaging findings who met the inclusion criteria. Ultrasound examination of the shoulder joint was performed in gray scale mode using a high resolution, MHz, linear array transducer. Rotator cuff tendons and muscles were studied by static and dynamic ultrasonography. Comparison with the contralateral side was also done. By USG, tendinosis is detected by focal thickening of the tendon and altered echopattern. Partial thickness tear is detected as focal discontinuity/ hypoechogenicity at the bursal or articular surfaces of the tendon. USG shows full thickness tear as discontinuity of tendons extending from bursal to articular surface with retraction of the torn tendon ends (figure 1-6). Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the shoulder joint was performed subsequently. Imaging was done with 1.5 Tesla MRI machine using shoulder coil. The following sequences were selected as required: Oblique coronal/oblique saggital T1W sequence, T2W and PD FSE sequences with or without fat saturation, Axial T2*W GRE sequence and Axial/oblique saggital STIR sequence. Field of view cm, slice thickness 3 mm and matrix size and TR/TE kept according to the selected sequence. In MRI, tendinosis presents as moderately increased signal intensity in short TE sequences such as T1 weighted and PD sequences while this increased signal intensity is not as high as fluid signal in T2 weighted sequence. These signal changes are seen along the long axis of the tendon, which may be focal or diffuse. On fat saturated sequences, the increased signal of tendinosis is as high as fluid and it should be differentiated from fluid signal seen in cases of tear. Severe tendinosis presents as diffuse thickening 9. In MRI, partial thickness tears presents as focal tendon fiber discontinuity with focal areas of hyperintensity on both short and long TE sequences on the articular or bursal surfaces. The hyperintensity does not extend through the entire thickness of the tendon. In MRI, full thickness tears are seen as high signal intensity traversing the whole thickness of tendon, extending from articular surface to bursal surface on at least one image. The high signal intensity is due to the presence of fluid. Full thickness tears are common in supraspinatus tendon. Fluid in the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa is a non-specific sign of full thickness tear in cases of tendon fiber discontinuity 10. The high resolution USG findings were correlated with the MRI findings (Figure 7-11). STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Both descriptive and inferential statistics were employed for data analysis. Diagnostic statistics such as sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy were computed to assess the correlation of USG findings with MRI findings. RESULTS Of the supraspinatous tendon pathologies, 9 patients (30%) found to have tendinosis in USG had tendinosis in MRI, 3 (10%) of the patients who were found to have tendinosis in USG were found to have partial tear in MRI. 4 (13.3%) patients who had normal sonographic appearance of supraspinatous tendon had tendinosis in MRI. All four partial thickness tears diagnosed by ultrasound had partial thickness tears in MRI also. One full thickness tear detected by USG was found to be a partial thickness tear in MRI. 6 patients (20%) had both normal sonographic and MRI appearances. Of the infraspinatous tendon pathologies, 28 patients (93.3%) were found to have normal tendon in both USG and MRI. One patient (3.3%) who had partial thickness tear in USG was confirmed by MRI. One patient (3.3%) found to Affected Tendon USG/MRI Tears Tendinosis Partial thickness tear Full thickness tear Normal Supraspinatus USG 12 (40.0%) 4 (13.3%) 4 (13.3%) 10 (30.0%) MRI 13 (43.3%) 8 (26.7%) 3 (10.0%) 6 (20.0%) Infraspinatus USG 0 (0.0%) 1 (3.3%) 0 (0.0%) 29 (96.7%) MRI 1 (3.3%) 1 (3.3%) 0 (0.0%) 28 (93.3%) Teres Minor USG 0 (0.0%) 0 (0.0%) 0 (0.0%) 30 (100%) MRI 0 (0.0%) 0 (0.0%) 0 (0.0%) 30 (100%) Subscapularis USG 3 (10.0%) 2 (6.7%) 0 (0.0%) 25 (83.3%) MRI 3 (10.0%) 3 (10.0%) 0 (0.0%) 24 (80.0%) Biceps Tendon USG 1 (3.3%) 0 (0.0%) 0 (0.0%) 29 (96.7%) MRI 0 (13.3%) 0 (13.3%) 0 (13.3%) 30 (13.3%) Table-1: Pathological correlation of USG and MRI Findings. 71
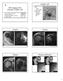
3 have tendinosis in MRI had normal sonographic appearance. Out of the 30 subscapularis tendons, 23 patients (76.7%) had normal appearance in both USG and MRI. Of the 3 patients found to have tendinosis by USG, one was tendinosis, one Figure-1: USG images showing focal hypoechogenicity and thickening of the supraspinatous tendon suggestive of tendinosis. Figure-3: USG image showing partial thickness tear of the supraspinatous tendon on the bursal surface. Figure-2: USG images of two patients showing partial thickness tear of the supraspinatous tendon on the articular surface. Figure-4: USG images of the supraspinatous tendon showing full thickness tear with retraction of tendon ends. Findings TP FP FN TN Total Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Minor Subscapularis Biceps Tendon (TP True positive; FP False positive; FN False negative; TN True Negative) Table-2: Observation of USG and MRI Findings. Findings Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV Accuracy p-value Supraspinatus < 0.01 Infraspinatus < 0.01 Teres Minor Subscapularis < 0.01 Biceps Tendon PPV Positive Predictive Value; NPV Negative Predictive Value Table-3: Evaluation of USG and MRI Findings. Tears TP FP FN TN Total Partial thickness Full thickness TP True positive; FP False positive; FN False negative; TN True Negative Table-4: Observation of USG and MRI Findings with respect to tears. Findings Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV Accuarcy Partial thickness Full thickness PPV Positive Predictive Value; NPV Negative Predictive Value Table-5: Evaluation of USG and MRI Findings with respect to tears. 72
4 Figure-5: USG images showing partial tear of the subscapularis tendon. Figure-9: MRI saggital image showing partial thickness tear of the supraspinatous tendon extending to the bursal surface. Figure-6: USG image showing partial tear of the infraspinatous tendon. Figure-10: MRI axial images showing partial tear of the subscapularis tendon. Figure-7: MRI images of two patients showing focal hyperintensity and thickening of the supraspinatous tendon suggestive of tendinosis. Figure-8: MRI coronal (A) and saggital (B) images showing partial thickness tear of the supraspinatous tendon on the articular surface. was partial thickness tear and one was normal by MRI. The two cases diagnosed as partial tears by USG were confirmed to have partial tears in MRI. Of the three cases found to have tendinosis in MRI, 2 cases (66.7%) had normal sonographic appearance. For supraspinatous tendon pathologies USG had sensitivity of 75%, specificity of 66.7%, PPV of 90%, NPV of 40% and accuracy of 73.3% with a p-value of <0.01. For subscapularis tendon pathologies, sensitivity of 66.7%, specificity of 95.8%, PPV of 80%, NPV of 92% and accuracy of 90% were Figure-11: MRI images showing full thickness tear of the supraspinatous tendon with retraction of tendon ends. obtained with a p-value of <0.01. Infraspinatous tendon pathologies had a sensitivity of 50%, specificity and PPV 100%, NPV of 96.6% and accuracy of 96.7% with a p-value of <0.01. p-value was not obtained for teres minor tendon evaluation as no abnormality was found by USG and MRI in all 30 patients. Biceps tendon had a specificity of 96.7% and NPV of 100%, p-value not obtained as MRI showed no abnormality in all 30 patients (table- 1-3). In detecting partial tears of all rotator cuff tendons, USG had a sensitivity of 58.3%, specificity of 100%, PPV of 100%, NPV of 78.2& and accuracy of 83.3%. For full thickness tear detection, USG had a sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 96.4%, PPV of 75%, NPV of 100% and accuracy of 100% (table- 4,5). DISCUSSION Shoulder pain is one of the common presenting complaints in orthopaedic department. Rotator cuff disorders are the most common cause of shoulder pain. MRI is the investigative modality of choice used to assess the rotator cuff tendons and is sensitive and specific, but it cannot be used as a first line of investigation due to cost factor and 73
5 availability. Ultrasonography being relatively inexpensive and non-invasive can be used as a first line imaging modality to assess rotator cuff pathologies. This is a prospective study of 30 patients who presented with shoulder pain or restricted movements. The patients were subjected to USG examination of the shoulder joint and then MRI examination of the affected shoulder joint was performed. Findings of USG were compared with MRI findings. Various rotator cuff pathologies were studied. The pathologies include tendinosis, partial thickness tear and full thickness tear of the rotator cuff tendons. Supraspinatus is the commonest tendon to be affected in this study group, followed by the subscapularis tendon. Only two patients (6.7%) in our study had pathologies in infraspinatous tendon. Teres minor tendon was not affected (0%) in any of the patients. USG detected 18 cases of supraspinatous pathologies out of the 24 MRI detected abnormal supraspinatous tendons, with a sensitivity of 75%. Supraspinatus tendon pathologies showed 75% sensitivity, 66.7% specificity, 90% PPV, 40% NPV and an accuracy of 73.7% and significance of P value <0.01. Subscapularis tendon pathologies showed 66.7% sensitivity, 95.8% specificity, 80% PPV, 92% NPV and an accuracy of 90% and significance of P value <0.01. Infraspinatous tendon pathologies showed 50% sensitivity, 100% specificity, 100% PPV, 96.6% NPV and an accuracy of 96.7%. Biceps tendon and teres minor tendons findings showed a 100% NPV. 4,6 USG had a sensitivity of 58.3% in identifying partial thickness tears of the rotator cuff tendons. It had a specificity and PPV of 100%, NPV of 78.2% and an accuracy of 83.3%. For full thickness tear, USG had 100% sensitivity, 96.4% specificity, 75% PPV, 100% NPV and an accuracy of 100%. 7-9 USG has many advantages, it is non-invasive, non-ionizing, widely available, inexpensive and has high spatial resolution. USG can be done in out-patient department without need for any patient preparation. Limitations of USG are high operator dependency with a long learning curve and it has high inter-observer variation. Not all pathologies of shoulder joint can be assessed by USG, evaluation is limited to assessment of rotator cuff pathologies and associated fluid collections. Labral and ligamentous pathologies, bony abnormalities and muscle atrophy changes are not well appreciated by USG. One important pitfall of USG is anisotropy, tendons appear echogenic when the ultrasound beam is perpendicular to the long axis of the tendon resulting in an erroneous hypoechogenicity which may be mistaken for tendinosis or partial tears. 10 MRI is non-invasive, non-ionizing, it has multiplanar capability and high soft tissue contrast. Labro-ligamentous pathologies, subtle bony changes like edema or contusion and muscular atrophic changes are best appreciated by MRI. Limitations of MRI include high cost and availability. Other limitations are claustrophobia, metallic implants and pacemakers. Magic angle artefact is a common pitfall in MRI shoulder examinations. Increased signal intensity is seen in normal cuff tendons in short TE sequences such as T1W and PD due to the orientation of tendon fibers at an angle of 55 degrees to the main magnetic field, which is commonly mistaken for tendinosis. This artefact is not seen in long TE sequences such as T2. CONCLUSION USG is comparable to MRI in evaluation of disorders of the rotator cuff disorders, particularly partial or full thickness tears. MRI is the most sensitive and specific investigative modality and has high accuracy for assessment of soft tissue structures, but the cost factor and availability are its disadvantages. MRI can be used in situations where the diagnosis is equivocal on USG or in patients in whom USG examination is difficult to perform or patient is not cooperative and in problematic cases. Cost effectiveness and ready availability are the biggest advantages of ultrasonography. The real time capability of ultrasound in conducting dynamic studies in areas like the shoulder is a very big asset. It helps to do quick comparison with the contralateral side, which is of great help in many difficult situation. USG can be used as the first line of investigation in suspected rotator cuff disorders. It can be the most cost effective screening modality for rotator cuff disorders. REFERENCES 1. Naredo E, Aguado P, De Miguel E, Uson J. Painful Shoulder: Comparison of physical examination and ultrasonographic findings. Ann Rheum Dis 2002; 61(3): Shrestha MS, Alam A. A comparative evaluation of Rotator Cuff injuries of the shoulder joint using High Resolution Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Medical Journal of Shree Birendra Hospital 2011;10(1). 3. Sharlene A. Teefey, William D. Middleton, William T. Payne, Ken Yamaguchi. Detection and measurement of rotator cuff tears with sonography: Analysis of diagnostic errors. AJR 2005;184(2): Arun Kinare. Musculoskeletal ultrasound symposium. Indian J Radiol and Imaging 2007;17(3): Josh B Moosikasuwan, Theodore T Miller, Brian J Burke. Rotator cuff tears: Clinical, Radiographic and US findings. Radiographics 2005;25(4): Yoav Morag, Jon A Jacobson, Bruce Miller, Michel De Maeseneer, Gandikota Girish, David Jamadar. MR Imaging of rotator cuff injury: What the clinician needs to know. Radiographics 2006;26(5): Alan D Massengill, Leanne L Seege, Lawrence Yao, Amilcare Gentili, Ronald C Shnier, Matthew S Shapiro, Richanrd H Gold. Labrocapsular ligamentous complex of the shoulder: Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variation and Pitfalls of MR Imaging and MR Arthrography. Radiographics 1994;14(1): Joseph O De Jesus, Laurence Parker, Andrea J Frangos, Levon N Nazarian. Accuracy of MRI, MR Arthrography, and Ultrasound in the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears: A Meta-analysis. AJR 2009;192(5): Bergman AG. Rotator cuff impingement: pathogenesis, MR imaging characteristics, and early dynamic MR results. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 1997;5(6): Farley TE, Neumann CH, Steinbach LS. Full-thickness 74
6 tears of the rotator cuff of the shoulder: Diagnosis with MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992; 158(1): Source of Support: Nil; Conflict of Interest: None Submitted: ; Published online:
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology
 Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal Derangement of Shoulder
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience
 The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience Poster No.: C-0596 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. A. Ahyad, Z.
The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience Poster No.: C-0596 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. A. Ahyad, Z.
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019
 AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
A prospective comparative study of high resolution ultrasound and MRI in the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 12-2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2018.04.12.013
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 12-2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2018.04.12.013
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders
 Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Rotator Cuff Injuries: Is Ultrasound Enough? A Correlation with MRI
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/28116:2279 Radiology Section Original Article Rotator Cuff Injuries: Is Ultrasound Enough? A Correlation with MRI Vishal Dhirenbhai Thakker, Dipu Bhuyan, Manali Arora, Mohsina Islam
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/28116:2279 Radiology Section Original Article Rotator Cuff Injuries: Is Ultrasound Enough? A Correlation with MRI Vishal Dhirenbhai Thakker, Dipu Bhuyan, Manali Arora, Mohsina Islam
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Painful Shoulder joint in rural population
 Original article: Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Painful Shoulder joint in rural population Dr. Pankaj Garg*, Dr. V.N. Marathe, Dr. S. G. Gandage, Dr.S.G.Kachewar Department of Radiology, Rural Medical
Original article: Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Painful Shoulder joint in rural population Dr. Pankaj Garg*, Dr. V.N. Marathe, Dr. S. G. Gandage, Dr.S.G.Kachewar Department of Radiology, Rural Medical
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
A Prospective Comparative Study of High Resolution Ultrasound and MRI in the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears in a Tertiary Hospital of North India
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 491-497 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.897830 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.01.29 Accepted: 2016.03.15 Published: 2016.10.19 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 491-497 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.897830 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.01.29 Accepted: 2016.03.15 Published: 2016.10.19 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
Detection and Measurement of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography: Analysis of Diagnostic Errors
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Teefey et al. Detection of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography Sharlene A. Teefey 1 William D. Middleton 1 William T. Payne 2 Ken Yamaguchi 3 Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Payne WT, Yamaguchi
Musculoskeletal Imaging Teefey et al. Detection of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography Sharlene A. Teefey 1 William D. Middleton 1 William T. Payne 2 Ken Yamaguchi 3 Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Payne WT, Yamaguchi
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Correlation between High Resolution Ultrasonography and MRI in Rotator Cuff Tear Diagnosis
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Correlation between High Resolution Ultrasonography and MRI in Rotator Cuff Tear Diagnosis
MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26026:2263 Radiology Section Original Article MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee Hemanth Purigali Naganna,
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26026:2263 Radiology Section Original Article MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee Hemanth Purigali Naganna,
Rotator cuff. MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff. Trauma. Trauma. Trauma. Tendon calcification. Acute. Degenerative. Trauma Calcific tendinitis
 Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff Tears. University of Medical Sciences, Iran. Medical Sciences, Iran.
 Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears
 Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
Ultrasound of the Shoulder: Asymptomatic Findings in Men
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Girish et al. Shoulder Ultrasound Findings Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gandikota Girish 1 Lucas G. Lobo 1 Jon A. Jacobson 1 Yoav Morag 1 Bruce Miller
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Girish et al. Shoulder Ultrasound Findings Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gandikota Girish 1 Lucas G. Lobo 1 Jon A. Jacobson 1 Yoav Morag 1 Bruce Miller
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when?
 Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기
 US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
Ultrasound of Shoulder Pathology and Intervention 서울대학교병원재활의학과 김기원
 Ultrasound of Shoulder Pathology and Intervention 서울대학교병원재활의학과 김기원 Ultrasound for Shoulder Disorder Advantage Dynamic evaluation Immediate clinical correlation + Intervention Weakness Diagnostic accuracy?
Ultrasound of Shoulder Pathology and Intervention 서울대학교병원재활의학과 김기원 Ultrasound for Shoulder Disorder Advantage Dynamic evaluation Immediate clinical correlation + Intervention Weakness Diagnostic accuracy?
IMAGING OF ROTATOR CUFF PATHOLOGY- IS ULTRASOUND AS GOOD AS MRI
 IMAGING OF ROTATOR CUFF PATHOLOGY- IS ULTRASOUND AS GOOD AS MRI Vinoth Alagappan 1, Nirmal Kumar Prabhu 2, Srikanth Moorthy 3, Sreekumar Karumathil Pullara 4, Rajesh Kanann Ramesh 5, Nazar P. K 6, Chinmay
IMAGING OF ROTATOR CUFF PATHOLOGY- IS ULTRASOUND AS GOOD AS MRI Vinoth Alagappan 1, Nirmal Kumar Prabhu 2, Srikanth Moorthy 3, Sreekumar Karumathil Pullara 4, Rajesh Kanann Ramesh 5, Nazar P. K 6, Chinmay
Ultras ono graphic Evaluation of Rotator Cuff Tendons in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, June: 395-399, 215 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Ultras ono graphic Evaluation of Rotator Cuff Tendons in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis HALA I. ELGENDY,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, June: 395-399, 215 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Ultras ono graphic Evaluation of Rotator Cuff Tendons in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis HALA I. ELGENDY,
Lawrence Gulotta Gillian Lieberman, MD October Gillian Lieberman, MD. Shoulder Imaging. Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02
 October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
Ultrasonography of the Rotator Cuff
 Ultrasonography of the Rotator Cuff A COMPARISON OF ULTRASONOGRAPHIC AND ARTHROSCOPIC FINDINGS IN ONE HUNDRED CONSECUTIVE CASES* BY SHARLENE A. TEEFEY, M.D., S. ASHFAQ HASAN, M.D., WILLIAM D. MIDDLETON,
Ultrasonography of the Rotator Cuff A COMPARISON OF ULTRASONOGRAPHIC AND ARTHROSCOPIC FINDINGS IN ONE HUNDRED CONSECUTIVE CASES* BY SHARLENE A. TEEFEY, M.D., S. ASHFAQ HASAN, M.D., WILLIAM D. MIDDLETON,
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Basics, Utility, and Clinical Applications
 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Basics, Utility, and Clinical Applications Andrew Lavigne, MD, FRCPC Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation CSCN Diplomat (EMG) Dip Sport Medicine Eugene Maida, MD, PGY-4 Resident
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Basics, Utility, and Clinical Applications Andrew Lavigne, MD, FRCPC Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation CSCN Diplomat (EMG) Dip Sport Medicine Eugene Maida, MD, PGY-4 Resident
Case study # 6 Sharon P
 Patient is a morbidly obese 70 year old female presenting with left shoulder pain after a severe fall. Patient is in moderate to severe pain with extremely limited range of motion due to extensive shoulder
Patient is a morbidly obese 70 year old female presenting with left shoulder pain after a severe fall. Patient is in moderate to severe pain with extremely limited range of motion due to extensive shoulder
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Role and Correlation of High Resolution Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation of Patients with Shoulder Pain
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 410-417 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901540 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.09.13 Accepted: 2016.11.10 Published: 2017.07.28 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 410-417 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901540 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.09.13 Accepted: 2016.11.10 Published: 2017.07.28 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Introduction. Al Kindy Col Med J 2012; Vol. 8 No. 1 P: 63
 Ultrasound of the Rotator Cuff: A Comparison of Ultrasonographic and Physical Examination Finding in Seventy Consecutive Cases *Mohammed S. Al- Iedani, F.I.C.M.S. * Ghadeer H. Majeed, F.I.C.M.S. ** Tamer
Ultrasound of the Rotator Cuff: A Comparison of Ultrasonographic and Physical Examination Finding in Seventy Consecutive Cases *Mohammed S. Al- Iedani, F.I.C.M.S. * Ghadeer H. Majeed, F.I.C.M.S. ** Tamer
What can Imaging tell us?
 What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 02 Page February 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i2.03 Clinical Presentation and Spectrum
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i2.03 Clinical Presentation and Spectrum
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities
 Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned
 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Technical Guidelines SHOULDER
 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections
 Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Intramuscular Rotator Cuff Cysts: Association with Tendon Tears on MRI and Arthroscopy
 Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Fundamentals
 Fundamentals Benjamin D. Levine, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Imaging Dept. of Radiological Sciences UCLA Health System I. Image Optimization II. Image Interpretation Artifacts
Fundamentals Benjamin D. Levine, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Imaging Dept. of Radiological Sciences UCLA Health System I. Image Optimization II. Image Interpretation Artifacts
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Office-based Versus Radiologist-based Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears
 Article ID: WMC003756 ISSN 2046-1690 Office-based Versus Radiologist-based Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears Corresponding Author: Mr. Chetan S Modi, Shoulder and Elbow Fellow, Toronto
Article ID: WMC003756 ISSN 2046-1690 Office-based Versus Radiologist-based Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears Corresponding Author: Mr. Chetan S Modi, Shoulder and Elbow Fellow, Toronto
Dr. Stefan C. Muzin, MD PM&R Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Consultant, GE Aviation, OEHN.
 Dr. Stefan C. Muzin, MD PM&R Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Consultant, GE Aviation, OEHN Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Think of the Big Picture
Dr. Stefan C. Muzin, MD PM&R Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Consultant, GE Aviation, OEHN Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Think of the Big Picture
Original Report. Sonography of Tears of the Distal Biceps Tendon. Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. Adler 3
 Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Role of MRI in Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears Hind Abdulelah Abdulsahib Altahhan 1 *, Maha Muhammed Abdelraoof 2, Marwa Elsayed Abdelrahman 2
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (2), Page 2573-2580 Role of MRI in Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears Hind Abdulelah Abdulsahib Altahhan 1 *, Maha Muhammed Abdelraoof 2, Marwa
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (2), Page 2573-2580 Role of MRI in Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears Hind Abdulelah Abdulsahib Altahhan 1 *, Maha Muhammed Abdelraoof 2, Marwa
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
9/18/18. Welcome- MSK Ultrasound Workshop. Introduction to Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Acknowledgement of Country. The Workshop.
 Acknowledgement of Country Welcome- MSK Ultrasound Workshop I would like to acknowledge that this meeting is being held on the traditional lands of the Wurundjeri and Boonwurrung people and pay my respect
Acknowledgement of Country Welcome- MSK Ultrasound Workshop I would like to acknowledge that this meeting is being held on the traditional lands of the Wurundjeri and Boonwurrung people and pay my respect
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation
 Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA
 Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA Consultant, OEHN (Occupational and Environmental Network)
Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA Consultant, OEHN (Occupational and Environmental Network)
Journal home page:
 Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences Research Journal home page: www.jamdsr.com doi: 10.21276/jamdsr (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599; (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805 SJIF (Impact factor) 2017= 6.261; Index
Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences Research Journal home page: www.jamdsr.com doi: 10.21276/jamdsr (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599; (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805 SJIF (Impact factor) 2017= 6.261; Index
Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder
 original research ARTICLE Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder Z Oschman (MB ChB, DCH, MSc (Sports Medicine)) 1 C Janse
original research ARTICLE Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder Z Oschman (MB ChB, DCH, MSc (Sports Medicine)) 1 C Janse
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease
 Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
A - Z of Rotator cuff radiology
 A - Z of Rotator cuff radiology Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Z. Al-Ani, A. Madhavan, J. Naqvi, D. Temperley, S. Basu ; 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 Manchester/UK, Wrightington/UK
A - Z of Rotator cuff radiology Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Z. Al-Ani, A. Madhavan, J. Naqvi, D. Temperley, S. Basu ; 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 Manchester/UK, Wrightington/UK
Dynamic Sonography Evaluation of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
 Sonography of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:216 220 0361 803X/06/1871 216 American Roentgen Ray Society
Sonography of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:216 220 0361 803X/06/1871 216 American Roentgen Ray Society
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
MRI and Sonography of the Shoulder
 Clinical Radiology (1991) 43, 323-327 and of the Shoulder J. HODLER, B. TERRIER*, G. K. yon SCHULTHESS and W. A. FUCHS Departments of Medical Radiology and *Rheumatology, University Hospital, Zurich, Switzerland
Clinical Radiology (1991) 43, 323-327 and of the Shoulder J. HODLER, B. TERRIER*, G. K. yon SCHULTHESS and W. A. FUCHS Departments of Medical Radiology and *Rheumatology, University Hospital, Zurich, Switzerland
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group
 Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
Supraspinatus tendon tears: comparison of US and MR arthrography with surgical correlation
 Eur Radiol (2002) 12:1211 1217 DOI 10.1007/s00330-001-1183-3 MUSCULOSKELETAL Francesco S. Ferrari Simone Governi Francesca Burresi Francesco Vigni Paolo Stefani Supraspinatus tendon tears: comparison of
Eur Radiol (2002) 12:1211 1217 DOI 10.1007/s00330-001-1183-3 MUSCULOSKELETAL Francesco S. Ferrari Simone Governi Francesca Burresi Francesco Vigni Paolo Stefani Supraspinatus tendon tears: comparison of
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
Lateral epicondylitis, or ``tennis elbow,'' is
 Comparison of Sonography and MRI for Diagnosing Epicondylitis Theodore T. Miller, MD, 1,2 Micheal A. Shapiro, MD, 1,2 Elizabeth Schultz, MD, 1,2 Paul E. Kalish, MD 3 1 Department of Radiology, North Shore
Comparison of Sonography and MRI for Diagnosing Epicondylitis Theodore T. Miller, MD, 1,2 Micheal A. Shapiro, MD, 1,2 Elizabeth Schultz, MD, 1,2 Paul E. Kalish, MD 3 1 Department of Radiology, North Shore
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
Principles of Ultrasound. Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012
 Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
The Shoulder. Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information. The Shoulder
 1 ! The most ACCESSIBLE to sonographic exam! The most MOBILE and VULNERABLE extremity AND Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information! The Goal for this section
1 ! The most ACCESSIBLE to sonographic exam! The most MOBILE and VULNERABLE extremity AND Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information! The Goal for this section
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology
 Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
CLINICAL ARTICLE. Abstract. Diagnostic applications of shoulder sonography Rotator cuff tears
 Page 66 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Autumn 2011 Vol 10 No 1 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Ultrasound and the shoulder surgeon Joe de Beer MBChB, MMed (Ortho) Karin van Rooyen MBChB Hans van der Bracht MD Cape
Page 66 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Autumn 2011 Vol 10 No 1 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Ultrasound and the shoulder surgeon Joe de Beer MBChB, MMed (Ortho) Karin van Rooyen MBChB Hans van der Bracht MD Cape
The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease: A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic shoulders
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2006 The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease: A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2006 The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease: A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography. Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears
 Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Shoulder MR arthrography
 Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Comparison of the results of ultrasonographic evaluation and arthroscopy in patients scheduled for surgery of the supraspinatus tendon rupture
 Comparison of the results of ultrasonographic evaluation and arthroscopy in patients scheduled for surgery of the supraspinatus tendon rupture Cemille Görmeli, a Gökay Görmeli, b Cüneyt Yücesoy, c Baybars
Comparison of the results of ultrasonographic evaluation and arthroscopy in patients scheduled for surgery of the supraspinatus tendon rupture Cemille Görmeli, a Gökay Görmeli, b Cüneyt Yücesoy, c Baybars
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide
 MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide Poster No.: C-1034 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, S. Connolly; Prescot/UK Keywords: Pathology, Arthrography, MR, Musculoskeletal
MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide Poster No.: C-1034 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, S. Connolly; Prescot/UK Keywords: Pathology, Arthrography, MR, Musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal Sonography of the Tendon
 SOUND JUDGMENT SERIES Musculoskeletal Sonography of the Tendon Kenneth S. Lee, MD Invited paper The Sound Judgment Series consists of invited articles highlighting the clinical value of using ultrasound
SOUND JUDGMENT SERIES Musculoskeletal Sonography of the Tendon Kenneth S. Lee, MD Invited paper The Sound Judgment Series consists of invited articles highlighting the clinical value of using ultrasound
Patient Presentation. Prevalence of Rotator Cu Tears. By Derek S. Shia, M.D.
 Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
Original Article pissn / eissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2016;75(6): https://doi.org/ /jksr
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the:
 1 1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the: a. Carrying angle of the arm b. Scapulohumeral rhythm c. Glenohumeral capsular pattern d. Abduction resistance
1 1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the: a. Carrying angle of the arm b. Scapulohumeral rhythm c. Glenohumeral capsular pattern d. Abduction resistance
2015 OPSC Annual Convention. syllabus. February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California
 2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:669 674 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0677-y SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff Jan E. Vandevenne & Filip Vanhoenacker & Jestinah
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:669 674 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0677-y SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff Jan E. Vandevenne & Filip Vanhoenacker & Jestinah
Original Research Article. Atul Bucha 1, Sunita Dashottar 2 *, Surabhi Sharma 2, Preeth Pany 2, Rushabh Bhikhanhai Suthar 2
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology
 Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2134/16
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2134/16 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: August 24, 2016 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: September 21, 2016 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2016
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2134/16 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: August 24, 2016 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: September 21, 2016 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2016
Tendinosis & Subacromial Impingement Syndrome. Gene Desepoli, LMT, D.C.
 Tendinosis & Subacromial Impingement Syndrome Gene Desepoli, LMT, D.C. What is the shoulder joint? Shoulder joint or shoulder region? There is an interrelatedness of all moving parts of the shoulder and
Tendinosis & Subacromial Impingement Syndrome Gene Desepoli, LMT, D.C. What is the shoulder joint? Shoulder joint or shoulder region? There is an interrelatedness of all moving parts of the shoulder and
