Test Bank Chapter 2: Manage Speech Anxiety
|
|
|
- Ralph Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test Bank Chapter 2: Manage Speech Anxiety Learning Objectives Identify problematic thought patterns. Recall methods for making self-messages more constructive. Name two distinct sensations caused by speaking anxiety. Review why speaking anxiety makes your mind go blank. Identify the effects of the fight-or-flight response on a speaker who is experiencing speaking anxiety. Define stress. Identify ethical expectations for helping classmates combat their speaking anxiety. Define anticipatory anxiety. Identify physical effects of speaking anxiety. Recall the five ways speaking anxiety affects behavior. Determine the primary effects of public speaking anxiety on the mind, body, and behavior. Identify five methods for working with speaking anxiety to help you present well. Know that speaking anxiety is normal. Define visualization. Define desensitization. Recall the benefits of positive self-talk. True/False 1. Public speaking anxiety can be irritating but rarely interferes with the ability to deliver a speech. Topics: Public speaking anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness 2. All-or-nothing thinking is a good technique to help overcome stage fright. Topics: Intrapersonal communication; All-or-nothing thinking 3. A speaker's fight-or-flight response can cause them to avoid eye contact with their audience. Answer: True Topics: Fight-or-flight response; Effects of public speaking anxiety
2 4. Stage fright is so common that scientists studying stress often use public speaking to make their experimental subjects anxious. Answer: True Topics: Stress; Effects of public speaking anxiety 5. Scientifically speaking, public speaking is only a stressor if it threatens someone's physical, financial, or academic well-being. Topics: Stress; Effects of public speaking anxiety 6. Public speaking anxiety can begin as early as several hours before a speech. Topics: Anticipatory anxiety; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Speech preparation 7. Public speaking anxiety is usually just as severe when discussing a topic you know well as when you are speaking about something you are less familiar with. Topics: Anticipatory anxiety; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Speech preparation 8. Scientists have found that people with a tendency to worry experience less physical stress from public speaking than do non-worriers, because worrying is a form of preparation. Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety 9. Men tend to develop higher levels of stress hormones as a result of public speaking anxiety than women do. Answer: True Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety 10. Most people can eliminate their public speaking anxiety with enough training and experience. Topics: Techniques to avoid speaking anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness 11. Anxiety can improve your public speaking performance. Answer: True
3 Topics: Public speaking anxiety awareness; Effects of public speaking anxiety 12. You should use visualization to imagine what could go wrong during your speech so you will be mentally prepared for problems. Topics: Visualization; Performance techniques 13. Because each public speaking experience is unique, the desensitization technique is of only moderate effectiveness in reducing stage fright. Topics: Desensitization; Performance techniques 14. Giving speeches online in front of avatars (graphical representations of people) is unlikely to help reduce stage fright. Topics: Desensitization; Performance techniques 15. Research has shown positivity to be the most effective technique for reducing stage fright. Topics: Performance techniques; Speech preparation 16. Most of the effects of stage fright are unnoticeable to the audience. Answer: True Topics: Speech preparation; Public speaking anxiety awareness Multiple Choice 1. Professional entertainers and public speakers A. do not experience stage fright. B. can suffer debilitating stage fright. C. experience minor stage fright at most. D. suffer different effects from stage fright than less experienced performers. Answer: B Topics: Public speaking anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness 2. Speech anxiety is essentially A. a fear that others will not like you. B. a fear that you will forget your speech.
4 C. a fear of strangers. D. an uncontrollable instinct. Topics: Public speaking anxiety; Self-messages 3. Intense public speaking anxiety A. can prevent someone from speaking effectively. B. requires professional psychological treatment. C. can be fought through without too much difficulty if one really wants to. D. is more common in women. Topics: Public speaking anxiety; Effects of public speaking anxiety 4. During his speech, Dwayne repeated himself a few times, and seldom made eye contact with the audience. He also demonstrated passion and knowledge about his subject matter. To reduce the possibility of speech anxiety in the future, after his speech he should A. focus on his mistakes and plan for the perfect speech next time. B. assume that he will receive a bad grade so he will not be disappointed. C. concentrate on what he did well. D. accept that he is mistake prone. Level: Applying Topics: Effects of public speaking anxiety; Self-messages; Speech preparation; Intrapersonal communication 5. Which of the following is a constructive self-message? A. Taking the pressure off by assuming your performance will go poorly B. Adopting an all-or-nothing attitude that mistakes in your speech are not acceptable C. Admitting right away that a speech went poorly, not pretending that others did not notice D. Thinking about ways you improved on poor performances in the past Level: Applying Topic: Intrapersonal communication; Self-messages 6. Which of the following is not a good method for combatting stage fright? A. Thinking of ways to make every speech perfect B. Remembering how you have improved after past mistakes C. Telling yourself that practice makes perfect D. Waiting for feedback from others before judging yourself Level: Applying
5 Topics: Intrapersonal communication; Self-messages 7. Which of the following are common effects of intense stage fright? A. The desire to run away; fainting B. Fainting; vomiting C. The desire to run away; your mind going blank. D. Your mind going blank; vomiting Topics: Fight-or-flight response; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Forgetfulness 8. When a speaker's mind goes blank due to stage fright, it is because A. most of their energy is committed to combatting the desire to flee. B. they did not spend enough time planning what they wanted to say. C. they are convinced that what they want to say is not good enough. D. most of their energy is directed toward managing their anxiety. Topics: Fight-or-flight response; Effects of public speaking anxiety 9. Hector is feeling very anxious about the presentation he is scheduled to give at work. He asks his boss if it can be rescheduled for next week. This is an example of A. his mind going blank. B. a fight-or-flight response. C. a negative self-message. D. a constructive coping technique. Answer: B Level: Analyzing Topics: Fight-or-flight response; Public speaking anxiety 10. Public speaking anxiety is experienced by roughly adults. A. 1 in 3 B. 1 in 5 C. 1 in 10 D. 1 in 25 Answer: B Topics: Stress; Effects of public speaking anxiety 11. Those who only risk personal embarrassment from an episode of public speaking may situations where someone's career success is at stake. A. suffer little stress compared to B. suffer less severe stress than in C. suffer stress just as debilitating as D. not suffer any stress at all, as opposed to in
6 Topics: Stress; Effects of public speaking anxiety 12. Communicating ethically requires you to A. ignore stage fright in your classmates. B. point out your classmates mistakes. C. help your classmates toughen up. D. help your classmates feel safe from ridicule. Topic: Ethics 13. Heckling is A. an important tool for teaching people to overcome stage fright. B. acceptable only if the class has agreed as much in advance. C. always unethical and inappropriate. D. an unethical but effective technique to relieve stress before a performance. Topic: Ethics 14. Public speaking anxiety A. can begin days or weeks before a speech. B. does not begin until shortly before a speech. C. generally peaks a few minutes into a speech. D. usually ends once a speaker is a few minutes into a speech. Topics: Anticipatory anxiety; Effects of public speaking anxiety 15. Preparing for a speech typically anticipatory anxiety. A. is the cause of B. increases C. reduces D. has no impact on Topics: Anticipatory anxiety; Speech preparation 16. Darius has devoted many hours to preparing for his speech tomorrow. He can expect to A. experience even more anxiety than usual due to over preparation. B. not experience any anxiety before or during his speech. C. still have a spike in anxiety before his performance. D. still have the same amount of anxiety as usual.
7 Level: Analyzing Topics: Anticipatory anxiety; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Speech preparation 17. Which of the following choices best characterizes the relationship between preparation time and public speaking anxiety? A. The amount of time available to prepare neither increases nor decreases public speaking anxiety. B. The more time is available to prepare, the less anxiety a speaker feels. C. Having a week or more to prepare leads to a decrease in anxiety. D. Spending too much time on preparation leads to overthinking and increased anxiety. Answer: B Topics: Anticipatory anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness; Speech preparation 18. All of the following are common physical symptoms of public speaking anxiety except A. elevated heart rate B. dilated pupils C. itchiness D. sweaty palms Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness 19. Angela noticed that Professor Dawkin delivered his lecture in a monotone today. This is a likely indication that A. he is moderating his voice to control his anxiety. B. he is feeling especially stress free. C. he is using anti-anxiety medication. D. his voice has been affected by stage fright. Level: Analyzing Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness 20. A facial twitch during speaking is likely a sign of A. a speaker's frustration at being unable to remember what he wanted to say. B. muscle tension in the speaker's face caused by speaking anxiety. C. a speaker's body relaxing as stress levels decrease. D. an unconscious desire by the speaker to avoid eye contact with the audience. Answer: B Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety
8 21. Javier gave a good presentation, but Rachel still suspected he was suffering from stage fright because he his speech. A. swayed and moved around a lot during B. cleared his throat before starting C. relied heavily on visual aids as part of D. did not incorporate any humor into Level: Analyzing Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness 22. All of the following are common behavioral effects of public speaking anxiety except A. stuttering. B. fidgeting. C. pacing. D. blinking. Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety 23. Choose all that apply. What are the three areas where speaking anxiety is most likely to affect someone? A. Behavior B. Beliefs C. Body D. Character E. Mind, C, E Topics: Public speaking anxiety awareness; Effects of public speaking anxiety 24. The best approach to speaking anxiety is to A. train hard to eliminate it before engaging in public speaking. B. avoid public speaking unless you are particularly relaxed. C. accept that it will prevent you from succeeding in public speaking. D. accept that it is normal and unlikely to ever go away completely. Topic: Techniques to avoid speaking anxiety 25. You are feeling jittery before going out to address the student council meeting. Your text recommends you try to A. direct your nervous energy into your performance. B. burn off the excess energy through pacing or exercise.
9 C. rest in a dark, quiet room to try and bring your energy back to normal. D. put off addressing the council for another day when you are less stressed. Level: Applying Topics: Techniques to avoid speaking anxiety; Performance techniques 26. The technique of visualization A. can be used to avoid stage fright entirely. B. will help you to control your breathing during a bout of public speaking anxiety. C. is primarily useful for actors and actresses. D. can help you perform well in spite of stage fright. Topics: Visualization; Performance techniques 27. Basil is feeling stressed out about the presentation he is giving tomorrow. Based on your text, you recommend that to reduce stage fright he A. imagine the worst thing that could happen during the presentation to desensitize himself. B. imagine the audience applauding or thanking him after the speech. C. envision himself giving the presentation successfully from start to finish. D. postpone the presentation until he is feeling less stressed. Level: Applying Topics: Techniques to avoid speaking anxiety; Performance techniques; Public speaking anxiety awareness 28. One good method for reducing speaking anxiety is A. setting low expectations for yourself by assuming that your speech will go poorly. B. restricting your public speaking to only when it is important. C. setting high expectations for yourself by insisting that the speech be perfect. D. taking as many opportunities as you can to speak in public. Level: Applying Topics: Techniques to avoid speaking anxiety; Performance techniques 29. Essentially, desensitization involves A. overcoming your fears by ignoring them. B. overcoming your fears by facing up to them. C. transferring your anxiety from public speaking to something else. D. imagining yourself giving a stress-free speech. Answer: B Topics: Desensitization; Performance techniques
10 30. Giving virtual speeches in front of online audiences A. will give you a false impression of what actual public speaking is like, leading to heightened stage fright. B. can help you to refine your speech, but is unlikely to affect your stage fright. C. can desensitize you to the experience of public speaking. D. is discouraged in favor of practicing in front of live audiences. Topics: Intrapersonal communication; Speech preparation 31. Engaging in positive self-talk A. often leads to a self-fulfilling prophecy. B. reduces the negative effects of stress. C. increases the positive effects of stress. D. has been shown to be ineffective in dealing with stress. Answer: B Topics: Intrapersonal communication; Speech preparation; Stress 32. Based on your text, which of the following techniques would you not recommend that Dave employ to help deal with his public speaking anxiety? A. Engaging in public speaking in front of a virtual audience on a regular basis B. Psyching himself up before a speech by telling himself how he is going to blow the audience away with his performance C. Engaging in vigorous exercise before his performance to burn off some nervous energy D. Imagining giving a successful performance of an upcoming speech Level: Analyzing Topics: Techniques to avoid speaking anxiety; Performance techniques; Intrapersonal communication; Speech preparation 33. The most effective technique for combating public speaking anxiety A. is desensitization. B. is positivity. C. is visualization. D. depends on the person. Topics: Public speaking anxiety awareness; Intrapersonal communication; Performance techniques 34. If you feel anxious in front of your audience A. they will probably not be able to tell. B. they will probably notice and feel sympathetic.
11 C. you should concentrate on acting normally so they will not notice. D. you should just admit it to them, as stage fright is very difficult hide. Topics: Public speaking anxiety; Effects of public speaking anxiety; Public speaking anxiety awareness 35. Generally speaking, the audience for a public speaker A. wants her to succeed. B. does not care if she succeeds or fails. C. will grow hostile if they detect her anxiety. D. enjoys watching her fail. Topics: Public speaking anxiety awareness Fill-in-the-Blank 1. Predicting that your speech is going to fail no matter how much you prepare is a problematic self-message known as. Answer: fortune telling Topics: Intrapersonal communication; Self-messages; Fortune-telling 2. Harvey gave a poorly received speech last week, and now he is convinced that he will never be able to give a successful performance. He is engaging in. Answer: over-generalization [alternatives: overgeneralization, over generalization] Topics: Intrapersonal communication; Self-messages; Over-generalization 3. You think that if anything whatsoever goes wrong with your speech, it is a complete failure. This is. Answer: all-or-nothing thinking [alternatives: all or nothing thinking] Topics: Intrapersonal communication; Self-messages; All-or-nothing thinking 4. As soon as class was over, Violet told her friends, "My speech was terrible. I'm failing for sure." She is. Answer: jumping to conclusions Topics: Self-messages; Jump to conclusions 5. The anxiety of public speaking can trigger a speaker's response, making them want to escape. Answer: fight-or-flight [alternative: fight or flight]
12 Topics: Fight-or-flight response; Effects of public speaking anxiety 6. When someone experiences stage fright, their desire to get away from an anxietyinducing public speech can cause them to avoid with the audience. Answer: eye contact Topics: Effects of public speaking anxiety; Fight-or-flight response 7. is the body's reaction to a threat. Answer: Stress Topics: Stress; Effects of public speaking anxiety 8. The scientific term for an event that causes stress is. Answer: stressor Topics: Stress; Effects of public speaking anxiety 9. is a psychological state of worry and unease. nxiety Topics: Public speaking anxiety; Anticipatory anxiety 10. Thinking about giving a speech in the future can cause anxiety. Answer: anticipatory Topic: Anticipatory anxiety 11. In general, speaking anxiety causes a greater elevation in heart rate among than it does among. Answer: women, men [alternative: females, males] Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety 12. People who are suffering from public speaking anxiety tend to swallow frequently than usual. Answer: more Topics: Physical noise; Effects of public speaking anxiety 13. Scientific study has shown that public speaking anxiety affects behavior in at least different areas. Answer: five [alternative: 5] Topics: Public speaking anxiety awareness; Effects of public speaking anxiety
13 14. People suffering from public speaking anxiety tend to use more like "um," and "you know," than they otherwise would. Answer: filler words Topics: Public speaking anxiety awareness; Effects of public speaking anxiety 15. The stress of public speaking increases your available stores. Answer: energy Topics: Public speaking anxiety awareness; Effects of public speaking anxiety 16. is the practice of imagining oneself giving a successful performance from start to finish. Answer: Visualization Topics: Visualization; Performance techniques 17. is the practice of imagining oneself giving a successful performance from start to finish. Answer: Visualization Topics: Visualization; Performance techniques 18. Mukesh wants to overcome his fear of heights, so every week he forces himself to go out on the observation deck of his office building. He is practicing the technique of. Answer: desensitization Topics: Desensitization; Performance techniques 19. In a virtual reality public speaking situation, the audience is represented by, graphical representations of people. Answer: avatars Topic: Speech preparation 20. Fiona could not stop worrying about forgetting her speech before the wedding. By the time it was her turn to toast the new couple, she was so anxious she couldn't speak. This is an example of a. Answer: self-fulfilling prophecy [alternative: self fulfilling prophecy] Topic: Speech preparation 21. For the most part you can expect your audience to want you to in your public speaking.
14 Answer: succeed Level: Remember Topic: Speech preparation
Problem Situation Form for Parents
 Problem Situation Form for Parents Please complete a form for each situation you notice causes your child social anxiety. 1. WHAT WAS THE SITUATION? Please describe what happened. Provide enough information
Problem Situation Form for Parents Please complete a form for each situation you notice causes your child social anxiety. 1. WHAT WAS THE SITUATION? Please describe what happened. Provide enough information
Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking
 Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking How do we challenge our unhelpful thoughts? Anxiety may decrease if we closely examine how realistic and true our unhelpful/negative thoughts are. We may find
Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking How do we challenge our unhelpful thoughts? Anxiety may decrease if we closely examine how realistic and true our unhelpful/negative thoughts are. We may find
TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. Anxiety Disorders. What Is Anxiety?
 TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. What Is Anxiety? Anxiety Disorders Liam had always looked out for his younger brother Sam. But whenever
TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. What Is Anxiety? Anxiety Disorders Liam had always looked out for his younger brother Sam. But whenever
Transforming Public Speaking Anxiety Workbook
 Transforming Public Speaking Anxiety Workbook This workbook is designed to accompany 5 Proven Methods to Transform Public Speaking Anxiety, which is Part 2 of Your True Voice: How to Speak with Power and
Transforming Public Speaking Anxiety Workbook This workbook is designed to accompany 5 Proven Methods to Transform Public Speaking Anxiety, which is Part 2 of Your True Voice: How to Speak with Power and
Mastering Emotions. 1. Physiology
 Mastering Emotions Emotional mastery is the key to living a life that you direct. The ability to have absolute direct power over what you feel in every single moment no matter what happens around you is
Mastering Emotions Emotional mastery is the key to living a life that you direct. The ability to have absolute direct power over what you feel in every single moment no matter what happens around you is
Anxiety and problem solving
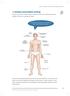 Anxiety and problem solving Anxiety is very common in ADHD, because it is diffi cult to relax with a restless body and racing thoughts. At night, worry may keep you awake. What physical sensations do you
Anxiety and problem solving Anxiety is very common in ADHD, because it is diffi cult to relax with a restless body and racing thoughts. At night, worry may keep you awake. What physical sensations do you
Class #5: THOUGHTS AND MY MOOD
 : THOUGHTS AND MY MOOD CLASS OUTLINE I. Announcements & Agenda II. III. IV. General Review Personal Project Review Relaxation Exercise V. New Material VI. Personal Project I. Any Announcements? II. GENERAL
: THOUGHTS AND MY MOOD CLASS OUTLINE I. Announcements & Agenda II. III. IV. General Review Personal Project Review Relaxation Exercise V. New Material VI. Personal Project I. Any Announcements? II. GENERAL
Anxiety. Top ten fears. Glossophobia fear of speaking in public or of trying to speak
 Glossophobia fear of speaking in public or of trying to speak Forget heights and sharks. Public speaking often makes it to the top of the Top Fears List, higher even than death. Think about that. That
Glossophobia fear of speaking in public or of trying to speak Forget heights and sharks. Public speaking often makes it to the top of the Top Fears List, higher even than death. Think about that. That
Public Speaking Chapter 1. Speaking in Public
 Public Speaking Chapter 1 Speaking in Public FATE OR OPPORTUNITY? Will you faint, shake, sweat, sway, look down, feel your mouth go dry, or perhaps worse even die? Will you blush, flush, stammer and trip
Public Speaking Chapter 1 Speaking in Public FATE OR OPPORTUNITY? Will you faint, shake, sweat, sway, look down, feel your mouth go dry, or perhaps worse even die? Will you blush, flush, stammer and trip
Test Anxiety. New Perspective Counseling Services Dr. Elyse Deleski, LMFT
 Test Anxiety New Perspective Counseling Services Dr. Elyse Deleski, LMFT What is Test Anxiety? Excessive worry about the test. Fear of being evaluated. A sick feeling you get when you are about to take
Test Anxiety New Perspective Counseling Services Dr. Elyse Deleski, LMFT What is Test Anxiety? Excessive worry about the test. Fear of being evaluated. A sick feeling you get when you are about to take
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide
 Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
Improve Your... Mental Training - SELF TALK
 Improve Your... Mental Training - SELF TALK Published May 2016 version 1.0 This document is part of "Mental Preparation for Basketball Referees" CHAPTER 4: SELF TALK When you think about something and
Improve Your... Mental Training - SELF TALK Published May 2016 version 1.0 This document is part of "Mental Preparation for Basketball Referees" CHAPTER 4: SELF TALK When you think about something and
Overcome anxiety & fear of uncertainty
 Psoriasis... you won t stop me! Overcome anxiety & fear of uncertainty Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Psoriasis You Won t Stop Me This booklet is part of the Psoriasis You Won t Stop Me series:
Psoriasis... you won t stop me! Overcome anxiety & fear of uncertainty Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Psoriasis You Won t Stop Me This booklet is part of the Psoriasis You Won t Stop Me series:
Helping Your Asperger s Adult-Child to Eliminate Thinking Errors
 Helping Your Asperger s Adult-Child to Eliminate Thinking Errors Many people with Asperger s (AS) and High-Functioning Autism (HFA) experience thinking errors, largely due to a phenomenon called mind-blindness.
Helping Your Asperger s Adult-Child to Eliminate Thinking Errors Many people with Asperger s (AS) and High-Functioning Autism (HFA) experience thinking errors, largely due to a phenomenon called mind-blindness.
Figure 3.2 Worksheet for Reactions to Starting This Treatment Program For
 Chapter 7 PSYCHOEDUCATION PART 3: ETIOLOGY AND TREATMENT RATIONALE Timeline: Typically one session Reading: Chapter 3 in Client Workbook Photocopies needed from Client Workbook: Figure 3.2 Worksheet for
Chapter 7 PSYCHOEDUCATION PART 3: ETIOLOGY AND TREATMENT RATIONALE Timeline: Typically one session Reading: Chapter 3 in Client Workbook Photocopies needed from Client Workbook: Figure 3.2 Worksheet for
Improving Your Sleep Course. Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind
 Improving Your Sleep Course Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind This session will: Help you to learn ways of overcoming the mental alertness, repetitive thoughts and
Improving Your Sleep Course Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind This session will: Help you to learn ways of overcoming the mental alertness, repetitive thoughts and
Emotional Intelligence and NLP for better project people Lysa
 Emotional Intelligence and NLP for better project people Lysa Morrison @lysam8 Copyright 2015 Lysa Morrison Reasons projects fail Three of the most common causes of project failure according to the National
Emotional Intelligence and NLP for better project people Lysa Morrison @lysam8 Copyright 2015 Lysa Morrison Reasons projects fail Three of the most common causes of project failure according to the National
The Power of Feedback
 The Power of Feedback 35 Principles for Turning Feedback from Others into Personal and Professional Change By Joseph R. Folkman The Big Idea The process of review and feedback is common in most organizations.
The Power of Feedback 35 Principles for Turning Feedback from Others into Personal and Professional Change By Joseph R. Folkman The Big Idea The process of review and feedback is common in most organizations.
Coach on Call. Letting Go of Stress. A healthier life is on the line for you! How Does Stress Affect Me?
 Coach on Call How Does Stress Affect Me? Over time, stress can affect the way you feel, think, and act. You need some time when you are free of stress. You need ways to get relief from stress. Without
Coach on Call How Does Stress Affect Me? Over time, stress can affect the way you feel, think, and act. You need some time when you are free of stress. You need ways to get relief from stress. Without
Controlling Worries and Habits
 THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
The Cognitive Model Adapted from Cognitive Therapy by Judith S. Beck
 The Cognitive Model Adapted from Cognitive Therapy by Judith S. Beck Automatic Thoughts The Cognitive Model is based on the idea that our emotions and behaviors are influenced by our perceptions of events.
The Cognitive Model Adapted from Cognitive Therapy by Judith S. Beck Automatic Thoughts The Cognitive Model is based on the idea that our emotions and behaviors are influenced by our perceptions of events.
5 Quick Tips for Improving Your Emotional Intelligence. and Increasing Your Success in All Areas of Your Life
 5 Quick Tips for Improving Your Emotional Intelligence and Increasing Your Success in All Areas of Your Life Table of Contents Self-Awareness... 3 Active Listening... 4 Self-Regulation... 5 Empathy...
5 Quick Tips for Improving Your Emotional Intelligence and Increasing Your Success in All Areas of Your Life Table of Contents Self-Awareness... 3 Active Listening... 4 Self-Regulation... 5 Empathy...
How to Reduce Test Anxiety
 How to Reduce Test Anxiety To reduce math test anxiety, you need to understand both the relaxation response and how negative self-talk undermines your abilities. Relaxation Techniques The relaxation response
How to Reduce Test Anxiety To reduce math test anxiety, you need to understand both the relaxation response and how negative self-talk undermines your abilities. Relaxation Techniques The relaxation response
WHAT IS STRESS? increased muscle tension increased heart rate increased breathing rate increase in alertness to the slightest touch or sound
 EXAM STRESS WHAT IS STRESS? Stress is part of the body s natural response to a perceived threat. We all experience it from time to time. When we feel under threat, our bodies go into fight or flight response,
EXAM STRESS WHAT IS STRESS? Stress is part of the body s natural response to a perceived threat. We all experience it from time to time. When we feel under threat, our bodies go into fight or flight response,
Psychological Sleep Services Sleep Assessment
 Psychological Sleep Services Sleep Assessment Name Date **************************************************** Insomnia Severity Index For each question, please CIRCLE the number that best describes your
Psychological Sleep Services Sleep Assessment Name Date **************************************************** Insomnia Severity Index For each question, please CIRCLE the number that best describes your
Overview of cognitive work in CBT
 Overview of cognitive work in CBT Underlying assumptions: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy How an individual interprets life events plays a role in determining how he or she responds to those events (Beck,
Overview of cognitive work in CBT Underlying assumptions: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy How an individual interprets life events plays a role in determining how he or she responds to those events (Beck,
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES
 Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
Self Motivation Inventory Find out whether you are naturally self-motivated and disciplined
 Self Motivation Inventory Find out whether you are naturally self-motivated and disciplined People often wonder what makes it hard for them to begin or complete activities and tasks. There are many factors
Self Motivation Inventory Find out whether you are naturally self-motivated and disciplined People often wonder what makes it hard for them to begin or complete activities and tasks. There are many factors
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School
 Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
Ingredients of Difficult Conversations
 Ingredients of Difficult Conversations Differing Perceptions In most difficult conversations, there are different perceptions of the same reality. I think I'm right and the person with whom I disagree
Ingredients of Difficult Conversations Differing Perceptions In most difficult conversations, there are different perceptions of the same reality. I think I'm right and the person with whom I disagree
FOREVER FREE STOP SMOKING FOR GOOD. Stop Smoking. For Good. Smoking, Stress, & Mood
 B O O K L E T 6 Stop Smoking For Good Smoking, Stress, & Mood Contents What Causes Stress? 2 What is Stress? 4 How is Stress Related to Smoking? 4 So, Why Not Smoke When Stressed? 6 Better Ways to Deal
B O O K L E T 6 Stop Smoking For Good Smoking, Stress, & Mood Contents What Causes Stress? 2 What is Stress? 4 How is Stress Related to Smoking? 4 So, Why Not Smoke When Stressed? 6 Better Ways to Deal
GROUP CBT FOR ANXIETY DISORDERS: WHAT TO EXPECT
 GROUP CBT FOR NXIETY DISORDERS: WHT TO EXPECT WHT IS CBT? Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based psychological treatment that is scientifically proven to reduce anxiety. CBT works by
GROUP CBT FOR NXIETY DISORDERS: WHT TO EXPECT WHT IS CBT? Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based psychological treatment that is scientifically proven to reduce anxiety. CBT works by
What is Stress? What Causes Stress?
 Stress Management What is Stress? Any situation can lead to stress too much to do, a conflict between people, disappointment, criticism, even compliments. These situations are not stress; they are stressors.
Stress Management What is Stress? Any situation can lead to stress too much to do, a conflict between people, disappointment, criticism, even compliments. These situations are not stress; they are stressors.
Panic. Information booklet. RDaSH leading the way with care
 Panic Information booklet RDaSH leading the way with care It is common to feel panicky from time to time. It could be because you think there is someone following you, you can t remember your words in
Panic Information booklet RDaSH leading the way with care It is common to feel panicky from time to time. It could be because you think there is someone following you, you can t remember your words in
MALE LIBIDO- EBOOKLET
 MALE LIBIDO- EBOOKLET Hi there, Thank you for ordering this Native Remedies ebooklet! ebooklets are modified from consultations with real people and cover some of the most frequently dealt with problems
MALE LIBIDO- EBOOKLET Hi there, Thank you for ordering this Native Remedies ebooklet! ebooklets are modified from consultations with real people and cover some of the most frequently dealt with problems
Stress & Mood Management. Managing Anxiety and Panic. Course Slides. Keeping Yourself Safe
 Course Slides Stress & Mood Management Managing Anxiety and Panic To obtain a copy of the course slides, log on to: www.inclusionthurrock.org Alternatively, email smm@sssft.nhs.uk. Please do not send any
Course Slides Stress & Mood Management Managing Anxiety and Panic To obtain a copy of the course slides, log on to: www.inclusionthurrock.org Alternatively, email smm@sssft.nhs.uk. Please do not send any
What is Stress? Stress can be defined as our mental, physical, emotional, and behavioral reactions to any perceived demands or threats.
 STRESS MANAGEMENT What is Stress? Stress can be defined as our mental, physical, emotional, and behavioral reactions to any perceived demands or threats. The Fight or Flight Response When situations seem
STRESS MANAGEMENT What is Stress? Stress can be defined as our mental, physical, emotional, and behavioral reactions to any perceived demands or threats. The Fight or Flight Response When situations seem
Test Anxiety 101. What Is Test Anxiety?
 You've participated in class, done all of your homework, studied hard, and you think you have a grip on the material. But then the day of the test comes. Suddenly, you blank out, freeze up, zone out, or
You've participated in class, done all of your homework, studied hard, and you think you have a grip on the material. But then the day of the test comes. Suddenly, you blank out, freeze up, zone out, or
ALCOHOL AND YOU Alcohol
 ALCOHOL AND YOU Alcohol BEYOND ALCOHOL, WITHIN YOURSELF As you transition to college, one of the decisions that you and your classmates face deals with alcohol. While most of you faced decisions about
ALCOHOL AND YOU Alcohol BEYOND ALCOHOL, WITHIN YOURSELF As you transition to college, one of the decisions that you and your classmates face deals with alcohol. While most of you faced decisions about
Optimal Health Questionnaire
 Optimal Health Questionnaire This questionnaire is intended to help you assess how well you are balancing the various elements in your life. The basis of the process is that we have 5 dimensions which
Optimal Health Questionnaire This questionnaire is intended to help you assess how well you are balancing the various elements in your life. The basis of the process is that we have 5 dimensions which
University Staff Counselling Service
 University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
From the scenario below please identify the situation, thoughts, and emotions/feelings.
 Introduction to Mental Gremlins: Example From the scenario below please identify the situation, thoughts, and emotions/feelings. Bob has been working for Big Corporation for 12 years and has his annual
Introduction to Mental Gremlins: Example From the scenario below please identify the situation, thoughts, and emotions/feelings. Bob has been working for Big Corporation for 12 years and has his annual
Workbook 3 Being assertive Dr. Chris Williams
 Workbook 3 Being assertive Dr. Chris Williams From: Overcoming Depression: A Five Areas Approach. Chris Williams, Arnold Publishers (2002) 2 Section 1: Introduction. In this workbook you will: Find out
Workbook 3 Being assertive Dr. Chris Williams From: Overcoming Depression: A Five Areas Approach. Chris Williams, Arnold Publishers (2002) 2 Section 1: Introduction. In this workbook you will: Find out
Uncovering Significant Emotional Events (S.E.E.'s):
 Uncovering Significant Emotional Events (S.E.E.'s): In this article I am going to explain to you what S.E.E. s are and why uncovering them is so important to achieve social confidence. You will read almost
Uncovering Significant Emotional Events (S.E.E.'s): In this article I am going to explain to you what S.E.E. s are and why uncovering them is so important to achieve social confidence. You will read almost
Managing Stress. pressure, fear, confusion, anger and sweating.
 Managing Stress Introduction Stress is a physical and emotional reaction that everyone experiences as they encounter changes in life. These reactions can have positive or negative effects. Stress has positive
Managing Stress Introduction Stress is a physical and emotional reaction that everyone experiences as they encounter changes in life. These reactions can have positive or negative effects. Stress has positive
Look to see if they can focus on compassionate attention, compassionate thinking and compassionate behaviour. This is how the person brings their
 Compassionate Letter Writing Therapist Notes The idea behind compassionate mind letter writing is to help people engage with their problems with a focus on understanding and warmth. We want to try to bring
Compassionate Letter Writing Therapist Notes The idea behind compassionate mind letter writing is to help people engage with their problems with a focus on understanding and warmth. We want to try to bring
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More. Postpartum mood disorders DRAFT. Emotional Changes After Giving Birth
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
Stress and Mood Management Managing Anxiety and Panic
 Managing Anxiety and Panic Anxiety is a word we use to describe feelings of unease, worry and fear. It incorporates both the emotions and the physical sensations we might experience when we are worried
Managing Anxiety and Panic Anxiety is a word we use to describe feelings of unease, worry and fear. It incorporates both the emotions and the physical sensations we might experience when we are worried
What is stress? Stress is an emotional/ bodily reaction to
 The Basics What is stress? What are some causes of stress? Stress is an emotional/ bodily reaction to a physical, psychological or emotional demand We all display stress in different ways Some stress is
The Basics What is stress? What are some causes of stress? Stress is an emotional/ bodily reaction to a physical, psychological or emotional demand We all display stress in different ways Some stress is
Changes to your behaviour
 Life after stroke Changes to your behaviour Together we can conquer stroke Because there is so much to deal with after a stroke, it s normal for your behaviour to change in some way. In this booklet we
Life after stroke Changes to your behaviour Together we can conquer stroke Because there is so much to deal with after a stroke, it s normal for your behaviour to change in some way. In this booklet we
Samantha Burns Artherholt, PhD
 Moving Beyond Cancer to Wellness Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center June 1, 2013 Samantha Burns Artherholt, PhD Clinical Psychologist Seattle Cancer Care Alliance University of Washington What I ll
Moving Beyond Cancer to Wellness Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center June 1, 2013 Samantha Burns Artherholt, PhD Clinical Psychologist Seattle Cancer Care Alliance University of Washington What I ll
July 2018 Coping with anxiety
 July 2018 Coping with anxiety This document is for parents and carers who have a child who is suffering with feelings of anxiety. We hope that this will enable you to respond effectively to your child
July 2018 Coping with anxiety This document is for parents and carers who have a child who is suffering with feelings of anxiety. We hope that this will enable you to respond effectively to your child
Helping YOU Reach YOUR Goals! Cindy Alfano, Counselor
 Helping YOU Reach YOUR Goals! Cindy Alfano, Counselor What is Stress? When we come to believe that the demands of our life are exceeding our abilities, our nervous system activates a set of reactions which
Helping YOU Reach YOUR Goals! Cindy Alfano, Counselor What is Stress? When we come to believe that the demands of our life are exceeding our abilities, our nervous system activates a set of reactions which
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) What is Addiction?
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) What is Addiction? https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents What is Addiction? Do You or a Loved One Have a Drug Abuse Problem? Signs of Drug Abuse and Addiction
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) What is Addiction? https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents What is Addiction? Do You or a Loved One Have a Drug Abuse Problem? Signs of Drug Abuse and Addiction
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure LIVING WELL
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure LIVING WELL Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 Who is affected by kidney failure? 6 How does kidney failure affect
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure LIVING WELL Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 Who is affected by kidney failure? 6 How does kidney failure affect
Helping Stutterers. who stutters, you understand
 Helping Stutterers By Lisa Scott From NJEA Review IF you've ever worked with a student who stutters, you understand that feeling of helplessness. How do you talk to the child about his or her speech? Should
Helping Stutterers By Lisa Scott From NJEA Review IF you've ever worked with a student who stutters, you understand that feeling of helplessness. How do you talk to the child about his or her speech? Should
Michael Norman International &
 FOUNDATION SERIES Episode #3 of 4 THE PANIC PARADOX The White Bear Effect Ironically, the very act of trying to suppress a thought makes it much more likely that we ll have it. Trying to suppress a thought
FOUNDATION SERIES Episode #3 of 4 THE PANIC PARADOX The White Bear Effect Ironically, the very act of trying to suppress a thought makes it much more likely that we ll have it. Trying to suppress a thought
Does anxiety cause some difficulty for a young person you know well? What challenges does this cause for the young person in the family or school?
 John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
The Wellbeing Course. Resource: Mental Skills. The Wellbeing Course was written by Professor Nick Titov and Dr Blake Dear
 The Wellbeing Course Resource: Mental Skills The Wellbeing Course was written by Professor Nick Titov and Dr Blake Dear About Mental Skills This resource introduces three mental skills which people find
The Wellbeing Course Resource: Mental Skills The Wellbeing Course was written by Professor Nick Titov and Dr Blake Dear About Mental Skills This resource introduces three mental skills which people find
Teen Stress and Anxiety Wayne Hills Counseling Dept. June, 2017
 Teen Stress and Anxiety Wayne Hills Counseling Dept. June, 2017 True or False? 1. Even something positive, such as being selected for an award, can be stressful 2. The amount of stress you feel depends
Teen Stress and Anxiety Wayne Hills Counseling Dept. June, 2017 True or False? 1. Even something positive, such as being selected for an award, can be stressful 2. The amount of stress you feel depends
did you feel sad or depressed? did you feel sad or depressed for most of the day, nearly every day?
 Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
Social Anxiety Disorder
 Social Anxiety Disorder More than Just Shyness Teena Social Anxiety Disorder: More than Just Shyness Introduction Are you extremely afraid of being judged by others? Are you very self-conscious in everyday
Social Anxiety Disorder More than Just Shyness Teena Social Anxiety Disorder: More than Just Shyness Introduction Are you extremely afraid of being judged by others? Are you very self-conscious in everyday
Study Guide for Why We Overeat and How to Stop Copyright 2017, Elizabeth Babcock, LCSW
 Study Guide for Why We Overeat and How to Stop Copyright 2017, Elizabeth Babcock, LCSW This book can be discussed in many different ways. Whatever feels productive and enlightening for you and/or your
Study Guide for Why We Overeat and How to Stop Copyright 2017, Elizabeth Babcock, LCSW This book can be discussed in many different ways. Whatever feels productive and enlightening for you and/or your
SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS. Appendix A: Cleveland Global Quality of Life (CGQL) [0 being the WORST and 10 being the BEST]
![SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS. Appendix A: Cleveland Global Quality of Life (CGQL) [0 being the WORST and 10 being the BEST] SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS. Appendix A: Cleveland Global Quality of Life (CGQL) [0 being the WORST and 10 being the BEST]](/thumbs/73/68207476.jpg) SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS Appendix A: Cleveland Global Quality of Life (CGQL) [0 being the WORST and 10 being the BEST] Q1. Current Quality of Life: Circle one 6 7 8 9 10 Q2. Current Quality of Health: Circle
SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS Appendix A: Cleveland Global Quality of Life (CGQL) [0 being the WORST and 10 being the BEST] Q1. Current Quality of Life: Circle one 6 7 8 9 10 Q2. Current Quality of Health: Circle
do? Childhood Anxiety Caitlin Tur pyn,
 t i s e o d t a d Wh n a e k i l k loo an we c t a h w do? Childhood Anxiety Caitlin Tur pyn, MA The Bad News 0 Anxiety disorders are the one of the most common mental health concerns among children and
t i s e o d t a d Wh n a e k i l k loo an we c t a h w do? Childhood Anxiety Caitlin Tur pyn, MA The Bad News 0 Anxiety disorders are the one of the most common mental health concerns among children and
BUT ANXIETY IS ABNORMAL
 Insights Counseling - 1- ANXIETY What Is Anxiety? Anxiety is related to WORRY. Worry is the tendency to fret about the things that are making us stressed, So ANXIETY is related to Stress, and reflects
Insights Counseling - 1- ANXIETY What Is Anxiety? Anxiety is related to WORRY. Worry is the tendency to fret about the things that are making us stressed, So ANXIETY is related to Stress, and reflects
QUESTIONS ANSWERED BY
 Module 16 QUESTIONS ANSWERED BY BERNIE SIEGEL, MD 2 Q How do our thoughts and beliefs affect the health of our bodies? A You can t separate thoughts and beliefs from your body. What you think and what
Module 16 QUESTIONS ANSWERED BY BERNIE SIEGEL, MD 2 Q How do our thoughts and beliefs affect the health of our bodies? A You can t separate thoughts and beliefs from your body. What you think and what
FIGURE 1-The Cognitive Model. Core belief. I m incompetent. Intermediate belief. If I don t understand something perfectly, then I m dumb
 FIGURE 1-The Cognitive Model Core belief I m incompetent Intermediate belief If I don t understand something perfectly, then I m dumb Situation Automatic thoughts Reactions Reading this book This is too
FIGURE 1-The Cognitive Model Core belief I m incompetent Intermediate belief If I don t understand something perfectly, then I m dumb Situation Automatic thoughts Reactions Reading this book This is too
How to Approach Someone Having a Mental Health Challenge
 How to Approach Someone Having a Mental Health Challenge Susan Allen-Samuel, M.S. NAMI NH Copyright NAMI NH, 2013. Do not use printed or web version of this document for other than personal use without
How to Approach Someone Having a Mental Health Challenge Susan Allen-Samuel, M.S. NAMI NH Copyright NAMI NH, 2013. Do not use printed or web version of this document for other than personal use without
Coping with Cancer. Patient Education Social Work and Care Coordination Cancer Programs. Feeling in Control
 Patient Education Coping with Cancer Many patients find that their first challenge is to feel in control of life again. These resources and tips may help. You can do it! Most people do not expect a serious
Patient Education Coping with Cancer Many patients find that their first challenge is to feel in control of life again. These resources and tips may help. You can do it! Most people do not expect a serious
M.O.D.E.R.N. Voice-Hearer
 Debra Lampshire Presents The M.O.D.E.R.N. Voice-Hearer Background Hearing Voices since childhood Developed unusual beliefs Long periods in institutions Stayed inside house for 18 years Got voices under
Debra Lampshire Presents The M.O.D.E.R.N. Voice-Hearer Background Hearing Voices since childhood Developed unusual beliefs Long periods in institutions Stayed inside house for 18 years Got voices under
ME Project Handouts Weeks 1-6
 ME Project Handouts Weeks 1-6 Note: This document is formatted so that the two-page handouts are double-side. In order to print this document correctly, please make sure that your printer is set to print
ME Project Handouts Weeks 1-6 Note: This document is formatted so that the two-page handouts are double-side. In order to print this document correctly, please make sure that your printer is set to print
THE SOCIALABILITY QUESTIONAIRE: AN INDEX OF SKILL
 JONATHAN BERENT, A.C.S.W. & ASSOCIATES 17 Maple Drive Great Neck, New York 11021 800-248-2034 THE SOCIALABILITY QUESTIONAIRE: AN INDEX OF SKILL In working with the Socially Challenged, we found a need
JONATHAN BERENT, A.C.S.W. & ASSOCIATES 17 Maple Drive Great Neck, New York 11021 800-248-2034 THE SOCIALABILITY QUESTIONAIRE: AN INDEX OF SKILL In working with the Socially Challenged, we found a need
Assessment Schedule 2015 Health: Demonstrate understanding of issues to make health-enhancing decisions in drug-related situations (90975)
 NCEA Level 1 Health (90975) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Health: Demonstrate understanding of issues to make health-enhancing decisions in drug-related situations (90975) Evidence Achievement
NCEA Level 1 Health (90975) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Health: Demonstrate understanding of issues to make health-enhancing decisions in drug-related situations (90975) Evidence Achievement
Practitioner Guidelines for Enhanced IMR for COD Handout #2: Practical Facts About Mental Illness
 Chapter II Practitioner Guidelines for Enhanced IMR for COD Handout #2: Practical Facts About Mental Illness There are four handouts to choose from, depending on the client and his or her diagnosis: 2A:
Chapter II Practitioner Guidelines for Enhanced IMR for COD Handout #2: Practical Facts About Mental Illness There are four handouts to choose from, depending on the client and his or her diagnosis: 2A:
Emotional Changes After a Traumatic Brain Injury
 Emotional Changes After a Traumatic Brain Injury EMOTIONAL LABILITY Emotional lability can be caused by damage to the parts of the brain that control emotion. Some people with Traumatic Brain Injury or
Emotional Changes After a Traumatic Brain Injury EMOTIONAL LABILITY Emotional lability can be caused by damage to the parts of the brain that control emotion. Some people with Traumatic Brain Injury or
AUB Counseling Center. Ola Ataya-Psychologist-AUB Counseling Center
 AUB 1 Why is it important to manage our time effectively? What is meant by time management? How to manage our time effectively & overcome procrastination?(to be continued in the next presentation) 2 Developing
AUB 1 Why is it important to manage our time effectively? What is meant by time management? How to manage our time effectively & overcome procrastination?(to be continued in the next presentation) 2 Developing
Worksheet # 1 Why We Procrastinate
 Worksheet # 1 Why We Procrastinate Directions. Take your best guess and rank the following reasons for why we procrastinate from 1 to 5 starting with 1 being the biggest reason we procrastinate and 5 being
Worksheet # 1 Why We Procrastinate Directions. Take your best guess and rank the following reasons for why we procrastinate from 1 to 5 starting with 1 being the biggest reason we procrastinate and 5 being
Personal Listening Profile Facilitator Report
 Personal Listening Profile Facilitator Report Sample Report (5 People) Friday, January 27, 12 This report is provided by: Jan Jenkins, President Legacy of Courage, Inc jan@legacyofcourage.com legacyofcourage.com
Personal Listening Profile Facilitator Report Sample Report (5 People) Friday, January 27, 12 This report is provided by: Jan Jenkins, President Legacy of Courage, Inc jan@legacyofcourage.com legacyofcourage.com
Module 3 - How Pain Affects You
 Module 3 - How Pain Affects You You have learned that pain is produced as a result of all of the incoming electrical or danger signals which reach your brain. Example: Mum Watching Her Son Play Footy Think
Module 3 - How Pain Affects You You have learned that pain is produced as a result of all of the incoming electrical or danger signals which reach your brain. Example: Mum Watching Her Son Play Footy Think
SUMMARY OF SESSION 6: THOUGHTS ARE NOT FACTS
 SUMMARY OF SESSION 6: THOUGHTS ARE NOT FACTS Our thoughts can have powerful effects on how we feel and what we do. Often those thoughts are triggered and occur quite automatically. By becoming aware, over
SUMMARY OF SESSION 6: THOUGHTS ARE NOT FACTS Our thoughts can have powerful effects on how we feel and what we do. Often those thoughts are triggered and occur quite automatically. By becoming aware, over
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More DRAFT. Knowing About This in Advance Can Help
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
Public Speaking Outline Session 2. Intros and warm-up: On The Spot Presentation Introductions
 1 Public Speaking Outline Session 2 Session 2: Anxiety, gestures, body language Intros and warm-up: On The Spot Presentation Introductions Check-in and follow-up from last session 30:00 Topic: Anxiety
1 Public Speaking Outline Session 2 Session 2: Anxiety, gestures, body language Intros and warm-up: On The Spot Presentation Introductions Check-in and follow-up from last session 30:00 Topic: Anxiety
Understanding Hypnosis
 Understanding Hypnosis Are the Results of Hypnosis Permanent? Suggestions stay with some individuals indefinitely, while others need reinforcement. The effects of hypnosis are cumulative: The more the
Understanding Hypnosis Are the Results of Hypnosis Permanent? Suggestions stay with some individuals indefinitely, while others need reinforcement. The effects of hypnosis are cumulative: The more the
PERFECTIONISM Inwardly-Focused Outwardly-Focused
 PERFECTIONISM People who are perfectionistic have unrealistically high standards for themselves and/or other people, and therefore end up feeling like they or other people are never good enough. Since
PERFECTIONISM People who are perfectionistic have unrealistically high standards for themselves and/or other people, and therefore end up feeling like they or other people are never good enough. Since
Understanding and helping your teen cope with medically unexplained symptoms
 Understanding and helping your teen cope with medically unexplained symptoms What are medically unexplained symptoms? Your son or daughter may have pain or other symptoms that have no known cause. The
Understanding and helping your teen cope with medically unexplained symptoms What are medically unexplained symptoms? Your son or daughter may have pain or other symptoms that have no known cause. The
THE MENTAL PREP PLAYBOOK BEING MENTALLY PREPARED TO PLAY YOUR BEST GAME
 THE MENTAL PREP PLAYBOOK BEING MENTALLY PREPARED TO PLAY YOUR BEST GAME STEP 1: CREATE A COMPELLING STORY Every athlete has a story about his sports life. For some athletes, it s a story about numerous
THE MENTAL PREP PLAYBOOK BEING MENTALLY PREPARED TO PLAY YOUR BEST GAME STEP 1: CREATE A COMPELLING STORY Every athlete has a story about his sports life. For some athletes, it s a story about numerous
Living Life with Persistent Pain. A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain
 Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
University of Oregon HEDCO Clinic Fluency Center. Diagnostic Intake Form for Adults Who Stutter
 University of Oregon HEDCO Clinic Fluency Center Phone 541-346-0923 Fax 541-346-6772 Physical Address: Mailing Address: HEDCO Education Complex HEDCO Clinic 1655 Alder Street, Eugene, OR 97403 5207 University
University of Oregon HEDCO Clinic Fluency Center Phone 541-346-0923 Fax 541-346-6772 Physical Address: Mailing Address: HEDCO Education Complex HEDCO Clinic 1655 Alder Street, Eugene, OR 97403 5207 University
COUNSELING INTERVIEW GUIDELINES
 Dr. Moshe ben Asher SOC 356, Introduction to Social Welfare CSUN, Sociology Department COUNSELING INTERVIEW GUIDELINES WHAT DISTINGUISHES A PROFESSIONAL FROM OTHER KINDS OF WORKERS? Education and training
Dr. Moshe ben Asher SOC 356, Introduction to Social Welfare CSUN, Sociology Department COUNSELING INTERVIEW GUIDELINES WHAT DISTINGUISHES A PROFESSIONAL FROM OTHER KINDS OF WORKERS? Education and training
Assessment of the Child s Experience of Stuttering (ACES) (DRAFT VERSION September 27, 2006)
 Assessment of the Child s Experience of Stuttering (ACES) (DRAFT VERSION September 27, 2006) Name: Age/Grade: Sex: M F Date: Instructions. This form includes four sets of questions that ask about your
Assessment of the Child s Experience of Stuttering (ACES) (DRAFT VERSION September 27, 2006) Name: Age/Grade: Sex: M F Date: Instructions. This form includes four sets of questions that ask about your
3 Managing Speech Anxiety
 14 1 GETTING STARTED Vocal Delivery Vocal delivery includes speech volume, pitch, rate, variety, pronunciation, and articulation. As you rehearse, do the following: Pay attention to how loudly or softly
14 1 GETTING STARTED Vocal Delivery Vocal delivery includes speech volume, pitch, rate, variety, pronunciation, and articulation. As you rehearse, do the following: Pay attention to how loudly or softly
The Power Of Self-Belief
 PERSPECTIVES EXPOSÉ The Power Of Self-Belief Our self-belief stems from our inner dialogue about our self-worth and the confidence we have in our ability. The way we feel about ourselves is reflected in
PERSPECTIVES EXPOSÉ The Power Of Self-Belief Our self-belief stems from our inner dialogue about our self-worth and the confidence we have in our ability. The way we feel about ourselves is reflected in
Step 2 Challenging negative thoughts "Weeding"
 Managing Automatic Negative Thoughts (ANTs) Step 1 Identifying negative thoughts "ANTs" Step 2 Challenging negative thoughts "Weeding" Step 3 Planting positive thoughts 'Potting" Step1 Identifying Your
Managing Automatic Negative Thoughts (ANTs) Step 1 Identifying negative thoughts "ANTs" Step 2 Challenging negative thoughts "Weeding" Step 3 Planting positive thoughts 'Potting" Step1 Identifying Your
Using EQ for Effective Communication Skills
 Using EQ for Effective Communication Skills Tips for the webinar Training Industry Sarah Turner Consultant The Faurote Group Predictors of Success Dedication Passion Confidence Drive Positive Attitude
Using EQ for Effective Communication Skills Tips for the webinar Training Industry Sarah Turner Consultant The Faurote Group Predictors of Success Dedication Passion Confidence Drive Positive Attitude
Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles
 Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles For most people, the things they do their behavior are predictable. We can pretty much guess what someone is going to do in a similar situation in the future
Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles For most people, the things they do their behavior are predictable. We can pretty much guess what someone is going to do in a similar situation in the future
ANGER MANAGEMENT. So What is Anger? What causes you to be angry? Understanding and Identifying the Cause of your Anger
 ANGER MANAGEMENT Georgia Association of Code Enforcement So What is Anger? Anger is "an emotional state that varies in intensity from mild irritation to intense fury and rage. An EMOTIONAL State What causes
ANGER MANAGEMENT Georgia Association of Code Enforcement So What is Anger? Anger is "an emotional state that varies in intensity from mild irritation to intense fury and rage. An EMOTIONAL State What causes
Stress is like an iceberg. We can see one-eighth of it above, but what about what s below?
 Chapter 4: Managing Stress & Coping With Loss Stress is like an iceberg. We can see one-eighth of it above, but what about what s below? Something to consider... The Japanese eat very little fat &... The
Chapter 4: Managing Stress & Coping With Loss Stress is like an iceberg. We can see one-eighth of it above, but what about what s below? Something to consider... The Japanese eat very little fat &... The
Dr Anita Rose Director of Clinical Service: Consultant in Neuropsychology & Rehabilitation
 Dr Anita Rose Director of Clinical Service: Consultant in Neuropsychology & Rehabilitation Hope this finishes soon as I am hungry Did I lock my car when I left it in the car park? Will today finish in
Dr Anita Rose Director of Clinical Service: Consultant in Neuropsychology & Rehabilitation Hope this finishes soon as I am hungry Did I lock my car when I left it in the car park? Will today finish in
The Power of Positive Thinking
 The Power of Positive Thinking Youhaveprobablyhadsomeonetellyouto'thinkpositive'whenyouwereinatrying situation. That is because the power of positive thinking is something that is a widely heldbelief-andnotwithoutgoodreason.
The Power of Positive Thinking Youhaveprobablyhadsomeonetellyouto'thinkpositive'whenyouwereinatrying situation. That is because the power of positive thinking is something that is a widely heldbelief-andnotwithoutgoodreason.
