Results Recipient Ordering Healthcare Professional Male Details Female Details
|
|
|
- Dorcas Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Results Recipient Ordering Healthcare Professional Male Details Details Report Date /2010 Attn: Jessica Jacobson, MD Counsyl, Inc Bridge Parkway, Suite 103 Redwood City, CA Phone: COUNSYL NPI: Ethnicity: Northern European Sample Type: Saliva (OG-300) Date of Collection: /2009 Indication: Carrier testing in individual of reproductive age Universal Genetic Test The Universal Genetic Test uses targeted DNA mutation analysis to simultaneously determine the carrier status of an individual or couple for 100+ Mendelian diseases. Counsyl reports which mutations, if any, were detected for each disease. The risk of conceiving a child affected with a disease is presented below and calculated using the test results as well as published data on each disease. The child risk summary is provided as an aid to genetic counseling. * DNA test shows that he is a carrier of HFE-associated hereditary hemochromatosis. Partner The child risk presented below is based on a hypothetical pairing with a partner of the same ethnic group. Child Risk Summary Your Universal Genetic Test indicates that your future children have a reduced risk for the diseases tested, including those listed below which are common in your ethnicity. Note that child risks are not calculated for mild diseases, including HFE-associated hereditary hemochromatosis, which are described in the next section. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease Cystic Fibrosis Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Deficiency Spinal Muscular Atrophy Medium Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency * Limitations: Interpretation is given as a probability due to the inheritance pattern of hese diseases and because only targeted mutations are detected. Other nearby genetic variants may interfere with this detection. Inaccurate reporting of ethnicity or clinical information may cause errors in risk calculation. Page 1 of 16
2 Mild Disease Summary The chart below shows carrier status for 3 mild diseases. The conditions on this list have been highlighted because they are extremely common in the general population and usually do not cause major health problems. In many cases, individuals with these mild conditions remain asymptomatic. For this reason, the results in this section of the report are unlikely to influence reproductive choices. However for those who do show symptoms, knowledge of one's genetic status for these conditions can be helpful to recognize the disease and direct treatment. Mild Disease Factor V Leiden Thrombophilia No disease-causing mutations detected. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency No disease-causing mutations detected. HFE-Associated Hereditary Hemochromatosis HFE:p.Cys282Tyr (C282Y) heterozygote. For details on HFE-associated hereditary hemochromatosis, see page 3. Page 2 of 16
3 Mild Disease Positive Report: HFE-Associated Hereditary Hemochromatosis This disease report is included due to positive result for Patient Results No partner tested Result: HFE:p.Cys282Tyr (C282Y) heterozygote. N/A Interpretation: This individual is a carrier of HFE-associated hereditary hemochromatosis. Carriers generally do not experience symptoms. Clinical symptoms are also uncommon in C282Y homozygotes. N/A Variants on the Counsyl panel 11 Gene HFE. Variants H63D, S65C, Q127H, E168Q, E168X, W169X, C282Y, Q283P, V53M, V59M, H63H. What is HFE-Associated Hereditary Hemochromatosis? HFE-associated hereditary hemochromatosis (HFE-HHC) is a common and treatable inherited disease in which the body absorbs and stores too much iron, potentially damaging organs such as the liver, heart, and pancreas. If the disease is diagnosed and treated before symptoms develop, people with HFE-HHC typically have a normal lifespan. If the disease is untreated, however, it can lead to fatal liver and heart failure. For reasons not well understood, the majority of people with the genetic mutations that cause HFE-HHC do not develop symptoms of the disease at any point in their lives. For these people, simple blood tests can determine whether or not the body is storing too much iron. If it is, beginning treatment early can leave a person virtually symptom-free for life. Depending on the specific mutation(s) a person has, he or she can be more or less likely to develop the iron overload symptoms of HFE-HHC. People who have two copies of the C282Y mutation are most likely to have dangerously elevated levels of iron in their blood. Studies have found that among those with the C282Y/C282Y combination, men are more likely to develop symptoms of iron overload than women, perhaps because women's menstrual cycles lower their iron levels on a regular basis. Do keep in mind, however, that the majority of people with two copies of the C282Y mutation do not develop any symptoms of HFE-HHC. Those who have C282Y in combination with another HFE-HHC mutation are much less likely to develop symptoms of the disease. Only 0.5% to 2% of people with C282Y in combination with another mutation are thought to have clinical signs of the disease. People with this genetic combination who have another disease of the liver may be more likely to develop HFE-HHC symptoms. Among people who have two copies of any other HFE-HHC mutation, including a very common mutation known as H63D, the likelihood of developing symptoms is extremely low. In the absence of another liver disease, two copies of any HFE-HHC mutation other than C282Y is unlikely to cause any health problems. In men who have not been treated for HFE-HHC, the first symptoms of the disease typically begin between the ages of 30 to 50; for untreated women, symptoms usually begin later, after menopause. Page 3 of 16
4 Early symptoms often include weakness, abdominal pain, joint pain, weight loss, loss of interest in sex, chest pain, and a progressive gray or bronze pigmentation to the skin. Liver disease (either fibrosis or the more serious cirrhosis) is a common problem associated with HFE-HHC. Cirrhosis can lead to fatal liver failure and/or an increased likelihood of developing cancer of the liver. The heart can also be affected by HFE-HHC, seen as an irregular heartbeat and/or congestive heart failure. Other problems caused by HFE-HHC can include diabetes, arthritis, impotence (in men), early menopause (in women), thyroid problems, and adrenal gland problems. How Common is HFE-Associated Hereditary Hemochromatosis? HFE-HHC mutations are extremely common, particularly among Caucasians. Roughly one-third (33%) of Caucasians are carriers of the condition, most commonly the H63D mutation. The H63D mutation is almost always associated with asymptomatic cases unless paired with the C282Y mutation. In the general population, 1 in 200 to 400 has two copies of the C282Y genetic mutation, the combination of mutations which is most likely to cause symptoms of HFE-HHC. Please bear in mind that most people who have these genetic mutations do not develop the disease. The disease is less common among Hispanics, African Americans, Asians, and Native Americans. Roughly 13% of Hispanics, 8.5% of Asians, and 6% of African Americans is a carrier for the mild mutation, H63D. An additional 3% of Hispanics, 2.3% of African Americans are carriers of the potentially disease-causing C282Y mutation. How is HFE-Associated Hereditary Hemochromatosis Treated? Ideally HFE-HHC is treated before the organs of the body are damaged. However, not everyone who has the mutations that cause HFE-HHC develops symptoms or requires treatment. A simple blood test of iron levels in the blood physicians specifically look at serum ferritin concentration and transferrin-iron saturation levels can determine whether the body is absorbing too much. When iron reaches a certain threshold, treatment is recommended. If iron levels have not reached that threshold, no treatment is necessary. Blood tests must be repeated periodically to check these iron levels. If a person has a high level of iron, treatment involves removing a certain quantity of blood at regular intervals. This is known as phlebotomy. Typically phlebotomy is performed frequently perhaps weekly or twice weekly until certain iron levels are reached, and then performed less frequently often 2 to 4 times a year on an indefinite basis. This treatment is simple, inexpensive, and safe. If a person is already suffering from symptoms of HFE-HHC, treatment can lessen or relieve some of the symptoms. Cirrhosis is unlikely to improve with treatment, although treatment may slow its progression. If liver disease has reached severe levels, liver transplantation may be an option. Those who have any amount of liver damage are advised to avoid alcohol. All people with symptoms of HFE-HHC are advised to eat only moderate amounts of iron-rich foods, avoid taking iron supplements or excess vitamin C, and refrain from eating uncooked seafood, as they are highly susceptible to a particular kind of bacterial infection. What is the Prognosis for Someone With HFE-Associated Hereditary Hemochromatosis? The prognosis for a person with the genetic mutations that cause HFE-HHC is generally good, as the majority of people in that situation do not develop symptoms of the disease. Most will not have dangerously elevated levels of iron in their blood, and therefore will not have any iron-overload problems. For those that do have dangerously high iron levels in their blood, beginning treatment before symptoms appear is a critical part of ensuring a long, healthy life. Nearly all symptoms of the disease can be prevented with early and ongoing treatment. If a person with HFE-HHC is treated before he or she develops cirrhosis of the liver, he or she can expect a normal lifespan. Among people who already have cirrhosis associated with HFE-HHC, 72% will survive at least 5 more years and 62% will survive at least 10 more years. People who already have cirrhosis are at an increased risk for developing a type of liver cancer. Page 4 of 16
5 What Next Steps Could You Take? The Universal Genetic Test has indicated that is a carrier of HFE-associated hereditary hemochromatosis. Because carriers of HFE-HHC do not have any symptoms of the disease, there may not be cause for concern. Even if his future children inherit the genes that cause HFE-HHC, it may not necessarily cause them to be sick. Most people with the genetic mutations that cause HFE-HHC do not have symptoms of the disease. Those who do have symptoms can be easily treated when identified early. Carriers of HFE-HHC do not face any known health risks, and need not take any further steps to protect their own health. Consult With a Physician or Genetic Counselor To schedule an appointment to speak with a genetic counselor at Counsyl, please call (888) COUNSYL or gc@counsyl.com. These medical professionals may be able to suggest actions the couple can take to lower the risk of their children developing HFEassociated hereditary hemochromatosis. Page 5 of 16
6 Full Results Below are the full test results for all diseases on the panel. Noted are the specific genetic mutations for which the patient tested positive or negative. If there was insufficient data to determine the genotype for any variant, this will be noted as "no call." Also listed in this section is the patient's post-test risk of being a carrier of each disease as well as the odds that his future children could inherit each disease. ABCC8-Related Hyperinsulinism 1 in 51,000 1 in 50, <10% detection rate. Gene ABCC8. Variants (3) F1388del, V187D, G>A. Achromatopsia 1 in 210,000 1 in 30, % detection rate. Gene CNGB3. Variants (6) R403Q, E336X, IVS8-3T>G, 819_826del8, T383fs, del11insT. Alkaptonuria % detection rate. Gene HGD. Variants (7) G161R, G270R, P230S, S47L, M368V, IVS1-1G>A, IVS5+1G>A. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency 1 in 740,000 1 in >99% detection rate. Gene SERPINA1. Variants (2) S allele, Z allele. Andermann Syndrome Gene SLC12A6. Variants (2) Thr813fsX813, R675X. ARSACS % detection rate. Gene SACS. Variants (2) 6594delT, 5254C>T. Aspartylglycosaminuria Gene AGA. Variants (2) 199_200delGA, C163S. Ataxia With Vitamin E Deficiency Gene TTPA. Variants (1) 744delA. Page 6 of 16
7 Ataxia-Telangiectasia 160. <10% detection rate. Gene ATM. Variants (1) R35X. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease 1 in 18,000 1 in 15, % detection rate. Gene PKHD1. Variants (5) Leu1965fs, 9689delA, T36M, R496X, V3471G. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome, BBS1-Related 1 in 500, % detection rate. Gene BBS1. Variants (1) M390R. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome, BBS10-Related 1 in 190, % detection rate. Gene BBS10. Variants (1) C91fs. Beta Thalassemia 1 in 250, % detection rate. Gene HBB. Variants (35) Poly A: AATAAA->AATGAA, Poly A: AATAAA->AATAAG, W15X, K17X, Q39X, 619 bp deletion, Pro5fs, Gly16fs, Glu6fs, Phe41fs, Lys8fs, Phe71fs, Ser9fs, IVS-II-654, IVS-II-705, IVS-II-745, IVS-II-850, IVS-I-6, IVS-I-110, IVS-I-5, IVS-II-844, IVS-I-1, IVS-I-1, IVS-II-849, IVS-II-849, Gly24 T>A, -30T>A, -88C>T, -28A>G, -29A>G, CAP+1 A>C, -87C>G, Hb C, Hb E, Hb O-Arab. Biotinidase Deficiency 1 in 410,000 1 in 55, % detection rate. Gene BTD. Variants (7) G98 d7i3, A171T, D252G, F403V, Q456H, R538C, D444H. Bloom Syndrome Gene BLM. Variants (2) 2281del6ins7, 2407insT. Canavan Disease % detection rate. Gene ASPA. Variants (4) E285A, Y231X, A305E, IVS2-2A>G. Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase IA Deficiency Gene CPT1A. Variants (2) P479L, G710E. Page 7 of 16
8 Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase II Deficiency 1 in 330, % detection rate. Gene CPT2. Variants (13) S38fs, Leu178_Ile186delinsPhe, Q413fs, P50H, S113L, R124X, P227L, R503C, G549D, Q550R, P604S, Y628S, R631C. Cartilage-Hair Hypoplasia Gene RMRP. Variants (2) 262G>T, g.70a>g. Choroideremia 1 in 200,000 1 in 200,000 No mutations detected. This does not rule out the poss bility of being affected by untested mutations. The post-test risk of being affected is < 1 in Gene CHM. Variants (1) IVS13+2dupT. CLN5-Related Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis Gene CLN5. Variants (1) 2467AT. Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation Type Ia 1 in 160, % detection rate. Gene PMM2. Variants (2) F119L, R141H. Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation Type Ib Gene MPI. Variants (1) R295H. Congenital Finnish Nephrosis Gene NPHS1. Variants (2) 121_122del, R1109X. Cystic Fibrosis 1 in 30,000 1 in 3,100 Non-disease-causing mutations: I506V. This does not rule out the possibility of being a carrier of untested mutations. The post-test risk of being a carrier is 1 in % detection rate. Gene CFTR. Variants (109) G85E, R117H, R334W, R347P, A455E, G542X, G551D, R553X, R560T, R1162X, W1282X, N1303K, F508del, I507del, 2184delA, 3659delC, 621+1G>T, 711+1G>T, G>A, G>A, G>A, G>A, kbC>T, E60X, R75X, G91R, E92X, R117C, Y122X, G178R, L206W, G330X, T338I, R347H, R352Q, S364P, G480C, Q493X, V520F, C524X, S549I, S549N, S549R, Q552X, A559T, P574H, G622D, R709X, K710X, Q890X, R1066C, R1070Q, W1089X, Y1092X, M1101K, D1152H, R1158X, S1196X, W1204X, S1235R, Q1238X, S1251N, S1255X, R1283M, dele2-3 21kb, 3199del6, F311del, 394delTT, 574delA, 663delT, 935delA, 936delTA, 1078delT, 1161delC, 1609delCA, 1677delTA, 1949del84, 2043delG, 2055del9>A, del13insAGAAA, 3171delC, 3667del4, 3821delT, 3876delA, 1288insTA, 2184insA, 2307insA, 2869insG, 3905insT, T>C, 405+1G>A, 405+3A>C, 406-1G>A, 711+5G>A, 712-1G>T, kbA>G, G>A, G>T, G>T, A>G, 3120G>A, 457TAT>G, 2183AA>G, S549R, W1204X, IVS8-5T, I148T, I506V, F508C. Cystinosis 1 in 240,000 1 in 200, % detection rate. Gene CTNS. Variants (4) 537del21, W138X, L158P, D205N. Page 8 of 16
9 Factor V Leiden Thrombophilia Non-disease-causing mutations: H1299R and D2222G. This does not rule out the possibility of being a carrier of untested mutations. The posttest risk of being a carrier is < 1 in 500. Gene F5. Variants (3) R506Q, H1299R, D2222G. M LD Factor XI Deficiency Gene F11. Variants (4) E117X, F283L, IVS14+1G>A, IVS14del14. Familial Dysautonomia Gene KBKAP. Variants (3) IVS20+6T>C, R696P, P914L. Familial Mediterranean Fever % detection rate. Gene MEFV. Variants (13) I692del, T267I, F479L, R653H, M680I, M694I, M694V, K695R, V726A, A744S, R761H, P369S, R408Q. Fanconi Anemia Type C 1 in 250, % detection rate. Gene FANCC. Variants (4) IVS4+4A>T, 322delG, Q13X, R548X. Fumarase Deficiency % detection rate. Gene FH. Variants (1) 1431_1433dupAAA. Galactosemia 1 in 30, % detection rate. Gene GALT. Variants (10) IVS2-2A>G, S135L, T138M, F171S, Q169K, Q188R, L195P, Y209C, K285N, X380R. Gaucher Disease 1 in 170,000 1 in 50, % detection rate. Gene GBA. Variants (9) N370S, L444P, 1035insG, IVS2+1G>A, V394L, D409V, R463C, R463H, R496H. GJB2-Related DFNB 1 Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss and Deafness 1 in 13,000 1 in 7, % detection rate. Gene GJB2. Variants (11) 35delG, 167delT, 313del14, E120del, W24X, V37I, W77R, W77X, Q124X, R184P, M34T. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency M LD No mutations detected. This does not rule out the poss bility of being affected by untested mutations. The post-test risk of being affected is 1 in 420. Gene G6PD. Variants (5) V68M, S188F, R459P, R459L, N126D. Page 9 of 16
10 Glutaric Acidemia Type 1 1 in 46,000 1 in 40, % detection rate. Gene GCDH. Variants (2) R402W, A421V. Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia 1 in 520,000 1 in 130, % detection rate. Gene G6PC. Variants (10) 727G>T, F327del, Q27fsdelC, 459insTA, R83H, R83C, G188R, Q242X, G270V, Q347X. Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ib 1 in 970,000 1 in 500, % detection rate. Gene G6PT1. Variants (4) 1211delCT, G339C, G339D, A367T. Glycogen Storage Disease Type III 1 in 110, <10% detection rate. Gene AGL. Variants (3) Q6X, 17delAG, 1484delT. Glycogen Storage Disease Type V 1 in 320, % detection rate. Gene PYGM. Variants (4) R49X, G204S, K542T, K542X. GRACILE Syndrome Gene BCS1L. Variants (1) S78G. Hereditary Fructose Intolerance 1 in 81,000 1 in 26, % detection rate. Gene ALDOB. Variants (4) Delta4E4, A149P, Y204X, N334K. Hereditary Thymine-Uraciluria 1 in 84,000 1 in 40, % detection rate. Gene DPYD. Variants (1) IVS14+1G>A. Herlitz Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa, LAMA3-Related Gene LAMA3. Variants (1) R650X. Page 10 of 16
11 Herlitz Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa, LAMB3-Related % detection rate. Gene LAMB3. Variants (5) 3024delT, R42X, R144X, Q243X, R635X. Herlitz Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa, LAMC2-Related Gene LAMC2. Variants (1) R95X. Hexosaminidase A Deficiency 500. Gene HEXA. Variants (8) 1278insTATC, IVS12+1G>C, R178C, R178H, G269S, IVS7+1G>A, IVS9+1G>A, R247W. HFE-Associated Hereditary Hemochromatosis Disease-causing mutations: HFE:p.Cys282Tyr (C282Y) heterozygote. This individual is a carrier of HFE-associated hereditary hemochromatosis. Carriers generally do not experience symptoms. Clinical symptoms are also uncommon in C282Y homozygotes. Gene HFE. Variants (11) H63D, S65C, Q127H, E168Q, E168X, W169X, C282Y, Q283P, V53M, V59M, H63H. M LD Homocystinuria Caused by Cystathionine Beta-Synthase Deficiency 1 in 200,000 1 in 130, % detection rate. Gene CBS. Variants (2) I278T, G307S. Hurler Syndrome 1 in 170, % detection rate. Gene DUA. Variants (2) A327P, W402X. Hyperornithinemia-Hyperammonemia-Homocitrullinuria Syndrome Gene SLC25A15. Variants (1) F188del. Hypophosphatasia, Autosomal Recessive 1 in 130, % detection rate. Gene ALPL. Variants (5) 1559delT, F310L, D361V, E174K, G317D. Inclusion Body Myopathy 2 Gene GNE. Variants (1) M712T. Infantile Refsum Disease 1 in 88,000 1 in 50, % detection rate. Gene PEX1. Variants (1) G843D. Page 11 of 16
12 Isovaleric Acidemia 1 in 470,000 1 in 250, % detection rate. Gene IVD. Variants (1) A311V. Krabbe Disease 1 in 120,000 1 in 63, % detection rate. Gene GALC. Variants (3) Ex11-17del, G270D, R168C. Leigh Syndrome, French-Canadian Type Gene LRPPRC. Variants (1) A354V. Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Type 2E Gene SGCB. Variants (1) S114F. Long Chain 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency 1 in 510,000 1 in 90, % detection rate. Gene HADHA. Variants (2) Q342X, E474Q. Maple Syrup Urine Disease Type 1B 1 in 420,000 1 in 250, % detection rate. Gene BCKDHB. Variants (3) R183P, G278S, E322X. Maple Syrup Urine Disease Type 3 Gene DLD. Variants (2) 105insA, G229C. Medium Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency 1 in 63,000 1 in 14, % detection rate. Gene ACADM. Variants (7) L59F, G170R, G242R, Y42H, K304E, R181C, R181H. Metachromatic Leukodystrophy 1 in 150,000 1 in 81, % detection rate. Gene ARSA. Variants (4) P377L, P426L, IVS2+1G>A, T274M. Page 12 of 16
13 Mucolipidosis IV Gene MCOLN1. Variants (2) 511_6944del, IVS3-2A>G. Muscle-Eye-Brain Disease % detection rate. Gene POMGNT1. Variants (1) IVS17+1G>A. MYH-Associated Polyposis 1 in 52,000 1 in 40, % detection rate. Gene MUTYH. Variants (1) Y165C. Niemann-Pick Disease Type A 1 in 260,000 1 in 250, <10% detection rate. Gene SMPD1. Variants (3) fsp330, L302P, R496L. Niemann-Pick Disease Type C 1 in 170,000 1 in 150, <10% detection rate. Gene NPC1. Variants (1) I1061T. Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome 1 in 460, % detection rate. Gene NBN. Variants (1) 657del5. Northern Epilepsy Gene CLN8. Variants (1) R24G. Pendred Syndrome 1 in 36,000 1 in 20, % detection rate. Gene SLC26A4. Variants (3) L236P, E384G, T416P. Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Deficiency 1 in 10, >99% detection rate. Gene PAH. Variants (11) IVS-10int-546, IVS12+1G>A, L48S, I65T, R158Q, R252W, R261Q, G272X, R408Q, R408W, Y414C. Page 13 of 16
14 Polyglandular Autoimmune Syndrome Type % detection rate. Gene A RE. Variants (2) Y85C, R257X. PPT1-Related Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis % detection rate. Gene PPT1. Variants (4) L10X, T75P, R122W, R151X. Primary Hyperoxaluria Type 1 1 in 760,000 1 in 500, % detection rate. Gene AGXT. Variants (3) F152I, G170R, I244T. Primary Hyperoxaluria Type % detection rate. Gene GRHPR. Variants (1) 103delG. Pycnodysostosis Gene CTSK. Variants (1) X330W. Rhizomelic Chondrodysplasia Punctata Type 1 1 in 230, % detection rate. Gene PEX7. Variants (2) G217R, L292X. Salla Disease Gene SLC17A5. Variants (2) Leu336fsX13, R39C. Segawa Syndrome Gene TH. Variants (1) R233H. Short Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency Non-disease-causing mutations: G185S. This does not rule out the possibility of being a carrier of untested mutations. The post-test risk of being a carrier is 1 in 160. <10% detection rate. Gene ACADS. Variants (2) R107C, G185S. Page 14 of 16
15 Sickle Cell Disease 500. >99% detection rate. Gene HBB. Variants (37) Hb S, Poly A: AATAAA->AATGAA, Poly A: AATAAA->AATAAG, W15X, K17X, Q39X, 619 bp deletion, Pro5fs, Gly16fs, Glu6fs, Phe41fs, Lys8fs, Phe71fs, Ser9fs, IVS- II-654, IVS-II-705, IVS-II-745, IVS-II-850, IVS-I-6, IVS-I-110, IVS-I-5, IVS-II-844, IVS-I-1, IVS-I-1, IVS-II-849, IVS-II-849, Gly24 T>A, -30T>A, -88C>T, -28A>G, -29A>G, CAP+1 A>C, -87C>G, Hb C, Hb E, Hb D-Punjab, Hb O-Arab. Sjogren-Larsson Syndrome 1 in 330,000 1 in 250, % detection rate. Gene ALDH3A2. Variants (1) P315S. Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome 1 in 98,000 1 in 40, % detection rate. Gene DHCR7. Variants (11) IVS8-1G>C, T93M, L109P, W151X, L157P, V326L, R352Q, R352W, C380Y, R404C, W151X. Spinal Muscular Atrophy 1 in 97,000 1 in 4, % detection rate. Gene SMN1. Variants (1) Exon 7 deletion. Sulfate Transporter-Related Osteochondrodysplasia 1 in 60,000 1 in 18, % detection rate. Gene SLC26A2. Variants (5) C653S, R178X, R279W, V340del, IVS1+2T>C. Tay-Sachs Disease 1 in 690,000 1 in 360, % detection rate. Gene HEXA. Variants (4) 1278insTATC, IVS12+1G>C, IVS7+1G>A, IVS9+1G>A. TPP1-Related Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis 1 in 950,000 1 in 350, % detection rate. Gene TPP1. Variants (4) G284V, R208X, IVS5-1G>C, IVS5-1G>A. Tyrosinemia Type I 1 in 240,000 1 in 120, % detection rate. Gene FAH. Variants (5) IVS8-1G>C, IVS12+5G>A, P261L, W262X, E357X. Usher Syndrome Type 1F 1 in 160,000 1 in 150, <10% detection rate. Gene PCDH15. Variants (1) R245X. Page 15 of 16
16 Usher Syndrome Type 3 Gene CLRN1. Variants (1) N48K. Wilson Disease 1 in 52,000 1 in 30, % detection rate. Gene ATP7B. Variants (5) 1340del4, 2337delC, R778G, W779X, H1069Q. X-Linked Juvenile Retinoschisis No mutations detected. This does not rule out the poss bility of being affected by untested mutations. The post-test risk of being affected is < 1 in % detection rate. Gene RS1. Variants (3) E72K, G74V, G109R. Page 16 of 16
CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA
 CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA SHUFFLING THE GENETIC DECK IN CML 9 9 (q+) 22 Ph (22q-) bcr bcr-abl abl Fusion protein causes cancer GLEEVEC AND BCR-ABL FUSION PROTEIN GENETIC MEDICINE A. Genetic diseases
CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA SHUFFLING THE GENETIC DECK IN CML 9 9 (q+) 22 Ph (22q-) bcr bcr-abl abl Fusion protein causes cancer GLEEVEC AND BCR-ABL FUSION PROTEIN GENETIC MEDICINE A. Genetic diseases
Foresight Carrier Screen
 4915 25th Ave NE, Suite 204W Seattle, WA 98105 Phone: (206) 588-1484 Fax: (206) 466-4696 Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 09/20/2017 Date Received: 09/22/2017 Date Tested: 09/27/2017 Indication:
4915 25th Ave NE, Suite 204W Seattle, WA 98105 Phone: (206) 588-1484 Fax: (206) 466-4696 Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 09/20/2017 Date Received: 09/22/2017 Date Tested: 09/27/2017 Indication:
NutraHacker. Carrier and Drug Response Report for Customer: b2b0b618-db91-447c-9470-ff7b79ae147d. Instructions:
 NutraHacker Carrier and Drug Response Report for Customer: b2b0b618-db91-447c-9470-ff7b79ae147d Instructions: In this report, NutraHacker examines single nucleotide polymorphisms that reveal carrier status
NutraHacker Carrier and Drug Response Report for Customer: b2b0b618-db91-447c-9470-ff7b79ae147d Instructions: In this report, NutraHacker examines single nucleotide polymorphisms that reveal carrier status
JOHN DOE JANE DOE. Reproductive Risk Summary. Counsyl Test Results Summary
 Results Recipient University Medical Center 827 Attn: Dr. Paul Smith 123 Main Street Houston, TX 10231 Phone: (800) 555-1212 Fax: (800) 555-1212 NPI: 7834324983 Report Date: 09/09/2013 Female Ethnicity:
Results Recipient University Medical Center 827 Attn: Dr. Paul Smith 123 Main Street Houston, TX 10231 Phone: (800) 555-1212 Fax: (800) 555-1212 NPI: 7834324983 Report Date: 09/09/2013 Female Ethnicity:
Foresight Carrier Screen
 4915 25th Ave NE, Suite 204W Seattle, WA 98105 Phone: (206) 588-1484 Fax: (206) 466-4696 Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 08/17/2017 Date Received: 08/18/2017 Date Tested: 08/24/2017 Indication:
4915 25th Ave NE, Suite 204W Seattle, WA 98105 Phone: (206) 588-1484 Fax: (206) 466-4696 Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 08/17/2017 Date Received: 08/18/2017 Date Tested: 08/24/2017 Indication:
Family Prep Screen POSITIVE: HIGH REPRODUCTIVE RISK. Cystic Fibrosis
 123 Main Street Houston, TX 10231 Phone: (800) 555-1212 Fax: (800) 555-1212 FE Sample Type: OG-510 Saliva Date of Collection: 07/08/2014 Date Received: 07/13/2014 Date Tested: 07/13/2014 Indication: No
123 Main Street Houston, TX 10231 Phone: (800) 555-1212 Fax: (800) 555-1212 FE Sample Type: OG-510 Saliva Date of Collection: 07/08/2014 Date Received: 07/13/2014 Date Tested: 07/13/2014 Indication: No
BROADENING YOUR PATIENT S OPTIONS FOR GENETIC CARRIER SCREENING.
 BROADENING YOUR PATIENT S OPTIONS FOR GENETIC CARRIER SCREENING. The Inheritest SM Carrier Screen provides relevant genetic screening for many inherited diseases found throughout the pan-ethnic US population.
BROADENING YOUR PATIENT S OPTIONS FOR GENETIC CARRIER SCREENING. The Inheritest SM Carrier Screen provides relevant genetic screening for many inherited diseases found throughout the pan-ethnic US population.
23andMe Reports GENETIC HEALTH RISK REPORTS. Increased risk for breast and ovarian cancer. function
 1 23andMe Reports GENETIC HEALTH RISK REPORTS BRCA1/BRCA2 Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Parkinson's Disease Age-Related Macular Degeneration Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Celiac Disease G6PD Deficiency
1 23andMe Reports GENETIC HEALTH RISK REPORTS BRCA1/BRCA2 Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Parkinson's Disease Age-Related Macular Degeneration Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Celiac Disease G6PD Deficiency
All diseases on Foresight
 All diseases on Foresight Disease 11-Beta-Hydroxylase- Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia 21-Hydroxylase-Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl- CoA Lyase Deficiency
All diseases on Foresight Disease 11-Beta-Hydroxylase- Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia 21-Hydroxylase-Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl- CoA Lyase Deficiency
SAMPLE. Carrier Screening Results Report v2.2 Page 1/8
 MM480: Pan-Ethnic Carrier Screen - Targeted Mutation Panel Report Prepared For: Patient: Name: Date of Birth: IDs (Internal / External): Reported Gender: Reported Ethnicity: Sample: Sample Collection Date:
MM480: Pan-Ethnic Carrier Screen - Targeted Mutation Panel Report Prepared For: Patient: Name: Date of Birth: IDs (Internal / External): Reported Gender: Reported Ethnicity: Sample: Sample Collection Date:
Foresight Carrier Screen
 4915 25th Ave NE, Suite 204W Seattle, WA 98105 Phone: (206) 588-1484 Fax: (206) 466-4696 Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: Date Received: 02/19/2018 Date Tested: 02/26/2018 Accession ID: CSL3P6DMJ324JJ4
4915 25th Ave NE, Suite 204W Seattle, WA 98105 Phone: (206) 588-1484 Fax: (206) 466-4696 Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: Date Received: 02/19/2018 Date Tested: 02/26/2018 Accession ID: CSL3P6DMJ324JJ4
disease carrier status PANEL DETAILS VERSION Risk Details JANE MILLER JOHN MILLER NEGATIVE CARRIER * NEGATIVE MILD CONDITION NEGATIVE
 123 Main Street City, CA 10231 Phone: (800) 555-1212 Fax: (800) 555-1212 FE Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 02/06/2014 Date Received: 02/16/2014 Date Tested: 02/16/2014 Indication: Screening
123 Main Street City, CA 10231 Phone: (800) 555-1212 Fax: (800) 555-1212 FE Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 02/06/2014 Date Received: 02/16/2014 Date Tested: 02/16/2014 Indication: Screening
23andMe Personal Genome Service (PGS) Carrier Status Tests Package Insert
 Table of contents Intended Use Important warnings and limitations Test performance User studies Specific test information 23andMe Personal Genome Service (PGS) Carrier Status Tests Package Insert For in-vitro
Table of contents Intended Use Important warnings and limitations Test performance User studies Specific test information 23andMe Personal Genome Service (PGS) Carrier Status Tests Package Insert For in-vitro
Foresight Carrier Screen
 321 Main Street San Francisco, CA 94080 Phone: (415) 555-5555 Fax: (415) 555-5555 FE Sample Type: OG-510 Saliva Date of Collection: 07/12/2017 Date Received: 07/17/2017 Date Tested: 07/17/2017 Indication:
321 Main Street San Francisco, CA 94080 Phone: (415) 555-5555 Fax: (415) 555-5555 FE Sample Type: OG-510 Saliva Date of Collection: 07/12/2017 Date Received: 07/17/2017 Date Tested: 07/17/2017 Indication:
Foresight Carrier Screen
 321 Main Street San Francisco, CA 94080 Phone: (415) 555-5555 Fax: (415) 555-5555 FE Sample Type: OG-510 Saliva Date of Collection: 06/23/2017 Date Received: 06/28/2017 Date Tested: 06/28/2017 Indication:
321 Main Street San Francisco, CA 94080 Phone: (415) 555-5555 Fax: (415) 555-5555 FE Sample Type: OG-510 Saliva Date of Collection: 06/23/2017 Date Received: 06/28/2017 Date Tested: 06/28/2017 Indication:
23andMe Personal Genome Service (PGS) Carrier Status Tests Package Insert
 Table of contents Intended Use Important warnings and limitations Test performance User studies Specific test information 23andMe Personal Genome Service (PGS) Carrier Status Tests Package Insert For in-vitro
Table of contents Intended Use Important warnings and limitations Test performance User studies Specific test information 23andMe Personal Genome Service (PGS) Carrier Status Tests Package Insert For in-vitro
Evolve FamilyReady Carrier Screen
 Evolve FamilyReady Carrier Screen Accurate & Comprehensive Expanded Carrier Screen of >200 genes for the most relevant genetic disorders for all ethnicities. Achromatopsia CNGB3 X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy
Evolve FamilyReady Carrier Screen Accurate & Comprehensive Expanded Carrier Screen of >200 genes for the most relevant genetic disorders for all ethnicities. Achromatopsia CNGB3 X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy
Foresight Carrier Screen
 321 Main Street San Francisco, CA 94080 Phone: (415) 555-5555 Fax: (415) 555-5555 FE Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 07/12/2017 Date Received: 07/17/2017 Date Tested: 07/17/2017 Indication:
321 Main Street San Francisco, CA 94080 Phone: (415) 555-5555 Fax: (415) 555-5555 FE Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 07/12/2017 Date Received: 07/17/2017 Date Tested: 07/17/2017 Indication:
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples
 A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal?
 Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal? Disclosures Research funding from Natera Mary E Norton MD University of California, San Francisco Antepartum and Intrapartum Management June 15, 2017 Burden
Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal? Disclosures Research funding from Natera Mary E Norton MD University of California, San Francisco Antepartum and Intrapartum Management June 15, 2017 Burden
Foresight Carrier Screen
 Freiburg Medical Laboratory, ME LLC Box 3068 Dubai, 00000 Phone: +971 4 396 2227 FE Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 04/23/2018 Date Received: 04/27/2018 Date Tested: 05/05/2018 Indication:
Freiburg Medical Laboratory, ME LLC Box 3068 Dubai, 00000 Phone: +971 4 396 2227 FE Sample Type: EDTA Blood Date of Collection: 04/23/2018 Date Received: 04/27/2018 Date Tested: 05/05/2018 Indication:
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks
 A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
CLINICAL AND HUMAN TESTING
 CLINICAL AND HUMAN TESTING CARRIER SCREENING FOR FAMILY PLANNING Let knowledge be your guide. Identify genetic conditions before or during a pregnancy to help predict the chances of having a child with
CLINICAL AND HUMAN TESTING CARRIER SCREENING FOR FAMILY PLANNING Let knowledge be your guide. Identify genetic conditions before or during a pregnancy to help predict the chances of having a child with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation Weizhen Ji, Jia Nee Foo, Brian J. O Roak, Hongyu Zhao, Martin G. Larson, David B.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation Weizhen Ji, Jia Nee Foo, Brian J. O Roak, Hongyu Zhao, Martin G. Larson, David B.
PATIENT EDUCATION. carrier screening INFORMATION
 PATIENT EDUCATION carrier screening INFORMATION carrier screening AT A GLANCE Why is carrier screening recommended? Carrier screening is one of many tests that can help provide information to you and your
PATIENT EDUCATION carrier screening INFORMATION carrier screening AT A GLANCE Why is carrier screening recommended? Carrier screening is one of many tests that can help provide information to you and your
modified dye uptake assay including formazan test EC 90 not tested plaque reduction assay
 Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
Expanded carrier screening for monogenic disorders: where are we now?
 DOI: 10.1002/pd.5109 SPECIAL TOPIC ISSUE ON ADVANCES IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SINGLE GENE DISORDERS Expanded carrier screening for monogenic disorders: where are we now? Davit Chokoshvili*, Danya Vears and
DOI: 10.1002/pd.5109 SPECIAL TOPIC ISSUE ON ADVANCES IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SINGLE GENE DISORDERS Expanded carrier screening for monogenic disorders: where are we now? Davit Chokoshvili*, Danya Vears and
Hemochromatosis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
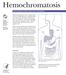 Hemochromatosis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Hemochromatosis, the most common form
Hemochromatosis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Hemochromatosis, the most common form
Expanded Carrier Screening: What s Best?
 Expanded Carrier Screening: What s Best? James D Goldberg, MD September 17, 2017 Disclosures James D. Goldberg, M.D. Chief Medical Officer, Counsyl 3 Learning Objectives Guidelines Data Design Practice
Expanded Carrier Screening: What s Best? James D Goldberg, MD September 17, 2017 Disclosures James D. Goldberg, M.D. Chief Medical Officer, Counsyl 3 Learning Objectives Guidelines Data Design Practice
Deliverable 2.1 List of relevant genetic variants for pre-emptive PGx testing
 GA N 668353 H2020 Research and Innovation Deliverable 2.1 List of relevant genetic variants for pre-emptive PGx testing WP N and Title: WP2 - Towards shared European Guidelines for PGx Lead beneficiary:
GA N 668353 H2020 Research and Innovation Deliverable 2.1 List of relevant genetic variants for pre-emptive PGx testing WP N and Title: WP2 - Towards shared European Guidelines for PGx Lead beneficiary:
An Effective Model to Communicate Complex Genetic Information to Families and Health Care Providers
 An Effective Model to Communicate Complex Genetic Information to Families and Health Care Providers Theresa Steckel, RN, BSN Newborn Screening Quality Assurance and Education Coordinator Oklahoma State
An Effective Model to Communicate Complex Genetic Information to Families and Health Care Providers Theresa Steckel, RN, BSN Newborn Screening Quality Assurance and Education Coordinator Oklahoma State
Pharmacogenomics in Rare Diseases: Development Strategy for Ivacaftor as a Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis
 Pharmacogenomics in Rare Diseases: Development Strategy for Ivacaftor as a Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Federico Goodsaid Vice President Strategic Regulatory Intelligence Vertex Pharmaceuticals Is there
Pharmacogenomics in Rare Diseases: Development Strategy for Ivacaftor as a Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Federico Goodsaid Vice President Strategic Regulatory Intelligence Vertex Pharmaceuticals Is there
Supplementary Figure 1
 Count Count Supplementary Figure 1 Coverage per amplicon for error-corrected sequencing experiments. Errorcorrected consensus sequence (ECCS) coverage was calculated for each of the 568 amplicons in the
Count Count Supplementary Figure 1 Coverage per amplicon for error-corrected sequencing experiments. Errorcorrected consensus sequence (ECCS) coverage was calculated for each of the 568 amplicons in the
TEST INFORMATION Test: CarrierMap GEN (Genotyping) Panel: CarrierMap Expanded Diseases Tested: 311 Genes Tested: 299 Mutations Tested: 2647
 Ordering Practice Jane Smith John Smith Practice Code: 675 Miller MD 374 Broadway New York, NY 10000 Physician: Dr. Frank Miller Report Generated: 2016-02-03 DOB: 1973-02-19 Gender: Female Ethnicity: European
Ordering Practice Jane Smith John Smith Practice Code: 675 Miller MD 374 Broadway New York, NY 10000 Physician: Dr. Frank Miller Report Generated: 2016-02-03 DOB: 1973-02-19 Gender: Female Ethnicity: European
Supplemental Table 1. The list of variants with their respective scores for each variant classifier Gene DNA Protein Align-GVGD Polyphen-2 CADD MAPP
 Supplemental Table 1. The list of variants with their respective scores for each variant classifier Gene DNA Protein Align-GVGD Polyphen-2 CADD MAPP Frequency Domain Mammals a 3 S/P b Mammals a 3 S/P b
Supplemental Table 1. The list of variants with their respective scores for each variant classifier Gene DNA Protein Align-GVGD Polyphen-2 CADD MAPP Frequency Domain Mammals a 3 S/P b Mammals a 3 S/P b
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Related Policies None
 Medical Policy MP 2.04.107 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.107 Last Review: 04/30/2018 Effective Date: 04/30/0218 Section: Medicine Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
Medical Policy MP 2.04.107 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.107 Last Review: 04/30/2018 Effective Date: 04/30/0218 Section: Medicine Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
Hemochromatosis - Genetic Inheritance
 Hemochromatosis - Genetic Inheritance Inheritance Combinations for HFE Hemochromatosis (Autosomal Recessive Inheritance) If both parents are carriers of one C282Y mutation for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene,
Hemochromatosis - Genetic Inheritance Inheritance Combinations for HFE Hemochromatosis (Autosomal Recessive Inheritance) If both parents are carriers of one C282Y mutation for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene,
Summary of Results CARRIER STATUS DNA INSIGHT. Result: Carrier, Heterozygote. Protected Health Information. Propionic Acidemia
 Test Results Reviewed & Approved by: Laboratory Director, Nilesh Dharajiya,.D. SAPLE REPORT CARRIER STATUS DNA INSIGHT PERSONAL DETAILS DOB Jan 1, 19XX ETHNICITY Asian ORDERING HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL
Test Results Reviewed & Approved by: Laboratory Director, Nilesh Dharajiya,.D. SAPLE REPORT CARRIER STATUS DNA INSIGHT PERSONAL DETAILS DOB Jan 1, 19XX ETHNICITY Asian ORDERING HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL
CarrierMap. Genetic Counseling. Technology TABLE OF. Sample Report CONTENTS. New Offerings. Recombine Facts. Disease List
 Recombine 2 CarrierMap 4 Genetic Counseling TABLE OF CONTENTS 8 12 14 Technology Sample Report New Offerings 18 Recombine Facts 19 Disease List CARRIERMA ROVIDES COMLETE We help families have healthy children
Recombine 2 CarrierMap 4 Genetic Counseling TABLE OF CONTENTS 8 12 14 Technology Sample Report New Offerings 18 Recombine Facts 19 Disease List CARRIERMA ROVIDES COMLETE We help families have healthy children
The Israeli population carrier screening program. Joël Zlotogora MD, PhD Hadassah medical school Hebrew University Jerusalem
 The Israeli population carrier screening program Joël Zlotogora MD, PhD Hadassah medical school Hebrew University Jerusalem The Israeli population 2015 8,134,500 inhabitants Jews (75.1%) Ashkenazi, non
The Israeli population carrier screening program Joël Zlotogora MD, PhD Hadassah medical school Hebrew University Jerusalem The Israeli population 2015 8,134,500 inhabitants Jews (75.1%) Ashkenazi, non
Information leaflet for people with hereditary haemochromatosis and their families. Hereditary Haemochromatosis
 Information leaflet for people with hereditary haemochromatosis and their families Hereditary Haemochromatosis What is hereditary haemochromatosis? Hereditary haemochromatosis (HH) is a treatable inherited
Information leaflet for people with hereditary haemochromatosis and their families Hereditary Haemochromatosis What is hereditary haemochromatosis? Hereditary haemochromatosis (HH) is a treatable inherited
EVOLVE CARRIER GENETIC SCREENS. Better health for generations to come! Be Proactive. SCREEN TODAY. PROTECT TOMORROW.
 EVOLVE CARRIER GENETIC SCREENS Better health for generations to come! Be Proactive. SCREEN TODAY. PROTECT TOMORROW. PROTECT THE HEALTH OF YOUR FUTURE CHILDREN BY KNOWING YOUR GENETIC RISKS, TODAY! Carrier
EVOLVE CARRIER GENETIC SCREENS Better health for generations to come! Be Proactive. SCREEN TODAY. PROTECT TOMORROW. PROTECT THE HEALTH OF YOUR FUTURE CHILDREN BY KNOWING YOUR GENETIC RISKS, TODAY! Carrier
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Open An empirical estimate of carrier frequencies for 400+ causal Mendelian variants: results from an ethnically diverse clinical sample of 23,453 individuals
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Open An empirical estimate of carrier frequencies for 400+ causal Mendelian variants: results from an ethnically diverse clinical sample of 23,453 individuals
Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E,
 Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E, TY93/H5N1 GFP-627K, or the TY93/H5N1 PB2(588-759) virus library. To establish our GFP- FACS screening platform, we compared
Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E, TY93/H5N1 GFP-627K, or the TY93/H5N1 PB2(588-759) virus library. To establish our GFP- FACS screening platform, we compared
The role of E148Q in FMF. Elon Pras Institute of Human Genetics Sheba Medical Center
 The role of E148Q in FMF Elon Pras Institute of Human Genetics Sheba Medical Center Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) Acute attacks of fever accompanied by: Peritonitis Pleuritis Arthritis Erysipelas
The role of E148Q in FMF Elon Pras Institute of Human Genetics Sheba Medical Center Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) Acute attacks of fever accompanied by: Peritonitis Pleuritis Arthritis Erysipelas
Residual risks by ethnicity
 Residual risks by ethnicity This table displays residual risks after a negative result for each of the genes and corresponding disorders. If a patient is reported to be a carrier of a disease, their residual
Residual risks by ethnicity This table displays residual risks after a negative result for each of the genes and corresponding disorders. If a patient is reported to be a carrier of a disease, their residual
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Exon I M1V 1A>G Kolker et al, delG Spector & Sharer, unpublished /90 delc Mushimoto et al, 2011
 Exon I M1V 1A>G Kolker et al, 2007 --- 11delG Spector & Sharer, unpublished 2006 --- 89/90 delc Mushimoto et al, 2011 Intron 1 IVS1+5G>T --- Greenberg et al, 1995 Exon II --- 109-110delCA Tsai et al, 2017
Exon I M1V 1A>G Kolker et al, 2007 --- 11delG Spector & Sharer, unpublished 2006 --- 89/90 delc Mushimoto et al, 2011 Intron 1 IVS1+5G>T --- Greenberg et al, 1995 Exon II --- 109-110delCA Tsai et al, 2017
The Counsyl Foresight Carrier Screen
 The Counsyl Foresight Carrier Screen 180 Kimball Way South San Francisco, CA 94080 www.counsyl.com contact@counsyl.com (888) COUNSYL The Counsyl Foresight Carrier Screen - Disease Reference Book 11-beta-hydroxylase-deficient
The Counsyl Foresight Carrier Screen 180 Kimball Way South San Francisco, CA 94080 www.counsyl.com contact@counsyl.com (888) COUNSYL The Counsyl Foresight Carrier Screen - Disease Reference Book 11-beta-hydroxylase-deficient
PREDICAGEN LLC REPORT
 The report below is a scientific interpretation of the DNA variants (referred as RS numbers) to the customer by a third party (for example 23andMe). The report should not be considered exclusive, because
The report below is a scientific interpretation of the DNA variants (referred as RS numbers) to the customer by a third party (for example 23andMe). The report should not be considered exclusive, because
Support. Overview. Auditory Dys-synchrony. Auditory Brainstem Response. Potential Causes
 Potential Role of Genetic Testing in Auditory Neuropathy/Dys-synchrony Christina Runge-Samuelson, Ph.D., CCC-A Associate Professor Co-Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Department of tolaryngology
Potential Role of Genetic Testing in Auditory Neuropathy/Dys-synchrony Christina Runge-Samuelson, Ph.D., CCC-A Associate Professor Co-Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Department of tolaryngology
Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
 The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
QUESTION. Personal Behavior History. Donor Genetic History. Donor Medical History. Family Medical History PERSONAL BEHAVIOR HISTORY. Never N/A.
 Donor 4576 Medical Profile S Personal Behavior History Donor Genetic History Donor Medical History Family Medical History PERSONAL BEHAVIOR HISTORY Current alcohol use: If yes, oz./week and type of alcohol:
Donor 4576 Medical Profile S Personal Behavior History Donor Genetic History Donor Medical History Family Medical History PERSONAL BEHAVIOR HISTORY Current alcohol use: If yes, oz./week and type of alcohol:
General Guidelines for Health professionals
 General Guidelines for Health professionals Page 1 Haemochromatosis Introduction Hereditary haemochromatosis (HH) now easily screened for as most symptomatic individuals are homozygous for the C282Y mutation
General Guidelines for Health professionals Page 1 Haemochromatosis Introduction Hereditary haemochromatosis (HH) now easily screened for as most symptomatic individuals are homozygous for the C282Y mutation
GENETIC TESTING AND COUNSELING FOR HERITABLE DISORDERS
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Laboratory Policy Number: VI-09 Effective Date: 03/17/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Laboratory Policy Number: VI-09 Effective Date: 03/17/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members
Utility of Microarrays in Molecular Genetics
 Utility of Microarrays in Molecular Genetics Madhuri Hegde, Ph.D., FACMG Associate Professor Senior Director Department of Human Genetics Emory Genetics Laboratory Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta,
Utility of Microarrays in Molecular Genetics Madhuri Hegde, Ph.D., FACMG Associate Professor Senior Director Department of Human Genetics Emory Genetics Laboratory Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta,
Intron 1 IVS1+5G>T --- Greenberg et al, Exon II del2 Tsai et al, 2017 K42R 125A>G Spector et al, unpublished
 Exon I M1V 1A>G Kolker et al, 2007 --- 11delG Spector & Sharer, unpublished S25L 74C>T Spector et al, unpublished --- 89/90 delc Mushimoto et al, 2011 88-91del4+IVS1 gtca Spector et al, unpublished Intron
Exon I M1V 1A>G Kolker et al, 2007 --- 11delG Spector & Sharer, unpublished S25L 74C>T Spector et al, unpublished --- 89/90 delc Mushimoto et al, 2011 88-91del4+IVS1 gtca Spector et al, unpublished Intron
Archived Reports Summary
 Archived Reports Summary 1 Archived Reports Summary This summary provides information that may be helpful when viewing your archived reports. The information in this document and in your reports is intended
Archived Reports Summary 1 Archived Reports Summary This summary provides information that may be helpful when viewing your archived reports. The information in this document and in your reports is intended
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs
 Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT MARCH 13, 2012
 IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT201208 MARCH 13, 2012 Updates to the 2012 Healthcare Common Coding System This bulletin updates information published by the Indiana Health Coverage Programs
IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT201208 MARCH 13, 2012 Updates to the 2012 Healthcare Common Coding System This bulletin updates information published by the Indiana Health Coverage Programs
Metabolic Disorders Screened Overseas but not Screened in Australia Condition Features Inherited Diagnosis Treatment Newborn Screen
 Metabolic Disorders ed Overseas but not ed in Australia Biotinidase Deficiency Severe form causes seizures & delay Biotin can prevent complications NZ, USA Tyrosinaemia Type I Coma & death before age 10
Metabolic Disorders ed Overseas but not ed in Australia Biotinidase Deficiency Severe form causes seizures & delay Biotin can prevent complications NZ, USA Tyrosinaemia Type I Coma & death before age 10
Genetic screening. Martin Delatycki
 7 Genetic screening Martin Delatycki Case study 1 Vanessa and John are planning a family. They see their general practitioner and ask whether they should have any tests prior to falling pregnant to maximise
7 Genetic screening Martin Delatycki Case study 1 Vanessa and John are planning a family. They see their general practitioner and ask whether they should have any tests prior to falling pregnant to maximise
CARRIER SCREEN - LIST OF DISORDERS
 1 11-Beta-Hydroxylase-Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia 2 17-Beta-Hydroxysteroid deyhdrogenase X deficiency 3 2-Methylbutytyrglycinuria 4 21-hydroxylase deficiency 5 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase
1 11-Beta-Hydroxylase-Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia 2 17-Beta-Hydroxysteroid deyhdrogenase X deficiency 3 2-Methylbutytyrglycinuria 4 21-hydroxylase deficiency 5 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase
Preparent Standard Panel
 Preparent Standard Panel Disorder Gene Variants Ethnicity Alpha-thalassemia HBA1 HBA2 -alpha3.7, -alpha4.2, -alpha20.5, --SEA, --MED, --FIL, --THAI Mediterranean 1 in 20 1 in 191 1 in 291 African American
Preparent Standard Panel Disorder Gene Variants Ethnicity Alpha-thalassemia HBA1 HBA2 -alpha3.7, -alpha4.2, -alpha20.5, --SEA, --MED, --FIL, --THAI Mediterranean 1 in 20 1 in 191 1 in 291 African American
Genetic Testing FOR DISEASES OF INCREASED FREQUENCY IN THE ASHKENAZI JEWISH POPULATION
 Carrier Screening and Diagnostic Testing for the Ashkenazi Jewish Population Genetic Testing FOR DISEASES OF INCREASED FREQUENCY IN THE ASHKENAZI JEWISH POPULATION Our Science. Your Care. An extensive
Carrier Screening and Diagnostic Testing for the Ashkenazi Jewish Population Genetic Testing FOR DISEASES OF INCREASED FREQUENCY IN THE ASHKENAZI JEWISH POPULATION Our Science. Your Care. An extensive
Kalydeco. Kalydeco (ivacaftor) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.45.03 Subject: Kalydeco Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Kalydeco Description Kalydeco
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.45.03 Subject: Kalydeco Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Kalydeco Description Kalydeco
Knowledge is power. Plan ahead with GeneAware.
 MATERNAL FETAL Many patients may have questions regarding specific genetic disorders that may arise when planning or expecting a baby. That s why Baylor Genetics developed GeneAware, a reproductive carrier
MATERNAL FETAL Many patients may have questions regarding specific genetic disorders that may arise when planning or expecting a baby. That s why Baylor Genetics developed GeneAware, a reproductive carrier
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Prime Therapeutics
Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Prime Therapeutics
High Impact Treatment Benefits X-Linked Moderate Impact. Disease Gene # Mutations Disease Group(s)
 CarrierMap Expanded v3 Panel: 314 Diseases CarrierMap screen for 316 diseases including DMD. Disease Groups High Impact Treatment Benefits X-Linked Moderate Impact These diseases have a significant impact
CarrierMap Expanded v3 Panel: 314 Diseases CarrierMap screen for 316 diseases including DMD. Disease Groups High Impact Treatment Benefits X-Linked Moderate Impact These diseases have a significant impact
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hereditary_hemochromatosis 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Description of Procedure or Service Policy
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hereditary_hemochromatosis 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Description of Procedure or Service Policy
For Your Baby s Health Department of Health
 Newborn Screening For Your Baby s Health Department of Health Why is my baby tested? To help make sure your baby will be as healthy as possible. The blood test provides important information about your
Newborn Screening For Your Baby s Health Department of Health Why is my baby tested? To help make sure your baby will be as healthy as possible. The blood test provides important information about your
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
 Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Clinical Laboratory Fee Schedule Annual Laboratory Public Meeting June 25, 2018 Anthony Sireci, MD, Msc Association for Molecular Pathology Outline Germline Procedures
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Clinical Laboratory Fee Schedule Annual Laboratory Public Meeting June 25, 2018 Anthony Sireci, MD, Msc Association for Molecular Pathology Outline Germline Procedures
QHerit Expanded Carrier Screen
 QHerit Expanded Carrier Screen Test Code: 94372 (X) Specimen Requirements: Preferred: 6 ml (4 ml minimum) room-temperature whole blood: 1.5 ml (1 ml minimum) in each of 4 lavender-top (EDTA) or yellow-top
QHerit Expanded Carrier Screen Test Code: 94372 (X) Specimen Requirements: Preferred: 6 ml (4 ml minimum) room-temperature whole blood: 1.5 ml (1 ml minimum) in each of 4 lavender-top (EDTA) or yellow-top
Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder. Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: preliminary results.
 Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: y preliminary results. Globotriaosylceramide, GL3 Brain -galactosidase A Eyes Lactosylceramide
Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: y preliminary results. Globotriaosylceramide, GL3 Brain -galactosidase A Eyes Lactosylceramide
Supplementary Table A: All Non-Mild Disease Statistics.
 Supplementary Table A: All Non-Mild Disease Statistics. Disease (OMIM Number) Total Patients Screened Carrier Frequency Wilson 95% CI n % a n % 1 in 26 Lower % Upper % TOTAL 23453 100.0% 5633 24.0% 4.2
Supplementary Table A: All Non-Mild Disease Statistics. Disease (OMIM Number) Total Patients Screened Carrier Frequency Wilson 95% CI n % a n % 1 in 26 Lower % Upper % TOTAL 23453 100.0% 5633 24.0% 4.2
Virological failure to Protease inhibitors in Monotherapy is linked to the presence of signature mutations in Gag without changes in HIV-1 replication
 Virological failure to Protease inhibitors in Monotherapy is linked to the presence of signature mutations in Gag without changes in HIV-1 replication Oscar Blanch-Lombarte Rome, 7-9 June, 2017 European
Virological failure to Protease inhibitors in Monotherapy is linked to the presence of signature mutations in Gag without changes in HIV-1 replication Oscar Blanch-Lombarte Rome, 7-9 June, 2017 European
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Phenotype Prediction Analyses In order to assess the phylogenetic properties of nssnvs, sequence conservation analysis was conducted using
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Phenotype Prediction Analyses In order to assess the phylogenetic properties of nssnvs, sequence conservation analysis was conducted using
HCV NS3 Protease Drug Resistance
 test code: cpt code: 10000 87902 category: Infectious Disease HCV genotype 1a CODON Glecaprevir 1a Grazoprevir 1a Paritaprevir 1a Simeprevir 1a Voxilaprevir 1a V36A S 13 R 10 Comment V36C V36G V36I V36L
test code: cpt code: 10000 87902 category: Infectious Disease HCV genotype 1a CODON Glecaprevir 1a Grazoprevir 1a Paritaprevir 1a Simeprevir 1a Voxilaprevir 1a V36A S 13 R 10 Comment V36C V36G V36I V36L
Genetic Diseases. SCPA202: Basic Pathology
 Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Lab Prior Authorization
 Lab Prior Authorization On July 22, 2015, BlueCross BlueShield of South Carolina announced that it will partner with Avalon Healthcare Solutions (Avalon) to administer a comprehensive suite of laboratory
Lab Prior Authorization On July 22, 2015, BlueCross BlueShield of South Carolina announced that it will partner with Avalon Healthcare Solutions (Avalon) to administer a comprehensive suite of laboratory
Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee
 Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee Hereditary Haemochromatosis A disorder of iron metabolism Inherited disorder Iron Essential micro-nutrient Toxicity when
Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee Hereditary Haemochromatosis A disorder of iron metabolism Inherited disorder Iron Essential micro-nutrient Toxicity when
Metabolic Liver Diseases
 Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Carrier Screening for Genetic Diseases
 Medical Policy Manual Genetic Testing, Policy No. 81 Carrier Screening for Genetic Diseases Next Review: September 2018 Last Review: December 2017 Effective: January 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical
Medical Policy Manual Genetic Testing, Policy No. 81 Carrier Screening for Genetic Diseases Next Review: September 2018 Last Review: December 2017 Effective: January 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Prime Therapeutics
Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Prime Therapeutics
Cystic fibrosis carrier screening in a North American population
 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Original Research Article Cystic fibrosis carrier screening in a North American population Val V. Zvereff, MD,PhD 1, Hawazin Faruki, DrPh 1, Marcia Edwards,
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Original Research Article Cystic fibrosis carrier screening in a North American population Val V. Zvereff, MD,PhD 1, Hawazin Faruki, DrPh 1, Marcia Edwards,
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hemochromatosis
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hemochromatosis File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hemochromatosis 5/2012 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hemochromatosis File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hemochromatosis 5/2012 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018
A Quick Guide to the. I507del. Mutation CFTR SCIENCE
 A Quick Guide to the I507del Mutation CFTR SCIENCE 2016 Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated VXR-HQ-02-00045a(1) 03/2016 Loss of CFTR activity is the underlying cause of cystic fibrosis (CF) 1 Spectrum
A Quick Guide to the I507del Mutation CFTR SCIENCE 2016 Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated VXR-HQ-02-00045a(1) 03/2016 Loss of CFTR activity is the underlying cause of cystic fibrosis (CF) 1 Spectrum
LABHORIZONS. New Procedures A NEWSLETTER FOR CLIENTS
 LABHORIZONS A NEWSLETTER FOR CLIENTS Volume XVII, No. 7 July 2017 New Procedures 5 HIAA, Plasma.................................. 504510 CPT 83497 Synonyms 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid Use Plasma 5-hydroxy-indoleacetic
LABHORIZONS A NEWSLETTER FOR CLIENTS Volume XVII, No. 7 July 2017 New Procedures 5 HIAA, Plasma.................................. 504510 CPT 83497 Synonyms 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid Use Plasma 5-hydroxy-indoleacetic
CMS will not implement the new tier codes for Medicare/Medicaid claims for calendar year 2012.
 January 1, 2012 Re: 2012 AMA CPT Code Changes Dear Valued Client: The American Medical Association (AMA) has made Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code changes to the 2012 edition of the CPT coding
January 1, 2012 Re: 2012 AMA CPT Code Changes Dear Valued Client: The American Medical Association (AMA) has made Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code changes to the 2012 edition of the CPT coding
TECHNICAL NOTICE. The CPT coding in this notice is effective January 1, 2013 and replaces the coding currently in use for these assays
 TECHNICAL NOTICE The CPT coding in this notice is effective January 1, 2013 and replaces the coding currently in use for these assays December 2012 The notation (MAAA) indicates "Multianalyte Assay with
TECHNICAL NOTICE The CPT coding in this notice is effective January 1, 2013 and replaces the coding currently in use for these assays December 2012 The notation (MAAA) indicates "Multianalyte Assay with
Sperm Donor Profile. Asian American Indian African American/Black. Caucasian/White East Indian Latino/Hispanic
 Sperm Donor Profile This packet is for informational purposes. All the questions have been answered by the donor and are unaltered with exception to the staff impressions, genetic screening results, and
Sperm Donor Profile This packet is for informational purposes. All the questions have been answered by the donor and are unaltered with exception to the staff impressions, genetic screening results, and
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
PA Update: Oral Cystic Fibrosis Modulators
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
TOO MUCH OF A GOOD THING: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT OF HEREDITARY HEMOCHROMATOSIS MARY JO DREW, MD, MHSA TRANSFUSION MEDICINE CONSULTANT
 TOO MUCH OF A GOOD THING: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT OF HEREDITARY HEMOCHROMATOSIS MARY JO DREW, MD, MHSA TRANSFUSION MEDICINE CONSULTANT DISCLOSURE STATEMENT I have no conflicts of interest to disclose CASE
TOO MUCH OF A GOOD THING: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT OF HEREDITARY HEMOCHROMATOSIS MARY JO DREW, MD, MHSA TRANSFUSION MEDICINE CONSULTANT DISCLOSURE STATEMENT I have no conflicts of interest to disclose CASE
Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hemochromatosis
 Medical Policy Manual Genetic Testing, Policy No. 48 Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hemochromatosis Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: December 2017 Effective: February 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Genetic Testing, Policy No. 48 Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hemochromatosis Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: December 2017 Effective: February 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy. Description/Scope. Position Statement
 Subject: Document #: Current Effective Date: 03/29/2017 Status: Reviewed Last Review Date: 02/02/2017 Description/Scope This document addresses preconceptional or prenatal genetic testing on a parent or
Subject: Document #: Current Effective Date: 03/29/2017 Status: Reviewed Last Review Date: 02/02/2017 Description/Scope This document addresses preconceptional or prenatal genetic testing on a parent or
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders
 Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
CPTR title slide. A Standardized System for Grading Mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis for Association with Drug Resistance
 CPTR title slide A Standardized System for Grading Mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis for Association with Drug Resistance PAOLO MIOTTO CPTR 2017 Workshop, March 20 23 The Need A lack of user-friendly
CPTR title slide A Standardized System for Grading Mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis for Association with Drug Resistance PAOLO MIOTTO CPTR 2017 Workshop, March 20 23 The Need A lack of user-friendly
Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.76 Genetic Counseling Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Created Local Policy/ 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 2.04.76 Genetic Counseling Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Created Local Policy/ 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
