PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
|
|
|
- Nigel Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PULIC HEALTH PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS Yaowalark Sukthana 1, Phuangphet Waree 1, Emsri Pongponratn 2, Urai Chaisri 2 and Mario Riganti 2 1 Department of Protozoology, 2 Department of Tropical Pathology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, angkok, Thailand Abstract. We studied the pathology of acute toxoplasmosis in experimental mice inoculated with RH strain tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii. All died from severe disseminated toxoplasmosis involving the liver, spleen and pancreas. Pathological features of acute toxoplasmosis in susceptible mice could be regarded as an excellent model for acute reactivation of Toxoplasma in the immunosuppressed host. INTRODUCTION Correspondence: Dr Yaowalark Sukthana, Department of Protozoology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, 420/ 6 Rajvithi Road, angkok 10400, Thailand. Tel: 66 (0) ext 1830; Fax: 66 (0) tmymv@mahidol.ac.th Toxoplasma gondii, an intracellular protozoan, was first discovered by Nicholle and Manceaux in 1908 from the liver of the African rodent, Ctenodactylus gondii. About 50% of the world s population is infected by that obligate intracellular parasite that multiplies in all nucleated cells of the vertebrate host (Cesbron- DeDelauw and Capron, 1994). It is a crescentshaped organism, size 2-3 µm in width and 4-8 µm in length, with one end slightly broader than another. There are three infectious stages of this parasite in humans that are relevant to the understanding and diagnosis of the disease. Firstly, the trophozoite includes a tachyzoite, the rapidly proliferative intracellular form and a bradyzoite, the low-diving form inside the tissue cyst. Secondly, the pseudocyst in the host cell contains tachyzoites. Lastly, the cyst, the chronic stage of the parasite, is filled with bradyzoites in a well-defined cyst wall. T. gondii, as well as other members of the Apicomplexans are intracellular parasites. Invasion of the host cell is a major step in its biology and pathogenesis. All three stages possess characteristic apical organelles; rhoptries, micronemes and dense granules that are involved in parasite attachment, penetration and parasitophorus vacuole maturation (Carruthers and Sibley, 1997; Conseil et al, 1999). Populations at risk of toxoplasmosis are immunocompromized persons, pregnant women and their fetuses in whom the clinical manifestations such as encephalitis, brain abscess, hydrocephalus, hepatosplenomegaly and retinitis are apparent. Conversely, in the immunocompetent host, clinical signs and symptoms are mostly mild, non-specific and acute toxoplasmosis thus usually passes unnoticed and is followed by a chronic quiescent stage. Presently, available evidence suggests that the host tissue pathology associated with T. gondii infection may play an important role in latent infection and the reactivation process (Herion and Saavedra, 1993). However, the pathological features of acute toxoplasmosis in humans are rarely documented since it is not often feasible. We, therefore, studied acute toxoplasmosis in experimental mice infected with RH strain tachyzoites. The findings from light and electron microscopic studies could be applied to humans for further understanding of the pathogenesis of Toxoplasma in the immunocompromized host. MATERIALS AND METHODS Toxoplasma gondii strain Tachyzoites of the RH strain of Toxo- 16 Vol 34 No. 1 March 2003
2 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS plasma gondii, maintained in inoculated mice passage, were used in this experiment. Animals Outbreed and disease-free, 3-4 week old mice of both sexes were used. They were supplied by the National Laboratory Animal Center, Mahidol University, Thailand. Diets and bedding materials were maintained free from pathogenic microorganisms by skilled tecical staff. Infection and autopsy Mice were intraperitoneally inoculated with 5x10 5 RH strain tachyzoites of T. gondii. At days 3-, 4-, 6- and 9-post infection (PI), peritoneal fluids were aspirated for electron microscopic study. Autopsies were performed for light microscopic examination on the 4 th, 6 th and 9 th days after infection. Light and electron microscopy The liver, spleen, pancreas and brain of each studied mouse were fixed in 10% formalin, dehydrated and embedded in wax for light histo-pathologic examination. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Giemsa staining were used. Tachyzoites in the peritoneal fluid of all acutely infected mice were processed for electron microscopic study as previously described (Ferguson et al, 1999). In brief, they were fixed in 4% gluteraldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, post-fixed in osmium tetroxide and treated with uranyl acetate prior to dehydration and embedded in Spurr s epoxy resin, before sectioning and staining for electron microscopy. RESULTS All studied mice were acutely ill with toxoplasmosis. They were less active and preferred to stay at the corners of their cages. Their entire body hair stood on end and they seldom took food or water. Light microscopy Different degrees of congestion were seen in all organ studies: the brain, liver, spleen and pancreas. In the brain, mild to moderate congestion of the meningeal and interstitial brain parenchyma were observed, but neither T. gondii tachyzoites nor pseudocysts were seen. In the liver, marked congestion was found in the central, portal and sinusoidal vessels. Generalized necrosis of the liver cells was present, including the portal areas, which were filled with numerous, intracellular and extracellular Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites (Fig 1A-). Numerous tachyzoites were located along the thickened liver capsule (Fig 1C). Pseudocysts with rosette formation were seen in the liver (Fig 1D). In the spleen, marked congestion and increased megakaryocytes were also found. Eosinophilic and histiocytic infiltrations containing intracellular and extracellular Toxoplasma organisms were seen in the spleen (Fig 2A- ). Trophozoites were found at the thickened capsule, and proteinaceous fluid mixed with fibrinous material was found adjacent to hepatic and splenic capsules (Fig 2C). As in the liver, pseudocysts were also present. In a piece of pancreas, fatty tissue septa and peripancreatic fatty tissue as well as cytoplasm of histiocytes were also filled with tachyzoites (Fig 3A-). Electron microscopy Numerous T. gondii tachyzoites were seen in the peritoneal fluid of the studied mice. They were crescent-shaped, with one end broader than the other. Organelles belonging to Apicomplexans such as conoid, rhoptries, dense body, micronemes as well as the nucleus were present (Fig 4A). There were numerous macrophages containing several tachyzoites. The parasites were in parasitophorus vacuoles and some appeared divided (Fig 4). Eosinophils with intracellular Toxoplasma organisms were also found (Fig 4C). DISCUSSION Most animals can be classified as either Vol 34 No. 1 March
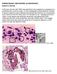
3 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PULIC HEALTH A C D Fig 1 Light microscopic features of acute toxoplasmosis in the liver of the studied mice. A, section stained with Giemsa showed generalized necrosis of the liver cells (arrows) x 400, the portal areas were filled with Toxoplasma tachyzoites (), both intracellular (arrowhead) and extracellular (arrows) x 1,000. C, thickened liver capsule stained with hematoxylin and eosin showed numerous tachyzoites along the capsule x 400. D, pseudocysts with rosette formation were observed in the liver. Note host cell nucleus (arrowhead) x 1,000. A X 100 X 400 C Fig 2 A-C Section of the spleen showed marked congestion and increase of megakaryocytes (A) (arrow) x100 and x 400. Note eosinophilic (arrows) and histiocytic (arrowhead) infiltration containing intracellular tachyzoites () x 1,000. C, proteinaceous fluid mixed with fibrinous material containing numerous Toxoplasma tachyzoites (arrows) x 1, Vol 34 No. 1 March 2003
4 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS resistant or susceptible to T. gondii with respect to clinical disease. In general, man, cattle, horses and rats belong to the resistant species, which may produce mild or non-specific clinical symptoms, whilst mice, guinea pigs and hamsters are susceptible hosts (Darcy and Zenner, 1993). The stage of the infected parasite (tachyzoite, bradyzoite and sporozoite), the route of inoculation (oral, intraperitoneal and subcutaneous) and the susceptibility of the host, influence the virulence of toxoplasmosis (Kaufman et al, 1959; Ferguson et al, 1981; Suzuki et al, 1989). With regard to the pathogenesis and virulence of toxoplasmosis, the presently available literature has only considered natural infection by the oral route acquired by oocyst and tissue cyst (De Rover-onnet, 1966; Reikvam and Lorentzen-Styr, 1976; Ferguson et al, 1981; Suzuki et al, 1989). Different strains of T. gondii have been observed to have very different outcomes on infection in intermediate hosts, with some strains being virulent and cause fatal, acute toxoplasmosis, while others causing chronic infection by forming cysts in the brain and muscle tissue of the infected animal (Miller et al, 1999). In the present study, we used the RH strain of T. gondii, which is well known to be the most virulent (Remington et al, 1958; Dubey and eattie, 1988). Moreover, the infected trophozoites derived from repeated passages in the mouse and had become more virulent. Thus the pathology found in the experimental mice was widespread into many organs. There are 3 stages of T. gondii in intermediate hosts, including humans that are relevant to the understanding and diagnosis of the disease; the trophozoite, pseudocyst and tissue cyst, all of which are intracellular. Oocysts contaminate an environment by cat excreta and are transmitted to the host via ingestion. The tachyzoite, which is one of the trophozoite stages, is the most aggressive when infecting the host. The bradyzoite is less aggressive, the organism dividing slowly within a tissue cyst (Dubey and Frenkel, 1973). The mice in the present study were infected with tachyzoites. The clinical manifestations were therefore present within a short time after infection and all died from severe disseminated toxoplasmosis. However, we could not demonstrate tachyzoites or pseudocysts in the brain. This may be due to the artificial route of infection, the intraperitoneal inoculation, which caused severe necrosis of the liver, spleen and pancreas. Many organs were severely damaged before toxoplasmic encephalitis developed. Only mild to moderate congestion was observed in the brain parenchyma and meninges. Among the susceptible hosts; mice, guinea pigs and hamsters, the mouse is the most susceptible (Darcy and Zenner, 1993). According to Dubey and eattie (1988) 100,000 oocyst of all strains of T. gondii were lethal to mice by the oral route. We used the most virulent strain given to the most susceptible host by the artificial infection route. The pathological features seen in our study were therefore widespread, involving many organs within a short period of time. A very severe disseminated toxoplasmosis caused death in all experimental mice, whether they were treated with pyrimethamine or not. In resistant hosts, including man, there are usually no major effects of infection with chronic cyst formation unless the immune system is weakened, at which time those cysts may be reactivated, resulting in acute toxoplasmosis and the death of the host. This is a common situation in human suffering from AIDS. Acute toxoplasmosis in susceptible mice in the present study was severe and life-threatening. In our opinion, this could be regarded as a model for acute reactivation of toxoplasmosis in the immunosuppressed host. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was financially supported by the Royal Golden Jubilee Fund. The authors would like to thank Assist Prof enjanee Punpoowong for her help in light microscopic work and Mr Saiyood Incheng for taking care of the experimental mice. Vol 34 No. 1 March
5 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PULIC HEALTH X 100 A X 400 Fig 3 A- A piece of the pancreas, many Toxoplasma tachyzoites (arrows) were seen at the fatty tissue septa and tissues surrounding it (A) x 100 and x 400., note intracellular Toxoplasma organism in the histiocyte x1,000. Conoid T Dense body T Nucleus PV Rhoptry 2 µm Microneme A 2 µm C T 2 µm Fig 4 A-C Electron micrograph of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite from peritoneal fluid of studied mice (A). Note the conoid, dense bodies, nucleus, rhoptry and micronemes, which are important for invading the cell, x 12,000 ar = 2 µm., macrophage with several intracellular Toxoplasma tachyzoites (T) and parasitophorus vacuole (PV) containing multiplication of tachyzoite. x 3,500 ar = 2 µm. Eosinophils with intracellular organisms were seen (C), x 9,000. Note host cell nucleus () and eosinophilic granule (arrows). ar = 2 µm. 20 Vol 34 No. 1 March 2003
6 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS REFERENCES Carruthers V, Sibley LD. Related sequential protein secretion from three distinct organelles of Toxoplasma gondii accompanies invasion of human fibroblast. Eur J Cell iol 1997; 73: Cesbron-Delauw MF, Capron A. Excreted/secreted antigens of Toxoplasma gondii their origin and role in the host-parasite interaction. Res Immunol 1993; 144: Conseil V, Soete M, Dubremetz JF. Serine protease inhibitor block invasion of host cells by Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1999; 43: Darcy F, Zenner L. Experimental models of toxoplasmosis. Res Immunol 1993; 144: De Roever-onnet H. Virulence of Toxoplasma. Trop Geogr Med 1966; 18: Dubey JP, eattie CP. Toxoplasmosis of animal and man. oca Raton, FL: CRC Press 1988: Dubey JP, Frenkel JK. Experimental Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice with strains producing oocysts. J Parasitol 1973; 59: Ferguson DJP, Cesbron-Delauw MF, Dubremertz JF, Sibley LD, Joiner KA, Wright SE. The expression and distribution of dense granule proteins in the enteric (coccidian) forms of Toxoplasma gondii in the small intestine of the cat. Exp Parasitol 1999; 91: Ferguson DJP, Hutchison WM. Comparison of the development of avirulent and virulent strain of Toxoplasma gondii in the peritoneal exudate of mice. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 1981; 75: Herion P, Saavedra R. The immunobiology of toxoplasmosis. Res Immunol 1993; 144: Kaufman HE, Melton ML, Remington JS, Jacobs I. Strain differences of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol 1959; 45: Miller CMD, Smith NC, Joson AM. Cytokines, nitric oxide, heat shock proteins and virulence. Parasitol Today 1999; 15: Reikvam A, Lorentzen-Styr AM. Virulence of different strains of Toxoplasma gondii and host response in mice. Nature 1976; 261: Remington JS, Jacobs L, Kaufman HE. Studies on chronic toxoplasmosis. Am J Ophthalmol 1958; 46: Suzuki Y, Conley FK, Remington JS. Difference in virulence and development of encephalitis during chronic infection vary with strain of Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis 1989; 159: Vol 34 No. 1 March
Coccidia. Eucoccidioside
 Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Short Video. shows/monsters-inside- me/videos/toxoplasma-parasite/
 The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016
 TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Toxoplasma gondii. Definitive Host adult forms sexual reproduction. Intermediate Host immature forms asexual reproduction
 Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
Extra-intestinal coccidians
 Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
PREDICTIVE VALUE OF LATEX AGGLUTINATION TEST IN SEROLOGICAL SCREENING FOR TOXOPLASMA GONDII
 PREDICTIVE VALUE OF LATEX AGGLUTINATION TEST IN SEROLOGICAL SCREENING FOR TOXOPLASMA GONDII Yaowalark Sukthana, Thaiyooth Chintana, Waraporn Supatanapong, Chutatip Siripan, Amorn Lekkla and Rachatawan
PREDICTIVE VALUE OF LATEX AGGLUTINATION TEST IN SEROLOGICAL SCREENING FOR TOXOPLASMA GONDII Yaowalark Sukthana, Thaiyooth Chintana, Waraporn Supatanapong, Chutatip Siripan, Amorn Lekkla and Rachatawan
All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction
 Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Toxoplasmosis. Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy
 Toxoplasmosis Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy Human Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease Caused by Coccidian
Toxoplasmosis Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy Human Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease Caused by Coccidian
Toxoplasmosis Objective :
 Toxoplasmosis Objective : Describe the Life cycle Mention the Infective stages Define Congenital Toxoplasmosis List the Lab.Diagnosis Illustrate the Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Show the relationship between
Toxoplasmosis Objective : Describe the Life cycle Mention the Infective stages Define Congenital Toxoplasmosis List the Lab.Diagnosis Illustrate the Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Show the relationship between
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Toxoplasma gondii. Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK
 Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
CASE REPORT PLASMODIUM MALARIAE-INFECTED ERYTHROCYTES IN THE PERIPHERAL BLOOD, LIVER, STOMACH AND DUODENUM: AN ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY
 CASE REPORT PLASMODIUM MALARIAE-INFECTED ERYTHROCYTES IN THE PERIPHERAL BLOOD, LIVER, STOMACH AND DUODENUM: AN ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY Emsri Pongponratn 1, Oranan Prommano 1,3, Urai Chaisri 1, Parnpen Viriyavejakul
CASE REPORT PLASMODIUM MALARIAE-INFECTED ERYTHROCYTES IN THE PERIPHERAL BLOOD, LIVER, STOMACH AND DUODENUM: AN ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY Emsri Pongponratn 1, Oranan Prommano 1,3, Urai Chaisri 1, Parnpen Viriyavejakul
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals. Taniawati Supali. Department of Parasitology
 Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Giardia lamblia (flagellates)
 Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
Toxoplasma gondii: , homage to Nicolle, Manceaux and Splendore
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(2): 133-148, March 2009 133 Toxoplasma gondii: 1908-2008, homage to Nicolle, Manceaux and Splendore David J P Ferguson Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(2): 133-148, March 2009 133 Toxoplasma gondii: 1908-2008, homage to Nicolle, Manceaux and Splendore David J P Ferguson Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory
Toxoplasmosis in Atlantic Bottle-Nosed Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus)
 Toxoplasmosis in Atlantic Bottle-Nosed Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Authors: W. Inskeep, C. H. Gardiner, R. K. Harris, J. P. Dubey, and R. T. Goldston Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 26(3) : 377-382
Toxoplasmosis in Atlantic Bottle-Nosed Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Authors: W. Inskeep, C. H. Gardiner, R. K. Harris, J. P. Dubey, and R. T. Goldston Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 26(3) : 377-382
Influence of calcium ion on host cell invasion and intracellular replication by Toxoplasma gondii
 The Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 42, No. 4. 185-193, December 2004 Influence of calcium ion on host cell invasion and intracellular replication by Toxoplasma gondii Hyun-Ouk SONG 1), Myoung-Hee
The Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 42, No. 4. 185-193, December 2004 Influence of calcium ion on host cell invasion and intracellular replication by Toxoplasma gondii Hyun-Ouk SONG 1), Myoung-Hee
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Apicomplexan structure: 1-polar ring, 2-conoid, 3- micronemes, 4-rhoptries, 5-nucleus, 6-nucleolus, 7- mitochondria, 8-posterior ring, 9-alveoli,
 Coccidia Protozoans, phylum Apicomplexa, class Sporozoasida, subclass Coccidiasina. Cryptosporidium parvum Isosporabelli Cyclosporacayetanensis Sarcocystisspp 1 Apicomplexan structure: 1-polar ring, 2-conoid,
Coccidia Protozoans, phylum Apicomplexa, class Sporozoasida, subclass Coccidiasina. Cryptosporidium parvum Isosporabelli Cyclosporacayetanensis Sarcocystisspp 1 Apicomplexan structure: 1-polar ring, 2-conoid,
Protozoa from tissues. Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp.
 Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Brachyspira & Lawsonia
 General Brachyspira & Lawsonia Gram-negative Anaerobic but with aerotolerance Colonize the large intestine of mammals and birds Infections with Brachyspira species are important in pigs Species & Disease
General Brachyspira & Lawsonia Gram-negative Anaerobic but with aerotolerance Colonize the large intestine of mammals and birds Infections with Brachyspira species are important in pigs Species & Disease
Cryptosporidiosis. By: Nikole Stewart
 Cryptosporidiosis By: Nikole Stewart Cryptosporidiosis ("Crypto"); Etiological agent- Cryptosporidium (1) Transmission: Transmission occurs via the fecal-oral route when individuals ingest water or food
Cryptosporidiosis By: Nikole Stewart Cryptosporidiosis ("Crypto"); Etiological agent- Cryptosporidium (1) Transmission: Transmission occurs via the fecal-oral route when individuals ingest water or food
SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS
 SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS Pages with reference to book, From 183 To 186 Mughisuddin Ahmed ( Department of Pathology, Dow Medical College and Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah
SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS Pages with reference to book, From 183 To 186 Mughisuddin Ahmed ( Department of Pathology, Dow Medical College and Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah
Toxoplasmosis. Yoshifumi Nishikawa. Toxoplasma gondii
 Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasma gondii Yoshifumi Nishikawa National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases, Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine FAO-APHCA/OIE Regional Workshop on Prevention
Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasma gondii Yoshifumi Nishikawa National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases, Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine FAO-APHCA/OIE Regional Workshop on Prevention
Ocular Toxoplasmosis Uveitis course Antalya Miles Stanford Medical Eye Unit St Thomas Hospital London
 Ocular Toxoplasmosis Uveitis course Antalya 2013 Miles Stanford Medical Eye Unit St Thomas Hospital London Toxoplasma gondii Obligate, intracellular, apicomplexan protozoan Infects > 1/3 world population
Ocular Toxoplasmosis Uveitis course Antalya 2013 Miles Stanford Medical Eye Unit St Thomas Hospital London Toxoplasma gondii Obligate, intracellular, apicomplexan protozoan Infects > 1/3 world population
R. B. MARSHALL Department of Veterinary Pathology and Public Health, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand
 THE ROUTE OF ENTRY OF LEPTOSPIRES INTO THE KIDNEY TUBULE R. B. MARSHALL Department of Veterinary Pathology and Public Health, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand PLATES X and XI IT has been
THE ROUTE OF ENTRY OF LEPTOSPIRES INTO THE KIDNEY TUBULE R. B. MARSHALL Department of Veterinary Pathology and Public Health, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand PLATES X and XI IT has been
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE
 TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
Acquired Retinochoroiditis in Hamsters Inoculated With ME 49 Strain Toxoplasma
 .,... «? '-Nt v -^. S=! *:!-,;:» 4 ^ Acquired Retinochoroiditis in Hamsters Inoculated With ME 49 Strain Toxoplasma CarlosE. N. Pavesio,*^ Mary Louise Chiappino* Paula Gormley,^ Paulette Y. Setzer,* and
.,... «? '-Nt v -^. S=! *:!-,;:» 4 ^ Acquired Retinochoroiditis in Hamsters Inoculated With ME 49 Strain Toxoplasma CarlosE. N. Pavesio,*^ Mary Louise Chiappino* Paula Gormley,^ Paulette Y. Setzer,* and
An elevated blood glucose level and increased incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant women with latent toxoplasmosis
 doi: http://folia.paru.cas.cz Research Article An elevated blood glucose level and increased incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant women with latent toxoplasmosis, and Czech Republic Toxoplasma
doi: http://folia.paru.cas.cz Research Article An elevated blood glucose level and increased incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant women with latent toxoplasmosis, and Czech Republic Toxoplasma
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran
 Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran Gholamreza Hatam 1*, Azra Shamseddin 2, Farhoud Nikouee 3 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, School of Medicine, Shiraz
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran Gholamreza Hatam 1*, Azra Shamseddin 2, Farhoud Nikouee 3 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, School of Medicine, Shiraz
SLIDE SEMINAR NON NEOPLASTIC LYMPH NODE DISORDERS DR SHEILA NAIR CMC, VELLORE
 SLIDE SEMINAR NON NEOPLASTIC LYMPH NODE DISORDERS DR SHEILA NAIR CMC, VELLORE Case 1 34 year old male, mass right cervical region, for 4 years. No other significant findings. Grossly, the mass was well
SLIDE SEMINAR NON NEOPLASTIC LYMPH NODE DISORDERS DR SHEILA NAIR CMC, VELLORE Case 1 34 year old male, mass right cervical region, for 4 years. No other significant findings. Grossly, the mass was well
BLOK 17 Dr.dr. Mahardika AW, DTM&H,MKes Dept.of Parasitology Fac.of Medicine GMU Yogyakarta
 BLOK 17 Dr.dr. Mahardika AW, DTM&H,MKes Dept.of Parasitology Fac.of Medicine GMU Yogyakarta 8/7/2012 dr.dika-prst 1 TOXOPLASMOSIS 8/7/2012 dr.dika-prst 2 Introduction Morphology & Life Cycle Transmission
BLOK 17 Dr.dr. Mahardika AW, DTM&H,MKes Dept.of Parasitology Fac.of Medicine GMU Yogyakarta 8/7/2012 dr.dika-prst 1 TOXOPLASMOSIS 8/7/2012 dr.dika-prst 2 Introduction Morphology & Life Cycle Transmission
Learning Objectives. 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic Morphology 5. Name of diesease 6. Prevention and Control
 Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
BRAIN TO BRAIN TRANSMISSION OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND VIRUS IN YOUNG GUINEA PIGS
 BRAIN TO BRAIN TRANSMISSION OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND VIRUS IN YOUNG GUINEA PIGS BY N. PAUL HUDSON, M.D., AI O FLOYD S. MARKHAM (From the Department of Hygiene and Bacteriology, The University of Chicago,
BRAIN TO BRAIN TRANSMISSION OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND VIRUS IN YOUNG GUINEA PIGS BY N. PAUL HUDSON, M.D., AI O FLOYD S. MARKHAM (From the Department of Hygiene and Bacteriology, The University of Chicago,
Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance
 Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance I. Symbiosis relationship in which 2 organisms spend a portion or all of their lifecycles associated with one another A. Commensalism
Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance I. Symbiosis relationship in which 2 organisms spend a portion or all of their lifecycles associated with one another A. Commensalism
José G. Montoya, John C. Boothroyd, and Joseph A. Kovacs SHORT VIEW SUMMARY
 280 Toxoplasma gondii José G. Montoya, John C. Boothroyd, and Joseph A. Kovacs Definition Toxoplasma gondii is a ubiquitous coccidian protozoan that usually causes asymptomatic infection in humans but
280 Toxoplasma gondii José G. Montoya, John C. Boothroyd, and Joseph A. Kovacs Definition Toxoplasma gondii is a ubiquitous coccidian protozoan that usually causes asymptomatic infection in humans but
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE
 ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
Chapter Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs
 Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Toxoplasma gondii Parasites Take Control within Host Cells
 Toxoplasma gondii Parasites Take Control within Host Cells This parasite puppet master lives mostly without causing disease for its hosts, establishing lifelong asymptomatic infections Eric Y. Denkers
Toxoplasma gondii Parasites Take Control within Host Cells This parasite puppet master lives mostly without causing disease for its hosts, establishing lifelong asymptomatic infections Eric Y. Denkers
HIV and Parasite Load. Keith Keller
 HIV and Parasite Load Keith Keller HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Retrovirus that infects CD4+ T Cells Uses host cell s mechanics to reproduce, by means of reverse transcriptase and integrase which
HIV and Parasite Load Keith Keller HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Retrovirus that infects CD4+ T Cells Uses host cell s mechanics to reproduce, by means of reverse transcriptase and integrase which
Experimental Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Genetically Susceptible and Resistant Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2005, p. 5160 5165 Vol. 73, No. 8 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.8.5160 5165.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Experimental
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2005, p. 5160 5165 Vol. 73, No. 8 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.8.5160 5165.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Experimental
Effect of hydroxyurea on the intracellular multiplication of. gondii, Leishmania amazonensis and Trypanosoma
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 65-69 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 65 Effect of hydroxyurea on the intracellular multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii, Leishmania amazonensis
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 65-69 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 65 Effect of hydroxyurea on the intracellular multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii, Leishmania amazonensis
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Graefe's Archive. Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Report of the 1 st NRL proficiency testing on Detection of anti-toxoplasma IgG in ovine serum samples. March - April, 2015
 Report of the 1 st NRL proficiency testing on Detection of anti-toxoplasma IgG in ovine serum samples March - April, 2015 page 1 of 12 Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope 3 3 Time frame 3 4 Test
Report of the 1 st NRL proficiency testing on Detection of anti-toxoplasma IgG in ovine serum samples March - April, 2015 page 1 of 12 Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope 3 3 Time frame 3 4 Test
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS
 BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
1. Toxoplasma gondii:
 Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff
 Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff Aize Kijlstra Rome 2009 Toxoplasmosis is a neglected disease entity Disease burden is similar to salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis
Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff Aize Kijlstra Rome 2009 Toxoplasmosis is a neglected disease entity Disease burden is similar to salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis
S Pinlaor 1, K Ieamviteevanich 2, P Pinlaor 3, W Maleewong 1 and V Pipitgool 1
 SEROPREVALENCE OF SPECIFIC TOTAL IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Ig), IgG AND IgM ANTIBODIES TO TOXOPLASMA GONDII IN BLOOD DONORS FROM LOEI PROVINCE, NORTHEAST THAILAND S Pinlaor 1, K Ieamviteevanich 2, P Pinlaor 3, W
SEROPREVALENCE OF SPECIFIC TOTAL IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Ig), IgG AND IgM ANTIBODIES TO TOXOPLASMA GONDII IN BLOOD DONORS FROM LOEI PROVINCE, NORTHEAST THAILAND S Pinlaor 1, K Ieamviteevanich 2, P Pinlaor 3, W
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients. Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP
 Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals.
 Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals. For the purposes of this presentation, "zoonotic disease" will be defined as a disease that is caused
Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals. For the purposes of this presentation, "zoonotic disease" will be defined as a disease that is caused
Research Article A Purification Method for Enrichment of the Toxoplasma gondii Cyst Wall
 Ashdin Publishing Journal of Neuroparasitology Vol. 1 (2010), Article ID N101001, 6 pages doi:10.4303/jnp/n101001 Research Article A Purification Method for Enrichment of the Toxoplasma gondii Cyst Wall
Ashdin Publishing Journal of Neuroparasitology Vol. 1 (2010), Article ID N101001, 6 pages doi:10.4303/jnp/n101001 Research Article A Purification Method for Enrichment of the Toxoplasma gondii Cyst Wall
Interaction and cystogenesis of Toxoplasma gondii within skeletal muscle cells in vitro
 170 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(2): 170-174, March 2009 Interaction and cystogenesis of Toxoplasma gondii within skeletal muscle cells in vitro Erick Vaz Guimarães 1, Laís de Carvalho
170 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(2): 170-174, March 2009 Interaction and cystogenesis of Toxoplasma gondii within skeletal muscle cells in vitro Erick Vaz Guimarães 1, Laís de Carvalho
IN SEARCH OF TROJAN HORSES: CHARACTERIZING EARLY CELL TARGETS OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII. A Dissertation. Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School
 IN SEARCH OF TROJAN HORSES: CHARACTERIZING EARLY CELL TARGETS OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Cornell University In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
IN SEARCH OF TROJAN HORSES: CHARACTERIZING EARLY CELL TARGETS OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Cornell University In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR
 ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases
 محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR
 IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR Zulhainan Hamzah 1, Songsak Petmitr 2, Mathirut Mungthin 3 and Porntip Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr 1 1 Department
IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR Zulhainan Hamzah 1, Songsak Petmitr 2, Mathirut Mungthin 3 and Porntip Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr 1 1 Department
Bioresearch Communications Volume 05, Issue 01, January 2019 Journal Homepage:
 Bioresearch Communications Volume 05, Issue 01, January 2019 Journal Homepage: www.bioresearchcommunications.com Review Article Parasitic Disease of Human Taibur Rahman* and Tanzina Tarannum 1 Department
Bioresearch Communications Volume 05, Issue 01, January 2019 Journal Homepage: www.bioresearchcommunications.com Review Article Parasitic Disease of Human Taibur Rahman* and Tanzina Tarannum 1 Department
Cross-regulation of host STATs for the survival of Toxoplasma gondii
 JITMM2010&IMC2010, 1-3 December 2010 Cross-regulation of host STATs for the survival of Toxoplasma gondii Ho-Woo Nam 1, Dong-Soo Kim 2, Sung-Jong Hong 3 Department of arasitology, College of Medicine,
JITMM2010&IMC2010, 1-3 December 2010 Cross-regulation of host STATs for the survival of Toxoplasma gondii Ho-Woo Nam 1, Dong-Soo Kim 2, Sung-Jong Hong 3 Department of arasitology, College of Medicine,
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Spontaneous stage differentiation of mouse-virulent Toxoplasma gondii RH parasites in skeletal muscle cells: an ultrastructural evaluation
 196 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(2): 196-200, March 2009 Spontaneous stage differentiation of mouse-virulent Toxoplasma gondii RH parasites in skeletal muscle cells: an ultrastructural
196 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(2): 196-200, March 2009 Spontaneous stage differentiation of mouse-virulent Toxoplasma gondii RH parasites in skeletal muscle cells: an ultrastructural
STUDIES ON THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN SOUTH AFRICA
 STUDIES ON THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN SOUTH AFRICA Kesenthri Kistiah Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in fulfilment of
STUDIES ON THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN SOUTH AFRICA Kesenthri Kistiah Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in fulfilment of
ABSENCE OF KNOBS ON PARASITIZED RED BLOOD CELLS IN A SPLENECTOMIZED PATIENT IN FATAL FALCIPARUM MALARIA
 ABSENCE OF KNOBS ON PARASITIZED RED BLOOD CELLS IN A SPLENECTOMIZED PATIENT IN FATAL FALCIPARUM Emsri Pongponratn 1, ParnpenViriyavejakul 1, Polrat Wilairatana 2, David Ferguson 3, Urai Chaisri 1, Gareth
ABSENCE OF KNOBS ON PARASITIZED RED BLOOD CELLS IN A SPLENECTOMIZED PATIENT IN FATAL FALCIPARUM Emsri Pongponratn 1, ParnpenViriyavejakul 1, Polrat Wilairatana 2, David Ferguson 3, Urai Chaisri 1, Gareth
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL
 EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
A QUANTITATIVE ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY OF THE LIVER AND THE SPLEEN IN FATAL FALCIPARUM MALARIA
 ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE LIVER AND THE SPLEEN IN FATAL MALARIA A QUANTITATIVE ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY OF THE LIVER AND THE SPLEEN IN FATAL FALCIPARUM MALARIA Oranan Prommano 1, Urai Chaisri 1, Gareth DH Turner
ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE LIVER AND THE SPLEEN IN FATAL MALARIA A QUANTITATIVE ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY OF THE LIVER AND THE SPLEEN IN FATAL FALCIPARUM MALARIA Oranan Prommano 1, Urai Chaisri 1, Gareth DH Turner
Mitral valve repair for functional regurgitation caused by Chagas disease
 Mitral valve repair for functional regurgitation caused by Chagas disease Stevan K Martins, Alberto T Kiyose, Frederico C Mendonça, Veridiana S Andrade, Jairo Pinheiro Jr, Jeffer Moraes, Adib D Jatene
Mitral valve repair for functional regurgitation caused by Chagas disease Stevan K Martins, Alberto T Kiyose, Frederico C Mendonça, Veridiana S Andrade, Jairo Pinheiro Jr, Jeffer Moraes, Adib D Jatene
AIDS at 25. Epidemiology and Clinical Management MID 37
 AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
Host Parasite Relationship. Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU
 Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
 3rd International Conference on Clinical Microbiology & Microbial Genomics September 24-26, 2014 Valencia, Spain Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
3rd International Conference on Clinical Microbiology & Microbial Genomics September 24-26, 2014 Valencia, Spain Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011
 1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Regulation and Function of T-Cell-Mediated Immunity during Toxoplasma gondii Infection
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 1998, p. 569 588 Vol. 11, No. 4 0893-8512/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Regulation and Function of T-Cell-Mediated
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 1998, p. 569 588 Vol. 11, No. 4 0893-8512/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Regulation and Function of T-Cell-Mediated
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about pathogens is true? Question #01 (A) Both viruses and bacteria need to infect
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about pathogens is true? Question #01 (A) Both viruses and bacteria need to infect
Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one
 Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale. Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum
 The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 1 Distribution Of Plasmodium vivax 2 Global Risk By Country-Proportionality
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 1 Distribution Of Plasmodium vivax 2 Global Risk By Country-Proportionality
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Distribution of the Pores of Epithelial Basement Membrane in the Rat Small Intestine
 FULL PAPER Anatomy Distribution of the Pores of Epithelial Basement Membrane in the Rat Small Intestine Takashi TAKEUCHI 1) and Tatsuo GONDA 1) 1) Institute of Experimental Animals, Shimane Medical University,
FULL PAPER Anatomy Distribution of the Pores of Epithelial Basement Membrane in the Rat Small Intestine Takashi TAKEUCHI 1) and Tatsuo GONDA 1) 1) Institute of Experimental Animals, Shimane Medical University,
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Schistosome life cycle.
 Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
International Conference on Parasitology August 24-26, 2015 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
 International Conference on Parasitology August 24-26, 2015 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA SYMPOSIA THE CHALLENGE OF PARASITES AND IMMUNOSUPRESSION: FROM DIAGNOSIS TO TREATMENT from the bench to the bed
International Conference on Parasitology August 24-26, 2015 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA SYMPOSIA THE CHALLENGE OF PARASITES AND IMMUNOSUPRESSION: FROM DIAGNOSIS TO TREATMENT from the bench to the bed
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND
 Research Article CODEN: IJPRNK B. V. Ramana, IJPRBS, 2013; Volume 2(4): 253-258 ISSN: 2277-8713 IJPRBS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMAC CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE SEROPREVALENCE OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS
Research Article CODEN: IJPRNK B. V. Ramana, IJPRBS, 2013; Volume 2(4): 253-258 ISSN: 2277-8713 IJPRBS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMAC CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE SEROPREVALENCE OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
