X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets across the lifespan
|
|
|
- Penelope Harris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets across the lifespan AACE Midwest Regional Meeting Erik A. Imel, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Indiana Center for Musculoskeletal Health July 28, 2018
2 Disclosures Research funding, consultation Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Inc. Ultragenyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Travel and meeting support Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Off-label use of medications Calcitriol Phosphate Cinacalcet
3 Goals Describe the clinical features and pathophysiology of hypophosphatemic rickets Discuss the clinical diagnosis of hypophosphatemic rickets Discuss medical management of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets
4 PTH FGF23 Intracellular space Phosphate Reabsorption Serum Phosphate Urinary Phosphate 1,25OHD Dietary intake
5 Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is a peptide hormone PTH FGF23 N FGF23 RXXR^ C Phosphate Reabsorption Pi FGF receptors/ Klotho Urinary Phosphate 1,25(OH)2D Intestinal phosphate absorption
6 Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is a peptide hormone PTH FGF23 Phosphate Reabsorption Pi Urinary Phosphate 1,25(OH)2D Intestinal phosphate absorption
7 Urine phosphate excretion mg/min Tubular maximum reabsorption of phosphate TmP/GFR r Serum phosphorus mg/dl Walton and Bijvoet. Lancet 1975; ii: , TP/GFR = Serum Pi (Urine Pi x Serum Cr/Urine Cr) Brodehl et al. Pediatr Nephrol 1988;2:
8 Know age-related normal ranges Phosphorus Alkaline phosphatase 600 Males, MAYO Alkaline phosphatas, U/L Age, years The TmP/GFR age normal range is numerically similar to the age normal range for phosphorus
9 Chronic Hypophosphatemia Intake deficiency: normal or high TmP/GFR Dietary phosphate depletion Phosphate binders, malabsorption Premature neonates (need more phosphate than term neonates) Renal phosphate wasting: low TmP/GFR
10 Renal hypophosphatemia Non-FGF23 mediated Hyperparathyroidism Fanconi syndrome: Genetic causes Drugs Toxins Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria NPT2c Diuretics FGF23 mediated XLH-PHEX-most common ADHR-FGF23 ARHR DMP1 ENPP1 FAM20C Fibrous dysplasia/ McCune- Albright Tumor induced osteomalacia
11 4 year old girl
12 Laboratory tests Values Normal SI Normal Phosphorus 2.1 mg/dl ( ) 0.68 mmol/l ( ) Calcium 9.4 mg/dl ( ) 2.35 mmol/l ( ) Creatinine 0.2 mg/dl (<0.7 ) Alkaline phosphatase 653 U/L ( ) 25-OHD 30 ng/ml (25-50) 74.9 nmol/l ( ) 1,25(OH) 2 D 41 pg/ml (15-75) pmol/l (39-195)
13 Laboratory tests Values Normal SI Normal Phosphorus 2.1 mg/dl ( ) 0.68 mmol/l ( ) Calcium 9.4 mg/dl ( ) 2.35 mmol/l ( ) Creatinine 0.2 mg/dl (<0.7 ) 17.7 mmol/l (<61.9) Urine glucose: 0 Alkaline phosphatase 653 U/L ( ) 10.9 μkat/l ( ) Urine amino acids not elevated 25-OHD 30 ng/ml (25-50) 74.9 nmol/l ( ) 1,25(OH) 2 D 41 pg/ml (15-75) pmol/l (39-195) TmP/GFR 1.8 mg/dl ( ) 0.7 mmol/l ( ) Urine Calcium/Creatinine 0.05 mg/mg (<0.42) 0.14 mmol/mmol (<1.18) PTH 37 pg/ml (10-65) 3.9 pmol/l ( ) FGF23 (intact) 173 pg/ml (<70) No generalized tubulopathy
14 XLH Most common genetic hypophosphatemia 1:20,000 Inactivating mutations in PHEX X-linked dominant Frequently sporadic Disease state Hyp Consortium Nat Genet 1995;11:130-6 Econs et al. Skeletal Radiology 1991;20:109-14
15 PHEX deficiency increases FGF23 Increases bone (osteocyte) FGF23 expression Elevates plasma intact FGF23 Intact FGF23 pg/ml Liu et al JBC 2003 & Imel et al JCEM N RXXR XLH Normal * P<0.05 C
16 At the renal tubular epithelium Excessive intact FGF23 mediates Renal tubular phosphate reabsorption Serum Pi Activation of 1,25(OH) 2 D Renal Tubular Cell Imel et al. ICE/ENDO 2014, Chicago, Illinois, Oral session OR
17 FGF23 induced hypophosphatemia impairs mineralization of bone Osteomalacia/excess unmineralized osteoid Rickets Bowing deformities Bone pain Insufficiency fractures or pseudofractures Aono et al. JBMR 2009:24;1879
18 X-linked Hypophosphatemia Features Osteomalacia Rickets Leg deformities Short stature ±Bone pain Insufficiency fractures Poor fracture healing Dental abscesses Enthesopathy/osteophytes Osteoarthritis Several features are related to the hypophosphatemia. Others are not direct effects of low phosphate. Carpenter, Imel et al JBMR 2011; ;26(7): , Peterson et al JBMR 1992;7(6):583, Reid et al Medicine 1989;68(6);336
19 XLH is not merely a pediatric disease! Adults with XLH Imel files
20 The pediatric consequences of short stature and leg deformities persist in adulthood Children Adults Sitting height Arm length Stature Leg length Zivicnjak et al Ped Nephr 2011 Beck-Nielsen et al Calcified Tissue Int 2010;87(2):108
21 Joint pains (knees, ankles) 82% Joint complications Enthesopathy was present in 30-84% or more Up to 100% with increasing with age More males affected with enthesopathy Osteoarthritis, especially in lower extremities: 61% of pts 40 yrs Linglart et al. Endocrine Connections 2014.doi: /EC ; Beck-Nielsen et al Calcified Tissue Int 2010;87(2):108; Liang et al Calcif Tissue Int 2009;85(3):235, Polisson et al NEJM 1985, Hardy et al Radiology 1989, Reid et al Medicine 1989;68(6)336; Connor et al. JCEM 2015:100(10);3625
22 Insufficiency fractures Up to half of adults have pseudofractures Sometimes asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic May fracture through Reid et al Medicine 1989;68(6);336 Imel files
23 Dental issues are common Tooth Abscess occur in up to 86%. Reid et al Medicine 1989;68(6)336 Impaired dentin mineralization Periodontal disease common In 34 adults with XLH, >75% with periodontitis on exam >25 % with severe periodontitis Less common and less severe in those on treatment as adults Biosse Duplan et al. J. Dent Res 2017;96(4):388; Boukpessi et al. Bone 2017; 95:151 XLH Control Linglart et al. Endocrine Connections 2014.doi: /EC
24 Muscle weakness Assessments influenced by leg deformities and decreased activity But, patients with XLH have Lower muscle density Lower peak muscle force and power Impaired walking and mobility JCEM 2012;97(8)E1492; JCEM 2013;98(5):E990; Ruppe et al. ASBMR 2016; and others
25 Craniosynostosis and Chiari 1 malformations Cranial bone abnormalities common Frontal bossing Dolicocephaly Flattened cranial base Decreased depth of posterior fossa Chiari Type 1 malformation- up to 44% Craniosynostosis, especially of sagittal suture May require surgery Vega et al. J Nurosurg Pediatr 2016;17(6);694 Caldemeyer et al Radiology 1995;195(3):733 Gjorup et al Am J Med Genet 2011;155a(11):2654
26 Treatment
27 Goals of conventional therapy for XLH Children ü Improve osteomalacia/rickets ü Straighten legs ü Improve growth ü Improve alkaline phosphatase ü Avoid complications The goal is not specifically to normalize the serum phosphorus. Adults ü Improve osteomalacia ü Improve bone pain ü Improve alkaline phosphatase ü Decrease or heal pseudofractures ü Improve healing after orthopedic surgery ü Decrease tooth abcesses? ü Avoid complications Carpenter, Imel et al JBMR 2011, Glorieux et al NEJM 1980, Harrell et al JCI 1985, many other citations
28 Conventional medical treatment for XLH Phosphate salts: mg/kg/day Never treat XLH with phosphate alone! Calcitriol [1,25(OH) 2 D]: ng/kg/day Requires multiple daily doses Start about 1/3 or 1/2 dose and titrate to target dose over several weeks based in part on tolerability Relatively frequent laboratory monitoring for safety Pi, Ca, PTH, ALP, Urine Calcium/creatinine Carpenter, Imel, Holm et al JBMR 2011, Glorieux et al NEJM 1980, Harrell et al JCI 1985, many other citations
29 Efficacy monitoring- Calcitriol/Pi Children Alkaline phosphatase Radiographic improvement Rickets Bowing deformities Height Bone pain Dental abscesses Adults Alkaline phosphatase Bone pain Fracture or pseudofracture healing Mobility Quality of Life measures Dental abscesses
30 Safety monitoring during Calcitriol/Pi Serum Phosphorus in normal or high range: Decrease phosphate and/or calcitriol Serum Calcium or Urine Calcium elevated: Decrease calcitriol PTH rising: Decrease the phosphate and/or increase calcitriol Creatinine elevated: Decrease or stop phosphate and calcitriol Renal ultrasound screen for nephrocalcinosis Decrease doses Carpenter, Imel, Holm et al JBMR 2011
31 What is the effect of calcitriol and phosphate treatment on FGF23? A. Increase? B. No change? C. Decrease? Percent of baseline Intact FGF23 500% 400% 300% 200% 100% 0% Treated Untreated Imel et al JCEM 2010
32 Limitations of current treatment of XLH Started treatment age 4 years Started treatment age 24 months At 8 yr old Height 10 th %ile At 8 yr old Height -3SD
33 Limitations of current treatment of XLH Sitting height Sitting Height Arm length Stature Leg length Zivicnjak et al Ped Nephr 2011
34 Benefit of early treatment: Starting before vs after 1 year old Gray: Group 1, n=8 (3F) Start treatment at median age of 0.35 yr (range yr). White: Group 2, n=11(9f) Start treatment at median age of 2.1 yr (range yr) Makitie et al JCEM 2003; 88(8):3591
35 There is no clear consensus on when to treat adults with calcitriol and phosphate Most patients stop treatment at adulthood Some untreated adults have few or no symptoms Many others have mild to severe symptoms and restart treatment for: Bone pain Osteomalacia Insufficiency fractures Planned orthopedic surgeries
36 What are the risks of Calcitriol/Pi?
37 Risks of calcitriol and phosphate Gastrointestinal side effects Dyspepsia, laxative effect of phosphate Hyperparathyroidism* Hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia Nephrocalcinosis-in up to 50 to 80% Chronic kidney disease* Grade 3 Other ectopic calcification reported *Exact incidence uncertain Peterson et al. JBMR 1992, Reid et al. Medicine 1989, Rivkees et al. JCEM 1992, Goodyer et al. J Pediatr 1987, Reusz et al. Arch Dis Child 1990, Verge et al. NEJM 1991, Taylor et al. Pediatr Nephrol 1995
38 Hyperparathyroidism Nearly half of XLH children have elevated PTH BEFORE starting treatment. Carpenter et al JCEM 1994;78(6):1378 Hyperparathyroidism also complicates treatment with phosphate. Many cases in the literature, but exact incidence not certain Longer treatment and higher phosphate dose may increase risk of tertiary (hypercalcemic) hyperparathyroidism. Makitie et al Clin Endocrinol 2003;58(2):163, Rivkees et al JCEM 1992;75(6):1514, several other series.
39 Tertiary hyperparathyroidism Multi-gland hyperplasia + autonomy Hypercalcemia Nephrolithiasis Hypertension Parathyroidectomy Removing only one gland often does not cure Three and a half gland resection Risk of recurrence Risk of post-surgical HYPOparathyroidism Which further complicates management Calcimimetic case reports Yavropoulou et al Hormones 2010
40 Common mistakes: Trying to normalize phosphorus Too much phosphate Too little calcitriol PTH I don t understand.i keep increasing the phosphate dose, but the PTH won t come down. What PTH concentration should we target? Ideally normal
41 Chronic kidney disease Nephrocalcinosis can lead to chronic kidney disease BUT, the exact incidence of CKD in XLH is not certain. End stage renal disease - rare Kidney transplantation rare Hypertension
42 Calcitriol and phosphate do not help some features Joint dysfunction/stiffness Osteoarthritis Osteophytes Enthesopathy Connor et al. JCEM 2015:100(10);3625; Karaplis et al 2012 Endocrinology 153(12): 5906
43 Conventional therapy may decrease tooth abscesses Those who were under treatment longer as adults had less severe dental disease Connor et al. JCEM 2015:100(10);3625; Biosse Duplan et al. J. Dent Res 2017;96(4):388; Boukpessi et al. Bone 2017; 95:151
44 Surgeries in XLH patients Childhood Leg straightening procedures Craniosynostosis Dental procedures Adulthood Rodding for insufficiency fractures Joint replacements (osteoarthritis) Laminectomies (spinal stenosis) Root canal Dental extractions Parathyroidectomy
45 New treatment option
46 Y Y Burosumab (KRN23) A recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to FGF23 and inhibits FGF23 biologic activity Renal Tubular Cell Y KRN23 FGF23 Imel et al. ICE/ENDO 2014, Chicago, Illinois, Oral session OR
47 FGF23 neutralizing antibody treatment of Hyp (XLH) mouse Increases serum phosphorus Increases 1,25(OH) 2 D Improves osteomalacia, and bone growth control control FGF23Ab(4mg/kg) FGF23Ab(16/mg/kg) Aono et al. JBMR 2009:24;1879
48 Burosumab (KRN23) Phase I/II trial in Adults with XLH, dosed every 4 weeks. N =28 N =22 Burosumab increases: Serum Pi TmP/GFR 1,25(OH) 2 D Imel et al. JCEM, 2015;100:
49 Burosumab Phase 2 study children age 5-12 with XLH 52 children randomized to Q2W or Q4W burosumab for 64 weeks Doses started low and titrated based on serum phosphorus Primary outcome: change from baseline in Rickets Severity Score Carpenter TO et al. N Engl J Med 2018;378:
50 Burosumab in children age 5-12 with XLH Burosumab improved Serum phosphorus TmP/GFR 1,25(OH)2D Rickets (measured by two different scales) Height Z-score modestly Walking distance in those with impairment at baseline PRO functional outcomes Carpenter TO et al. N Engl J Med 2018;378:
51 Phase 3 RCT: Burosumab vs placebo in adults with XLH RCT 24 weeks of burosumab 1 mg/kg vs placebo, dose could be decreased for Pi above target 134 adults with XLH Centers in North America, Europe, Japan, South Korea Primary outcome: % achieving mean serum Pi above the lower limit of normal at midpoint of dose cycle Secondary outcomes: Pharmacodynamic parameters, safety, healing of fractures/pseudofractures Insogna et al JBMR 2018
52 Burosumab vs placebo in adults with XLH Baseline Characteristics n Total 134 Mean age, years 40 ± 12.2 Female 64.9% Race, White 80.6% Confirmed PHEX mutation or VUS 95% Enthesopathy on radiographs 99.3% Active Fractures/Pseudofractures Nephrocalcinosis 54.5% Pain medications 67.9% (opioids 22.4%) Insogna et al JBMR % in burosumab, 57.6% in placebo
53 Burosumab vs placebo in adults with XLH Mid-cycle Pi TMP/GFR Trough Pi 1,25(OH)2D 5 had dose reductions due to Pi >4.5 mg/dl Maintained on lower dose. Insogna et al JBMR 2018
54 Burosumab vs placebo in adults with XLH Baseline fracture/pseudofracture Burosumab 32 (47.1%) had 65 fractures Placebo 38 (57.6%) had 91 fractures At week 24, greater healing in burosumab group The odds ratio of full healing at week for burosumab, p<0.001 Insogna et al JBMR 2018
55 Children Burosumab 64W AEs Adults Burosumab 24W Adults Placebo 24W Total subjects Injection site 57% 11.8% 12.1% reactions Restless leg syndrome % 7.6%
56 Nephrocalcinosis and Echo Children Burosumab 64W Adults Burosumab 24W Adults Placebo 24W Total subjects in study Increase nephrocalcinosis score 1 point 6 (11%) 11 (16.2%) 12 (18.2%) Decrease nephrocalcinosis score 1 point 2 (3.8%) 4 (5.9%) 4 (6.1%) Increase Echo Calcium score 1 point 1 (1.5%) 7 (10.6%) Decrease Echo calcium score 1 point 3 (4.4%) 1 (1.5%) No changes >1 point
57 FDA approved burosumab April 2018! The only FDA approved drug for XLH Starting dose Children 0.8 mg/kg SC every 2 weeks Adults 1 mg/kg SC every 4 weeks Can decrease dose if Pi above target range Ongoing studies: Phase 3 RCT in children active comparator Burosumab every 2 weeks vs conventional therapy Long-term 10 year disease monitoring study
58 Important clinical issues When to use burosumab vs conventional therapy? Transition pediatric dosing to adult dosing? What is the long term effect on: Attained adult height Leg deformity in growing children Surgical needs or outcomes Nephrocalcinosis risk Enthesopathy
59 Summary XLH is not just a childhood disease XLH has lifelong consequences in adults Impairing mobility and quality of life Conventional medical therapy for XLH (calcitriol and phosphate) Addresses (replaces) the consequences of FGF23 excess Has risks of significant side effects requiring careful monitoring Burosumab blocks effects of excess FGF23 Improves Pi and rickets Improves healing of pseudofractures/fractures Improves functional outcomes
60 Post-Test Questions Which is an effect of FGF23 in mineral metabolism? A. Increase renal phosphorus reabsorption B. Increase intestinal phosphorus reabsorption C. Decrease activation of 1,25(OH) 2 D D. Increase serum calcium E. Decrease catabolism of 1,25(OH) 2 D
61 Post-Test Questions Which characteristics of XLH are only seen in children? A. Short stature B. Rachitic changes at the growth plate C. Enthesopaty D. Dental abscesses E. Bone pain F. Pseudofractures G. Leg deformities
62 Post-Test Questions You are seeing this child with rickets, hypophosphatemia, high Tmp/GFR. Parents and siblings are unaffected. What is the likely etiology of low Pi? A. XLH B. ADHR C. ARHR D. Dietary phosphate depletion E. Tumor induced osteomalacia Hypophosphatemia
63 Post-Test Questions You are seeing this child with rickets, hypophosphatemia, low Tmp/GFR. The father also has hypophosphatemia. What is the most likely etiology of low Pi? A. XLH B. ADHR C. ARHR D. Dietary phosphate depletion E. Tumor induced osteomalacia Hypophosphatemia
64 Post-Test Questions Which is an appropriate treatment for XLH? A. Phosphate salts alone B. Cholecalciferol alone C. Calcium with cholecalciferol D. Calcitriol with phosphate salts E. Calcitriol with calcium F. Burosumab with calcitriol
65 Post-Test Questions In clinical trials, burosumab had which of the following effects in patients with XLH? A. Improve enthesopathy B. Improve healing of pseudofractures C. No effect on serum phosphorus D. Decrease 1,25(OH) 2 D E. Improve nephrocalcinosis F. Worsen rickets
66
X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets across the lifespan
 X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets across the lifespan AACE Midwest Regional Meeting Erik A. Imel, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Indiana Center for Musculoskeletal Health July 28,
X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets across the lifespan AACE Midwest Regional Meeting Erik A. Imel, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Indiana Center for Musculoskeletal Health July 28,
DIAGNOSING X-LINKED HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA (XLH) BIOCHEMICAL TESTING CONSIDERATIONS
 DIAGNOSING X-LINKED HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA (XLH) BIOCHEMICAL TESTING CONSIDERATIONS XLH IS CHARACTERIZED BY CHRONIC HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA XLH is a hereditary, progressive, lifelong disorder. In children and adults,
DIAGNOSING X-LINKED HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA (XLH) BIOCHEMICAL TESTING CONSIDERATIONS XLH IS CHARACTERIZED BY CHRONIC HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA XLH is a hereditary, progressive, lifelong disorder. In children and adults,
Hypophosphatemic rickets: new treatments
 Hypophosphatemic rickets: new treatments Gema Ariceta Pediatric Nephrology, University Hospital Vall d Hebron, Barcelona 1 11.06.18 Tubulopathies Disclosures Lectures and educational activities sponsored
Hypophosphatemic rickets: new treatments Gema Ariceta Pediatric Nephrology, University Hospital Vall d Hebron, Barcelona 1 11.06.18 Tubulopathies Disclosures Lectures and educational activities sponsored
Thomas Carpenter Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, Connecticut, USA
 A Randomized, Open-label Phase 2 Study of, a Fully Human Anti-FGF23 Monoclonal Antibody, in 52 Children with X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH): 40-Week Results Thomas Carpenter Yale University School of
A Randomized, Open-label Phase 2 Study of, a Fully Human Anti-FGF23 Monoclonal Antibody, in 52 Children with X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH): 40-Week Results Thomas Carpenter Yale University School of
The First Multi-Dose Trial of a Human Anti-FGF23 (Fibroblast Growth Factor 23) Antibody (KRN23) in Adults with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH)
 The First Multi-Dose Trial of a Human Anti-FGF23 (Fibroblast Growth Factor 23) Antibody (KRN23) in Adults with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Erik A. Imel, 1 Xiaoping Zhang, Mary D. Ruppe, 3 Thomas J.
The First Multi-Dose Trial of a Human Anti-FGF23 (Fibroblast Growth Factor 23) Antibody (KRN23) in Adults with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Erik A. Imel, 1 Xiaoping Zhang, Mary D. Ruppe, 3 Thomas J.
X-Linked Hypophosphatemia in Adults New Biology, New Therapies
 X-Linked Hypophosphatemia in Adults New Biology, New Therapies September 16, 2016 Karl L. Insogna, MD Ensign Professor of Medicine/Endocrinology Yale School of Medicine CONFLICT OF INTEREST Karl Insogna
X-Linked Hypophosphatemia in Adults New Biology, New Therapies September 16, 2016 Karl L. Insogna, MD Ensign Professor of Medicine/Endocrinology Yale School of Medicine CONFLICT OF INTEREST Karl Insogna
Conventional therapy n=32. RGI-C Score (Primary Endpoint) LS Mean* (0.83, 1.45) P< Substantial healing, % patients (RGI-C +2.
 Ultragenyx and Kyowa Kirin Announce Topline Phase 3 Study Results Demonstrating Superiority of Crysvita (burosumab) Treatment to Oral Phosphate and Active Vitamin D in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia
Ultragenyx and Kyowa Kirin Announce Topline Phase 3 Study Results Demonstrating Superiority of Crysvita (burosumab) Treatment to Oral Phosphate and Active Vitamin D in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia
Emerging Concepts in Pediatric Bone Disease
 Volume 10 Supplement 2, June 2013 Emerging Concepts in Pediatric Bone Disease Guest Editor: Francis H. Glorieux, MD, OC, PhD Y.S. Medical Media Ltd. 3 Forword Francis H. Glorieux...346 Nutritional Rickets:
Volume 10 Supplement 2, June 2013 Emerging Concepts in Pediatric Bone Disease Guest Editor: Francis H. Glorieux, MD, OC, PhD Y.S. Medical Media Ltd. 3 Forword Francis H. Glorieux...346 Nutritional Rickets:
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics
 Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Results Confirm and Extend 40-Week Findings that Treatment with Crysvita is Superior to Conventional Therapy
 Ultragenyx and Kyowa Kirin Announce Positive 64-Week Results for Crysvita (burosumab) from Phase 3 Study in Children with X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Results Confirm and Extend 40-Week Findings that
Ultragenyx and Kyowa Kirin Announce Positive 64-Week Results for Crysvita (burosumab) from Phase 3 Study in Children with X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Results Confirm and Extend 40-Week Findings that
About X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH)
 Ultragenyx and Kyowa Kirin Announce Publication of Phase 2 Study Results Demonstrating that Crysvita (burosumab) Improved Outcomes in Children with X-linked Hypophosphatemia in the New England Journal
Ultragenyx and Kyowa Kirin Announce Publication of Phase 2 Study Results Demonstrating that Crysvita (burosumab) Improved Outcomes in Children with X-linked Hypophosphatemia in the New England Journal
X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Case Study: A Dynamic Development Model for Rare Disease
 X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Case Study: A Dynamic Development Model for Rare Disease Alison Skrinar, PhD Executive Director, Clinical Outcomes Research and Evaluation (CORE) www.ultragenyx.com Dynamic
X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Case Study: A Dynamic Development Model for Rare Disease Alison Skrinar, PhD Executive Director, Clinical Outcomes Research and Evaluation (CORE) www.ultragenyx.com Dynamic
CLINICAL TRIAL. 1 Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA. 2 Centre d Evaluation des Maladies Osseuses, H^opital Cochin, Paris, France
 CLINICAL TRIAL JBMR A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial Evaluating the Efficacy of Burosumab, an Anti-FGF23 Antibody, in Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Week 24 Primary
CLINICAL TRIAL JBMR A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial Evaluating the Efficacy of Burosumab, an Anti-FGF23 Antibody, in Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Week 24 Primary
Discover CRYSVITA and Redefine XLH TREATMENT
 Discover CRYSVITA and Redefine XLH TREATMENT CRYSVITA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 1 year of age and older with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). 10 mg/ml, 20 mg/ml, 30 mg/ml
Discover CRYSVITA and Redefine XLH TREATMENT CRYSVITA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 1 year of age and older with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). 10 mg/ml, 20 mg/ml, 30 mg/ml
Conventional Therapy in Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Effects on Enthesopathy and Dental Disease
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional Therapy in Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Effects on Enthesopathy and Dental Disease Jessica Connor,* Elizabeth A. Olear,* Karl L. Insogna, Lee Katz, Suher Baker,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional Therapy in Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Effects on Enthesopathy and Dental Disease Jessica Connor,* Elizabeth A. Olear,* Karl L. Insogna, Lee Katz, Suher Baker,
Hypophosphatasia. Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX
 Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
burosumab (Crysvita )
 burosumab (Crysvita ) Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ),
burosumab (Crysvita ) Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ),
Do We Do Too Many Parathyroidectomies in Dialysis? Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital
 Do We Do Too Many Parathyroidectomies in Dialysis? Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital E-mail: snigwekar@mgh.harvard.edu March 13, 2017 Disclosures statement: Consultant: Allena, Becker
Do We Do Too Many Parathyroidectomies in Dialysis? Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital E-mail: snigwekar@mgh.harvard.edu March 13, 2017 Disclosures statement: Consultant: Allena, Becker
Persistent post transplant hyperparathyroidism. Shiva Seyrafian IUMS-97/10/18-8/1/2019
 Persistent post transplant hyperparathyroidism Shiva Seyrafian IUMS-97/10/18-8/1/2019 normal weight =18-160 mg In HPT= 500-1000 mg 2 Epidemiology Mild 2 nd hyperparathyroidism (HPT) resolve after renal
Persistent post transplant hyperparathyroidism Shiva Seyrafian IUMS-97/10/18-8/1/2019 normal weight =18-160 mg In HPT= 500-1000 mg 2 Epidemiology Mild 2 nd hyperparathyroidism (HPT) resolve after renal
Hyperparathyroidism: Operative Considerations. Financial Disclosures: None. Hyperparathyroidism. Hyperparathyroidism 11/10/2012
 Hyperparathyroidism: Operative Considerations Financial Disclosures: None Steven J Wang, MD FACS Associate Professor Dept of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Francisco
Hyperparathyroidism: Operative Considerations Financial Disclosures: None Steven J Wang, MD FACS Associate Professor Dept of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Francisco
STRENSIQ (asfotase alfa)
 STRENSIQ (asfotase alfa) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and
STRENSIQ (asfotase alfa) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and
Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia
 Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia Ana-Maria Chindris, MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Florida 2013 MFMER slide-1 Background Hypercalcemia is a problem frequently encountered in clinical
Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia Ana-Maria Chindris, MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Florida 2013 MFMER slide-1 Background Hypercalcemia is a problem frequently encountered in clinical
Magnesium Homeostasis
 ECTS PhD Training Course, Rome 3 rd September 2008 Disorders of Calcium, Phosphate h and Magnesium Homeostasis Richard Eastell Professor of Bone Metabolism Academic Unit of Bone Metabolism University of
ECTS PhD Training Course, Rome 3 rd September 2008 Disorders of Calcium, Phosphate h and Magnesium Homeostasis Richard Eastell Professor of Bone Metabolism Academic Unit of Bone Metabolism University of
CKD: Bone Mineral Metabolism. Peter Birks, Nephrology Fellow
 CKD: Bone Mineral Metabolism Peter Birks, Nephrology Fellow CKD - KDIGO Definition and Classification of CKD CKD: abnormalities of kidney structure/function for > 3 months with health implications 1 marker
CKD: Bone Mineral Metabolism Peter Birks, Nephrology Fellow CKD - KDIGO Definition and Classification of CKD CKD: abnormalities of kidney structure/function for > 3 months with health implications 1 marker
CKD-MBD CKD mineral bone disorder
 CKD Renal bone disease Dr Mike Stone University Hospital Llandough Affects 5 10 % of population Increasingly common Ageing, diabetes, undetected hypertension Associated with: Cardiovascular disease Premature
CKD Renal bone disease Dr Mike Stone University Hospital Llandough Affects 5 10 % of population Increasingly common Ageing, diabetes, undetected hypertension Associated with: Cardiovascular disease Premature
A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH)
 Case Reports A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH) M N Lucas 1, Savithri Dias 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2006; 35:141-3 (Key words: hereditary hypophosphataemic
Case Reports A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH) M N Lucas 1, Savithri Dias 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2006; 35:141-3 (Key words: hereditary hypophosphataemic
Figures and tables in this presentation were adopted from various printed and electronic resorces and serve strictly for educational purposes.
 Academic lectures 3rd year of Medical faculty Figures and tables in this presentation were adopted from various printed and electronic resorces and serve strictly for educational purposes. ENDOCRINOLOGY
Academic lectures 3rd year of Medical faculty Figures and tables in this presentation were adopted from various printed and electronic resorces and serve strictly for educational purposes. ENDOCRINOLOGY
FGF23 (and Klotho): what s new? Brief introduction to FGF23. Introduction to FGF23. FGF23: phosphorylation pathways. FGF23: phosphorylation pathways
 (and Klotho): what s new? Brief introduction to Justine Bacchetta, MD, PhD Reference Center for Rare Renal Diseases Long Beach, CA, 2017 Calcium and phosphate metabolism 1-25 vitamin D Introduction to
(and Klotho): what s new? Brief introduction to Justine Bacchetta, MD, PhD Reference Center for Rare Renal Diseases Long Beach, CA, 2017 Calcium and phosphate metabolism 1-25 vitamin D Introduction to
38 year old Male with Ankylosing Spondylitis. Olesya Krivospitskaya, MD April,
 38 year old Male with Ankylosing Spondylitis Olesya Krivospitskaya, MD April, 11 2013 HPI (Letter from the patient): Diagnosed with Ankylosing Spondylitis and prescribed a Sulfa drug to help with my back
38 year old Male with Ankylosing Spondylitis Olesya Krivospitskaya, MD April, 11 2013 HPI (Letter from the patient): Diagnosed with Ankylosing Spondylitis and prescribed a Sulfa drug to help with my back
Approach to a child presenting with rickets
 Current Practice Approach to a child presenting with rickets Navoda Atapattu 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2013; 42(1): 40-44 (Key words: Rickets; vitamin D; children) Introduction Rickets is a
Current Practice Approach to a child presenting with rickets Navoda Atapattu 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2013; 42(1): 40-44 (Key words: Rickets; vitamin D; children) Introduction Rickets is a
Management of Pediatric Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome
 Management of Pediatric Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome Alison Boyce, MD 3 rd Meeting of the FD/MAS International Consortium Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands Fibrous
Management of Pediatric Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome Alison Boyce, MD 3 rd Meeting of the FD/MAS International Consortium Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands Fibrous
AACE Southern States Chapter Lecture. Basics
 AACE Southern States Chapter Lecture Unusual Bone Cases Basics Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Renal Osteodystrophy Multiple Myeloma 1 Osteoporosis Definition Modeling, Bone Remodeling Bone Resorption > Bone
AACE Southern States Chapter Lecture Unusual Bone Cases Basics Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Renal Osteodystrophy Multiple Myeloma 1 Osteoporosis Definition Modeling, Bone Remodeling Bone Resorption > Bone
Agent(s) FDA Labeled Indications Dosage and Administration. Perinatal/Infantile-onset hypophosphatasia. Juvenile-onset hypophosphatasia
 Strensiq (asfotase alfa) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE Agent(s) FDA Labeled Indications Dosage and Administration Strensiq (asfotase alfa) injection Perinatal/Infantile-onset
Strensiq (asfotase alfa) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE Agent(s) FDA Labeled Indications Dosage and Administration Strensiq (asfotase alfa) injection Perinatal/Infantile-onset
Clinical/Regulatory Updates of Burosumab and The Current Pre-launch Activities in EU
 Clinical/Regulatory Updates of Burosumab and The Current Pre-launch Activities in EU Tomohiro Sudo, EVP Corporate Strategy and Planning Department, Kyowa Kirin, International, plc October 27th, 2017 1
Clinical/Regulatory Updates of Burosumab and The Current Pre-launch Activities in EU Tomohiro Sudo, EVP Corporate Strategy and Planning Department, Kyowa Kirin, International, plc October 27th, 2017 1
Case 4 Generalised bone pain
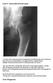 Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Approach to hypophosphataemia
 Approach to hypophosphataemia A/Prof Roderick Clifton-Bligh Kolling Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney Department of Endocrinology Royal North Shore Hospital, St Leonards, NSW Royal North
Approach to hypophosphataemia A/Prof Roderick Clifton-Bligh Kolling Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney Department of Endocrinology Royal North Shore Hospital, St Leonards, NSW Royal North
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health. Noah S. Schenkman, MD
 Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Vitamin D Hormone Du Jour
 Vitamin D Hormone Du Jour J R Minkoff MD, FACP Endocrinology Clinical Professor of Family and Community Medicine UCSF Why Is Vitamin D Important? Musculo-skeletal effects Possible other effects Immunomodulatory
Vitamin D Hormone Du Jour J R Minkoff MD, FACP Endocrinology Clinical Professor of Family and Community Medicine UCSF Why Is Vitamin D Important? Musculo-skeletal effects Possible other effects Immunomodulatory
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM. Hyperparathyroidism Etiology. Common Complex Insidious Chronic Global Only cure is surgery
 ENDOCRINE DISORDER PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Roseann P. Velez, DNP, FNP Francis J. Velez, MD, FACS Common Complex Insidious Chronic Global Only cure is surgery HYPERPARATHYROIDISM PARATHRYOID GLANDS
ENDOCRINE DISORDER PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Roseann P. Velez, DNP, FNP Francis J. Velez, MD, FACS Common Complex Insidious Chronic Global Only cure is surgery HYPERPARATHYROIDISM PARATHRYOID GLANDS
Rickets Simple complement 1. What factor influences on vitamin D absorption at the level of small intestine? A. Normal absorption of lipids B.
 Rickets Simple complement 1. What factor influences on vitamin D absorption at the level of small intestine? A. Normal absorption of lipids B. Increased concentration of proteins in foods C. Decreasing
Rickets Simple complement 1. What factor influences on vitamin D absorption at the level of small intestine? A. Normal absorption of lipids B. Increased concentration of proteins in foods C. Decreasing
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Where are we now?
 Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Where are we now? Dylan M. Barth, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2017 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify risk factors for the development of complications caused
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Where are we now? Dylan M. Barth, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2017 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify risk factors for the development of complications caused
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 2 Available Product Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone)
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 2 Available Product Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone)
"Asymptomatic" Hyperparathyroidism: Reasons for Parathyroidectomy
 "Asymptomatic" Hyperparathyroidism: Reasons for Parathyroidectomy Rebecca S. Sippel, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Section of Endocrine Surgery University of Wisconsin Primary Hyperparathyroidism
"Asymptomatic" Hyperparathyroidism: Reasons for Parathyroidectomy Rebecca S. Sippel, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Section of Endocrine Surgery University of Wisconsin Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics. Abstract. Keywords
 Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Human Monoclonal Anti-FGF23 Antibody (KRN23) in the First Multiple Ascending-Dose Trial Treating Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Human Monoclonal Anti-FGF23 Antibody (KRN23) in the First Multiple Ascending-Dose Trial Treating Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia
Chapter 5: Evaluation and treatment of kidney transplant bone disease Kidney International (2009) 76 (Suppl 113), S100 S110; doi: /ki.2009.
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2009 KDIGO Chapter 5: Evaluation and treatment of kidney transplant bone disease ; doi:10.1038/ki.2009.193 Grade for strength of recommendation a Strength Wording
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2009 KDIGO Chapter 5: Evaluation and treatment of kidney transplant bone disease ; doi:10.1038/ki.2009.193 Grade for strength of recommendation a Strength Wording
Vitamin D and Calcium Therapy: how much is enough
 Vitamin D and Calcium Therapy: how much is enough Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine VA Medical Center and University of California San Francisco DISCLOSURE Nothing to disclose 1 RECOMMENDATIONS
Vitamin D and Calcium Therapy: how much is enough Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine VA Medical Center and University of California San Francisco DISCLOSURE Nothing to disclose 1 RECOMMENDATIONS
The Endocrine Society Guidelines
 Vitamin D and Calcium Therapy: how much is enough DISCLOSURE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine VA Medical Center and University of California San Francisco Nothing to disclose RECOMMENDATIONS
Vitamin D and Calcium Therapy: how much is enough DISCLOSURE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine VA Medical Center and University of California San Francisco Nothing to disclose RECOMMENDATIONS
Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis
 Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis 1 Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis Calcium and phosphate are the major mineral constituents of bone. They are also two of the most important minerals
Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis 1 Agents that Affect Bone & Mineral Homeostasis Calcium and phosphate are the major mineral constituents of bone. They are also two of the most important minerals
Diagnosis and Management of X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH)
 Diagnosis and Management of X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) August 10, 2018 Eric T. Rush, MD, FAAP, FACMG Clinical Geneticist Children s Mercy Hospital Associate Professor of Pediatrics UMKC School of
Diagnosis and Management of X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) August 10, 2018 Eric T. Rush, MD, FAAP, FACMG Clinical Geneticist Children s Mercy Hospital Associate Professor of Pediatrics UMKC School of
Hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia: When to Worry, When to Treat! Mineral Metabolism : A Short Course
 Hypercalcemia: When to Worry, When to Treat! Michael A. Levine has no financial relationships to disclose or Conflicts of Interest to resolve. Michael A. Levine, M.D. This presentation will not involve
Hypercalcemia: When to Worry, When to Treat! Michael A. Levine has no financial relationships to disclose or Conflicts of Interest to resolve. Michael A. Levine, M.D. This presentation will not involve
Summary of late stage clinical trials. As of Jun. 30, 2018
 Summary of late stage clinical trials As of Jun. 30, 2018 The document contains information available on the date indicated in its cover page. The public information of clinicaltrials.gov is continuously
Summary of late stage clinical trials As of Jun. 30, 2018 The document contains information available on the date indicated in its cover page. The public information of clinicaltrials.gov is continuously
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM WITH RICKETS. KRITHIKA.P Dr.L.N.Padmasani Unit 1 Sri Ramachandra Medical College
 PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM WITH RICKETS KRITHIKA.P Dr.L.N.Padmasani Unit 1 Sri Ramachandra Medical College Presenting Complaints v 17 year old developmentally normal adolescent boy, first of a twin pregnancy,
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM WITH RICKETS KRITHIKA.P Dr.L.N.Padmasani Unit 1 Sri Ramachandra Medical College Presenting Complaints v 17 year old developmentally normal adolescent boy, first of a twin pregnancy,
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 Agent Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone) subcutaneous
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 Agent Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone) subcutaneous
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
 PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Inappropriate excess secretion of Parathyroid Hormone in Primary Hyperparathyroidism Appropriate Hypersecretion in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism PTH and
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Inappropriate excess secretion of Parathyroid Hormone in Primary Hyperparathyroidism Appropriate Hypersecretion in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism PTH and
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Strensiq (asfotase alfa) Page 1 of 5 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Strensiq (asfotase alfa) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Strensiq (asfotase alfa) Page 1 of 5 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Strensiq (asfotase alfa) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
OPINION. Endocrine Journal 2015, 62 (8),
 Endocrine Journal 2015, 62 (8), 665-671 OPINION Pathogenesis and diagnostic criteria for rickets and osteomalacia Proposal by an expert panel supported by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan,
Endocrine Journal 2015, 62 (8), 665-671 OPINION Pathogenesis and diagnostic criteria for rickets and osteomalacia Proposal by an expert panel supported by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan,
HYPERCALCEMIA. Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences
 HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
Outline. The Role of Vitamin D in CKD. Essential Role of Vitamin D. Mechanism of Action of Vit D. Mechanism of Action of Vit D 7/16/2010
 Outline The Role of Vitamin D in CKD Priscilla How, Pharm.D., BCPS Assistant Professor National University of Singapore Principal Clinical Pharmacist National University Hospital (Pharmacy and Nephrology,
Outline The Role of Vitamin D in CKD Priscilla How, Pharm.D., BCPS Assistant Professor National University of Singapore Principal Clinical Pharmacist National University Hospital (Pharmacy and Nephrology,
The hart and bone in concert
 The hart and bone in concert Piotr Rozentryt III Department of Cardiology, Silesian Centre for Heart Disease, Silesian Medical University, Zabrze, Poland Disclosure Research grant, speaker`s fee, travel
The hart and bone in concert Piotr Rozentryt III Department of Cardiology, Silesian Centre for Heart Disease, Silesian Medical University, Zabrze, Poland Disclosure Research grant, speaker`s fee, travel
A case of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: complications and the therapeutic use of cinacalcet
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2008) 159 S101 S105 ISSN 0804-4643 A case of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: complications and the therapeutic use of cinacalcet Helge Ræder 1,2, Nick Shaw 3, Coen
European Journal of Endocrinology (2008) 159 S101 S105 ISSN 0804-4643 A case of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: complications and the therapeutic use of cinacalcet Helge Ræder 1,2, Nick Shaw 3, Coen
Hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets: experience from a paediatric nephrology unit
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advance Access publication 22 November 2012 Hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets: experience from a paediatric nephrology unit Joana S. Caetano, Carolina Cordinhã, Clara Gomes, António
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advance Access publication 22 November 2012 Hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets: experience from a paediatric nephrology unit Joana S. Caetano, Carolina Cordinhã, Clara Gomes, António
Calcium metabolism and the Parathyroid Glands. Calcium, osteoclasts and osteoblasts-essential to understand the function of parathyroid glands
 Calcium metabolism and the Parathyroid Glands Calcium, osteoclasts and osteoblasts-essential to understand the function of parathyroid glands Calcium is an essential element for contraction of voluntary/smooth
Calcium metabolism and the Parathyroid Glands Calcium, osteoclasts and osteoblasts-essential to understand the function of parathyroid glands Calcium is an essential element for contraction of voluntary/smooth
Case Report ANovelPHEX Mutation in Japanese Patients with X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets
 Case Reports in Genetics Volume 2015, Article ID 301264, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301264 Case Report ANovelPHEX Mutation in Japanese Patients with X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets Tetsuya
Case Reports in Genetics Volume 2015, Article ID 301264, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301264 Case Report ANovelPHEX Mutation in Japanese Patients with X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets Tetsuya
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology
 Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology 2 (2015) 14e20 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jcte
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology 2 (2015) 14e20 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jcte
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Rickets
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
Protocol GTC : A Randomized, Open Label, Parallel Design Study of Sevelamer Hydrochloride (Renagel ) in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.
 Protocol GTC-68-208: A Randomized, Open Label, Parallel Design Study of Sevelamer Hydrochloride (Renagel ) in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. These results are supplied for informational purposes only.
Protocol GTC-68-208: A Randomized, Open Label, Parallel Design Study of Sevelamer Hydrochloride (Renagel ) in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. These results are supplied for informational purposes only.
The Calcium Conundrum: When, What and How to Give Calcium in Pediatric CKD/ESRD
 The Calcium Conundrum: When, What and How to Give Calcium in Pediatric CKD/ESRD Jess Tower MS RD LD 3/18/19 Children s Mercy Hospital jdtower@cmh.edu 816 460 1067 Disclosures Nothing to disclose 1 How
The Calcium Conundrum: When, What and How to Give Calcium in Pediatric CKD/ESRD Jess Tower MS RD LD 3/18/19 Children s Mercy Hospital jdtower@cmh.edu 816 460 1067 Disclosures Nothing to disclose 1 How
OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE. Nothing to Disclose. Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco
 OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco Nothing to Disclose 1 Case History 59 YO WM referred for evaluation of diffuse
OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco Nothing to Disclose 1 Case History 59 YO WM referred for evaluation of diffuse
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It!
 The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children. Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK
 Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
Hypophosphatemic Rickets with Hypercalciuria
 REFERENCES 1. Hasselbach H. Idiopathic myelo-fibrosis. A clinical study of 80 patients. Am J Hematol 1990, 34: 291-300. 2. McCarthy DM. Fibrosis of the bone marrow: content and cause. Br J Hematol 1985,
REFERENCES 1. Hasselbach H. Idiopathic myelo-fibrosis. A clinical study of 80 patients. Am J Hematol 1990, 34: 291-300. 2. McCarthy DM. Fibrosis of the bone marrow: content and cause. Br J Hematol 1985,
Sensipar (cinacalcet)
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Awaisheh. Mousa Al-Abbadi. Abdullah Alaraj. 1 Page
 f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
Metabolic Bone Disease Related to Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Bone Disease Related to Chronic Kidney Disease Deborah Sellmeyer, MD Director, Johns Hopkins Metabolic Bone Center Dept of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology Disclosure DSMB member for denosumab
Metabolic Bone Disease Related to Chronic Kidney Disease Deborah Sellmeyer, MD Director, Johns Hopkins Metabolic Bone Center Dept of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology Disclosure DSMB member for denosumab
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
FGF23 in CKD and ESRD Regulator of phosphorus balance, or much more than that?
 FGF23 in CKD and ESRD Regulator of phosphorus balance, or much more than that? Csaba P Kovesdy MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, TN USA Learning Objectives Review the pathogenesis
FGF23 in CKD and ESRD Regulator of phosphorus balance, or much more than that? Csaba P Kovesdy MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, TN USA Learning Objectives Review the pathogenesis
2.0 Synopsis. Paricalcitol Capsules M Clinical Study Report R&D/15/0380. (For National Authority Use Only)
 2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Inc. Name of Study Drug: ABT-358/Zemplar (paricalcitol) Capsules Name of Active Ingredient: paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National
2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Inc. Name of Study Drug: ABT-358/Zemplar (paricalcitol) Capsules Name of Active Ingredient: paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National
The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease
 The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease Howard Morris PhD, FAACB, FFSc(RCPA) President, IFCC Professor of Medical Sciences, University of South Australia, Clinical Scientist, SA Pathology
The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease Howard Morris PhD, FAACB, FFSc(RCPA) President, IFCC Professor of Medical Sciences, University of South Australia, Clinical Scientist, SA Pathology
Shon E. Meek, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine
 Shon E. Meek, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine meek.shon@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER 3561772-1 Update on Vitamin D Shon Meek MD, PhD 20 th Annual Endocrine Update January 30-Feb 3, 2017 Disclosure Relevant
Shon E. Meek, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine meek.shon@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER 3561772-1 Update on Vitamin D Shon Meek MD, PhD 20 th Annual Endocrine Update January 30-Feb 3, 2017 Disclosure Relevant
Hyper and hypocalcaemia. Prof Tricia Tan
 Hyper and hypocalcaemia Prof Tricia Tan Learning Objectives Basic physiology of Ca regulation Case presentations Take home messages Calcium Total body calcium content ~1300g 99% in bone 1% intracellular
Hyper and hypocalcaemia Prof Tricia Tan Learning Objectives Basic physiology of Ca regulation Case presentations Take home messages Calcium Total body calcium content ~1300g 99% in bone 1% intracellular
Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
CKD-Mineral Bone Disorder (MBD) Pathogenesis of Metabolic Bone Disease. Grants: NIH, Abbott, Amgen, OPKO, Shire
 Pathogenesis of Metabolic Bone Disease Stuart M. Sprague, D.O. Chief, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Professor of Medicine NorthShore University HealthSystem University of Chicago Pritzker School
Pathogenesis of Metabolic Bone Disease Stuart M. Sprague, D.O. Chief, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Professor of Medicine NorthShore University HealthSystem University of Chicago Pritzker School
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases. Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary
 Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
chapter 1 & 2009 KDIGO
 http://www.kidney-international.org chapter 1 & 2009 DIGO Chapter 1: Introduction and definition of CD MBD and the development of the guideline statements idney International (2009) 76 (Suppl 113), S3
http://www.kidney-international.org chapter 1 & 2009 DIGO Chapter 1: Introduction and definition of CD MBD and the development of the guideline statements idney International (2009) 76 (Suppl 113), S3
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Title Author(s) Citation Issue date 2009-09 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Kobe University Repository : Kernel Marked increase in bone formation markers after cinacalcet treatment by mechanisms
Title Author(s) Citation Issue date 2009-09 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Kobe University Repository : Kernel Marked increase in bone formation markers after cinacalcet treatment by mechanisms
Hypocalcemia 6/8/12. Normal value. Physiologic functions. Nephron a functional unit of kidney. Influencing factors in Calcium and Phosphate Balance
 Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
Klotho: renal and extra-renal effects
 Klotho: renal and extra-renal effects Juan F. Navarro-González, MD, PhD, FASN Nephrology Service and Research Division University Hospital Nuestra Señora de Candalaria Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Spain Klotho:
Klotho: renal and extra-renal effects Juan F. Navarro-González, MD, PhD, FASN Nephrology Service and Research Division University Hospital Nuestra Señora de Candalaria Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Spain Klotho:
HYPERPARATHYROIDIS M FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE
 HYPERPARATHYROIDIS M FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y PREAMBLE Anatomy & physiology of the
HYPERPARATHYROIDIS M FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y PREAMBLE Anatomy & physiology of the
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION. Burosumab Injection. Solution for Subcutaneous Injection 10 mg/ml 20 mg/ml 30 mg/ml
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr CRYSVITA TM Burosumab Injection Solution for Subcutaneous Injection 10 mg/ml 20 mg/ml 30 mg/ml Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) Inhibitor
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr CRYSVITA TM Burosumab Injection Solution for Subcutaneous Injection 10 mg/ml 20 mg/ml 30 mg/ml Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) Inhibitor
Sensipar. Sensipar (cinacalcet) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.46 Subject: Sensipar Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Sensipar Description Sensipar (cinacalcet)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.46 Subject: Sensipar Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Sensipar Description Sensipar (cinacalcet)
Vitamin D. Vitamin functioning as hormone. Todd A Fearer, MD FACP
 Vitamin D Vitamin functioning as hormone Todd A Fearer, MD FACP Vitamin overview Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential in small amounts for normal metabolism They are different from minerals
Vitamin D Vitamin functioning as hormone Todd A Fearer, MD FACP Vitamin overview Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential in small amounts for normal metabolism They are different from minerals
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Primary Hyperparathyroidism
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Primary Hyperparathyroidism Please use this Guideline in Conjunction with the Hypercalcaemia Guideline Definition Driven by hyperfunction of one or
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Primary Hyperparathyroidism Please use this Guideline in Conjunction with the Hypercalcaemia Guideline Definition Driven by hyperfunction of one or
What is the right calcium balance?
 For patients with hypoparathyroidism What is the right calcium balance? Indications and Usage1 NATPARA is a parathyroid hormone indicated as an adjunct to calcium and vitamin D to control hypocalcemia
For patients with hypoparathyroidism What is the right calcium balance? Indications and Usage1 NATPARA is a parathyroid hormone indicated as an adjunct to calcium and vitamin D to control hypocalcemia
Hypophosphatemia An Evidence-based Problem-Solving Approach to Clinical Cases
 Kidney Diseases Hypophosphatemia An Evidence-based Problem-Solving Approach to Clinical Cases Section of Pediatric Nephrology, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois, USA Keywords. hypophosphatemia,
Kidney Diseases Hypophosphatemia An Evidence-based Problem-Solving Approach to Clinical Cases Section of Pediatric Nephrology, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois, USA Keywords. hypophosphatemia,
Inherited Calcium and Magnesium Disorders
 Inherited Calcium and Magnesium Disorders Martin Konrad University Children s Hospital Münster, Germany IPNA / ESPN Master Class, Leuven, Sep 2nd 2015 Outline Hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia Outline Hypercalcemia
Inherited Calcium and Magnesium Disorders Martin Konrad University Children s Hospital Münster, Germany IPNA / ESPN Master Class, Leuven, Sep 2nd 2015 Outline Hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia Outline Hypercalcemia
Vitamin D Deficiency. Micol Rothman, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Metabolic Bone Program University of CO-Denver
 Vitamin D Deficiency Micol Rothman, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Metabolic Bone Program University of CO-Denver 50 yo woman referred for osteoporosis What is striking about her
Vitamin D Deficiency Micol Rothman, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Metabolic Bone Program University of CO-Denver 50 yo woman referred for osteoporosis What is striking about her
