(a) Describe how a B cell is activated. (3)
|
|
|
- Paulina Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 As part of the immune response, a B cell has to be activated. It then divides to form a clone of cells. These cells then differentiate into plasma cells, which produce antibodies. (a) Describe how a B cell is activated. (b) (i) Name the type of division that occurs when B cells are cloned. (ii) Suggest how a microscope slide could be prepared to observe cell division in B cells.
2 (c) The electronmicrograph below shows a plasma cell. Some structures inside this cell have been labelled. Q R P Magnification Place a cross in the box to identify each of the following structures. (i) Structure P A chloroplast B C Golgi apparatus mitochondrion D nucleus (ii) Structure R A cytoplasm B C lysosome nucleus D vacuole
3 (iii) Name structure Q. (iv) Describe the role of structure Q in the production of antibodies. (Total for Question 1 = 13 marks)
4 2 Phagocytosis is a non-specific response of the body to infection. (a) Explain the meaning of each of the following terms. (i) Phagocytosis (ii) Non-specific response (iii) Infection
5 (b) Phagocytosis requires a source of energy in the form of ATP. The diagram below shows the relationship between ATP and ADP. ADP reaction A reaction B ATP Place a cross in the box next to the name of reaction A and reaction B. Name of reaction Reaction autolysis decarboxylation hydrolysis phosphorylation polymerisation A B (c) ATP is synthesised in mitochondria. (i) In the space below, draw and label a diagram to show the structure of a mitochondrion. (4) (ii) Name one other organelle that synthesises ATP. (Total for Question 2 = 13 marks)
6 3 The human body responds to infection by bacteria in a number of ways. The non-specific response includes phagocytosis and lysozyme action, which can be followed by the specific immune response. The specific immune response requires antigen presentation by macrophages. (a) Explain how phagocytosis and lysozyme action lead to antigen presentation by macrophages. (4) (b) Explain how macrophages present antigens to T helper cells.
7 (c) There is an evolutionary race between some bacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB), and their hosts. Suggest how this could affect antigen presentation to T helper cells. Give an explanation for your answer. (Total for Question 3 = 9 marks)
8 4 Whooping cough is a disease that is particularly serious in young children. Whooping cough is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Children may be vaccinated against whooping cough. In an investigation, a group of rats was vaccinated. Sixty days later these rats were infected with Bordetella pertussis. In this investigation, the levels of two antibodies in the blood of the rats were measured. The graph below shows the mean levels of antibody A and antibody B. Mean level of antibody in blood /arbitrary units antibody A 0 antibody B Time after vaccination / days vaccination infection with Bordetella pertussis (a) (i) For antibody A, compare the increase in mean level after the vaccination with the increase in mean level after infection with Bordetella pertussis.
9 (ii) Explain the changes in mean level of antibody A after infection with Bordetella pertussis. (b) (i) Suggest why antibody B was not present in the blood of these rats until after infection with Bordetella pertussis. (ii) Place a cross in the box next to the term that describes the type of immunity that results in the production of antibody B. A artificial active B C artificial passive natural active D natural passive
10 (c) Comment on the reliability of the data shown in the graph. (Total for Question 4 = 11 marks)
(b) Describe the role of antigen presentation in the body s specific immune response to infection by viruses. (4)
 1 The human body responds to infection by viruses in a number of ways. The non-specific response involves interferon. The specific immune response requires antigen presentation to the cells of the immune
1 The human body responds to infection by viruses in a number of ways. The non-specific response involves interferon. The specific immune response requires antigen presentation to the cells of the immune
Answer Key. Chapter Test A
 Answer Key Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company Chapter Test A Multiple Choice 1. c 2. b 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. b 7. c 8. c 9. d 10. a 11. b 12. a 13. d 14. b 15. c Short Answer
Answer Key Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company Chapter Test A Multiple Choice 1. c 2. b 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. b 7. c 8. c 9. d 10. a 11. b 12. a 13. d 14. b 15. c Short Answer
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided.
 Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
By: Brooke Sheppard
 By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome
 Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Edexcel (A) Biology A-level
 Edexcel (A) Biology A-level Topic 6: Immunity, Infection and Forensics Notes Forensics and Time of Death Time of death of a mammal can be determined by looking at the following: Extent of decomposition
Edexcel (A) Biology A-level Topic 6: Immunity, Infection and Forensics Notes Forensics and Time of Death Time of death of a mammal can be determined by looking at the following: Extent of decomposition
St. Brigid Catholic Academy AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells:
 Name: St. Brigid Catholic Academy Date: Science AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells: Below are two types of cells. What similarities
Name: St. Brigid Catholic Academy Date: Science AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells: Below are two types of cells. What similarities
CELL THEORY- EQ: What are the 3 facts of the cell theory? - pp191. EQ- Which Scientists are connected to cell discovery?
 UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
centriole cytoskeleton plays a role in cell division centriole protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
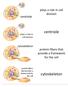 centriole plays a role in cell division plays a role in cell division centriole cytoskeleton protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
centriole plays a role in cell division plays a role in cell division centriole cytoskeleton protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Bio 103 Section A02 Summer 2003 Exam #2 Study Guide Dr. Largen
 Chapter 4 - Cell Structure Bio 103 Section A02 Summer 2003 Exam #2 Study Guide Dr. Largen Microscopes provide windows to the world of the cell compare light versus electron microscopes illumination type
Chapter 4 - Cell Structure Bio 103 Section A02 Summer 2003 Exam #2 Study Guide Dr. Largen Microscopes provide windows to the world of the cell compare light versus electron microscopes illumination type
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Are you ready for SK320?
 SK320 Infectious disease and public health Are you ready for SK320? Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Suggested prior study 2 3 Module content 2 4 Key concepts for SK320 4 4.1 Cell structure and function 4 4.2
SK320 Infectious disease and public health Are you ready for SK320? Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Suggested prior study 2 3 Module content 2 4 Key concepts for SK320 4 4.1 Cell structure and function 4 4.2
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
 Name Date Period Cells Alive Webquest Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and
Name Date Period Cells Alive Webquest Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Smart cell lesson (1).notebook February 02, 2015
 Cells 1 TEKS Related to the Lesson (12) Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The
Cells 1 TEKS Related to the Lesson (12) Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The
1 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an animal plasma membrane?
 1 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an animal plasma membrane? A) separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment B) helps the cell maintain homeostasis C)
1 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an animal plasma membrane? A) separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment B) helps the cell maintain homeostasis C)
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Cell Processes Review
 1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE
 Name: INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Introduction: If you missed the microscope lab we did in class, you will need to make it up by using a "virtual microscope" which can be accessed on the internet.
Name: INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Introduction: If you missed the microscope lab we did in class, you will need to make it up by using a "virtual microscope" which can be accessed on the internet.
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Pathogens and the immune system
 Pathogens and the immune system Veronica Leautaud, Ph.D. vl2@ rice.edu Keck Hall 224 / 232-lab Lecture 8 BIOE 301-Bioengineering and World Health Review of lecture 7 Science Science is the human activity
Pathogens and the immune system Veronica Leautaud, Ph.D. vl2@ rice.edu Keck Hall 224 / 232-lab Lecture 8 BIOE 301-Bioengineering and World Health Review of lecture 7 Science Science is the human activity
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
3.1. Cell Structure and Function CHAPTER 3. Cells are the basic unit of life. CELL THEORY Study Guide KEY CONCEPT
 SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell Early studies led to the development of the
SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell Early studies led to the development of the
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Cell Structure and Function
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Class Date. cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell. MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
 Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
In the lungs, the organisms are taken up by macrophages and carried to lymph nodes. State one characteristic symptom of TB other than coughing.
 1 Tuberculosis (TB) kills approximately three million people every year. Droplets containing the organisms that cause TB are released into the air when a person suffering from TB coughs. Transmission of
1 Tuberculosis (TB) kills approximately three million people every year. Droplets containing the organisms that cause TB are released into the air when a person suffering from TB coughs. Transmission of
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 4.1: Communicable diseases, disease prevention and the immune system Notes Pathogens Bacteria and viruses are the main disease causing pathogens in humans. Even though they
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 4.1: Communicable diseases, disease prevention and the immune system Notes Pathogens Bacteria and viruses are the main disease causing pathogens in humans. Even though they
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Peroxisomes. Endomembrane System. Vacuoles 9/25/15
 Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Figure 1. Base your answer to the question on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.
 Name: Teacher: Lathrop Topic 3 cells CR HW #3 Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Using a microscope and a wet-mount slide,
Name: Teacher: Lathrop Topic 3 cells CR HW #3 Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Using a microscope and a wet-mount slide,
Cell Structure and Function. Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells
 Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
BIOLOGY. James Ruse Agricultural High School. Total marks for this paper: 37. This paper has two parts, Part A and Part B. General Instructions
 James Ruse Agricultural High School 2007 PRELIMINARY COURSE TERM 2 (Y11) ASSESSMENT TASK THEORY EXAMINATION (PATTERNS IN NATURE) BIOLOGY Total marks for this paper: 37 General Instructions Reading time
James Ruse Agricultural High School 2007 PRELIMINARY COURSE TERM 2 (Y11) ASSESSMENT TASK THEORY EXAMINATION (PATTERNS IN NATURE) BIOLOGY Total marks for this paper: 37 General Instructions Reading time
Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions. Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18
 Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18 1. Which of the following would be least affected by defective receptor proteins on a cell membrane? a. Homeostasis b. Muscle activity
Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18 1. Which of the following would be least affected by defective receptor proteins on a cell membrane? a. Homeostasis b. Muscle activity
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Question Number. 1. prevents viruses attaching to {uninfected / eq} host cells / eq ; 2. by binding to receptors / eq ;
 1(a) 1. prevents viruses attaching to {uninfected / eq} host cells / eq ; 2. by binding to receptors / eq ; 3. (therefore) preventing virus from entering cell / eq ; 4. (therefore) viruses cannot replicate
1(a) 1. prevents viruses attaching to {uninfected / eq} host cells / eq ; 2. by binding to receptors / eq ; 3. (therefore) preventing virus from entering cell / eq ; 4. (therefore) viruses cannot replicate
5 Cell recognition and the immune system Exam-style questions. AQA Biology. 1 Figure 1 shows a phagocyte attracted to a bacterium.
 1 Figure 1 shows a phagocyte attracted to a bacterium. Figure 1 Describe how the phagocyte destroys the bacterium. (5 marks) 2 A child was given two vaccinations consisting of antigens from the virus which
1 Figure 1 shows a phagocyte attracted to a bacterium. Figure 1 Describe how the phagocyte destroys the bacterium. (5 marks) 2 A child was given two vaccinations consisting of antigens from the virus which
Review from Biology A
 Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Topic 1: Living Things
 Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Name Class Date. What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
d. When the salt concentration outside the cell is very low, diffusion causes water to
 4B EOC Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water movement into and out of cells is of prime importance to all living things. A single
4B EOC Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water movement into and out of cells is of prime importance to all living things. A single
C) amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the animal B) rate of respiration of the animal
 Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
Chapter 27 Bioenergetics; How the Body Converts Food to Energy
 Chapter 27 Bioenergetics; How the Body Converts Food to Energy 1 Metabolism Metabolism: The sum of all chemical reactions involved in maintaining the dynamic state of a cell or organism. Pathway: A series
Chapter 27 Bioenergetics; How the Body Converts Food to Energy 1 Metabolism Metabolism: The sum of all chemical reactions involved in maintaining the dynamic state of a cell or organism. Pathway: A series
Questions in Cell Biology
 Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
AQA Biology A-level. Notes.
 AQA Biology A-level Topic 2: Cells Notes Methods of studying cells There are many methods for studying cells and one way in which this is done is through the use of microscopes of which there are two main
AQA Biology A-level Topic 2: Cells Notes Methods of studying cells There are many methods for studying cells and one way in which this is done is through the use of microscopes of which there are two main
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level
 Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
The most valuable lipid ever?
 The most valuable lipid ever? Spermaceti whale oil Used by sperm whales in a special organ in the huge head cavity Largely comprised of cetyl palmitate ww.thisrecording.com www.greenpeace.org Peer Instruction
The most valuable lipid ever? Spermaceti whale oil Used by sperm whales in a special organ in the huge head cavity Largely comprised of cetyl palmitate ww.thisrecording.com www.greenpeace.org Peer Instruction
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level
 Centre Number Candidate Number Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/04 Paper 4 Structured Questions A2 Core Candidates answer on the Question
Centre Number Candidate Number Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/04 Paper 4 Structured Questions A2 Core Candidates answer on the Question
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Cells. A typical animal cell THE CELL MEMBRANE FIRST STOP
 WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Dalkeith High School Higher Human Biology Homework 3
 Dalkeith High School Higher Human Biology Homework 3 1. During which of the following chemical conversions is A T P produced? A B C Amino acids protein Glucose pyruvic acid Haemoglobin oxyhaemoglobin energy
Dalkeith High School Higher Human Biology Homework 3 1. During which of the following chemical conversions is A T P produced? A B C Amino acids protein Glucose pyruvic acid Haemoglobin oxyhaemoglobin energy
Cell Transport Unit Test
 Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
Cells. Cells are the best!
 Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Exam 2 Practice Problems
 Exam 2 Practice Problems Cell Structure and Function Practice Questions 1. One of the relationships that exists between ribosomes and lysosomes is that a. ribosomes produce enzymes that could be stored
Exam 2 Practice Problems Cell Structure and Function Practice Questions 1. One of the relationships that exists between ribosomes and lysosomes is that a. ribosomes produce enzymes that could be stored
Cells 2/2/2019. Cell Theory. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Life on Earth. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Bacterial Cell. Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cells Structure and Function All living things are made of cells New cells come from pre-existing cells NO Spontaneous Generation Francesco Redi Italian 17 th century Louis Pasteur French 19
Cell Theory Cells Structure and Function All living things are made of cells New cells come from pre-existing cells NO Spontaneous Generation Francesco Redi Italian 17 th century Louis Pasteur French 19
SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells
 SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology
 3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Review: Cellular Transport
 Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
IMMUNITY. Stage 1. Stage 2. Stage 3. Stage 4. (a) Describe one method by which antibodies specific to a disease might have been produced.
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a system for detecting the presence of a disease organism in the blood of an infected person. Stage 1 Antibody specific to the disease organism is bound to the surface
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a system for detecting the presence of a disease organism in the blood of an infected person. Stage 1 Antibody specific to the disease organism is bound to the surface
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
(A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids. A. Incorrect! Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have cell membranes.
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key. Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions
 Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/01/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Science- biology Cells 1. Below is an image of a plant cell. What processes require
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/01/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Science- biology Cells 1. Below is an image of a plant cell. What processes require
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Looking forward to an awesome year in IB Biology!
 WESTLAKE HIGH SCHOOL IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS IB Biology will be a very intensive course. Though we will have 90 minute periods every other day, there is still a lot of new material to
WESTLAKE HIGH SCHOOL IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS IB Biology will be a very intensive course. Though we will have 90 minute periods every other day, there is still a lot of new material to
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity.
 1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK
 NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
Looking Inside Cells
 Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
(a) (i) In the image above, the part of the cell labelled A contains chromosomes.
 Q1.The image below shows an epithelial cell from the lining of the small intestine. (a) (i) In the image above, the part of the cell labelled A contains chromosomes. What is the name of part A? How are
Q1.The image below shows an epithelial cell from the lining of the small intestine. (a) (i) In the image above, the part of the cell labelled A contains chromosomes. What is the name of part A? How are
Section 6.1 Defence mechanisms
 Section 6.1 Defence mechanisms Defence mechanisms Non-specific mechanisms that do not distinguish between one type of pathogen and another, but respond to all of them in the same way. These mechanisms
Section 6.1 Defence mechanisms Defence mechanisms Non-specific mechanisms that do not distinguish between one type of pathogen and another, but respond to all of them in the same way. These mechanisms
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
