CONTENT OUTLINE. Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine
|
|
|
- Doris Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PEDIATRICS CONTENT OUTLINE Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Subspecialty In-Training, Certification, and Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examinations
2 INTRODUCTION This document was prepared by the American Board of Pediatrics Subboard of Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine for the purpose of developing in-training, certification, and maintenance of certification examinations. The outline defines the body of knowledge from which the Subboard samples to prepare its examinations. The content specification statements located under each category of the outline are used by item writers to develop questions for the examinations; they broadly address the specific elements of knowledge within each section of the outline.
3 Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Each Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine exam is built to the same specifications, also known as the blueprint. This blueprint is used to ensure that, for the initial certification and in-training exams, each exam measures the same depth and breadth of content knowledge. Similarly, the blueprint ensures that the same is true for each Maintenance of Certification exam form. The table below shows the percentage of questions from each of the content domains that will appear on an exam. Please note that the percentages are approximate; actual content may vary. Content Categories Initial Certification and In-Training Maintenance of Certification (MOC) 1. Maternal-Fetal Medicine 6% 6% 2. Asphyxia and Resuscitation 4% 6% 3. Cardiovascular 9% 8% 4. Respiratory 12% 12% 5. Genetics/Dysmorphism 7% 6% 6. Nutrition 8% 8% 7. Water/Salt/Renal 5% 5% 8. Endocrine/Metabolic/Thermal 5% 5% 9. Immunology 3% 2% 10. Infectious Diseases 6% 7% 11. Gastroenterology 4% 4% 12. Bilirubin 2% 4% 13. Skin Disorders 2% 2% 14. Hematology/Oncology 5% 5% 15. Neurology 7% 7% 16. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes 3% 4% 17. Eyes, Ears, Nose, Mouth, Throat, and Neck 3% 3% 18. Basic Principles of Pharmacology 2% 2% 19. Health Services Delivery, Ethical Issues, and Family Counseling 2% 2% 20. Core Knowledge in Scholarly Activities 5% 2%
4 Neonatal Perinatal Medicine 1. Maternal-Fetal Medicine A. Pregnancy (For Reproductive genetics, see Section 5) 1. Factors of pregnancy (see also 6.A.1.b. and c.) a. Know the physiology of maternal adaptation to pregnancy and know the normal changes in maternal physiologic variables and in laboratory values that occur during pregnancy b. Know the essentials of prenatal care, including risk assessment, perinatal referral, screening, and standard monitoring c. Know the types of multiple gestation d. Know the normal morphologic development of the placenta e. Know the role of the placenta in gas exchange and oxygenation of the fetus f. Know the role of the placenta in the energy metabolism of the fetus, including the transfer of glucose, electrolytes, and amino acids to the fetus g. Know the components of pre- and periconceptional health care (including nutritional requirements during pregnancy) that influence pregnancy outcomes h. Know the types of assisted reproductive technologies and how they may influence pregnancy outcome i. Know how maternal obesity may influence pregnancy and pregnancy outcome j. Know the types of abnormal placentation, such as placenta previa and placenta accreta, and the potential influence on both maternal and fetal health and labor and delivery management 2. Maternal medical disorders affecting the fetus and/or newborn infant (see also 9.B.1.a) a. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal immunologic diseases and their management b. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of acute and chronic maternal renal diseases and their management c. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal or placental malignancy and its management d. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal diabetes mellitus (including gestational diabetes) and their management e. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal hematologic disorders and their management f. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal cardiac disease and its management g. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal pulmonary disease and its management h. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal central and peripheral nervous system and neuromuscular diseases and their management i. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal seizure disorders and their management j. Know the maternal and fetal risks and the management of a traumatic injury in a pregnant woman k. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal connective tissue disorders and their treatment
5 l. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal chronic hypertension and its management m. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of mild preeclampsia and its management n. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of severe preeclampsia, including HELLP syndrome, and its management o. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal thromboembolic or potential thromboembolic (eg, artificial valve) disorders and of their management, including the use of anticoagulants p. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal metabolic disorders, including PKU, and their management q. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal surgery and anesthesia (eg, appendectomy) r. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal HIV infection and its management and know the strategies employed to decrease fetal and neonatal HIV infection s. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal psychiatric disorders and their treatment t. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of other maternal infections (eg, malaria) and their management 3. Obstetric conditions and complications (fetus/newborn) a. Know the definition, risks to the fetus and/or newborn infant, and management of post-term pregnancy b. Know the differential diagnosis and potential risks to the fetus and/or newborn infant of first, second, and third trimester vaginal bleeding 4. Effect of drugs and environmental agents (fetus/newborn) (see also 1.B.5.) a. Know the gestational age at which teratogenic exposure (eg, rubella, alcohol, retinoic acid) will be most likely to produce fetal anomalies b. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of tocolytic agents used during pregnancy c. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal substance abuse (eg, heroin, cocaine, cannabis, methamphetamines, tobacco) d. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternal alcohol use e. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of exposure to ionizing radiation, including x-rays and radioactive substances used for diagnosis and/or treatment of maternal disorders f. Know the pulmonary and non-pulmonary effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of maternally administered steroids (including betamethasone, dexamethasone, and prednisone) g. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of exposure during pregnancy to environmental agents (eg, mercury, pesticides, etc.) B. Fetal assessment and treatment modalities during pregnancy 1. Screening a. Know the indications for and complications of methods of direct assessment of the fetus, including chorionic villus sampling, amniotic fluid sampling, and fetal blood sampling
6 b. Know the rationale for, and approaches to, screening for maternal Group B streptococcal colonization during pregnancy c. Know the rationale, methods, and interpretation of results of screening for maternal infections such as rubella, CMV, viral hepatitis, HIV, and syphilis d. Know the rationale, methods, and interpretation of results of first and second trimester screening for aneuploidy (eg, nuchal translucency, choroid plexus cysts) and neural tube defects e. Know the rationale, methods, and interpretation of results of screening for carrier status of genetic diseases such as cystic fibrosis, Tay Sachs, and hemoglobinopathies 2. Ultrasonography and imaging a. Know the general principles, applications, and limitations of ultrasonography, including Doppler blood flow measurements, in assessment of fetal conditions and well-being b. Know how to use obstetric and ultrasonographic data to determine gestational age, and know their limitations c. Know the importance and limitations of ultrasonographic findings of common fetal anomalies including congenital heart disease d. Know the role and risks of magnetic resonance imaging, as well as other nonultrasonographic imaging techniques in assessing fetal anatomy 3. Assessment of fetal status a. Understand the rationale, interpretation, and limitations of maternal detection of fetal movement, of the biophysical profile, the non-stress test, and the contraction stress test as means of assessing fetal well-being 4. Fetal conditions that jeopardize the fetus during pregnancy (see also 1.A.1.) a. Know the potential fetal complications of multiple gestation such as cord problems, twin-twin transfusion, "stuck twin," conjoined twins, etc. b. Know the diagnostic evaluation and perinatal management of fetal-maternal blood group incompatibility c. Know the differential diagnosis and the plan of evaluation and management of a fetus with non-immune hydrops d. Know the limitations in diagnosis and implications of fetal macrosomia e. Know how to evaluate fetal growth rate and fetal growth restriction and the management of fetal growth restriction f. Know the significance of oligohydramnios and the management of pregnancy when it is diagnosed g. Know the significance of polyhydramnios and the management of pregnancy when it is diagnosed h. Know the implications and treatment options for the surviving fetus when its twin dies in utero i. Know how specific fetal diagnoses, such as airway abnormalities, abdominal wall defects, myelomeningocele, or severe hydrocephalus might alter prenatal care and intrapartum management (eg, fetal intervention "Exit" strategy) 5. Evaluation of fetal lung maturity (See also 1.A.4. and 4.B.1) a. Know the indications for and interpretation of tests of fetal lung maturity C. Labor
7 1. Factors of labor (See also 1.B.3.) a. Know how to assess fetal well-being during labor b. Know the physiologic characteristics of normal labor and parturition c. Know the effects of normal labor on uteroplacental physiology and its effects on the fetus d. Know the risk factors, including the effects of choriodecidual infection and inflammation as contributing factors, for preterm labor 2. Complications of labor that affect the fetus (see also 2.B.) a. Know the diagnosis and management of maternal/fetal blood loss such as placenta previa, placenta abruption, vasa previa, and maternal-fetal hemorrhage b. Know the differential diagnosis and management of maternal hypotension in labor and its effect on the fetus c. Know the significance, interpretation, and management of abnormalities or changes in fetal heart rate patterns during labor including reassuring and nonreassuring and indeterminate patterns d. Know the effects on the fetus and/or newborn infant of analgesics and anesthetics administered to the mother during labor 3. Other (see also 1.C.1.) a. Know the significance of a maternal temperature increase during labor b. Know the complications and effects of chorioamnionitis in the mother and the fetus c. Know the causes, complications, and management of preterm premature rupture of membranes D. Delivery 1. Know how to recognize and differentiate complications of soft tissue injury to an infant's scalp, like caput and subgaleal bleed 2. Know the clinical features and prognosis of birth injuries, such as fractures, lacerations, and facial palsies 3. Know the neonatal complications of abnormal presentations (breech, shoulder dystocia, etc.) 4. Know the indications for and fetal/newborn complications of cesarean delivery 5. Know the indications for and perinatal complications of operative vaginal delivery (forceps, vacuum extraction, etc.) and of vaginal delivery after cesarean delivery 6. Know the rationale, risks, and benefits of delayed cord clamping E. Breast feeding (See Section 6.C.1.) 2. Asphyxia and Resuscitation A. Pathophysiology of acute and chronic asphyxia syndromes 1. General a. Know the incidence, causes and pathophysiology, including cellular abnormalities, of acute perinatal asphyxia b. Know the causes and pathophysiology, including cellular abnormalities, of chronic asphyxia syndromes (eg, chronic fetal hypoxia and placental insufficiency) c. Know the clinical features, diagnosis, and management of perinatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy 2. Organ effects a. Recognize the neonatal systemic complications and vascular redistribution of blood flow caused by perinatal hypoxia or asphyxia
8 b. Understand reperfusion injury 3. Biochemistry a. Know the biochemical responses to and consequences of asphyxia B. Diagnosis and management of asphyxia 1. Diagnosis a. Differentiate asphyxia from other causes of depression at birth, including drug effects and hypovolemia b. Understand the significance, limitations, and causes of low Apgar scores, including the relationship between Apgar scores and later outcomes in preterm and full-term infants c. Know the interpretation of umbilical cord blood gas and ph values 2. Management a. Airway (See also 1.C.2 and 4.C.2) 1. Know the proper approach to airway management in the delivery room 2. Know the potential complications of airway management in the delivery room and know their management 3. Know the current recommendations regarding suctioning meconium from the airway during and following delivery b. Ventilation and oxygenation 1. Know the indications for assisted ventilation, including continuous positive airway pressure, immediately after birth and how to assess its effectiveness 2. Understand how to use self-inflating and flow-inflating bags or T-piece resuscitators to provide assisted ventilation immediately after birth 3. Know indications for and proper administration of supplemental oxygen immediately after birth c. Circulatory support 1. Know the indications for, techniques, and potential complications of chest compression immediately after birth 2. Know the indications for and management of intravascular fluid volume replacement immediately after birth d. Pharmacologic management 1. Know the indications, contraindications, and methods of administration of drugs used for neonatal resuscitation 3. Cardiovascular A. Normal and abnormal cardiac morphogenesis and development 1. Know normal and abnormal morphogenesis and development of the heart and great arteries and the local regulatory factors involved 2. Know the neonatal developmental cardiac manifestations of maternal diseases and maternal drug and environmental exposures 3. Know the genetic and developmental mediators of heart and vascular development 4. Know the neonatal developmental cardiac manifestations of common perinatal syndromes (eg, congenital rubella) B. Cardiovascular physiology 1. Know the factors affecting and regulating myocardial performance and function in the fetus and newborn infant and during the perinatal transitional period
9 2. Know the factors affecting and regulating the systemic circulation in the fetus (including umbilical vessels) and newborn infant during the perinatal transitional period 3. Understand the factors affecting and regulating the pulmonary circulation in the fetus and newborn infant and during the perinatal transitional period 4. Know the appropriate techniques to assess cardiovascular function in the fetus and newborn infant 5. Know the physiology of the ductus arteriosus and understand the factors affecting and regulating the ductus arteriosus in the fetus and newborn infant during the perinatal transitional period C. Congenital heart disease 1. Cyanotic heart defects a. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for a cyanotic neonate b. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology (including genetics) of a cyanotic neonate c. Recognize the clinical features and possible associated defects of a cyanotic neonate d. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of a cyanotic neonate e. Formulate a differential diagnosis for a cyanotic neonate 2. Left-to-right shunt lesions (see also 15.H.3.) a. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology (including genetics) of a neonate with a left-to-right shunt lesion b. Recognize the clinical features of a neonate with a left-to-right shunt lesion c. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of a neonate with a left-to-right shunt lesion d. Formulate a differential diagnosis for a neonate with a left-to-right shunt lesion e. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for a neonate with a left-to-right shunt lesion f. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology of a preterm neonate with a patent ductus arteriosus g. Recognize the clinical features of a preterm neonate with a patent ductus arteriosus h. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of a preterm neonate with a patent ductus arteriosus i. Formulate a differential diagnosis of a preterm neonate with a patent ductus arteriosus j. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for a preterm neonate with a patent ductus arteriosus 3. Left-sided obstructive lesions a. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for a neonate with a left-sided cardiac obstructive lesion
10 b. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology, including genetics, of a neonate with a left-sided cardiac obstructive lesion c. Recognize the clinical features of a neonate with a left-sided cardiac obstructive lesion d. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of a neonate with a left-sided cardiac obstructive lesion e. Formulate a differential diagnosis of a neonate with a left-sided cardiac obstructive lesion 4. Right-sided lesions (cyanotic or acyanotic) a. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for a neonate with a right-sided cardiac lesion b. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology (including genetics) of a neonate with a right-sided cardiac lesion c. Recognize the clinical features of a neonate with a right-sided cardiac lesion d. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of a neonate with a right-sided cardiac lesion e. Formulate a differential diagnosis for a neonate with a right-sided cardiac lesion 5. Mixing lesions (bidirectional shunting) a. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for a neonate with a mixing cardiac lesion b. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology (including genetics) of a neonate with a mixing cardiac lesion c. Recognize the clinical features of a neonate with a mixing cardiac lesion d. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of a neonate with a mixing cardiac lesion e. Formulate a differential diagnosis of a neonate with a mixing cardiac lesion 6. Arterial vascular lesions a. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology (including genetics) of a neonate with an arterial vascular abnormality b. Recognize the clinical features of a neonate with an arterial vascular abnormality c. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of a neonate with an arterial vascular abnormality d. Formulate a differential diagnosis for a neonate with an arterial vascular abnormality e. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for a neonate with an arterial vascular abnormality D. Cardiopulmonary dysfunction in the absence of congenital heart disease 1. Myocardial disorders (eg, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, and tumors) a. Know the anatomy and pathophysiology (including genetics) of an infant with a condition affecting myocardial performance b. Recognize the clinical features in an infant with a condition affecting myocardial performance
11 c. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of an infant with a condition affecting myocardial performance d. Formulate a differential diagnosis of an infant with a condition affecting myocardial performance e. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for an infant with a condition affecting myocardial performance 2. Systemic blood pressure regulation (see 7.B.3.b) a. Know the pathophysiology of a term or preterm infant with a condition affecting the systemic blood pressure, such as hypotension or hypertension b. Recognize the clinical features of an infant with systemic hypotension c. Recognize the laboratory and imaging features of an infant with systemic hypotension d. Formulate a differential diagnosis for an infant with systemic hypotension e. Know the management of an infant with systemic hypotension and the adverse effects of such management f. Formulate a differential diagnosis for an infant with systemic hypertension in early infancy g. Know the management of an infant with systemic hypertension, including adverse effects of management h. Know the factors which regulate systemic blood pressure in term and preterm infants and know the normal range of pressures and pressure patterns i. Know the clinical and diagnostic features of an infant with systemic hypertension, including laboratory and imaging studies 3. Cardiovascular effects of birth a. Know the pathophysiology of an infant with cardiac manifestations produced by perinatal events such as asphyxia, hypovolemia, or hypervolemia b. Recognize the clinical features of an infant with cardiac manifestations produced by perinatal events such as asphyxia hypovolemia or hypervolemia c. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of an infant with cardiac manifestations produced by perinatal events such as asphyxia, hypovolemia, or hypervolemia d. Formulate a differential diagnosis of an infant with cardiac manifestations produced by perinatal events such as asphyxia, hypovolemia, or hypervolemia e. Know the evaluation and medical and/or surgical management and associated potential complications or adverse effects of such management for an infant with cardiac manifestations produced by perinatal events such as asphyxia, hypovolemia, or hypervolemia E. Electrocardiography, electrophysiology, and dysrhythmias 1. Differentiate normal from common abnormal electrocardiographic patterns and rhythms in the fetus and newborn infant 2. Know the physiologic consequences of an arrhythmia in a fetus or newborn infant 3. Know appropriate management of common arrhythmias in the fetus and newborn infant, and understand the potential complications or adverse effects of approaches and drugs used F. Pharmacologic therapy of heart disease
12 1. Vasopressor and inotropic drugs a. Know the mechanism of action of commonly used adrenergic vasopressor and/or inotropic drugs (eg, dopamine, dobutamine, epinephrine) b. Know the therapeutic indications for, and toxicity of, commonly used adrenergic drugs c. Know the mechanisms of action, therapeutic indications for, and toxicity of chronotropic drugs d. Know the mechanisms of action, therapeutic indications for, and toxicity of inotropic drugs 2. Diuretics a. Know the therapeutic indications for, and toxicity of, commonly used diuretic drugs in preterm and term infants with cardiovascular disease 3. Pharmacologic management of the ductus arteriosus a. Know the indications, application, and complications of the use of prostaglandin E1 to maintain patency of the ductus arteriosus in neonates 4. Nitric oxide (see 4.F.1.) G. Neurodevelopmental outcome of infants with congenital heart disease 1. Know the long-term prognosis and outcome, including neurodevelopmental outcome, of infants with cyanotic or acyanotic congenital heart disease 4. Respiratory A. Embryology and physiology 1. Morphologic development of the lung -- normal and abnormal a. Know the stages and mediators of normal and abnormal cellular and structural development of all components of the lung 2. Fetal respiration a. Know the mechanism of production and factors affecting the clearance of fetal lung liquid, its contribution to amniotic fluid, and its importance to fetal lung development 3. Control of Breathing -- normal and abnormal a. Know the effects of pulmonary reflexes and oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen ion concentrations on control of neonatal breathing 4. Pulmonary surfactant a. Know the effects of surface tension on alveolar and airway stability and lung mechanics (LaPlace law) b. Know the timing of the biochemical maturation of the lung and the physiological and biochemical factors affecting this timing 5. Pulmonary function -- normal and abnormal a. Ventilation/perfusion 1. Know the concepts of anatomic and physiologic dead space 2. Know the causes of and the effects of ventilation/perfusion mismatching 3. Know the determinants of gas exchange 4. Know the causes of and how to evaluate arterial hypoxemia in an infant with a structurally normal heart 5. Know the effects of changes in altitude on oxygenation 6. Know how to calculate an alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient b. Respiratory mechanics -- normal and abnormal
13 1. General a. Distinguish the differences in pulmonary mechanics between the neonate and the adult b. Know the basic gas laws and their clinical applications 2. Lung volume a. Know factors that determine residual lung volume, functional residual capacity, and tidal volume, and how they change with various pulmonary disorders 3. Lung and chest wall compliance a. Recognize the factors (including pressure-volume and flow-volume relationships) that alter lung compliance and chest wall compliance and how they change with various pulmonary disorders and with gestational age 4. Airway resistance a. Know the factors that affect airway resistance and how resistance changes with various lung disorders 5. Respiratory muscles a. Know the factors that influence upper airway patency b. Know the developmental characteristics of respiratory muscle function 6. Dynamic interactions a. Know the physical principles governing gas flow, including airway diameter, turbulence, and time constants b. Know the causes of pulmonary edema and its effects on lung function c. Know how intrapleural pressure affects cardiovascular function d. Know how acute and chronic lung disease affects cardiovascular function 6. Oxygen transport and delivery a. Know the various factors affecting oxygen uptake, transport, and delivery, including the blood and circulation 7. Pulmonary function testing a. Know how to interpret arterial blood gas measurements and noninvasive methods for estimating arterial oxygenation b. Know the interpretation and limitations of methods for measuring pulmonary function B. Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)/Transient tachypnea 1. RDS a. Know the pathophysiology and risk factors for RDS b. Recognize the clinical, imaging, and laboratory features of RDS c. Recognize the pathologic features of RDS d. Know the clinical strategies and therapies used to decrease the risk and severity of RDS e. Know the management of RDS, including surfactant replacement 2. Transient tachypnea a. Know the pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and risk factors of transient tachypnea of the newborn infant b. Know the clinical, laboratory, and imaging features of transient tachypnea of the newborn infant and formulate a differential diagnosis c. Know the prevention and management of transient tachypnea of the newborn infant
14 C. Pneumonias, meconium aspiration, and persistent pulmonary hypertension 1. Pneumonias a. Know the pathogenesis and causative agents in an infant in whom neonatal pneumonia is suspected b. Know the clinical, imaging, and laboratory features and plan the management of an infant in whom neonatal pneumonia is suspected 2. Meconium aspiration syndrome (See also 1.C.2 and 2.B.2.a) a. Know the pathogenesis, pathophysiology, pathologic features, and risk factors of meconium aspiration syndrome b. Know how to manage meconium aspiration syndrome c. Know the clinical, laboratory, and imaging features of meconium aspiration syndrome 3. Persistent pulmonary hypertension a. Know the pathogenesis, pathophysiology, pathologic features, and risk factors for persistent pulmonary hypertension b. Recognize the clinical features and differential diagnosis of persistent pulmonary hypertension c. Recognize the laboratory, imaging, and other diagnostic features of persistent pulmonary hypertension d. Know the management of persistent pulmonary hypertension including assisted ventilation, pharmacologic approaches, and ECMO D. Other causes of respiratory distress 1. Extrapulmonary (eg, diaphragmatic hernia, cord transection, etc.) a. Plan appropriate therapy for an infant with extrapulmonary causes of respiratory distress b. Recognize the clinical features of extrapulmonary causes of respiratory distress c. Recognize the imaging features of extrapulmonary causes of respiratory distress 2. Airway obstruction (eg, vascular rings, choanal atresia, etc.) a. Know the clinical features of an infant with airway obstruction b. Plan appropriate diagnostic evaluation and management for an infant with airway obstruction 3. Miscellaneous a. Recognize the clinical and imaging features of congenital malformations of the lung, including congenital pulmonary lymphangiectasia, the cystic lung diseases, such as congenital lobar emphysema, cystic adenomatoid malformation, and mediastinal tumors b. Know the appropriate management for an infant with congenital malformations of the lung, including congenital pulmonary lymphangiectasia, and the cystic lung diseases, such as congenital lobar emphysema, cystic adenomatoid malformation, and mediastinal tumors 4. Pleural disorders (effusion, chylothorax) a. Know the pathophysiology and recognize the clinical, radiographic, and laboratory manifestations of hydrothorax/chylothorax b. Plan the therapeutic management of hydrothorax/chylothorax E. Apnea of prematurity and neonatal respiratory depression 1. Know the pathophysiology of apnea of prematurity
15 2. Know the management of apnea of prematurity F. Treatment 1. Assisted ventilation a. Plan the ventilatory therapy for infants with respiratory failure of different etiologies b. Know the indications for and techniques of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) c. Know the effects and risks of CPAP d. Know the indications for and techniques of high-frequency ventilation e. Know the effects and risks of high-frequency ventilation f. Know the indications for and techniques of positive-pressure ventilation (PPV), including volume and pressure-targeted ventilator modes g. Know the effects and risks of PPV 2. ECMO a. Know the indications, techniques, effects, and risks of extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) 3. Pharmacologic agents a. Know the mechanism of action, indications, techniques of administration, effects, and risks of inhaled pulmonary vasodilators such as nitric oxide G. Air leaks 1. Know the pathophysiology of air leaks 2. Recognize the clinical, laboratory, and imaging features of air leaks 3. Know how to prevent and manage air leaks H. Chronic lung disease, bronchopulmonary dysplasia 1. Know the pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and pathologic features of bronchopulmonary dysplasia/chronic lung disease 2. Know the prenatal and postnatal risk factors for bronchopulmonary dysplasia/chronic lung disease and be aware of various preventive strategies 3. Recognize the clinical features of bronchopulmonary dysplasia/chronic lung disease 4. Recognize the laboratory, radiographic, and other imaging features of bronchopulmonary dysplasia/chronic lung disease 5. Know the management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia/chronic lung disease 6. Know the prognosis, long-term complications, and permanent sequelae of bronchopulmonary dysplasia 5. Genetics/Dysmorphism A. Basic understanding of molecular genetics (see also 5.B.3.) 1. Know the functions of messenger, ribosomal, and transfer RNA 2. Know concept of DNA and mrna sequence encoding amino acid structure of proteins 3. Know the function of DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase, and reverse transcriptase enzymes 4. Know the concepts of insertion, deletion, inversion, and translocation 5. Know the principles and clinical implications of anticipation and amplification in trinucleotide repeat syndromes 6. Know the significance of DNA methylation and epigenetics B. Specific patterns of congenital disorders
16 1. Chromosomal disorders a. Types of chromosomal abnormalities 1. Aneuploidy a. Autosomal 1. Recognize the physical findings and chromosomal pattern and know the prognosis in trisomy Identify the physical characteristics and chromosomal pattern and know the prognosis in trisomy Be aware of the maternal factors, incidence, and clinical manifestations, including common complications and prognosis, of Down syndrome b. Sex chromosome 1. Know the physical characteristics, chromosomal pattern, and long-term outcomes of sex chromosome aneuploidies c. Polyploidy 1. Know fetal and placental manifestations of triploidy d. Mosaicism 1. Know how mosaicism modifies clinical presentation 2. Structural chromosomal abnormalities a. Balanced translocations 1. Know the difference between balanced and unbalanced chromosome translocation 2. Know the appropriate cytogenetic evaluation of the family and infant with a structural chromosome abnormality 3. Deletion syndromes (eg, cri du chat, DiGeorge, etc) a. Recognize the clinical manifestations and laboratory methods for diagnosis of the common deletion syndromes b. Recognize clinical manifestations and laboratory methods for diagnosis of the microdeletion syndromes c. Recognize clinical manifestations and laboratory methods for diagnosis of the contiguous gene disorders 2. Single-gene (Mendelian) disorders a. Types 1. Differentiate between homozygous and heterozygous 2. Recognize specific patterns of Mendelian inheritance b. Clinical features 1. Autosomal dominant disorders a. Demonstrate understanding of inheritance patterns and recurrence risks for autosomal dominant disorders 2. Autosomal recessive disorders a. Demonstrate understanding of inheritance patterns and recurrence risks for autosomal recessive disorders 3. X-linked disorders a. Know the clinical features and diagnosis of fragile X syndrome b. Know the inheritance patterns and recurrence risks for X-linked dominant or recessive disorders 4. Mitochondrial disorders
17 a. Know the maternal/paternal and mitochondrial/chromosomal contributions to inheritance of mitochondrial disorders b. Recognize the clinical features associated with mitochondrial disorders 3. Non-Mendelian inheritance a. Genomic imprinting and parent of origin effects 1. Know the etiology, molecular phenotype, and clinical manifestations of disorders associated with genetic imprinting, such as Prader-Willi syndrome 2. Know the etiology, molecular phenotype, and clinical manifestations of disorders associated with uniparental disomy b. Genetic anticipation (eg, congenital myotonic dystrophy) 1. Recognize the DNA findings, clinical manifestations, and inheritance of trinucleotide repeat syndromes, such as myotonic dystrophy 4. Multifactorial disorders a. Differentiate between multifactorial and Mendelian inheritance b. Know the recurrence risks and factors of multifactorial disorders C. Non-genetic etiologies for congenital defects 1. Environmental factors (See 1.A.4) 2. Maternal metabolic disorders (See 1.A.2) 3. Deformations/disruptions a. Differentiate between a malformation, a deformation, and a disruption b. Recognize the characteristics of the amniotic band syndrome and know its consequences 4. Infections a. Maternal infections (See 1.A.2 and 10.B) 5. Birth defects associated with assisted reproductive technology a. Know the risk of congenital anomalies and chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with assisted reproductive technology D. Evaluation of infants with congenital anomalies (See also 1.B.1) 1. Diagnostic approach a. History 1. Know the components of a complete family history for genetic disorders 2. Know how age at presentation (in utero, neonate, infancy, or later) affects the differential diagnosis of the clinical presentation of genetic disorders 3. Know the relationship between ethnic origin of the parents and risk for specific genetic conditions b. Physical evaluation 1. Recognize the diagnostic implications of single vs. multiple anomalies 2. Know the frequency of minor congenital anomalies 3. Know the frequency of major congenital malformations 4. Recognize the clinical features and know how to diagnose craniofacial anomalies 5. Recognize the clinical features and know how to diagnose and manage congenital anomalies of the upper extremities, such as syndactyly, polydactyly, absent clavicles, absent radius, Sprengel deformity, limb reduction
18 6. Recognize the clinical features and know how to diagnose and manage congenital anomalies of the lower extremities, such as metatarsus adductus, talipes equinovarus, syndactyly, polydactyly, limb reduction 7. Recognize the clinical features and know how to diagnose and manage skeletal dysplasias, such as achondrogenesis, achondroplasia, chondrodermal dysplasia, epiphyseal dysostosis, osteogenesis imperfecta, hypophosphatasia, etc. 8. Know the clinical features and inheritance patterns of common syndromes or associations that can be recognized in the newborn period (eg, VATER association and DiGeorge syndrome) c. Cytogenetic studies 1. Know when to obtain karyotypes on the subject, parents, or other family members 2. Know the indications and limitations of molecular cytogenetic studies (eg, FISH), in the diagnosis of aneuploidy and microdeletion 3. Know the indications for and utility of comparative genomic hybridization studies d. DNA diagnostic studies 1. Know the disorders for which molecular genetic studies are clinically indicated, such as cystic fibrosis, and how to interpret test results e. Other diagnostic studies 1. Know the indications, limitations, and techniques for newborn screening for genetic disorders 6. Nutrition A. Nutrition and growth 1. The fetus a. Changes in body composition 1. Know how body composition changes during fetal growth b. Nutrient requirements (See also 1.A.1) 1. Determine the nutrients and the relative amounts required for normal fetal growth c. Factors that influence intrauterine growth (See also 1.A.1) 1. Know the hormonal factors that affect intrauterine fetal growth 2. Know the maternal, placental, and fetal factors that affect intra- uterine fetal growth 2. Newborn infants a. Changes in body composition 1. Know how body composition changes during postnatal growth and development and understand the effect of prematurity b. Energy requirements kcal/kg/day 1. Know the caloric requirements for optimal postnatal growth of preterm and term infants, accounting for caloric expenditures needed for physical activity and maintenance of body temperature c. Protein requirements 1. Distinguish between indispensable, essential, and non-essential amino acids 2. Know the protein requirements of preterm and full-term infants 3. Know the consequences of feeding preterm infants too little or too much protein
19 4. Know the physiology of protein/amino acid digestion (absorption and metabolism) in newborn infants d. Fat requirements 1. Know the clinical and laboratory features of essential fatty acid deficiency and how to prevent it 2. Distinguish between essential and nonessential fatty acids 3. Know the fat requirements of preterm and full-term infants 4. Know the physiology of fat digestion, absorption, and metabolism in newborn infants e. Carbohydrate requirements 1. Know the physiology of carbohydrate digestion, absorption, and metabolism in newborn infants 3. Large- and small-for-gestational age (LGA - SGA) infants a. Know the postnatal growth patterns of SGA infants b. Recognize the effects of fetal programming and nutrition on the prevalence and types of adult onset disorders c. Know the definitions, causes, clinical features, differential diagnosis, and typical laboratory findings of SGA and LGA infants B. Minerals, vitamins, and trace elements 1. Minerals (for calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium see Section 8.A.5) a. Know the changing requirements of sodium, potassium, and chloride by the neonate at various gestational ages b. Know the changing requirements of calcium and phosphorous by the neonate at various gestational ages 2. Vitamins a. Know the requirements for vitamins in newborn infants, and the differences between preterm and full-term infants b. Know the clinical and laboratory manifestations of deficiencies of water soluble vitamins c. Know the clinical and laboratory manifestations of deficiencies of fat soluble vitamins d. Know the potential adverse effects of pharmacologic use of fat soluble vitamins 3. Trace elements a. Iron (see 14.A.3.b.) b. Other 1. Know the clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and prevention of zinc, copper, selenium, manganese, and chromium deficiency 2. Know the potential toxicities of trace element supplementation in neonatal conditions such as cholestasis and renal insufficiency C. Enteral nutrition 1. Human milk a. Know the differences between the composition of breast milk of the mother of a preterm infant and that of a full-term infant b. Know the differences in the nutritional composition of human milk and infant formula
20 c. Know the immunologic and anti-infective constituents in human milk and their physiologic effects d. Recognize the effects of different methods of processing of human milk, such as freezing, pasteurization, sterilization, and microwaving e. Know that human milk needs to be fortified in order to meet the nutritional needs of preterm infants f. Know the physiology and pathophysiology of human milk production and secretion g. Realize common problems associated with breast milk production in the NICU, and their management h. Know the advantages and disadvantages of the use of donor human milk 2. Formulas a. Know the distribution of nutrients (protein, fat, and carbohydrates) in infant formulas b. Know the mineral and vitamin content of infant formulas c. Know the benefits and risks of formulae that contain non-standard soy proteins d. Know the medical indications for the use of non-standard infant formulas to meet the needs of infants with special health problems e. Know how standard infant formulas are modified in order to meet the needs of preterm infants D. Parenteral nutrition 1. Indications a. Know the indications and advantages of total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and combined enteral and parenteral nutrition 2. Composition and energy content a. Know the nutritional composition of parenteral solutions b. Know the importance of protein and non-protein nutrients in achieving optimal utilization of energy and nitrogen c. Know how to calculate the caloric content of parenteral nutrition solutions 3. Complications of parenteral nutrition (See also 11.D.2) a. Recognize the relationship between the calcium and phosphorus content of parenteral nutrition solutions and osteopenia b. Recognize the association of cholestasis with total parenteral nutrition, know how to manage this, and understand how to diagnose other possible causes c. Recognize the causes and clinical manifestations of catheter complications of parenteral nutrition d. Recognize the causes and clinical manifestations of metabolic complications of parenteral nutrition e. Recognize the potential toxicities associated with the use of parenteral nutrition 7. Water/Salt/Renal (see 13.A.) A. Water and electrolyte metabolism 1. Water metabolism a. Body water compartments during development 1. Know the changes in body water distribution and body fluid composition that occur during fetal and postnatal development b. Methods of monitoring water balance 1. Know how to evaluate neonatal hydration
21 2. Know how to evaluate and manage inadequate or excessive water intake c. Insensible water loss (see also 13.A.) 1. Know physiologic, environmental, and other factors such as thermal environment and gestational age that contribute to insensible water loss (IWL) 2. Know therapeutic interventions that can be used to decrease IWL 3. Be able to estimate IWL in infants at various gestational ages d. Endocrine control of water metabolism 1. Know the specific hormonal factors that influence water balance in newborn infants 2. Know how to diagnose and treat the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of arginine vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) and diabetes insipidus 3. Know the effects of arginine vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) on sodium and water balance e. Management of water balance 1. Know the impact of renal dysfunction on water requirements 2. Know the impact on water requirements of renal and metabolic fluid disorders associated with endocrine dysfunction in infants 2. Electrolyte metabolism a. Know the etiology of electrolyte abnormalities in the neonate b. Recognize the clinical and laboratory manifestations of electrolyte abnormalities in the neonate c. Know how to manage electrolyte abnormalities in the neonate d. Know the causes and differential diagnosis of metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis in infants e. Recognize the clinical and laboratory manifestations of metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis in infants f. Know how to manage metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis in infants B. Normal and abnormal renal function in the fetus and neonate 1. Development of renal function a. Glomerular and tubular function during development 1. Know the changes in glomerular and tubular function that occur during development, including the handling of glucose, sodium, potassium, calcium, bicarbonate, and phosphate 2. Recognize the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of renal tubular acidosis in the neonate 3. Be able to differentiate between proximal, distal, and transient renal tubular acidosis b. Hormonal controls of renal function during development (see 3.C.2.) 1. Know the production sites and actions of various types of vasoactive substances that affect renal function 2. Know the production pathway and the actions of the components of the reninangiotensin system 3. Know the effects of drugs such as cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors, angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors, prostaglandins, and catecholamines on renal function (antenatal and postnatal) c. Evaluation of renal function
22 1. Know how to interpret various renal function tests (eg, urinalysis, creatinine clearance) 2. Understand indications for and methods of antenatal assessment of renal function 2. Abnormal renal development a. Recognize the clinical manifestations of anatomic abnormalities of the kidneys and urinary tract in infants b. Know how to diagnose specific anatomic abnormalities of the kidneys and urinary tract in infants c. Know the recommended supportive and corrective treatment of anatomic abnormalities of the kidneys and urinary tract in infants d. Know how prenatal diagnosis of renal abnormalities affects postnatal management 3. Acquired renal disease a. Renal vascular thrombosis (see also 14.C.2.b.) 1. Know the etiology, clinical manifestations, laboratory features, differential diagnosis, and management of renal vein thrombosis 2. Know the etiology, clinical manifestations, laboratory features, and management of renal artery thrombosis b. Hypertension (see 3.D.2.) c. Acute renal failure 1. Know the causes of renal failure in the neonate 2. Know the clinical manifestations, imaging, and laboratory features of renal failure in the neonate 3. Know the management of renal failure in the neonate, including indications for and complications of the use of hemofiltration, peritoneal dialysis, and hemodialysis d. Urinary tract infections (See 10.A.10) e. Diuretics (see also 3.F.2) 1. Know the mechanism of action of commonly used diuretic drugs in infants 8. Endocrine/Metabolic/Thermal A. Endocrine and metabolism 1. Normal and abnormal sexual differentiation a. Normal sexual differentiation 1. Know normal fetal sexual differentiation b. Abnormal sexual differentiation 1. Disorders of sexual differentiation a. Differentiate among disorders of testicular hormone synthesis or action b. Know the etiology of abnormal sexual differentiation c. Know the diagnostic approaches to and management of abnormal sexual differentiation d. Know the etiology of and diagnostic approaches to an infant with ambiguous genitalia, not including congenital adrenal hyperplasia e. Know the clinical manifestations, laboratory features, and therapeutic management of an infant with ambiguous genitalia, not including congenital adrenal hyperplasia 2. Other disorders of sexual differentiation
23 a. Know the causes of micropenis, including pituitary deficiency b. Know how to evaluate and manage an infant with micropenis c. Know how to evaluate and manage an infant with hypospadias and epispadias d. Know how to evaluate and manage an infant with cryptorchidism 2. Adrenal disorders a. Recognize the clinical manifestations and laboratory features of the various types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia b. Define the appropriate therapy for the various types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia c. Understand the basic enzymatic defects involved in the various types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia 3. Thyroid disorders a. Embryology and physiology 1. Know the physiological roles of the hormones and other proteins involved in the regulation of thyroid function 2. Know the relationship between fetal and maternal thyroid physiology 3. Know the embryology and normal physiological function of the thyroid gland b. Tests of thyroid function 1. Know the proper use of laboratory tests (including screening tests) in the diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction c. Congenital hypothyroidism 1. Know the etiology and clinical manifestations of congenital hypothyroidism 2. Know the laboratory features and approach to therapy of congenital hypothyroidism d. Transient disorders of thyroid function 1. Know how to evaluate and manage the causes of transient hypothyroidism in newborn infants e. Thyrotoxicosis 1. Identify the etiology, clinical manifestations, laboratory features, and management of neonatal thyrotoxicosis 4. Glucose metabolism a. Normal fetal and neonatal carbohydrate metabolism 1. General a. Know the amino acid substrates for gluconeogenesis b. Know the fuels used for brain metabolism c. Know the relationship of maternal blood glucose to fetal glucose uptake and metabolism d. Know the normal range of endogenous glucose production in term and preterm infants 2. Hypoglycemia a. Know the causes (including hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia) of neonatal hypoglycemia syndromes b. Recognize the clinical and laboratory features of neonatal hypoglycemia c. Recognize the approach to therapy and prevention of neonatal hypoglycemia d. Know the potential sequelae of neonatal hypoglycemia
Lectures 4 Early fetal assessment, screening, ultrasound and treatment modalities during pregnancy. II. Asphyxia and Resuscitation (3 lectures)...
 Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
The high risk neonate
 The high risk neonate Infant classification by gestational (postmenstrual) age Preterm. Less than 37 completed weeks (259 days). Term. Thirty-seven to 416/7 weeks (260-294 days). Post-term. Forty-two weeks
The high risk neonate Infant classification by gestational (postmenstrual) age Preterm. Less than 37 completed weeks (259 days). Term. Thirty-seven to 416/7 weeks (260-294 days). Post-term. Forty-two weeks
Hyaline membrane disease. By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg
 Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
 Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
Neonatal Resuscitation. Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology
 Neonatal Resuscitation Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology Recognize complications Maternal-fetal factors Maternal DM PIH Chronic HTN Previous stillbirth Rh sensitization Infection Substance abuse/certain
Neonatal Resuscitation Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology Recognize complications Maternal-fetal factors Maternal DM PIH Chronic HTN Previous stillbirth Rh sensitization Infection Substance abuse/certain
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline.
 Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Hypoxic-İschemic Encephalopathy Encephalopathy due to hypoxic-ischemic injury [Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Hypoxic-İschemic Encephalopathy Encephalopathy due to hypoxic-ischemic injury [Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals
 Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
List of Chapters. 5. Care of the sick child Evidence-based pediatrics (page 77 to 80)
 Illustrated Textbook of Paediatrics, 4th Edition Tom Lissauer, and Graham Clayden, 2012 List of Chapters 1. The child in society 2. History and examination 3. Normal child development, hearing and vision
Illustrated Textbook of Paediatrics, 4th Edition Tom Lissauer, and Graham Clayden, 2012 List of Chapters 1. The child in society 2. History and examination 3. Normal child development, hearing and vision
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy
 An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
ADMISSION/DISCHARGE FORM FOR INFANTS BORN IN 2019 DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS AND
 TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
Diabetes in Pregnancy
 Disclosure Diabetes in Pregnancy I have no conflicts of interest to disclose Jennifer Krupp, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine St. Marys Hospital/SSM Health Madison, WI Objectives Classification of Diabetes Classifications
Disclosure Diabetes in Pregnancy I have no conflicts of interest to disclose Jennifer Krupp, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine St. Marys Hospital/SSM Health Madison, WI Objectives Classification of Diabetes Classifications
How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite
 Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Maternal and Fetal Physiology
 Background Maternal and Fetal Physiology Anderson Lo, DO Fellow, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine SEMCME Fetal Assessment Course July 20, 2018 Oxygen pathway Mother Placenta
Background Maternal and Fetal Physiology Anderson Lo, DO Fellow, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine SEMCME Fetal Assessment Course July 20, 2018 Oxygen pathway Mother Placenta
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes
 NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology
 Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
Medical Complications of Pregnancy
 Medical Complications of Pregnancy Systems Cardiovascular Pulmonary Endocrine Gastrointestinal Urologic Neurologic Cardiovascular System Physiologic anemia 3:1 increase of plasma volume:rbc mass Treat
Medical Complications of Pregnancy Systems Cardiovascular Pulmonary Endocrine Gastrointestinal Urologic Neurologic Cardiovascular System Physiologic anemia 3:1 increase of plasma volume:rbc mass Treat
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate. Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics
 Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Infection. Risk factor for infection ACoRN alerting sign with * Clinical deterioration. Problem List. Respiratory. Cardiovascular
 The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology
 Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
COURSE OUTLINE Pathophysiology
 Butler Community College Health, Education, and Public Services Division Denise LaKous Revised Spring 2014 Implemented Fall 2015 Textbook Update Fall 2015 COURSE OUTLINE Pathophysiology Course Description
Butler Community College Health, Education, and Public Services Division Denise LaKous Revised Spring 2014 Implemented Fall 2015 Textbook Update Fall 2015 COURSE OUTLINE Pathophysiology Course Description
Product Catalog. Pediatric Learning Solutions. Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association.
 Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara
 Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
Emergency Department Suite
 Emergency Department Suite This suite of Pediatric Learning Solutions (PLS) online courseware and curriculums provides 24/7 access to the foundational knowledge and just-in-time job aids clinicians working
Emergency Department Suite This suite of Pediatric Learning Solutions (PLS) online courseware and curriculums provides 24/7 access to the foundational knowledge and just-in-time job aids clinicians working
General Principles: 5% 7%
 General Principles: 5% 7% International Foundations of Medicine Clinical Science Exam Blueprint Infancy and Childhood (normal growth and development) Adolescence (sexuality, separation from parents/autonomy,
General Principles: 5% 7% International Foundations of Medicine Clinical Science Exam Blueprint Infancy and Childhood (normal growth and development) Adolescence (sexuality, separation from parents/autonomy,
TRAINING NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS
 TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
Adult Congenital Heart Disease Certification Examination Blueprint
 Adult Congenital Heart Disease Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the
Adult Congenital Heart Disease Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Pathophysiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Pathophysiology Course Design 2016-2017 Course Information Division Allied Health Course Number HCE 240 Title Human Pathophysiology Credits 4 Developed by Dr. Robert Richman
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Pathophysiology Course Design 2016-2017 Course Information Division Allied Health Course Number HCE 240 Title Human Pathophysiology Credits 4 Developed by Dr. Robert Richman
Hypoglycemia. Objectives. Glucose Metabolism
 Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
The Blue Baby. Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin
 The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care. Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN. Other. Other Diseases
 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period.
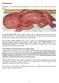 Prematurity Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period. Low birth weight (LBW): (birth weight
Prematurity Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period. Low birth weight (LBW): (birth weight
Diuretic Use in Neonates
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
There are four general types of congenital lung disorders:
 Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate. Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA
 Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide. 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia. Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year
 1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
Nutrition in the premie World
 SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
Legal aspects in accidents and neglect.
 Al-Al Bayt University Princess Salma Faculty of Nursing Adult Health nursing Course Title :Child Health Nursing Course Number :1001341 Credit Hours :3 Pre requisite :1001222 Placement : Instructor:,, Course
Al-Al Bayt University Princess Salma Faculty of Nursing Adult Health nursing Course Title :Child Health Nursing Course Number :1001341 Credit Hours :3 Pre requisite :1001222 Placement : Instructor:,, Course
Hypotension in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Hypotension in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/ Neonatal
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Hypotension in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/ Neonatal
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
Malignancy ; 191.6; Malignant neoplasm of brain
 APPENDIX 15 Comparison of ICD-9 Diagnostic Codes Used to Identify Children with Life-Threatening or Life-Limiting or Comple Chronic Conditions By Five CHI PACC Programs ICD-9 Category ICD-9 Description
APPENDIX 15 Comparison of ICD-9 Diagnostic Codes Used to Identify Children with Life-Threatening or Life-Limiting or Comple Chronic Conditions By Five CHI PACC Programs ICD-9 Category ICD-9 Description
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials
 Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident. Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents
 Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents Prerequisites: Successful completion of NRP course with certification
Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents Prerequisites: Successful completion of NRP course with certification
1
 1 2 3 RIFAI 5 6 Dublin cohort, retrospective review. Milrinone was commenced at an initial dose of 0.50 μg/kg/minute up to 0.75 μg/kg/minute and was continued depending on clinical response. No loading
1 2 3 RIFAI 5 6 Dublin cohort, retrospective review. Milrinone was commenced at an initial dose of 0.50 μg/kg/minute up to 0.75 μg/kg/minute and was continued depending on clinical response. No loading
I- Transformation of Food into nutrients: Digestion - Our Food. - Kinds of food. - Food tests. - Chemical transformation of food
 CURRICULUM Grade-9- Biology Cycle:Intermediate Textbook: Life and Earth Science (National Textbook) UNITS Learning Outcomes I- Transformation of Food into nutrients: Digestion - Our Food - Kinds of food
CURRICULUM Grade-9- Biology Cycle:Intermediate Textbook: Life and Earth Science (National Textbook) UNITS Learning Outcomes I- Transformation of Food into nutrients: Digestion - Our Food - Kinds of food
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Objectives. Introduction 11/2/2015
 Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
APR-DRG Description Ave Charge
 Abdominal Pain 16,500.25 2.8 6,000.09 Acute & Subacute Endocarditis 15,339.30 3.0 5,113.10 Acute Myocardial Infarction 17,687.46 2.6 6,802.87 Alcohol Abuse & Dependence 19,126.64 4.2 4,553.96 Alcoholic
Abdominal Pain 16,500.25 2.8 6,000.09 Acute & Subacute Endocarditis 15,339.30 3.0 5,113.10 Acute Myocardial Infarction 17,687.46 2.6 6,802.87 Alcohol Abuse & Dependence 19,126.64 4.2 4,553.96 Alcoholic
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function. GI Tract and Kidneys
 Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
4/19/2018. St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT
 St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2
 2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
FHR Monitoring: Maternal Fetal Physiology
 FHR Monitoring: Maternal Fetal Physiology M. Sean Esplin, MD and Alexandra Eller, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Intermountain Healthcare University of Utah Health Sciences Center Disclosures I have no financial
FHR Monitoring: Maternal Fetal Physiology M. Sean Esplin, MD and Alexandra Eller, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Intermountain Healthcare University of Utah Health Sciences Center Disclosures I have no financial
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care
 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Resuscitation 2 When To Resuscitate Need usually related Combination of Can occur in 3 Causes of Fetal Asphyxia 1 4 Apnea Hypoxia Stimulates chemoreceptors & baroreceptors
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Resuscitation 2 When To Resuscitate Need usually related Combination of Can occur in 3 Causes of Fetal Asphyxia 1 4 Apnea Hypoxia Stimulates chemoreceptors & baroreceptors
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport. Relevant Disclosure. Learning Objectives
 Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
8/20/12. Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate.
 Sharon Rush MSN NNP-BC Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate. To maintain correct body temperature range in order to: Reduce oxygen consumption Reduce calorie expenditure Maximize metabolic
Sharon Rush MSN NNP-BC Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate. To maintain correct body temperature range in order to: Reduce oxygen consumption Reduce calorie expenditure Maximize metabolic
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 413 Active treatment, survival rate and, 294 296 Air displacement plethysmography, 397 Airway obstruction, 309 310 Aluminum
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 413 Active treatment, survival rate and, 294 296 Air displacement plethysmography, 397 Airway obstruction, 309 310 Aluminum
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
By Dr.Asmaa Al sanjary
 By Dr.Asmaa Al sanjary Preterm delivery is defined by a birth occurring before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Prematurity is multifactorial and its incidence has increased during the last decade in most
By Dr.Asmaa Al sanjary Preterm delivery is defined by a birth occurring before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Prematurity is multifactorial and its incidence has increased during the last decade in most
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Dr. Fawaz Amin Saad
 Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Dr. Fawaz Amin Saad Senior Consultant OB/GYN, Al-Hayat Medical Center, Doha, Qatar DISCLOSURE OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST I am a full-time Employee at Al-Hayat Medical Center.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Dr. Fawaz Amin Saad Senior Consultant OB/GYN, Al-Hayat Medical Center, Doha, Qatar DISCLOSURE OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST I am a full-time Employee at Al-Hayat Medical Center.
Obstetrics and HIV An Update. Jennifer Van Horn MD University of Utah
 Obstetrics and HIV An Update Jennifer Van Horn MD University of Utah Obstetrics and HIV Perinatal transmission Testing Antiretroviral therapy Antepartum management Intrapartum management Postpartum management
Obstetrics and HIV An Update Jennifer Van Horn MD University of Utah Obstetrics and HIV Perinatal transmission Testing Antiretroviral therapy Antepartum management Intrapartum management Postpartum management
Neonatal Seizure. Dr.Nawar Yahya. Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan. Supervised by:
 Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
Diabetes: The Effects of Maternal Diabetes on Fetal Development and Outcomes Sherrie McElvy, MD May 18, 2016
 Diabetes: The Effects of Maternal Diabetes on Fetal Development and Outcomes Sherrie McElvy, MD May 18, 2016 Medical Director Sweet Success Sutter Medical Center Sacramento Perinatal Associates of Sacramento
Diabetes: The Effects of Maternal Diabetes on Fetal Development and Outcomes Sherrie McElvy, MD May 18, 2016 Medical Director Sweet Success Sutter Medical Center Sacramento Perinatal Associates of Sacramento
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen ultrasound of, 521 522 Abdominal diseases ultrasound in evaluation of, 529 540 gastrointestinal tract disease, 529 536 urinary tract
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen ultrasound of, 521 522 Abdominal diseases ultrasound in evaluation of, 529 540 gastrointestinal tract disease, 529 536 urinary tract
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 6.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 17, 26, 27, 31, 33, 37, 40 42, 44, 45, 51, 58 6.2 Describe the basic roles and structures
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 6.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 17, 26, 27, 31, 33, 37, 40 42, 44, 45, 51, 58 6.2 Describe the basic roles and structures
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Genetics
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
Management of MDR TB in special situations. Dr Sarabjit Chadha The Union
 Management of MDR TB in special situations Dr Sarabjit Chadha The Union MDR TB in special situations Pregnancy Breastfeeding Contraception Renal Insufficiency Diabetes Pregnancy and TB Pregnancy is not
Management of MDR TB in special situations Dr Sarabjit Chadha The Union MDR TB in special situations Pregnancy Breastfeeding Contraception Renal Insufficiency Diabetes Pregnancy and TB Pregnancy is not
Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview
 Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview Dr Ornella Lincetto, WHO Geneve Milano, 11June 2007 Vilka är Personality egenskaper med den astrologiska Tvillingarna? Objective of
Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview Dr Ornella Lincetto, WHO Geneve Milano, 11June 2007 Vilka är Personality egenskaper med den astrologiska Tvillingarna? Objective of
The Pharmacology of Hypotension: Vasopressor Choices for HIE patients. Keliana O Mara, PharmD August 4, 2018
 The Pharmacology of Hypotension: Vasopressor Choices for HIE patients Keliana O Mara, PharmD August 4, 2018 Objectives Review the pathophysiology of hypotension in neonates Discuss the role of vasopressors
The Pharmacology of Hypotension: Vasopressor Choices for HIE patients Keliana O Mara, PharmD August 4, 2018 Objectives Review the pathophysiology of hypotension in neonates Discuss the role of vasopressors
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT Rev. 2/2011 These
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT Rev. 2/2011 These
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
Internal Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint
 Internal Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint What Does the Examination Cover? The exam is designed to evaluate the extent of the candidate s knowledge and clinical judgment in the areas in which
Internal Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint What Does the Examination Cover? The exam is designed to evaluate the extent of the candidate s knowledge and clinical judgment in the areas in which
SHOCK. Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital
 SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
MEDICAL FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY QUESTION FOR ORAL PART OF EXAM MEDICAL STUDENTS
 MEDICAL FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY QUESTION FOR ORAL PART OF EXAM MEDICAL STUDENTS GENERAL PART (1 question) 1. Health and disease as a dynamic process 2. Stages of the disease development 3.
MEDICAL FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY QUESTION FOR ORAL PART OF EXAM MEDICAL STUDENTS GENERAL PART (1 question) 1. Health and disease as a dynamic process 2. Stages of the disease development 3.
GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP
 GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP University of New Mexico 1. General Description: UNM MFM fellows rotate through genetics during their PGY5 and PGY7 years. The PGY5 fellow
GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP University of New Mexico 1. General Description: UNM MFM fellows rotate through genetics during their PGY5 and PGY7 years. The PGY5 fellow
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education
 Date Adopted: July 1, 1980 Date Reviewed: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY
Date Adopted: July 1, 1980 Date Reviewed: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY
Drugs used in obstetrics
 Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
Experience. Initials Medical Staffing Network Rev. 06/15 F01201 NNICU 2 of 5
 Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
AMERICAN BOARD OF MEDICAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS
 AMERICAN BOARD OF MEDICAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS Logbook Guidelines for Certification in Clinical Genetics and Genomics for the 2017 Examination as of 10/5/2015 Purpose: The purpose of the logbook is to
AMERICAN BOARD OF MEDICAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS Logbook Guidelines for Certification in Clinical Genetics and Genomics for the 2017 Examination as of 10/5/2015 Purpose: The purpose of the logbook is to
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry
 Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
1. Changed level of a certain hormone Stimulation of the oxygen consumption 3. Decoupling of oxidative phosphorylation 2.
 1. How can endocrine disorders be classified? 1. Hereditary, acquired 2. Active, passive 3. Uncompensated, overcompensated 4. Primary, secondary 5.1, 4 6.1, 2, 3, 4. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 2. Which is the MAIN
1. How can endocrine disorders be classified? 1. Hereditary, acquired 2. Active, passive 3. Uncompensated, overcompensated 4. Primary, secondary 5.1, 4 6.1, 2, 3, 4. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 2. Which is the MAIN
NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives Competency 1. Patient Care: Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and
NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives Competency 1. Patient Care: Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and
NurseAchieve. CHAPTERS INCLUDED IN THE NURSEACHIEVE COMPREHENSIVE NCLEX REVIEW NURSING SKILLS AND FUNDAMENTALS:
 NurseAchieve www.nurseachieve.com CHAPTERS INCLUDED IN THE NURSEACHIEVE COMPREHENSIVE NCLEX REVIEW NCLEX TEST STRATEGIES: NCLEX EXAM OVERVIEW TEST TAKING STRATEGIES NURSING SKILLS AND FUNDAMENTALS: ADMINISTRATION
NurseAchieve www.nurseachieve.com CHAPTERS INCLUDED IN THE NURSEACHIEVE COMPREHENSIVE NCLEX REVIEW NCLEX TEST STRATEGIES: NCLEX EXAM OVERVIEW TEST TAKING STRATEGIES NURSING SKILLS AND FUNDAMENTALS: ADMINISTRATION
Gestational Diabetes. Benjamin Byers, D.O., FACOG Center for Maternal and Fetal Care Bryan Physician Network
 Gestational Diabetes Benjamin Byers, D.O., FACOG Center for Maternal and Fetal Care Bryan Physician Network Outline Definition Prevalence Risk factors complications Diagnosis Management Nonpharmacologic
Gestational Diabetes Benjamin Byers, D.O., FACOG Center for Maternal and Fetal Care Bryan Physician Network Outline Definition Prevalence Risk factors complications Diagnosis Management Nonpharmacologic
Genetic Disorders. PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders. Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test
 Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
