TOXIC EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE ON RABBIT KIDNEY
|
|
|
- Cathleen Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 38 Fluoride Vol. 35 No Research Report TOXIC EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE ON RABBIT KIDNEY A Shashi, a JP Singh, SP Thapar b Patiala, India Summary: The purpose of this study was to assess renal damage in experimental fluorosis. Young albino rabbits were injected with 5, 10, 20, and 50 mg NaF/kg body weight/day for fifteen weeks and then sacrificed. No significant clinical signs of toxicity were found in animals exposed to the lowest dose. At the higher doses, however, the cytoachitecture of the kidneys exhibited increasing amounts of cloudy swellings, degeneration of tubular epithelia, tissue necrosis, extensive vacuolization in renal tubules, hypertrophy and atrophy of glomeruli, exudation, interstitial oedema, and interstitial nephritis. These changes in the kidneys result in impaired renal function in chronic fluoride intoxication. Keywords: Albino rabbits, Fluorosis, Kidney pathology, Renal damage, Sodium fluoride. INTRODUCTION Kidneys are among the most sensitive body organs in their histopathological and functional responses to excessive amounts of fluoride. 1 They are the primary organs concerned with excretion and retention of fluoride and thus are generally involved in chronic fluoride intoxication. In humans, only a few reports 2-4 pertaining to kidney involvement in endemic fluorosis are available. Kono et al 6 reported impaired renal functions in fluoride-exposed workers. In contrast to cases of acute intoxication, 5 the records of only a few autopsy reports of patients dying of chronic fluoride intoxication are traceable in the literature. 4,7 No renal abnormality ascribed to fluoride was found at the autopsy examination of an elderly woman who for 30 years had consumed water containing 8 ppm fluoride. 8 In three autopsy cases Reddy et al 4 found multiple pyaemic abscesses in the fluorotic kidneys which grossly appeared like pyelonephritic kidneys with dilated ureters. In rats intoxicated with 190, 210, 452, 904, and 1356 ppm fluoride in their drinking water, renal injury was reported. 2 Other changes included tubular degeneration, inflammation, fibrosis, parenchymatous nephritis, cloudy swellings, and dilatation of convoluted tubules Shupe et al 15 reported renal degeneration and mineralization in cattle ingesting high fluoride levels. The aim of the present study was to examine histopathological effects of sodium fluoride on the kidneys of albino rabbits. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals: 60 young male and female albino rabbits weighing g each were used. The animals were maintained on standard laboratory rabbit chow. Water was given ad libitum. a For Correspondence: Dr Aggarwal Shashi, Department of Zoology, Punjabi University, Patiala , Punjab, India. aggarwalshashi@rediffmail.com; b Department of Anatomy, Dayanand Medicial College and Hospital, Ludhiana, India.
2 Toxic effects of fluoride on rabbit kidney 39 Experimental design: The animals were divided equally into five groups. Doses of 5, 10, 20, and 50 mg NaF/kg bw/day in 1 ml of double distilled water were injected subcutaneously into four groups for fifteen weeks. Control: The control animals were administered 1 ml of double distilled water/kg bw/day for the same period. Assessment of renal damage: All the animals were killed by ether anaesthesia, and the kidneys were fixed with Carnoy s fixative and Bouin s fluid for histopathological examination. The tissue was dehydrated in tertiary butyl alcohol, cleared in amyl acetate, and embedded in paraffin. Serial sections were cut at 7 µm and stained with iron haemotoxylin and eosin. RESULTS On gross examination the kidneys of the fluoridated rabbits appeared shrunken as compared to those of the controls. The renal changes varied with the concentration of fluoride but were not seen in any of the control rabbits (Figure 1). Figure 1. Photomicrograph showing the kidney of a control rabbit with normal microscopic features x 100. In the animals treated with 5 mg NaF/kg bw/day no abnormalities in the convoluted tubules, glomeruli, and interstitial tissue were detected. Moreo-
3 40 Shashi, Singh, Thapar ver, the malpighian corpuscles did not show any exudation of plasma into sub-cellular spaces. In rabbits treated with 10 mg NaF/kg bw/day, cells lining the convoluted tubules showed cloudy swellings and dim appearance (Figure 3) as compared to the controls (Figure 1). The glomeruli exhibited hypertrophic changes (Figure 3) as compared to the controls (Figure 2). The glomerular basement membrane did not show any thickening or periglomerular fibrosis. Interstitial nephritis was well marked (Figure 4) with 4-6 large vacuoles (Figure 5). Figure 2. Photomicrograph showing normal convoluted tubules (CT) and glomeruli (G) in the kidney of a control rabbit x 400. In animals in the 20 mg NaF group, convoluted tubules showed cloudy swellings and extensive vacuole formation. Due to vacuolization, the cell nucleus was pushed towards the basement membrane. In some places the cell showed necrosis (Figure 6). The glomeruli were hyperatrophied and markedly lobulated (Figure 7). The glomerular membrane was slightly thickened. There was round cell infiltration in the interstitial tissue, and cell necrosis was evident in the interstitium along with interstitial oedema (Figure 8).
4 Toxic effects of fluoride on rabbit kidney 41 Figure 3. Photomicrograph of the kidney of a rabbit treated with 10 mg NaF/kg bw/day showing cloudy swellings in convoluted tubules and hyperatrophied glomeruli x 400. Figure 4. Interstitial nephritis in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 10 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 100.
5 42 Shashi, Singh, Thapar Figure 5. Photomicrograph showing formation of large vacuoles in the interstitium of the kidney of a rabbit treated with 10 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 400. Figure 6. Convoluted tubules showing cloudy swellings, vacuolization, and cell necrosis in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 20 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 400.
6 Toxic effects of fluoride on rabbit kidney 43 Figure 7. Hyperatrophied glomeruli in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 20 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 400. Figure 8. Interstitial oedema in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 20 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 100.
7 44 Shashi, Singh, Thapar In the animals treated with 50 mg NaF/kg bw/day there was extensive cellular necrosis leading to degeneration of convoluted tubules (Figure 9). The remaining cells showed vacuolization of cytoplasm owing to which the cell nuclei were pushed to the basement membranes (Figure 10). The convoluted tubules showed cloudy swellings, tubular lumen was widened, nuclei showed disintegration, and there was exudation in the tubules. The glomeruli also exhibited atrophy and disintegration of cells, and formation of vacuoles was seen in the glomerular cells. The nuclei likewise showed disintegration, and the basement membrane was thickened in hyperatrophied glomeruli. Interstitial nephritis (Figure 11) and interstitial oedema and necrosis of cells in the interstitium (Figure 12) were most pronounced. Figure 9. Cell necrosis in the convoluted tubules and exudation in the tubules in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 50 mg/kg bw/day x 400.
8 Toxic effects of fluoride on rabbit kidney 45 Figure 10. Atrophied glomeruli and formation of vacuoles and degeneration of nuclei in the glomeruli in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 50 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 400. Figure 11. Interstitial nephritis in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 50 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 100.
9 46 Shashi, Singh, Thapar Figure 12. Necrosis and interstitial oedema in the kidney of a rabbit treated with 50 mg NaF/kg bw/day x 400. DISCUSSION In renal fluoride studies there are marked discrepancies in the histological findings of the kidney which can be attributed in part to differences in the fluoride compounds used, the method of their administration, and the various species of the animals used. During the present investigation, the kidneys of rabbits treated with 10, 20, and 50 mg NaF/kg bw/day showed cloudy swellings, interstitial oedema, and hypertrophy and atrophy of glomeruli. The appearance of cloudy swellings remained almost constant. The intensity of such swellings has been observed by others to increase with increasing dose of fluoride. 16,17 In monkeys treated with 80 ppm fluoride in their drinking water for 16 weeks, cloudy swellings and albuminuria were reported. 18 Ogilvie 12 likewise found oedema of the connective tissue between the convoluted tubules in rats ingesting 340 ppm fluoride for 100 days. Chronic fluoride intoxication at a level of 14 mg F/kg bw/day and higher has been claimed to result in a renal lesions. 2,10 Rats consuming 50 to 100
10 Toxic effects of fluoride on rabbit kidney 47 ppm NaF in the diet for 20 months developed dark, shrunken, and nodulated kidneys. In evidence were vascular, glomerular, and tubular degeneration leading to interstitial fibrosis. An increase in the amount of fibrous tissue in the renal lesions was also induced by chronic fluoride administration. 10 Such an increase in the amount of fibrous tissue was not found during the present investigation. However, other changes seen here, like vacuolization of the cells lining the convoluted tubules, widening of lumen of tubules, hypertrophic and lobulated glomeruli, interstitial nephritis, and varying degree of degeneration of tubular epithelium, have also been detected by others. 11,19 Shupe et al 20 found fatty degeneration and focal calcification in the stroma and tubules of the bovine kidney with bone fluoride as high as 900 ppm. Focal calcification in the tubules was not found during the present studies. According to Kawahara, 13 rabbits treated with mg fluoride/kg bw/day orally for 14 to 150 days, developed inflammatory kidney changes in the glomeruli with increased cellularity, capillary hyperaemia, hypertrophy or atrophy, tubular degeneration, cloudy swellings and protein casts or blood in the lumen. In the same report, in his study on rats ingesting ppm fluoride in drinking water for days, he observed progressive fibrosis, round cell infiltration, changes in the glomeruli, and tubular degeneration in the groups given 100 and 375 ppm fluoride. Ramseyer et al 21 also recorded hypertrophy and hyperplasia in the tubules of the rats given fluoride in the drinking water as 1, 5, and 10 ppm for 500 days. Pindborg 22 observed that in rats ingesting 0.05% NaF in their diet for days flattening of the epithelium of distal convoluted tubules and reduction in the size of the cytoplasm occurred, thereby causing the nuclei to project into the lumen. Interstitial renal oedema and inflammatory changes were also present. Kidneys of rats fed 0.05% NaF in their diet exhibited a hobnailed appearance. 23 There was extensive dilatation of the Henle loops and convoluted tubules. Focal fibrosis was responsible for the hobnailed appearance of kidneys. 24 However, such changes were not seen in the present study. Taylor et al 25 noted necrosis of the tubular cells and dilatations of the tubules in the corticomedullary region in rats given 200 to 500 ppm fluoride for 5 days. Bosworth and McCay 26 found that rats given 1, 2, 6, and 10 ppm fluoride up to 520 days of age developed casts in the cortical and medullary region and the hyperchromatism in the convoluted tubules. The nuclei were larger in diameter and cells appeared plump. There was also accumulation of mononuclear leukocytes, and lymphocytes termed as 'Nephritis' were present in the cortex and around the blood vessels. Nephritis occurred in the interstitial tissue of the kidneys of fluoridated rabbits during the present study. Fluoride-induced hyperplasia and hypertrophy of renal tubules have also been reported in hamsters. 27
11 48 Shashi, Singh, Thapar Kour and Singh 14 observed that mice fed with 10, 500, and 1000 ppm NaF for 3 months had shrunken kidneys showing subcapsular indentation on the surface. They recorded cloudy swellings, degeneration of tubular cells, dilatation in the convoluted tubules, patchy areas of necrosis of tubular cells, atrophy of glomeruli, and interstitial infiltration of round cells. Similar changes were seen in the fluoridated rabbits during the present investigation. Rioufol et al 28 found that guinea pigs fed with 20 ppm NaF in their diet for 12 months incurred dilatation of the proximal convoluted tubules with inflammatory infiltration in the cortical region. The glomeruli became swollen with thickening of the walls of Bowman's capsule. In the tubules cystic dilatation occurred along with hyaline cylinders. On the other hand, some workers failed to find any gross renal change in rats and squirrel monkeys. 29 de Camargo and Merzel 30 treated rats with 1 to 100 ppm fluoride in drinking water for 180 days but did not report any abnormality with respect to weight gain, morphology, and macroscopic appearance of kidneys as compared to the controls. From the histopathological changes seen here in kidneys in acute and chronic fluoride intoxication, it is clear that fluoride does lead to subtle renal damage which manifests itself in the form of cloudy swellings of the convoluted tubules, vacuolization and necrosis of tubules, hypertrophy and atrophy of glomeruli, interstitial oedema, and interstitial nephritis. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Financial assistance from the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, Government of India is gratefully acknowledged. REFERENCES 1 Hodge HC, Smith FA. Chronic effects of inorganic fluorides. In: Simons JH, editor. Fluorine Chemistry. Vol IV. New York and London: Academic Press, 1965: Roholm K. Fluorine intoxication. A clinical-hygienic study with a review of the literature and some experimental investigations. London: HK Lewis and Co Ltd, 1937: Shortt HE, McRobert GR, Banard TW, Nayar ASM. Endemic fluorosis in the Madras Presidency. Ind J Med Assoc 1937;25: Reddy DD, Mallikhagunarao SG, Sharda D. Endemic fluorosis. J Ind Med Assoc 1969;53: Pribilla O. Four cases of acute silicofluoride intoxication: clinical and pathological findings. Fluoride 1968;1: Kono K, Yoshida Y, Watanabe M, Usuda K, Shimahara M, Harada A, et al. Fluoride metabolism and kidney function: Health care of fluoride exposed workers. Fluoride 1995;28(1):40. 7 Singh A, Jolly SS, Bansal BC. Skeletal fluorosis and its neurological complications. Lancet 1961;I:
12 Toxic effects of fluoride on rabbit kidney 49 8 Leone NC, Liberman J, Geiser PB. Effect of the absorption of fluoride III Findings in tissues of persons drinking water of varying fluoride concentrations. AMA Arch Ind Health 1960;21: Phillips PH, Lamb AR. Histology of certain organs and teeth in chronic toxicosis due to fluorine. Arch Pathol 1934;17: Bond AM, Murray MM. Kidney function and structure in chronic fluorosis. Brit J Exp Pathol 1952;33: Wadhwani TK, Ramaswami AS. Pathological changes in the tissues of rats and monkeys in F toxicosis. J Ind Inst Sci 1953;35: Ogilvie AL. Histological findings in the kidney, liver, pancreas, adrenal and thyroid gland of the rat following administration of sodium fluoride. J Dent Res 1953;32: Kawahara H. Experimental studies on the changes of the kidney due to fluorosis. Part 3. Morphological studies on the changes of the kidney of rabbits and growing albino rats due to sodium fluoride. Shikoku Acta Med 1956;8: Kour K, Singh J. Histological findings in kidneys of mice following sodium fluoride administration. Fluoride 1980;13 (4): Shupe JL, Bruner RH, Seymour JL, Alden CL. The pathology of chronic bovine fluorosis. Toxicol Pathol 1992;20: Machle W, Jhamann F, Kitzmiller K, Cholak J. The effect of the inhalation of hydrogen fluoride I. The response following exposure to high concentrations. J Indust Hyg 1934;16: Geiger JC. Poisoning due to ingestion of a mixture of sodium bicarbonate and sodium fluoride. Calif West Med 1936;44: Pandit CG, Raghavachari TNS, Rao DS, Krishnamurthi V. Endemic fluorosis in south India: A study of the factors involved in the production of mottled enamel in children and severe bone manifestations in adults. Ind J Med Res 1940;28: Phillips PH, Hart EB, Bohstedt G. Chronic toxicosis in dairy cows due to ingestion of fluorine. Univ Wisconsin Agri Exp Stat Res Bull 1934; No. 123 pp Shupe JL, Miner ML, Binns W, Greenwood OA, Nielson HM, Stoddard GE et al. Pathology of chronic bovine fluorosis. Proc Amer Vet Med Assoc 1955; 92: Ramseyer WF, Smith CAH, McCay CM. Effect of sodium fluoride administration on body changes in old rats. J Gerontol 1957;12: Pindborg JJ. The effect of 0.05 percent dietary sodium fluoride in the rat kidney. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 1957;13: Hauck HM, Steenbock H, Parsons HT. Is the effect of fluorine on teeth produced through the parathyroid gland? Am J Physiol 1933b;103: Lindermann G, Pindborg JJ, Paulsen H. Recovery of the rat kidney in fluorosis. AMA Arch Path 1959;67: Taylor JM, Scott JK, Maynard EA, Smith FA, Hodge HC. Toxic effects of fluoride on the rat kidney I. Acute injury from single large doses. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1961;3: Bosworth EB, McCay CM. Pathological studies of rat kidneys. Absence of effects ascribed to fluoride following long term ingestion of drinking water containing fluoride. J Dent Res 1962;41:
13 50 Shashi, Singh, Thapar 27 Bersotti G, Frugis S. Morphological research in fluorotic kidneys and liver of experimental animals. Rass Int Stomatol Prat 1963;14: Rioufol C, Bourbon P, Philibert C. Histology and biochemistry of renal parenchyma in guinea pigs due to long term exposure to hydrogen fluoride. Fluoride 1982;15 (3): Manocha SL, Warner H, Olkowski Z. Cytochemical response of kidney, liver and nervous system to fluoride ions in drinking water. Histochem J 1975;7(4): de Camargo AM, Merzel J. Histological and histochemical appearance of livers and kidneys of rats after long-term treatment with different concentrations of sodium fluoride in drinking water. Acta Anat 1980;108: Published by the International Society for Fluoride Research Editorial Office: 727 Brighton Road, Ocean View, Dunedin 9051, New Zealand
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS
 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 43-50 2001 Research Report 43 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India Summary: Young albino rabbits were administered
Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 43-50 2001 Research Report 43 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India Summary: Young albino rabbits were administered
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS
 34 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 34-42 2000 Research Report HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India SUMMARY: The effect of chronic and acute exposure
34 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 34-42 2000 Research Report HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India SUMMARY: The effect of chronic and acute exposure
HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS
 12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF FLUORIDE- INDUCED NEUROTOXICITY IN RABBITS
 Fluoride Vol. 36 No. 2 95-105 2003 Research Report 95 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF FLUORIDE- INDUCED NEUROTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi Patiala, India SUMMARY: Brain tissues for neurohistopathological
Fluoride Vol. 36 No. 2 95-105 2003 Research Report 95 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF FLUORIDE- INDUCED NEUROTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi Patiala, India SUMMARY: Brain tissues for neurohistopathological
TOXICOPATHOLOGICAL AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THYROID GLAND OF RAT IN FLUOROSIS
 TOXICOPATHOLOGICAL AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THYROID GLAND OF RAT IN FLUOROSIS *Shashi A and Parveen Kumar Department of Zoology and Environmental Sciences, Punjabi University, Patiala-147002,
TOXICOPATHOLOGICAL AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THYROID GLAND OF RAT IN FLUOROSIS *Shashi A and Parveen Kumar Department of Zoology and Environmental Sciences, Punjabi University, Patiala-147002,
SODIUM FLUORIDE INDUCED HISTOPATHALOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER AND KIDNEY OF ALBINO MICE
 ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 4(1), 2014, 58-62 ISSN 2277-288X SODIUM FLUORIDE INDUCED HISTOPATHALOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER AND KIDNEY OF ALBINO MICE S. KHADAR BASHA * and K. JAYANTHA RAO Division Toxicology,
ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 4(1), 2014, 58-62 ISSN 2277-288X SODIUM FLUORIDE INDUCED HISTOPATHALOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER AND KIDNEY OF ALBINO MICE S. KHADAR BASHA * and K. JAYANTHA RAO Division Toxicology,
PATHOLOGICAL STUDY ON SOME RENAL LESION IN SHEEP AND GOATS IN DIYALA PROVINCE
 I.J.S.N., VOL.8 (3) 2017: 611-615 ISSN 2229 6441 PATHOLOGICAL STUDY ON SOME RENAL LESION IN SHEEP AND GOATS IN DIYALA PROVINCE Noura N. Ali & Khalil H. Aljeboori Department of Pathology, college of Vet,
I.J.S.N., VOL.8 (3) 2017: 611-615 ISSN 2229 6441 PATHOLOGICAL STUDY ON SOME RENAL LESION IN SHEEP AND GOATS IN DIYALA PROVINCE Noura N. Ali & Khalil H. Aljeboori Department of Pathology, college of Vet,
Neurotoxicity induced by Fluoride in Rat Cerebral Cortex
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 10 (2016) pp. 938-951 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.510.101
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 10 (2016) pp. 938-951 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.510.101
THE EFFECT OF FLUORINE UPON THE PHOSPHATASE CONTENT OF PLASMA, BONES, AND TEETH OF ALBINO RATS
 THE EFFECT OF FLUORINE UPON THE PHOSPHATASE CONTENT OF PLASMA, BONES, AND TEETH OF ALBINO RATS BY MARGARET CAMMACK SMITH AND EDITH M. LANTZ (From the Department oj Nutrition, Agricultural Experiment Station,
THE EFFECT OF FLUORINE UPON THE PHOSPHATASE CONTENT OF PLASMA, BONES, AND TEETH OF ALBINO RATS BY MARGARET CAMMACK SMITH AND EDITH M. LANTZ (From the Department oj Nutrition, Agricultural Experiment Station,
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY
 40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY FOLLOWING RUSSELL'S VIPER (VIPERA RUSSELLI) BITE
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY FOLLOWING RUSSELL'S VIPER (VIPERA RUSSELLI) BITE Soe ~oe', May Mya win2, Than Than Htwe', Myint win', Swe Swe ~het* and Wynn Wynn Kyawl 'Department of Medical Research No. 5. Ziwaka
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY FOLLOWING RUSSELL'S VIPER (VIPERA RUSSELLI) BITE Soe ~oe', May Mya win2, Than Than Htwe', Myint win', Swe Swe ~het* and Wynn Wynn Kyawl 'Department of Medical Research No. 5. Ziwaka
ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.*
 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
SULLIVAN, RICHARD A. HARVEY, Depletion of C3 has inhibited infiltration of acute inflammatory cells into the
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 50 (1977), 267-273 The Effects of Cobra Venom Factor, an Inhibitor of the Complement System, on the Sequence of Morphological Events in the Rat Kidney in Experimental
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 50 (1977), 267-273 The Effects of Cobra Venom Factor, an Inhibitor of the Complement System, on the Sequence of Morphological Events in the Rat Kidney in Experimental
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM
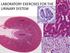 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features.
 Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
 128 PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Vandana KL, a Pauline George, b Charles M Cobb c Karnataka, India. SUMMARY: To date, studies on the effect of
128 PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Vandana KL, a Pauline George, b Charles M Cobb c Karnataka, India. SUMMARY: To date, studies on the effect of
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology
 Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
The evaluation of pathomorphological changes of intact by neoplastic process kidney parenchyma in patients with renal cell cancer
 The evaluation of pathomorphological changes of intact by neoplastic process kidney parenchyma in patients with renal cell cancer Serhyi Pasichnyk 1, Olga Voronina 2, Yulian Mytsyk 1 1 Lviv National Medical
The evaluation of pathomorphological changes of intact by neoplastic process kidney parenchyma in patients with renal cell cancer Serhyi Pasichnyk 1, Olga Voronina 2, Yulian Mytsyk 1 1 Lviv National Medical
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
27-Apr-15 1 UAF ANOMALIES OF DEVELOPMENT RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED UAF UAF
 RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS BY ANTI-KIDNEY MITOCHONDRIAL ANTISERUM IN THE RABBIT
 INTRODUCTION OF EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS BY ANTI-KIDNEY MITOCHONDRIAL ANTISERUM IN THE RABBIT A. Z. BARABAS,* B.V.M.&S., M.R.C.V.S., D.V.S.M., M.Sc., Ph.D., A. H. NAGI,* M.B., B.S. R. LANNIGAN,t
INTRODUCTION OF EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS BY ANTI-KIDNEY MITOCHONDRIAL ANTISERUM IN THE RABBIT A. Z. BARABAS,* B.V.M.&S., M.R.C.V.S., D.V.S.M., M.Sc., Ph.D., A. H. NAGI,* M.B., B.S. R. LANNIGAN,t
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Can Liv.52 Protect Mammalian Kidney Against Toxic Substances? Results and Possibilities
 [Indian Drugs (1987): (25), 1, 7] Can Liv.52 Protect Mammalian Kidney Against Toxic Substances? Results and Possibilities Rathore, H.S. School of Studies in Zoology, Vikram University, Ujjain, India. ABSTRACT
[Indian Drugs (1987): (25), 1, 7] Can Liv.52 Protect Mammalian Kidney Against Toxic Substances? Results and Possibilities Rathore, H.S. School of Studies in Zoology, Vikram University, Ujjain, India. ABSTRACT
5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176)
 Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
RENAL LESIONS IN EXPERIMENTAL CADMIUM POISONING
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1960, 17, 69. RENAL LESIONS IN EXPERIMENTAL CADMIUM POISONING BY J. A. BONNELL, J. H. ROSS, and E. KING From the Department for Research in Industrial Medicine, Medical Research
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1960, 17, 69. RENAL LESIONS IN EXPERIMENTAL CADMIUM POISONING BY J. A. BONNELL, J. H. ROSS, and E. KING From the Department for Research in Industrial Medicine, Medical Research
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
INDUCED CORNEAL OPACITIES IN THE RAT*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 124 INDUCED CORNEAL OPACITIES IN THE RAT*t BY R. J. FABIAN, J. M. BOND, AND H. P. DROBECK Experimental Pathology and Toxicology, Sterling- Winthrop Research Institute, Rensselaer,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 124 INDUCED CORNEAL OPACITIES IN THE RAT*t BY R. J. FABIAN, J. M. BOND, AND H. P. DROBECK Experimental Pathology and Toxicology, Sterling- Winthrop Research Institute, Rensselaer,
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 40 (1): 15-19, 2006 PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS Shilpa Sood 1 and P.C. Verma CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar - 125 004, India ABSTRACT The
Indian J. Anim. Res., 40 (1): 15-19, 2006 PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS Shilpa Sood 1 and P.C. Verma CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar - 125 004, India ABSTRACT The
QUANTITATIVE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE NEPHRON. V.
 QUANTITATIVE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE NEPHRON. V. ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE AND LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITIES IN LUPUS NEPHRITIS * By VICTOR E. POLLAK,t SJOERD L. BONTING, ROBERT C. MUEHRCKE AND ROBERT M. KARK
QUANTITATIVE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE NEPHRON. V. ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE AND LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITIES IN LUPUS NEPHRITIS * By VICTOR E. POLLAK,t SJOERD L. BONTING, ROBERT C. MUEHRCKE AND ROBERT M. KARK
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary
 Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT
 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy. Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA
 Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA Renal Transplant Biopsies Tissue Processing Ideal world process as
Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA Renal Transplant Biopsies Tissue Processing Ideal world process as
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE
 Indian J.Sci.Res.1(2) : 19-25, 2010 ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE a1 DUGESH NANDINI SHARMA AND LATA BHATTACHARYA
Indian J.Sci.Res.1(2) : 19-25, 2010 ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE a1 DUGESH NANDINI SHARMA AND LATA BHATTACHARYA
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Endemic Skeletal Fluorosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 4X, 686. Endemic Skeletal Fluorosis M. TEOTIA, S. P. S. TEOTIA, and K. B. KUNWAR From 'Wellcome' Metabolic Laboratory, Department of Medicine, King George's Medical
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 4X, 686. Endemic Skeletal Fluorosis M. TEOTIA, S. P. S. TEOTIA, and K. B. KUNWAR From 'Wellcome' Metabolic Laboratory, Department of Medicine, King George's Medical
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Some renal vascular disorders
 Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS
 HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ADDITIONAL FILE FOR THE MANUSCRIPT: Peritoneal Negative Pressure Therapy Prevents Multiple Organ Injury in a Chronic Porcine Sepsis and Ischemia/Reperfusion model Brian D. Kubiak
HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ADDITIONAL FILE FOR THE MANUSCRIPT: Peritoneal Negative Pressure Therapy Prevents Multiple Organ Injury in a Chronic Porcine Sepsis and Ischemia/Reperfusion model Brian D. Kubiak
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Effect of Alkali on Metastatic Calcification Produced by Hypervitaminosis D
 Effect of Alkali on Metastatic Calcification Produced by Hypervitaminosis D Pages with reference to book, From 345 To 348 Gulshan Naheed ( Present Address: Khyber Medical College, Peshawar. ) N.A. Jafarey
Effect of Alkali on Metastatic Calcification Produced by Hypervitaminosis D Pages with reference to book, From 345 To 348 Gulshan Naheed ( Present Address: Khyber Medical College, Peshawar. ) N.A. Jafarey
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
FLUORIDE+ALUMINIUM INDUCED TOXICITY IN MICE TESTIS WITH GIANT CELLS AND ITS REVERSAL BY VITAMIN C
 :109 114 Research report 109 FLUORIDE+ALUMINIUM INDUCED TOXICITY IN MICE TESTIS WITH GIANT CELLS AND ITS REVERSAL BY VITAMIN C NJ Chinoy a, HP Sorathia, DD Jhala Ahmedabad, India SUMMARY: Administration
:109 114 Research report 109 FLUORIDE+ALUMINIUM INDUCED TOXICITY IN MICE TESTIS WITH GIANT CELLS AND ITS REVERSAL BY VITAMIN C NJ Chinoy a, HP Sorathia, DD Jhala Ahmedabad, India SUMMARY: Administration
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
BENEFICIAL EFFECT OF TAMARIND INGESTION ON FLUORIDE TOXICITY IN DOGS
 Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 1 33-38 2000 Research Report 33 BENEFICIAL EFFECT OF TAMARIND INGESTION ON FLUORIDE TOXICITY IN DOGS Arjun L Khandare, a P Uday Kumar, Nakka Lakshmaiah, Hyderabad, India SUMMARY: The
Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 1 33-38 2000 Research Report 33 BENEFICIAL EFFECT OF TAMARIND INGESTION ON FLUORIDE TOXICITY IN DOGS Arjun L Khandare, a P Uday Kumar, Nakka Lakshmaiah, Hyderabad, India SUMMARY: The
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Urine Casts. Microscopic Sediment Casts. Unit 2; Session 6
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND ULTRAMICROSCOPIC CHANGES INDUCED BY FLUORIDE IN SOFT TISSUE ORGANS OF THE AIR-BREATHING TELEOST, CHANNA PUNCTATUS (BLOCH)
 263 Haque, Pal, Mukherjee, Ghosh 263 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND ULTRAMICROSCOPIC CHANGES INDUCED BY FLUORIDE IN SOFT TISSUE ORGANS OF THE AIR-BREATHING TELEOST, CHANNA PUNCTATUS (BLOCH) Smaranya Haque, Sandipan
263 Haque, Pal, Mukherjee, Ghosh 263 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND ULTRAMICROSCOPIC CHANGES INDUCED BY FLUORIDE IN SOFT TISSUE ORGANS OF THE AIR-BREATHING TELEOST, CHANNA PUNCTATUS (BLOCH) Smaranya Haque, Sandipan
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
(From the Laboratory of Pharmacology of the University of North Carolina, Ckapet Hilt.)
 THE FUNCTIONAL AND PATHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF THE KIDNEY IN DOGS SUBJECTED TO A SECOND SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION OF URANIUM NITRATE.* BY WILLIAM D~B. MxeNIDER, M.D. (From the Laboratory of Pharmacology of the
THE FUNCTIONAL AND PATHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF THE KIDNEY IN DOGS SUBJECTED TO A SECOND SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION OF URANIUM NITRATE.* BY WILLIAM D~B. MxeNIDER, M.D. (From the Laboratory of Pharmacology of the
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
