HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS
|
|
|
- Jack Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ADDITIONAL FILE FOR THE MANUSCRIPT: Peritoneal Negative Pressure Therapy Prevents Multiple Organ Injury in a Chronic Porcine Sepsis and Ischemia/Reperfusion model Brian D. Kubiak 1, Scott P. Albert 1, Louis A. Gatto 2, Kathleen P. Snyder 1, Kristopher G. Maier 1, Christopher J. Vieau 1, Shreyas Roy 1 Gary F. Nieman 1 1 Department of Surgery, Upstate University Hospital, Syracuse, NY and 2 Department of Biological Sciences, SUNY Cortland, Cortland NY
2 HISTOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OF THE LUNG List of Parameters: Atelectasis Fibrinous Deposits Hemorrhage in Air Compartment Vessel Congestion Alveolar Wall Thickness Leukocyte Infiltration
3 LUNG: NO LESIONS No atelectasis No fibrinous deposits (hyaline membrane) in air spaces No hemorrhage in air spaces No congestion of alveolar capillaries Alveolar walls are one-cell thick Less than 10 leukocytes per sample area (215x165 µm) SCORING: Scores of zero in all categories
4 LUNG: FIBRINOUS DEPOSITS Fibrin strands (hyaline membrane) visible within air spaces SCORING: The photomicrograph was divided into four quadrants and quantified using the following scoring system: 0 = no deposits 1 = deposits in one quadrant 2 = deposits in two quadrants 3 = deposits in three quadrants 4 = deposits in all quadrants
5 LUNG: HEMORRHAGE IN AIR SPACES Erythrocytes present within alveolar lumen SCORING: The photomicrograph was divided into four quadrants and quantified using the following scoring system: 0 = no hemorrhage 1 = hemorrhage in one quadrant 2 = hemorrhage in two quadrants 3 = hemorrhage in three quadrants 4 = hemorrhage in all quadrants
6 LUNG: VESSEL CONGESTION Alveolar capillaries filled with blood protrude into air space SCORING: The photomicrograph was divided into four quadrants and quantified using the following scoring system: 0 = no congested capillaries 1 = congestion in one quadrant 2 = congestion in two quadrants 3 = congestion in three quadrants 4 = congestion in all quadrants
7 LUNG: ALVEOLAR WALL THICKNESS Alveolar wall thicness exceeds one cell SCORING: The photomicrograph was divided into four quadrants and quantified using the following scoring system: 0 = no thickened alveolar walls 1 = thickened walls in one quadrant 2 = thickened walls in two quadrants 3 = thickened walls in three quadrants 4 = thickened walls in all quadrants
8 LUNG: LEUKOCYTE INFILTRATION Hematogenous (inflammatory?) wandering cells per sample area (215x165 µm) SCORING: The number of wandering cells in the photomicrograph was quantified using the following scoring system: 0 = less than 10 cells 1 = at least 10 cells 2 = at least 25 cells 3 = at least 50 cells 4 = over 75 cells
9 HISTOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OF KIDNEY CORTEX Histological changes were quantified in the renal cortex according to 5 parameters: Interstitial Edema Epithelial Changes Tubular Degeneration Capillary Congestion Leukocyte Infiltration (1) Interstitial Edema, present as either of the following: (1a) - Edematous vessel cuffs (1b) - Peritubular edema (1c) - Lymphatic vessel dilation (2) Epithelial Changes, present as either of the following: (2a) - Paracellular spaces (2b) - Loss of brush border (2c) - Tubular dilation (cell shortening) (2d) - Tubular cell apoptosis (3) Tubular Degeneration, present as either of the following: (3a) - Detached basement membrane (3b) - Loss of cellular definition (3c) - Epithelial sloughing (3d) - Loss of tubular architecture (3e) - Tubular necrosis (4) Capillary Congestion (5) Leukocyte Infiltration The pages that follow illustrate and describe morphological examples (a, b, c...) of each parameter (1 through 5).
10 Interstitial Edema: (1a) Edematous Vessel Cuffs Interstitial edema is most evident in the connective tissue compartments that carry vessels and nerves. Since the kidney has no prominent septa, the most obvious connective tissue occurs around vessels. In an edematous state, the connective tissue forms a prominent cuff around the vessel (arrowhead). Frequency of occurrence is highest when vessels of all sizes exhibit cuffs. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = cuffs not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of cuffs 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo [NOTE: scoring does not quantify size of cuff]
11 Interstitial Edema: (1b) Peritubular Edema The generalized presence of interstitial edema would expand the connective tissue framework (stroma) and separate all the tubules evenly. Notably, peritubular edema may be prominent around some tubules but not others. In this photo, peritubular edema (arrowhead) is conspicuous around some distal convoluted tubules. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = peritubular edema not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of peritubular edema 2 = incidence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo [NOTE: Scoring does not quantify grouping or anatomical distribution]
12 Interstitial Edema: (1c) Lymphatic Vessel Dilation Lymphatic vessels are ordinarily collapsed and inconspicuous. Dilated lymphatic vessels, however, stand out as prominent open areas bound only by very slender endothelium (arrowheads). Lymphatic capillaries occur among renal tubules, while larger lymphatic vessels generally extend along connective tissue compartments shared with blood vessels and nerves. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = no dilated lymphatics in the photo 1 = dilated lymphatics in one quadrant of the photo 2 = dilated lymphatics in two quadrants of the photo 3 = dilated lymphatics in three quadrants of the photo 4 = dilated lymphatics in four quadrants of the photo
13 Epithelial Changes: (2a) Paracellular Spaces Spaces within the tubular epithelium (arrowheads) indicate failure of gap junctions between adjoining cells. Impaired junctional complexes lead to loss of epithelial barrier function. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = paracellular gaps not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of paracellular gaps 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = paracellular gaps present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = paracellular gaps prevalent throughout the photo
14 Epithelial Changes: (2b) Loss of Brush Border Absorptive activity varies along the nephron and, accordingly, nephron tubule cells exhibit varying amounts of apical microvilli. Cortical tubules have prominent microvilli which can be seen at the level of the light microscope in the form of a brush border. Distal convoluted tubules have very discernable brush borders, even at medium magnification. Tubules that have lost their brush border (arrowheads) have the outer diameter of their normal counterparts, but their apical cytoplasm appears truncated. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = lesion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of the lesion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo
15 Epithelial Changes: (2c) Tubular Dilation (Cell Shortening) Loss of cytoplasmic mass by the cells of the renal tubule causes architectural changes described in the literature as tubular dilation (arrowheads). Close inspection, however, shows that the apparent dilation is caused by a shortening of the cell, as the inner diameter increases without a corresponding increase of the outer diameter of the tubule. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = lesion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of the lesion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo
16 Epithelial Changes: (2d) Tubular Cell Apoptosis Apoptosis can be determined in routine histological preparations by the identification of morphological characteristics such as cellular rounding and shrinkage. At higher magnifications, morphological criteria include chromatin compaction and formation of apoptotic bodies. The apoptotic nuclear appearance is distinctive with rounded, marginated, crescentic nuclear chromatin in condensed or fragmented nuclei (arrowheads). Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = apoptosis not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of apoptosis 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = apoptosis present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent apoptosis throughout the photo
17 Tubular Degeneration: (3a) Detached Basement Membrane The designation "Tubular Degeneration" refers to morphological changes which alter the basic architecture of the tubule and generally involve more than one cell. Detachment of the cell from its basement membrane (arrowhead) may occur in conjunction with intercellular gaps and may indicate loss of epithelial barrier function. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = lesion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of the lesion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo
18 Tubular Degeneration: (3b) Loss of Cellular Definition Loss of cellular definition in the tubular epithelium is marked by morphological distortion that renders cytoplasmic features indistinct, blurring the boundaries between cells and leaving portions of the tubule with a scanty, anuclear cytoplasmic presence (arrowhead). Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = lesion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of the lesion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo
19 Tubular Degeneration: (3c) Epithelial Sloughing Acute loss of tubular epithelium involves shedding of cytoplasmic material into the tubular lumen (arrowhead). Epithelial sloughing leaves portions of the nephron tubule denuded, thus devoid of functional epithelium. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = lesion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of the lesion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo
20 Tubular Degeneration: (3d) Loss of Tubular Architecture A gross degenerative change is the loss of basic tubular architecture as evidenced by interruptions in the otherwise continuous epithelial wall (arrowheads). Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = lesion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of the lesion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo
21 Tubular Degeneration: (3e) Tubular Necrosis In tubular necrosis the structure (arrowhead) amounts to a ghost of the tubule, where the area may remain circumscribed by a basement membrane although the cellular components are either inadequate or altogether missing. There is no infrastructure to carry out the functions of the tubule. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = lesion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of the lesion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = prevalent throughout the photo
22 (4) Capillary Congestion Congested capillaries (arrowhead) are blood filled and are also distended. Capillary congestion indicates impaired flow in the end-capillary bed. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = congestion not present in the photo 1 = sporadic occurrence of congestion 2 = presence amounts to half of the photo 3 = congestion present in up to 3/4 of the photo 4 = congestion is prevalent throughout the photo [NOTE: Scoring system does not quantify distension of the vascular compartment]
23 (5) Leukocyte Infiltration Wandering inflammatory cells represent diverse sources such as local populations of tissue macrophages, lymphoid tissue, or systemic blood. Specific identification is uncertain since expression of markers varies during maturation and activation. For example, expression of a marker may be weak in a circulating monocyte but strong after extravasation. The denomination "leukocyte" denotes white blood cell and is used as an umbrella term to designate wandering cells (arrowheads), probably of hematogenous origin. Scoring System: 0 to 4 0 = absent or infrequent 1 = sporadic, scattered and ungrouped 2 = focalized in dense groups 3 = dense foci + scattered presence 4 = dense infiltration throughout
24 HISTOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OF THE LIVER List of Parameters: Interstitial Edema Sinusoid Congestion Hepatocellular Necrosis Hepatocyte Vacuolation Leukocyte Infiltration
25 Lesion Description: Interstitial Edema Edema deposition is accompanied by an acute swelling of the connective tissues of the stroma, which is characterized by a rapid-onset enlargement of the matrix without a concurrent increase in numbers of cells or fibers. Histologically this process results in connective tissue areas of lower optical density. Edematous connective tissues can occur within interlobular septa (ils) and portal tracts (por). Since occurrences of interstitial edema may range from prominent (arrow) to sparse (arrowhead) in adjacent areas, they lend themselves to quantification on a per-lobule basis using a scoring system. SCORING RUBRIC: Quantification of edematous swelling of interlobular septum in lobule under survey. The perimeter of the lobule was divided into 4 quadrants and the septum was rated according to the incidence of prominent enlargement of the matrix (arrow) as follows: 0 = Slender septum (arrowhead) all around this lobule 1 = Enlarged septum in one quadrant of this lobule 2 = Enlarged septum in two quadrants of this lobule 3 = Enlarged septum in three quadrants of this lobule 4 = Enlarged septum in all 4 quadrants of this lobule
26 Lesion Description: Capillary Sinusoid Congestion The capillary sinusoids of the liver lobule can exhibit congestion, which is morphologically unequivocal since the vessels are conspicuously dilated and filled with blood (arrows). The physiological significance of this histological change rests with general hemodynamic implications of blood irrigation and perfusion of the capillary bed, paucity of venous drainage, and poor oxygenation of the hepatic parenchyma. Since the incidence of congestion is not uniform, this parameter is readily quantifiable per lobule with the use of a scoring system. SCORING RUBRIC: Quantification of incidence of capillary sinusoid congestion within the liver lobule under survey. The identified lobule was divided into 4 quadrants and it was rated according to the incidence of capillaries appearing dilated and filled with blood (arrows) as follows: 0 = No congested capillaries present in this lobule 1 = Congested capillaries present in one quadrant of this lobule 2 = Congested capillaries present in two quadrants of this lobule 3 = Congested capillaries present in three quadrants of this lobule 4 = Congested capillaries present in all four quadrants of this lobule
27 Lesion Description: Hepatocellular Necrosis The center of the photomicrograph shows a liver lobule bound by its interlobular septum (ils). Within the lobule, rows of hepatocytes (hc) alternate with liver sinusoids (ls) which drain into the central vein (cv). Hepatic lobules featuring hepatocellular necrosis are marked by degenerating hepatocytes with less cytoplasmic mass, and this occurrence may be focalized near the center of the lobule. Since the extent of necrotic change is particular to individual lobules, this parameter can be quantitatively assessed on a per-lobule basis. SCORING RUBRIC: Quantification of hepatocellualr necrosis within the liver lobule under survey. The identified lobule was was rated according to the extent of the area exhibiting hepatocellular necrosis as follows: 0 = No hepatocellular necrosis present in this lobule 1 = Hepatocellular necrosis present in one-fourth of this lobule 2 = Hepatocellular necrosis present in two-fourths of this lobule 3 = Hepatocellular necrosis present in three-fourths of this lobule 4 = Hepatocellular necrosis present throughout this entire lobule
28 Lesion Description: Hepatocyte Vacuolation Diffuse hepatocyte vacuolation is considered an indicator of metabolic change or distress, and consists of clear cytoplasmic vesicles (arrows) located within the hepatocyte (hc). It should be noted that some small clear openings are bile canaliculi, although these are not cytoplasmic but lie within the intercellular junction between adjoining hepatocytes. Other clear areas in the lobule are much larger and extracellular, and represent the lumina of liver sinusoids (ls) which drain into the central vein (cv). If the presence of vesicles is less diffuse and more focalized it may constitute microvesicular steatosis, which is common in the periportal areas and represents evidence of acute metabolic changes. In more severe instances of vacuolation, hepatic cells may display vacuolar degeneration with conspicuous loss of cytoplasmic architecture and failure of junctional complexes, leading to loss of liver lobule structure. SCORING RUBRIC: Quantification of hepatocyte vacuolation within the liver lobule under survey. The identified lobule was was rated according to the extent of the area exhibiting hepatocyte vacuolation as follows: 0 = No hepatocyte vacuolation present in this lobule 1 = Hepatocyte vacuolation present in one-fourth of this lobule 2 = Hepatocyte vacuolation present in two-fourths of this lobule 3 = Hepatocyte vacuolation present in three-fourths of this lobule 4 = Hepatocyte vacuolation present throughout this entire lobule
29 Lesion Description: Leukocyte Infiltration Parenchymal Leukocyte Infiltration Interstitial Leukocyte Infiltration The photomicrograph shows portions of three adjacent hepatic lobules (A, B and C) separated by interlobular septa (ils). Within the lobules, medium magnification shows the close architectural relationship between rows of hepatocytes (hc) and the intervening liver sinusoids (ls) which drain into the central vein (cv). Leukocyte infiltration refers to the accumulation of white blood cells (wbc). Within the lobule, leukocyte infiltration is manifested as high incidence of white blood cells in the liver sinusoids. In the interstitium, leukocyte accumulation takes place as extravascular accumulation of leukocytes in the connective tissues of the liver stroma. Prominent leukocyte infiltration underscores the septic nature of the model. SCORING RUBRIC: Semiquantitative assessment of leukocyte infiltration within either the parenchyma (liver sinusoid) or the interstitium (interlobular septa) of the liver lobule under survey. Estimated leukocyte density was rated as follows: 0 = Less than 10% of the nuclei in the sinusoid/septa of this lobule were from leukocytes 1 = Between 10% and 1/4th of the nuclei in the sinusoid/septa of this lobule were from leukocytes 2 = Between 1/4th and one-half of the nuclei in the sinusoid/septa of this lobule were from leukocytes 3 = Between one-half and 3/4th of the nuclei in the sinusoid/septa of this lobule were from leukocytes 4 = Leukocyte nuclei filled the area corresponding to sinusoid/septa in this lobule
30 SMALL INTESTINE HISTOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT EIGHT PARAMETERS (" ") RECEIVED 0-4 SCORES: Shortened or Flat VILLI (loss of slender villi extending into the lumen) EPITHELIAL BARRIER: Between intestinal lumen and intestinal wall Gruenhagen Spaces (subepithelial spaces / lifting of surface epithelium) Lesion to Epithelium (paracellular spaces / focal loss of epithelial architecture) Denuded Surface (lamina propria directly exposed to lumen) UPPER LAMINA PROPRIA: Core and base of villi, and opening of glands into lumen Sloughing (connective tissue disintegrating into intestinal lumen) Congested Capillaries (blood-filled vessels near base of villi) LOWER LAMINA PROPRIA: Base of tunica mucosa with bottom of intestinal glands Lesion to Gland (loss of epithelial barrier or loss of tubule architecture) Congested Capillaries (blood-filled vessels near base of lamina propria) The pages that follow present a pictorial description of each parameter
31 Shortened or Flat VILLI (loss of slender villi extending into the lumen) In the more severely injured specimens, villi were missing (bracket), leaving the connective tissue of the lamina propria directly exposed to the lumen. The photomicrograph illustrates transverse sections of intestinal glands (gl) within the lamina propria (lp). Scoring rubric for shortened or flat villi per photomicrograph: 0 - All villi were slender 1 - Shortened or flat villi present in 1/4 of the lumen width 2 - Shortened or flat villi present in 2/4 of the lumen width 3 - Shortened or flat villi present in 3/4 of the lumen width 4 - Shortened or flat villi present throughout the lumen width
32 Gruenhagen Spaces (subepithelial spaces / lifting of surface epithelium) The least severe histological disruption of the surface epithelial barrier was in the form of subepithelial spaces of Gruenhagen (arrows). In general, the lifting of the surface epithelium (bracket) was the only indication of tissue change in areas exhibiting Gruenhagen spaces. Villi (vi) remained slender and intestinal glands (gl) were not disrupted. Note that scores of zero occurred in undamaged tissue, as well as in completely denuded areas since subepithelial spaces entail the presence of epithelia. Scoring rubric for Gruenhagen spaces per photomicrograph: 0 - Gruenhagen spaces not present 1 - Gruenhagen spaces present in 1/4 of the lumen width 2 - Gruenhagen spaces present in 2/4 of the lumen width 3 - Gruenhagen spaces present in 3/4 of the lumen width 4 - Gruenhagen spaces present throughout the lumen width
33 Lesion to Epithelium (paracellular spaces / focal loss of epithelial architecture) Loss of epithelial barrier between the intestinal lumen and the organ wall was least extensive when presented in the form of paracellular spaces or gaps between or beneath the cells (arrowheads). This was deemed a low level histological disruption because the surface epithelial barrier was compromised but not lost. This focal lesion to the surface epithelium was often associated with comparable, low-level disruption of gland epithelia (scored separately). Scoring rubric for lesion to epithelium per photomicrograph: 0 - Focal epithelial lesion not present 1 - Focal epithelial lesion present in 1/4 of the lumen width 2 - Focal epithelial lesion present in 2/4 of the lumen width 3 - Focal epithelial lesion present in 3/4 of the lumen width 4 - Focal epithelial lesion present throughout the lumen width
34 Denuded Surface (lamina propria directly exposed to lumen) Denudation of the wall surface through loss of the epithelium constituted complete absence of surface epithelial barrier and left the connective tissues and capillaries of the lamina propria (lp) directly exposed to the intestinal lumen. This was deemed a severe histological disruption, which was commonly accompanied by congestion of the end-capillary bed and loss of architecture in glands (scored separately). Scoring rubric for denuded surface per photomicrograph: 0 - Denuded surface not present 1 - Denuded surface present in 1/4 of the lumen width 2 - Denuded surface present in 2/4 of the lumen width 3 - Denuded surface present in 3/4 of the lumen width 4 - Denuded surface present throughout the lumen width
35 Sloughing of Lamina Propria (connective tissue disintegrating into intestinal lumen) Sloughing (asterisks) of the upper compartment of the Lamina Propria (lp) entailed the loss of tissues constituting the base of villi and and the openings of glands into the intestinal lumen. The end-capillary bed was often lost among the more severe occurrences of this lesion. Scoring rubric for sloughing of Lamina Propria per photomicrograph: 0 - Sloughing not present 1 - Sloughing present in 1/4 of the lumen width 2 - Sloughing present in 2/4 of the lumen width 3 - Sloughing present in 3/4 of the lumen width 4 - Sloughing present throughout the lumen width
36 Congested Capillaries (Upper Lamina Propria) (blood-filled vessels near base of villi) Congested capillaries (arrows) are conspicuous for their bloodfilled appearance. The end-capillary bed consists of small capillaries located in the upper compartment of the tunica mucosa, such as those featured in this photomicrograph. This is evidence of poor blood drainage within the capillary bed, and pathological significance arises from the resulting hypoxia. Scoring rubric for congested upper capillaries per photomicrograph: 0 - Congested upper capillaries not present 1 - Congested upper capillaries present in 1/4 of the lumen width 2 - Congested upper capillaries present in 2/4 of the lumen width 3 - Congested upper capillaries present in 3/4 of the lumen width 4 - Congested upper capillaries present throughout the lumen width
37 Congested Capillaries (Lower Lamina Propria) (blood-filled vessels near base of lamina propria) Congested capillaries are conspicuous for their bloodfilled appearance. Large capillaries located in the lower compartment of the tunica mucosa (arrows) drain the endcapillary bed located in the upper mucosa. Congestion of drainage is further evidence of poor blood flow within the capillary bed, which results in hypoxia. Scoring rubric for congested lower capillaries per photomicrograph: 0 - Congested lower capillaries not present 1 - Congested lower capillaries present in 1/4 of the lumen width 2 - Congested lower capillaries present in 2/4 of the lumen width 3 - Congested lower capillaries present in 3/4 of the lumen width 4 - Congested lower capillaries present throughout the lumen width
38 Lesion to Gland (loss of epithelial barrier or loss of tubule architecture in lower mucosal compartment) Scoring rubric for lesion to intestinal gland: 0 to Paracellular spaces in the epithelium 2 - discontinuous gland epithelium (gap in tubule wall) 3 - focal loss of gland tubule architecture 4 - loss of tubule (or segment)
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
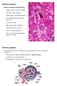
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs
 Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs Slide #77 (C007- H- 107A). Pancreas, dog. pancreatic islets CENTROACINAR CELLS ARE THE BEGINNING CELLS OF THE INTERCALATED DUCTS THAT DRAIN THE SECRETORY ACINI
Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs Slide #77 (C007- H- 107A). Pancreas, dog. pancreatic islets CENTROACINAR CELLS ARE THE BEGINNING CELLS OF THE INTERCALATED DUCTS THAT DRAIN THE SECRETORY ACINI
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Urinary system. Urinary system
 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Topics and aims. Introduction. Metabolism and Excretion
 Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION
 HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
LIVER & SPLEEN. Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra..
 LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Annals of RSCB Vol. XV, Issue 1
 AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Fourth Practical Pathology. Circulatory disturbances
 Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System
 Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with numerous trichomonads. (3 pt)
 Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Tissues organs system organism. pg151
 Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel
 Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel Now we will take about A granulocytes : Lymphocyte Monocytes 1- Lymphocyte - The second major type of presence
Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel Now we will take about A granulocytes : Lymphocyte Monocytes 1- Lymphocyte - The second major type of presence
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology
 Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
WSC , Conference 9. Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque.
 Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM
 1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy. Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA
 Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA Renal Transplant Biopsies Tissue Processing Ideal world process as
Interpretation of Renal Transplant Biopsy Arthur H. Cohen Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, North Carolina USA Renal Transplant Biopsies Tissue Processing Ideal world process as
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas
 Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Paneth Cells. Road Map to the Finish. No Review this Friday. Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs. Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I
 Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
