Online Supplemental Material. paying appropriate attention (Johnson, 2005), we established a minimum completion time
|
|
|
- Sibyl Patterson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 1 Online Supplemental Material Pilot time trial Because online samples often include participants who rush through studies without paying appropriate attention (Johnson, 2005), we established a minimum completion time (MCT) criterion for inclusion in the final sample for our two online experiments (2 and 3). One conventional procedure for eliminating outliers uses distributional criteria (e.g., 2 SDs above or below the mean). This method is not suitable here, however, because completion times are limited on the low end but not on the high end there is a minimum time in which it is possible to complete an experiment in good faith but there is no practical maximum. Instead, we conducted a pilot test to determine the shortest time in which one could reasonably participate in good faith. We asked 5 colleagues who were unfamiliar with the experiment to complete the online experiment as quickly as possible while still reading all essential instructions and questions but skipping the consent form, having a coin immediately accessible for flipping, and ignoring two open-ended questions at the end of the study to ensure they completed the study as quickly as possible. The mean completion time by our rushed testers was 3.09 minutes (SD = 0.55); this was set as our MCT. We emphasize that this is not the mean time in which a good faith participant would be expected to complete the experiment. Rather, it is the mean time in which a good faith participant could possibly be expected to complete the experiment. An even more conservative criterion (but, we believe, an unrealistic one given the already conservative instructions pilot participants were given) is the time in which our fastest rushed tester completed the experiment: 2.38 minutes. We report results of analyses using the 3.09-minute MCT in the main text. Analyses using the highly conservative 2.38-
2 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 2 minute criterion yield similar results and are reported in the Additional Analyses section below, as are results with no time-based exclusions. In Experiment 2, the 3.09-minute criterion excludes 5 people from the sample and the 2.38-minute criterion excludes 3. In Experiment 3, those two criteria exclude 32 and 19 people, respectively. The higher rate of time-based exclusions in this study was likely due to the ad hoc nature of the sample: Whereas participants in Experiment 2 had registered to take part in surveys regularly and had presumably set time aside for the study, the Experiment 3 sample consists of casual internet browsers who landed on the survey somewhat unexpectedly, clicking an ad they discovered while browsing Facebook. Therefore, the sample likely included a contingent of people who just clicked through quickly to see what the study was about. Analyses Using Different MCT Criteria Analyses using the 2.38-minute completion-time criterion In Experiment 2, using the highly conservative 2.38 minute time criterion, participants in the cheating condition claimed, on average, to have obtained 5.48 heads (SD=1.24) while those in the cheater condition claimed to have obtained 4.90 heads (SD=1.37), t(79)=1.97, p=0.053, d=0.44. The number of heads reported in the cheating condition was still significantly higher than the 5.00 expected by chance, t(39)=2.42, p=0.020, d=0.39, and the number of heads reported in the cheater condition was still not different from chance, t(40)=0.45, p>0.6. In Experiment 3, using the highly conservative 2.38-minute criterion, the omnibus effect of condition remained significant, F(2, 109)=4.62, p=0.012, as did the differences between the cheating and cheater conditions, t(109)=2.56, p=0.012, d=0.67, and between the baseline and cheater conditions, t(109)=2.81, p=0.006, d=0.71. The
3 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 3 difference between the baseline and cheating conditions remained non-significant, t(109)=0.25, p>0.80. Further, the number of heads claimed in both the cheating and baseline conditions remained significantly higher than chance, t(39)=4.81, p<0.0005, d=0.76 and t(41)=5.15, p<0.0005, d=0.79, respectively. The number of claimed heads in the cheater condition was still not significantly different from chance, t(29)=1.47, p>0.15. Analyses with no time-based exclusions In Experiment 2, including in the sample the 3 people who completed the experiment more quickly even than our highly conservative 2.38-minute criterion also did not change the results meaningfully. Participants in the cheating condition claimed, on average, to have obtained 5.59 heads (SD=1.41) while those in the cheater condition claimed to have obtained 4.86 head (SD=1.36), t(82)=2.40, p= The number of heads reported in the cheating condition was still significantly higher than the 5.00 expected by chance, t(40)=2.65, p=0.011, and the number of heads reported in the cheater condition was still not different from chance, t(42)=0.68, p>0.5. In Experiment 3, including in the sample the 19 people who completed the experiment more quickly even than our highly conservative 2.38-minute criterion did mask our effect, however. Including them, the omnibus effect of condition is no longer significant, F(2, 128)=0.94, p=0.394, nor are the differences between the cheating and cheater conditions, t(128)=1.25, p=0.215, or between the baseline and cheater conditions, t(128)=1.16, p= The difference between the baseline and cheating conditions remained non-significant, t(128)=0.11, p>0.91. Finally, the number of heads claimed in the cheater (M=5.82), cheating (M=6.27) and baseline (M=6.23)
4 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 4 conditions were all significantly higher than chance, t(38)=5.82, p<0.005, t(45)=6.27, p<0.0005, and t(48)=6.23, p<0.0005, respectively, suggesting that the 19 people who completed the experiment so quickly cheated at a much higher rate than our good-faith participants. Tests of Distribution in Studies 2 and 3 Please refer to Figures S1 and S2 for the full distribution of responses in Experiments 2 and 3. Below we present statistical analyses of these distributions beyond the mean differences reported in the main text. Test of Standard Deviations It might appear, on first glance, that the standard deviation in the cheater condition in Experiment 3 (SD=1.18) is low compared to the expected value if participants were indeed reporting their coin tosses honestly (E(s)=sqrt[Np(1- p)]=sqrt(10*.5*.5)=1.58), raising the possibility that participants in that condition opted to report the most honest-sounding number of heads (i.e., 5) without even tossing a coin. However, a computer simulation with 5,000 samples of 27 participants, each flipping a fair coin 10 times yields a 95% confidence interval for the SD of {1.16; 2.00}, which includes the observed SD. Thus the observed variability is within the range of what can be reasonably expected, and we cannot reject the null to assume a restriction of the range. Participants seem indeed to be reporting their tosses honestly in the cheater condition. Moreover, similar simulations show that the other two SDs in this study (as well as all SDs observed in Experiment 2) fall well within the expected 95% confidence intervals corresponding to those cell sizes.
5 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 5 Skewness and Kurtosis To further probe this question, we tested the distributions of numbers of claimed heads in the cheater conditions of both Experiments 2 and 3 (see supplementary figures S1 and S2). There is no significant skew or kurtosis in the cheater condition distributions in either experiment, z skew =0.47, p=0.64, z kurtosis =-0.47, p=0.64 (Experiment 2) and z skew =1.57, p=0.12, z kurtosis =1.59, p=0.11 (Experiment 3). Likelihood of Reporting Exactly 5 Heads Finally, we examined directly whether there was a difference between conditions, in either Experiment 2 or 3, in the likelihood of reporting exactly 5 heads. In Experiment 2, 35.0% of cheater condition participants reported exactly 5 and 35.9% of cheating condition participants did, χ 2 (1)=0.007, p=0.93. In Experiment 3, the difference was somewhat larger but still did not approach significance: 32.4% of cheater condition participants reported exactly 5 heads, 23.3% of cheating condition participants did, and 17.0% of baseline condition participants did, χ 2 (2)=2.73, p=0.26.
6 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 6 Reference Johnson, J. A. (2005). Ascertaining the validity of individual protocols from Web-based personality inventories. Journal of Research in Personality, 39, doi: /j.jrp
7 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 7 Figure S1. Distributions of the numbers of heads participants claimed to have obtained in the cheating and cheater conditions in Experiment 2.
8 Bryan, Adams & Monin; Online Supplemental Material 8 Figure S2. Distributions of the numbers of heads participants claimed to have obtained in the cheater, cheating, and baseline conditions in Experiment 3.
Statistical inference provides methods for drawing conclusions about a population from sample data.
 Chapter 14 Tests of Significance Statistical inference provides methods for drawing conclusions about a population from sample data. Two of the most common types of statistical inference: 1) Confidence
Chapter 14 Tests of Significance Statistical inference provides methods for drawing conclusions about a population from sample data. Two of the most common types of statistical inference: 1) Confidence
Chapter 23. Inference About Means. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Inference About Means Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Getting Started Now that we know how to create confidence intervals and test hypotheses about proportions, it d be nice to be able
Chapter 23 Inference About Means Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Getting Started Now that we know how to create confidence intervals and test hypotheses about proportions, it d be nice to be able
Checking the counterarguments confirms that publication bias contaminated studies relating social class and unethical behavior
 1 Checking the counterarguments confirms that publication bias contaminated studies relating social class and unethical behavior Gregory Francis Department of Psychological Sciences Purdue University gfrancis@purdue.edu
1 Checking the counterarguments confirms that publication bias contaminated studies relating social class and unethical behavior Gregory Francis Department of Psychological Sciences Purdue University gfrancis@purdue.edu
BAYESIAN HYPOTHESIS TESTING WITH SPSS AMOS
 Sara Garofalo Department of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge BAYESIAN HYPOTHESIS TESTING WITH SPSS AMOS Overview Bayesian VS classical (NHST or Frequentist) statistical approaches Theoretical issues
Sara Garofalo Department of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge BAYESIAN HYPOTHESIS TESTING WITH SPSS AMOS Overview Bayesian VS classical (NHST or Frequentist) statistical approaches Theoretical issues
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2009 AP Statistics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2009 free-response questions for AP Statistics were written by the Chief Reader, Christine Franklin of
Student Performance Q&A: 2009 AP Statistics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2009 free-response questions for AP Statistics were written by the Chief Reader, Christine Franklin of
appstats26.notebook April 17, 2015
 Chapter 26 Comparing Counts Objective: Students will interpret chi square as a test of goodness of fit, homogeneity, and independence. Goodness of Fit A test of whether the distribution of counts in one
Chapter 26 Comparing Counts Objective: Students will interpret chi square as a test of goodness of fit, homogeneity, and independence. Goodness of Fit A test of whether the distribution of counts in one
Type I Error Of Four Pairwise Mean Comparison Procedures Conducted As Protected And Unprotected Tests
 Journal of odern Applied Statistical ethods Volume 4 Issue 2 Article 1 11-1-25 Type I Error Of Four Pairwise ean Comparison Procedures Conducted As Protected And Unprotected Tests J. Jackson Barnette University
Journal of odern Applied Statistical ethods Volume 4 Issue 2 Article 1 11-1-25 Type I Error Of Four Pairwise ean Comparison Procedures Conducted As Protected And Unprotected Tests J. Jackson Barnette University
Promoting Academic Integrity
 Promoting Academic Integrity The Faculty Role Christine Harrington Ph.D. Director, Center for the Enrichment of Learning and Teaching (CELT) Middlesex County College Defining Academic Integrity Individuals
Promoting Academic Integrity The Faculty Role Christine Harrington Ph.D. Director, Center for the Enrichment of Learning and Teaching (CELT) Middlesex County College Defining Academic Integrity Individuals
Profile Analysis. Intro and Assumptions Psy 524 Andrew Ainsworth
 Profile Analysis Intro and Assumptions Psy 524 Andrew Ainsworth Profile Analysis Profile analysis is the repeated measures extension of MANOVA where a set of DVs are commensurate (on the same scale). Profile
Profile Analysis Intro and Assumptions Psy 524 Andrew Ainsworth Profile Analysis Profile analysis is the repeated measures extension of MANOVA where a set of DVs are commensurate (on the same scale). Profile
AP STATISTICS 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP STATISTICS 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 4 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) design an experiment to compare two treatments
AP STATISTICS 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 4 Intent of Question The primary goals of this question were to assess a student s ability to (1) design an experiment to compare two treatments
BATMAN/MR. FREEZE SUBZERO (GOLDEN LOOK-LOOK BOOK) BY SHELAGH CANNING
 BATMAN/MR. FREEZE SUBZERO (GOLDEN LOOK-LOOK BOOK) BY SHELAGH CANNING DOWNLOAD EBOOK : BATMAN/MR. FREEZE SUBZERO (GOLDEN LOOK- LOOK Click link bellow and free register to download ebook: BATMAN/MR. FREEZE
BATMAN/MR. FREEZE SUBZERO (GOLDEN LOOK-LOOK BOOK) BY SHELAGH CANNING DOWNLOAD EBOOK : BATMAN/MR. FREEZE SUBZERO (GOLDEN LOOK- LOOK Click link bellow and free register to download ebook: BATMAN/MR. FREEZE
Guidelines for reviewers
 Guidelines for reviewers Registered Reports are a form of empirical article in which the methods and proposed analyses are pre-registered and reviewed prior to research being conducted. This format of
Guidelines for reviewers Registered Reports are a form of empirical article in which the methods and proposed analyses are pre-registered and reviewed prior to research being conducted. This format of
The Impact of Relative Standards on the Propensity to Disclose. Alessandro Acquisti, Leslie K. John, George Loewenstein WEB APPENDIX
 The Impact of Relative Standards on the Propensity to Disclose Alessandro Acquisti, Leslie K. John, George Loewenstein WEB APPENDIX 2 Web Appendix A: Panel data estimation approach As noted in the main
The Impact of Relative Standards on the Propensity to Disclose Alessandro Acquisti, Leslie K. John, George Loewenstein WEB APPENDIX 2 Web Appendix A: Panel data estimation approach As noted in the main
11B Crazy Traits. What role does chance play in an organism s heredity? 1. Determining the genotype. 2. Stop and Think. Investigation 11B.
 11B Crazy Traits Investigation 11B What role does chance play in an organism s heredity? Your traits are determined by the genes you inherit from your parents. For each gene, you get at least one allele
11B Crazy Traits Investigation 11B What role does chance play in an organism s heredity? Your traits are determined by the genes you inherit from your parents. For each gene, you get at least one allele
Elementary statistics. Michael Ernst CSE 140 University of Washington
 Elementary statistics Michael Ernst CSE 140 University of Washington A dice-rolling game Two players each roll a die The higher roll wins Goal: roll as high as you can! Repeat the game 6 times Hypotheses
Elementary statistics Michael Ernst CSE 140 University of Washington A dice-rolling game Two players each roll a die The higher roll wins Goal: roll as high as you can! Repeat the game 6 times Hypotheses
Previously, when making inferences about the population mean,, we were assuming the following simple conditions:
 Chapter 17 Inference about a Population Mean Conditions for inference Previously, when making inferences about the population mean,, we were assuming the following simple conditions: (1) Our data (observations)
Chapter 17 Inference about a Population Mean Conditions for inference Previously, when making inferences about the population mean,, we were assuming the following simple conditions: (1) Our data (observations)
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA): TESTING DIFFERENCES INVOLVING THREE OR MORE MEANS
 ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA): TESTING DIFFERENCES INVOLVING THREE OR MORE MEANS REVIEW Testing hypothesis using the difference between two means: One-sample t-test Independent-samples t-test Dependent/Paired-samples
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA): TESTING DIFFERENCES INVOLVING THREE OR MORE MEANS REVIEW Testing hypothesis using the difference between two means: One-sample t-test Independent-samples t-test Dependent/Paired-samples
Before we get started:
 Before we get started: http://arievaluation.org/projects-3/ AEA 2018 R-Commander 1 Antonio Olmos Kai Schramm Priyalathta Govindasamy Antonio.Olmos@du.edu AntonioOlmos@aumhc.org AEA 2018 R-Commander 2 Plan
Before we get started: http://arievaluation.org/projects-3/ AEA 2018 R-Commander 1 Antonio Olmos Kai Schramm Priyalathta Govindasamy Antonio.Olmos@du.edu AntonioOlmos@aumhc.org AEA 2018 R-Commander 2 Plan
EXERCISE: HOW TO DO POWER CALCULATIONS IN OPTIMAL DESIGN SOFTWARE
 ...... EXERCISE: HOW TO DO POWER CALCULATIONS IN OPTIMAL DESIGN SOFTWARE TABLE OF CONTENTS 73TKey Vocabulary37T... 1 73TIntroduction37T... 73TUsing the Optimal Design Software37T... 73TEstimating Sample
...... EXERCISE: HOW TO DO POWER CALCULATIONS IN OPTIMAL DESIGN SOFTWARE TABLE OF CONTENTS 73TKey Vocabulary37T... 1 73TIntroduction37T... 73TUsing the Optimal Design Software37T... 73TEstimating Sample
Sheila Barron Statistics Outreach Center 2/8/2011
 Sheila Barron Statistics Outreach Center 2/8/2011 What is Power? When conducting a research study using a statistical hypothesis test, power is the probability of getting statistical significance when
Sheila Barron Statistics Outreach Center 2/8/2011 What is Power? When conducting a research study using a statistical hypothesis test, power is the probability of getting statistical significance when
PROBABILITY Page 1 of So far we have been concerned about describing characteristics of a distribution.
 PROBABILITY Page 1 of 9 I. Probability 1. So far we have been concerned about describing characteristics of a distribution. That is, frequency distribution, percentile ranking, measures of central tendency,
PROBABILITY Page 1 of 9 I. Probability 1. So far we have been concerned about describing characteristics of a distribution. That is, frequency distribution, percentile ranking, measures of central tendency,
Summary Report: The Effectiveness of Online Ads: A Field Experiment
 Summary Report: The Effectiveness of Online Ads: A Field Experiment Alexander Coppock and David Broockman September 16, 215 This document is a summary of experimental findings only. Additionally, this
Summary Report: The Effectiveness of Online Ads: A Field Experiment Alexander Coppock and David Broockman September 16, 215 This document is a summary of experimental findings only. Additionally, this
INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A MANAGER'S GUIDE TO HARNESSING TECHNOLOGY, V. 4.0 BY JOHN GALLAUGHER
 Read Online and Download Ebook INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A MANAGER'S GUIDE TO HARNESSING TECHNOLOGY, V. 4.0 BY JOHN GALLAUGHER DOWNLOAD EBOOK : INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A MANAGER'S GUIDE TO Click link bellow and
Read Online and Download Ebook INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A MANAGER'S GUIDE TO HARNESSING TECHNOLOGY, V. 4.0 BY JOHN GALLAUGHER DOWNLOAD EBOOK : INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A MANAGER'S GUIDE TO Click link bellow and
CHAPTER THIRTEEN. Data Analysis and Interpretation: Part II.Tests of Statistical Significance and the Analysis Story CHAPTER OUTLINE
 CHAPTER THIRTEEN Data Analysis and Interpretation: Part II.Tests of Statistical Significance and the Analysis Story CHAPTER OUTLINE OVERVIEW NULL HYPOTHESIS SIGNIFICANCE TESTING (NHST) EXPERIMENTAL SENSITIVITY
CHAPTER THIRTEEN Data Analysis and Interpretation: Part II.Tests of Statistical Significance and the Analysis Story CHAPTER OUTLINE OVERVIEW NULL HYPOTHESIS SIGNIFICANCE TESTING (NHST) EXPERIMENTAL SENSITIVITY
Margin of Error = Confidence interval:
 NAME: DATE: Algebra 2: Lesson 16-7 Margin of Error Learning 1. How do we calculate and interpret margin of error? 2. What is a confidence interval 3. What is the relationship between sample size and margin
NAME: DATE: Algebra 2: Lesson 16-7 Margin of Error Learning 1. How do we calculate and interpret margin of error? 2. What is a confidence interval 3. What is the relationship between sample size and margin
Comparing Direct and Indirect Measures of Just Rewards: What Have We Learned?
 Comparing Direct and Indirect Measures of Just Rewards: What Have We Learned? BARRY MARKOVSKY University of South Carolina KIMMO ERIKSSON Mälardalen University We appreciate the opportunity to comment
Comparing Direct and Indirect Measures of Just Rewards: What Have We Learned? BARRY MARKOVSKY University of South Carolina KIMMO ERIKSSON Mälardalen University We appreciate the opportunity to comment
Section 1: Goals and Attitudes
 Are you ready to lose weight? Find out how ready you are by taking the questionnaire below and see where your responses fall. Lifestyle changes begin with a person willing and able to make necessary changes.
Are you ready to lose weight? Find out how ready you are by taking the questionnaire below and see where your responses fall. Lifestyle changes begin with a person willing and able to make necessary changes.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Program Transcript
 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Program Transcript DR. JENNIFER ANN MORROW: Welcome to Analysis of Variance. My name is Dr. Jennifer Ann Morrow. In today's demonstration, I'll review with you the definition
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Program Transcript DR. JENNIFER ANN MORROW: Welcome to Analysis of Variance. My name is Dr. Jennifer Ann Morrow. In today's demonstration, I'll review with you the definition
Psychological. Influences on Personal Probability. Chapter 17. Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Psychological Chapter 17 Influences on Personal Probability Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 17.2 Equivalent Probabilities, Different Decisions Certainty Effect: people
Psychological Chapter 17 Influences on Personal Probability Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 17.2 Equivalent Probabilities, Different Decisions Certainty Effect: people
THE REFERENTIAL NATURE OF RULES AND INSTRUCTIONS: A RESPONSE TO INSTRUCTIONS, RULES, AND ABSTRACTION: A MISCONSTRUED RELATION BY EMILIO RIBES-IÑESTA
 Behavior and Philosophy, 29, 21-25 (2001). 2001 Cambridge Center for Behavioral Studies THE REFERENTIAL NATURE OF RULES AND INSTRUCTIONS: A RESPONSE TO INSTRUCTIONS, RULES, AND ABSTRACTION: A MISCONSTRUED
Behavior and Philosophy, 29, 21-25 (2001). 2001 Cambridge Center for Behavioral Studies THE REFERENTIAL NATURE OF RULES AND INSTRUCTIONS: A RESPONSE TO INSTRUCTIONS, RULES, AND ABSTRACTION: A MISCONSTRUED
Probability and Inheritance PSI Biology
 Probability and Inheritance PSI Biology Name Gregor Mendel studied inheritance in garden peas, and although he did not understand the mechanisms of inheritance, his work became the basis for the modern
Probability and Inheritance PSI Biology Name Gregor Mendel studied inheritance in garden peas, and although he did not understand the mechanisms of inheritance, his work became the basis for the modern
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables.
 bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
Chi Square Goodness of Fit
 index Page 1 of 24 Chi Square Goodness of Fit This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual grap on this topic. You may print this text out and use it as a textbook.
index Page 1 of 24 Chi Square Goodness of Fit This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual grap on this topic. You may print this text out and use it as a textbook.
Registered Reports - Guidelines for reviewers
 Registered Reports - Guidelines for reviewers Registered Reports are a form of publication of empirical research in which the methods and proposed analyses are pre-registered and reviewed prior to the
Registered Reports - Guidelines for reviewers Registered Reports are a form of publication of empirical research in which the methods and proposed analyses are pre-registered and reviewed prior to the
Acknowledge the depth of the pain that your affair brought to your marriage
 Acknowledge the depth of the pain that your affair brought to your marriage We ve already talked some about the pain and trauma that your spouse has experienced, but for a very long time most cheaters
Acknowledge the depth of the pain that your affair brought to your marriage We ve already talked some about the pain and trauma that your spouse has experienced, but for a very long time most cheaters
PERHAPS LOVE FROM HAL LEONARD - SHEET MUSIC - CHORAL SATB - 8 PAGES - - CHORAL SATB CHERRY LANE MUSIC CL1030 PERHAPS LOVE JOHN DENVER AUD
 Read Online and Download Ebook PERHAPS LOVE FROM HAL LEONARD - SHEET MUSIC - CHORAL SATB - 8 PAGES - - CHORAL SATB CHERRY LANE MUSIC CL1030 PERHAPS LOVE JOHN DENVER AUD DOWNLOAD EBOOK : PERHAPS LOVE FROM
Read Online and Download Ebook PERHAPS LOVE FROM HAL LEONARD - SHEET MUSIC - CHORAL SATB - 8 PAGES - - CHORAL SATB CHERRY LANE MUSIC CL1030 PERHAPS LOVE JOHN DENVER AUD DOWNLOAD EBOOK : PERHAPS LOVE FROM
2. Collecting agromyticin hormonal as a measure of aggression may not be a measure of aggression: (1 point)
 Psychology 9A: Fundamentals of Psychological Research Spring 7 Test 1 For this multiple-choice test, ONLY the mark-sense answer sheet will be graded. Be sure to bubble in the VERSION of the quiz and to
Psychology 9A: Fundamentals of Psychological Research Spring 7 Test 1 For this multiple-choice test, ONLY the mark-sense answer sheet will be graded. Be sure to bubble in the VERSION of the quiz and to
Registered Reports guidelines for reviewers and authors. Guidelines for reviewers
 Registered Reports guidelines for reviewers and authors Guidelines for reviewers Registered Reports are a form of empirical article offered at NFS Journal in which the methods and proposed analyses are
Registered Reports guidelines for reviewers and authors Guidelines for reviewers Registered Reports are a form of empirical article offered at NFS Journal in which the methods and proposed analyses are
ANOVA in SPSS (Practical)
 ANOVA in SPSS (Practical) Analysis of Variance practical In this practical we will investigate how we model the influence of a categorical predictor on a continuous response. Centre for Multilevel Modelling
ANOVA in SPSS (Practical) Analysis of Variance practical In this practical we will investigate how we model the influence of a categorical predictor on a continuous response. Centre for Multilevel Modelling
Chapter 12: Introduction to Analysis of Variance
 Chapter 12: Introduction to Analysis of Variance of Variance Chapter 12 presents the general logic and basic formulas for the hypothesis testing procedure known as analysis of variance (ANOVA). The purpose
Chapter 12: Introduction to Analysis of Variance of Variance Chapter 12 presents the general logic and basic formulas for the hypothesis testing procedure known as analysis of variance (ANOVA). The purpose
15.301/310, Managerial Psychology Prof. Dan Ariely Recitation 8: T test and ANOVA
 15.301/310, Managerial Psychology Prof. Dan Ariely Recitation 8: T test and ANOVA Statistics does all kinds of stuff to describe data Talk about baseball, other useful stuff We can calculate the probability.
15.301/310, Managerial Psychology Prof. Dan Ariely Recitation 8: T test and ANOVA Statistics does all kinds of stuff to describe data Talk about baseball, other useful stuff We can calculate the probability.
Quantifying the Association Between Discrete Event Time Series
 Quantifying the Association Between Discrete Event Time Series Christopher Galbraith Padhraic Smyth & Hal S. Stern Department of Statistics Department of Computer Science July 31, 2018 ics.uci.edu/~galbraic/
Quantifying the Association Between Discrete Event Time Series Christopher Galbraith Padhraic Smyth & Hal S. Stern Department of Statistics Department of Computer Science July 31, 2018 ics.uci.edu/~galbraic/
Lesson Overview 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles
 THINK ABOUT IT Nothing in life is certain. Lesson Overview 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles If a parent carries two different alleles for a certain gene, we can t be sure which of those alleles will be
THINK ABOUT IT Nothing in life is certain. Lesson Overview 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles If a parent carries two different alleles for a certain gene, we can t be sure which of those alleles will be
Chapter 20 Confidence Intervals with proportions!
 Chapter 20 Confidence Intervals with proportions! Statistic or Type of Variable Parameter Point Estimate Quantitative Categorical (Binary) Any Confidence Interval Point Estimate ± Margin of Error Point
Chapter 20 Confidence Intervals with proportions! Statistic or Type of Variable Parameter Point Estimate Quantitative Categorical (Binary) Any Confidence Interval Point Estimate ± Margin of Error Point
Does chewing gum have an impact on student performance? : An analysis of quiz grades
 Does chewing gum have an impact on student performance? : An analysis of quiz grades Abstract: In this paper, we will discuss the results of an experiment measuring whether chewing gum during a quiz impacts
Does chewing gum have an impact on student performance? : An analysis of quiz grades Abstract: In this paper, we will discuss the results of an experiment measuring whether chewing gum during a quiz impacts
When Intuition. Differs from Relative Frequency. Chapter 18. Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 When Intuition Chapter 18 Differs from Relative Frequency Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thought Question 1: Do you think it likely that anyone will ever win a state lottery
When Intuition Chapter 18 Differs from Relative Frequency Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thought Question 1: Do you think it likely that anyone will ever win a state lottery
Probabilities and Research. Statistics
 Probabilities and Research Statistics Sampling a Population Interviewed 83 out of 616 (13.5%) initial victims Generalizability: Ability to apply findings from one sample or in one context to other samples
Probabilities and Research Statistics Sampling a Population Interviewed 83 out of 616 (13.5%) initial victims Generalizability: Ability to apply findings from one sample or in one context to other samples
SEED HAEMATOLOGY. Medical statistics your support when interpreting results SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT APRIL 2015
 SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT APRIL 2015 SEED HAEMATOLOGY Medical statistics your support when interpreting results The importance of statistical investigations Modern medicine is often
SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT APRIL 2015 SEED HAEMATOLOGY Medical statistics your support when interpreting results The importance of statistical investigations Modern medicine is often
VIEW: An Assessment of Problem Solving Style
 VIEW: An Assessment of Problem Solving Style 2009 Technical Update Donald J. Treffinger Center for Creative Learning This update reports the results of additional data collection and analyses for the VIEW
VIEW: An Assessment of Problem Solving Style 2009 Technical Update Donald J. Treffinger Center for Creative Learning This update reports the results of additional data collection and analyses for the VIEW
Independent Variables Variables (factors) that are manipulated to measure their effect Typically select specific levels of each variable to test
 Controlled Experiments experimental investigation of a testable hypothesis, in which conditions are set up to isolate the variables of interest ("independent variables") and test how they affect certain
Controlled Experiments experimental investigation of a testable hypothesis, in which conditions are set up to isolate the variables of interest ("independent variables") and test how they affect certain
5.2 ESTIMATING PROBABILITIES
 5.2 ESTIMATING PROBABILITIES It seems clear that the five-step approach of estimating expected values in Chapter 4 should also work here in Chapter 5 for estimating probabilities. Consider the following
5.2 ESTIMATING PROBABILITIES It seems clear that the five-step approach of estimating expected values in Chapter 4 should also work here in Chapter 5 for estimating probabilities. Consider the following
Experimental evidence of massive-scale emotional contagion through social networks
 Experimental evidence of massive-scale emotional contagion through social networks September 26, 2016 Goal of Experiment Problems to be solved in Experiment Details of Experiment Conclusions Experiment
Experimental evidence of massive-scale emotional contagion through social networks September 26, 2016 Goal of Experiment Problems to be solved in Experiment Details of Experiment Conclusions Experiment
Missy Wittenzellner Big Brother Big Sister Project
 Missy Wittenzellner Big Brother Big Sister Project Evaluation of Normality: Before the analysis, we need to make sure that the data is normally distributed Based on the histogram, our match length data
Missy Wittenzellner Big Brother Big Sister Project Evaluation of Normality: Before the analysis, we need to make sure that the data is normally distributed Based on the histogram, our match length data
LAB ASSIGNMENT 4 INFERENCES FOR NUMERICAL DATA. Comparison of Cancer Survival*
 LAB ASSIGNMENT 4 1 INFERENCES FOR NUMERICAL DATA In this lab assignment, you will analyze the data from a study to compare survival times of patients of both genders with different primary cancers. First,
LAB ASSIGNMENT 4 1 INFERENCES FOR NUMERICAL DATA In this lab assignment, you will analyze the data from a study to compare survival times of patients of both genders with different primary cancers. First,
Title: A robustness study of parametric and non-parametric tests in Model-Based Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction for epistasis detection
 Author's response to reviews Title: A robustness study of parametric and non-parametric tests in Model-Based Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction for epistasis detection Authors: Jestinah M Mahachie John
Author's response to reviews Title: A robustness study of parametric and non-parametric tests in Model-Based Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction for epistasis detection Authors: Jestinah M Mahachie John
04/12/2014. Research Methods in Psychology. Chapter 6: Independent Groups Designs. What is your ideas? Testing
 Research Methods in Psychology Chapter 6: Independent Groups Designs 1 Why Psychologists Conduct Experiments? What is your ideas? 2 Why Psychologists Conduct Experiments? Testing Hypotheses derived from
Research Methods in Psychology Chapter 6: Independent Groups Designs 1 Why Psychologists Conduct Experiments? What is your ideas? 2 Why Psychologists Conduct Experiments? Testing Hypotheses derived from
What is probability. A way of quantifying uncertainty. Mathematical theory originally developed to model outcomes in games of chance.
 Outline What is probability Another definition of probability Bayes Theorem Prior probability; posterior probability How Bayesian inference is different from what we usually do Example: one species or
Outline What is probability Another definition of probability Bayes Theorem Prior probability; posterior probability How Bayesian inference is different from what we usually do Example: one species or
Probability and Sample space
 Probability and Sample space We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain but there is a regular distribution of outcomes in a large number of repetitions. The probability of any outcome
Probability and Sample space We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain but there is a regular distribution of outcomes in a large number of repetitions. The probability of any outcome
Chapter 9. Producing Data: Experiments. BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1
 Chapter 9 Producing Data: Experiments BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1 Experiment versus Observational Study Both typically have the goal of detecting a relationship between the explanatory and response variables.
Chapter 9 Producing Data: Experiments BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1 Experiment versus Observational Study Both typically have the goal of detecting a relationship between the explanatory and response variables.
Optimizing Communication of Emergency Response Adaptive Randomization Clinical Trials to Potential Participants
 1. Background The use of response adaptive randomization (RAR) is becoming more common in clinical trials (Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2011;29(6):606-609). Such designs will change the randomization
1. Background The use of response adaptive randomization (RAR) is becoming more common in clinical trials (Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2011;29(6):606-609). Such designs will change the randomization
Applied Statistical Analysis EDUC 6050 Week 4
 Applied Statistical Analysis EDUC 6050 Week 4 Finding clarity using data Today 1. Hypothesis Testing with Z Scores (continued) 2. Chapters 6 and 7 in Book 2 Review! = $ & '! = $ & ' * ) 1. Which formula
Applied Statistical Analysis EDUC 6050 Week 4 Finding clarity using data Today 1. Hypothesis Testing with Z Scores (continued) 2. Chapters 6 and 7 in Book 2 Review! = $ & '! = $ & ' * ) 1. Which formula
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
 Research Methods and Ethics in Psychology Week 4 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) One Way Independent Groups ANOVA Brief revision of some important concepts To introduce the concept of familywise error rate.
Research Methods and Ethics in Psychology Week 4 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) One Way Independent Groups ANOVA Brief revision of some important concepts To introduce the concept of familywise error rate.
Lessons in biostatistics
 Lessons in biostatistics The test of independence Mary L. McHugh Department of Nursing, School of Health and Human Services, National University, Aero Court, San Diego, California, USA Corresponding author:
Lessons in biostatistics The test of independence Mary L. McHugh Department of Nursing, School of Health and Human Services, National University, Aero Court, San Diego, California, USA Corresponding author:
Chapter 5: Producing Data
 Chapter 5: Producing Data Key Vocabulary: observational study vs. experiment confounded variables population vs. sample sampling vs. census sample design voluntary response sampling convenience sampling
Chapter 5: Producing Data Key Vocabulary: observational study vs. experiment confounded variables population vs. sample sampling vs. census sample design voluntary response sampling convenience sampling
SAMPLE SIZE AND POWER
 SAMPLE SIZE AND POWER Craig JACKSON, Fang Gao SMITH Clinical trials often involve the comparison of a new treatment with an established treatment (or a placebo) in a sample of patients, and the differences
SAMPLE SIZE AND POWER Craig JACKSON, Fang Gao SMITH Clinical trials often involve the comparison of a new treatment with an established treatment (or a placebo) in a sample of patients, and the differences
Stat 111 Final. 1. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for Alex and Sarah having the same mean lap time?
 Stat 111 Final Question 1 Alex and Sarah enjoy riding their bikes around Valley Forge park. Alex rode 25 laps, averaging 40 minutes with a standard deviation of 5 minutes, and Sarah rode 36 laps, averaging
Stat 111 Final Question 1 Alex and Sarah enjoy riding their bikes around Valley Forge park. Alex rode 25 laps, averaging 40 minutes with a standard deviation of 5 minutes, and Sarah rode 36 laps, averaging
To open a CMA file > Download and Save file Start CMA Open file from within CMA
 Example name Effect size Analysis type Level Tamiflu Symptom relief Mean difference (Hours to relief) Basic Basic Reference Cochrane Figure 4 Synopsis We have a series of studies that evaluated the effect
Example name Effect size Analysis type Level Tamiflu Symptom relief Mean difference (Hours to relief) Basic Basic Reference Cochrane Figure 4 Synopsis We have a series of studies that evaluated the effect
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Baldwin and Lammers 10.1073/pnas.1610834113 SI Methods and Results The patterns of predicted results were not affected when age, race (non-white = 0, White = 1), sex (female = 0,
Supporting Information Baldwin and Lammers 10.1073/pnas.1610834113 SI Methods and Results The patterns of predicted results were not affected when age, race (non-white = 0, White = 1), sex (female = 0,
NO LIFE OF MY OWN: AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY BY FRANK CHIKANE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : NO LIFE OF MY OWN: AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY BY FRANK CHIKANE PDF
 Read Online and Download Ebook NO LIFE OF MY OWN: AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY BY FRANK CHIKANE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : NO LIFE OF MY OWN: AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY BY FRANK Click link bellow and free register to download ebook:
Read Online and Download Ebook NO LIFE OF MY OWN: AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY BY FRANK CHIKANE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : NO LIFE OF MY OWN: AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY BY FRANK Click link bellow and free register to download ebook:
Chapter 1: Alternative Forced Choice Methods
 Chapter 1: Alternative Forced Choice Methods Section 1.1 Birdnapping Lewiston man confounded by stolen parrot art Lewiston, Minn Jim Schloegel stood under the shade of a giant bird cage and raised both
Chapter 1: Alternative Forced Choice Methods Section 1.1 Birdnapping Lewiston man confounded by stolen parrot art Lewiston, Minn Jim Schloegel stood under the shade of a giant bird cage and raised both
Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques)
 Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques) Dr Judy Sheard Senior Lecturer Co-Director, Computing Education Research Group Monash University judy.sheard@monash.edu
Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques) Dr Judy Sheard Senior Lecturer Co-Director, Computing Education Research Group Monash University judy.sheard@monash.edu
Q1 How would you rate the quality of Hollis Adams Water Aerobics?
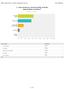 Q1 How would you rate the quality of Hollis Adams Water Aerobics? Answered: 19 Skipped: 1 Very high quality High quality Neither high nor low quality Low quality Very low quality Very high quality High
Q1 How would you rate the quality of Hollis Adams Water Aerobics? Answered: 19 Skipped: 1 Very high quality High quality Neither high nor low quality Low quality Very low quality Very high quality High
PROBABILITY and MENDELIAN GENETICS
 PROBABILITY and MENDELIAN GENETICS NAME BACKGROUND In 1866 Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, published the results of his study of inheritance on garden peas. Although Mendel did not understand the mechanics
PROBABILITY and MENDELIAN GENETICS NAME BACKGROUND In 1866 Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, published the results of his study of inheritance on garden peas. Although Mendel did not understand the mechanics
Post Hoc Analysis Decisions Drive the Reported Reading Time Effects in Hackl, Koster-Hale & Varvoutis (2012)
 Journal of Semantics, 2017, 1 8 doi: 10.1093/jos/ffx001 Article Post Hoc Analysis Decisions Drive the Reported Reading Time Effects in Hackl, Koster-Hale & Varvoutis (2012) Edward Gibson Department of
Journal of Semantics, 2017, 1 8 doi: 10.1093/jos/ffx001 Article Post Hoc Analysis Decisions Drive the Reported Reading Time Effects in Hackl, Koster-Hale & Varvoutis (2012) Edward Gibson Department of
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data
 Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Instructor Guide to EHR Go
 Instructor Guide to EHR Go Introduction... 1 Quick Facts... 1 Creating your Account... 1 Logging in to EHR Go... 5 Adding Faculty Users to EHR Go... 6 Adding Student Users to EHR Go... 8 Library... 9 Patients
Instructor Guide to EHR Go Introduction... 1 Quick Facts... 1 Creating your Account... 1 Logging in to EHR Go... 5 Adding Faculty Users to EHR Go... 6 Adding Student Users to EHR Go... 8 Library... 9 Patients
Chapter 10. Experimental Design: Statistical Analysis of Data
 10-1 Chapter 10. Experimental Design: Statistical Analysis of Data Purpose of Statistical Analysis Descriptive Statistics Central Tendency and Variability Measures of Central Tendency Mean Median Mode
10-1 Chapter 10. Experimental Design: Statistical Analysis of Data Purpose of Statistical Analysis Descriptive Statistics Central Tendency and Variability Measures of Central Tendency Mean Median Mode
A closer look at the Semantic Web journal s review process
 Semantic Web 10 (2019) 1 7 1 DOI 10.3233/SW-180342 IOS Press Editorial A closer look at the Semantic Web journal s review process Cogan Shimizu a, Pascal Hitzler a and Krzysztof Janowicz b a DaSe Lab,
Semantic Web 10 (2019) 1 7 1 DOI 10.3233/SW-180342 IOS Press Editorial A closer look at the Semantic Web journal s review process Cogan Shimizu a, Pascal Hitzler a and Krzysztof Janowicz b a DaSe Lab,
Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance
 Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance How do we talk about genetic information? Each cell in living organisms contains DNA. DNA is made of nucleotide subunits arranged in very long strands.
Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance How do we talk about genetic information? Each cell in living organisms contains DNA. DNA is made of nucleotide subunits arranged in very long strands.
Teaching Statistics with Coins and Playing Cards Going Beyond Probabilities
 Teaching Statistics with Coins and Playing Cards Going Beyond Probabilities Authors Chris Malone (cmalone@winona.edu), Dept. of Mathematics and Statistics, Winona State University Tisha Hooks (thooks@winona.edu),
Teaching Statistics with Coins and Playing Cards Going Beyond Probabilities Authors Chris Malone (cmalone@winona.edu), Dept. of Mathematics and Statistics, Winona State University Tisha Hooks (thooks@winona.edu),
Motor Programs Lab. 1. Record your reaction and movement time in ms for each trial on the individual data Table 1 below. Table I: Individual Data RT
 Motor Programs Lab Introduction. This lab will simulate an important experiment performed by Henry and Rogers (1960). The task involved the subject responding to an external signal then executing a simple,
Motor Programs Lab Introduction. This lab will simulate an important experiment performed by Henry and Rogers (1960). The task involved the subject responding to an external signal then executing a simple,
PRINTABLE VERSION. Quiz 10
 You scored 0 out of 100 Question 1 PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 10 The z-score associated with the 97 percent confidence interval is a) 2.170 b) 2.081 c) 1.829 d) 1.881 e) 2.673 Question 2 What will reduce the
You scored 0 out of 100 Question 1 PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 10 The z-score associated with the 97 percent confidence interval is a) 2.170 b) 2.081 c) 1.829 d) 1.881 e) 2.673 Question 2 What will reduce the
Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab Executive Training: Evaluating Social Programs Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab Executive Training: Evaluating Social Programs Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use,
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab Executive Training: Evaluating Social Programs Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use,
Improving Informed Consent to Clinical Research. Charles W. Lidz Ph.D.
 Improving Informed Consent to Clinical Research Charles W. Lidz Ph.D. Housekeeping Items Please note that this broadcast is being recorded and will be available soon for viewing on SPARC s website. Please
Improving Informed Consent to Clinical Research Charles W. Lidz Ph.D. Housekeeping Items Please note that this broadcast is being recorded and will be available soon for viewing on SPARC s website. Please
Bayesian and Classical Hypothesis Testing: Practical Differences for a Controversial Area of Research
 Other Methodology Articles Bayesian and Classical Hypothesis Testing: Practical Differences for a Controversial Area of Research J. E. Kennedy Version of 10/12/2014 (in press) Abstract: The use of Bayesian
Other Methodology Articles Bayesian and Classical Hypothesis Testing: Practical Differences for a Controversial Area of Research J. E. Kennedy Version of 10/12/2014 (in press) Abstract: The use of Bayesian
On the Performance of Maximum Likelihood Versus Means and Variance Adjusted Weighted Least Squares Estimation in CFA
 STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING, 13(2), 186 203 Copyright 2006, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. On the Performance of Maximum Likelihood Versus Means and Variance Adjusted Weighted Least Squares Estimation
STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING, 13(2), 186 203 Copyright 2006, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. On the Performance of Maximum Likelihood Versus Means and Variance Adjusted Weighted Least Squares Estimation
Psychology 2019 v1.3. IA2 high-level annotated sample response. Student experiment (20%) August Assessment objectives
 Student experiment (20%) This sample has been compiled by the QCAA to assist and support teachers to match evidence in student responses to the characteristics described in the instrument-specific marking
Student experiment (20%) This sample has been compiled by the QCAA to assist and support teachers to match evidence in student responses to the characteristics described in the instrument-specific marking
Please copy into your agenda:
 Monday, September 19 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Advanced only-project part 2 (due Fri) Tuesday: Vocab bonds (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Human inheritance (due Thur)
Monday, September 19 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Advanced only-project part 2 (due Fri) Tuesday: Vocab bonds (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Human inheritance (due Thur)
KENNY ROGERS..."LADY"...SHEET MUSIC. BY LIONEL RICHIE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : KENNY ROGERS..."LADY"...SHEET MUSIC. BY LIONEL RICHIE PDF
 Read Online and Download Ebook KENNY ROGERS..."LADY"...SHEET MUSIC. BY LIONEL RICHIE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : KENNY ROGERS..."LADY"...SHEET MUSIC. BY LIONEL Click link bellow and free register to download ebook:
Read Online and Download Ebook KENNY ROGERS..."LADY"...SHEET MUSIC. BY LIONEL RICHIE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : KENNY ROGERS..."LADY"...SHEET MUSIC. BY LIONEL Click link bellow and free register to download ebook:
Merck Index 13th Edition Guiglakatsarava
 Merck Index 13th Edition Guiglakatsarava 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Merck Index 13th Edition The Merck Index* Online offers the same highly authoritative information as the print edition in a convenient and easily
Merck Index 13th Edition Guiglakatsarava 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Merck Index 13th Edition The Merck Index* Online offers the same highly authoritative information as the print edition in a convenient and easily
Investigating the robustness of the nonparametric Levene test with more than two groups
 Psicológica (2014), 35, 361-383. Investigating the robustness of the nonparametric Levene test with more than two groups David W. Nordstokke * and S. Mitchell Colp University of Calgary, Canada Testing
Psicológica (2014), 35, 361-383. Investigating the robustness of the nonparametric Levene test with more than two groups David W. Nordstokke * and S. Mitchell Colp University of Calgary, Canada Testing
Research paper. One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Research paper. SPSS output. Learning objectives. Alcohol and driving ability
 Research paper Alcohol and driving ability One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Thirty-six people took part in an experiment to discover the effects of alcohol on drinking ability. They were randomly assigned
Research paper Alcohol and driving ability One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Thirty-six people took part in an experiment to discover the effects of alcohol on drinking ability. They were randomly assigned
Manifestation Of Differences In Item-Level Characteristics In Scale-Level Measurement Invariance Tests Of Multi-Group Confirmatory Factor Analyses
 Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Copyright 2005 JMASM, Inc. May, 2005, Vol. 4, No.1, 275-282 1538 9472/05/$95.00 Manifestation Of Differences In Item-Level Characteristics In Scale-Level Measurement
Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Copyright 2005 JMASM, Inc. May, 2005, Vol. 4, No.1, 275-282 1538 9472/05/$95.00 Manifestation Of Differences In Item-Level Characteristics In Scale-Level Measurement
A Brief (very brief) Overview of Biostatistics. Jody Kreiman, PhD Bureau of Glottal Affairs
 A Brief (very brief) Overview of Biostatistics Jody Kreiman, PhD Bureau of Glottal Affairs What We ll Cover Fundamentals of measurement Parametric versus nonparametric tests Descriptive versus inferential
A Brief (very brief) Overview of Biostatistics Jody Kreiman, PhD Bureau of Glottal Affairs What We ll Cover Fundamentals of measurement Parametric versus nonparametric tests Descriptive versus inferential
Demonstrating Client Improvement to Yourself and Others
 Demonstrating Client Improvement to Yourself and Others Understanding and Using your Outcome Evaluation System (Part 2 of 3) Greg Vinson, Ph.D. Senior Researcher and Evaluation Manager Center for Victims
Demonstrating Client Improvement to Yourself and Others Understanding and Using your Outcome Evaluation System (Part 2 of 3) Greg Vinson, Ph.D. Senior Researcher and Evaluation Manager Center for Victims
WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics. What is Statistics and how does it relate to you?
 WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics Time Interval/ Unit 1: Introduction to Statistics 1.1-1.3 2 weeks S-IC-1: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters
WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics Time Interval/ Unit 1: Introduction to Statistics 1.1-1.3 2 weeks S-IC-1: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters
Chapter 5 & 6 Review. Producing Data Probability & Simulation
 Chapter 5 & 6 Review Producing Data Probability & Simulation M&M s Given a bag of M&M s: What s my population? How can I take a simple random sample (SRS) from the bag? How could you introduce bias? http://joshmadison.com/article/mms-colordistribution-analysis/
Chapter 5 & 6 Review Producing Data Probability & Simulation M&M s Given a bag of M&M s: What s my population? How can I take a simple random sample (SRS) from the bag? How could you introduce bias? http://joshmadison.com/article/mms-colordistribution-analysis/
About Reading Scientific Studies
 About Reading Scientific Studies TABLE OF CONTENTS About Reading Scientific Studies... 1 Why are these skills important?... 1 Create a Checklist... 1 Introduction... 1 Abstract... 1 Background... 2 Methods...
About Reading Scientific Studies TABLE OF CONTENTS About Reading Scientific Studies... 1 Why are these skills important?... 1 Create a Checklist... 1 Introduction... 1 Abstract... 1 Background... 2 Methods...
Monday, February 8. Please copy into your agenda:
 Monday, February 8 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Tuesday: Genetics review (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Genetics quiz Thursday-Friday: Collect data (dues Tues) Reminder:
Monday, February 8 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Tuesday: Genetics review (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Genetics quiz Thursday-Friday: Collect data (dues Tues) Reminder:
Health Insight: A Consumer s Guide to Taking Charge of Health Information
 Harvard Center for Risk Analysis October 1999 Volume 7 Issue 7 Risk in Perspective Health Insight: A Consumer s Guide to Taking Charge of Health Information Kimberly M. Thompson, ScD...your attitude and
Harvard Center for Risk Analysis October 1999 Volume 7 Issue 7 Risk in Perspective Health Insight: A Consumer s Guide to Taking Charge of Health Information Kimberly M. Thompson, ScD...your attitude and
