THE A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ANATOMY OF GINKGO BILOBA. P. J. P. SHAW, A.R.C.S. (WITH TEXT-PIGS ).
|
|
|
- Rachel Hudson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE NEW PHYTOIiOGIST. VOL. VII., Nos. 4 & 5. MAY 31ST, A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ANATOMY OF GINKGO BILOBA. BY P. J. P. SHAW, A.R.C.S. (WITH TEXT-PIGS ). "VTOTWITH STAN DING the numerous speculations upon the J^ morphological nature of the " collar " in the ovule of Ginkgo none appears to have been based upon an adequate anatomical investigation of the organ in question. Most have been derived from a study of malformations, the phylogenetic value of which many modern botanists are disposed to doubt. It is hoped that the results put forward in the present short note may furnish a new standpoint from which to view the problem. The material consisted of about a dozen specimens of the female " flower" preserved in spirit. All the specimens showed two ovules, one fertile and one small aborted sterile ovule. The sections were cut by hand, stained with safranin, and mounted in glycerine jelly. Subsequently a model of the xylem was built up from the sections, after the method employed by Parmer and Hill in the case of Angiopteris. VASCULAR SYSTBM OP PEMALE PLOWER. As is well known, the female " flower " consists of a stalk or peduncle bearing two lateral stalked ovules. A series of transverse sections was cut from the base of the peduncle up into the fertile ovule. A transverse section taken from as near the base of the peduncle as the specimens allowed shows a ring of four collateral bundles, the bundles being definitely associated in pairs. A little higher up in the peduncle, the two bundles of each pair unite and form two collateral bundles facing one another (Text-fig. 16, i). Of these two bundles one is concerned with the vascular supply of the fertile ovule and the other with that of the frequently sterile
2 86 Fig. 16. For description seep, 87,
3 The Anatomy of Ginkgo biloba. 87 Text-flg. 16. Phloem is cross-hatched, tracheids cut transversely represented by series of dots, cut longitudinally by lines. Position of sterile ovule shown thus X A=:bundle of fertile ovule ; B=bundle of sterite ovule : V=anomalous tissue; C=cainbiuni ; H^" horns"; T.L.=tracheids cut longitudinally; T.S.=tracheids cut transversely ; M=metaxylem ; K=crushed parenchyma between two phloems ; D=place where "horns" unite. PX=median plane of the pair of ovules. Transverse sections. I. Bundles in peduncle. 2 Single bundle in pedicel points of origin of anomalous tissue marked by two dots. 3, 4. Lower part of collar anomalous vascular tissue present. 5. Commencement of approximation of "horns" some tracheids cut longitudinally. 6, 7, 8. Union of " horns" inverted vascular bundles splay outwards in the top of the collar. 9. Single concentric bundle in base of ovule. 10, 11. Splitting of bundle giving rise to two concentric bundles. ovule. The latter is usually small and in its passage up the peduncle gradually dwindles away and becomes lost in the mass of parenchyma and "transfusion tracheids " forming the bulk of the ground-tissue. In some cases in which the sterile ovule has developed to a rather greater extent this bundle can be traced as running definitely into it. It may be remarked that, as we proceed up towards the ovule, we find a gradually increasing number of " transfusion tracheids" intermingled with the ordinary parenchyma. These " transfusion tracheids" are short and are reticulately thickened; they form a very characteristic feature of the sections. One of the bundles has now been disposed of and we pass to the consideration of the other, which will eventually give rise to the vascular system of the large fertile ovule. In a section taken at the base of the collar, just above the sterile ovule, this bundle exhibits normal collateral structure, the xylem facing towards the sterile ovule (Text-fig. 16, 2). On the outer edge of the phloem there is a fairly continuous layer of large, thick-walled, parenchymatous elements stained with safranin. At one or two spots the ordinary parenchyma of the ground-tissue next to these large cells has an abnormal appearance. The cells are ^smaller, possess den^e contents with well-marked nuclei, and appear to be rapidly dividing. The divisions at first take place irregularly in all directions, but a little higher up they begin to assume a definite tangential direction. The result is that at one or two places on the outer side of the main bundle, next the phloem, a dividing cambium is produced. This cambium gives rise fo tracheids externally and to phloem internally, and several little vascular bundles with inverted
4 88 F.J. F.Shaw. orientation are seen to be scattered along the outer edge of the main bundle. Text-flg. 16, 3, represents a section taken from the lower part of the collar. Here there are three anomalous bundles in addition to the main bundle. Moreover in one case the cambium of the main bundle hns become continuous round its flnnu with that of the nearest inverted bundle. A little higher up, about the middle of the collar, the parenchyma on the other flank of the main bundle also becomes merismatic, and here likewise the cambium becomes continuous,with that of the nearest inverted bundle. Text-fig. 16, 4 shows the vascular tissue slightly crescent-shaped, the xylem of the main bundle being on the concave side of the crescent and the xylem of the inverted tissue on the convex. The cambium of the main bundle is continuous with that of the inverted tissue round the "horns" of the crescent these " horns " face towards the sterile ovule. At the back of the main bundle the inverted tissue consists of two small bundles. The crescent-shaped condition of the vascular tissue becomes more marked further up towards the ovule. The two ' horns' curve round and become much more prominent. So rapidly does this take place that the tracheids of the main bundle and of the inverted xylem at the " horns " run nearly horizontally through the parenchyma and are hence cut longitudinally in the transverse sections. The cambium remainscontinuous round the "horns" during this process (Text-flg. 16, 5 and 6). In Text-flg. 16, 7, the cambium of the inverted tissue appears continuous right round the convex side of the crescent. The space between the two cambiums isfliledwith phloem, and it is difficult to draw a line of demarcation between the phloem of the inverted tissue and the normal phloem, but remnants of large parenchymatous cells can sometimes be discerned between the two. The tracheids of the inverted tissue are, on the whole, running outwards towards the periphery and are cut longitudinally right round the outer edge of the crescent. The parenchyma enclosed between the " horns" is intermingled with numerous tracheids and forms a sort of metaxylem. As regards the main bundle the tracheids of this metaxylem are centripetal. In the upper region of the collar, the inverted tissue continues to splay outwards and disappears from the transverse sections; it persists longest at the "horns "(Text-flg. 16,8). The tracheids of the main bundle at each " horn," those on the inner side of the crescent, continue to run almost horizontally, and higher up in the collar they
5 The Anatomy of Ginkgo biloba. 89 gradually approach one another. At the extreme top of the collar they meet and the cambium of the main bundle becomes continuous all the way round (Text-flg. 16, 9). The number of " transfusion tracheids" in the general parenchyma is very large at this level. A single concentric bundle is thus formed at the base of the ovule; its central part consists of the metaxylem, mentioned above, and it is enclosed by the genuine xylem of the bundle, The latter shows a marked tendency to aggregate at two points on opposite sides of the bundle (Text-flg. 16, 9). The tracheids in one half of the bundle all appear to be running towards the region where the " horns" have recently united, in the other half of the bundle they trend towards a point exactly opposite. This behaviour of the tracheids is a foreshadowing of the splitting of the concentric bundle which takes place a few sections higher up in the ovule. Seeing that the two " horns," which united to form the concentric bundle, faced towards the sterile ovule, it is plain that the separation of this bundle into two takes place at right angles to the plane of the ovules the two resulting bundles lying in that plane (Text-flg. 16, 10). They rapidly divaricate and become flrst horseshoe-shaped and then mesarch and concentric (Text-flg. 16, 11). Ultimately they die out after passing up the side of the megaspore cavity for some little distance. The essential feature to which attention is drawn consists in the development of anomalous vascular tissue, with inverted orientation, throughout the region of the collar. This tissue is strictly conflned to the collar and takes no part in the vascular supply of the ovule. Besides the anomalous tissue the peculiar manner in which the main bundle becomes concentric is worthy of notice. Stress has already been laid on the fact that throughout this process its cambium remains continuous with that of the anomalous tissue; i.e., while the " horns " approach one another, during the passdge of the bundle upwards, the cambium remains continuous round the " horns." Since these approach one another fairly rapidly, as is shewn by the fact that their tracheids run longitudinally in the transverse sections, it follows that a sort of oblique gutter of cambium is formed on either flank of the main bundle. The outer wall of the gutter is the cambium of the anomalous tissue, the inner wall that of the main bundle. A consideration of the description together with the photograph of the model will make this clear (Text-flg. 18). / v"
6 90 F. J. F. Shaw. A series of longitudinal sections cut at right angles to the plane of the ovules affords a complete confirmation of the interpretation advanced above. Such a series is of course tangential to the main bundle. The sections begin on the side farthest from the sterile ovule hence we gradually cut through the main bundle and into the "horns." In Text-fig. 17, it the main bundle is shewn, flanked by two others with inverted orientation. Further across the main bundle the plane of section traverses the region where it is passing into the concentric state. A section here shows the main bundle with two lateral anomalous bundles; the cambium, however, is continuous, the latter appearing as wings of the former (Text-fig. 17, 13); all the tracheids mti longitudinally. Here is seen the first indication of the gutter of cambium, filled, of course, with phloem, as' described above^ In the succeeding sections, approaching the sterile ovule, the distance from the top of the main bundle to the bottom of the gutters decreases, this shows that the gutters are running obliquely upwards through the collar (Text-fig. 17,14 and 15). illll m U. Text-flg. 17. Longitudinal sections (tangential). 12, 13, 14. Sections passing through main bundle towards sterile ovule cambium of main bundle continuous with that of anomalous tissue. 15. Tracheids of anomalous tissue and those of main bundle at the " horns " cut transversely. 16. Union of "horns" above, the main bundle is giving rise to one of the smaller concentric bundles in the ovule.
7 The Anatomy of Ginkgo biloba. 91 It will be remembered that in describing the transverse sections it was pointed out that the tracheids of the " horns" were cut longitudinally. In the longitudinal sections these are of course cut transversely (Text-flg. 17, 15). It is easy to realise how, during the transition of the main bundle to the concentric state, the anomalous tissue encircles the newly-formed half of the main bundle. The Text-fig. 18. Photograph of model of vascular tissue in collar, model shows xylem only and is viewed from above and behind. " Horns" of main bundle point away from, and anomalous tissue points towards observer; white lines show curve of tracheids. Area marked M. filled with metaxylem (which is not shown in the model), hence the union of "horns" can be seen at D; the lighter area C is the cambium. Note on one side the oblique gutter G caused by union of cambium of the anomalous tissue with that of the main bundle. tracheids of the main bundle belonging to the "horns" are also cut transversely, and they are situated at the base and inner side of the gutters. The union of these tracheids, when the main bundle becomes concentric, is shown in Text-fig. 17, 16. Here they are seen running from either side of the main bundle across it to the centre, and at right angles to its length. CONCLUSIONS. The occasional occurrence of an apical bud between the ovules and the general anatomy, force us to consider the peduncle as a shoot bearing two lateral stalked ovules. Each ovule is attached to the peduncle by a short pedicel, and at the point of union of pedicel and ovule we have the collar. It is however difficult to account for the inverted vascular tissue of the collar if we consider it as a reduced carpel, a view which has often been expressed. The pedicel seems to have a petiolar structure relative to the main 8hoot, for the single vascular bundle which traverses it has xylem
8 92 The Anatomy of Ginkgo biloba. directed towards what would be the upper surface. The relationship is however obscured owing to the excessive development of one ovule, which comes to lie almost apically. The pedicel passes very rapidly into the collar with its inverted bundles. Now in the seed Lagenostonia Lomaxi it is stated that the pedicel has the structure of a petiole, and, what from our point of view is more important, in the cupule the vascular bundles are often inverted (Oliver and Scott Phil. Trans., Vol. 197 B, 1904). It is only fair to state however that the general impression in the minds of the authors seems to have been that the bundles were, as a rule, normally orientated although there was a considerable amount of variation. At all events for the present we would tentatively suggest that, in the light of anatomical investigation, the collar of the ovule in Ginkgo is better regarded as a vestigial cupule than as anything in the nature of a carpel. Perhaps when our knowledge of the Pteridosperm seeds with cupules is more extended we may flnd some in which the cupular bundles were, as a rule, inversely orientated. In this connection it is interesting to note that* at the base of the seeds of certain Cycads (C. revoluta, C. Rumphii) we have a state of affairs closely paralleled in the collar of Ginkgo, the single vascular bundle supplying the ovule being accompanied on its outer convex side by a number of inversely orientated strands (Worsdell, Annalsof Bot. XII., 1898, PI. XVII., Pig. 4). It seems therefore as if both Ginkgo and the Cycads might have been derived from forms with cupuliferous seeds, a conclusion which coincides with other evidence. By some writers the collar has been considered as an outer integument, but if we are to look for an outer integument in the lower Gymnosperms we are much more likely to flnd it in the double nature of the real integument of Ginkgo and the Cycads than in the " collar" of the former, which appears to be essentially a "cupule," an organ sui generis. Of course it may be urged that the vascular bundles described in the present paper simply indicate that Ginkgo originally possessed a vascular structure similar to that of the MeduUosese. This view however would take no account of the peculiar situation of the anomalous tissue and, further, it offers no explanation of the "collar." It should also be remembered that the seed is a large one, and this fact, taken in conjunction with the large development of " transfusion tracheids," renders it possible that the presence of additional vascular tissue may have a physiological, rather than a morphological, signiflcance.
9
SOME time ago, in the pages of this journal. Miss Saunders described
 [359] FLORAL ANATOMY OF RIVINA HUMILIS L., AND THE THEORY OF CARPEL POLYMORPHISM BY A. C. JOSHI AND V. S. Benares Hindu University, India (With 6 figures in the text) RAO SOME time ago, in the pages of
[359] FLORAL ANATOMY OF RIVINA HUMILIS L., AND THE THEORY OF CARPEL POLYMORPHISM BY A. C. JOSHI AND V. S. Benares Hindu University, India (With 6 figures in the text) RAO SOME time ago, in the pages of
ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme of
 ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
Overton,1 who has worked exhaustively at the subject, looked upon. considered by some to be due to the state of the fluid originally in the
 THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
BRIEFER ARTICLES OF GINKGO THE MICROSPOROPHYLLS
 BRIEFER ARTICLES THE MICROSPOROPHYLLS OF GINKGO CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY I34 (WITH, PLATE VII) This study was undertaken in the first place to determine the origin of the mucilage
BRIEFER ARTICLES THE MICROSPOROPHYLLS OF GINKGO CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY I34 (WITH, PLATE VII) This study was undertaken in the first place to determine the origin of the mucilage
GAMETOPHYTE OF PELLIA EPIPHYLLA
 GAMETOPHYTE OF PELLIA EPIPHYLLA CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY 206 A. H. HUTCHIN SON (WITH PLATES I-IV AND ONE. FIGURE) Three of the species of Pellia-P. epiphylla, P. calycina, and P.
GAMETOPHYTE OF PELLIA EPIPHYLLA CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY 206 A. H. HUTCHIN SON (WITH PLATES I-IV AND ONE. FIGURE) Three of the species of Pellia-P. epiphylla, P. calycina, and P.
Plant Terminology. Floral Symmetry
 Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
DR. SCOTT has recently been revising the catalogue of his
 i6 Mrs. D. H. Scott. ON THH MEGASPORE OP FOLIACEUS. LEPIDOSTROBUS BY RINA (MRS. D. H.) SCOTT, F.L.S, [WITH PLATE VIII. AND TEXT-FIGS 24, 25.] DR. SCOTT has recently been revising the catalogue of his collection
i6 Mrs. D. H. Scott. ON THH MEGASPORE OP FOLIACEUS. LEPIDOSTROBUS BY RINA (MRS. D. H.) SCOTT, F.L.S, [WITH PLATE VIII. AND TEXT-FIGS 24, 25.] DR. SCOTT has recently been revising the catalogue of his collection
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS
![[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS [396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS](/thumbs/84/89173932.jpg) [396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS I BY S. B. KAUSIK, M.SC. Central College, Bangalore With 5 figures in the text N the following study, a description is given of five cases of abnormalities
[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS I BY S. B. KAUSIK, M.SC. Central College, Bangalore With 5 figures in the text N the following study, a description is given of five cases of abnormalities
STIRLING, M.D., SC.D., F.R.S.R, Regius Professor of the Institutes
 ON THE EPITHELIUM OF THE CORNEA. By WM. STIRLING, M.D., SC.D., F.R.S.R, Regius Professor of the Institutes of Medicine, and D AVID SKINNER, M.A., Student of Medicine in the Universty of Aberdeen. (PI.
ON THE EPITHELIUM OF THE CORNEA. By WM. STIRLING, M.D., SC.D., F.R.S.R, Regius Professor of the Institutes of Medicine, and D AVID SKINNER, M.A., Student of Medicine in the Universty of Aberdeen. (PI.
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
Seed Plants: An Overview of Terms
 Topic 25. Introduction to the Seed Plants: The Gymnosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Conifers Genus Pinus The Cycads The Ginkgoes Gnetophyes (The Vessel Bearing Gymnosperms) Seed Plants: An Overview
Topic 25. Introduction to the Seed Plants: The Gymnosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Conifers Genus Pinus The Cycads The Ginkgoes Gnetophyes (The Vessel Bearing Gymnosperms) Seed Plants: An Overview
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
GENES AND CHROMOSOMES CHAPTER 5
 CHAPTER 5 GENES AND CHROMOSOMES For many years the standard authority on the chromosomes was Wilson s The Cell in Development and Inheritance. The second edition of this work was published in 1900; it
CHAPTER 5 GENES AND CHROMOSOMES For many years the standard authority on the chromosomes was Wilson s The Cell in Development and Inheritance. The second edition of this work was published in 1900; it
AN ADDITION TO THE BISPORIC EMBRYO SACS-THE DICRAEA TYPE
 AN ADDITION TO THE BISPORIC EMBRYO SACS-THE DICRAEA TYPE BY A. J. MUKKADA Department of Botany, University of Delhi, Delhi 6, India {Received io February 1964) SUMMARY The embryo sac in Dicraea is tetra-nucleate
AN ADDITION TO THE BISPORIC EMBRYO SACS-THE DICRAEA TYPE BY A. J. MUKKADA Department of Botany, University of Delhi, Delhi 6, India {Received io February 1964) SUMMARY The embryo sac in Dicraea is tetra-nucleate
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of th
 Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
FURTHER STUDIES OF THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE BIRD'S HEART
 FURTHER STUDIES OF THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE BIRD'S HEART By FRANCIS DAVIES, M.D. (LONDON) Anatomy Department, University College, London INTRODUCTION T1HE histological investigation of the conducting
FURTHER STUDIES OF THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE BIRD'S HEART By FRANCIS DAVIES, M.D. (LONDON) Anatomy Department, University College, London INTRODUCTION T1HE histological investigation of the conducting
[255 ] BY P. MAHESHWARI AND ASHRAFUL. (With 15 Figures in the Text)
![[255 ] BY P. MAHESHWARI AND ASHRAFUL. (With 15 Figures in the Text) [255 ] BY P. MAHESHWARI AND ASHRAFUL. (With 15 Figures in the Text)](/thumbs/81/83172300.jpg) [255 ] THE EMBRYO SAC OF CHRYSANTHEMUM '. PARTHENIUM L. (BERNH.)* BY P. MAHESHWARI AND ASHRAFUL HAQUE (With 15 Figures in the Text) Palm, in 1916, gave the first detailed account of the development of
[255 ] THE EMBRYO SAC OF CHRYSANTHEMUM '. PARTHENIUM L. (BERNH.)* BY P. MAHESHWARI AND ASHRAFUL HAQUE (With 15 Figures in the Text) Palm, in 1916, gave the first detailed account of the development of
GENERAL SCOPE AND USES OF PHYSICAL/BIOLOGICAL ANTHROPOLOGY. Paper No. & Title: B.A./B.Sc. (Honours) 2 dn semester. (Practical)
 GENERAL SCOPE AND USES OF PHYSICAL/BIOLOGICAL ANTHROPOLOGY Course name: Physical Anthropology Paper No. & Title: B.A./B.Sc. (Honours) 2 dn semester (Practical) Topic No. & Title: 5/12 (Part-I) Drawing
GENERAL SCOPE AND USES OF PHYSICAL/BIOLOGICAL ANTHROPOLOGY Course name: Physical Anthropology Paper No. & Title: B.A./B.Sc. (Honours) 2 dn semester (Practical) Topic No. & Title: 5/12 (Part-I) Drawing
frontalis muscle while the patient makes an attempt to open the eye. With the first and third classes I am not now concerned, except
 OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
Peony Flower Anatomy I
 Peony Flower Anatomy I Don Hollingsworth, APS Director Maryville, Missouri What Makes a Peony Flower Luxurious? Rich luxury of the flowers explains why peonies are wanted, why loved and why known in history
Peony Flower Anatomy I Don Hollingsworth, APS Director Maryville, Missouri What Makes a Peony Flower Luxurious? Rich luxury of the flowers explains why peonies are wanted, why loved and why known in history
On the STRUCTURE of the PROBOSCIS of Ophideres fidlonica, an ORANGE-SUCKING MOTH. By FRANCIS DARWIN, M.B.
 384 FRANCIS DARWIN. On the STRUCTURE of the PROBOSCIS of Ophideres fidlonica, an ORANGE-SUCKING MOTH. By FRANCIS DARWIN, M.B. IT rnusfc be -premised that the fact of some Lepidoptera piercing vegetable
384 FRANCIS DARWIN. On the STRUCTURE of the PROBOSCIS of Ophideres fidlonica, an ORANGE-SUCKING MOTH. By FRANCIS DARWIN, M.B. IT rnusfc be -premised that the fact of some Lepidoptera piercing vegetable
The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum.
 The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L.
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L. BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, Bedford College, Regent's Park, London, N.W.i {Received 4 January 1959) (With Plates 3
DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L. BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, Bedford College, Regent's Park, London, N.W.i {Received 4 January 1959) (With Plates 3
The arteries of the human kidney
 J. Anat. (1966), 100, 4, pp. 881-894 881 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain The arteries of the human kidney BY H. FINE AND E. N. KEEN Department of Anatomy, University of Natal INTRODUCTION A study
J. Anat. (1966), 100, 4, pp. 881-894 881 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain The arteries of the human kidney BY H. FINE AND E. N. KEEN Department of Anatomy, University of Natal INTRODUCTION A study
THE ENDOSPERM OF ANGIOSPERMS
 THE ENDOSPERM OF ANGIOSPERMS CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY I50 JOHN M. COULTER In a recent analysis of all the available testimony in reference to the morphological nature of the endosperm
THE ENDOSPERM OF ANGIOSPERMS CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY I50 JOHN M. COULTER In a recent analysis of all the available testimony in reference to the morphological nature of the endosperm
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
11 DO BEES SEE SHAPES?1
 11 DO BEES SEE SHAPES? 1 When the human eye looks at an object, it is almost impossible to avoid seeing its shape. We cannot imagine how we would not see the shape. So it might be difficult for readers
11 DO BEES SEE SHAPES? 1 When the human eye looks at an object, it is almost impossible to avoid seeing its shape. We cannot imagine how we would not see the shape. So it might be difficult for readers
Stretching. Knees: Rotate your knees in a circle, keeping them together and bending down slightly.
 Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 27, 2017 Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable N/A Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 27, 2017 Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable N/A Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the
![[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the [1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the](/thumbs/84/89127006.jpg) 'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]
![W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]](/thumbs/89/98832613.jpg) W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
THE FLORAL ANATOMY OF ELETTARIA CARDAMOMUM MATON, A RE-INVESTIGATION
 THE FLORAL ANATOMY OF ELETTARIA CARDAMOMUM MATON, A RE-INVESTIGATION BY R. M. PAI Department of Botany, Marathwada University, Aurangabad, India {Received 13 July 1964) SUMMARY The re-investigation indicates
THE FLORAL ANATOMY OF ELETTARIA CARDAMOMUM MATON, A RE-INVESTIGATION BY R. M. PAI Department of Botany, Marathwada University, Aurangabad, India {Received 13 July 1964) SUMMARY The re-investigation indicates
WILLIAM CLIFFORD MORSE.
 Nov., 1907.] Life History of Cornuz Florida. 197 CONTRIBUTION TO THE LIFE HISTORY OF CORNUS FLORIDA.* WILLIAM CLIFFORD MORSE. This study of the Flowering Dogwood was undertaken at the suggestion of Professor
Nov., 1907.] Life History of Cornuz Florida. 197 CONTRIBUTION TO THE LIFE HISTORY OF CORNUS FLORIDA.* WILLIAM CLIFFORD MORSE. This study of the Flowering Dogwood was undertaken at the suggestion of Professor
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
PROGRESSIVE AND RESOLVING INFANTILE IDIOPATHIC SCOLIOSIS. The Differential Diagnosis
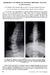 PROGRESSIVE AND RESOLVING INFANTILE IDIOPATHIC SCOLIOSIS The Differential Diagnosis J. H. FERREIRA, RIO DE JANEIRO, BRAZIL, and J. I. P. JAMES, EDINBURGH, SCOTLAND From the Princess Margaret Rose Orthopaedic
PROGRESSIVE AND RESOLVING INFANTILE IDIOPATHIC SCOLIOSIS The Differential Diagnosis J. H. FERREIRA, RIO DE JANEIRO, BRAZIL, and J. I. P. JAMES, EDINBURGH, SCOTLAND From the Princess Margaret Rose Orthopaedic
Anatomy Lecture #19 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE THORAX April 3, 2012
 Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Studies on the Nervous System of Crustacea.
 STUDIES ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OF CRUSTACEA. 33 Studies on the Nervous System of Crustacea. By Edgar.1. Allen, B.Sc, Director of the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological Association. With Plate
STUDIES ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OF CRUSTACEA. 33 Studies on the Nervous System of Crustacea. By Edgar.1. Allen, B.Sc, Director of the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological Association. With Plate
REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
 REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY I95 JOHN M. COULTER In connection with the vast accumulation of facts concerning reproduction, our morphological categories are in
REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE HULL BOTANICAL LABORATORY I95 JOHN M. COULTER In connection with the vast accumulation of facts concerning reproduction, our morphological categories are in
IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS.
 CULTIVATION IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS. (From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Pr~AT~ LXXVII. The growth of malignant
CULTIVATION IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS. (From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Pr~AT~ LXXVII. The growth of malignant
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
W.A. van Heel. of Palmae, which is distinguished by. ofthe Salacca fruit can be called an aril in a. seeds. The hard kernels are formed by the white
 BLUMEA 23 (1977) 371375 On the morphology of the ovules in Salacca (Palmae) W.A. van Heel Rijksherbarium, Leiden, Netherlands Female inflorescences in several stages of development of Salacca edulis Reinw.
BLUMEA 23 (1977) 371375 On the morphology of the ovules in Salacca (Palmae) W.A. van Heel Rijksherbarium, Leiden, Netherlands Female inflorescences in several stages of development of Salacca edulis Reinw.
Relationship between limbal incisions. angle. and the structures of the anterior chamber
 Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Sporocarp of Marsilea. Dr.Sukanya Baruah Chaliha. Asst. Professor Dept of Botany Class-3 rd Sem(Major) MDKG College,Dibrugarh.
 Sporocarp of Marsilea Dr.Sukanya Baruah Chaliha. Asst. Professor Dept of Botany Class-3 rd Sem(Major) MDKG College,Dibrugarh. External Morphology Soft and green when young but turns dark brown and hard
Sporocarp of Marsilea Dr.Sukanya Baruah Chaliha. Asst. Professor Dept of Botany Class-3 rd Sem(Major) MDKG College,Dibrugarh. External Morphology Soft and green when young but turns dark brown and hard
"^mz-cypo cricxj. dissection, we will examine the 3-dimensional structure of the mammalian brain and consider the functions of some of its parts.
 "^mz-cypo cricxj Sidogy083 ^ ^ furore fx^t-^tb ' BRAIN DISSECTION PURPOSE The brain, more than any other organ, is what determines the capabilities of an organism. It affects all aspects of the body from
"^mz-cypo cricxj Sidogy083 ^ ^ furore fx^t-^tb ' BRAIN DISSECTION PURPOSE The brain, more than any other organ, is what determines the capabilities of an organism. It affects all aspects of the body from
Vascular Pattern in Tumours
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Vascular Pattern in Tumours To cite this article: (1957) Vascular Pattern in Tumours, Acta Radiologica,
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Vascular Pattern in Tumours To cite this article: (1957) Vascular Pattern in Tumours, Acta Radiologica,
Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi
 Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi There are six extrinsic muscles of the eyeball, namely the (S), Medial (M), (I), & Lateral (L) recti, and (SO) and (IO) Obliques. In
Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi There are six extrinsic muscles of the eyeball, namely the (S), Medial (M), (I), & Lateral (L) recti, and (SO) and (IO) Obliques. In
DOUBLE TEETH IN THE SPERM WHALE (PHYSETER MACROCEPHALUS L.)
 DOUBLE TEETH IN THE SPERM WHALE (PHYSETER MACROCEPHALUS L.) by H. BOSCHMA Recently a fairly large number of teeth of the sperm whale were acquired for the collections of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke
DOUBLE TEETH IN THE SPERM WHALE (PHYSETER MACROCEPHALUS L.) by H. BOSCHMA Recently a fairly large number of teeth of the sperm whale were acquired for the collections of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Fellow of King's College, Cambridge.
 ON AN APPARENT MUSCULAR INHIBITION PRO- DUCED BY EXCITATION OF THE NINTH SPINAL NERVE OF THE FROG, WITH A NOTE ON THE WEDENSKY INHIBITION. BY V. J. WOOLLEY, Fellow of King's College, Cambridge. (From the
ON AN APPARENT MUSCULAR INHIBITION PRO- DUCED BY EXCITATION OF THE NINTH SPINAL NERVE OF THE FROG, WITH A NOTE ON THE WEDENSKY INHIBITION. BY V. J. WOOLLEY, Fellow of King's College, Cambridge. (From the
SPERM PENETRATION OF THE ZONA PELLUCIDA OF THE PIG EGG
 J. Exp. Biol. (1964), 4*. 603-608 603 With 3 plates and 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain SPERM PENETRATION OF THE ZONA PELLUCIDA OF THE PIG EGG BY Z. DICKMANN AND P. J. DZIUK Department of Obstetrics
J. Exp. Biol. (1964), 4*. 603-608 603 With 3 plates and 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain SPERM PENETRATION OF THE ZONA PELLUCIDA OF THE PIG EGG BY Z. DICKMANN AND P. J. DZIUK Department of Obstetrics
AND ANG., AND L. WITH REMARKS ON SOME UNDESCRIBED CHARAC- LORICELLA (ORDER POLYPLACOPHORA) TERS PRESENT IN LORICELLA ANGASI, AD.
 . DESCRIPTION OF A NEW SPECIES OF FOSSIL LORICELLA (ORDER POLYPLACOPHORA) WITH REMARKS ON SOME UNDESCRIBED CHARAC- TERS PRESENT IN LORICELLA ANGASI, AD. AND ANG., AND L. TORRI, ASHBY. By Edwin Asuby, F.L.S.,
. DESCRIPTION OF A NEW SPECIES OF FOSSIL LORICELLA (ORDER POLYPLACOPHORA) WITH REMARKS ON SOME UNDESCRIBED CHARAC- TERS PRESENT IN LORICELLA ANGASI, AD. AND ANG., AND L. TORRI, ASHBY. By Edwin Asuby, F.L.S.,
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
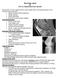 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
INSERTION* SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE LEVATOR PALPEBRAE. impossible to dissect and separate these layers. That the levator aponeurosis
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 503. SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE LEVATOR PALPEBRAE INSERTION* BY EDWARD EPSTEIN Johannesburg, Union of South Africa THE text-book description of the anatomy of the upper eyelid
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 503. SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE LEVATOR PALPEBRAE INSERTION* BY EDWARD EPSTEIN Johannesburg, Union of South Africa THE text-book description of the anatomy of the upper eyelid
seed embryo microscopic gametophytes Gymnospermes Angiosperms
 Gymnosperms Spermatophytes It is the group that includes seed-producing plants. The seed contains embryo, protects it during adverse conditions and contains all nutrients needed for the seedling development.
Gymnosperms Spermatophytes It is the group that includes seed-producing plants. The seed contains embryo, protects it during adverse conditions and contains all nutrients needed for the seedling development.
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Chapter 12. Biology of Non-Flowering Plants
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 12 Chapter 12 Biology of Non-Flowering Plants Objectives Overview of Non-Flowering Plants. Know the distinguishing characteristics of plants. Know the plant
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 12 Chapter 12 Biology of Non-Flowering Plants Objectives Overview of Non-Flowering Plants. Know the distinguishing characteristics of plants. Know the plant
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
GOMPHOTHERIUM ELEGANS, FROM THE PLEISTO-
 DESCRIPTION OF A NEW SPECIES OF MASTODON, GOMPHOTHERIUM ELEGANS, FROM THE PLEISTO- CENE OF KANSAS. By Oliver P. Hay, Research As.iu.iiitc of the Carnegie In-stituti'in of Wn-:]iingto)i. The specimen here
DESCRIPTION OF A NEW SPECIES OF MASTODON, GOMPHOTHERIUM ELEGANS, FROM THE PLEISTO- CENE OF KANSAS. By Oliver P. Hay, Research As.iu.iiitc of the Carnegie In-stituti'in of Wn-:]iingto)i. The specimen here
ON THE KINETIC AND INVASIVE POWER OF REGEN- ERATING TISSUE AND ON SIMILARITIES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF THYROID TRANSPLANTS AND CARCINOMAS
 ON THE KINETIC AND INVASIVE POWER OF REGEN- ERATING TISSUE AND ON SIMILARITIES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF THYROID TRANSPLANTS AND CARCINOMAS LEO LOEB Received for publication, December 22, 1919 The following observations
ON THE KINETIC AND INVASIVE POWER OF REGEN- ERATING TISSUE AND ON SIMILARITIES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF THYROID TRANSPLANTS AND CARCINOMAS LEO LOEB Received for publication, December 22, 1919 The following observations
A SIX-STAMENED FLOWER IN ZEA MAYS L.
 130 A SIX-STAMENED FLOWER IN ZEA MAYS L. BY B. C. Department of Botany, University of Leeds (With 2 figures in the text) During the examination of the tassel of a maize plant, a number of flowers were
130 A SIX-STAMENED FLOWER IN ZEA MAYS L. BY B. C. Department of Botany, University of Leeds (With 2 figures in the text) During the examination of the tassel of a maize plant, a number of flowers were
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
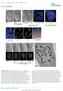 DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
Calculating volume scotomas for patients with central scotomas
 APPENDIX Calculating volume scotomas for patients with central scotomas This appendix provides formulas to derive the shape and extent of volume scotomas for some simple examples of bilateral central field
APPENDIX Calculating volume scotomas for patients with central scotomas This appendix provides formulas to derive the shape and extent of volume scotomas for some simple examples of bilateral central field
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown. By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi
 Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida
 Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Physiological and Morphogenetic Studies of Fern Gametophyte and Sporophyte by Aseptic Culture VI. Notes on the Alternation of Generations
 Bot. Map. Tokyo 78:187-193 (June 25, 1965) Physiological and Morphogenetic Studies of Fern Gametophyte and Sporophyte by Aseptic Culture VI. Notes on the Alternation of Generations by Yukio KATO * Received
Bot. Map. Tokyo 78:187-193 (June 25, 1965) Physiological and Morphogenetic Studies of Fern Gametophyte and Sporophyte by Aseptic Culture VI. Notes on the Alternation of Generations by Yukio KATO * Received
11.1 The Aortic Arch General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta
 456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
6. Gear Measurement And Testing
 6. Gear Measurement And Testing Introduction Gears are mainly used for transmission of power and motion. They are used in various automobiles, machines, equipments, electronic systems, etc. We already
6. Gear Measurement And Testing Introduction Gears are mainly used for transmission of power and motion. They are used in various automobiles, machines, equipments, electronic systems, etc. We already
Introduction. Rarely does a single muscle act in isolation at the shoulder complex.
 Shoulder complex 1 Introduction Our study of the upper limb begins with the shoulder complex, a set of four articulations involving the sternum, clavicle, ribs, scapula, and humerus. Rarely does a single
Shoulder complex 1 Introduction Our study of the upper limb begins with the shoulder complex, a set of four articulations involving the sternum, clavicle, ribs, scapula, and humerus. Rarely does a single
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions?
 Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter 22
 63 UNIT 5: GYMNOSPERMS th Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter 22 OBJECTIVES This lab considers the gymnosperms, vascular plants that produce seeds but lack flowers and fruits.
63 UNIT 5: GYMNOSPERMS th Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter 22 OBJECTIVES This lab considers the gymnosperms, vascular plants that produce seeds but lack flowers and fruits.
On Sporocarpon ornalum. 19
 On Sporocarpon ornalum. 19 Ashton-under-Lyne,' showing the existence of a canal in the centre of each of the projections or crenulations, whilst the peripheral clusters of large cells are wanting. The
On Sporocarpon ornalum. 19 Ashton-under-Lyne,' showing the existence of a canal in the centre of each of the projections or crenulations, whilst the peripheral clusters of large cells are wanting. The
Fig. 12 Trigonias?osborni Lucas, SMNH PI637.2, left maxillary fragment with pi to MI; occlusal view, x I. DESCRIPTION
 Fig. 12 Trigonias?osborni Lucas, SMNH PI637.2, left maxillary fragment with pi to MI; occlusal view, x I. DESCRIPTION SMNH P1637.1 has the teeth somewhat cracked but otherwise well preserved. p 2 is very
Fig. 12 Trigonias?osborni Lucas, SMNH PI637.2, left maxillary fragment with pi to MI; occlusal view, x I. DESCRIPTION SMNH P1637.1 has the teeth somewhat cracked but otherwise well preserved. p 2 is very
Improved Processing Research on Arc Tooth Cylindrical Gear
 International Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Analysis 2017; 5(3): 91-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijema doi: 10.11648/j.ijema.20170503.14 ISSN: 2328-7659 (Print); ISSN: 2328-7667
International Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Analysis 2017; 5(3): 91-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijema doi: 10.11648/j.ijema.20170503.14 ISSN: 2328-7659 (Print); ISSN: 2328-7667
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
DR. N. A. PURANDAKE, M.D., F.C.P.S.
 J Obs Gyn Brit Emp 1937 V-44 Radiograms taken during Labour from its onset until the Head is Born, indicating the Position of the Anterior and Posterior Shoulders BY DR. N. A. PURANDAKE, M.D., F.C.P.S.
J Obs Gyn Brit Emp 1937 V-44 Radiograms taken during Labour from its onset until the Head is Born, indicating the Position of the Anterior and Posterior Shoulders BY DR. N. A. PURANDAKE, M.D., F.C.P.S.
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Individual Differences in Texture Discrimination
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Individual Differences in Texture Discrimination Timothy N. Rubin (trubin@uci.edu) Michael D. Lee (mdlee@uci.edu) Charles F. Chubb (cchubb@uci.edu) Department of Cognitive
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Individual Differences in Texture Discrimination Timothy N. Rubin (trubin@uci.edu) Michael D. Lee (mdlee@uci.edu) Charles F. Chubb (cchubb@uci.edu) Department of Cognitive
Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology
 Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology For more detailed coverage of this subject, consult ANSI/AGMA Standard 1012-F90; Gear Nomenclature, Definitions with Terms and Symbols Active Profile- that part of the gear
Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology For more detailed coverage of this subject, consult ANSI/AGMA Standard 1012-F90; Gear Nomenclature, Definitions with Terms and Symbols Active Profile- that part of the gear
9700 BIOLOGY. Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for Teachers.
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/31 Paper 31 (Advanced Practical Skills 1), maximum raw
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/31 Paper 31 (Advanced Practical Skills 1), maximum raw
30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Transforming
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Transforming
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS
![[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS [485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS](/thumbs/90/101209894.jpg) [485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 3 November 1954) The thoracic or ' prothoracic'
[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 3 November 1954) The thoracic or ' prothoracic'
Safety Dissection tools are very sharp. Use appropriately and do not leave unattended in the presence of children.
 Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
MELANOCYTE PATTERN OF AN AREA OF FRECKLED EPIDERMIS COVERING A STRETCHED SCAR*
 MELANOCYTE PATTERN OF AN AREA OF FRECKLED EPIDERMIS COVERING A STRETCHED SCAR* Figure 1 illustrates the appearance after eighteen months of the scar resulting from the removal of an area of full thickness
MELANOCYTE PATTERN OF AN AREA OF FRECKLED EPIDERMIS COVERING A STRETCHED SCAR* Figure 1 illustrates the appearance after eighteen months of the scar resulting from the removal of an area of full thickness
An Electron-Microscope Study of Germination of Conidia of Botrytis cinerea
 J. gen. Microbiol. (1963), 33, 43-46 With 2 plates Printed in Great Britain 43 An Electron-Microscope Study of Germination of Conidia of Botrytis cinerea BY LILIAN E. HAWKER AND R. J. HENDY Department
J. gen. Microbiol. (1963), 33, 43-46 With 2 plates Printed in Great Britain 43 An Electron-Microscope Study of Germination of Conidia of Botrytis cinerea BY LILIAN E. HAWKER AND R. J. HENDY Department
THE sebaceous glands of the rabbit consist of clusters of about ten cells
 79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
DROSERA CAPENSIS L.: HISTO-ANATOMY OF THE VEGETATIVE ORGANS. Introduction
 Analele ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Al. I. Cuza Iaşi Tomul LV, fasc. 1, s.ii a. Biologie vegetală, 2009 DROSERA CAPENSIS L.: HISTO-ANATOMY OF THE VEGETATIVE ORGANS IRINA STĂNESCU *, C. TOMA ** Abstract.
Analele ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Al. I. Cuza Iaşi Tomul LV, fasc. 1, s.ii a. Biologie vegetală, 2009 DROSERA CAPENSIS L.: HISTO-ANATOMY OF THE VEGETATIVE ORGANS IRINA STĂNESCU *, C. TOMA ** Abstract.
7+ ASSESSMENTS FOR DAY BOY PLACES WHAT DO THEY INVOLVE?
 7+ ASSESSMENTS FOR DAY BOY PLACES WHAT DO THEY INVOLVE? In the January before their proposed year of entry, boys applying for 7+ (Year 3) day boy places at WCCS sit four written papers. English Comprehension
7+ ASSESSMENTS FOR DAY BOY PLACES WHAT DO THEY INVOLVE? In the January before their proposed year of entry, boys applying for 7+ (Year 3) day boy places at WCCS sit four written papers. English Comprehension
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
(12) United States Patent
 US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
perforated so as to allow irrigation even when it is in situ,
 A NEW INDIRECT IRRIGATING OBSERVATION AND DOUBLE CATHETERIZING CYSTOSCOPE. BY LEO BUERGER, M.D., OF NEW YORK, Assistant Adjunct Surgeon and Associate in Surgical Pathology, Mt. Sinai Hospital; Associate
A NEW INDIRECT IRRIGATING OBSERVATION AND DOUBLE CATHETERIZING CYSTOSCOPE. BY LEO BUERGER, M.D., OF NEW YORK, Assistant Adjunct Surgeon and Associate in Surgical Pathology, Mt. Sinai Hospital; Associate
UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES
 [218] UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES BY S. WOLDRING AND M. N. J. DIRKEN Physiological Institute, Groningen, Netherlands (Received 17 July 1950) (With Plate 2 and one Text-figure) Adrian
[218] UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES BY S. WOLDRING AND M. N. J. DIRKEN Physiological Institute, Groningen, Netherlands (Received 17 July 1950) (With Plate 2 and one Text-figure) Adrian
The University of Chicago Press is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to The Journal of Geology.
 Description of a New Species of Petalodus (P. Securiger) from the Carboniferous of Illinois Author(s): O. P. Hay Reviewed work(s): Source: The Journal of Geology, Vol. 3, No. 5 (Jul. - Aug., 1895), pp.
Description of a New Species of Petalodus (P. Securiger) from the Carboniferous of Illinois Author(s): O. P. Hay Reviewed work(s): Source: The Journal of Geology, Vol. 3, No. 5 (Jul. - Aug., 1895), pp.
Junctional Tissues of Human Heart
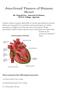 1 Junctional Tissues of Human Heart Mr. Rupajit Das, Associate Professor, M.B.B. College, Agartala Cardiac muscle consists essentially of certain specialised structures which are responsible for initiation
1 Junctional Tissues of Human Heart Mr. Rupajit Das, Associate Professor, M.B.B. College, Agartala Cardiac muscle consists essentially of certain specialised structures which are responsible for initiation
