Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
|
|
|
- Jeffrey Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 wrong right score Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar with a number of aspects of the vegetative structure of angiosperms from your previous laboratory work. Now you will concentrate on flower structure, since these are the parts of the plant that are most closely associated with sexual reproduction, and are widely used in the classification of the angiosperms. Over 250,000 species of angiosperms are recognized, and they include the principal plants covering the land surface and provide the great majority of the plants used for a variety of economic purposes. Flower Structure Although in gross appearance, the flowers of the angiosperms show a tremendous diversity, the parts which make up the flower are basically the same throughout. The most widely accepted interpretation of the nature of the flower is that it is a specialized branch; a stem with leaves. The flower has many parts. The plant stem below the flower is called the pedicel. At the very tip of this is the receptacle. The receptacle is the stem portion of the flower. It is found at the base in the center of the flower. Its internodes are short and the number of leaves is usually small, so the receptacle is not usually a large or obvious part of the flower. Sepals make up the lower (or outermost) whorl of floral leaves. They are frequently, but not always, green and rather leaf-like in appearance, although they usually are smaller than the foliage leaves of the plant. Collectively, all sepals of a flower constitute the calyx. The major function appears to be protection of the flower parts from herbivores during early development. Petals are attached above (inside) the sepals on the receptacle. They are usually larger than the sepals, brightly colored, and rather leaf-like in that they are broad and rather thin organs. Collectively they constitute the corolla. They serve as additional protection against herbivores in the bud stage, and also attract insects and/or facilitate the pollination of the flower when the insect reaches it. The two leaflike appendages, the sepals and petals (calyx and corolla), together make up the perianth of a complete flower. They may be similar in appearance to one another, or one or the other or both may be missing from an incomplete flower. Stamens, which are found above (inside) the corolla, are rarely leaflike in appearance. Each usually is composed of two distinct parts: an elongated narrow filament rising from the receptacle and a terminal enlarged anther which contains many pollen grains. All stamens of the flower, taken together, make up the androecium. One or more carpels, are located in the center (top) of the flower. Collectively they constitute the gynoecium. Each carpel has three parts. Starting at the base these are: the ovary, an enlarged hollow region bearing one or more ovules; a narrower, short to long style; and a terminal stigma of various sizes and shapes. If more than one carpel occurs in a flower, all may be separate from one another, but more frequently they are joined to one another to form a compound structure. The term pistil is often used in conjunction with the gynoecium of a flower; this may or may not be synonymous with carpel. If carpels are not fused to one another in a flower, then each carpel can be called a pistil and the flower has one or more simple pistils. If, however, more than one carpel occurs in the flower and these are all joined to one another, the flower has a single compound pistil. The cavity in the ovary portion of carpel or pistil is called the locule. There is one locule in a simple pistil and one or more in a compound pistil. The portion of the ovary to which the ovule is attached is the placenta. The number of ovules varies from one to several hundred per locule, depending upon the species. Document Ross E. Koning Permission granted for non-commercial instruction. Koning, Ross. E Flower Morphology. Plant Physiology Information Website.
2 Page 2 Carpels are not the only flower parts that may be joined to one another. Members of each whorl in the flower may be fused to other members of the same whorl. There may also be fusion between whorls; for example, the stamens of many flowers appear to diverge from the surface of the corolla. In an extreme case, the perianth and stamens are fused to the ovary wall and become free from it only at the top of the ovary. In flowers where the floral whorls diverge below the gynoecium, the ovary is said to be superior and the flower hypogynous. In contrast, when the free floral whorls arise from the top of the ovary, the ovary is called inferior and the flower epigynous. An intermediate condition can be found in which the several floral whorls are attached around the middle of the ovary; such a flower is called perigynous. Flowers are perfect, if both stamens and carpels are present but imperfect if one or the other is lacking. In the latter case, both staminate and carpellate flowers may occur on the same plant (monoecious) or may be on separate plants (dioecious). Flowers may be regular, exhibiting radial symmetry, or be irregular and show bilateral symmetry. Note, that in a longitudinal section such as the one below, it is not possible to be sure of the symmetry! Use as many of the terms in bold type in the description above as possible to label the longitudinal section below (there should be at least 24 labels!): /24
3 Page 3 Dissecting Alstroemeria Flowers Examine one of the flowers provided; draw and label the flower below to show all parts and their relation to one another. Then answer the following questions about your flower: What is the symmetry of your flower? radial bilateral. Are both calyx and corolla present? yes no.? The sepals are: free fused. The petals are: free fused. How many sepals are there? Petals? Stamens? Pistils? Where are the stamens in relation to the sepals and petals? If one, the pistil is: simple compound. If compound, of how many carpels is it composed? How did you determine this? I counted the and The ovary is: superior inferior. : The flower is: hypogynous perigynous epigynous. : How many ovules are there? one less than 20 many. Where is/are the placenta(e) to which they are attached? axile radial parietal. Give the complete flower formula for your flower (8 pts): -- Diagram and label your flower in the space provided below. Use as many structure name labels as possible based upon the description on pages 1 and 2 (16 labels required). /41
4 Page 4 Sex and Development in the Flower THE POLLEN GRAIN. Look carefully at the stamen of the flower. How many anther sacs do you find? In most species there are four, one in each corner of the anther, but at maturity the two in each half fuse. Cells produced in the anther sacs divide by meiosis to produce four microspores each. These separate from one another and each divides once by mitosis to produce a pollen grain composed of a tube cell and a smaller generative cell within the pollen wall. It is at this stage that the anther sac opens, most often longitudinally, and the pollen is shed. Observe the demonstration slide showing a cross section of a Lilium anther containing mature pollen grains. How can you distinguish the tube nucleus from the generative nucleus? The tube nucleus is The generative nucleus is Examine fresh pollen from one of the flowers in the lab. In the space below, sketch a diagram of the pollen grain (from a prepared slide) and label it completely. THE EMBRYO SAC. The carpel bears ovules which consist of one or two protective integuments which meet at the tip, leaving a narrow opening or micropyle. The ovule is connected to the ovary by means of a stalk, the funiculus. Inside the integument, meiosis has taken place and an haploid embryo sac develops within. This is organized into seven cells: three cells at the micropylar end (two synergids and one egg), three antipodal cells at the opposite end, and the one central cell containing two polar nuclei. /8
5 Page 5 Observe the demonstration slide(s) of the ovule and embryo sac in Rhododendron and, in the space below, sketch a diagram of the ovule with embryo sac and label completely. Place your labels for the integument, micropyle, and funiculus on the left side of the diagram. Place your labels for the parts of the embryo sac on the right side. POLLINATION AND SPERM PRODUCTION. When the pollen grain is shed from the anther, it is carried (usually by insect, bird, or wind) to the stigma of a carpel. The pollen grain germinates there, sending out the tube cell, which grows through the tissues of the stigma and style to reach the ovary. Keeping in mind the very small size of the pollen grain, and its non-green color, what is the source of nutrition of the pollen tube? The nuclei remain near the tip of the pollen tube as it passes through the style, and the generative nucleus undergoes mitosis to form two sperm nuclei. On reaching the ovary, the pollen tube enters an ovule via the micropyle, penetrating a synergid and there bursting at the tip. The two sperm nuclei are discharged. SYNGAMY. One of the two sperm nuclei moves to the egg cell and fuses with its nucleus to form the zygote. The second sperm nucleus fuses with the two polar nuclei in the central cell to form a primary endosperm cell. This double syngamy is characteristic of all angiosperms. If each nucleus in the syngamy has one set of chromosomes, how many sets would be found in the zygote? How many sets of chromosomes would be found in Observe the demonstration slide showing double syngamy in Lilium. the primary endosperm cell? The primary endosperm cell, the zygote, and the rest of the ovule form the seed, a subject for future study. /11
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
ANGIOSPERM L.S. POLLEN GRAIN
 ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S.
 POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
The Flower - what is it? 1/31/18. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants
 - what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
- what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12
 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Reproductive Development and Structure
 Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12
 BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
Plant Reproduction fertilization
 Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization)
 Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting
 Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
3/18/2012. Chapter 36. Flower Parts. Flower Parts. Reproduction in Angiosperms
 Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2
 NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
Reproduction in plants
 Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
 CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
Plant Terminology. Floral Symmetry
 Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits
 BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name: Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back and
Name: Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back and
BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION
 BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction MODES OF REPRODUCTION (1) Asexual one parent cell divides into two by mitosis to produce 2 identical cells which are clones of the parent (2) Sexual
BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction MODES OF REPRODUCTION (1) Asexual one parent cell divides into two by mitosis to produce 2 identical cells which are clones of the parent (2) Sexual
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Angiosperms. The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species.
 Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/22/10
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Original content Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
LABORATORY 2: Flowers
 LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
Reproduction 19/02/2016. Asexual Reproduction. Budding: Types of asexual reproduction: SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL
 Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS
 BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed
 Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction
 Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Downloaded from CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER
 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER Autogamy : When pollen grains of a flower are transferred from anther to stigma of the same flower. Coleorhiza : A protective sheath
CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER Autogamy : When pollen grains of a flower are transferred from anther to stigma of the same flower. Coleorhiza : A protective sheath
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS WITH SEEDS
 There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
Flowering plants can be pollinated by wind or animals.
 Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Botany Physiology. Due Date Code Period Earned Points
 Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
Nyla Phillips-Martin 2013 mscraftynyla.blogspot.com
 1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
Unit 2: Multicellular Organisms
 Unit 2: Multicellular Organisms Sub Topic 2.3 Reproduction On completion of the sub topic I will be able to state that: Gametes are sex cells. Gametes are haploid. Haploid cells contain one set of chromosomes.
Unit 2: Multicellular Organisms Sub Topic 2.3 Reproduction On completion of the sub topic I will be able to state that: Gametes are sex cells. Gametes are haploid. Haploid cells contain one set of chromosomes.
Unit E: Plant Propagation. Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction
 Unit E: Plant Propagation Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction 1 Vocabulary Cross-pollination Diploid Endosperm Fertilization Gametes Genes Haploid Hybrids Pollination Seed Self-pollination Sexual
Unit E: Plant Propagation Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction 1 Vocabulary Cross-pollination Diploid Endosperm Fertilization Gametes Genes Haploid Hybrids Pollination Seed Self-pollination Sexual
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. E2-4 Flower Anatomy
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
A2 WJEC BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Sexual reproduction in plants
 A2 WJEC BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Sexual reproduction in plants Biology Department - Gower College Swansea The generalised structure of flowers to be able to compare wind and insect pollinated flowers Learners should
A2 WJEC BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Sexual reproduction in plants Biology Department - Gower College Swansea The generalised structure of flowers to be able to compare wind and insect pollinated flowers Learners should
Plant Life Cycles. Plant life cycles alternate between. producing gametes. Life cycle phases look different among various
 Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Transforming
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Transforming
Seed Plants Lab. Learning Objectives. Procedure and Questions
 Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc.
 BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc. KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN Vegetatif vs generatif VEGETATIF VS GENERATIF Menurut pendapat Anda, makanah jenis reproduksi yang lebih baik bagi tumbuhan?
BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc. KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN Vegetatif vs generatif VEGETATIF VS GENERATIF Menurut pendapat Anda, makanah jenis reproduksi yang lebih baik bagi tumbuhan?
Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction
 3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida
 Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Safety Dissection tools are very sharp. Use appropriately and do not leave unattended in the presence of children.
 Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Parts of a Flower. Stamen = Pistil = Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel. anther + filament
 Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
16B Flower Dissection
 16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Operation Flower Dissection
 Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION
 UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL
 SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION?
 LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
Plant Reproduction. In a nutshell
 Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Pre Fertilisation Events Several hormonal and structural changes result in the development of a flower. Inflorescences bear the flower buds, and then the flowers.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Pre Fertilisation Events Several hormonal and structural changes result in the development of a flower. Inflorescences bear the flower buds, and then the flowers.
How To Make A Seed EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT AND THE LIFE CYCLE OF ANGIOSPERMS NORA COOPER JAZMIN SAMANO DOMINIC SAADI
 How To Make A Seed EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT AND THE LIFE CYCLE OF ANGIOSPERMS NORA COOPER JAZMIN SAMANO DOMINIC SAADI Why Study Seeds? o Within the next fi*y years we will need to produce more food than in
How To Make A Seed EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT AND THE LIFE CYCLE OF ANGIOSPERMS NORA COOPER JAZMIN SAMANO DOMINIC SAADI Why Study Seeds? o Within the next fi*y years we will need to produce more food than in
Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38)
 Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38) Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Rafflesia arnoldii, monster flower of Indonesia Orchid (Lemboglossum
Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38) Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Rafflesia arnoldii, monster flower of Indonesia Orchid (Lemboglossum
Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations
 ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
the reproductive organs of a flower
 Life Cycles, Reproduction & Heredity flower power the reproductive organs of a flower Frameworks SCIENCE LS 2.6.5 Model and explain the function of plant organs: leaves, roots, stems, flowers. LS 3.7.6
Life Cycles, Reproduction & Heredity flower power the reproductive organs of a flower Frameworks SCIENCE LS 2.6.5 Model and explain the function of plant organs: leaves, roots, stems, flowers. LS 3.7.6
CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants. Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences
 CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences Rafflesiaarnoldii in Indonesia Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Seeds and Fruits Flower Plant Reproduction Many
CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences Rafflesiaarnoldii in Indonesia Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Seeds and Fruits Flower Plant Reproduction Many
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE
 HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE Reproduction It is the formation of new similar young living organisms by the existing or grown up organisms of a species or race. In simple words reproduction is the creation
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE Reproduction It is the formation of new similar young living organisms by the existing or grown up organisms of a species or race. In simple words reproduction is the creation
o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into 2
 Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
W.4.1 Write opinion pieces on topics or texts, supporting a point of view with reasons and information.
 Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process. They will
Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process. They will
Objectives. Standards (NGSS and Common Core) For state specific standards visit edu.zspace.com/activities. Differentiation
 Dicot Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process.
Dicot Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process.
Name that Pollinator
 Name that Pollinator Name Date Part A: A short history of pollen The evolutionary success of plants can be easily appreciated by everyone. As autotrophs, plants form the basis of food chains without which
Name that Pollinator Name Date Part A: A short history of pollen The evolutionary success of plants can be easily appreciated by everyone. As autotrophs, plants form the basis of food chains without which
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet
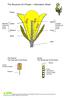 The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction?
 1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction? Sexual Reproduction - Genetic information from two cells is combined to produce a new genetically unique organism. Sexual reproduction occurs when
1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction? Sexual Reproduction - Genetic information from two cells is combined to produce a new genetically unique organism. Sexual reproduction occurs when
IGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 SCHEME OF WORK 1
 IGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 SCHEME OF WORK 1 UNIT 6: Reproduction in plants Recommended Prior Knowledge: A basic knowledge of cell structure will be helpful, but otherwise the Unit requires very little previous
IGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 SCHEME OF WORK 1 UNIT 6: Reproduction in plants Recommended Prior Knowledge: A basic knowledge of cell structure will be helpful, but otherwise the Unit requires very little previous
We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower.
 5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
REPRODUCTION: THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE
 Suggested time allotment: 5 to 6 hours MODULE 4 REPRODUCTION: THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE Overview The beginning of a new life is truly a remarkable event. The sight of a chick making its way out of the cracked
Suggested time allotment: 5 to 6 hours MODULE 4 REPRODUCTION: THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE Overview The beginning of a new life is truly a remarkable event. The sight of a chick making its way out of the cracked
"Our Flowering World" PRE-TEST. Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below:
 1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
Chapter 17. Part 1 Plants. Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land. Lecture by Dr. Prince
 Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land Part 1 Plants Lecture by Dr. Prince Plants and Fungi A Beneficial Partnership Plants and fungi colonized land together Mycorrhizae, mutually beneficial
Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land Part 1 Plants Lecture by Dr. Prince Plants and Fungi A Beneficial Partnership Plants and fungi colonized land together Mycorrhizae, mutually beneficial
Page 1 BHUPINDRA ROAD, NEAR SAHNI BAKERY, 22 NO. PHATAK ,
 8. HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE Reproduction: The process of producing new individual of the same species is called reproduction. Type of Reproduction Living organisms reproduce mainly by two methods: (i)
8. HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE Reproduction: The process of producing new individual of the same species is called reproduction. Type of Reproduction Living organisms reproduce mainly by two methods: (i)
Review of the previous lecture
 Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
 CHAPTER 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth. Reproduction
CHAPTER 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth. Reproduction
