ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme of
|
|
|
- Johnathan Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme of Digitalis purpiirea was observed during the past summer by Dr T. G. Hill in a specimen occurring in his garden, but most probably derived from wild seed; and in view of the exceptional nature of the abnormality it was felt that the occurrence ought to be placed on record. Various types of teratological flower forms have been recorded in the Foxglove, and both synanthy and peloria(1,2) arc common; the latter most often affects the flower at the summit of the inflorescence and may be associated with fasciation. Various abnormalities are also known in the androecium, and the inheritance of a heptandrous condition in which the corolla was absent has been worked out by Saunders(3). The present record is concerned with the lowermost flower in an inflorescence of D. purpurea which was otherwise normal in every respect; the malformation consisted essentially in a proliferation of this lateral floral axis and was attended by several minor abnormalities. The peduncle of the flower in question, the basal one of the inflorescence, arose normally in the axil of a leafy bract, and at a distance of some 3 cm. bore the flower which was not only abnormal in every floral whorl, but which was proliferated, gi^'ing rise to another inflorescence axis; on this the flower buds were arranged in a clockwise spiral around the axis. There was no apparent tendency for all the buds to be turned to one side, although the older buds had reached a stage of development at which this could be detected in a normal specimen. A general view of the monstrosity as seen from the side is given in Fig. I, in which one well-developed flower bud [B) is seen arising from the axil of one of the sepals, and another (E) is borne on the proliferated axis above the flower. Within the corolla, the axis bears a large number of flower buds. An examination of the specimeij PHYT. XXVII. z; 8
2 VIOLET L. ANDERSON (for diagram see Fig, 2) showed the calyx to include three normal sepals, of which two were the anterior ones and the other a lateral member of the whorl. The opposite lateral sepal (Fig. I, C, Fig, 2, B) was normal at the base, but it was prolonged to twice the usual length, the distal portion being petaloid. This structure bore a flower bud (Fig. i, B) in its a.xil. The posterior sepal was reduced to less than half the normal size and was slightly displaced in the downward direction on the peduncle. In its axil was a tiny bud Fig, I, View of specimen as seen from the side, A, small bud in axil of posterior sepal. B. well-developed flower bud arising in axil of petaloid sepal C, D, the new inflorescence axis produced within the flower and bearing many flower buds, of which E is one, (Figs. I and 2, A) which contained the rudiments of another flower, but which was so immature that it was not possible to determine whether or not it was in any way abnormal. The corolla was petaloid, and showed the usual characteristic coloration and markings of the species; but it was split between the two posterior components, the two edges thus formed being fused in their basal portions with the posterior sides of the proliferated axis (Fig. 2, D) which was produced forwards within the remaining part of the corolla. It would thus be possible to regard this new
3 On an Abnormality in Digitalis purpurea 119 axis as a development arising in the axil of the posterior sepal, but as this already carried one bud (Fig. 2, A) such an interpretation would involve the postulation of an accessory bud and the occurrence of two buds in the axil of a sepal is difficult to accredit. The corolla was perhaps chiefly remarkable for the possession of a spur-like outgrowth in the median plane of the anterior petal. This "spur" was well marked and conspicuous, being over i cm. in Fif 2. General diagram of the specimen. A, immature flower bud in axil of posterior sepal. B, bud in axil of lateral petaloid sepal. C, flower bud m axil of leaf contributing to the formation of the gynoecium. D, proliferated axis bearing many flower buds. E, "placenta" in axis of open carpellary leaf. G, petaloid stamen. length; it tapered distally but produced neither honey nor glandular tissue. Of the four stamens normally occurring in this species only two were represented, and these were the anterior ones. Flsewhere in this family when there are normally only two stamens, as in Veronica, the tendency is to suppress the posterior stamen and the anterior pair, but in the present teratological specimen all three posterior
4 120 VIOLET L. ANDERSON stamens were absent. Only one of the two stamens represented was normal and functional; the other was entirely lacking in any indication of differentiation into anther or filament; it was simply an elongated and free petaloid member showing the characteristic markings and texture of the corolla to which it was fused at the base. In the position of the gynoecium were two green and leaf-like structures arising from the proliferated axis of the flower, but fused in the anterior median plane below the new axis. One of these structures bore a flower bud in its axil (Fig. 2, C), the other had, in a similar position, a short solid outgrowth bearing ovules on its abaxial surface, and somewhat suggestive of the axile placenta of normal forms. The line of fusion between the two carpellary leaves was somewhat thickened and was prolonged distally into a structure which produced two forks reminiscent of the normal stigma but of more massive proportions and without any stigmatic surface. Below the line of fusion of these two carpellary leaves, and confined to tbe more basal portion were attached a number of ovules; these were enclosed on the anterior side by a leafy growth which was completely fused at each side with the other two carpellary leaves thus forming a loculus which might be taken to correspond to the anterior of tbe two loculi of tbe normal gynoecium. This anterior carpellary wall could, in the present specimen be taken to represent a leaf arising from the floral axis, enclosing in its axil a placenta apparently formed by the fusion of its own margins with those of the two neighbouring leaf-like structures contributing to this abnormal gynoecium. The ovules appeared to be normal both with regard to external form and internal structure. An examination of the fiower buds arising on the proliferated floral axis showed some of them to be abnormal. The first (Figs. I and 2, A) was at such an early stage of development that it was not possible to detect any abnormalities. The next in order of origin was that arising in the axil of the lateral petaloid sepal of the original flower. This bud (Figs, i and 2, B, also Fig. 3) possessed a normal calyx, and a corolla in which the normal zygomorphic features were present, but were not very strongly marked. The chief feature of interest in this bud was the presence of five perfect and regular stamens of equal length, such as might occur in a peloric flower. The gynoecium was normal except that the style was rather short. The next bud, the third on the new axis (Fig. i, E, also Fig. 4), was that arising in the axil of a green and leafy bract on the side of the axis opposite to that occupied by the flower, that is, above it.
5 On an Abnormality in Digitalis purpurea 121 This flower bud showed only a very slight abnormality, and except for the fusion of the two anterior sepals it was quite normal. A flower bud with a distinctive structure was that arising in the axil of one of those leafy bracts associated with the gynoecium of the original flower (Fig, 2, C and Fig. 5). Here the posterior sepal Fig- 5. Fig. 6. Fig, 3, Diagram of second flower bud (Fig, i, B). Fig, 4, Diagram of third flower bud (Fig, 2, C). Fig. 5, Diagram of fourth flower bud. Fig, 6, Diagram of fifth flower bud, and one adjacent to it were normal; the others were fused together, and in the anterior median plane were apparently also fused with the anterior corolla member. The median portion of this composite structure was petaloid and it carried a small but definitely marked enation, the "spur" being directed inwards and backwards towards
6 122 VIOLET L. ANDERSON the axis, and the opening being external. The remainder of the corolla -which was quite separate from the anterior fused structure, formed a hood in the posterior and lateral positions on which distally could be distinguished the lobing normal on that part of the corolla. The stamens were four in number, apparently normal, and attached to the base of the hooded portion of the corolla. The gynoecium was also normal. In the fifth bud on the new axis (Fig. 6) the posterior portion of the calyx was normal, but one of the anterior sepals was petaloid, and was fused with the sepals on either side of it. The corolla was normal except in a position immediately inside the petaloid sepal, where two free phalanges were developed on the outside. These may have represented an early fission between the two petals in that position, which was subsequently healed by a fusion occurring parallel to the cut margins but a little away from them, thus leaving them free on the outside. The androecium consisted of three stamens only, the missing member being one of the lateral posterior ones, on the side opposite to that on which the other abnormalities occurred. The gynoecium was normal. The sixth flower bud arising on the new inflorescence axis was in structure essentially the same as the fourth (see Fig. 5). It exhibited the same fusion of calyx members, wth the anterior member of the corolla, the floral envelope in this region consisting of a single composite structure. The absence of an enation in the younger bud was the only respect in which the structure of the two buds differed. More distally the proliferated axis bore a large number of other flower buds, all of which arose in the axils of leafy bracts: the seven immediately above that last described were sufficiently developed for their structure to be discerned with a hand lens, and they all appeared to be quite normal. The remaining buds were probably also normal, but they were too immature for any definite verdict to be given. The outstanding problem raised by the specimen is the status of the proliferated axis. The presence of five sepals, a complete though divided coroua, and two carpels, suggests that the origin of the new structure might be in the staminal whorl. This view obtains further support from a consideration of the new structure in relation to the gynoecium of the original flower. The lower (anterior) carpel remains comparatively unaltered and aloof, but the upper one is an open leafy structure arising apparently on the new axis and bearing a placenta in its axil. It would therefore appear that the proliferation has occurred posterior but closely adjacent to the gynoecium.
7 On an Abnormality in Digitalis purpurea 123 It has been mentioned above that a possible interpretation would regard the new axis as arising from a second bud in the axil of the posterior sepal, but on the whole its point of origin would seem to be within the corolla. In addition to the lack of a posterior stamen normal in the genus, the present specimen showed a suppression of the adj acent pair of stamens, unless these could be traced in the green and leafy structures arising further up on the new axis, and bearing flower buds in their axils. The posterior stamen might perhaps be similarly represented. Since one stamen is normally suppressed it is in accordance with the tendencies exhibited elsewhere in this family to postulate the suppression of all three posterior stamens; one is therefore led to suggest that the new inflorescence axis represents either a bud in the axil of the suppressed posterior stamen, or the combined product of the metamorphosed stamens themselves. It must be noted that the specimen provides a long series in the suppression of stamens; thus the bud represented in Fig. 3 contained five stamens, several buds had the usual complement of four, and that portrayed in Fig. 6 had three. In the original flower only two stamens were represented, and of these only one was functional, the other being completely petaloid. The presence of a "spur" on the corolla of the originalfloweris of considerable interest, since it suggests an affinity with other zygomorphic genera of this family, more especially Linaria; and to this suggestion considerable weight must be added by the fact that such spur-like tubes have previously been recorded both in Digitalis purpurea and Antirrhinum majusii). The danger of stressing unduly the value of evidence of affinity afforded by teratological specimens is, however, well known; and in the present instance the fact that the "spur" was non-functional must detract considerably from its importance. Further, in one of the buds on the proliferated axis (Fig. 5) was an enation in a similar position, and in each case the abnormality may simply represent an expression of superfluous vitality producing an extra growth at a place of weakness. In conclusion I should like to express my thanks to Dr T. G. Hill not only for his kindness in providing me with the specimen but also for his helpful criticism and advice. REFERENCES (1) VuiLLEMiN. Ann. Set. Nat. Bot. 16, pp. isj et seq (2) WORSDELL. Principles of Plant Teratology. London, (3) SAUNDERS. Journ. Genetics (4) MASTERS. Vegetable Teratology. London, 1869.
8
The Flower - what is it? 1/31/18. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants
 - what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
- what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
Plant Terminology. Floral Symmetry
 Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12
 BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
SOME time ago, in the pages of this journal. Miss Saunders described
 [359] FLORAL ANATOMY OF RIVINA HUMILIS L., AND THE THEORY OF CARPEL POLYMORPHISM BY A. C. JOSHI AND V. S. Benares Hindu University, India (With 6 figures in the text) RAO SOME time ago, in the pages of
[359] FLORAL ANATOMY OF RIVINA HUMILIS L., AND THE THEORY OF CARPEL POLYMORPHISM BY A. C. JOSHI AND V. S. Benares Hindu University, India (With 6 figures in the text) RAO SOME time ago, in the pages of
BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12
 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS
![[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS [396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS](/thumbs/84/89173932.jpg) [396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS I BY S. B. KAUSIK, M.SC. Central College, Bangalore With 5 figures in the text N the following study, a description is given of five cases of abnormalities
[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS I BY S. B. KAUSIK, M.SC. Central College, Bangalore With 5 figures in the text N the following study, a description is given of five cases of abnormalities
Botany Physiology. Due Date Code Period Earned Points
 Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae)
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part II, Number 3, May 1979, pp. 183-188, printed in India. Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae) V SINGH and D K JAIN* Department of Botany,
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part II, Number 3, May 1979, pp. 183-188, printed in India. Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae) V SINGH and D K JAIN* Department of Botany,
LABORATORY 2: Flowers
 LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. E2-4 Flower Anatomy
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Nyla Phillips-Martin 2013 mscraftynyla.blogspot.com
 1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]
![W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]](/thumbs/89/98832613.jpg) W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
Reproductive Development and Structure
 Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S.
 POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
PREFACE. Best of luck to all the aspirants!
 PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
ANGIOSPERM L.S. POLLEN GRAIN
 ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
Angiosperms. The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species.
 Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/22/10
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Reproduction 19/02/2016. Asexual Reproduction. Budding: Types of asexual reproduction: SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL
 Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
 CHAPTER 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth. Reproduction
CHAPTER 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth. Reproduction
3/18/2012. Chapter 36. Flower Parts. Flower Parts. Reproduction in Angiosperms
 Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
THE FLORAL ANATOMY OF ELETTARIA CARDAMOMUM MATON, A RE-INVESTIGATION
 THE FLORAL ANATOMY OF ELETTARIA CARDAMOMUM MATON, A RE-INVESTIGATION BY R. M. PAI Department of Botany, Marathwada University, Aurangabad, India {Received 13 July 1964) SUMMARY The re-investigation indicates
THE FLORAL ANATOMY OF ELETTARIA CARDAMOMUM MATON, A RE-INVESTIGATION BY R. M. PAI Department of Botany, Marathwada University, Aurangabad, India {Received 13 July 1964) SUMMARY The re-investigation indicates
Operation Flower Dissection
 Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
 CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS
 BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
A SIX-STAMENED FLOWER IN ZEA MAYS L.
 130 A SIX-STAMENED FLOWER IN ZEA MAYS L. BY B. C. Department of Botany, University of Leeds (With 2 figures in the text) During the examination of the tassel of a maize plant, a number of flowers were
130 A SIX-STAMENED FLOWER IN ZEA MAYS L. BY B. C. Department of Botany, University of Leeds (With 2 figures in the text) During the examination of the tassel of a maize plant, a number of flowers were
[56] TERATOLOGICAL STUDIES
![[56] TERATOLOGICAL STUDIES [56] TERATOLOGICAL STUDIES](/thumbs/89/99842029.jpg) [56] TERATOLOGICAL STUDIES I. RECEPTACULAR OUTGROWTHS IN ANTIRRHINUM MAjfUS L. BY B. BARNES, B.Sc, PH.D. (LOND.), F.L.S. Department of Botany, Birkbeck College, University of London (With 6 fiigures in
[56] TERATOLOGICAL STUDIES I. RECEPTACULAR OUTGROWTHS IN ANTIRRHINUM MAjfUS L. BY B. BARNES, B.Sc, PH.D. (LOND.), F.L.S. Department of Botany, Birkbeck College, University of London (With 6 fiigures in
Reproduction in plants
 Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA
 SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits
 BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
Flower Shapes and their function. Describing Flower Shapes
 Flower Shapes and their function Describing Flower Shapes Flower Shapes As with leaf shapes and the arrangement of flowers, these descriptions can only give you a general idea of the shapes of flowers.
Flower Shapes and their function Describing Flower Shapes Flower Shapes As with leaf shapes and the arrangement of flowers, these descriptions can only give you a general idea of the shapes of flowers.
Original content Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
Parts of a Flower. Stamen = Pistil = Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel. anther + filament
 Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Correspondence. To the Editor of the NEW PHYTOLOGIST.
 ' 16 Correspondence. To the Editor of the NEW PHYTOLOGIST. DEAR SIR, With reference to my article in the February number of this journal on the subject of the Origin of the Perianth, I have received from
' 16 Correspondence. To the Editor of the NEW PHYTOLOGIST. DEAR SIR, With reference to my article in the February number of this journal on the subject of the Origin of the Perianth, I have received from
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals
 Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Regulation of Floral-Organ- Type by SUPERMAN
 Regulation of Floral-Organ- Type by SUPERMAN 1. Need for regulators of the organ-identity genes. 2. The Superman mutant phenotype-predicting the role of SUPERMAN. 3. Testing our hypothesis of the role
Regulation of Floral-Organ- Type by SUPERMAN 1. Need for regulators of the organ-identity genes. 2. The Superman mutant phenotype-predicting the role of SUPERMAN. 3. Testing our hypothesis of the role
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Safety Dissection tools are very sharp. Use appropriately and do not leave unattended in the presence of children.
 Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers
 WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning
 Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning John L Bowman, University of California, Davis, California, USA The development of flowers and floral organs is directed by genetic programmes likely to be
Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning John L Bowman, University of California, Davis, California, USA The development of flowers and floral organs is directed by genetic programmes likely to be
DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L.
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L. BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, Bedford College, Regent's Park, London, N.W.i {Received 4 January 1959) (With Plates 3
DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L. BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, Bedford College, Regent's Park, London, N.W.i {Received 4 January 1959) (With Plates 3
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology. Station 1. Whole plant structure. Differences between roots, stems, and leaves:
 Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus terrestris L.
 ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS WITH SEEDS
 There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
IB 168 Plant Systematics
 IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations
 ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
16B Flower Dissection
 16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION
 UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
Peony Flower Anatomy I
 Peony Flower Anatomy I Don Hollingsworth, APS Director Maryville, Missouri What Makes a Peony Flower Luxurious? Rich luxury of the flowers explains why peonies are wanted, why loved and why known in history
Peony Flower Anatomy I Don Hollingsworth, APS Director Maryville, Missouri What Makes a Peony Flower Luxurious? Rich luxury of the flowers explains why peonies are wanted, why loved and why known in history
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity. Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara
 Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes
 Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Anatomy of a New Sepaloid Mutant Flower in Sugarbeet 1
 January-June, 1991 Anatomy of a New SepaJoid Mutant Flower in Sugarbeet 23 Anatomy of a New Sepaloid Mutant Flower in Sugarbeet 1 J. C. Theurer, S. A. Owens 3, and F. W. Ewers 4 2Sugarbeet, Bean and Cereal
January-June, 1991 Anatomy of a New SepaJoid Mutant Flower in Sugarbeet 23 Anatomy of a New Sepaloid Mutant Flower in Sugarbeet 1 J. C. Theurer, S. A. Owens 3, and F. W. Ewers 4 2Sugarbeet, Bean and Cereal
Publishing. Telephone: Fax:
 Publishing Australian Journal of Botany An international journal for the publication of original research in plant science Volume 49, 2001 CSIRO 2001 All enquiries and manuscripts should be directed to:
Publishing Australian Journal of Botany An international journal for the publication of original research in plant science Volume 49, 2001 CSIRO 2001 All enquiries and manuscripts should be directed to:
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Floral Organ Mutants and the Study of Organ Morphogenesis
 Floral Organ Mutants and the Study of Organ Morphogenesis Objectives: 1. How does one use mutants to understand floral organ morphogenesis? 2. What are the phenotypes of some floral organ mutants? 3. What
Floral Organ Mutants and the Study of Organ Morphogenesis Objectives: 1. How does one use mutants to understand floral organ morphogenesis? 2. What are the phenotypes of some floral organ mutants? 3. What
 In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
the reproductive organs of a flower
 Life Cycles, Reproduction & Heredity flower power the reproductive organs of a flower Frameworks SCIENCE LS 2.6.5 Model and explain the function of plant organs: leaves, roots, stems, flowers. LS 3.7.6
Life Cycles, Reproduction & Heredity flower power the reproductive organs of a flower Frameworks SCIENCE LS 2.6.5 Model and explain the function of plant organs: leaves, roots, stems, flowers. LS 3.7.6
On the Use of Some Common Botanical Terms
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 2, Issue 5 (March, 1902) 1902-03 On the Use of Some Common Botanical
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 2, Issue 5 (March, 1902) 1902-03 On the Use of Some Common Botanical
SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL
 Name... Index Number... Student s Signature... 231/3 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 PRACTICAL JUNE, 2017 1 ¾ HOURS SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY Paper 3 Practical TIME: 1
Name... Index Number... Student s Signature... 231/3 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 PRACTICAL JUNE, 2017 1 ¾ HOURS SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY Paper 3 Practical TIME: 1
FILAMENTOUS FLOWER Controls the Formation and Development of Arabidopsis Inflorescences and Floral Meristems
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 11, 69 86, January 1999, www.plantcell.org 1999 American Society of Plant Physiologists FILAMENTOUS FLOWER Controls the Formation and Development of Arabidopsis Inflorescences and
The Plant Cell, Vol. 11, 69 86, January 1999, www.plantcell.org 1999 American Society of Plant Physiologists FILAMENTOUS FLOWER Controls the Formation and Development of Arabidopsis Inflorescences and
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
W.4.1 Write opinion pieces on topics or texts, supporting a point of view with reasons and information.
 Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process. They will
Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process. They will
AESTIVATION IN RANUNCULUS REPENS L.
 ESTVTON N RNUNCULUS REENS L. BY G. J. CUNNELL Birkbeck College, University of London {Received September 1) (With figures in the text) SUMMRY The aestivation of the caljrx and corolla in mature flower
ESTVTON N RNUNCULUS REENS L. BY G. J. CUNNELL Birkbeck College, University of London {Received September 1) (With figures in the text) SUMMRY The aestivation of the caljrx and corolla in mature flower
Key Anatomical Directions
 Dissection Anatomical Direction Before beginning a dissection, it is important to have an understanding of some of the basic directional terminology associated with the dissection of specimens. Some of
Dissection Anatomical Direction Before beginning a dissection, it is important to have an understanding of some of the basic directional terminology associated with the dissection of specimens. Some of
Core Asterids! Lamiids Part 1!
 Core Asterids! Lamiids Part 1! Announcements! Guest Lecture next Monday: Conservation and management of rare plants in Washington.! MHG Project due next Wednesday.! !Basal eudicots"! Phylogeny of Eudicots
Core Asterids! Lamiids Part 1! Announcements! Guest Lecture next Monday: Conservation and management of rare plants in Washington.! MHG Project due next Wednesday.! !Basal eudicots"! Phylogeny of Eudicots
Plant Reproduction fertilization
 Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction
 Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet
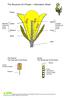 The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
Review of the previous lecture
 Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
BIOLOGY PAPER - 1. (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology)
 BIOLOGY PAPER - 1 (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) Answer all questions
BIOLOGY PAPER - 1 (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) Answer all questions
Floral Ontogeny of Pelargonium domesticum
 J. AMER. SOC. HORT. SCI. 125(1):36 40. 2000. Floral Ontogeny of Pelargonium domesticum Marietta Loehrlein 1 and Richard Craig 2 Department of Horticulture, The Pennsylvania State University, University
J. AMER. SOC. HORT. SCI. 125(1):36 40. 2000. Floral Ontogeny of Pelargonium domesticum Marietta Loehrlein 1 and Richard Craig 2 Department of Horticulture, The Pennsylvania State University, University
Floral development in Impatiens chishuiensis (Balsaminaceae): formation of two well-developed anterolateral sepals and four carpels
 Plant Syst Evol (2010) 286:21 26 DOI 10.1007/s00606-010-0273-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Floral development in Impatiens chishuiensis (Balsaminaceae): formation of two well-developed anterolateral sepals and four
Plant Syst Evol (2010) 286:21 26 DOI 10.1007/s00606-010-0273-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Floral development in Impatiens chishuiensis (Balsaminaceae): formation of two well-developed anterolateral sepals and four
Flowering Development in Algerie Loquat under Scanning Electron Microscopy
 Flowering evelopment in Algerie Loquat under canning Electron Microscopy M.C. Rodríguez 1, J.J Hueso 2 and J. Cuevas 1 1 epartamento de Producción Vegetal, Universidad de Almería, Almería, pain. 2 Estación
Flowering evelopment in Algerie Loquat under canning Electron Microscopy M.C. Rodríguez 1, J.J Hueso 2 and J. Cuevas 1 1 epartamento de Producción Vegetal, Universidad de Almería, Almería, pain. 2 Estación
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the:
 1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization)
 Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
