Introduction. Research
|
|
|
- Garry Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of the micro-catt, CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense, and LATEX/T. b. gambiense methods for serodiagnosis and surveillance of human African trypanosomiasis in West and Central Africa Philippe Truc, 1 Veerle Lejon, 2 Eddy Magnus, 2 Vincent Jamonneau, 3 Auguste Nangouma, 4 Didier Verloo, 2 Laurent Penchenier, 5 & Philippe Büscher 2 Objective To evaluate the performance of serological tests using dried blood on filter-papers (micro-card agglutination test for trypanosomiasis (micro-catt)) performed under field and laboratory conditions and using whole blood ((CATT/T.b. gambiense) (wb- CATT) and latex agglutination (LATEX/T.b. gambiense) (wb-latex)) for the serodiagnosis and surveillance of human African trypanosomiasis in West and Central Africa. Methods We evaluated the micro-catt, wb-catt and wb-latex methods in Côte d Ivoire and the Central African Republic by screening 940 people. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated for each serological test; only patients with the confirmed presence of trypanosomes in the blood or lymph aspirate were considered true positives. Positive and negative predictive values were also calculated. Findings Each of the tests showed a lower sensitivity in the Central African Republic than in Côte d Ivoire. Conclusion The results confirmed the efficiency of the classic wb-catt to detect sleeping sickness patients. The micro-catt method can be used for human African trypanosomiasis surveillance if the test is performed on the same day as the blood collection, or if samples are stored at 4 o C. Otherwise, micro-catt can be used when absolute sensitivity is not required. wb-latex should only be used for highspecificity screening. Key words Agglutination tests; Sensitivity and specificity; Predictive value of tests, Trypanosomiasis, African/diagnosis; Comparative study; Côte d Ivoire; Central African Republic (source: MeSH, NLM ). Mots clés Réaction agglutination; Sensibilité et spécificité (Epidémiologie); Valeur prédictive tests; Trypanosomiase africaine/ diagnostic; Etude comparative; Côte d Ivoire; Républic centrafricaine (source: MeSH, INSERM). Palabras clave Tests de aglutinación; Sensibilidad y especificidad; Valor predictivo de los tests; Tripanosomiasis africana/diagnóstico; Estudio comparativo; Côte d Ivoire; República Centroafricana (fuente: DeCS, BIREME ). Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2002;80: Voir page 885 le résumé en français. En la página 886 figura un resumen en español. Introduction Human African trypanosomiasis remains a major health problem in sub-saharan Africa, where about 60 million people are exposed daily to infecting tsetse fly bites. In 1998 a total of new cases were reported. Despite this, only 3 million people at risk are under surveillance. WHO estimates that about persons are infected with human African trypanosomiasis (1), a level that permits active cyclical transmission of the disease, as confirmed by current epidemics in Central Africa. In order to follow the spread of the disease within historical foci and to detect emerging foci, national control programmes should increase epidemiological surveillance. In 1995, WHO initiated an international human African trypanosomiasis surveillance programme in 18 countries in West and Central Africa, where the chronic form of the disease due to Trypanosoma brucei gambiense occurs. One of the main objectives was to stimulate national control programmes to set up active serological surveillance of the disease among their populations. WHO recommended the use of a serological test (micro-card agglutination test for trypanosomiasis) (micro-catt) (2), a variant of the card agglutination test for trypanosomiasis (CATT/T.b. gambiense) used with whole blood (wb-catt) (3). The micro-catt is considered to be inexpensive, easy to use under field conditions, and allows the collection and storage of dried blood samples on filter-paper for future serological analysis. 1 Scientist, Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) UR 035, Organisation de Coordination pour la Lutte contre les Endémies en Afrique Centrale (OCEAC), BP 288, Yaoundé, Cameroon ( truc@iccnet.cm). Correspondence should be addressed to this author. 2 Scientist, Department of Parasitology, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium. 3 Scientist, IRD UR 035, Laboratoire de Génétique des Parasites et Vecteurs, Institut Pierre Richet, Bouaké, Côte d Ivoire. 4 Medical Officer, Programme National de Lutte contre la THA, Ministère de la Santé Publique, Bangui, Central African Republic. 5 Laboratoire de Recherche et de Coordination sur les Trypanosomoses, IRD UR 035, Campus International de Baillarguet, Montpellier, France. Ref. No Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2002, 80 (11)
2 Tests for serodiagnosis and surveillance of African trypanosomiasis in West and Central Africa The major objectives of the study were to determine the sensitivity and specificity of the micro-catt using dried blood and to compare the results with the sensitivities and specificities obtained using two other card agglutination tests for detecting antibodies in whole blood (wb-catt) and the latex agglutination test (LATEX/T.b. gambiense) (wb- LATEX). The study was carried out in two epidemiological and geographical situations: Batangafo (Central African Republic), and Bonon (Côte d Ivoire). Because of the difficulty of performing micro-catt under field conditions, the micro- CATT results were compared using the same filter-papers under field or laboratory conditions. Methods Study areas and populations The study was carried out in 1999 during two medical surveys and included 940 consenting persons. The first survey was conducted in Batangafo, in the north of Central African Republic, by the National Control Programme of the Central African Republic and the human African trypanosomiasis team of the Organisation de Coordination pour la Lutte contre les Endémies en Afrique Centrale (OCEAC), Yaoundé, Cameroon; and the second in Côte d Ivoire, in the Bonon area, 80 km west of Bouaflé, by the Institut Pierre Richet,Bouaké,Côte d Ivoire. In Batangafo, 540 people were examined; and in Bonon, 400 people. Sample collection To avoid multiple finger-pricks, samples of venous blood were obtained from each individual by venepuncture using two 5-ml Venoject t tubes (available from VWR International, Darmstadt, Germany). One tube without anticoagulant was used for immediate tests, including the standard field protocol of the micro-catt (2) and the parasitological quantitative buffy coat (QBC) test (4). The whole blood was quickly transferred to a QBC tube coated with heparin, which was then centrifuged and examined under the microscope for trypanosomes. The remaining whole blood from this sample was adsorbed onto four 20 cm 2 sheets of filter-paper (Whatman No. 4) for subsequent micro-catt tests. Micro-CATT tests were performed at three times: in the field on the day of sample collection (day 0); on day 3; and on day 7. To evaluate the influence of time and storage conditions of the samples on these results, we divided the dried blood samples into equal aliquots and stored them either at local room temperature or refrigerated. A second tube containing an anticoagulant ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) was used to collect blood for immediate serological tests by wb-catt on whole blood. Some of the blood was also stored on four sheets of Whatman No. 4 filter-paper and the samples sent to the Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium, for further analysis. EDTA was used as a coagulant instead of heparin to avoid the prozone effect, previously observed when performing wb-catt with heparin-treated samples (5). All dried blood samples collected on the filter-paper were stored in glass containers containing silica gel at 4 o C. The protocol for micro-catt was modified at the Institute for Tropical Medicine, as described below. During the study, the same serological and parasitological tests were used, as well as the same batches of filter-paper and serological reagents. Serological and parasitological tests in the field The tests described below were performed immediately after collection of the blood samples (day 0):. wb-catt (3) using whole blood according to the instructions of the manufacturer (Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium). No CATT tests were performed on plasma or serum.. wb-latex (6, 7) a card agglutination test, similar to wb- CATT, but the reagent is a mixture of three purified variable surface glycoproteins (LiTat 1.3, 1.5, and 1.6) adsorbed on latex beads. The reagent was provided desiccated and reconstituted with 2 ml of phosphate-buffered saline. The reagent solution (40 ml) was then dispensed on each reaction zone of a plastic card, and 5 ml of blood was mixed together with the reagent on each reaction zone. Subsequently, the card was placed on a flat-bed rotator (Type B2, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium) and agitated at 70 rpm for 5 minutes. The agglutination was read macroscopically.. On day 0, the field micro-catt was performed according to a previously described protocol (2).. The QBC test was carried out using a modified protocol (4).. A cervical palpation was performed on each individual to detect lymphadenopathy. If present, a puncture was performed and the aspirate examined by light microscope for parasites.. The micro-catt was repeated on day 3 and on day 7 on dried blood samples from individuals with positive results for at least one of the serological tests, wb-catt, micro- CATT (day 0), or wb-latex. The same dried blood samples used for the day 0 test were used for the repeat tests. Filter-paper samples were stored at local room temperature (described above). For all serological tests (micro-catt, wb-catt, wb-latex), agglutination was considered to be a positive result (8). Serological test in the laboratory At the Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, micro-catt was performed on EDTA-treated blood samples eluted from dried filter-papers at least 6 weeks after sample collection, using a modified protocol from that originally described (2). For each blood sample, disks (6 mm) were punched out of areas of the filter-papers with dried blood, placed into one well of a 96-well flat-bottomed microplate (Greiner Bio-One, Longwood, FL, USA), and the blood extracted with 30 ml CATT buffer for 1 hour at room temperature (20 25 o C) with gentle shaking every 15 minutes. CATT reagent was reconstituted by adding 1.25 ml of CATT buffer, instead of the usual 2.5 ml in order to concentrate the reagent. Sample eluate (10 ml) was then mixed with 5 ml of concentrated CATT reagent on the reaction zones (10-mm diameter) of the test cards. The card was placed on a flat-bed rotator (Type B2, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium) and agitated for 7 minutes at 70 rpm. The agglutination patterns were read immediately using a X 3.5 magnifying glass. The same lot of Whatman filter-paper and the same batch of serological reagents were used to collect and test all field and laboratory samples. The laboratory personnel were not aware of results we had obtained in the field. Statistical analysis The following statistical parameters were calculated for each serological test: sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2002, 80 (11) 883
3 (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV). 95% symmetrical confidence intervals of sensitivity and specificity were calculated using JavaStat. Only patients in whom trypanosomes had been confirmed in blood or lymph aspirates were considered to be true positives. Since the parasitological reference tests (QBC and detection of trypanosomes in lymph aspirate) were not 100% sensitive (4), cases of false seropositivity were likely. Thus, the observed specificity should be considered minimal. Also, some seronegative individuals may have been infected, which would lead to an overestimation of the observed sensitivity. Sensitivities and specificities of the serological tests were all compared by the McNemar w 2 test (one degree of freedom with continuity correction). Results Based on parasite detection either in the blood (QBC) or lymph aspirate, 66 individuals were diagnosed to have human African trypanosomiasis: 56 in Batangafo, and 10 in Bonon. All patients were treated by the local medical staff according to the national drug policy, as recommended by WHO (1). Table 1 shows the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of the different serological tests in Central African Republic and Côte d Ivoire. In Batangafo, 16 of 56 patients had trypanosomes in their lymph aspirates, 50 were micro-catt positive on day 0, 55 were wb-catt positive, and 38 were wb-latex positive. Of 484 persons with no detected trypanosomes, 32 were micro- CATT positive on day 0, 29 were wb-catt positive, and 3 wb- LATEX positive (false-positive cases). At the Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, blood samples from 53 of 56 patients from the Central African Republic were found to be micro-catt positive. Of the 484 people in whom trypanosomes were not detected, 16 were micro-catt positive, but were not confirmed parasitologically. In Bonon, trypanosomes were detected in lymph aspirates from 4 of 10 patients, 9 patients were micro-catt positive on day 0, 10 patients were wb-catt positive, and 9 were wb-latex positive. Of the 390 persons with no detectable trypanosomes, 7 were micro-catt positive on day 0, 13 were wb-catt positive, and 4 were wb-latex positive (false-positive cases). All 10 patients from Bonon were found to be micro-catt positive by the laboratory in Antwerp. Of 390 people with no detectable trypanosomes, 14 were micro- CATT positive (false-positive cases). The wb-latex method was significantly less sensitive (P = ) and more specific than all other tests (P<0.0001). The micro-catt performed in the field was significantly less sensitive than the wb-catt (89.4% vs 98.5%, P = ), but both had the same specificity. We found no significant difference in sensitivity and specificity between micro-catt performed in the field and in Antwerp. Micro-CATT performed in Antwerp was, however, more specific than wb-catt (96.6% vs 95.2%, P = ). The micro-catt was repeated three and seven days after blood collection for all parasitologically confirmed patients, since the single patient from Batangafo who was wb-catt negative was positive by the wb-latex assay. The sensitivity of the micro-catt at days 0, 3, and 7 is shown in Table 2. The overall sensitivity decreased from 89.4% to 50% when filter-papers were stored for 7 days at room temperature. Discussion The sensitivity of all serological tests used in this study was higher in Bonon (Côte d Ivoire) than in Batangafo (Central African Republic). This confirms previous results obtained in the northern foci of the Democratic Republic of Congo and in the Republic of Congo (7), where both wb-catt and wb- LATEX were found to be less sensitive than in Côte d Ivoire (8). One explanation for this is that the main antigenic variants used in the serological tests (LiTat 1.3, 1.5 and 1.6) are not the predominant antigenic types expressed by T.b. gambiense in Central Africa. Indeed, it was found that the LiTat 1.3 gene was missing from some strains of trypanosomes isolated in Cameroon (9). Table 1. Sensitivity and specificity of micro-catt, CATT/T. b. gambiense and LATEX/T. b. gambiense in Batangafo (Central African Republic) and Bonon (Côte d Ivoire) a Test Population Sensitivity PPV b (%) Specificity NPV c (%) micro-catt field Batangafo 50/56 (89.3) d /484 (93.4) 98.7 Bonon 9/10 (90.0) /390 (98.2) 99.7 Total 59/66 (89.4); e 835/874 (95.5); micro-catt, ITMA Batangafo 53/56 (94.6) /484 (96.7) 99.4 Bonon 10/10 (100.0) /390 (96.4) 100 Total 63/66 (95.5); /874 (96.6); wb-catt field Batangafo 55/56 (98.2) /484 (94.0) 99.8 Bonon 10/10 (100.0) /390 (96.7) 100 Total 65/66 (98.5); /874 (95.2); wb-latex field Batangafo 38/56 (67.9) /484 (99.4) 96.4 Bonon 9/10 (90.0) /390 (99.0) 99.7 Total 47/66 (71.2); /874 (99.2); a The micro-catt test was performed in the field on day 0 (micro-catt field), or at the Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp (micro-catt, IMTA). Both the CATT/T. b. gambiensis test (wb-catt field) and the LATEX/T. b. gambiensis test (wb-latex field) were performed in the field using whole blood. b PPV = Positive predictive value. c NPV = Negative predictive value. d Figures in parentheses are percentages. e Figures in italics are 95% confidence intervals. 884 Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2002, 80 (11)
4 Tests for serodiagnosis and surveillance of African trypanosomiasis in West and Central Africa Table 2. Effects on sensitivity of storing micro-catt filterpapers at room temperature for 0, 3 and 7 days a Sensitivity Focus Day 0 Day 3 Day 7 Batangafo, Central 50/56 (89.3) b 38/56 (67.8) 26/56 (46.4) African Republic Bonon, Côte d Ivoire 9/10 (90.0) 9/10 (90.0) 7/10 (70.0) Total 59/66 (89.4) 47/66 (71.2) 33/66 (50) a The tests were performed in the field on patients with confirmed parasite infections. b Figures in parentheses are percentages. Under field conditions, the micro-catt at day 0 had sufficient sensitivity and specificity in both Central African Republic and Côte d Ivoire. However, the 3- and 7-day results indicated that storing filter-papers at local room temperature for one week led to a rapid decrease in sensitivity. Despite this, we found no significant difference in performance (sensitivity or specificity) between the micro-catt performed in the field (day 0), or in the laboratory (6 weeks after sample collection), indicating that results are influenced by the storage condition of samples. Therefore, samples must be kept at 4 o C until use. The micro-catt appears to be suitable for the serodiagnosis of human African trypanosomiasis when performed on the day of sample collection or when the blood samples are kept at 4 o C, which confirms previous results (2, 10). However, such stringent conditions are unrealistic in the field. If blood samples have to be tested immediately after collection, there would be no point in performing a micro- CATT rather than a wb-catt. Moreover, the highest sensitivity was obtained when the wb-catt was performed in the field this test was significantly more sensitive than micro-catt and wb-latex tests in the field and had a similar specificity to the micro-catt assay performed in the field on day 0. While the micro-catt might be preferred for logistical or technical reasons, it is more expensive than the wb- CATT test, even if less reagent is required. Indeed, both tests require the same basic equipment (rotator, refrigerator), but the micro-catt requires additional consumables (Whatman No. 4 filter-paper, silica gel for storage, 96-well microplates). While it may be possible in some areas to refrigerate dried blood samples, our experience has been that when blood collection is performed by community health workers, samples are generally stored at local room temperature and are often in the field for several days before reaching the laboratory for the micro-catt test. As demonstrated by the present study, this leads to an important decrease in test sensitivity. However, the micro-catt could still be considered for HAT surveillance when optimal sensitivity is not required, or when it is difficult for the medical teams to access the infection foci. Although the wb-latex assay was less sensitive than the other tests, it was more specific. In Batangafo, the low sensitivity of the wb-latex compared to wb-catt may be explained by differences in antigen composition. wb-latex is based on a mixture of LiTat 1.3 (the same as the wb-catt), LiTat 1.5, and LiTat 1.6 antigens (6, 7). The main reacting epitopes are variable, with some invariant epitopes on the rest of the variable surface glycoprotein molecules. In the wb- CATT reagent, by contrast, the variable surface glycoproteins bearing simultanously highly specific variable and less specific invariable epitopes and other invariable antigens can contribute to a positive reaction (agglutination). In addition, if only anti- LiTat 1.3 antibodies are present in the test sample, the reaction obtained using wb-catt will be stronger than that obtained with the wb-latex test, since in the wb-latex reagent LiTat 1.3 antigens comprise only one-third of the total antigens. Consequently, wb-latex assays, performed as recommended by this study, should only be used for highspecificity testing in West Africa. In conclusion, we confirm that wb-catt can efficiently detect sleeping sickness patients in both West and Central Africa. In the absence of other cheap and simple techniques, it remains the reference test for control activities under field conditions. The micro-catt assay can be used for HAT surveillance when high sensitivity is not essential. Finally, it is recommended that the wb-latex assay be used only for high-specificity testing in West Africa, but not in Central Africa. n Acknowledgements We would like to express our sincere thanks to the teams of the human African trypanosomiasis National Control Programme of the Central African Republic, of OCEAC (Cameroon), and of the Institut Pierre Richet, Côte d Ivoire, for their excellent technical help. We thank Mr Pierre Cattand and Dr L.K. Basco (OCEAC, Yaoundé, Cameroon) for their constructive feedback on earlier drafts of this paper. This work was supported by the Fonds d Aide à la Coopération, Ministère Français des Affaires Etrangères, de la Coopération et de la Francophonie, and by the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement, France. Conflicts of interest: none declared. Résumé Evaluation des méthodes micro-catt, CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense et LATEX/T. b. gambiense pour le sérodiagnostic et la surveillance de la trypanosomiase humaine africaine en Afrique de l Ouest et en Afrique centrale Objectif Evaluer la performance de tests sérologiques utilisant du sang séché sur papier filtre (micro-test d agglutination sur carte pour la trypanosomiase (micro-catt)) réalisés sur le terrain et en laboratoire, et de tests utilisant du sang total (CATT/T. b. gambiense (wb-catt)) et agglutination sur latex (LATEX/T. b. gambiense (wb- LATEX)) pour le sérodiagnostic et la surveillance de la trypanosomiase humaine africaine en Afrique de l Ouest et en Afrique centrale. Méthodes Nous avons évalué les méthodes micro-catt, wb-catt et wb-latex en Côte d Ivoire et en République centrafricaine en procédant à un dépistage sur 940 personnes. La sensibilité et la spécificité ont été calculées pour chaque test ; seuls les patients chez qui la présence de trypanosomes dans le sang ou le suc ganglionnaire était confirmée ont été considérés comme vrais positifs. Les valeurs prédictives positive et négative ont également été calculées. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2002, 80 (11) 885
5 Résultats Tous les tests présentaient une plus faible sensibilité en République centrafricaine qu en Côte d Ivoire. Conclusion Les résultats ont confirmé l efficacité du wb-catt classique pour détecter les patients atteints de maladie du sommeil. La méthode micro-catt peut être utilisée pour la surveillance de la trypanosomiase humaine africaine si le test est réalisé le jour même du prélèvement de sang ou si les échantillons sont conservés à 4 o C. Sinon, le micro-catt peut être utilisé lorsqu il n est pas nécessaire d avoir une sensibilité absolue. Le test wb-latex ne doit être utilisé que pour les dépistages hautement spécifiques. Resumen Evaluación de los métodos micro-catt (CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense y LATEX/T. b. gambiense) como medio de serodiagnóstico y vigilancia de la tripanosomiasis africana humana en África occidental y central Objetivo Evaluar el funcionamiento de las pruebas serológicas tripanosomas en la sangre o el aspirado linfático. Se calcularon basadas en la aplicación de sangre seca en papel de filtro (prueba también los valores predictivos positivo y negativo. de aglutinación en microtarjetas para la tripanosomiasis (micro- Resultados En cada una de las pruebas la sensibilidad fue menor CATT)), sobre el terreno y en el laboratorio, utilizando sangre en la República Centroafricana que en Côte d Ivoire. entera (CATT/T.b. gambiense (wb-catt )) y aglutinación en látex Conclusión Los resultados confirmaron la eficiencia de la prueba (LATEX/T.b. gambiense (wb-latex)), con fines de serodiagnóstico tradicional de wb-catt como medio de detección de los pacientes y vigilancia de la tripanosomiasis africana humana en África con enfermedad del sueño.elmétodo micro-catt puede utilizarse occidental y central. para vigilar la tripanosomiasis africana humana si la prueba se Métodos Los métodos micro-catt, wb-catt y wb-latex se realiza el mismo día de obtención de la sangre, o si las muestras se evaluaron sometiendo a cribado a 940 personas en Côte d Ivoire y almacenan a 4 o C. En caso contrario, también es posible utilizar esa en la República Centroafricana. Se calcularon la sensibilidad y la técnica si no se requiere una sensibilidad absoluta. La prueba wbespecificidad de cada prueba serológica; sólo se consideraron LATEX sólo debe utilizarse en las iniciativas de cribado que exijan verdaderos positivos los pacientes con presencia confirmada de una alta especificidad. References 1. Control and surveillance of African trypanosomiasis. Geneva: World Health Organization; Technical Report Series No Miézan T, Doua F, Cattand P, De Raadt P. [Evaluation of Testryp CATT applied to blood samples on filter-paper and on diluted blood in a focus of trypanosomiasis due to Trypanosoma brucei gambiense in Côte d Ivoire] Bulletin of the World Health Organization 1991;69: In French. 3. Magnus E, Vervoort T, Van Meirvenne N. A card-agglutination test with stained trypanosomes (CATT) for the serological diagnosis of T. b. gambiense trypanosomiasis. Annales de la Société Belge de Médecine Tropicale 1978;59: Truc P, Jamonneau V, N Guessan P, Diallo PB, Garcia A. Parasitological diagnosis of human African trypanosomiasis: a comparison of the QBC and the miniature anion-exchange centrifugation technique. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1998:92: Pansaerts R, Van Meirvenne N, Magnus E, Verhelst L. Increased sensitivity of the card agglutination test CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense by inhibition of complement. Acta Tropica 1998;70: Büscher P, Draelants E, Magnus E, Vervoort T, Van Meirvenne N. An experimental latex agglutination test for antibody detection in human African trypanosomiasis. Annales de la Société Belge de Médecine Tropicale 1991;71: Büscher P, Lejon V, Magnus E, Van Meirvenne N. Improved latex agglutination test for detection of antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense infected patients. Acta Tropica 1999;73: Jamonneau V, Truc P, Garcia A, Magnus E, Büscher P. Preliminary evaluation of LATEX/T. b. gambiense and alternative versions of CATT/T. b. gambiense for serodiagnosis of Human African Trypanosomiasis of a population at risk in Côte d Ivoire: considerations for mass-screening. Acta Tropica 2000;76: Dukes P, Gibson WC, Gashumba JK, Hudson KM, Bromidge TJ, Kaukus A, et al. Absence of the LiTat 1.3 (CATT antigen) gene in Trypanosoma brucei gambiense stocks Cameroon. Acta Tropica 1992;51: Noireau F, Force-Barge P, Cattand P. Evaluation of Testryp CATT applied to samples of dried blood for the diagnosis of sleeping sickness. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 1991;69: Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2002, 80 (11)
F. Chappuis 1, A. Pittet 1, P. A. Bovier 2, K. Adams 1, V. Godineau 1, S. Y. Hwang 1, E. Magnus 3 and P. Büscher 3
 Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 7 no 11 pp 942 948 november 2002 Field evaluation of the CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense on blood-impregnated filter papers for diagnosis of human African
Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 7 no 11 pp 942 948 november 2002 Field evaluation of the CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense on blood-impregnated filter papers for diagnosis of human African
Evaluation of an EDTA version of CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense. Prince Leopold Institute of Tropical Medicine, Department of Parasitology,
 Evaluation of an EDTA version of CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense for serological screening of human blood samples Eddy Magnus 1 *, Veerle Lejon 1, Dominique Bayon 2, Dirk Buyse 3, Pere Simarro 4, Didier
Evaluation of an EDTA version of CATT/Trypanosoma brucei gambiense for serological screening of human blood samples Eddy Magnus 1 *, Veerle Lejon 1, Dominique Bayon 2, Dirk Buyse 3, Pere Simarro 4, Didier
V. Jamonneau 1, P. Solano 1, A. Garcia 2, V. Lejon 3, N. Djé 4, T. W. Miezan 4, P. N Guessan 1, G. Cuny 5 and P. Büscher 3
 Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 8 no 7 pp 589 594 july 2003 Stage determination and therapeutic decision in human African trypanosomiasis: value of polymerase chain reaction and immunoglobulin
Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 8 no 7 pp 589 594 july 2003 Stage determination and therapeutic decision in human African trypanosomiasis: value of polymerase chain reaction and immunoglobulin
Confirmation of the use of Latex IgM on cerebrospinal fluid for improving stage determination of Human African Trypanosomiasis
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 4 (6), pp. 517-521, June 2005 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2005 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Confirmation
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 4 (6), pp. 517-521, June 2005 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2005 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Confirmation
Authors Chappuis, F; Stivanello, E; Adams, K; Kidane, S; Pittet, A; Bovier, P A. Published by: American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
 MSF Field Research Card Agglutination Test for Trypanosomiasis (CATT) End- Dilution Titer and Cerebrospinal Fluid Cell Count as Predictors of Human African Trypanosomiasis (Trypanosoma brucei gambiense)
MSF Field Research Card Agglutination Test for Trypanosomiasis (CATT) End- Dilution Titer and Cerebrospinal Fluid Cell Count as Predictors of Human African Trypanosomiasis (Trypanosoma brucei gambiense)
Articles. Copyright Büscher et al. Open Access article distributed under the terms of CC BY-NC-ND.
 Sensitivity and specificity of HAT Sero-K-SeT, a rapid diagnostic test for serodiagnosis of sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense: a case-control study Philippe Büscher, Pascal Mertens,
Sensitivity and specificity of HAT Sero-K-SeT, a rapid diagnostic test for serodiagnosis of sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense: a case-control study Philippe Büscher, Pascal Mertens,
Detection of trypanosome-specific antibodies in saliva, towards non-invasive serological diagnosis of sleeping sickness
 Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01620.x volume 11 no 5 pp 620 627 may 2006 Detection of trypanosome-specific antibodies in saliva, towards non-invasive serological
Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01620.x volume 11 no 5 pp 620 627 may 2006 Detection of trypanosome-specific antibodies in saliva, towards non-invasive serological
Confirmation of antibodies against L-tryptophan-like epitope in human African trypanosomosis serological diagnostic
 Vol. 15(36), pp. 1986-1990, 7 September, 2016 DOI: 10.5897/AJB2016.15575 Article Number: 273864A60390 ISSN 1684-5315 Copyright 2016 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb
Vol. 15(36), pp. 1986-1990, 7 September, 2016 DOI: 10.5897/AJB2016.15575 Article Number: 273864A60390 ISSN 1684-5315 Copyright 2016 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb
Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta State, Nigeria
 JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-28-32 Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta
JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-28-32 Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta
Stage determination in sleeping sickness: comparison of two cell counting and two parasite detection techniques
 Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:1.1111/tmi.11 volume 1 no pp 77 7 june 13 Stage determination in sleeping sickness: comparison of two cell counting and two parasite detection techniques
Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:1.1111/tmi.11 volume 1 no pp 77 7 june 13 Stage determination in sleeping sickness: comparison of two cell counting and two parasite detection techniques
Accepted 3 December 2003
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 3 (1), pp. 94-98, January 2004 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2004 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Characterization
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 3 (1), pp. 94-98, January 2004 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2004 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Characterization
TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI GAMBIENSE TRYPANOSOMIASIS IN TEREGO COUNTY, NORTHERN UGANDA, 1996: A LOT QUALITY ASSURANCE SAMPLING SURVEY
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 70(4), 2004, pp. 390 394 Copyright 2004 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI GAMBIENSE TRYPANOSOMIASIS IN TEREGO COUNTY, NORTHERN UGANDA,
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 70(4), 2004, pp. 390 394 Copyright 2004 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI GAMBIENSE TRYPANOSOMIASIS IN TEREGO COUNTY, NORTHERN UGANDA,
The effectiveness of active population screening and treatment for sleeping sickness control in the Democratic Republic of Congo
 Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 9 no 5 pp 542 550 may 2004 The effectiveness of active population screening and treatment for sleeping sickness control in the Democratic Republic of Congo
Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 9 no 5 pp 542 550 may 2004 The effectiveness of active population screening and treatment for sleeping sickness control in the Democratic Republic of Congo
IgM quantification in the cerebrospinal fluid of sleeping sickness patients by a latex card agglutination test
 Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 7 no 8 pp 685 692 august 2002 IgM quantification in the cerebrospinal fluid of sleeping sickness patients by a latex card agglutination test V. Lejon 1,2,
Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 7 no 8 pp 685 692 august 2002 IgM quantification in the cerebrospinal fluid of sleeping sickness patients by a latex card agglutination test V. Lejon 1,2,
Cost-effectiveness of Algorithms for Confirmation Test of Human African Trypanosomiasis
 Cost-effectiveness of Algorithms for Confirmation Test of Human African Trypanosomiasis Pascal Lutumba,* Filip Meheus, Jo Robays, Constantin Miaka,* Victor Kande,* Philippe Büscher, Bruno Dujardin, and
Cost-effectiveness of Algorithms for Confirmation Test of Human African Trypanosomiasis Pascal Lutumba,* Filip Meheus, Jo Robays, Constantin Miaka,* Victor Kande,* Philippe Büscher, Bruno Dujardin, and
The development of new diagnostic tools for sleeping sickness
 The development of new diagnostic tools for sleeping sickness P. Büscher Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp WHO CC for Research and Training on Human African Trypanosomiasis Diagnosis 1 1 Distribution
The development of new diagnostic tools for sleeping sickness P. Büscher Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp WHO CC for Research and Training on Human African Trypanosomiasis Diagnosis 1 1 Distribution
TDR/DDR/98.1 WHO, GENEVA, 14 JULY 1998 CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS RELAPSING PATIENTS. The 14-day regimen is highly effective.
 TDR/DDR/98.1 REPORT ON A MEETING OF THE PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT TEAM FOR AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS CHEMOTHERAPY TO REVIEW THE COMPARATIVE STUDY OF 14-DAY VERSUS 7-DAY TREATMENT OF LATE STAGE T.B. GAMBIENSE AFRICAN
TDR/DDR/98.1 REPORT ON A MEETING OF THE PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT TEAM FOR AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS CHEMOTHERAPY TO REVIEW THE COMPARATIVE STUDY OF 14-DAY VERSUS 7-DAY TREATMENT OF LATE STAGE T.B. GAMBIENSE AFRICAN
Revisiting the Immune Trypanolysis Test to Optimise Epidemiological Surveillance and Control of Sleeping Sickness in West Africa
 Revisiting the Immune Trypanolysis Test to Optimise Epidemiological Surveillance and Control of Sleeping Sickness in West Africa Vincent Jamonneau 1,2 *, Bruno Bucheton 1,2, Jacques Kaboré 2, Hamidou Ilboudo
Revisiting the Immune Trypanolysis Test to Optimise Epidemiological Surveillance and Control of Sleeping Sickness in West Africa Vincent Jamonneau 1,2 *, Bruno Bucheton 1,2, Jacques Kaboré 2, Hamidou Ilboudo
Performance of Parasitological and Molecular Techniques for the Diagnosis and Surveillance of Gambiense Sleeping Sickness
 Performance of Parasitological and Molecular Techniques for the Diagnosis and Surveillance of Gambiense Sleeping Sickness Dieudonné Mumba Ngoyi 1,2, Rosine Ali Ekangu 1, Marie France Mumvemba Kodi 1, Patient
Performance of Parasitological and Molecular Techniques for the Diagnosis and Surveillance of Gambiense Sleeping Sickness Dieudonné Mumba Ngoyi 1,2, Rosine Ali Ekangu 1, Marie France Mumvemba Kodi 1, Patient
P PDF [Page: 1 of 8]
![P PDF [Page: 1 of 8] P PDF [Page: 1 of 8]](/thumbs/94/122070429.jpg) P152603.PDF [Page: 1 of 8] P152603.PDF [Page: 2 of 8] P152603.PDF [Page: 3 of 8] Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 52(3), 1995, pp. 281-286 Copyright C 1995 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygie-ne
P152603.PDF [Page: 1 of 8] P152603.PDF [Page: 2 of 8] P152603.PDF [Page: 3 of 8] Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 52(3), 1995, pp. 281-286 Copyright C 1995 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygie-ne
Options for Field Diagnosis of Human African Trypanosomiasis
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 2005, p. 133 146 Vol. 18, No. 1 0893-8512/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.18.1.133 146.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Options
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 2005, p. 133 146 Vol. 18, No. 1 0893-8512/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.18.1.133 146.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Options
_- ~ Exploration of the distribution of Trypanosoma bnicei ssp. in West Africa, by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis
 ~ l i... --- i Annals of Tropical Medicine & Parasitology, Vol. 94, No. 6, 643-649 (2000) Exploration of the distribution of Trypanosoma bnicei ssp. in West Africa, by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis
~ l i... --- i Annals of Tropical Medicine & Parasitology, Vol. 94, No. 6, 643-649 (2000) Exploration of the distribution of Trypanosoma bnicei ssp. in West Africa, by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis
Characterization of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense variant surface glycoprotein LiTat 1.5
 Short Communication Characterization of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense variant surface glycoprotein LiTat 1.5 L. Van Nieuwenhove 1 *, S. Rogé 1 *, V. Lejon 1, Y. Guisez 2 and P. Büscher 1 1 Department of
Short Communication Characterization of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense variant surface glycoprotein LiTat 1.5 L. Van Nieuwenhove 1 *, S. Rogé 1 *, V. Lejon 1, Y. Guisez 2 and P. Büscher 1 1 Department of
Evaluation of a rapid screening test for sleeping sickness. Lumbala C, Bisser S, Nguertoum E, Flevaud L, Jacquet D, Büscher P, Biéler S, Ndung u JM
 Evaluation of a rapid screening test for sleeping sickness Lumbala C, Bisser S, Nguertoum E, Flevaud L, Jacquet D, Büscher P, Biéler S, Ndung u JM 1 Performance evaluation of prototype in the field Prototype
Evaluation of a rapid screening test for sleeping sickness Lumbala C, Bisser S, Nguertoum E, Flevaud L, Jacquet D, Büscher P, Biéler S, Ndung u JM 1 Performance evaluation of prototype in the field Prototype
How to Shorten Patient Follow-Up after Treatment for Trypanosoma brucei gambiense Sleeping Sickness
 MAJOR ARTICLE How to Shorten Patient Follow-Up after Treatment for Trypanosoma brucei gambiense Sleeping Sickness Dieudonné Mumba Ngoyi, 1,4 Veerle Lejon, 4 Pati Pyana, 1,4 Marleen Boelaert, 5 Médard Ilunga,
MAJOR ARTICLE How to Shorten Patient Follow-Up after Treatment for Trypanosoma brucei gambiense Sleeping Sickness Dieudonné Mumba Ngoyi, 1,4 Veerle Lejon, 4 Pati Pyana, 1,4 Marleen Boelaert, 5 Médard Ilunga,
and latex agglutination, are commercially available. CSF samples from HAT and non-hat patients and RID and Rapi Tex IgM.
 Research/Recherche Human African trypanosomiasis: a latex agglutination field test for quantifying IgM in cerebrospinal fluid V. Lejon,1 P. BOscher, N.H. Sema, E. Magnus, & N. Van Meirvenne LATEX/lgM,
Research/Recherche Human African trypanosomiasis: a latex agglutination field test for quantifying IgM in cerebrospinal fluid V. Lejon,1 P. BOscher, N.H. Sema, E. Magnus, & N. Van Meirvenne LATEX/lgM,
Received 19 February 2007/Returned for modification 2 April 2007/Accepted 4 April 2007
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, June 2007, p. 732 737 Vol. 14, No. 6 1556-6811/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00103-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Treatment Failure
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, June 2007, p. 732 737 Vol. 14, No. 6 1556-6811/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00103-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Treatment Failure
Résumé de l évaluation multicentrique du. COLORATEUR AEROSPRAY BK series 2 / CYTOCENTRIFUGEUSE (Réf : 7722)
 Résumé de l évaluation multicentrique du COLORATEUR AEROSPRAY BK series 2 / CYTOCENTRIFUGEUSE (Réf : 7722) Abstract The new Aerospray TB Slide Stainer/Cytocentrifuge Model 7722 (ELITechGroup Inc., www.elitechgroup.com)
Résumé de l évaluation multicentrique du COLORATEUR AEROSPRAY BK series 2 / CYTOCENTRIFUGEUSE (Réf : 7722) Abstract The new Aerospray TB Slide Stainer/Cytocentrifuge Model 7722 (ELITechGroup Inc., www.elitechgroup.com)
Herd sensitivity in relation to test sensitivity in swine vesicular disease serological tests
 Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 2005, 24 (3), 1077-1083 Herd sensitivity in relation to test sensitivity in swine vesicular disease serological tests A. Dekker Virology Department, CIDC-Lelystad, Wageningen
Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 2005, 24 (3), 1077-1083 Herd sensitivity in relation to test sensitivity in swine vesicular disease serological tests A. Dekker Virology Department, CIDC-Lelystad, Wageningen
HAT. Platform EDITORIAL CONTENT P. 2 P. 2 P. 3 P. 3 P. 4 P. 4 P. 5 P. 5 P. 6 P. 6 TRAINING WORKSHOP FOR MEMBERS OF THE STEERING COMMITTEE MEETING
 HAT Platform EDITORIAL Dr Augustin Kadima Ebeja HAT Platform Coordinator We are proud to present our design for a bilingual logo that will help underscore our efforts to conduct clinical trials against
HAT Platform EDITORIAL Dr Augustin Kadima Ebeja HAT Platform Coordinator We are proud to present our design for a bilingual logo that will help underscore our efforts to conduct clinical trials against
HAT DNDi program progress and evolution in the path to elimination. Dr Antoine Tarral. HAT Platform, Kampala October 2018
 HAT DNDi program progress and evolution in the path to elimination Dr Antoine Tarral HAT Platform, Kampala October 2018 DNDi s Mission To develop new drugs or new formulations of existing drugs for people
HAT DNDi program progress and evolution in the path to elimination Dr Antoine Tarral HAT Platform, Kampala October 2018 DNDi s Mission To develop new drugs or new formulations of existing drugs for people
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين
 اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
Report of the second WHO stakeholders meeting on gambiense human African trypanosomiasis elimination. Geneva, March 2016
 Report of the second WHO stakeholders meeting on gambiense human African trypanosomiasis elimination Geneva, 21 23 March 2016 WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: Report of the second WHO stakeholders
Report of the second WHO stakeholders meeting on gambiense human African trypanosomiasis elimination Geneva, 21 23 March 2016 WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: Report of the second WHO stakeholders
590 La Revue de Santé de la Méditerranée orientale, Vol. 14, N o 3, 2008
 590 La Revue de Santé de la Méditerranée orientale, Vol. 4, N o 3, 2008 Rubella serology in pregnant women attending health centres of Tehran University of Medical Sciences F. Majlessi, A. Batebi, M. Shariat,
590 La Revue de Santé de la Méditerranée orientale, Vol. 4, N o 3, 2008 Rubella serology in pregnant women attending health centres of Tehran University of Medical Sciences F. Majlessi, A. Batebi, M. Shariat,
Diagnostic Accuracy of Loopamp Trypanosoma brucei Detection Kit for Diagnosis of Human African Trypanosomiasis in Clinical Samples
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Loopamp Trypanosoma brucei Detection Kit for Diagnosis of Human African Trypanosomiasis in Clinical Samples Patrick Mitashi 1,2,3, Epco Hasker 1, Dieudonné Mumba Ngoyi 2,3, Pati
Diagnostic Accuracy of Loopamp Trypanosoma brucei Detection Kit for Diagnosis of Human African Trypanosomiasis in Clinical Samples Patrick Mitashi 1,2,3, Epco Hasker 1, Dieudonné Mumba Ngoyi 2,3, Pati
Untreated Human Infections by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense Are Not 100% Fatal
 Untreated Human Infections by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense Are Not 100% Fatal Vincent Jamonneau 1,2 *, Hamidou Ilboudo 2, Jacques Kaboré 2, Dramane Kaba 3, Mathurin Koffi 4, Philippe Solano 1,2, André
Untreated Human Infections by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense Are Not 100% Fatal Vincent Jamonneau 1,2 *, Hamidou Ilboudo 2, Jacques Kaboré 2, Dramane Kaba 3, Mathurin Koffi 4, Philippe Solano 1,2, André
Stability and Compatibility of Granisetron Alone and in Combination with Dexamethasone in 0.9% Sodium Chloride and 5% Dextrose in Water Solutions
 ARTICLE Stability and Compatibility of Granisetron Alone and in Combination with Dexamethasone in 0.9% Sodium Chloride and 5% Dextrose in Water Solutions Scott E. Walker and Shirley Law ABSTRACT Background:
ARTICLE Stability and Compatibility of Granisetron Alone and in Combination with Dexamethasone in 0.9% Sodium Chloride and 5% Dextrose in Water Solutions Scott E. Walker and Shirley Law ABSTRACT Background:
Trypanosomiasis. By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy
 Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course
 Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or
Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or
Diagnosis of tuberculosis in developing countries in the era of high HIV transmission; alternative approaches Yassin, M.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Diagnosis of tuberculosis in developing countries in the era of high HIV transmission; alternative approaches Yassin, M.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Diagnosis of tuberculosis in developing countries in the era of high HIV transmission; alternative approaches Yassin, M.A. Link to publication Citation for published
Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course
 Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy
Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy
Prevalence of domestic animal trypanosomiasis in the Fontem sleeping sickness focus, Cameroon
 PROTOZOOLOGIE T. Asonganyi S. Suh 2 M.D. Tetuh 3 I Prevalence of domestic animal trypanosomiasis in the Fontem sleeping sickness focus, Cameroon ASONGANYI (T.), SUH (S.), TETUH (M. D.). Prévalence des
PROTOZOOLOGIE T. Asonganyi S. Suh 2 M.D. Tetuh 3 I Prevalence of domestic animal trypanosomiasis in the Fontem sleeping sickness focus, Cameroon ASONGANYI (T.), SUH (S.), TETUH (M. D.). Prévalence des
Short term pollen storage in almond
 Short term pollen storage in almond Martínez-Gómez P., Dicenta F., Ortega E. in Ak B.E. (ed.). XI GREMPA Seminar on Pistachios and Almonds Zaragoza : CIHEAM Cahiers Options Méditerranéennes; n. 56 2001
Short term pollen storage in almond Martínez-Gómez P., Dicenta F., Ortega E. in Ak B.E. (ed.). XI GREMPA Seminar on Pistachios and Almonds Zaragoza : CIHEAM Cahiers Options Méditerranéennes; n. 56 2001
ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS
 Molecular Diagnostics Symposium 2014 Zurich, 27 February 2014 ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS Stijn Deborggraeve Parasite Diagnostics Unit, Institute of Tropical Medicine
Molecular Diagnostics Symposium 2014 Zurich, 27 February 2014 ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS Stijn Deborggraeve Parasite Diagnostics Unit, Institute of Tropical Medicine
Intrathecal Immune Response Pattern for Improved Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Involvement in Trypanosomiasis
 MAJOR ARTICLE Intrathecal Immune Response Pattern for Improved Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Involvement in Trypanosomiasis Veerle Lejon, 1 Hansotto Reiber, 3 Dominique Legros, 4 Norbert Djé, 5 Eddy
MAJOR ARTICLE Intrathecal Immune Response Pattern for Improved Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Involvement in Trypanosomiasis Veerle Lejon, 1 Hansotto Reiber, 3 Dominique Legros, 4 Norbert Djé, 5 Eddy
The elimination of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness in the focus of Luba, Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea
 Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01624.x volume 11 no 5 pp 636 646 may 2006 The elimination of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness in the focus of Luba,
Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01624.x volume 11 no 5 pp 636 646 may 2006 The elimination of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness in the focus of Luba,
Rapid diagnostic tests for dengue and leptospirosis: antibody detection is insensitive at presentation
 Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01752.x volume 12 no 1 pp 47 51 january 2007 Rapid diagnostic tests for dengue and leptospirosis: antibody detection is insensitive
Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01752.x volume 12 no 1 pp 47 51 january 2007 Rapid diagnostic tests for dengue and leptospirosis: antibody detection is insensitive
Needle and Syringe exchange program/ provision of condoms
 Needle and Syringe exchange program/ provision of condoms Introduction Program started in 2005 Exists in 2 prisons ( CPL and CPG) Started on international recommandation It s a harm reduction measure,
Needle and Syringe exchange program/ provision of condoms Introduction Program started in 2005 Exists in 2 prisons ( CPL and CPG) Started on international recommandation It s a harm reduction measure,
Strategies for laboratory HIV testing: an
 Strategies for laboratory HIV testing: an examination of alternative approaches not requiring Western blot P.A. Sato,1 W.J. Maskill,2 H. Tamashiro,3 & D.L. Heymann4 Advances in laboratory tests for antibodies
Strategies for laboratory HIV testing: an examination of alternative approaches not requiring Western blot P.A. Sato,1 W.J. Maskill,2 H. Tamashiro,3 & D.L. Heymann4 Advances in laboratory tests for antibodies
Pattern and outcome of diabetic admissions at a federal medical center: A 5-year review
 Annals of African Medicine Vol. 8, No. 4; 2009:271-275 Short Report Pattern and outcome of diabetic admissions at a federal medical center: A 5-year review E. A. Ajayi, A. O. Ajayi Page 271 Department
Annals of African Medicine Vol. 8, No. 4; 2009:271-275 Short Report Pattern and outcome of diabetic admissions at a federal medical center: A 5-year review E. A. Ajayi, A. O. Ajayi Page 271 Department
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates
 Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Manulife Vitality. Condensed brand guidelines
 Manulife Vitality Condensed brand guidelines October 2016 Table of contents Use of Vitality in text...3 When to use Vitality in italics...3 When italics are not required...3 Disclaimers...4 Trademarks...5
Manulife Vitality Condensed brand guidelines October 2016 Table of contents Use of Vitality in text...3 When to use Vitality in italics...3 When italics are not required...3 Disclaimers...4 Trademarks...5
Luminescent Multiplex Viability Assay for T.b. gambiense
 Luminescent Multiplex Viability Assay for T.b. gambiense Van Reet N., Pyana P., Rogé S., Claes F. and Büscher, P. Institute of Tropical Medicine Antwerp 32nd ISCTRC conference 8th 12th September 2013 Introduction
Luminescent Multiplex Viability Assay for T.b. gambiense Van Reet N., Pyana P., Rogé S., Claes F. and Büscher, P. Institute of Tropical Medicine Antwerp 32nd ISCTRC conference 8th 12th September 2013 Introduction
Education Performance on ABA- ASA In-training Examination predicts success for RCPSC certification
 914 Education Performance on ABA- ASA In-training Examination predicts success for RCPSC certification Ramona A. Kearney MD FRCPC, Patrick Sullivan MD FRCPC, Ernest Skakun PhD Purpose: Most Canadian University
914 Education Performance on ABA- ASA In-training Examination predicts success for RCPSC certification Ramona A. Kearney MD FRCPC, Patrick Sullivan MD FRCPC, Ernest Skakun PhD Purpose: Most Canadian University
Voir page 1293 le résumé en français. En la página 1294 figura un resumen en español.
 Research Short-course eflornithine in Gambian trypanosomiasis: a multicentre randomized controlled trial Jacques Pépin, 1 Nzambi Khonde, 2 Faustine Maiso, 3 Félix Doua, 4 Shabbar Jaffar, 5 Stéphane Ngampo,
Research Short-course eflornithine in Gambian trypanosomiasis: a multicentre randomized controlled trial Jacques Pépin, 1 Nzambi Khonde, 2 Faustine Maiso, 3 Félix Doua, 4 Shabbar Jaffar, 5 Stéphane Ngampo,
M E M O R A N D U M. No new drug is in clinical development for second stage HAT treatment.
 M E M O R A N D U M From: Director, NTD To: Secretary, Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines Our ref: EML 2009 Attention: Dr Suzanne Hill Date: 13 February 2009 Your ref: E19/81/17
M E M O R A N D U M From: Director, NTD To: Secretary, Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines Our ref: EML 2009 Attention: Dr Suzanne Hill Date: 13 February 2009 Your ref: E19/81/17
KINETOPLASTIDS. Kinetoplast. Nucleus
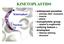 KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
A LENGTH BASED ASSESSMENT FOR ATLANTIC BONITO (SARDA SARDA)
 SCRS/2015/112 Collect. Vol. Sci. Pap. ICCAT, 72(8): 2208-2220 (2015) A LENGTH BASED ASSESSMENT FOR ATLANTIC BONITO (SARDA SARDA) B. Sid'Ahmed, N. Abid, and C. Palma and L. Kell 1 SUMMARY This document
SCRS/2015/112 Collect. Vol. Sci. Pap. ICCAT, 72(8): 2208-2220 (2015) A LENGTH BASED ASSESSMENT FOR ATLANTIC BONITO (SARDA SARDA) B. Sid'Ahmed, N. Abid, and C. Palma and L. Kell 1 SUMMARY This document
2.1 HIV antibody tests
 Over 100 different kinds of HIV test are currently available worldwide. More are likely to become available in the future. The choice of test depends on factors including laboratory requirements, how easy
Over 100 different kinds of HIV test are currently available worldwide. More are likely to become available in the future. The choice of test depends on factors including laboratory requirements, how easy
Clinical Development of New Treatments for Sleeping Sickness. Sleeping sickness: New oral treatments
 Clinical Development of New Treatments for Sleeping Sickness Supporting WHO HAT elimination goals WHO set goals for Global Elimination of sleeping sickness by 2020, supported by London Declaration (2012)
Clinical Development of New Treatments for Sleeping Sickness Supporting WHO HAT elimination goals WHO set goals for Global Elimination of sleeping sickness by 2020, supported by London Declaration (2012)
A retrospective study of Rift Valley fever in Saudi Arabia
 Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 2003, 22 (3), 867-871 A retrospective study of Rift Valley fever in Saudi Arabia A.I. Al-Afaleq (1), E.M.E. Abu Elzein (1), S.M. Mousa (2) & A.M. Abbas (2) (1) College
Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 2003, 22 (3), 867-871 A retrospective study of Rift Valley fever in Saudi Arabia A.I. Al-Afaleq (1), E.M.E. Abu Elzein (1), S.M. Mousa (2) & A.M. Abbas (2) (1) College
Tap Sign in Tuberculoid and Borderline Tuberculoid Leprosy 1
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LEPROSY Volume 72, Number 3 Printed in the U.S.A. (ISSN 0148-916X) Tap Sign in Tuberculoid and Borderline Tuberculoid Leprosy 1 Sujith Prasad W. Kumarasinghe, M. P. Kumarasinghe,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LEPROSY Volume 72, Number 3 Printed in the U.S.A. (ISSN 0148-916X) Tap Sign in Tuberculoid and Borderline Tuberculoid Leprosy 1 Sujith Prasad W. Kumarasinghe, M. P. Kumarasinghe,
Malaria Slide Reading
 Malaria Slide Reading La Lecture des lames pour le diagnostic du paludisme Malaria Slide Reading Training/La Lecture des lames pour le diagnostic du paludisme Content Contenu Malaria in general Le paludisme
Malaria Slide Reading La Lecture des lames pour le diagnostic du paludisme Malaria Slide Reading Training/La Lecture des lames pour le diagnostic du paludisme Content Contenu Malaria in general Le paludisme
Introduction. Research
 Research Tetanus toxoid coverage as an indicator of serological protection against neonatal tetanus Michael S. Deming, 1 Jean-Baptiste Roungou, 2 Max Kristiansen, 3 Iver Heron, 4 Alphonse Yango, 5 Alexis
Research Tetanus toxoid coverage as an indicator of serological protection against neonatal tetanus Michael S. Deming, 1 Jean-Baptiste Roungou, 2 Max Kristiansen, 3 Iver Heron, 4 Alphonse Yango, 5 Alexis
Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test
 Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1109 Pkg.Size:100T Intended use The Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test is a simple and rapid latex agglutination test for the qualitative
Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1109 Pkg.Size:100T Intended use The Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test is a simple and rapid latex agglutination test for the qualitative
Mouse C-Peptide ELISA Kit
 Mouse C-Peptide ELISA Kit Cat.No: DEIA4507 Lot. No. (See product label) Size 96T Intended Use The Mouse C-Peptide ELISA kit is for the quantitative determination of c-peptide in mouse serum, plasma, and
Mouse C-Peptide ELISA Kit Cat.No: DEIA4507 Lot. No. (See product label) Size 96T Intended Use The Mouse C-Peptide ELISA kit is for the quantitative determination of c-peptide in mouse serum, plasma, and
Rubella Latex Agglutination Test
 Rubella Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1088 Pkg.Size:30T Intended use The Rubella Latex Agglutination Test is a rapid latex particle agglutination test for the qualitative and semi-quantitative
Rubella Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1088 Pkg.Size:30T Intended use The Rubella Latex Agglutination Test is a rapid latex particle agglutination test for the qualitative and semi-quantitative
Common EQA Mistakes - A provider Perspective. Experience from East African Regional External Quality Assessment Scheme (EA-REQAS)
 Common EQA Mistakes - A provider Perspective Experience from East African Regional External Quality Assessment Scheme (EA-REQAS) Overview of Amref Health Africa Leading health development INGO in Africa
Common EQA Mistakes - A provider Perspective Experience from East African Regional External Quality Assessment Scheme (EA-REQAS) Overview of Amref Health Africa Leading health development INGO in Africa
Molecular analysis of archived blood slides reveals an atypical human Trypanosoma. infection
 Molecular analysis of archived blood slides reveals an atypical human Trypanosoma infection Running head: Molecular analysis of Trypanosoma infection Stijn Deborggraeve a,f,*, Mathurin Koffi b, Vincent
Molecular analysis of archived blood slides reveals an atypical human Trypanosoma infection Running head: Molecular analysis of Trypanosoma infection Stijn Deborggraeve a,f,*, Mathurin Koffi b, Vincent
PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2010;4(12):e783. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. Archived with thanks to PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases
 MSF Field Research The Unknown Risk of Vertical Transmission in Sleeping Sickness--a Literature Review Item type Authors Citation DOI Journal Rights Article Lindner, A K; Priotto, G PLoS Negl Trop Dis
MSF Field Research The Unknown Risk of Vertical Transmission in Sleeping Sickness--a Literature Review Item type Authors Citation DOI Journal Rights Article Lindner, A K; Priotto, G PLoS Negl Trop Dis
Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle
 Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 1 no 9 pp 833 839 september 5 Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle P. Van den Bossche, A. Ky-Zerbo, J. Brandt, T. Marcotty,
Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 1 no 9 pp 833 839 september 5 Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle P. Van den Bossche, A. Ky-Zerbo, J. Brandt, T. Marcotty,
Strengthening Immunization in a West African Country: Mali
 O R I G I N A L R E S E A R C H P A P E R Strengthening Immunization in a West African Country: Mali JB Milstien 1, M Tapia 1, SO Sow 2, L Keita 2, K Kotloff 1 1 University of Maryland School of Medicine,
O R I G I N A L R E S E A R C H P A P E R Strengthening Immunization in a West African Country: Mali JB Milstien 1, M Tapia 1, SO Sow 2, L Keita 2, K Kotloff 1 1 University of Maryland School of Medicine,
OF Al INFLUENZA ON SUSCEPTIBILITY TO A2 VIRUS DURING THE 1957 OUTBREAK
 Bull. Org. mond. Sante 1959, 20, 297-301 Bull. Wld Hlth Org. THE EFFECT OF A PREVIOUS ATTACK OF Al INFLUENZA ON SUSCEPTIBILITY TO A2 VIRUS DURING THE 1957 OUTBREAK A. N. SLEPUSHKIN Influenza Department,
Bull. Org. mond. Sante 1959, 20, 297-301 Bull. Wld Hlth Org. THE EFFECT OF A PREVIOUS ATTACK OF Al INFLUENZA ON SUSCEPTIBILITY TO A2 VIRUS DURING THE 1957 OUTBREAK A. N. SLEPUSHKIN Influenza Department,
Trypanosomiasis. Introduction. Epidemiology. Global Epidemiology. Trypanosomiasis Risk in UK Travellers
 Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
Standard Operation Procedure (SOP) for Biobanking Sampling Procedure Manual Use
 Standard Operation Procedure (SOP) for Biobanking Sampling Procedure Manual Use 1. Plasma, Serum and PAXgene Blood Collection 1.1. Equipment and reagents to be supplied by user 1.1.1. For blood withdrawal
Standard Operation Procedure (SOP) for Biobanking Sampling Procedure Manual Use 1. Plasma, Serum and PAXgene Blood Collection 1.1. Equipment and reagents to be supplied by user 1.1.1. For blood withdrawal
Working Papers du CEPED
 juin 2009 03 Working Papers du CEPED Estimating effect of non response on HIV prevalence estimates from Demographic and Health Surveys Joseph Larmarange, Roselyne Vallo, Seydou Yaro, Philippe Msellati,
juin 2009 03 Working Papers du CEPED Estimating effect of non response on HIV prevalence estimates from Demographic and Health Surveys Joseph Larmarange, Roselyne Vallo, Seydou Yaro, Philippe Msellati,
maect PRODUCTION SOP M/10 June 2007 version page: 1 Sterility control
 maect PRODUCTION SOP M/10 June 2007 version page: 1 Sterility control Intended use: Material Consumables maect columns are produced in batches. Each batch is identified by its production date. Quality
maect PRODUCTION SOP M/10 June 2007 version page: 1 Sterility control Intended use: Material Consumables maect columns are produced in batches. Each batch is identified by its production date. Quality
Simo et al. Parasites & Vectors 2012, 5:201
 Simo et al. Parasites & Vectors 2012, 5:201 RESEARCH Open Access Identification of different trypanosome species in the mid-guts of tsetse flies of the Malanga (Kimpese) sleeping sickness focus of the
Simo et al. Parasites & Vectors 2012, 5:201 RESEARCH Open Access Identification of different trypanosome species in the mid-guts of tsetse flies of the Malanga (Kimpese) sleeping sickness focus of the
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II. Table of Contents
 E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit
 HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3509 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use GHbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human GHbA1c. General Description vhemoglobin,
HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3509 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use GHbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human GHbA1c. General Description vhemoglobin,
General Anesthesia Gender patterns amongst Canadian anesthesiologists
 437 General Anesthesia Gender patterns amongst Canadian anesthesiologists [La proportion hommes-femmes chez les anesthésiologistes canadiens] Mark Otto Baerlocher MD,* Rumana Hussain BSc, John Bradley
437 General Anesthesia Gender patterns amongst Canadian anesthesiologists [La proportion hommes-femmes chez les anesthésiologistes canadiens] Mark Otto Baerlocher MD,* Rumana Hussain BSc, John Bradley
WHO/CDS/NTD/IDM/ Recommendations of the Informal Consultation on Issues for Clinical Product Development for Human African Trypanosomiasis
 WHO/CDS/NTD/IDM/2007.1 Recommendations of the Informal Consultation on Issues for Clinical Product Development for Human African Trypanosomiasis Geneva, Switzerland 9 10 September 2004 World Health Organization
WHO/CDS/NTD/IDM/2007.1 Recommendations of the Informal Consultation on Issues for Clinical Product Development for Human African Trypanosomiasis Geneva, Switzerland 9 10 September 2004 World Health Organization
Isolation of an equine influenza virus strain and epizootiological study of the outbreak in Argentina
 Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 1989, 8 (1), 123-128. Isolation of an equine influenza virus strain and epizootiological study of the 1985-86 outbreak in Argentina E. NOSETTO 1,3, M. PECORARO 2,3 CM.
Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 1989, 8 (1), 123-128. Isolation of an equine influenza virus strain and epizootiological study of the 1985-86 outbreak in Argentina E. NOSETTO 1,3, M. PECORARO 2,3 CM.
Control and surveillance of human African trypanosomiasis
 In the 1960s, it appeared that human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) could be effectively controlled, but by the beginning of the twenty-first century several decades of neglect had led to alarming numbers
In the 1960s, it appeared that human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) could be effectively controlled, but by the beginning of the twenty-first century several decades of neglect had led to alarming numbers
African trypanosomiasis or Sleeping sickness. A bio-mathematical study of the disease
 African trypanosomiasis or Sleeping sickness A bio-mathematical study of the disease YASMINE SAMIA 008 African trypanosomiasis or Sleeping sickness A bio-mathematical study of the disease African trypanosomiasis,
African trypanosomiasis or Sleeping sickness A bio-mathematical study of the disease YASMINE SAMIA 008 African trypanosomiasis or Sleeping sickness A bio-mathematical study of the disease African trypanosomiasis,
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture
 Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
Suicide in the Canadian Forces 1995 to 2012
 Suicide in the Canadian Forces 1995 to 2012 Laura Bogaert MSc, Jeff Whitehead MD MSc FRCPC, Miriam Wiens MSc, Elizabeth Rolland MSc PhD Directorate of Force Health Protection Surg Gen Report Surg Gen Health
Suicide in the Canadian Forces 1995 to 2012 Laura Bogaert MSc, Jeff Whitehead MD MSc FRCPC, Miriam Wiens MSc, Elizabeth Rolland MSc PhD Directorate of Force Health Protection Surg Gen Report Surg Gen Health
Monkeypox-specific antibodies in human
 Monkeypox-specific antibodies in human and simian sera from the Ivory Coast and Nigeria* R. GISPEN,1 B. BRAND-SAATHOF,2 & A. C. HEKKER3 A test for monkeypox-specific antibodies is described. Monkeypox
Monkeypox-specific antibodies in human and simian sera from the Ivory Coast and Nigeria* R. GISPEN,1 B. BRAND-SAATHOF,2 & A. C. HEKKER3 A test for monkeypox-specific antibodies is described. Monkeypox
Early stages of embryonic development in two rabbit genotypes
 Early stages of embryonic development in two rabbit genotypes Suzanne TORRÈS, Françoise HULOT, Claude SEVELLEC To cite this version: Suzanne TORRÈS, Françoise HULOT, Claude SEVELLEC. Early stages of embryonic
Early stages of embryonic development in two rabbit genotypes Suzanne TORRÈS, Françoise HULOT, Claude SEVELLEC To cite this version: Suzanne TORRÈS, Françoise HULOT, Claude SEVELLEC. Early stages of embryonic
temperature by Weil et al. (1975). The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian
 The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian state and serum gonadotropin level K. BIENIARZ P. EPLER B. BRETON Luong Noc THUY Institute of Applied Zoology, Academy of Agriculture, 30-059
The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian state and serum gonadotropin level K. BIENIARZ P. EPLER B. BRETON Luong Noc THUY Institute of Applied Zoology, Academy of Agriculture, 30-059
Precipitating antibodies against bluetongue and foot and mouth disease viruses in cattle between the two Niles in Khartoum Province, Sudan
 Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 1983, 2 (4), 1059-1066 Precipitating antibodies against bluetongue and foot and mouth disease viruses in cattle between the two Niles in Khartoum Province, Sudan E.M.E.
Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 1983, 2 (4), 1059-1066 Precipitating antibodies against bluetongue and foot and mouth disease viruses in cattle between the two Niles in Khartoum Province, Sudan E.M.E.
Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for stage determination and treatment outcome evaluation in patients affected by Human African trypanosomiasis
 Thesis Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for stage determination and treatment outcome evaluation in patients affected by Human African trypanosomiasis TIBERTI, Natalia Abstract Human African trypanosomiasis
Thesis Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for stage determination and treatment outcome evaluation in patients affected by Human African trypanosomiasis TIBERTI, Natalia Abstract Human African trypanosomiasis
Tilt table exercise echocardiography assessment in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease
 Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases 101 (2008) 170 174 Available on www.sciencedirect.com CLINICAL RESEARCH Tilt table exercise echocardiography assessment in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease Évaluation
Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases 101 (2008) 170 174 Available on www.sciencedirect.com CLINICAL RESEARCH Tilt table exercise echocardiography assessment in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease Évaluation
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 9, No. 4,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 9, No. 4, 2003 837 Antimony-resistant Leishmania donovani in eastern Sudan: incidence and in vitro correlation M.G. Abdo, 1 W.M. Elamin, 1 E.A.G. Khalil 1 and
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 9, No. 4, 2003 837 Antimony-resistant Leishmania donovani in eastern Sudan: incidence and in vitro correlation M.G. Abdo, 1 W.M. Elamin, 1 E.A.G. Khalil 1 and
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION ORGANISATION MONDIALE DE LA SANTÉ ENGLISH ONLY. Working Paper No. 32
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION ORGANISATION MONDIALE DE LA SANTÉ CD/WP/70.32 ENGLISH ONLY INTER-REGIONAL SEMINAR ON METHODS OF EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEILLANCE Working Paper No. 32 Prague, 5-17 October 1970 SURVEILLANCE
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION ORGANISATION MONDIALE DE LA SANTÉ CD/WP/70.32 ENGLISH ONLY INTER-REGIONAL SEMINAR ON METHODS OF EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEILLANCE Working Paper No. 32 Prague, 5-17 October 1970 SURVEILLANCE
NEW ONE-STAGE PROCEDURES FOR THE QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF PROTHROMBIN AND LABILE FACTOR*
 NEW ONE-STAGE PROCEDURES FOR THE QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF PROTHROMBIN AND LABILE FACTOR* MARIO STEFANINI, M.D.f From the Department ofbiochemistry, Marquette University School of Medicine, Milwaukee,
NEW ONE-STAGE PROCEDURES FOR THE QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF PROTHROMBIN AND LABILE FACTOR* MARIO STEFANINI, M.D.f From the Department ofbiochemistry, Marquette University School of Medicine, Milwaukee,
THE EFFECT OF AGE AND SAFETY MARGIN ON LOCAL RECURRENCE AND SURVIVAL AFTER BREAST CONSERVATIVE SURGERY FOR EARLY BREAST CANCER
 Copyright 2017 Balkan Medical Union vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 176-180 June 2017 ORIGINAL PAPER THE EFFECT OF AGE AND SAFETY MARGIN ON LOCAL RECURRENCE AND SURVIVAL AFTER BREAST CONRVATIVE SURGERY FOR EARLY BREAST
Copyright 2017 Balkan Medical Union vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 176-180 June 2017 ORIGINAL PAPER THE EFFECT OF AGE AND SAFETY MARGIN ON LOCAL RECURRENCE AND SURVIVAL AFTER BREAST CONRVATIVE SURGERY FOR EARLY BREAST
= 0.002) 117 #!. 12, : = 0.45; P
 Background: Psychosocial factors governing the use of postoperative, intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) have received little attention in spite of the fact that PCA is the most common modality
Background: Psychosocial factors governing the use of postoperative, intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) have received little attention in spite of the fact that PCA is the most common modality
Inconsistent dosing of anti-tuberculosis drugs in Taipei, Taiwan
 INT J TUBERC LUNG DIS 14(7):878 883 2010 The Union Inconsistent dosing of anti-tuberculosis drugs in Taipei, Taiwan C-Y. Chiang,* K-J. Bai, C-N. Lee, D. A. Enarson,* J. Suo, K-T. Luh * International Union
INT J TUBERC LUNG DIS 14(7):878 883 2010 The Union Inconsistent dosing of anti-tuberculosis drugs in Taipei, Taiwan C-Y. Chiang,* K-J. Bai, C-N. Lee, D. A. Enarson,* J. Suo, K-T. Luh * International Union
