Fictive Lung Ventilation in the Isolated Brainstem Preparation of the Aquatic Frog, Xenopus Laevis
|
|
|
- Blaze Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2 Fictive Lung Ventilation in the Isolated Brainstem Preparation of the Aquatic Frog, Xenopus Laevis Naofumi Kimura Department of Pharmacology, Jikei University School of Medicine, Nishishinbashi , Minato-ku, Tokyo 105, Japan, Abstract Aquatic pipid frogs, unlike other anurans, never show sole buccal ventilation cycle, and exhale air from the lung before aspirating air into the buccal cavity. To study the mechanism that pipid frogs lack the buccal cycle, respiratory motor activities were recorded from the isolated brainstem-spinal cord preparation of Xenopus laevis. Brainstem preparations of Xenopus exhibited the intermittent burst complex (lung bursts) similar to the lung ventilation cycle in vivo. Lung bursts spontaneously occurred in the cranial nerve V, IX and X, and in the hypoglossal and third spinal nerves. Small bursts with regular cycle similar to buccal oscillation in ranid frogs, were observed in the cranial nerve V and X but not in the hypoglossal and the third spinal nerve. These results suggest that Xenopus is capable of oscillating buccal rhythm within the brainstem. 1 Introduction Pipid frogs including Xenopus laevis are entirely aquatic and have interesting characteristics from the viewpoint of comparative physiology. First, pipid frogs, unlike other anurans, lack sole buccal ventilation cycle, and have only lung ventilation cycle. Second, they are different from other anurans in the sequence of lung ventilation. Although ranid frogs inspire air into buccal cavity before exhaling air from the lung, pipids fill the buccal cavity with fresh air after exhaling air (Brett and Shelton 1979). During the ventilation cycle, other anurans open nares except when they stuff air into the lung, while the pipids close the nares except when they exhale air from the lung and inhale air into the buccal cavity. Third, pipids have inherent muscles, musculus pulmonum proprius (Mpp) and ventral diaphragm, suspected homologous to the mammalian diaphragm, though the muscles do not separate the pleural cavity from the abdominal cavity (Keith 1905, Snapper et al. 1974). Furthermore, these muscles are innervated with nerve branches of brachial plexus. A recent study suggested that the pipid diaphragm might be capable of acting as an esophageal sphincter, like the mammalian rural diaphragm (Pickering I. Homma et al. (eds.), New Frontiers in Respiratory Control, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 669, DOI / _2, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
2 10 N. Kimura et al. 2004). To study whether adult pipid frogs had lost buccal oscillator itself, the respiratory motor activity was recorded from the isolated brainstem of Xenopus laevis without any peripheral reflex loops. 2 Methods Experiments were performed on nine juvenile and adult (15 35 g, both sexes) African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis). Care of animals and experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Research Committees of the Jikei University School of Medicine. All animals were acquired from commercial suppliers (Watanabe Zoushoku). Each frog was anesthetized in the 0.6% saline containing 0.01% tricaine methane sulfonate until unresponsive to toe pinch. The cranium was opened and the animal decerebrated. The dura and choroid plexus were removed and the brainstem superfused with oxygenated artificial cerebrospinal fluid (acsf) buffered sodium bicarbonate at Bicarbonate acsf (in mm): NaCl, 104; KCl, 4; MgCl 2, 1.4; D-glucose, 10; NaHCO 3, 25; CaCl 2 2.4; ph 9. Bicarbonate acsf was equilibrated with 98%O 2 and 2% CO 2 to yield a bath ph of 7.9. The brainstem was isolated with two transections, one just caudal to the cranial nerve III and other caudal to the 4th spinal nerve. Electrical signals were recorded from the roots of cranial and spinal nerves, with some combinations of V, IX, X, hypoglossal nerve (SN2), and the third spinal nerve (SN3), using glass suction electrodes. These signals were amplified ( 10,000) and filtered (1 5 khz) using differential AC amplifiers (model 1700, A-M Systems), digitized at 400 /s (Powerlab 8sp, ADInstruments) and archived on a HDD. To test the pharmacological properties of the fictive lung ventilation, CNQX (1 μm), strychnine (1 μm), and bicuculline (5 10 μm) were given to the superfusate. 3 Results The isolated brainstem-spinal cord preparation of Xenopus laevis exhibited intermittent bursts (lung bursts) similar to the lung ventilation in vivo in all the V, IX, X, SN2 and SN3 recorded. The lung bursts spontaneously occurred as doublet (a pair of bursts), triplet or multiple burst complexes (Fig. 1A). The period of lung bursts are ranging from 10 to 150 s (53+54 s, n = 9). Small bursts with relatively regular cycle, low amplitude, short duration and interval (buccal-like bursts) similar to the buccal oscillation in ranid frogs, were observed in the cranial nerve V and X, but not in SN2 and SN3 (Fig. 1B and C). The period of buccal-like bursts are ranging from 1.3 to 3.1 s ( s, n = 6). Bath application of 1μM of CNQX prolonged the interval between the lung bursts without reduction in the amplitude (Fig. 2, n = 3). Strychnine (1 μm) changed the lung bursts into a decrementing shape (n = 3), and the burst shape did not re-
3 Fictive Lung Ventilation in the Aquatic Frog 11 cover with washing over 1hr by acsf. Lower concentration of bicuculline (5 μm) increased buccal-like bursts (Fig. 2C, n=3). Higher concentration of bicuculline (10 μm) decreased buccal-like bursts and changed the lung bursts into decrementing bursts with short duration. Fig. 1 Lung bursts and buccal-like bursts recorded from the isolated brainstem of Xenopus laevis. A: Various patterns of lung burst complex in the cranial nerve X. B and C: Lung bursts (L) and buccal-like busrts (b) in the trigeminal (V) and vagus (X) nerves 4 Discussion Patterns of the burst complex recorded from the isolated brainstem of Xenopus laevis were similar to their lung-ventilation in vivo. The activation sequence of motor outputs within a burst complex was consistent with that of the normal ventilation in vivo. Similarities in the effects of CNQX, strychnine, and bicuculline on the bursts to ranid frogs are also consistent with their homology (Kimura and Remmers 1994, Kimura et al. 1997, Kawasaki et al. 1995). Occurrence of buccal-like bursts in the isolated brainstem suggests that Brainstem of adult Xenopus is capable of oscillating with buccal cycle. Buccal oscillation of Xenopus might be suppressed by some reflex mechanism in vivo. However, it is unknown whether buccal-like burst actually functions as some role. Although the reason for lacking buccal-like bursts in SN2 is also unknown, it seems to be convenient not to aspirate water into buccal cavity for their aquatic life. Because of recording nerve rootlet, reciprocally active bursts in SN2 might
4 12 N. Kimura mutually bury those activities. To prove this point, it needs recording separately from nerve branches in the in situ brainstem preparation (Kimura et al. 1997). Absence of buccal-like bursts in SN3 containing branches innervating pipid diaphragm may suggest that motor outputs from buccal oscillator had been not supplied to diaphragm at the first point in tetrapod evolution. Fig. 2 Effects of CNQX (A), strychnine (B) and bicuculline (C) on lung bursts from the isolated brainstem-spinal cord preparations of Xenopus laevis References Brett, S.S. and Shelton, G. (1979) Ventilatory mechanisms of the amphibian, Xenopus laevis; the role of the buccal force pump. J.Exp. Biol. 80, Kawasaki, H., Kimura, N., and Remmers, J.E. (1995) The role of GABA in the respiratory related activity in the isolated brainstem of the frog. Jpn. J. Physiol. 45(Suppl 1), S86. Keith, A. (1905) The nature of the mammalian diaphragm and pleural cavities. J. Anat. Physiol. 39, Kimura, N., Perry, S.F., and Remmers, J.E. (1997) Srychnine eliminates reciprocation and augmentation of respiratory bursts of the in vitro frog brainstem. Neurosci. Lett. 225, Kimura, N. and Remmers, J.E. (1994) Effect of non-nmda receptor antagonists on respiratory related activity in the isolated brainstem of the frog, Rana pipiens. Jpn. J. Physiol. 44(Suppl 1), S109. Pickering, M., Campion, D., Jones, J.F.X. (2004) A gastrointestinal role for the amphibian diaphragm of Xenopus laevis. J. Zool. Lond. 264, Snapper, J.R., Tenny, S.M., and McCann, F.V. (1974) Observations on the amphibian diaphragm. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Comp. Physiol. 49,
5
IS THE VERTEBRATE RESPIRATORY CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR CONSERVED? Insights from in vitro and in vivo amphibian models
 IS THE VERTEBRATE RESPIRATORY CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR CONSERVED? Insights from in vitro and in vivo amphibian models M.S. Hedrick, L. Broch, M. Martinez, J.L. Powell, R.E. Wade * 1. INTRODUCTION There
IS THE VERTEBRATE RESPIRATORY CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR CONSERVED? Insights from in vitro and in vivo amphibian models M.S. Hedrick, L. Broch, M. Martinez, J.L. Powell, R.E. Wade * 1. INTRODUCTION There
The influence of descending inputs on breathing pattern formation in the isolated bullfrog brainstem-spinal cord
 Respiration Physiology 120 (2000) 197 211 www.elsevier.com/locate/resphysiol The influence of descending inputs on breathing pattern formation in the isolated bullfrog brainstem-spinal cord Stephen G.
Respiration Physiology 120 (2000) 197 211 www.elsevier.com/locate/resphysiol The influence of descending inputs on breathing pattern formation in the isolated bullfrog brainstem-spinal cord Stephen G.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Corticosterone promotes emergence of fictive air breathing in Xenopus laevis Daudin tadpole brainstems
 1144 The Journal of Experimental Biology 215, 1144-115 212. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/jeb.61234 RESEARCH ARTICLE Corticosterone promotes emergence of fictive air breathing in
1144 The Journal of Experimental Biology 215, 1144-115 212. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/jeb.61234 RESEARCH ARTICLE Corticosterone promotes emergence of fictive air breathing in
Respiratory pattern formation in the isolated bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) brainstem-spinal cord
 Respiration Physiology 114 (1998) 239 255 Respiratory pattern formation in the isolated bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) brainstem-spinal cord Stephen G. Reid *, William K. Milsom Department of Zoology, Uni
Respiration Physiology 114 (1998) 239 255 Respiratory pattern formation in the isolated bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) brainstem-spinal cord Stephen G. Reid *, William K. Milsom Department of Zoology, Uni
ONTOGENY OF CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTION DURING FICTIVE GILL AND LUNG VENTILATION IN AN IN VITRO BRAINSTEM PREPARATION OF RANA CATESBEIANA
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 2, 263 272 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 JEB858 263 ONTOGENY OF CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTION DURING FICTIVE GILL AND LUNG VENTILATION
The Journal of Experimental Biology 2, 263 272 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 JEB858 263 ONTOGENY OF CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTION DURING FICTIVE GILL AND LUNG VENTILATION
Potential switch from eupnea to fictive gasping after blockade of glycine transmission and potassium channels
 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283: R721 R731, 2002. First published July 8, 2002; 10.1152/ajpregu.00004.2002. Potential switch from eupnea to fictive gasping after blockade of glycine transmission
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283: R721 R731, 2002. First published July 8, 2002; 10.1152/ajpregu.00004.2002. Potential switch from eupnea to fictive gasping after blockade of glycine transmission
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
SEROTONERGIC MODULATION OF RESPIRATORY RHYTHMOGENESIS AND CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTION
 SEROTONERGIC MODULATION OF RESPIRATORY RHYTHMOGENESIS AND CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTION In addition to evidence supporting serotonergic modulation of respiratory rhythmogenesis, serotonergic mechanisms play a
SEROTONERGIC MODULATION OF RESPIRATORY RHYTHMOGENESIS AND CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTION In addition to evidence supporting serotonergic modulation of respiratory rhythmogenesis, serotonergic mechanisms play a
Early Onset of Ventilatory and Airway Response to Hypercapnia is Mediated by Medullary 5-HT 1A Receptors in Infant Rats
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 26 3, 211 217, September 2014 Original Early Onset of Ventilatory and Airway Response to Hypercapnia is Mediated by Medullary 5-HT 1A Receptors in Infant Rats Shingo MATSUDAIRA, Mitsuko
Showa Univ J Med Sci 26 3, 211 217, September 2014 Original Early Onset of Ventilatory and Airway Response to Hypercapnia is Mediated by Medullary 5-HT 1A Receptors in Infant Rats Shingo MATSUDAIRA, Mitsuko
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
1. In a normal negative feedback loop the Comparator sends a(n) signal to the.
 Quiz 1-G 1. In a normal negative feedback loop the Comparator sends a(n) signal to the. a. Actuating, Sensor b. Effector, Sensor c. Error, Effector d. Actuating, Effector 2. What organ, discussed in lecture
Quiz 1-G 1. In a normal negative feedback loop the Comparator sends a(n) signal to the. a. Actuating, Sensor b. Effector, Sensor c. Error, Effector d. Actuating, Effector 2. What organ, discussed in lecture
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
Nitric oxide changes its role as a modulator of respiratory motor activity during development in the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) B
 Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A 142 (25) 231 24 www.elsevier.com/locate/cbpa Nitric oxide changes its role as a modulator of respiratory motor activity during development in the bullfrog
Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A 142 (25) 231 24 www.elsevier.com/locate/cbpa Nitric oxide changes its role as a modulator of respiratory motor activity during development in the bullfrog
64 Chiharu Ashida and Tomoshige Koga of blood gases as well as afferent gag reflex activities are sent to secondary NTS neurons in the medulla oblonga
 Kawasaki Journal of Medical Welfare Vol. 11, No. 2, 2006 63 68 Original Paper Effects of Arterial Oxygen Saturation on Gag Reflex in Humans Chiharu ASHIDA Λ and Tomoshige KOGA ΛΛ (Accepted November 4,
Kawasaki Journal of Medical Welfare Vol. 11, No. 2, 2006 63 68 Original Paper Effects of Arterial Oxygen Saturation on Gag Reflex in Humans Chiharu ASHIDA Λ and Tomoshige KOGA ΛΛ (Accepted November 4,
Cellular and Synaptic Modulation Underlying Substance P-Mediated Plasticity of the Lamprey Locomotor Network
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 1998, 18(19):8095 8110 Cellular and Synaptic Modulation Underlying Substance P-Mediated Plasticity of the Lamprey Locomotor Network David Parker and Sten Grillner
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 1998, 18(19):8095 8110 Cellular and Synaptic Modulation Underlying Substance P-Mediated Plasticity of the Lamprey Locomotor Network David Parker and Sten Grillner
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Development of the respiratory response to hypoxia in the isolated brainstem of the bullfrog Rana catesbeiana
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 28, 213-222 Published by The Company of Biologists 25 doi:1.1242/jeb.1399 213 Development of the respiratory response to hypoxia in the isolated brainstem of the bullfrog
The Journal of Experimental Biology 28, 213-222 Published by The Company of Biologists 25 doi:1.1242/jeb.1399 213 Development of the respiratory response to hypoxia in the isolated brainstem of the bullfrog
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 594.21 (216) pp 6349 6367 6349 Environmentally induced return to juvenile-like chemosensitivity in the respiratory control system of adult bullfrog, Lithobates catesbeianus Joseph M. Santin 1,2
J Physiol 594.21 (216) pp 6349 6367 6349 Environmentally induced return to juvenile-like chemosensitivity in the respiratory control system of adult bullfrog, Lithobates catesbeianus Joseph M. Santin 1,2
Tricaine (MS-222) is a safe anesthetic compound compared to benzocaine and pentobarbital to induce anesthesia in leopard frogs (Rana pipiens)
 Pharmacological Reports 2005, 57, 467 474 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2005 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Tricaine (MS-222) is a safe anesthetic compound compared to benzocaine and
Pharmacological Reports 2005, 57, 467 474 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2005 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Tricaine (MS-222) is a safe anesthetic compound compared to benzocaine and
The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience
 J Physiol 590.19 (2012) pp 4735 4759 4735 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience Neuronal activity in the isolated mouse spinal cord during spontaneous deletions in fictive locomotion: insights into locomotor
J Physiol 590.19 (2012) pp 4735 4759 4735 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience Neuronal activity in the isolated mouse spinal cord during spontaneous deletions in fictive locomotion: insights into locomotor
Abdominal expiratory activity in the rat brainstem spinal cord in situ: patterns, origins and implications for respiratory rhythm generation
 J Physiol 587.14 (2009) pp 3539 3559 3539 Abdominal expiratory activity in the rat brainstem spinal cord in situ: patterns, origins and implications for respiratory rhythm generation A. P. L. Abdala 1,I.A.Rybak
J Physiol 587.14 (2009) pp 3539 3559 3539 Abdominal expiratory activity in the rat brainstem spinal cord in situ: patterns, origins and implications for respiratory rhythm generation A. P. L. Abdala 1,I.A.Rybak
VENTRAL ROOT RESPONSES OF THE HEMISECTED AMPHIBIAN SPINAL CORD TO PERFUSED AMINO ACIDS IN THE PRESENCE OF PROCAINE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1975), 55 519-526 VENTRAL ROOT RESPONSES OF THE HEMISECTED AMPHIBIAN SPINAL CORD TO PERFUSED AMINO ACIDS IN THE PRESENCE OF PROCAINE R.H. EVANS & J.C. WATKINS Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1975), 55 519-526 VENTRAL ROOT RESPONSES OF THE HEMISECTED AMPHIBIAN SPINAL CORD TO PERFUSED AMINO ACIDS IN THE PRESENCE OF PROCAINE R.H. EVANS & J.C. WATKINS Department of Pharmacology,
DO FROGS DRINK? (Received 30 May 1978) SUMMARY
 J. exp. BioL (1979), 79. 41-46 Printed in Great Britain DO FROGS DRINK? BY P. J. BENTLEY AND T. YORIO Departments of Pharmacology and Ophthalmology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University
J. exp. BioL (1979), 79. 41-46 Printed in Great Britain DO FROGS DRINK? BY P. J. BENTLEY AND T. YORIO Departments of Pharmacology and Ophthalmology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
THE ACTION OF CHLORPHENESIN CARBAMATE ON THE FROG SPINAL CORD
 Japan. J. Pharmacol. 30, 29-36 (1980) 29 THE ACTION OF CHLORPHENESIN CARBAMATE ON THE FROG SPINAL CORD Hironaka AIHARA, Michio KURACHI, Sadao NAKANE, Michitada SASAJIMA and Masahiro OHZEKI Research Laboratories,
Japan. J. Pharmacol. 30, 29-36 (1980) 29 THE ACTION OF CHLORPHENESIN CARBAMATE ON THE FROG SPINAL CORD Hironaka AIHARA, Michio KURACHI, Sadao NAKANE, Michitada SASAJIMA and Masahiro OHZEKI Research Laboratories,
Instructor s Review for Final Exams. The Nervous System
 Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 21, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 21, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 21, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Rhythm generation, coordination, and initiation in the vocal pathways of male African clawed frogs
 J Neurophysiol 117: 178 194, 217. First published October 19, 216; doi:1.1152/jn.628.216. RESRCH ARTICLE Central Pattern Generators Rhythm generation, coordination, and initiation in the vocal pathways
J Neurophysiol 117: 178 194, 217. First published October 19, 216; doi:1.1152/jn.628.216. RESRCH ARTICLE Central Pattern Generators Rhythm generation, coordination, and initiation in the vocal pathways
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Brown EN, Lydic R, Schiff ND, et al. General anesthesia, sleep,
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Brown EN, Lydic R, Schiff ND, et al. General anesthesia, sleep,
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
IMPORTANCE OF CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM IONS FOR POSTEXCITATORY HYPERSENSITIVITY IN THE JUMPING SPIDER (MENEMERUS) EYE
 y. exp. Biol. (1982), 97, 187-195 187 With* figures Printed in Great Britain IMPORTANCE OF CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM IONS FOR POSTEXCITATORY HYPERSENSITIVITY IN THE JUMPING SPIDER (MENEMERUS) EYE BY SHIGEKI
y. exp. Biol. (1982), 97, 187-195 187 With* figures Printed in Great Britain IMPORTANCE OF CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM IONS FOR POSTEXCITATORY HYPERSENSITIVITY IN THE JUMPING SPIDER (MENEMERUS) EYE BY SHIGEKI
(Received 12 December 1967)
 J. Physiol. (1968), 195, pp. 755-759 755 With 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain A NOTE ON TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL IN DERMAL MELANOPHORES OF THE FROG AND MOVEMENT OF MELANIN GRANULES BY A. R. MARTIN
J. Physiol. (1968), 195, pp. 755-759 755 With 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain A NOTE ON TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL IN DERMAL MELANOPHORES OF THE FROG AND MOVEMENT OF MELANIN GRANULES BY A. R. MARTIN
Blockade and Recovery of Spontaneous Rhythmic Activity after Application of Neurotransmitter Antagonists to Spinal Networks of the Chick Embryo
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 1, 1998, 18(1):294 306 Blockade and Recovery of Spontaneous Rhythmic Activity after Application of Neurotransmitter Antagonists to Spinal Networks of the Chick Embryo
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 1, 1998, 18(1):294 306 Blockade and Recovery of Spontaneous Rhythmic Activity after Application of Neurotransmitter Antagonists to Spinal Networks of the Chick Embryo
Business. Midterm #1 is Monday, study hard!
 Business Optional midterm review Tuesday 5-6pm Bring your Physio EX CD to lab this week Homework #6 and 7 due in lab this week Additional respiratory questions need to be completed for HW #7 Midterm #1
Business Optional midterm review Tuesday 5-6pm Bring your Physio EX CD to lab this week Homework #6 and 7 due in lab this week Additional respiratory questions need to be completed for HW #7 Midterm #1
Brainstem. Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem
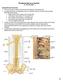
 Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Circulation and Respiration
 Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System
 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:"
50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:"
Control of Respiration
 Control of Respiration Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction The basic rhythm of breathing is
Control of Respiration Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction The basic rhythm of breathing is
V1-ophthalmic. V2-maxillary. V3-mandibular. motor
 4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
2. Langendorff Heart
 2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
RESPIRATION. a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen. c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy
 RESPIRATION 01. The process of respiration is concerned with a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy 02. The narrowest and most numerous tubes
RESPIRATION 01. The process of respiration is concerned with a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy 02. The narrowest and most numerous tubes
Control of breathing in anuran amphibians
 Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A 147 (2007) 665 684 www.elsevier.com/locate/cbpa Review Control of breathing in anuran amphibians Luciane H. Gargaglioni a,, William K. Milsom b a Department
Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A 147 (2007) 665 684 www.elsevier.com/locate/cbpa Review Control of breathing in anuran amphibians Luciane H. Gargaglioni a,, William K. Milsom b a Department
J. Physiol. (I957) I36,
 569 J. Physiol. (I957) I36, 569-584 THE EFFECT OF CHANGES IN SODIUM CHLORIDE CONCENTRATION ON THE SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE GUINEA-PIG'S TAENIA COLI By MOLLIE E. HOLMAN* From the Department of Pharmacology,
569 J. Physiol. (I957) I36, 569-584 THE EFFECT OF CHANGES IN SODIUM CHLORIDE CONCENTRATION ON THE SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE GUINEA-PIG'S TAENIA COLI By MOLLIE E. HOLMAN* From the Department of Pharmacology,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
The Neurologic Examination
 The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria
 Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Effect of hypothermia on respiratory rhythm generation in hamster brainstem spinal cord preparations
 Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology 142 (2004) 237 249 Effect of hypothermia on respiratory rhythm generation in hamster brainstem spinal cord preparations M. Beth Zimmer, W.K. Milsom University of British
Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology 142 (2004) 237 249 Effect of hypothermia on respiratory rhythm generation in hamster brainstem spinal cord preparations M. Beth Zimmer, W.K. Milsom University of British
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
to Regulation of the Brain Vessels
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34,193-197,1984 The Relevance of Cardio-pulmonary-vascular Reflex to Regulation of the Brain Vessels Masatsugu NAKAI and Koichi OGINO Department of Cardiovascular
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34,193-197,1984 The Relevance of Cardio-pulmonary-vascular Reflex to Regulation of the Brain Vessels Masatsugu NAKAI and Koichi OGINO Department of Cardiovascular
EE 791 Lecture 10. FES April 1, EE 791 Lecture 10 1
 EE 791 Lecture 10 FES April 1, 2013 EE 791 Lecture 10 1 Normal Functional Control EE 791 Lecture 10 2 Current uses of FES Cardiovascular Exercise Breathing assist Grasping and Reaching Transfer and Standing
EE 791 Lecture 10 FES April 1, 2013 EE 791 Lecture 10 1 Normal Functional Control EE 791 Lecture 10 2 Current uses of FES Cardiovascular Exercise Breathing assist Grasping and Reaching Transfer and Standing
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
CENTRALLY GENERATED RHYTHMIC AND NON-RHYTHMIC BEHAVIOURAL RESPONSES IN RANA TEMPORARIA EMBRYOS
 J. exp. Biol. 156, 81-99 (1991) 81 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1991 CENTRALLY GENERATED RHYTHMIC AND NON-RHYTHMIC BEHAVIOURAL RESPONSES IN RANA TEMPORARIA EMBRYOS BY S. R.
J. exp. Biol. 156, 81-99 (1991) 81 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1991 CENTRALLY GENERATED RHYTHMIC AND NON-RHYTHMIC BEHAVIOURAL RESPONSES IN RANA TEMPORARIA EMBRYOS BY S. R.
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS
 www.kopfinstruments.com A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS V. S. EREMEEV, Ph.D. R. S. KHRUSTALEVA, Ph.D. V. A. TSYRLIN, Ph.D. Yu. I.
www.kopfinstruments.com A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS V. S. EREMEEV, Ph.D. R. S. KHRUSTALEVA, Ph.D. V. A. TSYRLIN, Ph.D. Yu. I.
Control of Ventilation
 CHAPTER 9 Control of Ventilation Respiratory Components of the Medulla Oblongata The Respiratory Centers Dorsal Respiratory Group Ventral Respiratory Group Respiratory Components of the Lower Brainstem
CHAPTER 9 Control of Ventilation Respiratory Components of the Medulla Oblongata The Respiratory Centers Dorsal Respiratory Group Ventral Respiratory Group Respiratory Components of the Lower Brainstem
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD
 THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
['j.~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. ij.:wjj. 111 ;b Lii-1 j L. synchronism (Fig. 1). From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Cambridge
 106 _ - ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~... _.. J. Physiol. (I953) I21, Io6-iI6 SYNCHRONIZATION OF ACTION POTENTIALS IN THE SPINAL FROG BY T. GUALTIEROTTI* (Fellow of the Rockefeller Foundation) From the Physiological
106 _ - ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~... _.. J. Physiol. (I953) I21, Io6-iI6 SYNCHRONIZATION OF ACTION POTENTIALS IN THE SPINAL FROG BY T. GUALTIEROTTI* (Fellow of the Rockefeller Foundation) From the Physiological
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response
 A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Circulation and Gas Exchange
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Facilitation of reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx
 167 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 2, 167-171, 2009 Original Facilitation of reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx Junichi Kitagawa 1,5), Kazuharu Nakagawa 2), Momoko Hasegawa 3), Tomoyo
167 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 2, 167-171, 2009 Original Facilitation of reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx Junichi Kitagawa 1,5), Kazuharu Nakagawa 2), Momoko Hasegawa 3), Tomoyo
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination
 The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
(Received 30 April 1947)
 107 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, I07-II4 546.264.I3I-3I:6i2.288 THE ACTION OF PHOSGENE ON THE STRETCH RECEPTORS OF THE LUNG BY D. WHITTERIDGE From the University Laboratory of Physiology, Oxford (Received 30
107 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, I07-II4 546.264.I3I-3I:6i2.288 THE ACTION OF PHOSGENE ON THE STRETCH RECEPTORS OF THE LUNG BY D. WHITTERIDGE From the University Laboratory of Physiology, Oxford (Received 30
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Regulation of respiration
 Regulation of respiration Breathing is controlled by the central neuronal network to meet the metabolic demands of the body Neural regulation Chemical regulation Respiratory center Definition: A collection
Regulation of respiration Breathing is controlled by the central neuronal network to meet the metabolic demands of the body Neural regulation Chemical regulation Respiratory center Definition: A collection
University of Leeds.)
 6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
(Axelsson & Thesleff, 1959; Miledi, 1960). Recently, it has become
 J. Physiol. (1973), 230, pp. 613-618 613 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain INFLUENCE OF CHRONIC NEOSTIGMINE TREATMENT ON THE NUMBER OF ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS AND THE RELEASE OF ACETYLCHOLINE
J. Physiol. (1973), 230, pp. 613-618 613 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain INFLUENCE OF CHRONIC NEOSTIGMINE TREATMENT ON THE NUMBER OF ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS AND THE RELEASE OF ACETYLCHOLINE
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
Unit Six The Nervous System
 Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 36, 403-409, 1986 The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions Shun-ichi MIYAMAE
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 36, 403-409, 1986 The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions Shun-ichi MIYAMAE
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
