RESPIRATION. a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen. c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESPIRATION 01. The process of respiration is concerned with a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy 02. The narrowest and most numerous tubes of lungs are a) Hilum b) Bronchus c) Trachea d) Bronchioles 03. The amount of air that moves in and out of the lungs, in each respiratory cycle a) Residual volume b) Vital capacity c) Tidal volume d) Tidal capacity 04. Which of the following prevents collapsing of trachea? a) Muscles b) Diaphragm c) Ribs d) Cartilaginous rings 05. The process in which chloride ions pass into RBC and bicarbonate ions pass out, is called a) Chloride shift b) Buffer system c) Enzyme shift d) Bicarbonate shift 06. At the time of inspiration, the diaphragm a) Contract b) Expand c) Relax d) Show no change 07. The vital capacity of lungs in a healthy man is about a) 500 ml b) 1000 ml c) 4500 ml d) 3000 ml 08. A normal man respires in a minute a) times b) times c) times d) times 09. The covering of lungs is a) Pericardium b) Peritoneum c) Pleural membrane d) Glisson s capsule
2 10. The ventilation movements of the lungs in mammals are governed by a) Muscular walls of the lungs b) Costal muscles c) Diaphragm d) Costal muscles and diaphragm 11. The sum of vital capacity and residual volume is known as a) Total Lung capacity b) Respiratory minute volume c) Respiratory capacity d) Functional capacity 12. The function of tracheal hairs is to a) Pass the mucus out b) Pass the mucus in c) Pass the air out d) Pass the air in 13. Gaseous exchange takes place in a) Alveoli b) Bronchi c)bronchioles d) Bronchus 14. After normal inspiration it is possible to send more air into lungs it is called a) Vital capacity b) Inspiratory reserve volume c) Tidal volume d) Residual volume 15. Mammalian lungs have enormous number of minute alveoli (air sacs).it is to allow a) More space for increasing the volume of inspired air b) More surface area for diffusion of gases c) More spongy texture for keeping lungs in proper shape d) More nerve supply to keep organs active when working 16. In man, expired air contains oxygen about a) 4% b) 16% c) 10% d) 20%
3 17. Blood contains maximum CO 2 in which of the following forms? a) NaHCO 3 b) Carbonic acid c) Hb-CO 2 d) Hb-CO 2 and CO 18. Glottis is an opening of a) Bronchus b) Mouth c) Pharynx d) Trachea 19. Which of the following prevents the entry of the food into respiratory tract? a) Epiglottis b) Glottis c) Larynx d) Pharynx 20. Percentage of O 2 present in inhaled air in man a) 21% b) 14% c) 16% d) 20% 21. Asthma is a respiratory disease caused due to a) Infection of trachea b) Infection of lungs c) Bleeding in pleural cavity d) Spasm in bronchial muscles 22. Which cartilage of Larynx is commonly called Adam s apple a) Arytenoid b) cricoid c) thyroid d) epiglottis 23 Emphysema is characterized by a) Inflammation of the mucus membrane of trachea b) Spasm of bronchial muscle c) Dissolution of alveolar well d) Increased vascularization of epithelium 24. Acute inflammation of mucus membrane of trachea and bronchi is a symptom of a) Hay fever b) Bronchitis c) Asthma d) emphysema
4 25. Match the disorders given column 1 with symptoms under column 2. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of alphabets with numbers. Column 1 Column 2 a. Asthma 1. Inflammation of nasal tract b. Bronchitis 2. Spasm of tracheal muscle c. Rhinitis 3. Fully blown out alveoli d. Emphysema 4. Inflammation of bronchial tree 5. Cough with blood stained sputum a) A-1, B-2, C-5, D-1 b) A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3 c) A-5, B-3, C-2, D-1 d) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
5 NERVOUS SYSTEM 01. In mammals, the corpus callosum connects a) Bone to muscle b) Bone to a bone c) The two cerebral hemispheres d) The two optic lobes 02. Some cells in our body can be over a feet long. They are a) Muscle cells b) Bone cells c) Nerve cells d) Gland cells 03. Power of regeneration is lowest in a) Nerve cell b) Liver cell c) Bone cell d) Muscle cell 04. Learning is related to which part of human brain? a) Hypothalamus b) Medulla c) Cerebrum d) Cerebellum 05. Which part of the brain is directly concerned with the control of heart? a) Cerebellum b) Cerebrum c) Medulla d) Diencephalon 06. The largest number of cell bodies of neurons in our body is found in a) Brain b) Retina c) Spinal cord d) Tongue 07. The outermost layer of brain is called a) Piamater b) Duramater c) Pericardium d) Grey matter 08. The self governing nervous system is known as a) Central nervous system b) Peripheral nervous system c) Autonomic nervous system d) Sympathetic nervous system 09. Which one of the following contains practically no neurons? a) Grey matter b) Synapse c) White matter d) Nerve 10. Which one of the following is responsible for the control of reflex actions?
6 a) Motor nerves b) Sensory nerves c) Central nervous system d) Sympathetic nervous system 11. The number of cranial nerves in a mammal including man is a) 10 pairs b) 12 pairs c) 24 pairs d) 36 pairs 12. A motor nerve carries impulses from a)central nervous system to the effectors b)effectors to central nervous system c) Cranial nerves to the effectors d) Effectors to the cranial nerves 13. The lungs, heart, intestine etc. are supplied by cranial nerve a) Trigeminal b) Vagus c) Abducens d) Oculomotor 14. How many spinal nerves are in man? a) 20 pairs b) 30 pairs c) 31 pairs d) 37 pairs 15. The conduction of nerve impulse is a a) Biochemical phenomenon b) Electrochemical phenomenon c) Physical phenomenon d) Bio-physiological phenomenon 16. In reflex action, the reflex arc is formed by a) Brain - spinal cord - muscles b) Receptor spinal cord - muscles c) Muscles receptor brain d) Muscles spinal cord receptor 17. Loss of memory can be done by the destruction of a) Cerebrum b) Cerebellum c) Medulla d) Diencephalon 18. Which one is not a reflex action? a) Closing of eye lids against flicking b) Release of saliva seeing sweets c) Perspiration due to heat d) Obeying the order
7 19. The chemical causing the transmission of nerve impulse across synapsis is a) Acetylcholine b) Choline esterase c) Choline d) Acetic acid 20. In which part of the following, the vomiting centre is situated? a) Cerebrum b) Cerebellum c) Medulla oblongata d) Hypothalamus 21. Medulla oblongata controls a) Blood circulation and heart beat b) Respiration c) Movement of digestive organs and digestive gland secretion d) All of these 22. The correct sequence of meninges from inner to outer side is a) Arachnoid duramater piamater b) Arachnoid piamater duramater c) Piamater duramater arachnoid d) Piamater arachnoid duramater 23. Diencephalon is not a control centre of a) Heart beat b) Anger c) Hate d) Love 24. Vagus nerve is a) Spinal nerve b) Sympathetic nerve c) Xth cranial nerve d) Parasympathetic nerve 25. Fissure of Rolando of human brain occurs between a) Two cerebral hemispheres b) The cerebellum and medulla c) The temporal and frontoparietal lobes of the cerebrum d) The frontal and parietal lobes of cerebrum 26. What is the other name for Fits or seizures? a) Paralysis b) Diplegia c) Parkinson d) Epilepsy 27. The degenerative genetic disorder characterized by chorea, shrinkage of Brain and Enlargement of ventricles.
8 a) Epilepsy b)alzheimer s disease c) Huntington s chorea d) Parkinson s disease 28. Which one of the nervous disorder is characterized by symptoms like bradykinesia, akinesia, and tremors? 29. Decrease in secretion of dopamine in the basal ganglia causes a) Epilepsy b) Alzheimer s disease c) Huntington s chorea d) Parkinson s disease 30. In epilepsy, the person a) Has fits of convulsions b) Loses consciousness c) Becomes unaware of surroundings & falls down d) All the above
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to
 1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day)
 Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Chapter 11. The respiratory system. Glossary. Anthony Wheeldon
 Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY
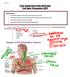 Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system
 3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system 1 3.02 Essential Questions What are the functions of the nervous system? What are some disorders of the nervous system? How are nervous
3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system 1 3.02 Essential Questions What are the functions of the nervous system? What are some disorders of the nervous system? How are nervous
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
RESPIRATION- Life function. Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Homeostasis Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: RESULTS/SCORES FROM LEARNING ASSESSMENTS
 MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Instructor s Review for Final Exams. The Nervous System
 Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Q: A.1. Answer (b) neurolemma Q: A.2. Answer (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3. Answer (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Q: A.1 (b) neurolemma Q: A.2 (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3 (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.1 (a) Cerebrospinal fluid (b) Synapse (c) Cerebrum (d) Hypothalamus Q: B.2 (a)
NERVOUS SYSTEM Q: A.1 (b) neurolemma Q: A.2 (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3 (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.1 (a) Cerebrospinal fluid (b) Synapse (c) Cerebrum (d) Hypothalamus Q: B.2 (a)
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
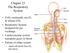 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. This figure depicts a typical neuron. What structures
BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. This figure depicts a typical neuron. What structures
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. 1) List the anatomical subdivisions.
 S T U D Y G U I D E 8 1. Divisions of the Nervous System 1) List the anatomical subdivisions. Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. Somatic N.S. Autonomic N.S. 2. Nerve Tissue
S T U D Y G U I D E 8 1. Divisions of the Nervous System 1) List the anatomical subdivisions. Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. Somatic N.S. Autonomic N.S. 2. Nerve Tissue
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Respiratory System
 C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of
 Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
The respiratory system
 Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
