Anesth Pain Med 2018;13: pissn ㆍ eissn
|
|
|
- Erika Kathryn Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anesth Pain Med 2018;13: pissn ㆍ eissn Case Report Received March 15, 2018 Revised April 19, 2018 Accepted May 18, 2018 Successful application of high-flow nasal cannula in a patient with postoperative respiratory disturbance after bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy surgery - A case report - Ki Tae Jung 1,2, In Gook Ji 2, and Sang Hun Kim 1,2 Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, 1 Chosun University School of Medicine, 2 Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea Corresponding author Sang Hun Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, 365 Pilmun-dearo, Donggu, Gwangju 61453, Korea Tel: Fax: ksh3223@chosun.ac.kr ORCID Bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy (BSSRO) is generally indicated for mandibular setback, to improve occlusion, masticatory function, and aesthetics by altering the mandibular position. However, BSSRO narrows the pharyngeal airway and increases airway resistance, resulting in postoperative respiratory disturbances during emergence from anesthesia. Oxygen delivery system via high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) has been known to improve airway patency and oxygenation via low-level positive pressure as well as reduce the respiratory load. We report a case of postoperative respiratory disturbance, following a large mandibular setback, despite nasotracheal extubation in the fully awake patient. Respiratory disturbance was successfully controlled after oxygen delivery via HFNC until self-respiration was completely restored. Therefore, the use of HFNC may facilitate the control of postoperative respiratory disturbances induced by anatomical changes in upper airway after BSSRO surgery. Key Words: Adult respiratory distress syndrome, Dyspnea, High-flow nasal cannula, Orthognathic surgical procedures, Oxygen inhalation therapy. Bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy (BSSRO), a type of mandibular setback surgery, is generally indicated for mandibular setback, resulting in improved occlusion, masticatory function, and aesthetic outcomes by changing the mandibular position [1]. However, BSSRO surgery narrows the pharyngeal airway and increases airway resistance, which can induce respiratory disturbances such as obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) [1,2]. Therefore, anesthesiologists, as well as surgeons, should consider the possibility of postoperative respiratory disturbance in patients diagnosed with a large mandibular setback [1]. The oxygen delivery system via high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) has been introduced in many areas of anesthesia. The system improves airway patency and oxygenation through low-level positive pressure as well as reduces the respiratory load, in hypercapnic and hypoxemic respiratory failures, and obstructive sleep apnea [3,4]. Here, we report a case of successful use of HFNC in a patient diagnosed with respiratory disturbance during emergence from BSSRO surgery. CASE REPORT A 27-year-old male (height: 175 cm, weight: 92 kg) was scheduled for BSSRO surgery to rectify mandible prognathism (Fig. 1A). The patient was a non-smoke with any history of medical illness except obesity and snoring. However, This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Copyright c the Korean Society of Anesthesiologists,
2 Anesth Pain Med Vol. 13 No. 3 he was not evaluated for OSAS before surgery. Preoperative laboratory tests showed no abnormal results. Physical examination was unremarkable. Preoperative anesthetic airway evaluation yielded the following results: Mallampati class 3; thyromental distance, 6 cm; mouth opening, 4 cm; and posterior airway space (PAS) diameter in the mandibular plane, 15.4 mm. PAS PAS: 15.4 mm A PAS: 9.8 mm Fig. 1. Dental X-ray shows anatomical changes in the upper airway before (A) and after (B) bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy surgery. Cephalometric analysis of the posterior airway space (PAS) in the mandibular plane shows a decreased diameter (9.8 mm) compared with the preoperative diameter (15.4 mm). He was pre-medicated with intramuscular midazolam 0.04 mg/kg 30 minutes before the induction of anesthesia and was transferred to the operating room (OR). He was monitored via an electrocardiogram, non-invasive blood pressure measurement, pulse oximetry, esophageal temperature, neuromuscular monitor, and bispectral index (BIS). Anesthesia was induced and maintained by total intravenous anesthesia using propofol and sufentanil to maintain the BIS score within 40 to 60. Manual mask ventilation with facemask was done before neuromuscular blockade, without any limitations. After adequate neuromuscular blockade by rocuronium bromide (0.6 mg/kg), nasotracheal intubation (internal diameter: 7.5 mm) was performed in the sniffing position. Mechanical ventilation (volume control mode) was used with 50% oxygen-air mixture, with a tidal volume (TV) of 8 10 ml/ kg of ideal body weight and adjusted to maintain the peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) below 30 cmh 2 O during anesthesia. After the nasotracheal intubation, the graph of end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO 2 ) showed an increased slope of phase III and a slight obstructive pattern was suspected. The TV was PAS B maintained between ml with respiratory rates 12 breaths per minute, and a PIP of 23 mmhg. No changes were detected after nasotracheal tube suction or administration of nebulized salbutamol. However, no challenges were detected with oxygenation and the levels of ETCO 2 were maintained below 45 mmhg throughout the surgery. Thus, we believed that the changes associated with ETCO 2 graph were physiological changes induced by obesity. BSSRO for mandibular setback was performed followed by posterior repositioning of the mandible (right, 22.5 mm; left, 24.0 mm; transverse shift to right side 3.0 mm). The surgery ended after 150 minutes, and the patient s vital signs were maintained within normal limits. Administered fluid and estimated blood losses were 1,500 ml and 700 ml, respectively. The patient s mental state was clear after discontinuing propofol and sufentanil. Naloxone 0.15 mg was administered to stimulate respiration. The patient recovered from neuromuscular blockade (train-of-four > 99%) following treatment with 200 mg of sugammadex, and spontaneous respiration was maintained (TV > 500 ml). He was fully awake and responded well, and extubation was done. However, the patient could not breathe well immediately after extubation. He exhibited difficulty during inhalation and stridor was heard. Nasal cannulation followed by manual mask ventilation with two-handed jaw-thrust maneuver was performed to maintain the airway without damaging the operated jaw. However, TV during mask ventilation was only ml and ETCO 2 was increased more than 55 mmhg. The patient complained of choking and became irritable. Despite manual ventilation, sustained dyspnea was developed, and pulse oxygen saturation (SpO 2 ) decreased to 90%. Manual mask ventilation with 10 cmh 2 O of positive airway pressure (PEEP) increased TV to more than 300 ml, but the effects were temporary, and dyspnea continued during spontaneous ventilation. Salbutamol nebulization had no effect. We suspected that anatomical changes of the upper airway triggered the respiratory disturbance. Re-intubation was performed with Glidescope videolaryngoscope (Saturn Biomedical Systems Inc., Canada) under mild sedation with propofol because of the expected airway challenges. Videolaryngoscopy revealed small oral cavity, with mild laryngeal edema. After reintubation, ETCO 2 decreased to 45 mmhg and SpO 2 increased to 95%. We discussed with the surgeon and confirmed the narrow 342
3 HFNC for the postoperative dyspnea airway after surgery. Reoperation was needed for correct the posterior repositioning of the mandible. The patient complained deeply about the inconvenience of intubation and failed to cooperate well. Therefore, we delivered a humidified air-oxygen mixture via HFNC to provide PEEP and increase end-expiratory lung volume [4]. After advising the patient appropriately, we used HFNC (Airvo 2, Fisher & Paykel Healthcare, New Zealand). After careful extubation, the nasal cannula was used, and supplemental oxygen was initiated with an airflow rate of 10 L/min. The flow rate was increased according to the patient s breathing difficulty. An airflow rate of 15 to 20 L/min was comfortable and oxygen saturation was maintained above 99%. Respiratory disturbance was successfully controlled with HFNC, and the patient was transferred to the recovery room (RR). Arterial blood gas analysis at the RR yielded the following findings: ph, 7.364; PaCO 2, 47.5 mmhg; and PaO mmhg. We suggested careful reoperation because HFNC was used to eliminate respiratory disturbance and maintain oxygenation of the patient very effectively. He was transferred to the OR for emergent reoperation on the next day. He was in good condition under HFNC. Anesthesia was induced and maintained using the same maneuver. The correction of posterior repositioning of the mandible (right: 12.5 mm, left: 14.0 mm) reduced the anatomical changes of the upper airway (Fig. 1B). Surgery ended after 60 minutes, and emergence was smooth. Adequate recovery from neuromuscular blockade was followed by careful extubation without eliciting any complaints of respiratory disturbance. The TV was maintained more than 500 ml during manual mask ventilation. No dyspnea was detected, and the patient was sustained adequately with oxygen supplied via nasal cannula. No respiratory disturbance was detected and the patient was discharged after 6 days. DISCUSSION Complications post-bssro surgery including hemorrhage, airway obstruction, mechanical problems, nerve injury, infection, and foreign body presence are well known. Lifethreatening complications such as airway obstruction may require reoperation even though most of the respiratory distress was reduced after the early release of mandibular fixation. Prevention of potential postoperative complications requires evaluation of possible risks of complication, and awareness of significant reduction in the pharyngeal airway space after mandibular setback surgery resulting in respiratory complications [5]. Anteroposterior and cross-sectional area dimensions of the pharyngeal airway space are significantly decreased at the level of the soft palate and tongue base in computerized tomography images after mandibular setback surgery [6]. Yajima et al. [1] reported that mandibular setback surgery is associated with a significant decrease in the minimum cross-sectional area as well as pressure in the pharyngeal airway space. The pressure in pharyngeal airway space decreased greatly when its minimum sectional area was less than 1 cm 2. This decrease leads to further narrowing of pharyngeal airway space, and results ultimately in iatrogenic obstructive sleep apnea [7]. Postoperative OSAS occurs in patients experiencing mandibular setback greater than 5 mm [2,8]. Therefore, only a small amount of mandibular setback is recommended for BSSRO in patients with high preoperative Mallampati scores [9]. If patients express risk factors such as obesity, sleep-disordered breathing, and undergo a large mandibular setback of more than 5 mm, a combination surgery for mandibular setback and maxillary advancement is recommended to prevent the development of OSAS [8]. In the current case, the patient was diagnosed with obesity, preoperative snoring, and a large mandibular setback. Especially, the PAS diameter at the mandibular plane was 15.4 mm (normal range: ± 2.78, Fig. 1A) based on the dental X-ray, which showed significant clinical correlation with anatomic parameters of patients with OSAS [10]. However, the PAS diameter significantly decreased to 9.8 mm after the second operation (Fig. 1B), suggesting that PAS diameter after the first operation was similar to the average PAS diameter of the patient with OSAS (7.16 ± 4.01). Although we failed to obtain a dental X-ray after the first surgery, it was expected that the PAS diameter after the first surgery was significantly smaller, especially in the supine position. Consequently, anatomical changes of the upper airway were suspected as the cause of respiratory disturbance after the extubation. To control postoperative respiratory disturbance, manual mask ventilation with PEEP may be used during emergence from anesthesia. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), or oxygen delivery system via HFNC is recommended to relieve upper airway obstruction by stabilizing the hypotonic upper airway dilators, by monitoring the respiratory rate and capnography [11]. Especially, the oxygen delivery 343
4 Anesth Pain Med Vol. 13 No. 3 system via HFNC improves the overall performance of the anesthesiologist in a difficult scenario because it improves airway patency via low-level positive pressure, improves oxygenation, and reduces the respiratory load [3]. In addition, HFNC facilitates emergency airway management of the patient with difficult airway, for instance, in patients with a history of or indications for maxillofiacial surgery as it delivers continuous high-flow humidified oxygen during intubation [12]. In this case, the patient suffered from sustained respiratory distress after nasotracheal extubation in fully awake state after obtaining Train-of-four ratio of above 0.9. First, we applied manual mask ventilation with PEEP 10 cmh 2 O, without successful resolution. We hypothesized that the upper airway anatomical changes in patients exposed to BSSRO during emergence from anesthesia may be similar to those of patients with OSAS undergoing surgery under sedation. Wong et al. [13] suggested that high-flow nasal oxygen therapy led to satisfactory oxygenation, maintained the partial carbon dioxide pressure within a reasonable range in a patient with moderate OSAS treated with surgery under deep sedation. Moreover, the present case was morbidly obese, with a reduced functional residual capacity and increased risk of atelectasis, and ventilation-perfusion mismatch leading to hypoxia [14]. Thus, HFNC application facilitates effective correction or prevention of hypoxemia. Therefore, HFNC was used successfully to control the respiratory disturbances until full recovery of self-respiration. The use of HFNC in patients with postoperative respiratory disturbance after BSSRO surgery results in the following physiological advantages [4,13,15]: - It reduces airway collapse by PEEP and leads to improved oxygenation and ventilation. Application of PEEP effectively reduces airway collapse and atelectasis, and increases end-expiratory lung volume (EELV). Moreover, HFNC is more effective in increasing airway pressure facemask. Thus, the current use of HFNC improves airway patency by reducing upper airway resistance and preventing airway collapse due to anatomical changes induced by BSSRO surgery. - HFNC increases EELV due to the CPAP effect resulting in a decreased respiratory workload. It is also effective for carbon dioxide washout of anatomical dead space. Thus, minute alveolar ventilation remains unchanged despite a decrease in respiratory rate during HFNC, which reduces the respiratory workload. - HFNC provides heat and humidification to reduce mucosal drying and triggers bronchoconstriction. Dry cold gas induces mucosal drying, mucociliary impairment, and atelectasis. It also triggers bronchoconstriction and reduces respiratory compliance. Thus, the application of HFNC may facilitate respiratory compliance, at least partially. - HFNC may provide greater patient comfort than nasotracheal intubation or CPAP, leading to better compliance and outcomes. In conclusion, anesthesiologists should expect respiratory disturbances after mandibular setback surgery exceeding 5 mm. Preoperative determination of the degree of setback using radiological tools during surgical planning is important to prevent postoperative respiratory disturbance during emergence from anesthesia. Furthermore, the application of HFNC may aid in the control of postoperative respiratory disturbance triggered by anatomical changes of upper airway after BSSRO surgery. REFERENCES 1. Yajima Y, Oshima M, Iwai T, Kitajima H, Omura S, Tohnai I. Computational fluid dynamics study of the pharyngeal airway space before and after mandibular setback surgery in patients with mandibular prognathism. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2017; 46: Riley RW, Powell NB, Guilleminault C, Ware W. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome following surgery for mandibular prognathism. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1987; 45: Keshishyan S, Harris K, Mohan A, Patil M. Bronchoscopic management of central airway obstruction secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol 2018; 25: e Nishimura M. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in adults: physiological benefits, indication, clinical benefits, and adverse effects. Respir care 2016; 61: Mattos CT, Vilani GN, Sant Anna EF, Ruellas AC, Maia LC. Effects of orthognathic surgery on oropharyngeal airway: a metaanalysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011; 40: Degerliyurt K, Ueki K, Hashiba Y, Marukawa K, Simsek B, Okabe K, et al. The effect of mandibular setback or two-jaws surgery on pharyngeal airway among different genders. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009; 38: Degerliyurt K, Ueki K, Hashiba Y, Marukawa K, Nakagawa K, 344
5 HFNC for the postoperative dyspnea Yamamoto E. A comparative CT evaluation of pharyngeal airway changes in class III patients receiving bimaxillary surgery or mandibular setback surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2008; 105: Demetriades N, Chang DJ, Laskarides C, Papageorge M. Effects of mandibular retropositioning, with or without maxillary advancement, on the oro-naso-pharyngeal airway and development of sleep-related breathing disorders. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2010; 68: Choi SK, Yoon JE, Cho JW, Kim JW, Kim SJ, Kim MR. Changes of the airway space and the position of hyoid bone after mandibular set back surgery using bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy technique. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 2014; 36: Barrera JE, Pau CY, Forest VI, Holbrook AB, Popelka GR. Anatomic measures of upper airway structures in obstructive sleep apnea. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2017; 3: Subramani Y, Singh M, Wong J, Kushida CA, Malhotra A, Chung F. Understanding phenotypes of obstructive sleep apnea: applications in anesthesia, surgery, and perioperative medicine. Anesth Analg 2017; 124: Patel A, Nouraei SA. Transnasal humidified rapid-insufflation ventilatory exchange (THRIVE): a physiological method of increasing apnoea time in patients with difficult airways. Anaesthesia 2015; 70: Wong JW, Kong AH, Lam SY, Woo PY. High-flow nasal oxygen in patient with obstructive sleep apnea undergoing awake craniotomy: a case report. A A Case Rep 2017; 9: Domi R, Laho H. Anesthetic challenges in the obese patient. J Anesth 2012; 26: Onodera Y, Akimoto R, Suzuki H, Masaki N, Kawamae K. A highflow nasal cannula system set at relatively low flow effectively washes out CO 2 from the anatomical dead space of a respiratorysystem model. Korean J Anesthesiol 2017; 70:
Combitube insertion in the situation of acute airway obstruction after extubation in patients underwent two-jaw surgery
 Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2015;15(4):235-239 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2015.15.4.235 Combitube insertion in the situation of acute airway obstruction after
Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2015;15(4):235-239 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2015.15.4.235 Combitube insertion in the situation of acute airway obstruction after
Three-dimensional analysis of pharyngeal airway change of skeletal class III patients in cone beam computed tomography after bimaxillary surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.1.9 Three-dimensional analysis of pharyngeal airway change of skeletal class III patients in cone beam computed tomography after bimaxillary surgery
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.1.9 Three-dimensional analysis of pharyngeal airway change of skeletal class III patients in cone beam computed tomography after bimaxillary surgery
Capnography. Capnography. Oxygenation. Pulmonary Physiology 4/15/2018. non invasive monitor for ventilation. Edward C. Adlesic, DMD.
 Capnography Edward C. Adlesic, DMD University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine 2018 North Carolina Program Capnography non invasive monitor for ventilation measures end tidal CO2 early detection
Capnography Edward C. Adlesic, DMD University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine 2018 North Carolina Program Capnography non invasive monitor for ventilation measures end tidal CO2 early detection
yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management
 yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management Overview: Managing a patient s airway may be necessitated due to upper or lower airway obstruction, inadequate
yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management Overview: Managing a patient s airway may be necessitated due to upper or lower airway obstruction, inadequate
Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation. Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016
 Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016 Introduction Repetitive collapse of the upper airway > sleep fragmentation, > hypoxemia, hypercapnia, > marked variations in intrathoracic
Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016 Introduction Repetitive collapse of the upper airway > sleep fragmentation, > hypoxemia, hypercapnia, > marked variations in intrathoracic
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation.
 Chapter 1: Principles of Mechanical Ventilation TRUE/FALSE 1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation. F
Chapter 1: Principles of Mechanical Ventilation TRUE/FALSE 1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation. F
Patient-Ventilation Asynchrony Causing Negative Pressure Pulmonary Edema in an Intubated Obese Patient
 Patient-Ventilation Asynchrony Causing Negative Pressure Pulmonary Edema in an Intubated Obese Patient Sahar M. Siddik-Sayyid *, Waseem AlFahel ** and Mohamad F. El-Khatib * Negative pressure pulmonary
Patient-Ventilation Asynchrony Causing Negative Pressure Pulmonary Edema in an Intubated Obese Patient Sahar M. Siddik-Sayyid *, Waseem AlFahel ** and Mohamad F. El-Khatib * Negative pressure pulmonary
Case Presentation Topic: Difficult to Ventilate Difficult to Intubate
 Case Presentation Topic: Difficult to Ventilate Difficult to Intubate Dr. K. Shruthi Jeevan 1 st Year Post Graduate Department of Anaesthesiology CASE SCENARIO : 1 A 65 years old female patient, resident
Case Presentation Topic: Difficult to Ventilate Difficult to Intubate Dr. K. Shruthi Jeevan 1 st Year Post Graduate Department of Anaesthesiology CASE SCENARIO : 1 A 65 years old female patient, resident
Respiratory insufficiency in bariatric patients
 Respiratory insufficiency in bariatric patients Special considerations or just more of the same? Weaning and rehabilation conference 6th November 2015 Definition of obesity Underweight BMI< 18 Normal weight
Respiratory insufficiency in bariatric patients Special considerations or just more of the same? Weaning and rehabilation conference 6th November 2015 Definition of obesity Underweight BMI< 18 Normal weight
Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CCRN Clinical Nurse Specialist
 Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CCRN Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Define capnography vs. end tidal CO2 (EtCO 2 ) Identify what normal vs. abnormal EtCO2 values mean and what to do Understand when to
Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CCRN Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Define capnography vs. end tidal CO2 (EtCO 2 ) Identify what normal vs. abnormal EtCO2 values mean and what to do Understand when to
PHYSICIAN PROCEDURAL SEDATION AND ANALGESIA QUIZ
 PHYSICIAN PROCEDURAL SEDATION AND ANALGESIA QUIZ 1. Which of the following statements are TRUE? (Select ALL that apply) o Sedative/analgesic drugs should be given in small, incremental doses that are titrated
PHYSICIAN PROCEDURAL SEDATION AND ANALGESIA QUIZ 1. Which of the following statements are TRUE? (Select ALL that apply) o Sedative/analgesic drugs should be given in small, incremental doses that are titrated
PHYSICIAN COMPETENCY FOR ADULT DEEP SEDATION (Ages 14 and older)
 Name Score PHYSICIAN COMPETENCY FOR ADULT DEEP SEDATION (Ages 14 and older) 1. Pre-procedure evaluation for moderate sedation should involve all of the following EXCEPT: a) Airway Exam b) Anesthetic history
Name Score PHYSICIAN COMPETENCY FOR ADULT DEEP SEDATION (Ages 14 and older) 1. Pre-procedure evaluation for moderate sedation should involve all of the following EXCEPT: a) Airway Exam b) Anesthetic history
Fiberoptic bronchoscope and C-MAC video laryngoscope assisted nasal-oral tube exchange: two case reports
 Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(3):219-223 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.3.219 Fiberoptic bronchoscope and C-MAC video laryngoscope assisted nasal-oral
Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(3):219-223 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.3.219 Fiberoptic bronchoscope and C-MAC video laryngoscope assisted nasal-oral
Change of the airway space in mandibular prognathism after bimaxillary surgery involving maxillary posterior impaction
 Lee et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:23 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0071-3 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Change of the airway space in
Lee et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:23 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0071-3 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Change of the airway space in
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Postoperative Respiratory failure( PRF) Dr.Ahmad farooq
 Postoperative Respiratory failure( PRF) Dr.Ahmad farooq Is it really or/only a postoperative issue Multi hit theory first hits second hits Definition Pulmonary gas exchange impairment that presents after
Postoperative Respiratory failure( PRF) Dr.Ahmad farooq Is it really or/only a postoperative issue Multi hit theory first hits second hits Definition Pulmonary gas exchange impairment that presents after
Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. By: Lillian Han
 Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: Lillian Han Background: Respiratory anesthetic emergencies are the most common complications during the administration of anesthesia
Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: Lillian Han Background: Respiratory anesthetic emergencies are the most common complications during the administration of anesthesia
Capnography Connections Guide
 Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution
 Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
Learning Objectives. 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence
 Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Supplementary Online Content 2
 Supplementary Online Content 2 van Meenen DMP, van der Hoeven SM, Binnekade JM, et al. Effect of on demand vs routine nebulization of acetylcysteine with salbutamol on ventilator-free days in intensive
Supplementary Online Content 2 van Meenen DMP, van der Hoeven SM, Binnekade JM, et al. Effect of on demand vs routine nebulization of acetylcysteine with salbutamol on ventilator-free days in intensive
Causes and Consequences of Respiratory Centre Depression and Hypoventilation
 Causes and Consequences of Respiratory Centre Depression and Hypoventilation Lou Irving Director Respiratory and Sleep Medicine, RMH louis.irving@mh.org.au Capacity of the Respiratory System At rest During
Causes and Consequences of Respiratory Centre Depression and Hypoventilation Lou Irving Director Respiratory and Sleep Medicine, RMH louis.irving@mh.org.au Capacity of the Respiratory System At rest During
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
POLICY All patients will be assessed for risk factors associated with OSA prior to any surgical procedures.
 Revised Date: Page: 1 of 7 SCOPE All Pre-Admission Testing (PAT) and Same Day Surgery (SDS) nurses at HRMC. PURPOSE The purpose of this policy is to provide guidelines for identifying surgical patients
Revised Date: Page: 1 of 7 SCOPE All Pre-Admission Testing (PAT) and Same Day Surgery (SDS) nurses at HRMC. PURPOSE The purpose of this policy is to provide guidelines for identifying surgical patients
(To be filled by the treating physician)
 CERTIFICATE OF MEDICAL NECESSITY TO BE ISSUED TO CGHS BENEFICIAREIS BEING PRESCRIBED BILEVEL CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BI-LEVEL CPAP) / BI-LEVEL VENTILATORY SUPPORT SYSTEM Certification Type
CERTIFICATE OF MEDICAL NECESSITY TO BE ISSUED TO CGHS BENEFICIAREIS BEING PRESCRIBED BILEVEL CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BI-LEVEL CPAP) / BI-LEVEL VENTILATORY SUPPORT SYSTEM Certification Type
Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients
 Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients Objectives Describe nocturnal ventilation characteristics that may indicate underlying conditions and benefits of bilevel therapy for specific
Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients Objectives Describe nocturnal ventilation characteristics that may indicate underlying conditions and benefits of bilevel therapy for specific
BiPAPS/TVAPSCPAPASV???? Lori Davis, B.Sc., R.C.P.T.(P), RPSGT
 BiPAPS/TVAPSCPAPASV???? Lori Davis, B.Sc., R.C.P.T.(P), RPSGT Modes Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): One set pressure which is the same on inspiration and expiration Auto-PAP (APAP) - Provides
BiPAPS/TVAPSCPAPASV???? Lori Davis, B.Sc., R.C.P.T.(P), RPSGT Modes Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): One set pressure which is the same on inspiration and expiration Auto-PAP (APAP) - Provides
Sleep Diordered Breathing (Part 1)
 Sleep Diordered Breathing (Part 1) History (for more topics & presentations, visit ) Obstructive sleep apnea - first described by Charles Dickens in 1836 in Papers of the Pickwick Club, Dickens depicted
Sleep Diordered Breathing (Part 1) History (for more topics & presentations, visit ) Obstructive sleep apnea - first described by Charles Dickens in 1836 in Papers of the Pickwick Club, Dickens depicted
Management of OSA. saurabh maji
 Management of OSA saurabh maji INTRODUCTION Obstructive sleep apnea is a major public health problem Prevalence of OSAS in INDIA is 2.4% to 4.96% in men and 1% to 2 % in women In the rest of the world
Management of OSA saurabh maji INTRODUCTION Obstructive sleep apnea is a major public health problem Prevalence of OSAS in INDIA is 2.4% to 4.96% in men and 1% to 2 % in women In the rest of the world
SESSION 3 OXYGEN THERAPY
 SESSION 3 OXYGEN THERAPY Harith Eranga Yapa Department of Nursing Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka 1 Outline Methods of delivery Complications of oxygen therapy Artificial airways
SESSION 3 OXYGEN THERAPY Harith Eranga Yapa Department of Nursing Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka 1 Outline Methods of delivery Complications of oxygen therapy Artificial airways
I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP
 I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP II. Policy: PSV with BiPAP device/nasal CPAP will be initiated upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel trained
I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP II. Policy: PSV with BiPAP device/nasal CPAP will be initiated upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel trained
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Identification and Treatment of the Patient with Sleep Related Hypoventilation
 Identification and Treatment of the Patient with Sleep Related Hypoventilation Hillary Loomis-King, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care of NW MI Munson Sleep Disorders Center X Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Identification and Treatment of the Patient with Sleep Related Hypoventilation Hillary Loomis-King, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care of NW MI Munson Sleep Disorders Center X Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point Using the Cricoid Cartilage as Landmark Through X-ray Review
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Respiratory Depression and Considerations for Monitoring Following Ophthalmologic Surgery
 Respiratory Depression and Considerations for Monitoring Following Ophthalmologic Surgery Athir Morad, M.D. Division of Neurocritical care Departments of Anesthesiology/ Critical Care Medicine and Neurology
Respiratory Depression and Considerations for Monitoring Following Ophthalmologic Surgery Athir Morad, M.D. Division of Neurocritical care Departments of Anesthesiology/ Critical Care Medicine and Neurology
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Tracheal Intubation in ICU: Life saving or life threatening?
 Tracheal Intubation in ICU: Life saving or life threatening? Prof. Sheila Nainan Myatra Department of Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain Tata Memorial Hospital Mumbai, India sheila150@hotmail.com Three
Tracheal Intubation in ICU: Life saving or life threatening? Prof. Sheila Nainan Myatra Department of Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain Tata Memorial Hospital Mumbai, India sheila150@hotmail.com Three
It costs you nothing, but gains everything for your patient!
 It costs you nothing, but gains everything for your patient! Attend the entire presentation Complete and submit the evaluation This session is approved for: ANCC hours CECBEMS hours No partial credit will
It costs you nothing, but gains everything for your patient! Attend the entire presentation Complete and submit the evaluation This session is approved for: ANCC hours CECBEMS hours No partial credit will
A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation
 1 A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation The following 3 minute polysomnogram (PSG) tracing was recorded in a 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy
1 A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation The following 3 minute polysomnogram (PSG) tracing was recorded in a 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy
APRV Ventilation Mode
 APRV Ventilation Mode Airway Pressure Release Ventilation A Type of CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) with an intermittent release phase. Patient cycles between two levels of CPAP higher
APRV Ventilation Mode Airway Pressure Release Ventilation A Type of CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) with an intermittent release phase. Patient cycles between two levels of CPAP higher
INternational observational study To Understand the impact and BEst practices of airway management in critically ill patients CASE REPORT FORM
 INternational observational study To Understand the impact and BEst practices of airway management in critically ill patients Study acronym identifier: INTUBE CASE REPORT FORM Centre ID number: Patient
INternational observational study To Understand the impact and BEst practices of airway management in critically ill patients Study acronym identifier: INTUBE CASE REPORT FORM Centre ID number: Patient
PEDIATRIC OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA (OSA)
 PEDIATRIC OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA (OSA) DEFINITION OSA Inspiratory airflow is either partly (hypopnea) or completely (apnea) occluded during sleep. The combination of sleep-disordered breathing with daytime
PEDIATRIC OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA (OSA) DEFINITION OSA Inspiratory airflow is either partly (hypopnea) or completely (apnea) occluded during sleep. The combination of sleep-disordered breathing with daytime
Emergency Department/Trauma Adult Airway Management Protocol
 Emergency Department/Trauma Adult Airway Management Protocol Purpose: A standardized protocol for management of the airway in the setting of trauma in an academic center, with the goal of maximizing successful
Emergency Department/Trauma Adult Airway Management Protocol Purpose: A standardized protocol for management of the airway in the setting of trauma in an academic center, with the goal of maximizing successful
Association for Radiologic & Imaging Nursing
 Overview: Radiology and Imaging Nurses provide procedural sedation to a variety of patients. The administration of procedural sedation in the interventional radiology and diagnostic imaging suites presents
Overview: Radiology and Imaging Nurses provide procedural sedation to a variety of patients. The administration of procedural sedation in the interventional radiology and diagnostic imaging suites presents
Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study
 D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
STATE OF OKLAHOMA 2014 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PROTOCOLS
 3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
Foundation in Critical Care Nursing. Airway / Respiratory / Workbook
 Foundation in Critical Care Nursing Airway / Respiratory / Workbook Airway Anatomy: Please label the following: Tongue Larynx Epiglottis Pharynx Trachea Vertebrae Oesophagus Where is the ET (endotracheal)
Foundation in Critical Care Nursing Airway / Respiratory / Workbook Airway Anatomy: Please label the following: Tongue Larynx Epiglottis Pharynx Trachea Vertebrae Oesophagus Where is the ET (endotracheal)
PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING
 PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING ALL PHASES OF THE RESPIRATORY CYCLE Rachael L. Parke, RN, MHSc (Hons) Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit Auckland City Hospital Private
PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING ALL PHASES OF THE RESPIRATORY CYCLE Rachael L. Parke, RN, MHSc (Hons) Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit Auckland City Hospital Private
Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics
 Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics Dr E McMaster, Dr E Gent, Dr T Mahendrayogam, Dr A Surendran
Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics Dr E McMaster, Dr E Gent, Dr T Mahendrayogam, Dr A Surendran
Anaesthetic considerations for laparoscopic surgery in canines
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Anaesthetic considerations for laparoscopic surgery in canines Author : Chris Miller Categories : Canine, Companion animal,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Anaesthetic considerations for laparoscopic surgery in canines Author : Chris Miller Categories : Canine, Companion animal,
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
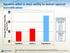 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Inselspital Universitätsklinik für Anästhesiologie und Schmerztherapie. 73. Berner Anästhesie-Symposium Mittwoch, 15. November 2017 Kinderanästhesie
 Inselspital Universitätsklinik für Anästhesiologie und Schmerztherapie 73. Berner Anästhesie-Symposium Mittwoch, 15. November 2017 Kinderanästhesie HFNC Von Spontanatmung bis zur apnoischen Oxygenierung
Inselspital Universitätsklinik für Anästhesiologie und Schmerztherapie 73. Berner Anästhesie-Symposium Mittwoch, 15. November 2017 Kinderanästhesie HFNC Von Spontanatmung bis zur apnoischen Oxygenierung
Comparison of the Berman Intubating Airway and the Williams Airway Intubator for fibreoptic orotracheal intubation in anaesthetised patients.
 Title Comparison of the Berman Intubating Airway and the Williams Airway Intubator for fibreoptic orotracheal intubation in anaesthetised patients Author(s) Greenland, KB; Ha, ID; Irwin, MG Citation Anaesthesia,
Title Comparison of the Berman Intubating Airway and the Williams Airway Intubator for fibreoptic orotracheal intubation in anaesthetised patients Author(s) Greenland, KB; Ha, ID; Irwin, MG Citation Anaesthesia,
Angkana Lurngnateetape,, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Angkana Lurngnateetape,, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital Perhaps the most important responsibility of the anesthesiologist is management of the patient s airway Miller
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Angkana Lurngnateetape,, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital Perhaps the most important responsibility of the anesthesiologist is management of the patient s airway Miller
Anesthetic Challenges in Morbid Obesity
 Anesthetic Challenges in Morbid Obesity The Challenge Postoperative pain management of the morbid obese patient The number of patients who present for elective surgery, with a BMI of greater than 30 kgm
Anesthetic Challenges in Morbid Obesity The Challenge Postoperative pain management of the morbid obese patient The number of patients who present for elective surgery, with a BMI of greater than 30 kgm
Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management. Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS
 Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS Objectives How it works COPD Management today The role of NHFC Evidence Research/Case Studies Types
Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS Objectives How it works COPD Management today The role of NHFC Evidence Research/Case Studies Types
Kugelman A, Riskin A, Said W, Shoris I, Mor F, Bader D.
 Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
Objectives. Apnea Definition and Pitfalls. Pathophysiology of Apnea. Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes 5/18/2015
 Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
High Flow Nasal Cannula in Children During Sleep. Brian McGinley M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Utah
 High Flow Nasal Cannula in Children During Sleep Brian McGinley M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Utah Disclosures Conflicts of Interest: None Will discuss a product that is commercially
High Flow Nasal Cannula in Children During Sleep Brian McGinley M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Utah Disclosures Conflicts of Interest: None Will discuss a product that is commercially
KENNEDY DISEASE PULMONARY CONSIDERATIONS: SCIENCE & MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
 KENNEDY DISEASE PULMONARY CONSIDERATIONS: SCIENCE & MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES When you can t breathe nothing else matters American Lung Association Noah Lechtzin, MD; MHS Associate Professor of Medicine Johns
KENNEDY DISEASE PULMONARY CONSIDERATIONS: SCIENCE & MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES When you can t breathe nothing else matters American Lung Association Noah Lechtzin, MD; MHS Associate Professor of Medicine Johns
1/27/2017 RECOGNITION AND MANAGEMENT OF OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA: STRATEGIES TO PREVENT POST-OPERATIVE RESPIRATORY FAILURE DEFINITION PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 RECOGNITION AND MANAGEMENT OF OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA: STRATEGIES TO PREVENT POST-OPERATIVE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Peggy Hollis MSN, RN, ACNS-BC March 9, 2017 DEFINITION Obstructive sleep apnea is a disorder
RECOGNITION AND MANAGEMENT OF OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA: STRATEGIES TO PREVENT POST-OPERATIVE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Peggy Hollis MSN, RN, ACNS-BC March 9, 2017 DEFINITION Obstructive sleep apnea is a disorder
BTS sleep Course. Module 10 Therapies I: Mechanical Intervention Devices (Prepared by Debby Nicoll and Debbie Smith)
 BTS sleep Course Module 10 Therapies I: Mechanical Intervention Devices (Prepared by Debby Nicoll and Debbie Smith) S1: Overview of OSA Definition History Prevalence Pathophysiology Causes Consequences
BTS sleep Course Module 10 Therapies I: Mechanical Intervention Devices (Prepared by Debby Nicoll and Debbie Smith) S1: Overview of OSA Definition History Prevalence Pathophysiology Causes Consequences
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither?
 Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION FOR RESPIRATORY CARE TMC DETAILED CONTENT OUTLINE COMPARISON
 A. Evaluate Data in the Patient Record I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Patient history e.g., admission data orders medications progress notes DNR status / advance directives social history
A. Evaluate Data in the Patient Record I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Patient history e.g., admission data orders medications progress notes DNR status / advance directives social history
Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo
 Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Alexandria Workshop on
 Alexandria Workshop on 1 Snoring & OSA Surgery Course Director: Yassin Bahgat MD Claudio Vicini MD Course Board: Filippo Montevecchi MD Pietro Canzi MD Snoring & Obstructive ti Sleep Apnea The basic information
Alexandria Workshop on 1 Snoring & OSA Surgery Course Director: Yassin Bahgat MD Claudio Vicini MD Course Board: Filippo Montevecchi MD Pietro Canzi MD Snoring & Obstructive ti Sleep Apnea The basic information
Genioglossus Advancement Accompanied by Mandibular Setback and Maxillary Advancement Surgery in Severely Obese Patient
 Shimane J. Med. Sci., Vol.33 pp.93-98, 2017 Genioglossus Advancement Accompanied by Mandibular Setback and Maxillary Advancement Surgery in Severely Obese Patient Taichi IDE, Takahiro KANNO, Masaaki KARINO,
Shimane J. Med. Sci., Vol.33 pp.93-98, 2017 Genioglossus Advancement Accompanied by Mandibular Setback and Maxillary Advancement Surgery in Severely Obese Patient Taichi IDE, Takahiro KANNO, Masaaki KARINO,
Diagnosis & Management of the Difficult Airway
 Diagnosis & Management of the Difficult Airway Dr. E. Rawlings Plymouth Anaesthetic Department Complications of Airway Management Medicolegal Serious morbidity Mortality Complications of Airway Management
Diagnosis & Management of the Difficult Airway Dr. E. Rawlings Plymouth Anaesthetic Department Complications of Airway Management Medicolegal Serious morbidity Mortality Complications of Airway Management
POINT Peri-Operative Insufflatory Nasal Therapy
 PINT Peri-perative Insufflatory Nasal Therapy by Armstrong Medical Helping prevent peri-operative pulmonary complications PST-P RECVERY PERATING RMS Hypoxia; a peri-operative risk Pulmonary complications
PINT Peri-perative Insufflatory Nasal Therapy by Armstrong Medical Helping prevent peri-operative pulmonary complications PST-P RECVERY PERATING RMS Hypoxia; a peri-operative risk Pulmonary complications
NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION. Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018
 NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018 Learning objectives What is NIV The difference between CPAP and BiPAP The indication of the use of NIV Complication of NIV application Patient monitoring
NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018 Learning objectives What is NIV The difference between CPAP and BiPAP The indication of the use of NIV Complication of NIV application Patient monitoring
Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Bernadette Zelaya, RRT. Area Clinical Manager
 High Velocity Nasal Insufflation An Important Therapeutic Approach for Use in the Emergency Department Presented by Vapotherm Accredited for 1 CEU by the American Association for Respiratory Care Provider
High Velocity Nasal Insufflation An Important Therapeutic Approach for Use in the Emergency Department Presented by Vapotherm Accredited for 1 CEU by the American Association for Respiratory Care Provider
Recognizing the Difficult Airway in Pediatric Patients. Nancy L. Glass, MD, MBA,
 Recognizing the Difficult Airway in Pediatric Patients Nancy L. Glass, MD, MBA, FAAP nglass@bcm.edu @DrNancyGlass1 None Disclosures Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation, participants will
Recognizing the Difficult Airway in Pediatric Patients Nancy L. Glass, MD, MBA, FAAP nglass@bcm.edu @DrNancyGlass1 None Disclosures Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation, participants will
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim
 Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Original Article. Summary. Introduction. F. Mir, 1 A. Patel, 2 R. Iqbal, 1 M. Cecconi 1 and S. A. R. Nouraei 3
 Original Article doi:10.1111/anae.13799 A randomised controlled trial comparing transnasal humidified rapid insufflation ventilatory exchange (THRIVE) pre-oxygenation with facemask pre-oxygenation in patients
Original Article doi:10.1111/anae.13799 A randomised controlled trial comparing transnasal humidified rapid insufflation ventilatory exchange (THRIVE) pre-oxygenation with facemask pre-oxygenation in patients
Procedures/Risks: pulmonology, sleep, critical care
 Procedures/Risks: pulmonology, sleep, critical care Bronchoscopy (and bronchoaveolar lavage) Purpose: The purpose of the bronchoscopy is to collect cells and fluid from the lung, so that information can
Procedures/Risks: pulmonology, sleep, critical care Bronchoscopy (and bronchoaveolar lavage) Purpose: The purpose of the bronchoscopy is to collect cells and fluid from the lung, so that information can
Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal and Anterior Mediastinal Abscess
 Hindawi Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 1848945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1848945 Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal
Hindawi Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 1848945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1848945 Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Common sleep disorder causes high blood pressure and heart attacks
 Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Common sleep disorder causes high blood pressure and heart attacks Message: Sleep apnea is very common. It is estimated that 158 million people worldwide suffer from sleep
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Common sleep disorder causes high blood pressure and heart attacks Message: Sleep apnea is very common. It is estimated that 158 million people worldwide suffer from sleep
High Flow Humidification Therapy, Updates.
 High Flow Humidification Therapy, Updates. Bernardo Selim, M.D. I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Assistant Professor, Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Mayo Clinic What
High Flow Humidification Therapy, Updates. Bernardo Selim, M.D. I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Assistant Professor, Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Mayo Clinic What
HOSPITAL PROCEDURE Collaborative Practice Committee
 Title: Capnography (ETC0 2 ) Monitoring Code: CPC-2012AUG-1.C.35 HOSPITAL PROCEDURE Collaborative Practice Committee Title of Responsible Party: Director of Medical-Surgical Services Origination Date:
Title: Capnography (ETC0 2 ) Monitoring Code: CPC-2012AUG-1.C.35 HOSPITAL PROCEDURE Collaborative Practice Committee Title of Responsible Party: Director of Medical-Surgical Services Origination Date:
What you need to know about: High flow nasal oxygen therapy
 What you need to know about: High flow nasal oxygen therapy Main introduction Adequate oxygenation is essential in many disorders, and this article will discuss the physiology, practicalities and indications
What you need to know about: High flow nasal oxygen therapy Main introduction Adequate oxygenation is essential in many disorders, and this article will discuss the physiology, practicalities and indications
Cricoid pressure: useful or dangerous?
 Cricoid pressure: useful or dangerous? Francis VEYCKEMANS Cliniques Universitaires Saint Luc Bruxelles (2009) Controversial issue - Can J Anaesth 1997 JR Brimacombe - Pediatr Anesth 2002 JG Brock-Utne
Cricoid pressure: useful or dangerous? Francis VEYCKEMANS Cliniques Universitaires Saint Luc Bruxelles (2009) Controversial issue - Can J Anaesth 1997 JR Brimacombe - Pediatr Anesth 2002 JG Brock-Utne
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Survey of the sevoflurane sedation status in one provincial dental clinic center for the disabled
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(4):283-288 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.4.283 Survey of the sevoflurane sedation status in one provincial dental
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(4):283-288 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.4.283 Survey of the sevoflurane sedation status in one provincial dental
Other methods for maintaining the airway (not definitive airway as still unprotected):
 Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Web Appendix 1: Literature search strategy. BTS Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure (AHRF) write-up. Sources to be searched for the guidelines;
 Web Appendix 1: Literature search strategy BTS Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure (AHRF) write-up Sources to be searched for the guidelines; Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) Database of
Web Appendix 1: Literature search strategy BTS Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure (AHRF) write-up Sources to be searched for the guidelines; Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) Database of
Advanced Airway Management PRESENTED BY: JOSIAH POIRIER RN, JOHN GRUBER FP-C
 Advanced Airway Management PRESENTED BY: JOSIAH POIRIER RN, JOHN GRUBER FP-C Advanced Airway Objectives Advanced airway management is a relatively low frequency, high risk intervention. The following education
Advanced Airway Management PRESENTED BY: JOSIAH POIRIER RN, JOHN GRUBER FP-C Advanced Airway Objectives Advanced airway management is a relatively low frequency, high risk intervention. The following education
11/20/2015. Beyond CPAP. No relevant financial conflicts of interest. Kristie R Ross, M.D. November 12, Describe advanced ventilation options
 Beyond CPAP Kristie R Ross, M.D. November 12, 2015 No relevant financial conflicts of interest Sponsored by The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Describe advanced ventilation options Compare
Beyond CPAP Kristie R Ross, M.D. November 12, 2015 No relevant financial conflicts of interest Sponsored by The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Describe advanced ventilation options Compare
Disclosures. Objectives. Defining Adult Obesity. Body Mass Index vs. Central Obesity 9/6/2017
 Disclosures Why is the Morbidly Obese Patient at Increased Risk for Perioperative Morbidity? Lisa R. Farmer, MD Associate Professor No conflicts of interests concerning the content of this presentation
Disclosures Why is the Morbidly Obese Patient at Increased Risk for Perioperative Morbidity? Lisa R. Farmer, MD Associate Professor No conflicts of interests concerning the content of this presentation
Effectiveness of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia
 Original Article Effectiveness of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia Eun Sun Kim, Hongyeul Lee, Se Joong Kim, Jisoo Park, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park,
Original Article Effectiveness of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia Eun Sun Kim, Hongyeul Lee, Se Joong Kim, Jisoo Park, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park,
Airway Management. Teeradej Kuptanon, MD
 Airway Management Teeradej Kuptanon, MD Outline Anatomy Detect difficult airway Rapid sequence intubation Difficult ventilation Difficult intubation Surgical airway access ICU setting Intubation Difficult
Airway Management Teeradej Kuptanon, MD Outline Anatomy Detect difficult airway Rapid sequence intubation Difficult ventilation Difficult intubation Surgical airway access ICU setting Intubation Difficult
ARDS Management Protocol
 ARDS Management Protocol February 2018 ARDS Criteria Onset Within 1 week of a known clinical insult or new or worsening respiratory symptoms Bilateral opacities not fully explained by effusions, lobar/lung
ARDS Management Protocol February 2018 ARDS Criteria Onset Within 1 week of a known clinical insult or new or worsening respiratory symptoms Bilateral opacities not fully explained by effusions, lobar/lung
The use of laryngeal mask airway in dental treatment during sevoflurane deep sedation
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(1):49-53 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.1.49 The use of laryngeal mask airway in dental treatment during sevoflurane
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(1):49-53 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.1.49 The use of laryngeal mask airway in dental treatment during sevoflurane
I. Subject. Moderate Sedation
 I. Subject II. III. Moderate Sedation Purpose To establish criteria for the monitoring and management of patients receiving moderate throughout the hospital Definitions A. Definitions of three levels of
I. Subject II. III. Moderate Sedation Purpose To establish criteria for the monitoring and management of patients receiving moderate throughout the hospital Definitions A. Definitions of three levels of
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Michael Kelly, MD Division of Pediatric Critical Care Dept. of Pediatrics
 RESPIRATORY FAILURE Michael Kelly, MD Division of Pediatric Critical Care Dept. of Pediatrics What talk is he giving? DO2= CO * CaO2 CO = HR * SV CaO2 = (Hgb* SaO2 * 1.34) + (PaO2 * 0.003) Sound familiar??
RESPIRATORY FAILURE Michael Kelly, MD Division of Pediatric Critical Care Dept. of Pediatrics What talk is he giving? DO2= CO * CaO2 CO = HR * SV CaO2 = (Hgb* SaO2 * 1.34) + (PaO2 * 0.003) Sound familiar??
Maria Tracey, Director-Perioperative and Elaine Warren, Directory-Surgery Level. III (Three)
 PAGE 1/6 MANAGEMENT OF ADULT SURGICAL CLIENTS WITH KNOWN OR SUSPECTED OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA (OSA) Patient Care Issuing Authority Dr. James Flynn, Clinical Chief Surgical Services (Perioperative) Signed
PAGE 1/6 MANAGEMENT OF ADULT SURGICAL CLIENTS WITH KNOWN OR SUSPECTED OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA (OSA) Patient Care Issuing Authority Dr. James Flynn, Clinical Chief Surgical Services (Perioperative) Signed
NI 60. Non-invasive ventilation without compromise. Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia. Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support
 NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
Airway and Airflow Characteristics In OSAS
 Airway and Airflow Characteristics In OSAS 16 th Annual Advances in Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Apnea and Snoring February 12-13, 2010 San Francisco, CA Nelson B. Powell M.D., D.D.S. Adjunct Clinical
Airway and Airflow Characteristics In OSAS 16 th Annual Advances in Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Apnea and Snoring February 12-13, 2010 San Francisco, CA Nelson B. Powell M.D., D.D.S. Adjunct Clinical
