International Journal of Research and Review ISSN:
|
|
|
- Silvester Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Research and Review ISSN: Original Research Article Spectrum of Liver Pathology at Autopsy Umesh Babu R 1, Gayathri B.N 2, Harendra Kumar M.L 3 1 Professor, Department of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, Sri Devraj Urs Medical College Tamaka, Kolar, Karnataka, India 2 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Kodagu Institute of Medical Sciences, Madikeri, Kodagu, Karnataka, India 3 Professor, Department of Pathology, Sri Devraj Urs Medical College, Tamaka, Kolar, Karnataka, India Corresponding author: Umesh babu R Received: 20/02/2015 Revised: 14/03/2015 Accepted: 24/03/2015 ABSTRACT Background: Most of the chronic liver diseases, even in advanced stages, may cause no prominent clinical signs or symptoms. They either go undiagnosed or are found incidentally during general health check-ups, investigations for other diseases, surgery, or autopsy. The underlying causes of chronic liver diseases vary in different geographic areas and are based on various factors such as socioeconomic status, life style, diet, local or regional infections, and other endemic diseases. Objectives: To study the spectrum of liver pathology at autopsy Method: We collected liver samples from 105 cases for histopathological study. Information regarding age, sex, marital status, place, food habit, alcoholic usage and previous history of any disease particularly liver disease etc., were collected from the first degree of the deceased during autopsy in which ever cases possible. Bits form right and left lobe and one bit from deeper areas of the liver was taken. Processed tissue sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin. The cases were analysed by descriptive statistics. Results: Satisfactory tissue samples for histologic evaluation were available in all the cases with a mean age of 39 years. Normal histology was found in 5 (4.7%) cases. Important findings included steatosis in 24 (22.8%), steatohepatitis in 37 (35.2%), chronic hepatitis in 22 (20.9%), congestion in 10 (9.5%), hepatic granulomas in 4 (3.8%) cases. Causes of death were: Road traffic accident (41.9%), poisoning (24.8%), burns (6.7%), snake bite (5.7%), fall from tree/wall (2.9%). Conclusion: Silent diseases of the liver are not uncommon. Steatohepatitis and chronic hepatitis comprise a significant finding in our locality. Key words: autopsy, liver disease, steatohepatitis INTRODUCTION Liver is vulnerable to a wide variety of metabolic, toxic, microbial and circulatory insults. In some instances, the disease is primary while in others the hepatic involvement is secondary to cardiac de-compensation, alcoholism or extrahepatic infections. Quite rightly liver is called as the custodian of milieu interior. Autopsy study is useful to monitor the cause of death and to plan medical strategy. [ 1] International Journal of Research & Review ( 79
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS 105 specimens of liver were received from Forensic Department of cases subjected for clinical autopsy, or medicolegal autopsy. Liver specimens received either as a part of examination of multiple viscera, or whole liver taken out from the deceased was examined. Information regarding age, sex, marital status, place, food habit, alcoholic usage and previous history of any disease particularly liver disease etc., were collected from the first degree of the deceased during autopsy in which ever cases possible. Consent for examination of liver was taken from next of kin. Samples from grossly visible lesions were studied and random bits from right lobe, left lobe, caudate and quadrate lobe and one bit from deeper areas of the liver was studied. All the bits were fixed in 10% formalin. Processed tissue sections were stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin according to standard procedures. Special stains were performed whenever necessary. The cases were analysed by descriptive statistics. Inclusion criteria: Patients above 3 years on whom clinical and medico legal autopsies had been done to ascertain the cause of death. Exclusion criteria: Autopsies on exhumed bodies. On microscopic examination degree of steatosis, steatohepatitis and chronic hepatitis were graded as follows shown in table 1, 2 & 3: Table 1: Grading of steatosis. I When micro and macrovesicular steatosis affected 5-25% of the liver parenchyma II When 26-50% of the parenchyma was affected III When 51-75% was affected IV When more than 75% of the parenchyma was involved Necroinflammatory grading Grade I (mild) Grade 2 (moderate) Grade 3 (severe) Fibrosis staging Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Table 2: A scoring system for steatohepatitis Steatosis ( mainly macrovesicular) involving up to 66% of lobules; occasional ballooned perivenular hepatocytes; scattered neutrophils with or without lymphocytes; no or mild chronic portal inflammation steatosis of anydegree; obvious ballooning (mainly perivenular); intralobular neutrophils, may be associated with perivenular pericellular fibrosis if evident; mild to moderate portal and intralobular chronic inflammation Panlobular steatosis; obvious perivenular ballooning and disarray; marked lobular inflammation; neutrophils may be concentrated in perivenular areas of ballooning and in areas of pericellular fibrosis if evident. Portal inflammation mild or moderate Pericellular fibrosis in perivenular areas, focal or extensive As above, plus focal or extensive Periportal fibrosis Bridging fibrosis, focal or extensive Cirrhosis Table 3: A simple scoring system for chronic hepatitis 1 Grade A Portal inflammation and interface hepatitis 0 Absent or minimal 1 Portal inflammation only 2 Mild or localized interface hepatitis 3 Moderate or more extensive interface hepatitis 4 Severe and widespread interface hepatitis B Lobular activity 0 None 1 Inflammatory cells but no hepatocellular damage 2 Focal necrosis or apoptosis 3 Severe hepatocellular damage 4 Damage includes bridging confluent necrosis 2 Stage 0 No fibrosis 1 Fibrosis confined to portal tracts 2 Periportal or portal-portal septa but intact vascular relationships 3 Fibrosis with distorted structure but no obvious cirrhosis 4 Probable or definite cirrhosis RESULTS In the present study, the age ranged from 3-72 years. Mean age was 39 years. Majority of patients belonged to the 4 th decade of life, followed by 5 th decade as shown in table 4. Table 4: Age distribution Age groups Number Percentage Total International Journal of Research & Review ( 80
3 The number of males was 69 (65.7%) and number of females was 36 (34.9%). The male to female ratio was 1.9 as shown in table 5 Table 5: Gender distribution Age groups Female Male Total Number Total Table-6 Cause of death distribution Cause of death Total Number Percentage (%) Road traffic accident Poison Burns Snake Bite Drowning Hanging Fall from height Assault Natural death Pregnancy complication Bee sting Head Injury Police custody TOTAL In the current study, the most common cause of death was road traffic accidents (RTA) which occurred in 44 cases (41.9%), followed by poisoning in 26 cases (24.8%) as shown in table 6 Table 7: History of alcohol and smoking History Number Percentage (%) Both smoking & alcohol Alcohol Smoking None In present study none of the female cases had history of smoking & alcohol consumption Table 8: Liver weight and sex Liver weight(grams) Male Female Total < > Total (maximum number) livers weighed between grams, followed by 26 livers <1000 grams, 16 between grams, 4 livers between grams and 4 > 2500 grams. Table 9: Gross findings Size Weight Colour Consistency Cut surface Number Increased >N Grey yellow Soft Greasy 24 Slightly Incr >N Red brown Soft Nutmeg 10 Slightly Incr >N Yellow green Firm Micronodular 02 Slightly Incr N Greenish Grey Soft Greenish 01 Normal N Normal Soft to firm Normal 68 Total 105 Also a few gross anomalies were noted, there was absence of caudate lobe in 3 cases and quadrate lobe in one case. Small nodules were seen in 3 cases. Micronodular cirrhosis was seen in two cases, Nutmeg liver was seen in 10 cases. Laceration/raw areas were seen in 8 cases with road traffic accidents. Also there were two notches on the external surface on the right lobe of liver each ms 4cm x3cm in one case could be rib impressions. Table 10: Histopathological findings Histopathological findings Cases Percentage Steatohepatitis Steatosis Chronic hepatitis Congestion Hepatic granulomas Micronodular cirrhosis Bile duct hamartoma Normal Predominantly macrovesicular steatosis was seen with fatty cyst. Few cases had mixed steatosis, with grading of III and IV (fig 1). Diffuse congestion was seen International Journal of Research & Review ( 81
4 with, centrilobular and sinusoidal congestion and mild periportal fatty change (fig 2). Fig 3. Microphotograph showing inflammatory infiltrate with lobular activitiy and foci of steatosis.hex40 Fig 1. Microphotograph showing diffuse macrovascular steatosis. HEx100 Fig 4. Microphotograph showing periportal fibrosis. HEx40 Fig 2. Microphotograph showing CVC liver with mild periportalfatty change.hex40 The main pathological feature was steatohepatitis characterised by steatosis with hepatocellular damage, inflammation, and fibrosis (fig 3). A scoring system for steatohepatitis was done with necroinflammatory grading of Grade 1 (mild) to Grade 2 (moderate) in 30 cases. There was pericellular fibrosis in 4 cases and periportal fibrosis in 3 cases (fig 4). In most of our cases mildest forms of chronic hepatitis was seen, the infiltrate was confined to portal tracts and the margins of the tracts remained regular. We also encountered cases of interface hepatitis, the inflammatory cells extended from the portal tracts into the adjacent parenchyma and there was destruction of hepatocytes. Chronic hepatitis with lobular activity was noted. Clumps of inflammatory cells, extended through the parenchyma with hepatocytes loss (fig 5). A simple scoring system was done for chronic hepatitis. Most of the cases had mild to moderate portal inflammation and mild or localized interface hepatitis. There was periportal and portal portal fibrosis in 6 cases. International Journal of Research & Review ( 82
5 micro nodular cirrhosis had bridging fibrous septa between portal to portal tracts and central vein (fig 8). Fig 5. Microphotograph showing dense lymphocytic infiltrate in the portal tract in a case of chronic hepatitis.hex100 Microhamartomas are multiple biliary channels lined by regular epithelium and set in a stroma of dense fibrous tissue. The lumens of the biliary structure contained inspissated bile (fig 6). They are usually found incidentally and do not normally give rise to symptoms or abnormalities of liver function. We found one case of microhamartoma in our study. Fig 7. Microphotograph showing mild anisokaryosis of hepatocytes in a case of cirrhosis.hex100 Fig 8. Microphotograph showing bridging fibrous septae between portal to portal tracts and central vein.hex40 Fig 6. Microphotograph showing bile duct hamartoma.hex100 Hepatocellular changes in cirrhosis in the form of regenerative hyperplasia were noted. In a minority of cirrhotic livers, the hepatocytes showed structural atypia and the one we encountered was large cell dysplasia. The cells were enlarged and their nuclei hyperchromatic and irregular in shape, with prominent nucleoli (fig 7). One case with Fig 9. Microphotograph showing perivenular hepatocytes with lipofuscin pigment.hex100 International Journal of Research & Review ( 83
6 epithelioid cells were seen forming granuloma which was parenchymal in location (fig 11). Z-N stain for AFB was negative. Two were drug induced granulomas. One was lipogranuloma. Fig 10. Microphotograph showing glycogen vacuoles within the nucleus of hepatocytes.hex100 Fig 11. Microphotograph showing hepatic granuloma.hex100 Age related changes which were observed included increased in the number of binucleated cells and increased number of lipofuscin pigment (fig 9). The pathological findings seen in burns cases included focal degeneration and necrosis of hepatocytes and proliferation of kupffer cells showing active phagocytosis. There was focal centrilobular necrosis in two of the poisoning cases. An autopsy case with history of diabetes mellitus, showed glycogen vacuoles within nucleus (fig 10). Also there were four cases of hepatic granulomas. One was suspicious of infectious origin, probably tuberculosis, since the case had previous history of tuberculosis. On microscopy giant cells and DISCUSSION Alcohol abuse generally leads to the pathological distinct liver diseases; in which the most frequent hepatic lesions are fatty change, hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis. Person can have any one or all three can occur at the same time. [ 2] These diseases are presently the most common chronic liver disease problem in western and developing countries like India. Short term ingestion of up to 8 gm of alcohol generally produce mild to severe hepatic changes such as fatty liver, ingestion increase up to 160 gm or more per day for more than 20 years results in cirrhosis of liver. Occurrence is between years but peak incidence is between 40 and 50 years as seen in our study. Apart from the major three liver diseases, chronic congestion, abscess and malignancy, yellow atrophy, infarcts and cysts can be seen as silent liver disease in histological findings. [ 3] In the study of 4908 autopsy cases from Russia, the most frequent hepatic lesions were steatosis and inflammatory [ 2] disorders. Berry in 1500 autopsies performed in the coronal system in South- East London reported cirrhosis, adenoma, metastatic carcinoma, and hamartoma as the most common findings. Space occupying lesions were found in about 5% of livers in [ 4] that study. Another study based on analysis of 1839 necropsies in Singapore revealed that unanticipated liver lesions are common. The most important ones were cholelithiasis, cirrhosis, and primary carcinoma of the liver. [ 5] In our study steatohepatitis, steatosis and chronic hepatitis were frequent hepatic lesions. International Journal of Research & Review ( 84
7 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) includes a spectrum of liver diseases, ranging from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis, advanced fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) represents a stage in the spectrum of NAFLD, characterized by presence of inflammation leading to gradual fibrosis in some of the affected patients. This disease is presently the most common chronic liver problem in western societies. The clinical importance of NAFLD is related to its prevalence and natural history. According to a recent study, the prevalence of NAFLD and NASH in western general population is approximately 20% and 30% respectively. But the true incidence and prevalence of NAFLD and NASH are not well known in different populations. [ 6] This is partly because liver histology is required as the gold standard for precise diagnosis of this condition and the relatively invasive procedure of liver biopsy is still not considered essential for management of NAFLD by many physicians. [ 6] Most of the reports about the prevalence rates of this disease are based on ultrasonographic studies and/or the presence of elevated serum levels of aminotransferases in the absence of any other known liver disease or significant alcohol consumption. [ 7] The prevalence of NAFLD in patients undergoing liver biopsy for any reason ranges between 15% and 39%. This wide range is naturally related to the differences in the populations studied. In these studies, the prevalence of NASH ranges between 1.4% and 4.8%. [ 6] In clinical practice, diagnostic liver biopsy is only performed for highly selected patients. Therefore, the reported rates which are based on liver biopsies cannot reflect the true prevalence of NAFLD in the general population. Autopsies, performed for those who have passed away for reasons other than liver diseases, are certainly better sources for determination of a more reliable prevalence of NAFLD and NASH. In our study both males and females were diagnosed of having NAFLD and NASH with a prevalence of 16% and 3.2% respectively. The particular characteristics of forensic autopsies are the relatively young age of subjects and usually better general health condition before death. Among our cases male gender was predominant, most of the subjects had no history of chronic diseases, and in more than 70% of the cases the cause of death was acute events like road traffic accident, trauma, and poisoning. Most patients with steatohepatitis are alcohol abusers, overweight or diabetic, or have a combination of these attributes. In our study also we found the above combination in few cases. The histological lesion of NASH is rarely very severe compared with ASH. The presence of abundant neutrophils and Mallory bodies should lead to a suspicion of alcohol abuse. Glycogen vacuolation of nucleus is common in NASH. We had 35.2% of cases with steatohepatitis and 20.9% of cases with chronic hepatitis. This incidence is more compared to previous studies in the [ 8, 10] literature. Venous congestion of liver is terminal end stage of death seen in most of the liver autopsies. Copeland reported congestion with fatty change in 3.4% of liver autopsies of alcoholics who died suddenly. The present study revealed congestion in 9.5% cases, slightly more as compared Copeland s findings. [ 9] Drugs are an important cause of otherwise unexplained granulomas. They are sometimes the only or main manifestation of a drug reaction, but can also form part of a cholestatic or hepatitis picture. The granuloma was portal in one of our case and was thought as lipogranuloma, as they were International Journal of Research & Review ( 85
8 associated with macrovesicular steatosis and fatty cyst. [ 8] Bal M.S, et al study was conducted in Patiala (Punjab) observed that out of 100 cases of liver specimens fatty liver 39%, normal 30%, cirrhosis 14%, congestion 9%, hepatitis and malignancy each 3% and chronic abscess 2%; male were predominate 83% and female 17%; fatty liver seen between years of age. [ 1] In a study by Tamil Selvi et al from Salem, the most common findings were fatty changes seen in age group of years and started with 40 years due to chronic consumption of alcohol in the population of Salem district, Tamil Nadu. [ 10] In our study Steatohepatitis, steatosis and chronic hepatitis were the leading silent liver diseases compared to other studies. [ 1, 6, 10] CONCLUSION Histopathological study is a great value in improving the vision and diagnostic setup for clinical assessment. In this prospective study steatohepatitis and hepatitis were common silent liver diseases compared to steatosis. The incidence of liver diseases is more in males as compared to females. REFERENCES 1. Bal MS, Singh SP, Bodal VK, Oberoi SS, Surinder K. Pathological findings in Liver autopsy. JIAFM 2004; 26(2): Voinova LV. Aetiological and nosological structure of liver diseases (on autopsy data of clinics of I.M. Sechenov Moscow Medical Academy in ). Arkh patol. 2000; 62: Saphir O. Liver 4 th ed. Autopsy diagnosis and techniques by Paul B, Hobber, New York. 1958: Berry CL. Liver lesions in an autopsy population. Hum Toxicol. 1987; 6: Lee YS. The pattern of liver diseases in Singapore. An autopsy study. Trop Geogr Med. 1979: 31; Sotoudehmanesh R, Sotoudeh M, Asgary AA, Adedi-Ardakani B, Tavangar SM, Khakinejad A et al. Silent Liver Diseases in Autopsies from Forensic Medicine of Tehran. Arch Iranian Med 2006; 9(4): Hultcrantz R, Glaumann H, Lindberg G, Nilsson LH. Liver investigation in 149 asymptomatic patients with moderately elevated activities of serum aminotransferases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986; 21: Kochar N, Lowes J, Teague RH. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in South West England. Gasteroenterology. 2002; 122: Copeland AR. Sudden death in the alcoholics. Jr. Forens. Sci. Inter. 1985;29: Selvi RT, Selvam V, subramaniam PM. Common silent liver disease in and around of Salem population: an autopsy study. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2012;6(2): How to cite this article: Umesh BR, Gayathri BN, Harendra Kumar ML. Spectrum of liver pathology at autopsy. Int J Res Rev. 2015; 2(3): ******************* International Journal of Research & Review ( 86
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology
 Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
MAGNITUDE OF PULMONARY DISEASES - INCIDENTALLY DIAGNOSED ON AUTOPSY AT LARGEST HOSPITAL & MEDICAL COLLEGE OF RAJASTHAN
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.6 Original Research Article MAGNITUDE OF PULMONARY DISEASES - INCIDENTALLY DIAGNOSED ON AUTOPSY AT LARGEST HOSPITAL & MEDICAL COLLEGE OF RAJASTHAN
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.6 Original Research Article MAGNITUDE OF PULMONARY DISEASES - INCIDENTALLY DIAGNOSED ON AUTOPSY AT LARGEST HOSPITAL & MEDICAL COLLEGE OF RAJASTHAN
Silent Liver Diseases in Autopsies from Forensic Medicine of Tehran
 Arch Iranian Med 2006; 9 (4): 324 328 Original Article Silent Liver Diseases in Autopsies from Forensic Medicine of Tehran Rasoul Sotoudehmanesh MD *, Masoud Sotoudeh MD*, Ali Ali-Asgari MD*, Behnoush
Arch Iranian Med 2006; 9 (4): 324 328 Original Article Silent Liver Diseases in Autopsies from Forensic Medicine of Tehran Rasoul Sotoudehmanesh MD *, Masoud Sotoudeh MD*, Ali Ali-Asgari MD*, Behnoush
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Liver Pathology in the 0bese
 Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
LIVER DISEASES. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) Case n 2 ( B 00 / 8249 ) Case n 3 ( B 98 / 8352 )
 Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel. Basel,
 Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Common Liver Diseases Hemangioma Cyst FNH Focal Fat/Sparing THID Non-Cirrhotic
Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Common Liver Diseases Hemangioma Cyst FNH Focal Fat/Sparing THID Non-Cirrhotic
Section 8 Liver and Gallbladder
 General and Systemic Histopathology C601 and C602 Section 8 As we will see in this unit, the liver is subject to many types of injury. Additionally, many systemic diseases have a liver component and sometimes
General and Systemic Histopathology C601 and C602 Section 8 As we will see in this unit, the liver is subject to many types of injury. Additionally, many systemic diseases have a liver component and sometimes
DILI PATHOLOGY. PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting
 DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
New insights into fatty liver disease. Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College
 New insights into fatty liver disease Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Prevalence of NASH Global prevalence of NAFLD is 25% with highest prevalence in the Middle
New insights into fatty liver disease Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Prevalence of NASH Global prevalence of NAFLD is 25% with highest prevalence in the Middle
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions. American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course
 Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Pathology of The Liver - Practice. 2017/ semester
 Pathology of The Liver - Practice 2017/2018 2. semester Classification of Liver Diseases Non-neoplastic Metabolic diseases Congenital anomalies Circulatory disorders Hepatitis Infectious Toxic Autoimmune
Pathology of The Liver - Practice 2017/2018 2. semester Classification of Liver Diseases Non-neoplastic Metabolic diseases Congenital anomalies Circulatory disorders Hepatitis Infectious Toxic Autoimmune
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER
 HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT. Lecture 5. Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Steatosis/Steatohepatitis
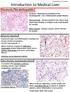 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1
 PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
Liver Failure. The most severe clinical consequence of liver disease is liver failure:
 Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Cell injury, adaptation and death. Unite one Second Lab.
 Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
CHAPTER 1. Alcoholic Liver Disease
 CHAPTER 1 Alcoholic Liver Disease Major Lesions of Alcoholic Liver Disease Alcoholic fatty liver - >90% of binge and chronic drinkers Alcoholic hepatitis precursor of cirrhosis Alcoholic cirrhosis end
CHAPTER 1 Alcoholic Liver Disease Major Lesions of Alcoholic Liver Disease Alcoholic fatty liver - >90% of binge and chronic drinkers Alcoholic hepatitis precursor of cirrhosis Alcoholic cirrhosis end
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
-sheet 3. -Waseem Alhaj. Maha Shomaf
 -sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
-sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY
 2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: a rare cause of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
 Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: a rare cause of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Naoki Tanaka 1, Akira Horiuchi 2, Takahide Yokoyama 3, Shigeyuki Kawa 1, and Kendo Kiyosawa 1 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: a rare cause of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Naoki Tanaka 1, Akira Horiuchi 2, Takahide Yokoyama 3, Shigeyuki Kawa 1, and Kendo Kiyosawa 1 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology
 REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
Improving Access to Quality Medical Care Webinar Series
 Improving Access to Quality Medical Care Webinar Series Presented by The Arizona Telemedicine Program and the Southwest Telehealth Resource Center 2015 UA Board of Regents Welcome AZ, UT, CO, NM & NV FLEX
Improving Access to Quality Medical Care Webinar Series Presented by The Arizona Telemedicine Program and the Southwest Telehealth Resource Center 2015 UA Board of Regents Welcome AZ, UT, CO, NM & NV FLEX
Liver Tumors. Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy
 Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the liver Reasons for imaging Focal lesions Diffuse disease Can we do more? The Liver The Liver The Liver
Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the liver Reasons for imaging Focal lesions Diffuse disease Can we do more? The Liver The Liver The Liver
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
Liver Diseases. Yasmine Lashine MD, PhD
 Liver Diseases Yasmine Lashine MD, PhD ILOs Recognize different causes of Live failure Recall and understand clinical picture and complication of Liver failure Discuss causes and clinical picture of hepatic
Liver Diseases Yasmine Lashine MD, PhD ILOs Recognize different causes of Live failure Recall and understand clinical picture and complication of Liver failure Discuss causes and clinical picture of hepatic
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 2 Developmental, Circulatory and Metabolic Disorders
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 2 Developmental, Circulatory and Metabolic Disorders Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMOLIES Congenital Cysts Congenital
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 2 Developmental, Circulatory and Metabolic Disorders Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMOLIES Congenital Cysts Congenital
Case year old Chinese female. Radiological echo-distortion in the right breast at o clock. Core biopsy of the o clock lesion.
 Case 3 64 year old Chinese female. Radiological echo-distortion in the right breast at 10-12 o clock. Core biopsy of the 11-12 o clock lesion. Division of Pathology Courtesty of Dr Lester Leong ill-defined,
Case 3 64 year old Chinese female. Radiological echo-distortion in the right breast at 10-12 o clock. Core biopsy of the 11-12 o clock lesion. Division of Pathology Courtesty of Dr Lester Leong ill-defined,
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
(C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes
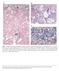 (A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
(A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system
 XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
LIVER PATHOLOGY. Thursday 28 th November 2013
 LIVER PATHOLOGY Thursday 28 th November 2013 Liver biopsy assessment of steatosis Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free Hospital RIBA, London Thursday 28th November 2013 NAFLD didn t exist before 2001 and liver
LIVER PATHOLOGY Thursday 28 th November 2013 Liver biopsy assessment of steatosis Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free Hospital RIBA, London Thursday 28th November 2013 NAFLD didn t exist before 2001 and liver
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma
 July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar
 Original Research Article Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar Naresh Kumar 1, Jyoti Kumar Dinkar 2*, Chandrakishore
Original Research Article Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar Naresh Kumar 1, Jyoti Kumar Dinkar 2*, Chandrakishore
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Challenges in the Diagnosis of Steatohepatitis
 The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D
 BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free & University College Medical School Thurs 10
BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free & University College Medical School Thurs 10
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS
 34 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 34-42 2000 Research Report HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India SUMMARY: The effect of chronic and acute exposure
34 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 34-42 2000 Research Report HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India SUMMARY: The effect of chronic and acute exposure
Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes. Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD
 Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Parenchymal Cells -Hepatocytes -Cholangiocytes
Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Parenchymal Cells -Hepatocytes -Cholangiocytes
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER
 CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
Updates from the AASLD
 Updates from the AASLD Washington Rob Goldin Imperial College Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Death rates for chronic liver disease and cirrhosis rose 31% among those age 45 to 64 between 2000
Updates from the AASLD Washington Rob Goldin Imperial College Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Death rates for chronic liver disease and cirrhosis rose 31% among those age 45 to 64 between 2000
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS
 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
Chronic Biliary Disease. Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths
 Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids. Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada
 Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
There is extensive literature addressing both the histopathologic
 Approach to the Liver Biopsy in the Patient With Chronic Low-Level Aminotransferase Elevations Pathologists sometimes encounter a liver biopsy from an asymptomatic patient with unexplained low-level parenchymal
Approach to the Liver Biopsy in the Patient With Chronic Low-Level Aminotransferase Elevations Pathologists sometimes encounter a liver biopsy from an asymptomatic patient with unexplained low-level parenchymal
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Histology. The pathology of the. bile ducts. pancreas. liver. The lecture in summary. Vt-2006
 Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
National Liver EQA Scheme. Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004
 National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
Liver National EQA Scheme. Circulation Q Birmingham, March 15 th 2005
 Liver National EQA Scheme Circulation Q Birmingham, March 15 th 2005 Images from circulations Virtualpathology@leeds.ac.uk/uvw View slides from current circulation, Aperio see and navigate whole slide
Liver National EQA Scheme Circulation Q Birmingham, March 15 th 2005 Images from circulations Virtualpathology@leeds.ac.uk/uvw View slides from current circulation, Aperio see and navigate whole slide
IDIOPATHIC CHOLESTASIS IN THE NEONATAL PERIOD
 IDIOPATHIC CHOLESTASIS IN THE NEONATAL PERIOD BY H. STEIN and C. ISAACSON From the Departments of Paediatrics and Pathology, Baragwanath Hospital, and the South African Institute for Medical Research,
IDIOPATHIC CHOLESTASIS IN THE NEONATAL PERIOD BY H. STEIN and C. ISAACSON From the Departments of Paediatrics and Pathology, Baragwanath Hospital, and the South African Institute for Medical Research,
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
HEPATO-BILIARY IMAGING
 HEPATO-BILIARY IMAGING BY MAMDOUH MAHFOUZ MD PROF.OF RADIOLOGY CAIRO UNIVERSITY mamdouh.m5@gmail.com www.ssregypt.com CT ABDOMEN Indications Patient preparation Patient position Scanogram Fasting 4-6 hours
HEPATO-BILIARY IMAGING BY MAMDOUH MAHFOUZ MD PROF.OF RADIOLOGY CAIRO UNIVERSITY mamdouh.m5@gmail.com www.ssregypt.com CT ABDOMEN Indications Patient preparation Patient position Scanogram Fasting 4-6 hours
Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Liver Pathology Lab 1. Shannon Martinson, 2017
 Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
Invited Re vie W. Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic liver diseases
 Histol Histopathol (1 998) 13: 1077-1 087 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic
Histol Histopathol (1 998) 13: 1077-1 087 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis
 Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
Recently role of non-invasive diagnostics methods
 CERTAIN ASPECTS OF NLS-DIAGNOSTICS OF LIVER FOCAL PATHOLOGY A.Y. Shvack, V.I. Nesterov, N.L. Ogluzdina This article contains information about NLS-graphy application in diagnostics of liver focal affections:
CERTAIN ASPECTS OF NLS-DIAGNOSTICS OF LIVER FOCAL PATHOLOGY A.Y. Shvack, V.I. Nesterov, N.L. Ogluzdina This article contains information about NLS-graphy application in diagnostics of liver focal affections:
Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary
 2015 69 3 137144 Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary Cirrhosis a a,b* a a a a a,b a a a,b c d
2015 69 3 137144 Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary Cirrhosis a a,b* a a a a a,b a a a,b c d
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease An Update
 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease An Update Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham First described in 1980
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease An Update Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham First described in 1980
Malignant Focal Liver Lesions
 Malignant Focal Liver Lesions Other Than HCC Pablo R. Ros, MD, MPH, PhD Departments of Radiology and Pathology University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Case Western Reserve University Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org
Malignant Focal Liver Lesions Other Than HCC Pablo R. Ros, MD, MPH, PhD Departments of Radiology and Pathology University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Case Western Reserve University Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org
Chapter 18 LIVER BILIARY TRACT
 Chapter 18 LIVER & BILIARY TRACT DUCT SYSTEM N O FIBROUS TISSUE PORTAL TRIAD CENTRAL VEIN PATTERNS OF HEPATIC INJURY Degeneration: Balooning, feathery degeneration, fat, pigment Inflammation:
Chapter 18 LIVER & BILIARY TRACT DUCT SYSTEM N O FIBROUS TISSUE PORTAL TRIAD CENTRAL VEIN PATTERNS OF HEPATIC INJURY Degeneration: Balooning, feathery degeneration, fat, pigment Inflammation:
Liver Involvement in Falciparum Malaria A Histo-pathological Analysis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2003; 4(1): 34-8 Liver Involvement in Falciparum Malaria A Histo-pathological Analysis Rajesh Baheti*, Purnima Laddha**, RS Gehlot*** Abstract The present study has been undertaken
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2003; 4(1): 34-8 Liver Involvement in Falciparum Malaria A Histo-pathological Analysis Rajesh Baheti*, Purnima Laddha**, RS Gehlot*** Abstract The present study has been undertaken
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ WELCOME! Dr Boute is the coordinator Course
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ WELCOME! Dr Boute is the coordinator Course
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis. Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K.
 Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Relationship between Serum Iron Indices and Hepatic Iron Quantitation in Patients with Fatty Liver Disease
 International Journal of Business, Humanities and Technology Vol. 2 No. 5; August 2012 Relationship between Serum Iron Indices and Hepatic Iron Quantitation in Patients with Fatty Liver Disease Dr. Mariana
International Journal of Business, Humanities and Technology Vol. 2 No. 5; August 2012 Relationship between Serum Iron Indices and Hepatic Iron Quantitation in Patients with Fatty Liver Disease Dr. Mariana
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas
 Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
