Hepatic vein lesions in alcoholic liver disease:
|
|
|
- Clifton Warren Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hepatic vein lesions in alcoholic liver disease: retrospective biopsy and necropsy study AD BURT, RNM MacSWEEN University Department of Pathology Western Infirmary, Glasgow J Clin Pathol 1986;39:63-67 SUMMARY Obliteration of the terminal hepatic venules with perivenular fibrosis (phlebosclerosis) is a well recognised feature in alcoholic liver disease. Veno-occlusive lesions with intimal obliteration of hepatic veins and a lymphocytic phlebitis of hepatic veins may also be present. We looked for these lesions in 256 liver biopsies and 50 livers obtained at necropsy from patients with alcoholic liver disease. Phlebosclerosis was a universal finding in alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis and showed increasing severity with progressive liver injury. Veno-occlusive lesions, however, were found in only 25 of 256 (9-8%) of biopsies and 11 of 50 (22%) of livers obtained at necropsy, showing alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis: lymphocytic phlebitis was found in 10 of 256 (3 9%) and two of 50 (4%), respectively. Moreover, veno-occlusive lesions were generally mild. The prevalence of veno-occlusive lesions and lymphocytic phlebitis was considerably less than has been previously documented. Phlebosclerosis may have a different mechanism and be a more important contributory factor in progressive liver injury. The histological features of alcoholic liver disease have been reviewed in several recent publications.` 1- The presence of hepatic vein lesions, however, has been little emphasised. Edmondson et al emphasised the importance of the obliteration of hepatic vein branches by a process of perivenular fibrosis.6 In their review of alcoholic liver disease Baptista et al noted that the venous radicles eventually become obliterated in alcoholic hepatitis and may, consequently, be difficult to identify.4 Venous occlusion by a process of intimal proliferation was noted by Patrick and McGee,7 but Popper et al considered this lesion to be rare and seldom of substantial functional importance.3 Goodman and Ishak, however, in a retrospective necropsy study showed these veno-occlusive lesions in 25 of 48 (52-1%) cases of alcoholic hepatitis and in 103 of 139 (74%) cases with established alcoholic cirrhosis. In addition, they reported on the universal prevalence of perivenular phlebosclerotic lesions in both hepatitis and cirrhosis and described a lymphocytic phlebitis in eight (16 7%) cases with alcoholic hepatitis. In this retrospective study we reviewed a series of 256 liver biopsies and 50 livers obtained at necropsy from patients with alcoholic liver disease: we specifically looked for hepatic vein lesions as defined by Goodman and Ishak.8 Accepted for publication 17 September 1985 Material and methods The material comprised 256 liver biopsies submitted to the department of pathology at this hospital over five years (from 1977 to 1982). This was a consecutive series selected on the basis of: histological diagnosis; a documented clinical history of alcohol abuse; and clinical exclusion of any other known cause of liver injury. There was a male to female ratio of 1.56:1 with a mean age at the time of biopsy of 51 1 years (range 20-76) and 51-8 (range 31-76), respectively. Liver tissue obtained after death was examined from a similarly selected group of 50 cases, comprising 37 men and 13 women (mean age 56 3 and 58-3 years, respectively). Thirty eight (78%) of the patients had died from complications related to their liver disease; the proximate causes of death in eight of the remaining patients were: acute pancreatitis (3), pneumonia (3), fungal septicaemia (1), and Gram negative peritonitis (1). In the final four death was attributed to congestive cardiac failure (rheumatic heart disease (2), congestive cardiomyopathy (1), and cor pulmonale (1)): in all four cases there was established cirrhosis, but cardiac failure was not thought to have been a major contributor to the liver disease. Sections (5 pm) from all specimens were routinely stained with haematoxylin and eosin, Masson's trichrome, Gordon and Sweet's reticulin, Shikata's 63
2 64 Burt, MacSween Fig. la Moderate (grade 2+) veno-occlusive lesion with accompanying phlebitis andperivenularfibrosis in alcoholic hepatitis. (Massons trichrome.) x 300. (b) Serial section stained with Shikata's orcein showing presence ofintimal proliferation within elastic lamina. x 300. orcein, periodic acid Schiff (before and after diastase treatment), and Perls's reaction. In selected cases additional sections were stained with elastic van Gieson. Vascular lesions were assessed according to the criteria of Goodman and Ishak8: Veno-occlusive lesions These were characterised by intimal proliferation and fibrosis occurring within the 42Xi *; i Ṣ & X s'm 2 s ' >- i ' 8 - *,0 o *ND.s.re'w4 a* W,.st-F Fig. 2 Severe (grade 3 +) veno-occlusive lesion in cirrhotic liver affecting interlobular vein and tributary. Necropsy series. (Elastic van Gieson.) x 140. elastic lamina of the vein radicles, ranging from mild (1+), intimal thickening with one third occlusion, through to moderate (2 +), with two thirds occlusion, to severe (3 +), when there was more than two thirds occlusion to complete obliteration (Figs. 1 and 2). Individual cases were scored on the basis of the most severe lesion present. Phlebosclerosis This consisted of compression of Fig. 3 Mild (grade 1+) phlebosclerosis in alcoholic hepatitis. (Elastic van Gieson.) x 180.
3 w #t.#/ Hepatic vein lesions in alcoholic liver disease 65 Fig. 4a Obliterative lesion in hepatic vein branch in cirrhotic liver at necropsy (Hamatoxylin and eosin.) x 375. (b) Elastic tissue admixed with collagen in obliterative lesion. (Elastic van Gieson.) x 375. hepatic vein radicles by perivenular fibrosis and was an inflammatory infiltrate, predominantly graded as: mild (1+), perivenular fibrosis with lymphocytic, within the walls of hepatic vein branches minimal compression of the vein lumen (Fig. 3); (Figs la and 5). Spillover of neutrophil polymorphs moderate (2+), more marked fibrosis and from foci of hepatocyte necrosis in the perivenular compression of the vein lumen; severe (3 +), complete zone was excluded. obliteration of the vein radicle with extensive perivenular fibrosis (Fig. 4). Individual cases were Results also scored on the basis of the most severe lesion present. The biopsy cases were classified as follows: fatty liver Lymphocytic phlebitis was defined as the presence of (71), fatty liver with pericellular or perivenular fibrosis, or both (20), alcoholic hepatitis (82), and cirrhosis (83). Of the 83 cases of cirrhosis, 76 showed sfo evidence of continuing active alcoholic hepatitis. Cirrhosis was present in 44 livers obtained at necropsy and alcoholic hepatitis in six. * r" a X The Table summarises the incidence of hepatic vein %., :*r a lesions in the various subgroups. Veno-occlusive lesions were found in only one case of fatty liver, although they were present in 13 (15-8%) of the 82 ~ ; rs v biopsy specimens with alcoholic hepatitis and in 12 (14-4%) of those with cirrhosis; they were generally tu '. *4 A % mild (1 +). Phlebosclerotic lesions were much more common; lesions were found in 20 (22%) of the 91 cases with fatty liver and in all but one instance they 40 were of mild degree and concomitant with mild pericellular fibrosis. When we compared the subgroups with alcoholic hepatitis with these with cirrhosis, the severity of the phlebosclerotic lesion was greater in the group with cirrhosis; 65 of 83 (78%) were severe (3+) compared with four of 82 (5%) in the group with alcoholic hepatitis. A lymphocytic Fig. 5 Mild lymnphocytic phlebitis affiecting interlobular vein phlebitis occurred in eight (9-7%) of the 82 cases of in established cirrhosis. (Haemaroxylin and eosin.) x 280. alcoholic hepatitis and in two (2 4%) of the cases of >. ; t s->s** S?
4 66 Table Prevalence ofhepatic vein lesions in subgroups ofalcoholic liver disease Burt, MacSween Veno-occlusive lesions Phlebosclerosis Lymphocytic phlebitis Mild moderate severe Mild moderate severe (%) Total (%) Total (%) Fattyliver(n = 71) (1.4) Fatty liver with fibrosis (n = 20) (100) 0 Alcoholic hepatitis: Biopsy(n = 82) (15-8) (975) 8(9-7) Necropsy(n = 6) (50) (100) 1(16-6) Cirrhosis: Biopsy(n = 83) (14-4) (100) 2(2.4) Necropsy (n = 44) (18-1) (150) 1 (2.3) cirrhosis. In the necropsy group veno-occlusive lesions were seen in three of six (50%) of those with alcoholic hepatitis but were present in only eight of 44 (18%) of the cirrhotic livers. Phlebosclerosis was universally present and severe lymphocytic phlebitis was rare. Discussion Edmondson noted that obliterative sclerosis of hepatic veins and perivenular sinusoids was a feature of alcoholic hepatitis and termed this "sclerosing hyaline necrosis."' This phlebosclerosis has subsequently been referred to in several other accounts of alcoholic liver disease,1 5 but its prevalence, pathogenesis, and its possible contribution to the progression of the liver injury have remained uncertain. Furthermore, in some accounts distinction has been drawn between phlebosclerosis and veno-occlusive lesions. The veno-occlusive lesions resemble those described by Bras et al in their classical studies of pyrollizidine related liver disease.9 Goodman and Ishak in their retrospective necropsy study also distinguished between phlebosclerosis and veno-occlusive lesions, finding phlebosclerosis in all their cases of alcoholic hepatitis or alcoholic cirrhosis and veno-occlusive lesions in 52% and 74%, respectively.8 The authors also described a lymphocytic phlebitis, which was found much less often. In this study we looked for hepatic vein lesions as defined by Goodman and Ishak. The veno-occlusive lesions were readily identified and usually affected the larger hepatic vein branches. The prevalence of these lesions was, however, considerably less than that noted by Goodman and Ishak. The histological diagnosis of phlebosclerosis presented some difficulties. In sections stained with haematoxylin and eosin it was often difficult to identify hepatic vein radicles within areas of fibrous scarring that topographically corresponded to the venular and perivenular zones. Residual elastic lamina, however, could usually be shown within these areas on either the orcein stain or the elastic van Gieson stain (Fig. 4). In a small number of biopsies some hepatic vein branches showed features of intimal veno-occlusion as defined by Goodman and Ishak8 but accompanied by perivenular adventitial fibrosis. Possibly, progression of both the intimal proliferation and the adventitial fibrosis could have produced a totally obliterative lesion which we then regarded as being phlebosclerotic. Nakanuma et al showed transitions between veno-occlusive and phlebosclerotic lesions in cirrhosis on serial sectioning. 1 2 The pathogenesis of veno-occlusion and phlebosclerosis in alcoholic liver disease is unclear. These conditions may represent direct toxic injury to vascular endothelium in a manner similar to that proposed for lesions seen with certain toxins and chemotherapeutic agents.9-1l Veno-occlusive disease produced by pyrollizidine alkaloids, however, may be related to injury at the sinusoidal level with subsequent damage to both endothelial cells and hepatocytes There is a consequent decrease in hepatic vein flow and a narrowing in the luminal diameter to a size appropriate for the reduced blood flow. In cirrhotic livers studied after death by Nakanuma et al focal veno-occlusive lesions were found in 75-90%, and the incidence and morphology of the lesions seemed to be similar irrespective of the aetiological type of the cirrhosis-that is, alcoholic, primary biliary, posthepatitic, or cryptogenic. 14 They suggested that these focal lesions represented a secondary response to a reduced blood flow, the reduction resulting from microvascular disturbance by fibrous scarring or nodular regeneration, or both. Although such an explanation could apply to the veno-occlusive lesions which we saw in this study, we believe that the phlebosclerotic lesions represent a different form of injury. They were seen at a stage of alcoholic fatty liver in which there was no evident swelling of the liver cells and when reduction in venous flow seemed improbable. These early lesions were accompanied by a mild degree of pericellular
5 Hepatic vein lesions in alcoholic liver disease fibrosis, which is being increasingly recognised as an early component of liver disease induced by alcohol and which, indeed, may progress to cirrhosis without an intervening stage of alcoholic hepatitis It seems likely to us that the early phlebosclerotic lesion is part of the fibrosis induced by alcohol, which commences in the perivenular zone and which may be the very earliest evidence of incipient and progressive liver injury. It is evident from our results that the severity of the phlebosclerosis increases with progressive liver injury and may of itself be important in the further evolution of the disease. References 1Edmnondson HA. Pathology of alcoholism. Am J Clin Pathol 1963;74: MacSween RNM. Alcoholic liver disease. In: Anthony PP, Woolf N, eds. Recent advances in histopathology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1978: Popper H, Thung SN, Gerber MA. Pathology of alcoholic liver diseases. Semin Liver Dis 1981;1: 'Baptista A, De Groote J, Bianchi L, et al. Alcoholic liver disease: morphological manifestations. Lancet 1981;i:707-1 I. sfleming KA, McGee JO'D. Alcohol induced liver disease. J Clin Pathol 1984;37: Edmondson HA, Peters RL, Reynolds TB, Kuyura OT. Sclerosing hyaline necrosis in the liver of the chronic alcoholic. A recognisable lesion. Ann Intern Med 1963;59: 'Patrick RS, McGee JO'D. Alcoholic liver disease. Biopsy pathology of the liver. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott Co, 1980: Goodman ZD, Ishak KG. Occlusive venous lesions in alcoholic liver disease: a study of 200 cases. Gastroenterology 1982;83: Bras G, Jellifee DB, Stuart KL. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver with non-portal type of cirrhosis occurring in Jamaica. Archives of Pathology 1954;57: ' Griner PF, Elbadawi A, Packman CH. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver after chemotherapy. Ann Intern Med 1976;85: 'Gill RA, Onstad GR, Cardainone JM. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease caused by 6-thioguanine. Ann Intern Med 1982;96: Stirling GA, Bras G, Urquhart AE. The early lesions in venoocclusive disease of the liver. Arch Dis Child 1962;37: Brooks SEH, Miller CG, McKenzie K, Audretsh JJ, Bras G. Acute veno-occlusive disease of the liver. Archives of Pathology 1970;89: Nakanuma Y, Ohta G, Doishita K. Quantitation and serial section observations of focal veno-occlusive lesions of hepatic veins in liver cirrhosis. Virchows Arch (Pathol Anat) 1985;405: "Van Waes L, Lieber CS. Early perivenular sclerosis in alcoholic fatty liver: an index of progressive liver injury. Gastroenterology 1977;73: Nasrallah SM, Nassar VH, Galambos JT. Importance of terminal hepatic venule thickening. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1980;104: Nakano M, Worner TM, Lieber CS. Perivenular fibrosis in alcoholic liver injury: ultrastructure and histologic progression. Gastroenterology 1982;83: Requests for reprints to: Professor RNM MacSween, University Department of Pathology, Western Infirmary, Glasgow GI 1 6NT, Scotland. 67 J Clin Pathol: first published as /jcp on 1 January Downloaded from on 19 September 2018 by guest. Protected by
Occlusive Venous Lesions in Alcoholic Liver Disease
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1982;83:786-96 Occlusive Venous Lesions in Alcoholic Liver Disease A Study of 200 Cases ZACHARY D. GOODMAN and KAMAL G. ISHAK From the Department of Hepatic Pathology, Armed Forces Institute
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1982;83:786-96 Occlusive Venous Lesions in Alcoholic Liver Disease A Study of 200 Cases ZACHARY D. GOODMAN and KAMAL G. ISHAK From the Department of Hepatic Pathology, Armed Forces Institute
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis. Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K.
 Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION
 Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Effect of fulvine on pulmonary arteries
 Thorax (1974), 29, 522. Effect of fulvine on pulmonary arteries and veins of the rat C. A. WAGENVOORT, N. WAGENVOORT, and H. J. DIJK Department of Pathological Anatomy, Wilhelmina Gasthuis, University
Thorax (1974), 29, 522. Effect of fulvine on pulmonary arteries and veins of the rat C. A. WAGENVOORT, N. WAGENVOORT, and H. J. DIJK Department of Pathological Anatomy, Wilhelmina Gasthuis, University
Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
Hepatic cirrhosis: A clinico-pathological review
 J. cliil. Path., 1973, 26, 936-942 Hepatic cirrhosis: A clinico-pathological review of 520 cases R. N. M. MacSWEEN AND A. R. SCOTT' From the University of Glasgow, Department ofpathology, Western Infirmary,
J. cliil. Path., 1973, 26, 936-942 Hepatic cirrhosis: A clinico-pathological review of 520 cases R. N. M. MacSWEEN AND A. R. SCOTT' From the University of Glasgow, Department ofpathology, Western Infirmary,
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology
 REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
Mesenchymal Tumors MESENCHYMAL TUMORS OF THE LIVER: WHAT S NEW AND UNUSUAL (MY PERSPECTIVE)
 MESENCHYMAL TUMORS OF THE LIVER: WHAT S NEW AND UNUSUAL (MY PERSPECTIVE) CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY MAY 23, 2014 Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF Mesenchymal Tumors Focus on Vascular Tumors Benign and
MESENCHYMAL TUMORS OF THE LIVER: WHAT S NEW AND UNUSUAL (MY PERSPECTIVE) CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY MAY 23, 2014 Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF Mesenchymal Tumors Focus on Vascular Tumors Benign and
Mesenchymal Tumors. Cavernous Hemangioma (CH) VASCULAR TUMORS MESENCHYMAL TUMORS OF THE LIVER: WHAT S NEW AND UNUSUAL (MY PERSPECTIVE)
 Mesenchymal Tumors MESENCHYMAL TUMORS OF THE LIVER: WHAT S NEW AND UNUSUAL (MY PERSPECTIVE) CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY MAY 23, 2014 Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF Focus on Vascular Tumors Benign and
Mesenchymal Tumors MESENCHYMAL TUMORS OF THE LIVER: WHAT S NEW AND UNUSUAL (MY PERSPECTIVE) CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY MAY 23, 2014 Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF Focus on Vascular Tumors Benign and
Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A. OLUSEGUN FAYEMI, M.D.* Department of Pathology, The Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University of New York, New York, New York 129
Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A. OLUSEGUN FAYEMI, M.D.* Department of Pathology, The Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University of New York, New York, New York 129
Relationship between Serum Iron Indices and Hepatic Iron Quantitation in Patients with Fatty Liver Disease
 International Journal of Business, Humanities and Technology Vol. 2 No. 5; August 2012 Relationship between Serum Iron Indices and Hepatic Iron Quantitation in Patients with Fatty Liver Disease Dr. Mariana
International Journal of Business, Humanities and Technology Vol. 2 No. 5; August 2012 Relationship between Serum Iron Indices and Hepatic Iron Quantitation in Patients with Fatty Liver Disease Dr. Mariana
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids. Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada
 Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure
 Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Light and electron microscopy of globular
 Light and electron microscopy of globular hyaline inclusions in liver cells J. C. E. UNDERWOOD From the Department ofpathology, University of Sheffield J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 821-826 synopsis Numerous
Light and electron microscopy of globular hyaline inclusions in liver cells J. C. E. UNDERWOOD From the Department ofpathology, University of Sheffield J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 821-826 synopsis Numerous
A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease
 A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease R. M. CROSS J. clini. Path. (1968), 21, 0-10 From the Royal Air Force Institute ofpathology and Tropical Medicine, Halton, Buckinghamshire
A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease R. M. CROSS J. clini. Path. (1968), 21, 0-10 From the Royal Air Force Institute ofpathology and Tropical Medicine, Halton, Buckinghamshire
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology
 Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
ACP-BSG meeting The liver in systemic inflammatory disorders. Dr Adrian C Bateman Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust
 ACP-BSG meeting 10.12.09 The liver in systemic inflammatory disorders Dr Adrian C Bateman Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust Wide range of diseases General inflammatory disorders Connective tissue
ACP-BSG meeting 10.12.09 The liver in systemic inflammatory disorders Dr Adrian C Bateman Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust Wide range of diseases General inflammatory disorders Connective tissue
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
Control material was obtained in cases in which necropsy was performed and in which there was no history of peripheral vascular disease or
 Blood Vessels of the Skin in Chronic Venous Insufficiency By MYRON H. KULWIN, M.D., AND EDGAR A. HINES, JR., M.D. This study concerns ain evaluation of the anatomicopathologic changes found in blood vessels
Blood Vessels of the Skin in Chronic Venous Insufficiency By MYRON H. KULWIN, M.D., AND EDGAR A. HINES, JR., M.D. This study concerns ain evaluation of the anatomicopathologic changes found in blood vessels
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013
 Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV. Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA
 Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Value of copper-associated protein in diagnostic assessment of liver biopsy
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36: 18-23 Value of copper-associated protein in diagnostic assessment of liver biopsy PAOLO GUARASCIO, FRANCES YENTIS, UGUR CEVIKBAS, BERNARD PORTMANN, ROGER WILLIAMS From the Liver
J Clin Pathol 1983;36: 18-23 Value of copper-associated protein in diagnostic assessment of liver biopsy PAOLO GUARASCIO, FRANCES YENTIS, UGUR CEVIKBAS, BERNARD PORTMANN, ROGER WILLIAMS From the Liver
Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver
 Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
Liver Pathology in the 0bese
 Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08. Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
 CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ANALGESIC HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBIT
 A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ANALGESIC HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBIT Pages with reference to book, From 41 To 43 M. Ashraf Qamar, S.M. Alam ( Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ANALGESIC HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBIT Pages with reference to book, From 41 To 43 M. Ashraf Qamar, S.M. Alam ( Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Lymph node hyalinisation in rheumatoid arthritis
 138 17 Clin Pathol 1994;47:138-142 Department of Pathology, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast W G McCluggage Queen's University, Belfast H Bharucha Correspondence to: Dr W G McCluggage, Department of Pathology,
138 17 Clin Pathol 1994;47:138-142 Department of Pathology, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast W G McCluggage Queen's University, Belfast H Bharucha Correspondence to: Dr W G McCluggage, Department of Pathology,
Liver Pathology: Cirrhosis, Hepatitis, and Primary Liver Tumors. Update and Diagnostic Problems
 SHORT COURSE Liver Pathology: Cirrhosis, Hepatitis, and Primary Liver Tumors. Update and Diagnostic Problems Linda Ferrell, M.D. Department of Anatomic Pathology, University of California San Francisco,
SHORT COURSE Liver Pathology: Cirrhosis, Hepatitis, and Primary Liver Tumors. Update and Diagnostic Problems Linda Ferrell, M.D. Department of Anatomic Pathology, University of California San Francisco,
Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in
 J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
What s new in liver transplantation? Romil Saxena, MD, FRCPath (UK) Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis
 What s new in liver transplantation? Romil Saxena, MD, FRCPath (UK) Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis A combination of improved surgical techniques, donor organ preservation, selection
What s new in liver transplantation? Romil Saxena, MD, FRCPath (UK) Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis A combination of improved surgical techniques, donor organ preservation, selection
hepatocellular carcinoma
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1124-1128 Incidence in South-west Scotland of hepatitis B surface antigen in the liver of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma M. L. TURBITT, R. S. PATRICK, R.
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1124-1128 Incidence in South-west Scotland of hepatitis B surface antigen in the liver of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma M. L. TURBITT, R. S. PATRICK, R.
S ince the discovery of hepatitis C, there have been several
 402 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Steatosis and fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C J Wyatt, H Baker, P Prasad, Y Y Gong, C Millson... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr
402 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Steatosis and fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C J Wyatt, H Baker, P Prasad, Y Y Gong, C Millson... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY
 2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
HEART BLOCK IN MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY
 HEART BLOCK IN YOCARDIAL INFARCTION: A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY by B. A. SIS,.D.,.R.C.P.* Department of Pathology, Queen's University, Belfast THE CASE with apoplectic attacks described by Robert Adams
HEART BLOCK IN YOCARDIAL INFARCTION: A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY by B. A. SIS,.D.,.R.C.P.* Department of Pathology, Queen's University, Belfast THE CASE with apoplectic attacks described by Robert Adams
glands: a correlation in postmortem subjects
 J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 690-694 Lymphocytic sialadenitis in the major and minor glands: a correlation in postmortem subjects D. M. CHISHOLM, J. P. WATERHOUSE, AND D. K. MASON From the Department of Oral
J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 690-694 Lymphocytic sialadenitis in the major and minor glands: a correlation in postmortem subjects D. M. CHISHOLM, J. P. WATERHOUSE, AND D. K. MASON From the Department of Oral
Wilms' tumour and renal dysplasia: an hypothesis
 J Clin Pathol 1982;35:1069-1073 Wilms' tumour and renal dysplasia: an hypothesis HB MARSDEN, W LAWLER* From the Royal Manchester Children's Hospital, Manchester M27 I HA and the *Department of Pathology,
J Clin Pathol 1982;35:1069-1073 Wilms' tumour and renal dysplasia: an hypothesis HB MARSDEN, W LAWLER* From the Royal Manchester Children's Hospital, Manchester M27 I HA and the *Department of Pathology,
The Nature and Origin of Proliferated Bile Ductules in Alcoholic Liver Disease
 The Nature and Origin of Proliferated Bile Ductules in Alcoholic Liver Disease TOSHIKAZU UCHIDA, M.D. AND ROBERT L. PETERS, M.D. Proliferation of bile ductules is commonly seen in expanded portal tracts
The Nature and Origin of Proliferated Bile Ductules in Alcoholic Liver Disease TOSHIKAZU UCHIDA, M.D. AND ROBERT L. PETERS, M.D. Proliferation of bile ductules is commonly seen in expanded portal tracts
Liver histopathology of the hepatitis A virus infection: a comparison with hepatitis type B and
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36:65-654 Liver histopathology of the hepatitis A virus infection: a comparison with hepatitis type B and non-a, non-b* PETER KRYGER, PER CHRISTOFFERSEN From the Enterovirus and Rubella
J Clin Pathol 1983;36:65-654 Liver histopathology of the hepatitis A virus infection: a comparison with hepatitis type B and non-a, non-b* PETER KRYGER, PER CHRISTOFFERSEN From the Enterovirus and Rubella
LIVER DISEASES. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
Interpretation of Biopsy Findings in the Transplant Liver
 Interpretation of Biopsy Findings in the Transplant Liver Kirk D. Jones, MD and Linda D. Ferrell, MD W i several thousand liver transplants being performed each year and many patients being managed in
Interpretation of Biopsy Findings in the Transplant Liver Kirk D. Jones, MD and Linda D. Ferrell, MD W i several thousand liver transplants being performed each year and many patients being managed in
Banff Schema for Grading Liver Allograft Rejection: Utility in Clinical Practice
 Banff Schema for Grading Liver Allograft Rejection: Utility in Clinical Practice Donald G. Ormonde,* W. Bastiaan de Boer, Anthony Kierath, Roger Bell, Keith B. Shilkin, Anthony K. House, Gary P. Jeffrey,*,
Banff Schema for Grading Liver Allograft Rejection: Utility in Clinical Practice Donald G. Ormonde,* W. Bastiaan de Boer, Anthony Kierath, Roger Bell, Keith B. Shilkin, Anthony K. House, Gary P. Jeffrey,*,
Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
Annals of RSCB Vol. XV, Issue 1
 AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
Disappearance of hepatic parenchymal nerves in
 Gut, 1992, 33, 87-91 87 LIVER, BILIARY, AND PANCREAS University of Newcastle upon Tyne, School of Pathological Sciences, Division of Pathology, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne J A Lee Q Ahmed
Gut, 1992, 33, 87-91 87 LIVER, BILIARY, AND PANCREAS University of Newcastle upon Tyne, School of Pathological Sciences, Division of Pathology, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne J A Lee Q Ahmed
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
Autoimmune hepatitis
 Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Liver and gall bladder curriculum for ST1, presented at Northern block teaching, January 2017.
 Liver and gall bladder curriculum for ST1, presented at Northern block teaching, January 2017. 1 The 2015 RCPath Stage A curriculum for hepatobiliary pathology and gall bladder. 2 The stage A curriculum
Liver and gall bladder curriculum for ST1, presented at Northern block teaching, January 2017. 1 The 2015 RCPath Stage A curriculum for hepatobiliary pathology and gall bladder. 2 The stage A curriculum
Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk. 123, , 1981
 323 Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk. 123, 323-327, 1981 Department of Veterinary Patho1ogy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht, The Netherlands l Institute of Animal Patho1ogy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine,
323 Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk. 123, 323-327, 1981 Department of Veterinary Patho1ogy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht, The Netherlands l Institute of Animal Patho1ogy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine,
No evidence of C4d association with AMR However, C3d and AMR correlated well
 C4d positivity Poor prognostic factor Reversal to C4d negativity did not change prognosis, with current therapy Prognostic factor for CAV Variable time line for CAV/death No correlation with cellular rejection
C4d positivity Poor prognostic factor Reversal to C4d negativity did not change prognosis, with current therapy Prognostic factor for CAV Variable time line for CAV/death No correlation with cellular rejection
Perivenular Fibrosis in Alcoholic Liver Injury: Ultrastructure and Histologic Progression
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1982;83:777-85 Perivenular Fibrosis in Alcoholic Liver Injury: Ultrastructure and Histologic Progression MASAYUKI NAKANO, THERESA M. WORNER, and CHARLES S. LIEBER Alcohol Research and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1982;83:777-85 Perivenular Fibrosis in Alcoholic Liver Injury: Ultrastructure and Histologic Progression MASAYUKI NAKANO, THERESA M. WORNER, and CHARLES S. LIEBER Alcohol Research and
Steatohepatitic Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a Morphologic Indicator of Associated Metabolic Risk Factors
 Steatohepatitic Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a Morphologic Indicator of Associated Metabolic Risk Factors A Study From India Deepali Jain, MD, DNB; Nabeen C. Nayak, MD, FRCPath; Vinay Kumaran, MS, MCh; Sanjiv
Steatohepatitic Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a Morphologic Indicator of Associated Metabolic Risk Factors A Study From India Deepali Jain, MD, DNB; Nabeen C. Nayak, MD, FRCPath; Vinay Kumaran, MS, MCh; Sanjiv
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION
 HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis
 Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
GINGIVAL VASCULAR BASEMENT MEMBRANE CHANGES IN DIABETES MELLITUS
 GINGIVAL VASCULAR BASEMENT MEMBRANE CHANGES IN DIABETES MELLITUS * Dr. Giju George Baby, ** Dr. Sheeba Padiyath Abstract Diabetes mellitus is a heterogenous primary disorder of carbohydrate metabolism
GINGIVAL VASCULAR BASEMENT MEMBRANE CHANGES IN DIABETES MELLITUS * Dr. Giju George Baby, ** Dr. Sheeba Padiyath Abstract Diabetes mellitus is a heterogenous primary disorder of carbohydrate metabolism
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
(C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes
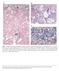 (A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
(A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER
 HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles
 J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 481-485 Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles and small arteries in infancy S. R. KENDEEL AND J. A. J. FERRIS' From the Department ofpathology, University of Newcastle
J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 481-485 Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles and small arteries in infancy S. R. KENDEEL AND J. A. J. FERRIS' From the Department ofpathology, University of Newcastle
Original Article. Spontaneous Healing of Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Vol. 12 No. 2 April 2005 Original Article Rie Horii 1, 3, Futoshi Akiyama 1, Fujio Kasumi 2, Morio Koike 3, and Goi Sakamoto 1 1 Department of Breast Pathology, the Cancer Institute of the
Breast Cancer Vol. 12 No. 2 April 2005 Original Article Rie Horii 1, 3, Futoshi Akiyama 1, Fujio Kasumi 2, Morio Koike 3, and Goi Sakamoto 1 1 Department of Breast Pathology, the Cancer Institute of the
Plan. Sarcoidosis 21/07/2017. Sarcoidosis Liver involvement. Sarcoidosis GI involvement. Sarcoidosis Diagnosis
 Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia. Shannon Martinson, Feb
 Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia Shannon Martinson, Feb 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case #1 Signalment and History: 6-month old feeder lamb found dead on pasture
Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia Shannon Martinson, Feb 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case #1 Signalment and History: 6-month old feeder lamb found dead on pasture
Neal S. Goldstein, MD, 1 Anjina Soman, MD, 1 and Stuart C. Gordon, MD 2. Abstract
 Anatomic Pathology / DISTINGUISHING PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS FROM AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Portal Tract Eosinophils and Hepatocyte Cytokeratin 7 Immunoreactivity Helps Distinguish Early-Stage, Mildly Active
Anatomic Pathology / DISTINGUISHING PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS FROM AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Portal Tract Eosinophils and Hepatocyte Cytokeratin 7 Immunoreactivity Helps Distinguish Early-Stage, Mildly Active
Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association
 CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
Ordering Physician. Collected REVISED REPORT. Performed. IgG IF, Renal MCR. Lambda IF, Renal MCR. C1q IF, Renal. MCR Albumin IF, Renal MCR
 RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
Case Report. A Surgical Case of Venous Aneurysm of the Cephalic Vein. with Unique Clinicopathological Findings for Venous Dissection
 Case Report A Surgical Case of Venous Aneurysm of the Cephalic Vein with Unique Clinicopathological Findings for Venous Dissection Takashi Kobata, 1 Sohsuke Yamada, 2,3* Ken-ichi Mizutani, 2 Nozomu Kurose,
Case Report A Surgical Case of Venous Aneurysm of the Cephalic Vein with Unique Clinicopathological Findings for Venous Dissection Takashi Kobata, 1 Sohsuke Yamada, 2,3* Ken-ichi Mizutani, 2 Nozomu Kurose,
There is extensive literature addressing both the histopathologic
 Approach to the Liver Biopsy in the Patient With Chronic Low-Level Aminotransferase Elevations Pathologists sometimes encounter a liver biopsy from an asymptomatic patient with unexplained low-level parenchymal
Approach to the Liver Biopsy in the Patient With Chronic Low-Level Aminotransferase Elevations Pathologists sometimes encounter a liver biopsy from an asymptomatic patient with unexplained low-level parenchymal
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
New insights into fatty liver disease. Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College
 New insights into fatty liver disease Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Prevalence of NASH Global prevalence of NAFLD is 25% with highest prevalence in the Middle
New insights into fatty liver disease Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Prevalence of NASH Global prevalence of NAFLD is 25% with highest prevalence in the Middle
UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions
 2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma
 Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Invited Re vie W. Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic liver diseases
 Histol Histopathol (1 998) 13: 1077-1 087 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic
Histol Histopathol (1 998) 13: 1077-1 087 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic
PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
 Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
Cirrhosis: Morphologic Dynamics for the NonMorphologist
 CLINICAL SEMINAR Cirrhosis: Morphologic Dynamics for the NonMorphologist Henry D. Appelman, MD Cirrhosis is an irreversible end-stage liver disease characterized by septate scars dividing a distorted liver
CLINICAL SEMINAR Cirrhosis: Morphologic Dynamics for the NonMorphologist Henry D. Appelman, MD Cirrhosis is an irreversible end-stage liver disease characterized by septate scars dividing a distorted liver
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology. Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta )
 Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome due to herbal ingestion in South African children - An 8 year review
 UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome due to herbal ingestion in South African children - An 8 year review L. Hendricks, A. Meyer, A. Terblanche Dept of paediatric gastroenterology
UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome due to herbal ingestion in South African children - An 8 year review L. Hendricks, A. Meyer, A. Terblanche Dept of paediatric gastroenterology
Special stains in liver pathology
 Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
Liver cell dysplasia: a premalignant condition
 Liver cell dysplasia: a premalignant condition P. P. ANTHONY, C. L. VOGEL, AND L. F. BARKER J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 217-223 From The Bland-Sutton Institute ofpathology, The Middlesex Hospital Medical
Liver cell dysplasia: a premalignant condition P. P. ANTHONY, C. L. VOGEL, AND L. F. BARKER J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 217-223 From The Bland-Sutton Institute ofpathology, The Middlesex Hospital Medical
Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
AASLD: Boston Rob Goldin
 AASLD: Boston 2014 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Autoimmune hepatitis 31 Does genuine acute autoimmune hepatitis have a better prognosis? 32 Patients with Autoimmune Hepatitis and Advanced Disease
AASLD: Boston 2014 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Autoimmune hepatitis 31 Does genuine acute autoimmune hepatitis have a better prognosis? 32 Patients with Autoimmune Hepatitis and Advanced Disease
Fibrosis and other histological features in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a statistical model
 J Clin Pathol 1996;49:465-469 Department of Medicine, University of Cambridge School of Clinical Medicine, Addenbrooke's NHS Trust, Cambridge CB2 2QQ V S Wong G J M Alexander Departnent of Histopathology
J Clin Pathol 1996;49:465-469 Department of Medicine, University of Cambridge School of Clinical Medicine, Addenbrooke's NHS Trust, Cambridge CB2 2QQ V S Wong G J M Alexander Departnent of Histopathology
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Pages January 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact actor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.156 umen of the Appendix Author Swayam Jothi
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact actor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.156 umen of the Appendix Author Swayam Jothi
THE INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL FACTORS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE PERIPHERAL ARTERIES AND
 J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 199. THE INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL FACTORS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE PERIPHERAL ARTERIES AND THE LOCALIZATION OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS BY From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University,
J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 199. THE INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL FACTORS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE PERIPHERAL ARTERIES AND THE LOCALIZATION OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS BY From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University,
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
