Disappearance of hepatic parenchymal nerves in
|
|
|
- Christiana Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut, 1992, 33, LIVER, BILIARY, AND PANCREAS University of Newcastle upon Tyne, School of Pathological Sciences, Division of Pathology, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne J A Lee Q Ahmed J E Hines A D Burt Correspondence to: Dr A D Burt, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, School of Pathological Sciences, Division of Pathology, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne NE1 4LP. Accepted for publication 4 March 1991 Disappearance of hepatic parenchymal nerves in human liver cirrhosis J A Lee, Q Ahmed, J E Hines, A D Burt Abstract The normal human liver receives a substantial autonomic innervation that is thought to subserve motor, metabolic, and sensory functions. In this study an antibody to a neural axoplasmic protein (PGP 9.5) was used to visualise autonomic nerves in tissue from normal, precirrhotic, and cirrhotic livers. Nerve fibres were readily identified in the parenchyma and portal tracts of normal livers, and in those where the histological diagnosis was non-specific reactive hepatitis or acute liver injury. In precirrhotic and cirrhotic livers nerves in portal tracts and fibrous septae remained prominent, but the parenchymal innervation was reduced in precirrhotic livers and was absent from regenerating nodules in established cirrhosis. The causes and functional consequences of this parenchymal denervation in cirrhosis remain to be established. The liver is innervated by both branches of the autonomic nervous system, receiving sympathetic input via the coeliac plexus and parasympathetic input mainly from the vagus. Most of these nerves enter the liver in association with blood vessels and bile ducts, and for many years it was assumed that motor functions related to these structures were the sole function of the hepatic nerves. It is now known, however, that in addition to blood vessels and bile ducts, the liver parenchyma also receives a substantial innervation in many species. Furthermore, there is now strong evidence that these hepatic parenchymal nerves have important metabolic and sensory, as well as motor functions."a Metabolic effects include direct actions on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, while sensory roles include osmoreception, baroreception, and possibly also responses to the concentrations of various metabolites present in portal blood. Although some species - for example the rat' - have only a scanty parenchymal innervation, the liver of primates,6 including humans,4 has a high density of parenchymal nerves, which may thus have important modulatory roles in normal liver function. In developing and established cirrhosis, there are gross structural changes in liver tissue, as well as functional abnormalities. Since alterations in the hepatic innervation may have a role to play in these problems, we have investigated Histological diagnoses Diagnosis Normal/non-specific reactive changes 8 Acute liver injury: Extrahepatic biliary obstruction 6 Acute hepatitis 2 Intrahepatic cholestasis 5 Precirrhotic chronic liver disease: Alcoholic hepatitis with perivenular fibrosis 6 Primary biliary cirrhosis stage I or II 5 Established cirrhosis: Alcoholic cirrhosis 6 Primary biliary cirrhosis 7 Haemochromatosis 3 Autoimmune liver disease 2 Cryptogenic cirrhosis 4 Total 54 No ofcases the distribution of hepatic nerves in samples obtained from normal and diseased human livers. The results show that hepatic parenchymal nerves are reduced in precirrhotic liver disease and are absent from regenerating hepatic nodules in established cirrhosis. Methods SPECIMENS Wedge biopsy specimens were obtained at laparotomy from patients with suspected liver disease. Tissue was fixed in 10% buffered formalin and processed for paraffin wax embedding. In some cases (n=6) normal liver was obtained from cadaveric renal transplant donors. This tissue was perfusion fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde in 0-1 mmol/l phosphate buffer through vessel openings at the cut surface and was then processed for paraffin wax embedding. The histological diagnoses of the samples (obtained from sections stained with routine haematoxylin and eosin) are shown in the Table. IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY A peroxidase-antiperoxidase technique was used with the anti-pgp 9-5 antibody. Deparaffinised sections (3 rim) were treated in the following way: (a) incubated in 0-5% hydrogen peroxide in methanol; (b) washed in tap water, then incubated with 0-1% porcine trypsin.(sigma, UK; T8128) in 0-1% CaCl2, ph 7-8, 37 C for 10 minutes; (c) washed in tap water, then Tris buffered saline (TBS); (d) incubated with normal swine saline (NSS)/TBS for five minutes,
2 88 Lee, Ahmed, Hines, Burt Figure 1: Normal liver. (A) PGP 9.5 immunoreactive fibres and bundles are seen with this large portal tract (arrows) (magnification x25). (B) Abundant intrasinusoidal PGP 9 5 immunoreactive fibres are seen (magnification x 150). Fig IA Fig lb then incubated with rabbit polyclonal anti-pgp 9-5 (Ultraclone, UK; dilution 1:20 in 20% NSS/ TBS), for 30 minutes at room temperature; (e) rinsed in TBS, then incubated with swine anti-rabbit immunoglobulin (Dako - dilution 1/20 in NSS/TBS) for 30 minutes at room temperature, and finally incubated with peroxidase-antiperoxidase complex (Dakopatts, Denmark; dilution 1:50 in NSS/TBS) for 30 minutes at room temperature; (f) rinsed in TBS, then incubated with 3,3'diaminobenzidine in the presence of hydrogen peroxide; (g) washed in tap water, counterstained with haematoxylin and mounted in DPX. As negative controls, sections were incubated with normal rabbit serum in NSS/TBS in place of anti-pgp 9-5; no staining was observed in these controls. Results NERVE FIBRES IN NORMAL LIVER Nerve fibres and bundles were prominent within the portal tracts (Fig IA). They were mainly identified closely applied to hepatic artery and portal vein branches and only occasionally around bile duct radicles. In confirmation of previous studies,4 fibres were also seen within the liver parenchyma (Fig ib). These fibres were seen to run along the sinusoidal walls within the
3 Disappearance ofhepatic parenchymal nerves in human livercirrhosis 89 Figure 2: Cirrhotic liver. (A) PGP 9-5 immunoreactive fibres are seen within thefibrous septa and residual portal tracts, but are absentfrom the regenerative nodules (N) (original magnification x20). (B) Higher power field shows absence oj intrasinusoidal nerve fibres. Fibres are seen within the fibrous septum (arrow) (original magnification x 100). Fig2A I' Fig 2B space of Disse and were also observed between individual hepatocytes. The parenchymal nerves were generally most abundant within zone 1 (periportal) of the acinus, but were also frequently seen in zones II and III and within the walls of terminal hepatic vein branches. NERVE FIBRES IN DISEASED LIVER In wedge biopsy specimens showing non-specific reactive changes or evidence of acute cholestatic liver injury, the density and distribution of parenchymal nerve fibres were indistinguishable from normal livers. In the cases of acute hepatitis studied, there was an apparent increase in parenchymal fibres, but the histological changes included the presence of appreciable bridging hepatic necrosis. In precirrhotic alcoholic liver disease and in stage I or II (precirrhotic) primary biliary cirrhosis there was a reduction in the numbers of parenchymal nerve fibres seen. In two cases of alcholic hepatitis and three cases of early primary biliary cirrhosis, only occasional fibres could be observed in periportal zones. In the remaining six cases of precirrhotic chronic liver disease, parenchymal fibres could be identified but were much less abundant than normal liver. The most dramatic change, however, was seen in established cirrhosis. Irrespective of the aetiology of the cirrhosis, whether caused by
4 90 Lee, Ahmed, Hines, Burt alcohol, primary biliary cirrhosis, haemachromatosis, or autoimmune chronic liver disease, nerve fibres were absent from the regenerating nodules of hepatic tissue in all but three cases (Fig 2, A and B). An internal control was present in cirrhotic livers in that nerve fibres were readily identified within the fibrous septa separating regenerative nodules (Fig 2, A and B). Indeed, in many cases, nerves within the fibrous septa were particularly prominent, in spite of a complete absence of parenchymal fibres. Discussion In this study we have used an antibody to PGP 9 5 to localise autonomic nerve fibres in normal and diseased human livers. Initial studies7 showed that with our material this antibody detected a greater number of intrahepatic nerve fibres in normal liver than antibodies to neurofilament, S 100 protein, or neuron specific enolase. PGP 9-5 has recently been shown to be a ubiquitin carboxy terminal peptidase which is abundantly expressed by both peripheral and central nerve fibres and is present within the axoplasm.8 It is thus an excellent marker for small, possibly unsheathed neurons, and has been used for the detection of nerves in several tissues.9 In normal liver we observed nerves within the portal tracts, as expected, but the presence of nerves in association with terminal hepatic vein branches suggests that some fibres may also enter the liver along the vena cava and major hepatic veins. Parenchymal nerves were easily identified in normal human livers. There has previously been little information on the changes in hepatic innervation in liver disease. In the rat, changes in the distribution of intrahepatic nerves after carbon tetrachloride induced necrosis10 and partial hepatectomy" have been noted, and it has also been suggested that nerves have a role in the control of regenerative activity in hepatocytes."1 However, as mentioned earlier, the normal rat liver has only a scanty parenchymal innervation,5 so the relevance of these observations to human disease is unclear. In human liver, one previous study'3 has shown that in chronic active hepatitis there is an apparent proliferation of nerve fibres within developing fibrous septa and a reduction in the number of fibres within developing nodules. In the present study, we have confirmed that in developing cirrhosis caused by alcohol or primary biliary cirrhosis the numbers of parenchymal nerve fibres are reduced. We have also shown that in established cirrhosis, irrespective of aetiology, parenchymal nerve fibres are absent from regenerating hepatic nodules. These observations raise two interesting questions: what are the causes of nerve fibre loss in cirrhosis and what are the possible functional consequences? The mechanisms responsible for the loss of parenchymal nerve fibres in cirrhosis are as yet undetermined. Miyazawa et al'3 suggested that nerve fibres might degenerate in evolving cirrhosis as part of the primary liver injury. Our finding of an essentially normal distribution of parenchymal nerve fibres in various forms of acute liver injury suggests, however, that there are likely to be other mechanisms. The increased parenchymal nerve fibre density in our case of acute hepatitis with bridging necrosis was probably caused by the effects of parenchymal collapse rather than true nerve proliferation. In chronic liver disease, it is possible that parenchymal nerves may be damaged by progressive fibrosis within the space of Disse. It seems unlikely, however, that this is entirely responsible for the lack of parenchymal nerves in cirrhosis, in view of the relative abundance of nerves in the fibrous septa. A cardinal feature of established cirrhosis is the presence of regenerative parenchymal nodules, and it is possible that this abnormal mode of growth is an important factor contributing to sinusoidal denervation. We are currently studying the relative roles offibrosis and nodular regeneration in parenchymal denervation using sequential biopsy specimens from patients with progressive liver disease (primary biliary cirrhosis and alcoholic liver disease) and quantitation of nerve density using image analysis. It seems that although there are sufficient growth factors to stimulate hepatocyte and sinusoidal cell proliferation in cirrhotic liver, ingrowth of nerves into the regenerative nodules is not stimulated. In normal livers, adrenergic innervation seems to play an important role in regeneration.'2 It remains to be established whether the lack of parenchymal innervation in cirrhosis contributes to abnormal regenerative growth patterns. The functional consequences of hepatic parenchymal denervation in cirrhosis also remain to be established. Clearly, intact hepatic innervation is not an absolute requirement for adequate function, as is evidenced by the success of liver transplantation as organ replacement therapy. Also gross metabolic derangements - for example of carbohydrate metabolism which has been intensively studied - are rare even in advanced liver disease.'4 This may, however, be partly due to compensation by other organs. The parenchymal denervation seen in cirrhosis means that afferent - that is, sensory - as well as efferent neural function will be absent in cirrhosis. Since sensory functions are thought to include baroreception, osmoreception, and metabolic sensors, it is possible that denervation may contribute to circulatory disturbances in the liver, and to systemic fluid and electrolyte abnormalities. Further work will be necessary to establish the relative functional importance of changes in the parenchymal innervation in developing and established cirrhosis. 1 Sawchenko PE, Friedman MI. Sensory functions of the liver - a review. AmJI Physiol 1979; 236: R Lautt WW. Hepatic nerves: a review of their functions and effects. Canj Physiol Pharmacol 1980; 58: Friedman MI. Hepatic nerve function. In: Arias IM, Jakoby WB, Popper H, Schacter D, Shafritz DA, eds. The liver: biology and pathobiology. New York: Raven Press, Bioulac-Sage P, Lafon ME, Saric J, Balabaud C. Nerves and perisinusoidal cells in human liver. J Hepatol 1990; 10: Burt AD, Tiniakos D, MacSween RNM, Griffiths MR, Wisse E, Polak JM. Localization of adrenergic and neuropeptide tyrosine-containing nerves in the mammalian liver. Hepatology 1989; 9: Forssmann WG, Ito S. Hepatocyte innervation in primates. J'CellBiol 1977; 74: Burt AD, Ahmed Q, Lee JA. Innervation of human hepatic sinusoids: alterations in liver disease. Hepatol Rep Lit Rev 1990; 20: Section 6. 8 Wilkinson KD, Lee SK, Deshpande 5, Duerksen-Hughes P, Boss JM, Pohl J. The neuron-specific protein PGP 9-5 is a
5 Disappearance ofhepaticparenchymal nerves in human liver cirrhosis 91 ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase. Science 1989; 246: Wilson POG, Barber PC, Hamid QA. The immunolocalisation of protein gene product 9 5 using rabbit polyclonal and mouse monoclonal antibodies. Br J Exp Pathol 1988; 69: Ungvary GY, Donath T. Changes of the peripheral autonomic nervous system in altered internal environment. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 1980; 94: Pietroletti R, Chamuleau RAFM, Speranza V, Lygidakis NJ. Immunocytochemical study of the hepatic innervation in the rat after partial hepatectomy. HistochemJ 1987; 19: Aschrif S, Gillespie JS, Pollock D. The effects of drugs or denervation on thymidine uptake into rat regenerating liver. EurJ Pharmacol 1974; 29: Miyazawa Y, Fukuda Y, Imoto M, Koyama Y, Nagura H. Iomnunohistochemical studies on the distribution of nerve fibres in chronic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 1988; 83: Alberti KGMM, Johnston DG, Taylor R. Carbohydrate metabolism in liver disease. In: Wright R, Millward- Sadler GH,. Alberti KGMM, Karran S, eds. Liver and biliary disease. 2nd ed. London: Balliere-Tindall, 1985:
Decreased Hepatic Nerve Fiber Innervation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 1, No. 2, December 2007, pp. 165-170 original article Decreased Hepatic Nerve Fiber Innervation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Soon Woo Nam*, Hyun Joo Song, Su Jung Back, Tae Hun
Gut and Liver, Vol. 1, No. 2, December 2007, pp. 165-170 original article Decreased Hepatic Nerve Fiber Innervation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Soon Woo Nam*, Hyun Joo Song, Su Jung Back, Tae Hun
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis. Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K.
 Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Paneth Cells. Road Map to the Finish. No Review this Friday. Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs. Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I
 Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Hepatic vein lesions in alcoholic liver disease:
 Hepatic vein lesions in alcoholic liver disease: retrospective biopsy and necropsy study AD BURT, RNM MacSWEEN University Department of Pathology Western Infirmary, Glasgow J Clin Pathol 1986;39:63-67
Hepatic vein lesions in alcoholic liver disease: retrospective biopsy and necropsy study AD BURT, RNM MacSWEEN University Department of Pathology Western Infirmary, Glasgow J Clin Pathol 1986;39:63-67
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
Immunolocalisation of a interferon in liver disease
 J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1065-1069 Immunolocalisation of a interferon in liver disease C G G SUTHERLAND, A M T AL-BADRI, A G HOWATSON, M A FARQUHARSON, A K FOULIS From the Department of Pathology, Royal Infirmary,
J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1065-1069 Immunolocalisation of a interferon in liver disease C G G SUTHERLAND, A M T AL-BADRI, A G HOWATSON, M A FARQUHARSON, A K FOULIS From the Department of Pathology, Royal Infirmary,
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER
 HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder
 Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association
 CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
Value of copper-associated protein in diagnostic assessment of liver biopsy
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36: 18-23 Value of copper-associated protein in diagnostic assessment of liver biopsy PAOLO GUARASCIO, FRANCES YENTIS, UGUR CEVIKBAS, BERNARD PORTMANN, ROGER WILLIAMS From the Liver
J Clin Pathol 1983;36: 18-23 Value of copper-associated protein in diagnostic assessment of liver biopsy PAOLO GUARASCIO, FRANCES YENTIS, UGUR CEVIKBAS, BERNARD PORTMANN, ROGER WILLIAMS From the Liver
Anaesthesia For Liver Resection: The Physiology
 Anaesthesia For Liver Resection: The Physiology M C Bellamy, St James s Hospital, Leeds The anaesthetic issues relating to patients undergoing liver resection need to be considered hand in hand with the
Anaesthesia For Liver Resection: The Physiology M C Bellamy, St James s Hospital, Leeds The anaesthetic issues relating to patients undergoing liver resection need to be considered hand in hand with the
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver
 Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ WELCOME! Dr Boute is the coordinator Course
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ WELCOME! Dr Boute is the coordinator Course
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids. Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada
 Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Supplemental Tables. Parasitic Schistosomiasis increase < 1. Genetic Hemochromatosis increase < 1. autoimmune Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) increase < 1
 Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1 Various etiologies of liver cirrhosis and their association with liver stiffness and AST/ALT ratio Disease category Cause Example LS AST/ALT Inflammatory liver
Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1 Various etiologies of liver cirrhosis and their association with liver stiffness and AST/ALT ratio Disease category Cause Example LS AST/ALT Inflammatory liver
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
The Groningen hypothermic liver perfusion system for improved preservation in organ transplantation Plaats, Arjan van der
 University of Groningen The Groningen hypothermic liver perfusion system for improved preservation in organ transplantation Plaats, Arjan van der IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen The Groningen hypothermic liver perfusion system for improved preservation in organ transplantation Plaats, Arjan van der IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
-sheet 3. -Waseem Alhaj. Maha Shomaf
 -sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
-sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology
 REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
Topics and aims. Introduction. Metabolism and Excretion
 Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel. Basel,
 Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D
 BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free & University College Medical School Thurs 10
BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free & University College Medical School Thurs 10
carcinoembryonic antigen
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 219-224 Granular cell myoblastoma: positive staining for carcinoembryonic antigen SAMI SHOUSHA AND THEO LYSSIOTIS From the Departments of Histopathology, The Charing
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 219-224 Granular cell myoblastoma: positive staining for carcinoembryonic antigen SAMI SHOUSHA AND THEO LYSSIOTIS From the Departments of Histopathology, The Charing
PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features?
 22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
Histological subclassification of cirrhosis based on histological haemodynamic correlation
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Histological subclassification of cirrhosis based on histological haemodynamic correlation M. KUMAR*, P. SAKHUJA, A.KUMAR*,N.MANGLIK*,A.CHOUDHURY*,S.HISSAR*,A.RASTOGI
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Histological subclassification of cirrhosis based on histological haemodynamic correlation M. KUMAR*, P. SAKHUJA, A.KUMAR*,N.MANGLIK*,A.CHOUDHURY*,S.HISSAR*,A.RASTOGI
LIVER DISEASES. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
liver disease Collagen synthesis Collagen synthesis may readily be studied in mouse
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1977), 36, Supplement p. 29 Collagen deposition in liver disease J. O'D. McGEE From the Department ofpathology, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford Collagen forms a small component of the total
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1977), 36, Supplement p. 29 Collagen deposition in liver disease J. O'D. McGEE From the Department ofpathology, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford Collagen forms a small component of the total
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013
 Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
Liver Transplantation
 1 Liver Transplantation Department of Surgery Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine Kim Myoung Soo M.D. ysms91@wonju.yonsei.ac.kr http://gs.yonsei.ac.kr History Development of Liver transplantation
1 Liver Transplantation Department of Surgery Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine Kim Myoung Soo M.D. ysms91@wonju.yonsei.ac.kr http://gs.yonsei.ac.kr History Development of Liver transplantation
Cirrhosis: Morphologic Dynamics for the NonMorphologist
 CLINICAL SEMINAR Cirrhosis: Morphologic Dynamics for the NonMorphologist Henry D. Appelman, MD Cirrhosis is an irreversible end-stage liver disease characterized by septate scars dividing a distorted liver
CLINICAL SEMINAR Cirrhosis: Morphologic Dynamics for the NonMorphologist Henry D. Appelman, MD Cirrhosis is an irreversible end-stage liver disease characterized by septate scars dividing a distorted liver
Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes. Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD
 Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Parenchymal Cells -Hepatocytes -Cholangiocytes
Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Parenchymal Cells -Hepatocytes -Cholangiocytes
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary
 2015 69 3 137144 Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary Cirrhosis a a,b* a a a a a,b a a a,b c d
2015 69 3 137144 Aberrant Expression of Keratin 7 in Hepatocytes as a Predictive Marker of Rapid Progression to Hepatic Failure in Asymptomatic Primary Biliary Cirrhosis a a,b* a a a a a,b a a a,b c d
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis
 Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
Liver Failure. The most severe clinical consequence of liver disease is liver failure:
 Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders
 Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
Histology of the liver, and the biliary system
 Histology of the liver, and the biliary system Dr. Zsuzsanna Tóth Semmelweis University Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology http://www.mgtowforums.com/forums/lads-night-inn/3969-give-your-liver-art.html
Histology of the liver, and the biliary system Dr. Zsuzsanna Tóth Semmelweis University Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology http://www.mgtowforums.com/forums/lads-night-inn/3969-give-your-liver-art.html
Liver Pathology in the 0bese
 Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver, Pancreas and Gall Bladder Pathology
 Liver, Pancreas and Gall Bladder Pathology SCBM342 Systemic Pathology Witchuda Payuhakrit, Ph.D. (Pathobiology) Email: witchuda.pay@mahidol.ac.th Objectives 1. Understand etiology and pathogenesis of common
Liver, Pancreas and Gall Bladder Pathology SCBM342 Systemic Pathology Witchuda Payuhakrit, Ph.D. (Pathobiology) Email: witchuda.pay@mahidol.ac.th Objectives 1. Understand etiology and pathogenesis of common
Ms Amanda Clements ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE LIVER. Pre-Conference Nurse s Course. Plymouth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 12/12/2014
 Pre-Conference Nurse s Course in partnership with Ms Amanda Clements Plymouth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE LIVER Amanda Clements Nurse Consultant Hepatology 1 Anatomy Largest
Pre-Conference Nurse s Course in partnership with Ms Amanda Clements Plymouth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE LIVER Amanda Clements Nurse Consultant Hepatology 1 Anatomy Largest
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
LIVER & SPLEEN. Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra..
 LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
LIVER PATHOLOGY. Thursday 28 th November 2013
 LIVER PATHOLOGY Thursday 28 th November 2013 Liver biopsy assessment of steatosis Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free Hospital RIBA, London Thursday 28th November 2013 NAFLD didn t exist before 2001 and liver
LIVER PATHOLOGY Thursday 28 th November 2013 Liver biopsy assessment of steatosis Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free Hospital RIBA, London Thursday 28th November 2013 NAFLD didn t exist before 2001 and liver
Vasculature and innervation of the heart. A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department
 Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY
 2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
Diagnostic Paediatric Pathology
 Annals of Diagnostic Paediatric Pathology 2006, 10(1 2):37 42 Copyright by Polish Paediatric Pathology Society Annals of Comparison of histological changes in liver biopsy specimens in patients with biliary
Annals of Diagnostic Paediatric Pathology 2006, 10(1 2):37 42 Copyright by Polish Paediatric Pathology Society Annals of Comparison of histological changes in liver biopsy specimens in patients with biliary
National Liver EQA Scheme. Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004
 National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Early Heterogeneous Enhancement of the Liver: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings and Clinical Significance
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:242 249 (2004) Original Research Early Heterogeneous Enhancement of the Liver: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings and Clinical Significance Masayuki Kanematsu,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:242 249 (2004) Original Research Early Heterogeneous Enhancement of the Liver: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings and Clinical Significance Masayuki Kanematsu,
Pathology Primer: Common Liver Biopsy Findings in Patients Who Have Recently Undergone Liver Transplant or Resection
 REVIEW Pathology Primer: Common Liver Biopsy Findings in Patients Who Have Recently Undergone Liver Transplant or Resection Oyedele A. Adeyi, M.D., F.C.A.P., F.R.C.P.C. Two general sources of liver biopsy
REVIEW Pathology Primer: Common Liver Biopsy Findings in Patients Who Have Recently Undergone Liver Transplant or Resection Oyedele A. Adeyi, M.D., F.C.A.P., F.R.C.P.C. Two general sources of liver biopsy
Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions
 2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure
 Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Liver Pathology Lab 1. Shannon Martinson, 2017
 Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL
 Lecture 2 ESS_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER - is the largest gland of
Lecture 2 ESS_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER - is the largest gland of
Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in
 J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease. Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC
 Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Hepatocelluar nodules in liver cirrhosis: hemodynamic evaluation (angiographyassisted CT) with special reference to multi-step hepatocarcinogenesis
 Abdominal Imaging ª The Author(s) 2011. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Published online: 26 January 2011 Abdom Imaging (2011) 36:264 272 DOI: 10.1007/s00261-011-9685-1 INVITED
Abdominal Imaging ª The Author(s) 2011. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Published online: 26 January 2011 Abdom Imaging (2011) 36:264 272 DOI: 10.1007/s00261-011-9685-1 INVITED
Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine
 Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System 6 th March, 2015 & 19 th March, 2015 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Autonomic Nervous System Role
Autonomic Nervous System 6 th March, 2015 & 19 th March, 2015 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Autonomic Nervous System Role
Mass Histology Service
 Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings
 6 Jan 2018 Vol 11 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings Simpal Gill, MD* Pathology Laboratory services, Houston Medical
6 Jan 2018 Vol 11 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings Simpal Gill, MD* Pathology Laboratory services, Houston Medical
PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target
 Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
hepatocellular carcinoma
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1124-1128 Incidence in South-west Scotland of hepatitis B surface antigen in the liver of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma M. L. TURBITT, R. S. PATRICK, R.
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1124-1128 Incidence in South-west Scotland of hepatitis B surface antigen in the liver of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma M. L. TURBITT, R. S. PATRICK, R.
CD56-immunostaining of the extrahepatic biliary tree as an indicator of clinical outcome in biliary atresia: a preliminary report
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 8; 5: 54-548 Original CD56-immunostaining of the extrahepatic as an indicator of clinical outcome in atresia: a preliminary report Tadao Okada, Tomoo Itoh, Fumiaki Sasaki,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 8; 5: 54-548 Original CD56-immunostaining of the extrahepatic as an indicator of clinical outcome in atresia: a preliminary report Tadao Okada, Tomoo Itoh, Fumiaki Sasaki,
Liver failure &portal hypertension
 Liver failure &portal hypertension Objectives: by the end of this lecture each student should be able to : Diagnose liver failure (acute or chronic) List the causes of acute liver failure Diagnose and
Liver failure &portal hypertension Objectives: by the end of this lecture each student should be able to : Diagnose liver failure (acute or chronic) List the causes of acute liver failure Diagnose and
Chronic Biliary Disease. Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths
 Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Evangelos Chartampilas Bioclinic Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece
 Evangelos Chartampilas Bioclinic Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece Hepatospecificcontrast agents Gadobenate dimeglumine (Multihance) Gadoxeticacid (Primovist) 3-5% liver uptake 50% liver uptake Hepatobiliary
Evangelos Chartampilas Bioclinic Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece Hepatospecificcontrast agents Gadobenate dimeglumine (Multihance) Gadoxeticacid (Primovist) 3-5% liver uptake 50% liver uptake Hepatobiliary
Expression of Galactin-3 in Chronic Hepatitis C: Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study
 Academic Journal of Cancer Research 10 (1): 05-09, 2017 ISSN 1995-8943 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajcr.2017.05.09 Expression of Galactin-3 in Chronic Hepatitis C: Histopathological and
Academic Journal of Cancer Research 10 (1): 05-09, 2017 ISSN 1995-8943 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajcr.2017.05.09 Expression of Galactin-3 in Chronic Hepatitis C: Histopathological and
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1
 Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Financial Disclosure
 Benign Liver Masses Adil Abdalla, MBBS Creighton University-CHI Health August 25, 2018 Financial Disclosure Nothing to disclose Financial Disclosure 1 Objectives To assess patients with benign liver tumors
Benign Liver Masses Adil Abdalla, MBBS Creighton University-CHI Health August 25, 2018 Financial Disclosure Nothing to disclose Financial Disclosure 1 Objectives To assess patients with benign liver tumors
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
Module 1: Part 3 The Nervous System 2016 The Neuroscience School Welcome to part 3 of module 1 where we look at how the nervous system is organized.
 Module 1: Part 3 The Nervous System Welcome to part 3 of module 1 where we look at how the nervous system is organized. By Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=10187018
Module 1: Part 3 The Nervous System Welcome to part 3 of module 1 where we look at how the nervous system is organized. By Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=10187018
Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) Case n 2 ( B 00 / 8249 ) Case n 3 ( B 98 / 8352 )
 Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
TREATMENT FOR HCC AND CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA. Shawn Pelletier, MD
 TREATMENT FOR HCC AND CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA Shawn Pelletier, MD Treatment for HCC Treatment strategies Curative first line therapy Thermal ablation vs Resection vs Transplant Other first line therapies TACE
TREATMENT FOR HCC AND CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA Shawn Pelletier, MD Treatment for HCC Treatment strategies Curative first line therapy Thermal ablation vs Resection vs Transplant Other first line therapies TACE
Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark
 Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark Study of Prognosis of PSC Difficulties: Disease is rare The duration of the course of disease may be very
Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark Study of Prognosis of PSC Difficulties: Disease is rare The duration of the course of disease may be very
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
H irschsprung s disease (HD) is a congenital disorder
 712 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The loss of calretinin expression indicates aganglionosis in Hirschsprung s disease I Barshack, E Fridman, I Goldberg, Y Chowers, J Kopolovic... See end of article for authors affiliations...
712 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The loss of calretinin expression indicates aganglionosis in Hirschsprung s disease I Barshack, E Fridman, I Goldberg, Y Chowers, J Kopolovic... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease
 Gut, 1968, 9, 193-198 Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease TEN FEIZI From the Department of Medicine, Royal Free Hospital, London The association of high gamma globulin levels with hepatic cirrhosis
Gut, 1968, 9, 193-198 Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease TEN FEIZI From the Department of Medicine, Royal Free Hospital, London The association of high gamma globulin levels with hepatic cirrhosis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
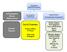 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
