APECED: monogenic autoimmune disease
|
|
|
- Martin Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APECED: monogenic autoimmune disease Pärt Peterson University of Tampere, Finland University of Tartu, Estonia
2 APS1 or APECED APS1 (autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1) or APECED (autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy) Autosomal recessive inheritance More prevalent in some populations such as Finns (1:25000), Iranian Jews (1:9000) and Sardinians (1:14400). Very high incidence (1/4400) reported in a small town Bassa del Grappa, in Northern Italy No HLA association Autoimmune regulator (AIRE) is a gene mutated in APECED
3 Clinical Features Endocrinopathies Hypoparathyreoidism Addison s disease Gonadal dysfunction Type 1 diabetes mellitus Autoimmune thyroiditis Autoimmune gastritis Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis Ectodermal dystrophies dental enamel nails alopecia vitiligo Autoimmune hepatitis Keratopathy
4 Candida infection and vitiligo of APS1 patient From Prof. Olle Kämpe, Uppsala University
5 APS1/APECED and APS2 are two different syndromes Disease components APS1 APS2 Addison s disease Hypoparathyroidism absent Chronic candidiasis absent Ectodermal dysplasia absent Autoimmune thyroid disease Type 1 diabetes Hypogonadism Alopecia Vitiligo Keratopathy absent Autoimmune hepatitis Pernicious anemia Chronic gastritis 6 11
6 Autoantigens in Addison s disease Steroid 17a-hydroxylase, P450c17 Steroid 21-hydroxylase, P450c21 Side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc Thomas Addison All three P450 enzymes are active in steroidogenesis in adrenal cortex. P450c21 is expressed only in adrenal cortex, P450c17 and P450scc are also expressed in gonads Krohn et al. Lancet 339: 770, 1992 Uibo et al. JCEM 78: 323, 1994
7 APS1/APECED autoantigens Autoantigen Prevalence % Steroid 21 hydroxylase (P450c21) 66 Side-chain cleavage enzyme (P450scc) 52 Steroid 17 alpha hydroxylase (P450c17) 44 Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) 51 Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65) 37 Histidine decarboxylase (HDC) 37 Cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSAD) 3.6 Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) 45 Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) 44 Thyroglobulin (TG) 36 Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) 36 Transcription factor SOX10 22 Cytochrome P4501A2 (P4501A2) 8 Tyrosine phosphatase-like protein IA-2 (IA-2) 7
8 AIRE protein N-terminal HSR domain: homodimerisation SAND domain: putative DNA binding PHD finger: transcriptional regulation Proline rich region LXXLL motif: binding to nuclear receptors Nagamine et al. Nat Genetics 17: 393, 1997 The Finnish-German Consortium. Nat Genetics 17: 399, 1997
9 Similarity to Nuclear Proteins Mi-2: TIF1: helicase, involved in chromatin remodelling, autoantigen in dermatomyositis transcriptional coactivator Sp100: interferon responsive, transcription activator, autoantigen in PBC, lymphoid restricted Sp140: homologous protein to Sp100, autoantigen in PBC
10 Expression in the Thymus The major AIRE expressing tissue is the thymus Lower levels of expression are seen in the fetal liver, spleen and lymph nodes In the thymus, AIRE is seen in a distinct subset of cells in situ hybridisation Anti-AIRE ab Heino et al. BBRC 257: 821, 1999
11 Subcellular localization Aire localizes to nuclear dots in thymus medulla and in transfected Cos cells
12 Human and Mouse AIRE proteins are 77% identical aa PRR (23.5%) aa AIRE L L NLS HSR/ASS SAND PHD L PHD L Aire L HSR/ASS L NLS SAND PHD PRR (16%) L PHD L mouse : MAGGDGMLRRLLRLHRTEIAVAIDSAFPLLHALADHDVVPEDKFQETLRLKEKEGCPQAFHALLSWLLTRDSGAILDFWRILFKDYNLERYSRLHSILDGFPKDVDLNQSR : 111 human : MA-TDAALRRLLRLHRTEIAVAVDSAFPLLHALADHDVVPEDKFQETLHLKEKEGCPQAFHALLSWLLTQDSTAILDFWRVLFKDYNLERYGRLQPILDSFPKDVDLSQPR : 110 L mouse : KGRKPLAGPKAAVLPPRPPTKRKALEEPRATPPATLASKSVSSPGSHLKTKPPKKPDGNLESQHLPLGNGIQTMAASVQRAVTVASGDVPGTRGAVEGILIQQVFESGRSK : 222 human : KGRKPPAVPKALVPPPRLPTKRKASEEARAAAPAALTPRGTASPGSQLKAKPPKKPESSAEQQRLPLGNGIQTMSASVQRAVAMSSGDVPGARGAVEGILIQQVFESGGSK : 221 NLS mouse : KCIQVGGEFYTPNKFEDPSGNLKNKARSGSSLKPVVRAKGAQVTIPGRDEQKVGQQCGVPPLPSLPSEPQVNQKNEDECAVCHDGGELICCDGCPRAFHLACLSPPLQEIP : 333 human : KCIQVGGEFYTPSKFED-SGSGKNKARSSSGPKPLVRAKGAQGAAPGGGEARLGQQGSVPAPLALPSDPQLHQKNEDECAVCRDGGELICCDGCPRAFHLACLSPPLREIP : 331 SAND mouse : SGLWRCSCCLQGRVQQNLSQPEVSRPPELPAETPILVGLRSASEKTRGPSRELKASSDAAVTYVNLLAPHPAAPL--LEPSALCPLLSAGNEGRPGPAPSARCSVCGDGTE : 442 human : SGTWRCSSCLQATVQEVQPRAEEPRPQEPPVETPLPPGLRSAGEEVRGPPGEPLAGMDTTLVYKHLPAPPSAAPLPGLDSSALHPLLCVGPEGQQNLAPGARCGVCGDGTD : 442 mouse : VLRCAHCAAAFHWRCHFPTAAARPGTNLRCKSCSADSTPTPGTPGEAVPTSGPRPAPGLAKVGDDSASHDPVLHRDDLESLLNEHSFDGILQWAIQSMSRPLAETPPFSS : 552 human : VLRCTHCAAAFHWRCHFPAGTSRPGTGLRCRSCSGDVTPAP-VEGVLAPSP-ARLAPGPAK--DDTASHEPALHRDDLESLLSEHTFDGILQWAIQSMARPAA---PFPS : 545 PHD ASS L L L PHD Mittaz et al. BBRC, 255: 483, 1999
13 Aire co-localizes with epithelial cell markers in thymus medulla MTS5 MTS10
14 Thy CD8 + DC Thy CD8 lo/- DC Spl CD DC Spl CD4-8 - DC Spl CD4-8+DC Thymocytes Spl macroph. AIRE is expressed in Dendritic cells Aire β-actin Several subclasses of mouse dendritic cells express Aire AIRE mrna is upregulated in vitro stimulated human DCs
15 Cortex Thymocyte differentiation Double negative CD4- CD8- No T-cell receptor Medulla Double positive CD4+ CD8+ T-cell receptor Single positive CD4+ CD8- or CD4- CD8+ T-cell receptor
16 Thymocytes are selected differentially according to their reactivity TCR reactive to non-self antigens T-cell precursor Cells survive and when meeting pathogen will proliferate TCR reactive to self antigens Cell death
17 Autoimmune diseases and autoantigens Addison s disease Autoimmune gastritis Pernicious anemia Hashimoto thyroiditis Graves disease Myasthenia gravis Type 1 diabetes Vitiligo Rheumatoid arthritis Multiple sclerosis steroid P450 cytochromes H + /K + ATPase intrinsic factor thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin thyroid receptor Acetylcholine receptor insulin, GAD65 tyrosinase, MART type 2 collagen myelin basic protein
18 Ectopic (promiscuous) expression of self antigens in thymus Many tissue specific autoantigens are expressed in thymus. During negative selection, T- cells to these antigens are deleted. If antigen is not expressed in thymus or is expressed in a different way, this may cause autoimmunity From Gotter et al. 2004
19 Diverse genes expressed in thymic epithelial cells Tissues specific antigens (pancreas, stomach, brain, eye, liver, muscle, kidney specific genes) Expression of genes expressed during fetal stages, pregnancyassociated genes Expression of male specific genes in females and vice versa Expression of cancer specific antigens Conserved in mice and humans Estimation of 3000 genes (5-10% of known genes) in addition to basal expression of thymic epithelial cells
20 AIRE (autoimmune regulator) gene is central in expressing tissue specific antigens
21 Aire deficient mice have autoantibodies and lymphocytic infiltration in multiple tissues Anderson et al. Science, 2002
22 Microarray analysis of gene expression in wild-type and Aire deficient mouse The expression of tissue specific genes is lower or non-existing in Aire deficient mouse Anderson et al. Science, 2002
23 The PHD zinc fingers form the activation domain of AIRE HSR NLS SAND PHD PRR PHD
24 AIRE Interacts with CBP AIRE binds CBP at its CH1 and CH3 domains by far western and yeast two-hybrid assays CH1 also binds STAT2 and HIF-1a; CH3 binds E1A and TFIIB
25 CBP: camp response element binding (CREB) protein binding protein CBP is implicated in various transcriptional responses regulating growth, differentiation or apoptosis Belongs to the class of transcription co-activators possessing histone acetyltransferase activity (HAT) and thus have the potential to regulate the chromatin structure CBP/p300 interacts with many transcription activators and coactivators From Hottiger and Nabel, 2000
26 AIRE Colocalises with CBP AIRE CBP merge
27 3D picture of AIRE dots Nuclear Bodies Most prominent nuclear bodies are promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear body or POD (PML oncogenic domain) Approximately 0.3 to 1 micrometers in diameter Other proteins in nuclear dots are involved in transcription or suspected in chromatin binding (Sp100, CBP, BLM, p53) Function unknown, activation or degradation site? Some of the proteins like CBP move in and out.
28 AIRE Function AIRE induces the expression of autoantigens that lead to the elimination of the autoreactive T cells T cell autoreactive to APECED autoantigen Thymus AIRE Thymic epithelial cell expressing autoantigens
29 Loss of Function When AIRE is defective, autoreactive T cells escape selection, and autoimmunity develops T cell autoreactive to APECED autoantigen Thymus No AIRE Thymic epithelial cell expressing autoantigens
30 University of Tampere Jukka Pitkänen Camelia Magureanu Ulla Aapola Niko Sillanpää Astrid Murumägi Maarit Heino Pärt Peterson Kai Krohn WEHI, Melbourne Hamish Scott Li Wu University of Tokushima Mitsuru Matsumoto Keio University, Tokyo Jun Kudoh Nobuyoshi Shimizu University of Würzburg Philipp Ströbel Alex Marx University of Geneva Laureane Mittaz Stylianos Antonarakis University of Birmingham Graham Anderson Eric Jenkinson
31 University of Tartu Ana Rebane Vivian Kont Kaidi Möll Tõnis Org Ingrid Liiv Eneli Õis Annika Reimets Rainis Venta Mario Saare
ﺖاﻀﻴﺒﻤﻠا ﺾﻴﺒﻠا ﻦﻤزﻤﻠا ﻰﻠﻋ ﺔﻴﺸﻐأﻠا ﺔﻴﻄاﺨﻤﻠا
 اﻠﻤﺨاﻄﻴﺔ اﻠأﻐﺸﻴﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ اﻠﻤزﻤﻦ اﻠﺒﻴﺾ اﻠﻤﺒﻴﻀاﺖ داء= candidiasis_chronic_mucocutaneos 1 / 19 اﻠﻤﺨاﻄﻴﺔ اﻠأﻐﺸﻴﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ اﻠﻤزﻤﻦ اﻠﺒﻴﺾ اﻠﻤﺒﻴﻀاﺖ داء= candidiasis_chronic_mucocutaneos 2 / 19 Chronic Mucocutaneous 3 /
اﻠﻤﺨاﻄﻴﺔ اﻠأﻐﺸﻴﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ اﻠﻤزﻤﻦ اﻠﺒﻴﺾ اﻠﻤﺒﻴﻀاﺖ داء= candidiasis_chronic_mucocutaneos 1 / 19 اﻠﻤﺨاﻄﻴﺔ اﻠأﻐﺸﻴﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ اﻠﻤزﻤﻦ اﻠﺒﻴﺾ اﻠﻤﺒﻴﻀاﺖ داء= candidiasis_chronic_mucocutaneos 2 / 19 Chronic Mucocutaneous 3 /
The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production
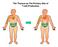 The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production Thymus Histology Lobulated organ with outer cortex and inner medulla C M Ordered Microenvironments Support T-cell Development CD4-CD8- precursors CD4+CD8+
The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production Thymus Histology Lobulated organ with outer cortex and inner medulla C M Ordered Microenvironments Support T-cell Development CD4-CD8- precursors CD4+CD8+
1. Supplemental Table 1. Autoimmune regulator (AIRE) mutations and deletions detected in the
 List of Supplemental Material 1. Supplemental Table 1. Autoimmune regulator (AIRE) mutations and deletions detected in the American Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED)
List of Supplemental Material 1. Supplemental Table 1. Autoimmune regulator (AIRE) mutations and deletions detected in the American Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED)
FOCiS. Lecture outline. The immunological equilibrium: balancing lymphocyte activation and control. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
Immunology 2011 Lecture 20 Autoimmunity 18 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 20 Autoimmunity 18 October APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes Antigenspecific triggering B T ANTIGEN Proliferation Differentiation
Immunology 2011 Lecture 20 Autoimmunity 18 October APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes Antigenspecific triggering B T ANTIGEN Proliferation Differentiation
Characterization of Human AIRE Promoter and Analysis of AIRE Expression in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Thymomas
 ASTRID MURUMÄGI Characterization of Human AIRE Promoter and Analysis of AIRE Expression in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Thymomas ACADEMIC DISSERTATION To be presented, with the permission of the
ASTRID MURUMÄGI Characterization of Human AIRE Promoter and Analysis of AIRE Expression in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Thymomas ACADEMIC DISSERTATION To be presented, with the permission of the
California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology. Distance Learning Program
 California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Distance Learning Program ORGAN SPECIFIC AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES by Paula J. D Amore, Ph.D., D(AMBLI) Assistant Professor, Division of Health Sciences
California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Distance Learning Program ORGAN SPECIFIC AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES by Paula J. D Amore, Ph.D., D(AMBLI) Assistant Professor, Division of Health Sciences
Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases
 Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases Immune tolerance Central: negative selection during thymic education deletion of autoreactive B-lymphocytes in bone marrow Positive selection in the thymus Negative
Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases Immune tolerance Central: negative selection during thymic education deletion of autoreactive B-lymphocytes in bone marrow Positive selection in the thymus Negative
Pituitary autoantibodies in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis - ectodermal dystrophy (APECED)
 ACTA BIOMED 2007; 78; Suppl 1: 248-254 Mattioli 1885 L E C T U R E Pituitary autoantibodies in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis - ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) Damien T. O Dwyer 1, Patrick McElduff
ACTA BIOMED 2007; 78; Suppl 1: 248-254 Mattioli 1885 L E C T U R E Pituitary autoantibodies in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis - ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) Damien T. O Dwyer 1, Patrick McElduff
Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies
 Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies Directions: Each of the numbered items or incomplete statements in this section is followed by answers or by completions of the statement.
Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies Directions: Each of the numbered items or incomplete statements in this section is followed by answers or by completions of the statement.
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection
 T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
[AUTOIMMUNITY] July 14, 2013
![[AUTOIMMUNITY] July 14, 2013 [AUTOIMMUNITY] July 14, 2013](/thumbs/72/66734585.jpg) This sheet includes only the extra notes. Slide 5,6: [AUTOIMMUNITY] July 14, 2013 Autoimmunity is the condition or case where the immune system is activated by self antigensand when the immune system no
This sheet includes only the extra notes. Slide 5,6: [AUTOIMMUNITY] July 14, 2013 Autoimmunity is the condition or case where the immune system is activated by self antigensand when the immune system no
Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens
 Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
Development of B and T lymphocytes
 Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism
 MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
Immune responses in autoimmune diseases
 Immune responses in autoimmune diseases Erika Jensen-Jarolim Dept. of Pathophysiology Medical University Vienna CCHD Lecture January 24, 2007 Primary immune organs: Bone marrow Thymus Secondary: Lymph
Immune responses in autoimmune diseases Erika Jensen-Jarolim Dept. of Pathophysiology Medical University Vienna CCHD Lecture January 24, 2007 Primary immune organs: Bone marrow Thymus Secondary: Lymph
What is Autoimmunity?
 Autoimmunity What is Autoimmunity? Robert Beatty MCB150 Autoimmunity is an immune response to self antigens that results in disease. The immune response to self is a result of a breakdown in immune tolerance.
Autoimmunity What is Autoimmunity? Robert Beatty MCB150 Autoimmunity is an immune response to self antigens that results in disease. The immune response to self is a result of a breakdown in immune tolerance.
What is Autoimmunity?
 Autoimmunity What is Autoimmunity? Robert Beatty MCB150 Autoimmunity is an immune response to self antigens that results in disease. The immune response to self is a result of a breakdown in immune tolerance.
Autoimmunity What is Autoimmunity? Robert Beatty MCB150 Autoimmunity is an immune response to self antigens that results in disease. The immune response to self is a result of a breakdown in immune tolerance.
4. Definition and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus type 1
 4. Definition and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus type 1 4.1. Definition of diabetes mellitus type1 Key question: What is diabetes mellitus type 1? Diabetes mellitus (DM) comprises a group of
4. Definition and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus type 1 4.1. Definition of diabetes mellitus type1 Key question: What is diabetes mellitus type 1? Diabetes mellitus (DM) comprises a group of
The autoimmune regulator: a key toward understanding the molecular pathogenesis of autoimmune polyendocrinopathycandidiasis-ectodermal
 REVIEW The autoimmune regulator: a key toward understanding the molecular pathogenesis of autoimmune polyendocrinopathycandidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy Tanja Meriluoto,1,2 Maria Halonen,1,2 Markku Pelto-Huikko,3
REVIEW The autoimmune regulator: a key toward understanding the molecular pathogenesis of autoimmune polyendocrinopathycandidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy Tanja Meriluoto,1,2 Maria Halonen,1,2 Markku Pelto-Huikko,3
Pteridine Dependent Hydroxylases as Autoantigens in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1
 Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 999 Pteridine Dependent Hydroxylases as Autoantigens in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1 BY OLOV EKWALL ACTA UNIVERSITATIS
Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 999 Pteridine Dependent Hydroxylases as Autoantigens in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1 BY OLOV EKWALL ACTA UNIVERSITATIS
HOST DEFENSE SMALL GROUP PROBLEM SOLVING SESSION AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
 HOST DEFENSE SMALL GROUP PROBLEM SOLVING SESSION AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES Monday, May 5, 2008 1:30 PM 3:30 PM Small Group Classrooms LEARNING GOALS You will understand how the immune system maintains tolerance
HOST DEFENSE SMALL GROUP PROBLEM SOLVING SESSION AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES Monday, May 5, 2008 1:30 PM 3:30 PM Small Group Classrooms LEARNING GOALS You will understand how the immune system maintains tolerance
Central tolerance. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance. Regulation of the T cell response
 Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance)
Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance)
Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance
 Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance) Autoimmunity Immunodeficiency
Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance) Autoimmunity Immunodeficiency
Bachelor of Chinese Medicine ( ) AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
 Bachelor of Chinese Medicine (2002 2003) BCM II Dr. EYT Chan February 6, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 134 UPB AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES 1. Introduction Diseases may be the consequence of an aberrant immune response,
Bachelor of Chinese Medicine (2002 2003) BCM II Dr. EYT Chan February 6, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 134 UPB AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES 1. Introduction Diseases may be the consequence of an aberrant immune response,
Alida R Harahap & Farida Oesman Department of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia
 Alida R Harahap & Farida Oesman Department of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia Foreign molecules = antigens Immune response Immune system non-specific specific cellular humoral
Alida R Harahap & Farida Oesman Department of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia Foreign molecules = antigens Immune response Immune system non-specific specific cellular humoral
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Autoimmunity Origins. Horror autotoxicus: Literally, the horror of self-toxicity.
 Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Origins Horror autotoxicus: Literally, the horror of self-toxicity. A term coined by the German immunologist Paul Ehrlich (1854-1915) to describe the body's innate aversion to
Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Origins Horror autotoxicus: Literally, the horror of self-toxicity. A term coined by the German immunologist Paul Ehrlich (1854-1915) to describe the body's innate aversion to
Autoantibody Targets in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1 and Lymphocytic Hypophysitis
 Autoantibody Targets in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1 and Lymphocytic Hypophysitis CASEY JO ANNE SMITH B.BiomedSci (Hons) Degree: PhD (Medicine) Submission Date: May 2009 Declarations This
Autoantibody Targets in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1 and Lymphocytic Hypophysitis CASEY JO ANNE SMITH B.BiomedSci (Hons) Degree: PhD (Medicine) Submission Date: May 2009 Declarations This
Introduction. Introduction. Lymphocyte development (maturation)
 Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
Autoimmunity. By: Nadia Chanzu, PhD Student, UNITID Infectious Minds Presentation November 17, 2011
 Molecular Mechanisms of Autoimmunity By: Nadia Chanzu, PhD Student, UNITID Infectious Minds Presentation November 17, 2011 Introduction 3m Pick an organ, any organ... Autoimmunity can affect ANY organ/organ
Molecular Mechanisms of Autoimmunity By: Nadia Chanzu, PhD Student, UNITID Infectious Minds Presentation November 17, 2011 Introduction 3m Pick an organ, any organ... Autoimmunity can affect ANY organ/organ
BDC Keystone Genetics Type 1 Diabetes. Immunology of diabetes book with Teaching Slides
 BDC Keystone Genetics Type 1 Diabetes www.barbaradaviscenter.org Immunology of diabetes book with Teaching Slides PRACTICAL Trailnet screens relatives and new onset patients for autoantibodies and HLA
BDC Keystone Genetics Type 1 Diabetes www.barbaradaviscenter.org Immunology of diabetes book with Teaching Slides PRACTICAL Trailnet screens relatives and new onset patients for autoantibodies and HLA
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology. Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc.
 Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc. Autoimmunity Reflects a loss of immunologic tolerance Mechanisms Auto-antibodies
Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc. Autoimmunity Reflects a loss of immunologic tolerance Mechanisms Auto-antibodies
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
HLA Antigen Expression in Autoimmune Endocrinopathies
 Physiol. Res. 53: 191-197, 2004 HLA Antigen Expression in Autoimmune Endocrinopathies P. HRDÁ 1,2, I. ŠTERZL 1,2, P. MATUCHA 2, F. KORIOTH 3, A. KROMMINGA 3 1 Institute of Immunology and Microbiology First
Physiol. Res. 53: 191-197, 2004 HLA Antigen Expression in Autoimmune Endocrinopathies P. HRDÁ 1,2, I. ŠTERZL 1,2, P. MATUCHA 2, F. KORIOTH 3, A. KROMMINGA 3 1 Institute of Immunology and Microbiology First
Adrenal Insufficiency
 Adrenal Insufficiency Normal adrenal physiology Clinical features, Laboratory findings Common causes of primary adrenal insufficiency Evaluation of suspected adrenal insufficiency Acute and chronic management
Adrenal Insufficiency Normal adrenal physiology Clinical features, Laboratory findings Common causes of primary adrenal insufficiency Evaluation of suspected adrenal insufficiency Acute and chronic management
Self-tolerance. Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens. Central Tolerance. Peripheral tolerance
 Autoimmunity Self-tolerance Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens Central Tolerance Peripheral tolerance Factors Regulating Immune Response Antigen availability Properties
Autoimmunity Self-tolerance Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens Central Tolerance Peripheral tolerance Factors Regulating Immune Response Antigen availability Properties
T Cell Development. Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD. November 3, 2015
 T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Alex Cioffi June 22 nd 2013
 Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Alex Cioffi June 22 nd 2013 Implications in Human Disease Adenovirus Early Region 1A (E1A) and Cancer α-synuclein and Parkinson s Disease Amyloid β and Alzheimer s Disease
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Alex Cioffi June 22 nd 2013 Implications in Human Disease Adenovirus Early Region 1A (E1A) and Cancer α-synuclein and Parkinson s Disease Amyloid β and Alzheimer s Disease
Defects of Innate Immunity
 Defects of Innate Immunity TLR signalling IRAK4 and MyD88 AR Same clinical phenotype for both genes (Recurrent) invasive bacterial infections: Meningitis and septicemia >> skin Pneumococcus >> Staph aureus
Defects of Innate Immunity TLR signalling IRAK4 and MyD88 AR Same clinical phenotype for both genes (Recurrent) invasive bacterial infections: Meningitis and septicemia >> skin Pneumococcus >> Staph aureus
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases. Autoantibodies. Autoimmune diseases relatively common
 Autoimmune diseases Fundamental abnormality: the adaptive immune system is triggered by self antigens to initiate a sustained immune response against self molecules that results in tissue injury Specificity
Autoimmune diseases Fundamental abnormality: the adaptive immune system is triggered by self antigens to initiate a sustained immune response against self molecules that results in tissue injury Specificity
Autoimmune diagnostics. A comprehensive product line for the detection of autoantibodies
 Autoimmune diagnostics A comprehensive product line for the detection of autoantibodies Autoimmune diagnostics Autoimmune diseases are chronic inflammatory processes with an indeterminate etiology. They
Autoimmune diagnostics A comprehensive product line for the detection of autoantibodies Autoimmune diagnostics Autoimmune diseases are chronic inflammatory processes with an indeterminate etiology. They
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
DISSERTATIONES MEDICINAE UNIVERSITATIS TARTUENSIS 195
 DISSERTATIONES MEDICINAE UNIVERSITATIS TARTUENSIS 195 DISSERTATIONES MEDICINAE UNIVERSITATIS TARTUENSIS 195 VIVIAN KONT Autoimmune regulator: characterization of thymic gene regulation and promoter methylation
DISSERTATIONES MEDICINAE UNIVERSITATIS TARTUENSIS 195 DISSERTATIONES MEDICINAE UNIVERSITATIS TARTUENSIS 195 VIVIAN KONT Autoimmune regulator: characterization of thymic gene regulation and promoter methylation
T cell development October 28, Dan Stetson
 T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
Immunological Tolerance
 Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Autoimmune diseases, their pathogenic mechanisms and treatment of unwanted immune responses (Janeway s Immunobiology)
 Autoimmune diseases, their pathogenic mechanisms and treatment of unwanted immune responses (Janeway s Immunobiology) Picture source: https://www.klini kum.uniheidelberg.de/fil eadmin/pressest elle/pm_neu/20
Autoimmune diseases, their pathogenic mechanisms and treatment of unwanted immune responses (Janeway s Immunobiology) Picture source: https://www.klini kum.uniheidelberg.de/fil eadmin/pressest elle/pm_neu/20
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I
 Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I Novel diagnostic assays and immune regulation Bergithe E. V. Oftedal Dissertation for the degree philosophiae doctor (PhD) at the University of Bergen 2012 Dissertation
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I Novel diagnostic assays and immune regulation Bergithe E. V. Oftedal Dissertation for the degree philosophiae doctor (PhD) at the University of Bergen 2012 Dissertation
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
A. Incorrect! The duodenum drains to the superior mesenteric lymph nodes. B. Incorrect! The jejunum drains to the superior mesenteric lymph nodes.
 USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 11: Immunology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 67 year old man is discovered to have metastatic disease involving his inferior mesenteric lymph nodes. His primary cancer is most likely
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 11: Immunology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 67 year old man is discovered to have metastatic disease involving his inferior mesenteric lymph nodes. His primary cancer is most likely
Overview B cell development T cell development
 Topics Overview B cell development T cell development Lymphocyte development overview (Cont) Receptor diversity is produced by gene rearrangement and is random Includes specificities that will bind to
Topics Overview B cell development T cell development Lymphocyte development overview (Cont) Receptor diversity is produced by gene rearrangement and is random Includes specificities that will bind to
Autoimmunity. Mark S. Anderson, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
 Autoimmunity Mark S. Anderson, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco Autoimmunity Definition: immune response against self (auto-) antigen General principles: Significant health burden, 5% of
Autoimmunity Mark S. Anderson, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco Autoimmunity Definition: immune response against self (auto-) antigen General principles: Significant health burden, 5% of
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
CD4+ T Helper T Cells, and their Cytokines in Immune Defense and Disease
 CD4+ T Helper T Cells, and their Cytokines in Immune Defense and Disease Andrew Lichtman M.D., Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Intro to T cell mediated immunity
CD4+ T Helper T Cells, and their Cytokines in Immune Defense and Disease Andrew Lichtman M.D., Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Intro to T cell mediated immunity
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy
 Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
Immune tolerance. Lu,Linrong Institute of Immunology, ZJU
 免疫耐受 Immune tolerance Lu,Linrong Institute of Immunology, ZJU Lu.Linrong@gmail.com g http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/llr Immunological Tolerance *Definition *History (Early observations ) *Mechanism Central Tolerance
免疫耐受 Immune tolerance Lu,Linrong Institute of Immunology, ZJU Lu.Linrong@gmail.com g http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/llr Immunological Tolerance *Definition *History (Early observations ) *Mechanism Central Tolerance
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Clinical, Endocrinological and Immunological Characteristics of Japanese Patients With Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome Type 3a
 Elmer ress Original Article J Endocrinol Metab. 2016;6(2):46-51 Clinical, Endocrinological and Immunological Characteristics of Japanese Patients With Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome Type 3a Sumie Moriyama
Elmer ress Original Article J Endocrinol Metab. 2016;6(2):46-51 Clinical, Endocrinological and Immunological Characteristics of Japanese Patients With Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome Type 3a Sumie Moriyama
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
PROBLEMS WITH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. Blood Types, Transplants, Allergies, Autoimmune diseases, Immunodeficiency Diseases
 PROBLEMS WITH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Blood Types, Transplants, Allergies, Autoimmune diseases, Immunodeficiency Diseases Antigens on red blood cells determine whether a person has type A, B, AB, or O blood
PROBLEMS WITH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Blood Types, Transplants, Allergies, Autoimmune diseases, Immunodeficiency Diseases Antigens on red blood cells determine whether a person has type A, B, AB, or O blood
Assistant Professor of Endocrinology
 Pathophysiology Of Adrenal Disorder Dr.Rezvan Salehidoost Assistant Professor of Endocrinology Pathophysiology Of Adrenal Disorder The adrenal glands lie at the superior pole of each kidney and are composed
Pathophysiology Of Adrenal Disorder Dr.Rezvan Salehidoost Assistant Professor of Endocrinology Pathophysiology Of Adrenal Disorder The adrenal glands lie at the superior pole of each kidney and are composed
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Immunologic endocrine disorders
 Immunologic endocrine disorders Aaron W. Michels, MD, a and George S. Eisenbarth, MD, PhD b,c Aurora, Colo Autoimmunity affects multiple glands in the endocrine system. Animal models and human studies
Immunologic endocrine disorders Aaron W. Michels, MD, a and George S. Eisenbarth, MD, PhD b,c Aurora, Colo Autoimmunity affects multiple glands in the endocrine system. Animal models and human studies
A Rare Case of Autoimmuno Polyglandular Syndrome Type I in two Siblings: First Case from Eastern India
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 50-54 http://www.ijcmas.com Case Study A Rare Case of Autoimmuno Polyglandular Syndrome Type I in two Siblings: First Case from Eastern India Nupur Pal 1 *,
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 50-54 http://www.ijcmas.com Case Study A Rare Case of Autoimmuno Polyglandular Syndrome Type I in two Siblings: First Case from Eastern India Nupur Pal 1 *,
Environmental Influence in Autoimmune Diseases. Mark Gourley, MD
 Environmental Influence in Autoimmune Diseases Mark Gourley, MD Newsweek January, 2003 Current Knowledge of Environment and Myositis Environment Genes Autoimmunity What Is an Environmental Exposure?
Environmental Influence in Autoimmune Diseases Mark Gourley, MD Newsweek January, 2003 Current Knowledge of Environment and Myositis Environment Genes Autoimmunity What Is an Environmental Exposure?
This is a free sample of content from Immune Tolerance. Click here for more information or to buy the book.
 A ACPAs. See Antibodies to citrullinated peptide antigens Activation-induced cell death (AICD), 25 AICD. See Activation-induced cell death AIRE, 3, 18 19, 24, 88, 103 104 AKT, 35 Alefacept, 136 ALPS. See
A ACPAs. See Antibodies to citrullinated peptide antigens Activation-induced cell death (AICD), 25 AICD. See Activation-induced cell death AIRE, 3, 18 19, 24, 88, 103 104 AKT, 35 Alefacept, 136 ALPS. See
THE ASSOCIATION OF SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS IN INTRONIC REGIONS OF ISLET CELL AUTOANTIGEN 1 AND TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS.
 THE ASSOCIATION OF SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS IN INTRONIC REGIONS OF ISLET CELL AUTOANTIGEN 1 AND TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS by Carrie Lynn Blout B.S., Dickinson College, 2004 Submitted to the Graduate
THE ASSOCIATION OF SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS IN INTRONIC REGIONS OF ISLET CELL AUTOANTIGEN 1 AND TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS by Carrie Lynn Blout B.S., Dickinson College, 2004 Submitted to the Graduate
HLA and antigen presentation. Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol
 HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Evgenija Homšak,M.Ph., M.Sc., EuSpLM. Department for laboratory diagnostics University Clinical Centre Maribor Slovenia
 Evgenija Homšak,M.Ph., M.Sc., EuSpLM. Department for laboratory diagnostics University Clinical Centre Maribor Slovenia 14th EFLM Continuing Postgraduate Course in Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Evgenija Homšak,M.Ph., M.Sc., EuSpLM. Department for laboratory diagnostics University Clinical Centre Maribor Slovenia 14th EFLM Continuing Postgraduate Course in Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine
An Update On Autoimmune Diseases
 California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Distance Learning Program An Update On Autoimmune Diseases by Paula J. D Amore, Ph.D., D(AMBLI) Assistant Professor, Division of Health Sciences
California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Distance Learning Program An Update On Autoimmune Diseases by Paula J. D Amore, Ph.D., D(AMBLI) Assistant Professor, Division of Health Sciences
Autoantibodies to steroidogenic enzymes in patients with premature ovarian failure with and without Addison s disease
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2003) 148 565 570 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Autoantibodies to steroidogenic enzymes in patients with premature ovarian failure with and without Addison s disease
European Journal of Endocrinology (2003) 148 565 570 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Autoantibodies to steroidogenic enzymes in patients with premature ovarian failure with and without Addison s disease
Autoantibodies panel ANA
 Autoantibodies panel ANA Anti-nuclear antibodies, ANA screening General: Anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) contain all kinds of autoantibodies against nuclear antigens. Their targets are cell components in
Autoantibodies panel ANA Anti-nuclear antibodies, ANA screening General: Anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) contain all kinds of autoantibodies against nuclear antigens. Their targets are cell components in
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Review Article Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy Candidiasis Ectodermal Dystrophy: Insights into Genotype-Phenotype Correlation
 International Journal of Endocrinology Volume 2012, Article ID 353250, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/353250 Review Article Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy Candidiasis Ectodermal Dystrophy: Insights into Genotype-Phenotype
International Journal of Endocrinology Volume 2012, Article ID 353250, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/353250 Review Article Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy Candidiasis Ectodermal Dystrophy: Insights into Genotype-Phenotype
Identification and characterization of genes responsive to apoptosis: Application of DNA chip technology and mrna differential display
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 1271-1 284 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and H istopat hology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Revie W Identification and characterization of genes
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 1271-1 284 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and H istopat hology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Revie W Identification and characterization of genes
Recommended reading: Abbas et al. 5th edition, chapters 7 and 10; Janeway and Travers, 5th edition, chapter 7.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
. Autoimmune disease. Dr. Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology
 . Autoimmune disease Dr. Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology, Paul Ehrich The term coined by the German immunologist paul Ehrich ( 1854-1915) To describe the bodys innate aversion to immunological
. Autoimmune disease Dr. Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology, Paul Ehrich The term coined by the German immunologist paul Ehrich ( 1854-1915) To describe the bodys innate aversion to immunological
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE
 CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
Mechanisms of an autoimmunity syndrome in mice caused by a dominant mutation in Aire
 Research article Mechanisms of an autoimmunity syndrome in mice caused by a dominant mutation in Aire Maureen A. Su, 1,2 Karen Giang, 1 Kristina Žumer, 3 Huimin Jiang, 3 Irena Oven, 3 John L. Rinn, 4 Jason
Research article Mechanisms of an autoimmunity syndrome in mice caused by a dominant mutation in Aire Maureen A. Su, 1,2 Karen Giang, 1 Kristina Žumer, 3 Huimin Jiang, 3 Irena Oven, 3 John L. Rinn, 4 Jason
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. STAT3 expression in HEK293 cells
 Supplementary Figure 1 STAT3 expression in HEK293 cells Western blot showing the expression of STAT3 protein in HEK293 cells transfected with STAT3 constructs. HEK293 cells were lysed, and protein extracts
Supplementary Figure 1 STAT3 expression in HEK293 cells Western blot showing the expression of STAT3 protein in HEK293 cells transfected with STAT3 constructs. HEK293 cells were lysed, and protein extracts
Molecular Targets in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type1 and Their Clinical Implications
 Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 417 Molecular Targets in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type1 and Their Clinical Implications MOHAMMAD ALIMOHAMMADI
Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 417 Molecular Targets in Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type1 and Their Clinical Implications MOHAMMAD ALIMOHAMMADI
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
AUTOIMMUNE POLYENDOCRINE SYNDROME TYPE 1: A RARE CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 Case Report AUTOIMMUNE POLYENDOCRINE SYNDROME TYPE 1: A RARE CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Imran Sarker, MD 1 ; Mohammad Bahadur Ali Miah, MD 1 ; Mohammad Abdul Hannan, MD 1 ; Nusrat Sultana,
Case Report AUTOIMMUNE POLYENDOCRINE SYNDROME TYPE 1: A RARE CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Imran Sarker, MD 1 ; Mohammad Bahadur Ali Miah, MD 1 ; Mohammad Abdul Hannan, MD 1 ; Nusrat Sultana,
Disruption of Healthy Tissue by the Immune Response Autoimmune diseases: Inappropriate immune response against self-components
 Chapter 13 Disruption of Healthy Tissue by the Immune Response Autoimmune diseases: Inappropriate immune response against self-components Humoral imm 胞外 胞內 CMI: CD8 T Self Ag Self(Auto) antigen (encoded
Chapter 13 Disruption of Healthy Tissue by the Immune Response Autoimmune diseases: Inappropriate immune response against self-components Humoral imm 胞外 胞內 CMI: CD8 T Self Ag Self(Auto) antigen (encoded
Identification of the Autoimmune Regulator Gene, its Mutation Pattern in APECED Patients and Localisation of the Gene Expression
 MAARIT HEINO Identification of the Autoimmune Regulator Gene, its Mutation Pattern in APECED Patients and Localisation of the Gene Expression ACADEMIC DISSERTATION to be presented, with the permission
MAARIT HEINO Identification of the Autoimmune Regulator Gene, its Mutation Pattern in APECED Patients and Localisation of the Gene Expression ACADEMIC DISSERTATION to be presented, with the permission
Immune System. Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Slide 1. Slide 2. Organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Prof Peter Gergely
 Slide 1 Organ-specific autoimmune diseases Prof Peter Gergely Slide 2 Ssystemic autoimmune diseases systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Sjögren
Slide 1 Organ-specific autoimmune diseases Prof Peter Gergely Slide 2 Ssystemic autoimmune diseases systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Sjögren
Autoimmunity and Principles of Transplantation Immunology
 Module Code: Module Title: IMM III Autoimmunity and Principles of Transplantation Immunology Module Convenors: Emeritus Professor Jennifer Rolland and Dr Karla Lemmert Discipline: Professor Allan Cripps
Module Code: Module Title: IMM III Autoimmunity and Principles of Transplantation Immunology Module Convenors: Emeritus Professor Jennifer Rolland and Dr Karla Lemmert Discipline: Professor Allan Cripps
Pathophysiology, Mechanisms for the Induction and Animal Models of
 Pathophysiology, Mechanisms for the Induction and Animal Models of Autoimmune Diseases Eun Wha Choi, DVM, PhD Laboratory Animal Research Center, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute (From New therapeutic
Pathophysiology, Mechanisms for the Induction and Animal Models of Autoimmune Diseases Eun Wha Choi, DVM, PhD Laboratory Animal Research Center, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute (From New therapeutic
Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy
 Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy Johanne Kaplan, PhD VP Neuroimmunology Research Genzyme March 26, 2013 RESTRICTED USE SEE TRAINING MEMO 2011 DO Genzyme NOT 1COPY Corporation
Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy Johanne Kaplan, PhD VP Neuroimmunology Research Genzyme March 26, 2013 RESTRICTED USE SEE TRAINING MEMO 2011 DO Genzyme NOT 1COPY Corporation
Genetic lesions in thymic T cell clonal deletion and thresholds for autoimmunity
 Genetic lesions in thymic T cell clonal deletion and thresholds for autoimmunity Adrian Liston & Christopher C. Goodnow. John Curtin School of Medical Research and The Australian Phenomics Facility, The
Genetic lesions in thymic T cell clonal deletion and thresholds for autoimmunity Adrian Liston & Christopher C. Goodnow. John Curtin School of Medical Research and The Australian Phenomics Facility, The
Immune System. Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Regulatory T Cells and Maintenance of Tolerance
 Regulatory Cells and Maintenance of olerance Stephen Canfield, MD, PhD Asst. Prof. Medicine smc12@columbia.edu What constitutes immune tolerance? Discrimination between: non-self and self e.g., virally
Regulatory Cells and Maintenance of olerance Stephen Canfield, MD, PhD Asst. Prof. Medicine smc12@columbia.edu What constitutes immune tolerance? Discrimination between: non-self and self e.g., virally
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
