UNICORNS, DRAGONS, POLYMYOSITIS AND OTHER MYTHOLOGICAL BEASTS: THE TRUTH ABOUT POLYMYOSITIS
|
|
|
- Cameron Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNICORNS, DRAGONS, POLYMYOSITIS AND OTHER MYTHOLOGICAL BEASTS: THE TRUTH ABOUT POLYMYOSITIS Tahseen Mozaffar, MD University of California, Irvine Polymyositis is a commonly diagnosed condition in Neurology, Internal Medicine and Rheumatology. 1 The traditional diagnosis of polymyositis calls for presence of proximal muscle weakness, elevated creatinine phosphokinase, needle electromyography evidence of irritable myopathy and muscle biopsy features of an inflammatory myopathy with endomysial inflammation with cytotoxic T-cell and invasion of non-necrotic muscle fibers with inflammatory cells. 2 However, a number of cases have been diagnosed using only some of these criteria, most commonly proximal muscle weakness and elevated creatinine phosphokinase. A number of physicians, especially rheumatologists, often avoid muscle biopsies to establish a diagnosis of polymyositis. They depend on the Bohan and Peter criteria, introduced for the first time in 1975, 3 prior to true recognition of inclusion body myositis. 4 Through this talk I will provide evidence that the Bohan and Peter criteria are no longer appropriate for diagnosis of inflammatory myopathies and the time has come to use criteria that combine clinical, pathological and serological data to make a definitive diagnosis. Many such criteria have been proposed. 5-8 Furthermore many diseases mimic polymyositis and need to be considered when making a diagnosis of polymyositis. Finally I will show evidence that polymyositis is much rarer than what would be apparent from the somewhat common diagnosis that we encounter day to day in clinical practice. Bohan and Peter Criteria In a seminal two-part review of the topic titled Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis, Anthony Bohan and James B. Peter, both from the University of California, Los Angeles, they set forth the diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. 3,9 This system was introduced before the entity of sporadic inclusion body myositis was fully described - even though it was reported for the first time in 1971 (actually the case described was a case of hereditary inclusion body myopathy), 4 the first detailed description of what we now consider classic sporadic inclusion body myositis was not published till Thus this diagnostic classification does not take into consideration sporadic inclusion body myositis. The Bohan and Peter criteria defined five major criteria to define polymyositis and dermatomyositis: 1) symmetrical weakness of the limb-girdle muscles and anterior neck flexors, progressing over weeks to months, with or without dysphagia or respiratory muscle involvement; 2) muscle-biopsy evidence of necrosis of Type I and II fibers, phagocytosis, regeneration with basophilia, large vesicular sarcolemmal nuclei and prominent nucleoli, atrophy in a perifascicular distribution, variation in fiber size, and an inflammatory exudate, often perivascular; 3) elevation in serum of skeletal-muscle enzymes, particularly creatine phosphokinase and often aldolase, serum glutamate oxaloacetate and pyruvate transaminases, and lactate dehydrogenase; 4) electromyographic triad of short, small, polyphasic motor units, fibrillations, positive sharp waves and insertional irritability, and bizarre, high-frequency repetitive discharges; and 5) dermatologic features including a lilac discoloration of the eyelids (heliotrope) with periorbital edema, a scaly, erythematous dermatitis over the dorsum of the hands (especially the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, Gottron's sign), and involvement of the knees, elbows and medial malleoli, as well as the face, neck, and upper torso (this type of distribution is considered by many to be virtually pathognomonic of dermatomyositis). They defined confidence level as: 1) definite, consisting of three or four criteria (plus the rash) for dermatomyositis, and four criteria (without the rash) for polymyositis; 2) probable, comprising two criteria (plus the rash) for dermatomyositis, three criteria (without the rash), for polymyositis; and 3) possible, including one criterion (plus the rash) for dermatomyositis, and two criteria (without the rash) for polymyositis. Limitations of the Bohan and Peter Criteria A number of diseases would easily fulfill the possible or probable criteria for polymyositis using the Bohan and Peter criteria. For example a patient with Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy type 2B with dysferlin mutations can easily fulfill the definite criteria for polymyositis (with inflammatory biopsy, elevated CK, myopathic EMG and proximal muscle weakness). 11 Similarly Late-Onset Pompe Disease (LOPD) will make the probable criteria easily (other than inflammatory changes on the biopsy). 12 Even patients with inclusion body myositis may fulfill the criteria for definite IBM early in their disease. About 20% of patients, especially female patients, with IBM may
2 have symmetric weakness and early on in the disease rimmed vacuoles may not be seen on the muscle biopsy. 13 Some IBM patients may also respond briefly to immunosuppressive treatment, although Bohan and Peter discouraged use of steroid responsiveness (and now IVIG responsiveness) as diagnostic criteria. 13 Even criteria for dermatomyositis may not be as sensitive. Heliotropic rash of the eyelids is now established as the most characteristic rash in dermatomyositis but the other skin rashes, including Gottron s papules, mechanic s hands, etc. can be seen in other forms of inflammatory myopathy including anti-synthetase syndrome, which is pathologically and serological very different from dermatomyositis, and overlap myositis, especially those associated with PM/Scl antibodies. 6,14 Furthermore it is now well described that DM patients may have normal levels of CK (despite abnormal EMG and muscle biopsy). 15 Certain forms of DM may have an entirely different type of skin rash, for instance forms of DM associated with antibodies to Melanoma Differentiation Antigen-5 (MDA-5) may not have muscle weakness and have a skin rash that is different with ulcerating lesions on the tips of the fingers. 6 Also up to 6% of DM patients may not have skin rash (dermatomyositis sans dermatitis). 16 Five distinct antibodies are associated with DM (Mi-2, NXP-2, SAE, MDA-5 and TIF-. Each of these has direct influence on disease phenotype and prognostication. For instance antibodies to TIF- predict a malignancy either one-year prior to or after the discovery of the myositis. 17 NXP-2 antibodies predict calcinosis, while MDA-5 predicts an amyopathic disease with very high risk of interstitial lung disease. 6 Newer Entities that Need to be Considered when Diagnosing Polymyositis There are a number of conditions that had not been described in 1975 when Bohan and Peter criteria were described. These include anti-synthetase syndrome, which most authorities now consider a separate entity from DM and PM; 6,14 necrotizing autoimmune myopathies (NAM), such as those associated with Signal Recognition Particle (SRP) antibodies 18,19 and antibodies to HMGcoA reductase (HMGCR antibodies), and sporadic inclusion body myositis. 10 SRP antibody associated necrotizing myopathy is a severe necrotizing myopathy that is associated with a severe muscle weakness, high CK and poor response to immunosuppressive therapy. 18,23 There is now evidence that the myositis may respond to intravenous rituxamab. 24 HMGCR antibody associated necrotizing autoimmune myopathy may also be a severe necrotizing myopathy, associated with markedly elevated CK values and requires often 3-drug regimen to control the disease. 21,25 There is some emerging data however, that suggests that intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) may be useful as a single agent to control the disease. 26 Anti-synthetase syndrome encompasses a group of myositides where antibodies to aminoacyl t-rna synthetase are found. 14 The most classic of this is Jo-1 myositis, where the clinical features are that of proximal weakness and elevated CK. However muscle pathology shows a very characteristic pathology of predominantly perimysial pathology, with inflammation, fragmentation of perimysial connective tissue, preservation of intramuscular capillaries (in sharp contrast to DM) and pathognomonic intranuclear Actin inclusions. 27,28 A very high risk of developing interstitial lung disease exists. Skin lesions include mechanic s hands, Gottron s papules and other skin rashes. A seronegative erosive arthritis may co-exist. 14 How rare is polymyositis and how do we refine the diagnosis of polymyositis? A number of papers have now reviewed the issue of how rare polymyositis is. 13,16,29 Most of these studies have shown that at long term follow up (5-10 years) over 90% of these cases diagnosed with polymyositis were found to have an alternate diagnosis. Common alternate diagnoses included inclusion body myositis, overlap syndrome (including PM/Scl syndrome) and necrotizing autoimmune myopathies. 16,29 This realization that polymyositis is really rare was editorialized and equated polymyositis to unicorns and dragons and other mythical beasts. 30 Serology: Newer studies have focused on increasing sensitivity to diagnosis of other diagnoses that may mimic Polymyositis. Obviously the role of serology has really vastly increased our ability to stratify different diseases. In addition to the myositis specific antibodies that are already described above, a couple of new antibodies are important to mention here. 31 HMGCR antibodies are associated with necrotizing autoimmune myopathies and usually predict a severe myopathy with high CK in patients often exposed to statin class anti-cholesterol medications. 21 However, this antibody has also been seen in adult patients who have never been exposed to statins or in pediatric patients who obviously have not been treated with statins. 32 HMGCR antibody associated myositis may look like polymyositis and would have met the criteria for definite polymyositis in the Bohan and Peter criteria but is a very different disease.
3 Serum NT5c1A antibodies are the new biomarker in inclusion body myositis and has remarkably high specificity (upwards of 94%) in patients with muscle weakness for the diagnosis of IBM Even though this antibody can be found in patients with lupus and Sjögren s disease, no muscle weakness was seen in those patients. 33,35 Thus the presence of this antibody in these disorders may just represent presymptomatic disease. The antibody is known to be present many years prior to their diagnosis of IBM; 36 we recently diagnosed a patient with IBM who had NT5c1A antibodies present in his serum 14 years prior to his definitive diagnosis. Furthermore our group has shown that seropositivity for the NT5c1A antibody predicts a more severe motor phenotype, with greater need for assistive devices, such as walker and wheelchair, and higher frequency of dysphagia. 37 This was recently reaffirmed in a European study; their study also showed reduced life expectancy in the seropositive IBM patients. 34 Seronegative patients had higher incidence of proximal limb weakness. Seropositive patients have significantly more cytochrome oxidase negative fibers. 34 There is also a suggestion that seropositive patients may have less rimmed vacuoles on muscle biopsy. 38 Myopathology: Muscle biopsy plays an important role in differentiating polymyositis from IBM and NAM. Even though endomysial inflammatory cell infiltrate with cytotoxic T-cells is the hallmark for PM, it can be seen in IBM. In fact without the presence of rimmed vacuoles PM is indistinguishable from IBM on light microscopy MHC class 1 upregulation is common to both. 41 Rimmed vacuoles may not be seen in all cases and may not be present early on in the disease. 13 Female patients have less rimmed vacuoles and may present with more symmetric weakness. 13 Furthermore seropositive patients have less rimmed vacuoles than seronegative patients. Additional stains such as cytochrome oxidase staining and staining for autophagy marker p62 really distinguishes IBM from PM and provides high sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis of IBM in cases of rimmed vacuolar as well as nonrimmed vacuolar myopathies. 43 Presence of COX negative fibers provides a sensitivity and specificity of 86% for diagnosis of IBM when rimmed vacuoles are present and sensitivity of 78% and specificity of 91% when rimmed vacuoles are not present for a diagnosis of IBM. 43 Similarly presence of p62 immunostaining provides a sensitivity of 87% and specificity of 86% for diagnosis of IBM when rimmed vacuoles are present and a sensitivity of only 22% but specificity of 91% for diagnosis of IBM when rimmed vacuoles are not seen. 43 Newer studies have questioned the specificity of muscle fiber invasion of non-necrotic muscle fibers in PM. 13 When followed long term, an overwhelming majority individuals who had muscle fiber invasion manifested clinical features consistent with diagnosis of IBM. Rimmed vacuoles on the initial muscle biopsy was seen in only 60% of the cases and men tended to have more rimmed vacuoles than women. Thus muscle biopsy diagnosis of IBM should not solely depend on demonstration of rimmed vacuoles on muscle biopsy, and should take into consideration additional features, such as muscle fiber invasion of non-necrotic fibers, cytochrome oxidase negative fibers and presence of p62 or TDP-43 immunostaining in rimmed vacuolar or non-rimmed vacuolar muscle fibers. 44 Time has come to abandon Bohan and Peter criteria for diagnosis of inflammatory myositis I have demonstrated that reliance on Bohan and Peter criteria for diagnosis of inflammatory myositis leads to over diagnosis of PM and is no longer adequate given the advances in the field of inflammatory myositides since A number of new classification systems have been proposed that have used either phenotypic characteristics or more important used either serology or myopathology or sometimes all three (clinical, serological and myopathological) to classify inflammatory myositides. 5-8 A number of workshops under the auspices of the European Neuromuscular Center (ENMC) have tried to address this issue; at this time concordance amongst these criteria is low. 49 Despite this there continues to be a heavy reliance on the Bohan and Peter criteria and this criteria is still used to determine subject eligibility in clinical trials in inflammatory myositides. Bibliography 1. Dalakas MC. Inflammatory muscle diseases. N Engl J Med 2015;372: Findlay AR, Goyal NA, Mozaffar T. An overview of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Muscle Nerve 2015;51: Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 1975;292: Yunis EJ, Samaha FJ. Inclusion body myositis. Lab Invest 1971;25: Pestronk A. Acquired immune and inflammatory myopathies: pathologic classification. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011;23: Allenbach Y, Benveniste O, Goebel HHH, Stenzel W. Review: Integrated classification of inflammatory myopathies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2017; doi: /nan
4 7. Zong M, Lundberg IE. Pathogenesis, classification and treatment of inflammatory myopathies. Nature Rev Rheumatol 2011;7: Love LA, Leff RL, Fraser DD, et al. A new approach to the classification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy: myositis-specific autoantibodies define useful homogeneous patient groups. Medicine 1991;70: Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 1975;292: Carpenter S, Karpati G, Heller I, Eisen A. Inclusion body myositis: a distinct variety of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Neurology 1978;28: Takahashi T, Aoki M, Suzuki N, et al. Clinical features and a mutation with late onset of limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2013;84: Laforêt P, Laloui K, Granger B, et al. The French Pompe registry. Baseline characteristics of a cohort of 126 patients with adult Pompe disease. Rev Neurol 2013;169: van de Vlekkert J, Hoogendijk JE, de Visser M. Myositis with endomysial cell invasion indicates inclusion body myositis even if other criteria are not fulfilled. Neuromuscul Disord 2015;25: Hervier B, Benveniste O. Clinical heterogeneity and outcomes of antisynthetase syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2013;15: Dalakas MC, Hohlfeld R. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet 2003;362: van der Meulen MF, Bronner IM, Hoogendijk JE, et al. Polymyositis: an overdiagnosed entity. Neurology 2003;61: Hida A, Yamashita T, Hosono Y, et al. Anti-TIF1-γ antibody and cancer-associated myositis: A clinicohistopathologic study. Neurology 2016;87: Pinal-Fernandez I, Parks C, Werner JL, et al. Longitudinal course of disease in a large cohort of myositis patients with autoantibodies recognizing the signal recognition particle. Arthritis Care Res 2017;69: Suzuki S, Nishikawa A, Kuwana M, et al. Inflammatory myopathy with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies: case series of 100 patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2015;10: Mammen AL. Autoimmune myopathies: autoantibodies, phenotypes and pathogenesis. Nature Rev Neurol 2011;7: Mammen AL. Statin-Associated Autoimmune Myopathy. N Engl J Med 2016;374: Musset L, Allenbach Y, Benveniste O, et al. Anti-HMGCR antibodies as a biomarker for immune-mediated necrotizing myopathies: A history of statins and experience from a large international multi-center study. Autoimmun Rev 2016;15: Suzuki S, Hayashi YK, Kuwana M, Tsuburaya R, Suzuki N, Nishino I. Myopathy associated with antibodies to signal recognition particle: disease progression and neurological outcome. Arch Neurol 2012;69: Valiyil R, Casciola-Rosen L, Hong G, Mammen A, Christopher-Stine L. Rituximab therapy for myopathy associated with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies: a case series. Arthritis Care Res 2010;62: Kassardjian CD, Lennon VA, Alfugham NB, Mahler M, Milone M. Clinical Features and Treatment Outcomes of Necrotizing Autoimmune Myopathy. JAMA Neurol 2015;72: Mammen AL, Tiniakou E. Intravenous Immune Globulin for Statin-Triggered Autoimmune Myopathy. N Engl J Med 2015;373: Mozaffar T, Pestronk A. Myopathy with anti-jo-1 antibodies: pathology in perimysium and neighbouring muscle fibres. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2000;68: Stenzel W, Preuße C, Allenbach Y, et al. Nuclear actin aggregation is a hallmark of anti-synthetase syndrome-induced dysimmune myopathy. Neurology 2015;84: Vilela VS, Prieto-González S, Milisenda JCC, Selva-O Callaghan A, Grau JM. Polymyositis, a very uncommon isolated disease: clinical and histological re-evaluation after long-term follow-up. Rheumatol Int 2015;35: Amato AA, Griggs RC. Unicorns, dragons, polymyositis, and other mythological beasts. Neurology 2003;61: Benveniste O, Stenzel W, Allenbach Y. Advances in serological diagnostics of inflammatory myopathies. Curr Opin Neurol 2016;29: Watanabe Y, Uruha A, Suzuki S, et al. Clinical features and prognosis in anti-srp and anti-hmgcr necrotising myopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2016;87: Herbert MK, Pruijn GJ. Novel serology testing for sporadic inclusion body myositis: disease-specificity and diagnostic utility. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2015;27:
5 34. Lilleker JB, Rietveld A, Pye SR, et al. Cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase 1A autoantibody profile and clinical characteristics in inclusion body myositis. Ann Rheum Dis 2017; doi: /annrheumdis Lloyd TE, Mammen AL, Amato AA, Weiss MD, Needham M, Greenberg SA. Evaluation and construction of diagnostic criteria for inclusion body myositis. Neurology 2014;83: Larman HB, Salajegheh M, Nazareno R, et al. Cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase 1A autoimmunity in sporadic inclusion body myositis. Ann Neurol 2013;73: Goyal NA, Cash TM, Alam U, et al. Seropositivity for NT5c1A antibody in sporadic inclusion body myositis predicts more severe motor, bulbar and respiratory involvement. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2016;87: Lloyd TE, Christopher-Stine L, Pinal-Fernandez I, et al. Cytosolic 5'-Nucleotidase 1A As a Target of Circulating Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Care Res 2016;68: Arahata K, Engel AG. Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. V: Identification and quantitation of T8+ cytotoxic and T8+ suppressor cells. Ann Neurol 1988;23: Arahata K, Engel AG. Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. IV: Cellmediated cytotoxicity and muscle fiber necrosis. Ann Neurol 1988;23: Emslie-Smith AM, Arahata K, Engel AG. Major histocompatibility complex class I antigen expression, immunolocalization of interferon subtypes, and T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in myopathies. Human Pathol 1989;20: Engel AG, Arahata K. Mononuclear cells in myopathies: quantitation of functionally distinct subsets, recognition of antigen-specific cell-mediated cytotoxicity in some diseases, and implications for the pathogenesis of the different inflammatory myopathies. Human Pathol1986;17: Brady S, Squier W, Sewry C, Hanna M, Hilton-Jones D, Holton JL. A retrospective cohort study identifying the principal pathological features useful in the diagnosis of inclusion body myositis. BMJ open 2014;4: e Machado PM, Dimachkie MM, Barohn RJ. Sporadic inclusion body myositis: new insights and potential therapy. Curr Opin Neurol 2014;27: Benveniste O, Rider LG, Group E. 213th ENMC International Workshop: Outcome measures and clinical trial readiness in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, Heemskerk, The Netherlands, September Neuromuscul Disord 2016;26: De Bleecker JL, De Paepe B, Aronica E, et al. 205th ENMC International Workshop: Pathology diagnosis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies part II March 2014, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 2015;25: De Bleecker JL, Lundberg IE, de Visser M, Group E. 193rd ENMC International workshop Pathology diagnosis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies 30 November - 2 December 2012, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 2013;23: Hoogendijk JE, Amato AA, Lecky BR, et al. 119th ENMC international workshop: trial design in adult idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, with the exception of inclusion body myositis, October 2003, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 2004;14: Danielsson O, Lindvall B, Gati I, Ernerudh J. Classification and diagnostic investigation in inflammatory myopathies: a study of 99 patients. J Rheumatol 2013;40:
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis
 Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis Marianne de Visser, Dept. of Neurology, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs),
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis Marianne de Visser, Dept. of Neurology, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs),
The many faces of myositis. Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Centre Dept of Neurology Amsterdam The Netherlands
 The many faces of myositis Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Centre Dept of Neurology Amsterdam The Netherlands Outline of the presentation Classification Diagnosis Therapy Prognosis Diagnostic criteria
The many faces of myositis Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Centre Dept of Neurology Amsterdam The Netherlands Outline of the presentation Classification Diagnosis Therapy Prognosis Diagnostic criteria
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
 Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES AND RELATED DISORDERS. Franclo Henning Division of Neurology Tygerberg Hospital
 IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES AND RELATED DISORDERS Franclo Henning Division of Neurology Tygerberg Hospital Classification systems Clinical (Bohan and Peter) Clinico-pathological (Dalakas & others)
IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES AND RELATED DISORDERS Franclo Henning Division of Neurology Tygerberg Hospital Classification systems Clinical (Bohan and Peter) Clinico-pathological (Dalakas & others)
Autoantibodies andprognosis. Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic
 Autoantibodies andprognosis Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic HeterogeneityofIIMs Diagnosis Polymyositis Dermatomyositis IBM Necrotising myopathy Paraneoplastic Amyopathic
Autoantibodies andprognosis Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic HeterogeneityofIIMs Diagnosis Polymyositis Dermatomyositis IBM Necrotising myopathy Paraneoplastic Amyopathic
Significance of antibody testing in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
 2/0/20 Significance of antibody testing in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague Diagnosis Polymyositis Juvenile DM (JPM) Paraneoplastic Myositis in overlap
2/0/20 Significance of antibody testing in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Jiří Vencovský Institute of Rheumatology, Prague Diagnosis Polymyositis Juvenile DM (JPM) Paraneoplastic Myositis in overlap
 MURDOCH RESEARCH REPOSITORY This is the author s final version of the work, as accepted for publication following peer review but without the publisher s layout or pagination. The definitive version is
MURDOCH RESEARCH REPOSITORY This is the author s final version of the work, as accepted for publication following peer review but without the publisher s layout or pagination. The definitive version is
Myosites du sujet âgé
 Myosites du sujet âgé Olivier Benveniste Département de Médecine Interne Centre de Référence Maladies Neuro-Musculaires Equipe Muscle Inflammatoire U974 Groupe Hospitalier Pitié-Salpêtrière Myositis classification
Myosites du sujet âgé Olivier Benveniste Département de Médecine Interne Centre de Référence Maladies Neuro-Musculaires Equipe Muscle Inflammatoire U974 Groupe Hospitalier Pitié-Salpêtrière Myositis classification
Case 1: History of J.H. Outside Evaluation. Outside Labs. Question #1
 Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Myositis 101. Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
 Myositis 101 Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Rheumatology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Myositis Association Annual Conference Louisville, KY Sept. 6 & 7, 2018 Disclosures Consulting: Dynavax Pfizer Off-label use:
Myositis 101 Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Rheumatology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Myositis Association Annual Conference Louisville, KY Sept. 6 & 7, 2018 Disclosures Consulting: Dynavax Pfizer Off-label use:
Polymyositis, a very uncommon isolated disease: clinical and histological re evaluation after long term follow up
 Rheumatol Int (2015) 35:915 920 DOI 10.1007/s00296-014-3198-5 Rheumatology INTERNATIONAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE - CASES WITH A MESSAGE Polymyositis, a very uncommon isolated disease: clinical and histological
Rheumatol Int (2015) 35:915 920 DOI 10.1007/s00296-014-3198-5 Rheumatology INTERNATIONAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE - CASES WITH A MESSAGE Polymyositis, a very uncommon isolated disease: clinical and histological
Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Vidya Limaye Rheumatology Department Royal Adelaide Hospital
 Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Vidya Limaye Rheumatology Department Royal Adelaide Hospital Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM) Heterogeneous group of systemic autoimmune syndromes
Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Vidya Limaye Rheumatology Department Royal Adelaide Hospital Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM) Heterogeneous group of systemic autoimmune syndromes
CURRENT ESSENTIALS IN INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES
 CURRENT ESSENTIALS IN INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES Maren Breithaupt, 1 Jens Schmidt 1,2 1. Clinic for Neurology, University Medical Center Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany 2. Department of Neuroimmunology, Institute
CURRENT ESSENTIALS IN INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES Maren Breithaupt, 1 Jens Schmidt 1,2 1. Clinic for Neurology, University Medical Center Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany 2. Department of Neuroimmunology, Institute
Expression of anti-srp19 antibody in muscle tissues from patients with autoimmune necrotizing myopathy
 Expression of anti-srp19 antibody in muscle tissues from patients with autoimmune necrotizing myopathy Q. Wang 1, F. Duan 2, P. Liu 3, P.F. Wang 4 and M.X. Wang 5 1 EmergencyDepartment, General Hospital
Expression of anti-srp19 antibody in muscle tissues from patients with autoimmune necrotizing myopathy Q. Wang 1, F. Duan 2, P. Liu 3, P.F. Wang 4 and M.X. Wang 5 1 EmergencyDepartment, General Hospital
Inflammatory Myopathies 4 th year MBBS. Marwan Adwan MBChB, MSc, MRCPI, MRCP(rheum) Consultant Rheumatologist
 Inflammatory Myopathies 4 th year MBBS Marwan Adwan MBChB, MSc, MRCPI, MRCP(rheum) Consultant Rheumatologist Case A 64 woman presents with erythematous itchy rash over back of hands & forehead. For 1 month
Inflammatory Myopathies 4 th year MBBS Marwan Adwan MBChB, MSc, MRCPI, MRCP(rheum) Consultant Rheumatologist Case A 64 woman presents with erythematous itchy rash over back of hands & forehead. For 1 month
TMA San Diego September 7, 2017
 Myositis 101: Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Management Namita Goyal, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Director, Neuromuscular Medicine Fellowship Director, Neuromuscular Diagnostic Laboratory Associate
Myositis 101: Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Management Namita Goyal, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Director, Neuromuscular Medicine Fellowship Director, Neuromuscular Diagnostic Laboratory Associate
Rheumatology E-learning. University of Szeged Department of Rheumatology and Immunology
 Rheumatology E-learning University of Szeged Department of Rheumatology and Immunology Introduction Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of systemic diseases characterized by an immune
Rheumatology E-learning University of Szeged Department of Rheumatology and Immunology Introduction Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of systemic diseases characterized by an immune
Myopathy with anti-hmgcr antibodies: Perimysium and myofiber pathology
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Myopathy with anti-hmgcr antibodies: Perimysium and myofiber pathology Ali Alshehri Washington University School
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Myopathy with anti-hmgcr antibodies: Perimysium and myofiber pathology Ali Alshehri Washington University School
What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease. Mark Gourley, MD
 What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease Mark Gourley, MD The Importance of the Immune System Defends us against foreign invaders Self (cancer) and Nonself (virus, bacteria, etc.) But, if the
What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease Mark Gourley, MD The Importance of the Immune System Defends us against foreign invaders Self (cancer) and Nonself (virus, bacteria, etc.) But, if the
*Pari Basharat ABSTRACT OVERVIEW OF IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES
 IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES: ASSOCIATION WITH OVERLAP MYOSITIS AND SYNDROMES: CLASSIFICATION, CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS, AND ASSOCIATED AUTOANTIBODIES *Pari Basharat University of Western Ontario,
IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES: ASSOCIATION WITH OVERLAP MYOSITIS AND SYNDROMES: CLASSIFICATION, CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS, AND ASSOCIATED AUTOANTIBODIES *Pari Basharat University of Western Ontario,
Myopathy with anti-jo-1 antibodies: pathology in perimysium and neighbouring muscle fibres
 472 Department of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO 63110, USA T MozaVar A Pestronk Correspondence to: Dr Alan Pestronk, Department of Neurology, Box 8111, 660 South Euclid
472 Department of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO 63110, USA T MozaVar A Pestronk Correspondence to: Dr Alan Pestronk, Department of Neurology, Box 8111, 660 South Euclid
4/16/2018. Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis. Objectives. Disclosures. Off-label uses for medications will be discussed
 Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis Jemima Albayda, MD Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins Myositis center Disclosures Off-label uses for medications will be discussed Objectives To
Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis Jemima Albayda, MD Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins Myositis center Disclosures Off-label uses for medications will be discussed Objectives To
POLYMYOSITIS (PM) DERMATOMYOSITIS (DM) Body myositis Eosinophilic myositis Giant cell myositis Focal / localised myositis Myopathies caused by
 POLYMYOSITIS (PM) DERMATOMYOSITIS (DM) Body myositis Eosinophilic myositis Giant cell myositis Focal / localised myositis Myopathies caused by infections, drugs, toxins Definition Epidemiology Pathogenesis
POLYMYOSITIS (PM) DERMATOMYOSITIS (DM) Body myositis Eosinophilic myositis Giant cell myositis Focal / localised myositis Myopathies caused by infections, drugs, toxins Definition Epidemiology Pathogenesis
Discovery, Understanding, and Progress in Myositis
 Discovery, Understanding, and Progress in Myositis Steven Ytterberg, M.D. TMA Annual Patient Conference New Orleans, LA Sept. 2, 2016 Disclosures Financial: Dynavax Corp. Pfizer Mallinckrodt American Board
Discovery, Understanding, and Progress in Myositis Steven Ytterberg, M.D. TMA Annual Patient Conference New Orleans, LA Sept. 2, 2016 Disclosures Financial: Dynavax Corp. Pfizer Mallinckrodt American Board
I mmune mediated and inflammatory myopathies are usually
 420 PAPER Myopathy with antibodies to the signal recognition particle: clinical and pathological features T Miller, M T Al-Lozi, G Lopate, A Pestronk... J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2002;73:420 428 See
420 PAPER Myopathy with antibodies to the signal recognition particle: clinical and pathological features T Miller, M T Al-Lozi, G Lopate, A Pestronk... J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2002;73:420 428 See
This month, we are very pleased to introduce some new tests for Scleroderma as well as some test changes to our existing scleroderma tests/panels.
 February 20, 2017 Client Letter Test Update February 2017 Dear Colleague: This month, we are very pleased to introduce some new tests for Scleroderma as well as some test changes to our existing scleroderma
February 20, 2017 Client Letter Test Update February 2017 Dear Colleague: This month, we are very pleased to introduce some new tests for Scleroderma as well as some test changes to our existing scleroderma
INCREASING INCIDENCE OF IMMUNE MEDIATED NECROTIZING MYOPATHY SINGLE CENTRE EXPERIENCE
 INCREASING INCIDENCE OF IMMUNE MEDIATED NECROTIZING MYOPATHY SINGLE CENTRE EXPERIENCE Martin Klein 1,2*, Heřman Mann 1,2*, Lenka Pleštilová 1,2, Josef Zámečník 3, Zoe Betteridge 4, Neil McHugh 4, Jiří
INCREASING INCIDENCE OF IMMUNE MEDIATED NECROTIZING MYOPATHY SINGLE CENTRE EXPERIENCE Martin Klein 1,2*, Heřman Mann 1,2*, Lenka Pleštilová 1,2, Josef Zámečník 3, Zoe Betteridge 4, Neil McHugh 4, Jiří
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy
 Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
Cytosolic 5 0 -Nucleotidase 1A As a Target of Circulating Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Diseases
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 68, No. 1, January 2016, pp 66 71 DOI 10.1002/acr.22600 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Cytosolic 5 0 -Nucleotidase 1A As a Target of Circulating Autoantibodies
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 68, No. 1, January 2016, pp 66 71 DOI 10.1002/acr.22600 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Cytosolic 5 0 -Nucleotidase 1A As a Target of Circulating Autoantibodies
Idiopathic inflammatory muscle diseases. Dr. Paul Etau Ekwom MBChB, MMED Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi-Kenya
 Idiopathic inflammatory muscle diseases. Dr. Paul Etau Ekwom MBChB, MMED Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi-Kenya I.W, 28 YRS, FEMALE SHOP STEWARD Referred to KNH on 16/06/09 from Thika Nursing Home Weakness
Idiopathic inflammatory muscle diseases. Dr. Paul Etau Ekwom MBChB, MMED Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi-Kenya I.W, 28 YRS, FEMALE SHOP STEWARD Referred to KNH on 16/06/09 from Thika Nursing Home Weakness
Complex repetitive discharge on electromyography as a risk factor for malignancy in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:814-821 Complex repetitive discharge on electromyography as a risk factor for malignancy in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy Na Ri Kim 1, Eon Jeong Nam 1, Jong
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:814-821 Complex repetitive discharge on electromyography as a risk factor for malignancy in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy Na Ri Kim 1, Eon Jeong Nam 1, Jong
Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis
 Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis Thomas Lloyd, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Neurology and Neuroscience Co-director, Johns Hopkins Myositis Center Sporadic IBM (IBM) Age at onset usually > 50 Prevalence
Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis Thomas Lloyd, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Neurology and Neuroscience Co-director, Johns Hopkins Myositis Center Sporadic IBM (IBM) Age at onset usually > 50 Prevalence
Paraneoplastic necrotizing myopathy in association with metastatic malignant melanoma: two case reports and a review of the literature
 CASE REPORT Paraneoplastic necrotizing myopathy in association with metastatic malignant melanoma: two case reports and a review of the literature Molly S Peterson 1, Bjoern Buehring 2, Patrick S Rush
CASE REPORT Paraneoplastic necrotizing myopathy in association with metastatic malignant melanoma: two case reports and a review of the literature Molly S Peterson 1, Bjoern Buehring 2, Patrick S Rush
The spectrum of elderly myopathies in an Asian population
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(2) : 177 181 The spectrum of elderly myopathies in an Asian population Shereen Ng, *Kum-Thong Wong FRCPath MD, Khean-Jin Goh FRCP Division of Neurology, Department of Medicine and
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(2) : 177 181 The spectrum of elderly myopathies in an Asian population Shereen Ng, *Kum-Thong Wong FRCPath MD, Khean-Jin Goh FRCP Division of Neurology, Department of Medicine and
Disorders of Muscle. Disorders of Muscle. Muscle Groups Involved in Myopathy. Needle Examination of EMG. History. Muscle Biopsy
 Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
바터팽대부의신경내분비종양환자에서발생한피부근염
 대한내과학회지 : 제 92 권제 6 호 2017 https://doi.org/10.3904/kjm.2017.92.6.552 바터팽대부의신경내분비종양환자에서발생한피부근염 1 건국대학교의과대학건국대학교충주병원류마티스내과, 연세대학교원주의과대학원주세브란스기독병원 2 류마티스내과, 3 내과, 4 한림대학교의과대학춘천성심병원류마티스내과 박정은 1 ㆍ강태영 2 ㆍ유진세
대한내과학회지 : 제 92 권제 6 호 2017 https://doi.org/10.3904/kjm.2017.92.6.552 바터팽대부의신경내분비종양환자에서발생한피부근염 1 건국대학교의과대학건국대학교충주병원류마티스내과, 연세대학교원주의과대학원주세브란스기독병원 2 류마티스내과, 3 내과, 4 한림대학교의과대학춘천성심병원류마티스내과 박정은 1 ㆍ강태영 2 ㆍ유진세
Chapter 5 Inclusion Body Myositis
 Chapter 5 Inclusion Body Myositis Lawrence J. Kagen Abstract Inclusion body myositis is an insidious, slowly progressive myopathy of middle-aged and older individuals. Because of these characteristics,
Chapter 5 Inclusion Body Myositis Lawrence J. Kagen Abstract Inclusion body myositis is an insidious, slowly progressive myopathy of middle-aged and older individuals. Because of these characteristics,
Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18
![Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18 Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18](/thumbs/95/125595183.jpg) Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Rheumatoid Factor
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Rheumatoid Factor
Myositis and Your Lungs
 Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
An autoimmune perspective on neuromuscular diseases
 An autoimmune perspective on neuromuscular diseases Colin Chalk MD,CM FRCPC Montreal General Hospital McGill University Schlomchik 2001 The proportion of neuromuscular patients who have an autoimmune cause
An autoimmune perspective on neuromuscular diseases Colin Chalk MD,CM FRCPC Montreal General Hospital McGill University Schlomchik 2001 The proportion of neuromuscular patients who have an autoimmune cause
Inflammatory muscle diseases.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology 4-30-2015 Inflammatory muscle diseases. Marinos C Dalakas Department of Neurology, Neuromuscular
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology 4-30-2015 Inflammatory muscle diseases. Marinos C Dalakas Department of Neurology, Neuromuscular
2 nd Global Conference on Myositis May 5-8, 2017 Bolger Center, Potomac, MD, USA All Times Listed are US Eastern Standard Time
 2 nd Global Conference on Myositis May 5-8, 2017 Bolger Center, Potomac, MD, USA All Times Listed are US Eastern Standard Time Friday May 5 7:00-8:00 am Pre-Conference Registration Pathology Pre-Conference
2 nd Global Conference on Myositis May 5-8, 2017 Bolger Center, Potomac, MD, USA All Times Listed are US Eastern Standard Time Friday May 5 7:00-8:00 am Pre-Conference Registration Pathology Pre-Conference
III./10.4. Diagnosis. Introduction. A.) Laboratory tests. Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques
 III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
Evaluation and construction of diagnostic criteria for inclusion body myositis
 Evaluation and construction of diagnostic criteria for inclusion body myositis Thomas E. Lloyd, MD, PhD Andrew L. Mammen, MD, PhD Anthony A. Amato, MD Michael D. Weiss, MD Merrilee Needham, MBBS Steven
Evaluation and construction of diagnostic criteria for inclusion body myositis Thomas E. Lloyd, MD, PhD Andrew L. Mammen, MD, PhD Anthony A. Amato, MD Michael D. Weiss, MD Merrilee Needham, MBBS Steven
2 nd Global Conference on Myositis May 5-8, 2017 Bolger Center, Potomac, MD, USA All Times Listed are US Eastern Standard Time
 2 nd Global Conference on Myositis May 5-8, 2017 Bolger Center, Potomac, MD, USA All Times Listed are US Eastern Standard Time Friday May 5 7:00-8:00 am Pre-Conference Registration Pathology Pre-Conference
2 nd Global Conference on Myositis May 5-8, 2017 Bolger Center, Potomac, MD, USA All Times Listed are US Eastern Standard Time Friday May 5 7:00-8:00 am Pre-Conference Registration Pathology Pre-Conference
Case Report Repository Corticotropin Injection for Treatment of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
 Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2016, Article ID 9068061, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9068061 Case Report Repository Corticotropin Injection for Treatment of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2016, Article ID 9068061, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9068061 Case Report Repository Corticotropin Injection for Treatment of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
The Role of Electron Microscopy in the Assessment of Dermatomyositis: A Retrospective Pilot Study on Skeletal Muscle Biopsies
 British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 3(4): 962-970, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org The Role of Electron Microscopy in the Assessment of : A Retrospective Pilot Study on
British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 3(4): 962-970, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org The Role of Electron Microscopy in the Assessment of : A Retrospective Pilot Study on
What are Autoantibodies and how do they work in Myositis?
 What are Autoantibodies and how do they work in Myositis? Neil McHugh, University of Bath and Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases Orlando September 2015 Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic
What are Autoantibodies and how do they work in Myositis? Neil McHugh, University of Bath and Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases Orlando September 2015 Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic
Identifying statin-associated autoimmune necrotizing myopathy
 REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will recognize autoimmune necrotizing myopathy if it occurs in their patients taking statins JEMIMA ALBAYDA, MD Division of Rheumatology, Department of
REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will recognize autoimmune necrotizing myopathy if it occurs in their patients taking statins JEMIMA ALBAYDA, MD Division of Rheumatology, Department of
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: diagnosis, treatment and outcome van de Vlekkert, Janneke
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: diagnosis, treatment and outcome van de Vlekkert, Janneke Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van de Vlekkert,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: diagnosis, treatment and outcome van de Vlekkert, Janneke Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van de Vlekkert,
Clinical Laboratory. [None
 Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG ELISA Detected * [None 18-289-900151 Detected] Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG ELISA Detected * [None 18-289-900151 Detected] Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
 Myositis and cancer Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Primary idiopathic polymyositis Primary idiopathic dermatomyositis Juvenile poly/dermatomyositis Myositis associated with another CTD Myositis associated
Myositis and cancer Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies Primary idiopathic polymyositis Primary idiopathic dermatomyositis Juvenile poly/dermatomyositis Myositis associated with another CTD Myositis associated
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Rituximab Therapy for Myopathy Associated With Anti Signal Recognition Particle Antibodies: A Case Series
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 62, No. 9, September 2010, pp 1328 1334 DOI 10.1002/acr.20219 2010, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rituximab Therapy for Myopathy Associated With Anti
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 62, No. 9, September 2010, pp 1328 1334 DOI 10.1002/acr.20219 2010, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rituximab Therapy for Myopathy Associated With Anti
L. Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 2012
 L. Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 2012 L Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 09 17 yo Ashkenazi male with proximal muscle pain and weakness, mild malar erythema and erythema over knees and dorsal aspect of PIPs Mild tenderness
L. Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 2012 L Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 09 17 yo Ashkenazi male with proximal muscle pain and weakness, mild malar erythema and erythema over knees and dorsal aspect of PIPs Mild tenderness
HUNGARIAN MYOSITIS COHORT
 CLINICAL ADVANCES OF ANTI- TIF1Γ AUTOANTIBODY IN A HUNGARIAN MYOSITIS COHORT Melinda Nagy-Vincze 1, Zoltán Griger 1, Levente Bodoki 1, Zsuzsa Szankai 1, Zoe E. Betteridge 2, Katalin Dankó 1 1 University
CLINICAL ADVANCES OF ANTI- TIF1Γ AUTOANTIBODY IN A HUNGARIAN MYOSITIS COHORT Melinda Nagy-Vincze 1, Zoltán Griger 1, Levente Bodoki 1, Zsuzsa Szankai 1, Zoe E. Betteridge 2, Katalin Dankó 1 1 University
Arthritis Superspeciality Center, Hubli, Karnataka and 2 Department of Rheumatology, SDM Medical College, Dharwad, Karnataka, India.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(1):147-151 A Rare Case of Juvenile Dermatomyositis Vikram Haridas 1,2, Kiran Haridas 1 1,2 Arthritis Superspeciality Center, Hubli, Karnataka and 2 Department of Rheumatology,
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(1):147-151 A Rare Case of Juvenile Dermatomyositis Vikram Haridas 1,2, Kiran Haridas 1 1,2 Arthritis Superspeciality Center, Hubli, Karnataka and 2 Department of Rheumatology,
Medicine. Observational Study OPEN
 Observational Study Medicine Atorvastatin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myositis An emerging dominant entity in patients with autoimmune myositis presenting with a pure polymyositis phenotype Yves Troyanov,
Observational Study Medicine Atorvastatin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myositis An emerging dominant entity in patients with autoimmune myositis presenting with a pure polymyositis phenotype Yves Troyanov,
Clinical Study A Clinical Analysis of Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 648570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/648570 Clinical Study A Clinical Analysis of Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 648570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/648570 Clinical Study A Clinical Analysis of Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients
Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in MDs clinical practice
 4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 2 How to proceed with a suspected myopathy? - Level 2 Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in MDs clinical
4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 2 How to proceed with a suspected myopathy? - Level 2 Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in MDs clinical
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction
 Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
 REVIEW Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Current Trends in Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Up-to-Date Treatment Recommendations Floranne C. Ernste, MD, and Ann M. Reed, MD Abstract Recently, there
REVIEW Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Current Trends in Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Up-to-Date Treatment Recommendations Floranne C. Ernste, MD, and Ann M. Reed, MD Abstract Recently, there
Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of. Connective Tissue Disease
 Connective Tissue Disease Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of Connective Tissue Disease Connective Tissue Disease High quality assays and novel tests Inova offers a complete array of assay methods,
Connective Tissue Disease Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of Connective Tissue Disease Connective Tissue Disease High quality assays and novel tests Inova offers a complete array of assay methods,
STUDIES ON INTERLEUKIN-1 IN IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES
 From the Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden STUDIES ON INTERLEUKIN-1 IN IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES Christina Dorph Stockholm 2009 All previously
From the Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden STUDIES ON INTERLEUKIN-1 IN IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES Christina Dorph Stockholm 2009 All previously
Kumaraswamy Sivakumar, Christina Semino-Mora and Marinos C. Dalakas
 braini0310 Brain (1997), 120, 653 661 An inflammatory, familial, inclusion body myositis with autoimmune features and a phenotype identical to sporadic inclusion body myositis Studies in three families
braini0310 Brain (1997), 120, 653 661 An inflammatory, familial, inclusion body myositis with autoimmune features and a phenotype identical to sporadic inclusion body myositis Studies in three families
pathophysiologic features and prognosis. The emergence of myositis-specific autoantibodies suggests that subgroups of patients exist.
 Research JAMA Neurology Original Investigation Development of a New Classification System for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Based on Clinical Manifestations and Myositis-Specific Autoantibodies Kubéraka
Research JAMA Neurology Original Investigation Development of a New Classification System for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Based on Clinical Manifestations and Myositis-Specific Autoantibodies Kubéraka
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for the treatment of dermatomyositis and polymyositis (Adults) Reference: NHS England A13X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for the treatment of dermatomyositis and polymyositis (Adults) Reference: NHS England A13X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside
Clinical Laboratory. 14:41:00 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl Oct-18
 Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Antibody 5.0 IU/mL [0.0-9.0] 18-289-900139 16-Oct-18 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl 18-289-900139
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Antibody 5.0 IU/mL [0.0-9.0] 18-289-900139 16-Oct-18 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl 18-289-900139
Research Article Soluble IL-2 Receptor: A Biomarker for Assessing Myositis Activity
 Disease Markers, Article ID 76, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/1/76 Research Article Soluble IL- Receptor: A Biomarker for Assessing Myositis Activity Anne Tournadre, 1 Jean-Jacques Dubost, 1 Martin
Disease Markers, Article ID 76, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/1/76 Research Article Soluble IL- Receptor: A Biomarker for Assessing Myositis Activity Anne Tournadre, 1 Jean-Jacques Dubost, 1 Martin
MYOSITIS. A physician s guide to the
 MYOSITIS A physician s guide to the TABLE OF CONTENTS Myositis basics... 1 contents... 3 Causes... 7... 11 Affected populations... 15 Diagnosis... 17... 25... 31 PHYSICIAN S GUIDE TO MYOSITIS matory
MYOSITIS A physician s guide to the TABLE OF CONTENTS Myositis basics... 1 contents... 3 Causes... 7... 11 Affected populations... 15 Diagnosis... 17... 25... 31 PHYSICIAN S GUIDE TO MYOSITIS matory
investigations. We will also discuss some rare neuromuscular problems presenting for the first time in later life.
 Musculoskeletal 29 Muscle disorders in the elderly Myopathy is the term used to describe diseases of the muscle that are not attributable to nerve dysfunction. It is an umbrella term that encompasses myopathies
Musculoskeletal 29 Muscle disorders in the elderly Myopathy is the term used to describe diseases of the muscle that are not attributable to nerve dysfunction. It is an umbrella term that encompasses myopathies
Inflammatory Myopathies: Evaluation and Management
 Inflammatory Myopathies: Evaluation and Management Steven A. Greenberg, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT The inflammatory myopathies, including dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis, and polymyositis, are poorly understood
Inflammatory Myopathies: Evaluation and Management Steven A. Greenberg, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT The inflammatory myopathies, including dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis, and polymyositis, are poorly understood
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 Pedss Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Juvenile Dermatomyositis. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
Pedss Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Juvenile Dermatomyositis. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
RIG-I expression in perifascicular myofibers is a reliable biomarker of dermatomyositis
 Suárez-Calvet et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:174 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1383-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access RIG-I expression in perifascicular myofibers is a reliable biomarker of dermatomyositis
Suárez-Calvet et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:174 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1383-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access RIG-I expression in perifascicular myofibers is a reliable biomarker of dermatomyositis
Prevalence and reactivity of anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (anti-mda-5) autoantibody in Brazilian patients with dermatomyositis *
 Investigation 517 Particular characteristics Soares de Sá BC, of atopic Moredo eczema LF, Gomes in tropical EE, de environments. Araújo ESS, Duprat The Tropical JP Environment... 517 s Prevalence and reactivity
Investigation 517 Particular characteristics Soares de Sá BC, of atopic Moredo eczema LF, Gomes in tropical EE, de environments. Araújo ESS, Duprat The Tropical JP Environment... 517 s Prevalence and reactivity
Prognosis and prognostic factors in sporadic inclusion body myositis
 Acta Neurol Scand 212: 125: 353 358 DOI: 1.1111/j.16-44.211.1584.x Ó 211 John Wiley & Sons A S ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Prognosis and prognostic factors in sporadic inclusion body myositis Lindberg
Acta Neurol Scand 212: 125: 353 358 DOI: 1.1111/j.16-44.211.1584.x Ó 211 John Wiley & Sons A S ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Prognosis and prognostic factors in sporadic inclusion body myositis Lindberg
Dermatomyositis Advice from Experts: Improving Your Medical Dermatology Diagnostic and Management Skills Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine
 Dermatomyositis Advice from Experts: Improving Your Medical Dermatology Diagnostic and Management Skills Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine (Dermatology) University of Louisville Learning Objectives
Dermatomyositis Advice from Experts: Improving Your Medical Dermatology Diagnostic and Management Skills Jeffrey P. Callen, MD Professor of Medicine (Dermatology) University of Louisville Learning Objectives
A48-year-old Hispanic woman
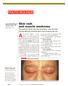 Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light.
 Cơ vân Cơ vân Cơ vân (cắt dọc) Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light. (A, Congo Red). Amyloid neuropathy:
Cơ vân Cơ vân Cơ vân (cắt dọc) Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light. (A, Congo Red). Amyloid neuropathy:
IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHY: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN THE INDIAN POPULATION
 British Journal of Rheumatology ;3:83-83 IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHY: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN THE INDIAN POPULATION BY M. L. PRASAD*t, C. SARKAR*, S. ROY*, U. BAGCHI*, R. R. SINGHf Y.
British Journal of Rheumatology ;3:83-83 IDIOPATHIC INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHY: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN THE INDIAN POPULATION BY M. L. PRASAD*t, C. SARKAR*, S. ROY*, U. BAGCHI*, R. R. SINGHf Y.
Budsakorn Darawankul, MD. Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital
 Budsakorn Darawankul, MD. Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical application Common autoantibody in ANA diseases Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical
Budsakorn Darawankul, MD. Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima Hospital Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical application Common autoantibody in ANA diseases Outline What is ANA? How to detect ANA? Clinical
Inclusion body myositis clinical features, diagnosis and management
 Inclusion body myositis clinical features, diagnosis and management Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Center Dept. of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands Inclusion body myositis Most frequent myopathy
Inclusion body myositis clinical features, diagnosis and management Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Center Dept. of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands Inclusion body myositis Most frequent myopathy
Magnetic resonance imaging changes of thigh muscles in myopathy with antibodies to signal recognition particle
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2015;54:1017 1024 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keu422 Advance Access publication 21 November 2014 Original article Magnetic resonance imaging changes of thigh muscles in myopathy
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2015;54:1017 1024 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keu422 Advance Access publication 21 November 2014 Original article Magnetic resonance imaging changes of thigh muscles in myopathy
Pattern of muscle involvement in inclusion body myositis: a sonographic study
 Pattern of muscle involvement in inclusion body myositis: a sonographic study J. Albayda 1, L. Christopher-Stine 1, C.O. Bingham III 1, J.J. Paik 1, E. Tiniakou 1, S. Billings 2, O.M. Uy 2, P. Burlina
Pattern of muscle involvement in inclusion body myositis: a sonographic study J. Albayda 1, L. Christopher-Stine 1, C.O. Bingham III 1, J.J. Paik 1, E. Tiniakou 1, S. Billings 2, O.M. Uy 2, P. Burlina
Case Report J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(6): ress. Elmer. John O Grady a, c, Len Harty a, Nick Mayer b, Val Critcher b, John Ryan b.
 Elmer ress Case Report J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(6):490-494 Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy, Associated With Antibodies to Signal Recognition Particle, Together With Lupus Nephritis: Case Presentation
Elmer ress Case Report J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(6):490-494 Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy, Associated With Antibodies to Signal Recognition Particle, Together With Lupus Nephritis: Case Presentation
Contributed equally. Columbia, Vancouver BC, Canada. Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey.
 DR PETER SCHUTZ (Orcid ID : 0000-0001-7962-1560) PROFESSOR THOMAS S JACQUES (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-7833-2158) Article type : Original Article HISTOLOGICAL HETEROGENEITY IN A LARGE CLINICAL COHORT OF JUVENILE
DR PETER SCHUTZ (Orcid ID : 0000-0001-7962-1560) PROFESSOR THOMAS S JACQUES (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-7833-2158) Article type : Original Article HISTOLOGICAL HETEROGENEITY IN A LARGE CLINICAL COHORT OF JUVENILE
INCLUSION BODY MYOSITIS. Bill Tillier Calgary, Alberta February, 2014.
 INCLUSION BODY MYOSITIS. Bill Tillier Calgary, Alberta February, 2014. IBM classification. 2 Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis (sibm) is classified as a type of muscle disease. Idiopathic inflammatory myositis
INCLUSION BODY MYOSITIS. Bill Tillier Calgary, Alberta February, 2014. IBM classification. 2 Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis (sibm) is classified as a type of muscle disease. Idiopathic inflammatory myositis
Inclusion body myositis Steven A. Greenberg
 Inclusion body myositis Steven A. Greenberg Division of Neuromuscular Disease, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, and Children s Hospital Informatics Program, Harvard Medical School,
Inclusion body myositis Steven A. Greenberg Division of Neuromuscular Disease, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, and Children s Hospital Informatics Program, Harvard Medical School,
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Pathomechanisms of Anti Cytosolic 5 0 -Nucleotidase 1A Autoantibodies in Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Pathomechanisms of Anti Cytosolic 5 0 -Nucleotidase 1A Autoantibodies in Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis Nozomu Tawara, MD, 1 Satoshi Yamashita, MD, PhD, 1 Xiao Zhang, 1 Mai Korogi, 1
RESEARCH ARTICLE Pathomechanisms of Anti Cytosolic 5 0 -Nucleotidase 1A Autoantibodies in Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis Nozomu Tawara, MD, 1 Satoshi Yamashita, MD, PhD, 1 Xiao Zhang, 1 Mai Korogi, 1
A Case of Erythrodermic Dermatomyositis Associated with Gastric Cancer
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 21, No. 4, 2009 CASE REPORT A Case of Erythrodermic Dermatomyositis Associated with Gastric Cancer Sung Woo Kim, M.D., Yoo Seok Kang, M.D., Sang Hoon Park, M.D., Un Ha Lee, M.D., Hyun
Ann Dermatol Vol. 21, No. 4, 2009 CASE REPORT A Case of Erythrodermic Dermatomyositis Associated with Gastric Cancer Sung Woo Kim, M.D., Yoo Seok Kang, M.D., Sang Hoon Park, M.D., Un Ha Lee, M.D., Hyun
Long-term follow-up of sporadic inclusion body myositis treated with intravenous immunoglobulin: a retrospective study of 16 patients
 Long-term follow-up of sporadic inclusion body myositis treated with intravenous immunoglobulin: a retrospective study of 16 patients C. Dobloug, R. Walle-Hansen, J.T. Gran, Ø. Molberg Section of Rheumatology,
Long-term follow-up of sporadic inclusion body myositis treated with intravenous immunoglobulin: a retrospective study of 16 patients C. Dobloug, R. Walle-Hansen, J.T. Gran, Ø. Molberg Section of Rheumatology,
Inclusion body myositis: clinical review and current practice
 & ur- Inclusion body myositis: clinical review and current practice Practice points Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is the commonest acquired myopathy in patients aged over 50 years with males more frequently
& ur- Inclusion body myositis: clinical review and current practice Practice points Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is the commonest acquired myopathy in patients aged over 50 years with males more frequently
Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan
 CASE REPORT Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan Kenichiro Tokunaga 1 and Noboru Hagino 2 Abstract We performed a retrospective
CASE REPORT Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan Kenichiro Tokunaga 1 and Noboru Hagino 2 Abstract We performed a retrospective
2/23/18. Disclosures. Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood. Making Room for Rheumatology. I have nothing to disclose. James J.
 Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Expression of myxovirus-resistance protein A: a possible marker of muscle disease activity and. autoantibody specificities in juvenile dermatomyositis
 Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology (2018) doi: 10.1111/nan.12498 Expression of myxovirus-resistance protein A: a possible marker of muscle disease activity and autoantibody specificities in juvenile
Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology (2018) doi: 10.1111/nan.12498 Expression of myxovirus-resistance protein A: a possible marker of muscle disease activity and autoantibody specificities in juvenile
Pediatric rheumatology. MHC class I and II expression in juvenile dermatomyositis skeletal muscle
 Pediatric rheumatology MHC class I and II expression in juvenile dermatomyositis skeletal muscle A.M.E. Sallum 1, M.H.B. Kiss 2, C.A.A. Silva 3, A. Wakamatsu 4, S. Sachetti 5, S. Lotufo 6, N. Matsumura
Pediatric rheumatology MHC class I and II expression in juvenile dermatomyositis skeletal muscle A.M.E. Sallum 1, M.H.B. Kiss 2, C.A.A. Silva 3, A. Wakamatsu 4, S. Sachetti 5, S. Lotufo 6, N. Matsumura
Strong correlation between cancer progression and anti-transcription intermediary factor 1γ antibodies in dermatomyositis patients
 Strong correlation between cancer progression and anti-transcription intermediary factor γ antibodies in dermatomyositis patients M. Ogawa-Momohara, Y. Muro, T. Mitsuma 2, M. Katayama 3, K. Yanaba 4, M.
Strong correlation between cancer progression and anti-transcription intermediary factor γ antibodies in dermatomyositis patients M. Ogawa-Momohara, Y. Muro, T. Mitsuma 2, M. Katayama 3, K. Yanaba 4, M.
JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS
 JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS - how to diagnose, how to treat? Miloš Nikolić, MD, PhD Professor and Chairman Department of Dermatology, Division of Pediatric Dermatology University of Belgrade, School of Medicine,
JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS - how to diagnose, how to treat? Miloš Nikolić, MD, PhD Professor and Chairman Department of Dermatology, Division of Pediatric Dermatology University of Belgrade, School of Medicine,
Evolving Uses of IVIG in myositis
 Evolving Uses of IVIG in myositis Rossitza I. Chichkova, MD, MS Associate Professor Depts of Neurology and Internal Medicine University of South Florida, Tampa, FL Immune Function In Normal State: Protects
Evolving Uses of IVIG in myositis Rossitza I. Chichkova, MD, MS Associate Professor Depts of Neurology and Internal Medicine University of South Florida, Tampa, FL Immune Function In Normal State: Protects
Myositis and Autoimmune ILD
 Myositis and Autoimmune ILD 2018 AURA Annual Meeting Sedona, Arizona June 2, 2018 Chester V. Oddis, MD Director, Myositis Center University of Pittsburgh Disclosures Genentech: Clinical trial support Idera:
Myositis and Autoimmune ILD 2018 AURA Annual Meeting Sedona, Arizona June 2, 2018 Chester V. Oddis, MD Director, Myositis Center University of Pittsburgh Disclosures Genentech: Clinical trial support Idera:
