investigations. We will also discuss some rare neuromuscular problems presenting for the first time in later life.
|
|
|
- Ashlee Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal 29 Muscle disorders in the elderly Myopathy is the term used to describe diseases of the muscle that are not attributable to nerve dysfunction. It is an umbrella term that encompasses myopathies that are inherited and those that are acquired. Here, we consider the common myopathies that can occur in later life. We discuss the clinical manifestations, investigation and management of drug-induced, toxic and endocrine myopathies as well as the inflammatory muscle disorders. We also consider the inherited muscle disorders that can present in older patients, including myotonic and oculopharyngeal dystrophy, and facioscapulohumeral. We briefly discuss the neuromuscular disorder myasthenia gravis, which whilst not a primary disorder of muscle, has many overlapping features of a myopathy. Dr Katie Nolan* Specialist Trainee Year 2 in Acute Care Common Stem, University of Birmingham, Queen Elizabeth Dr Atef Michael Consultant Geriatrician, Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley, UK; Honorary Senior Lecturer of Medicine, Birmingham University * katienolan34@hotmail.com Te diagnosis of muscle disorders in the elderly presents a clinical challenge. Tis is not only because many of these conditions are complex and overlapping, but also due to a misguided acceptance among many clinicians that deterioration in function and muscle strength among the elderly is usually a result of the ageing process rather than a pathological disease entity. The importance of reaching the correct diagnosis is apparent for a number of reasons. Many muscular disorders presenting in the elderly are acquired 1 and therefore potentially reversible. The complications of such disorders, including recurrent falls and aspiration, have significant morbidity and mortality and in the case of certain inherited disorders presenting in the elderly, the potential implications for future generations in establishing a correct diagnosis are vitally important. 2 In the following article, we present a brief overview of muscle diseases affecting the elderly, highlighting typical presenting features and diagnostic investigations. We will also discuss some rare neuromuscular problems presenting for the first time in later life. Muscle disorders Myopathy Symptoms suggestive of a myopathy presenting in an older person are similar to those presenting at any age and weakness is usually the predominant feature. This weakness is commonly proximal and presents as difficulty rising from a chair or climbing the stairs. Tis may be due to the increased eccentric contractions of proximal muscles as part of their antigravity role. These eccentric contractions have been shown to be more greatly affected when the muscle becomes weaker. However, distal weakness is also recognised (ofen in inherited conditions) and in this case, the patient may present with problems when writing, or with hand grip or grasp. 2 Patients also complain of malaise and may experience a fever. Discolouration of the urine can occur, and represents rhabdomyolysis. 3 Sensory symptoms are not associated with pure myopathies and reflexes are preserved until very late in the disease process, although in older patients with multiple comorbidities such distinctions are ofen difficult to demonstrate clinically. Muscle atrophy is also generally a late sign. 4 A clue to the aetiology of a new onset myopathy may be indicated from the time course of the illness. Weakness over a period of hours may suggest a toxic cause whereas that presenting over days is more likely to represent an acute dermatomyositis or rhabdomyolysis. Symptoms developing over weeks or months may be a result of an endocrine disorder, polymyositis or drugs, and that occurring over months to years may indicate a hereditary illness. 5 Te investigations needed to confirm a diagnosis and identify a likely cause for an individual myopathy will depend on the clinical picture. Tese will include assessments of full blood count, renal and liver function, and thyroid function as well as calcium, March 2012 Midlife and Beyond GM
2 30 Musculoskeletal magnesium and phosphate, creatine kinase (CK) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Urine dipstick is also vital in every case to look for myoglobinuria. Autoantibodies may also be requested. Electrophysiology can be helpful. Electromyography (EMG), which can localise the pathology to the muscle rather than the nerve or anterior horn cell, is widely used to aid diagnosis. EMG findings will depend on the cause of the myopathy, but hallmark changes include low amplitude, polyphasic, brief duration potentials with voluntary contraction. Muscle biopsy is ofen used if an inflammatory disorder is postulated and MRI can also be helpful in this regard. Genetic testing may be offered if a muscular dystrophy is a possibility. Mild cases progress slowly and the patient may have a normal life span. In such cases, the patient may go undiagnosed until later life. Drug-induced myopathy A number of common and widelyprescribed drugs have been identified as causing features of myopathy which can either be fleeting or progressive, painful or painless and, in severe cases, can cause rhabdomyolysis and renal failure. 3 It is well known that statin therapy can cause such effects, 6 but other commonly used drugs, including steroids, beta-blockers, and a host of other cardiac drugs, can cause myopathy. 4 Such drugs used in combination can increase the risk of such effects. Hypokalaemia, a common sideeffect of many diuretics, can also produce a myopathy. Patients presenting with a drug-induced myopathy tend to have proximal weakness, which in severe cases can progress to muscle atrophy. CK is usually elevated in statin-induced as well as other painful myopathies but may be normal. Treatment involves removal of the offending drug, which usually results in good recovery. 4 Toxic myopathy Toxic myopathy encompasses not only alcohol-induced disease but also myopathy associated with drugs of abuse. Although drug abuse is rare amongst the elderly, it is worth remembering that heroin, methadone and cocaine can all induce symptoms of muscle weakness and rhabdomyolysis. 4 Alcohol abuse among the elderly, however, is not rare and this can cause both an acute as well as a chronic myopathy. Acute myopathy may follow an alcoholic binge 4 or can be secondary to hypokalaemia associated with vomiting and can usually be reversed by removing the toxin or by potassium replacement. 4. In the chronic form associated with long-standing alcoholism, where there is proximal weakness and wasting of the shoulder and pelvic girdle, effects are ofen difficult to reverse. 3 CK levels may or may not be elevated and patients may not offer an alcohol history. In such situations, a collateral history may be useful and other clues should be sought including macrocytosis and deranged LFT s. Endocrine myopathies Endocrine dysfunction is common in later life and a number of these disorders can present with, or have been linked to, muscle dysfunction. Both hyper- and hypothyroidism can present with features of proximal muscle weakness and myopathy, the latter being more common and more severe in hyperthyroidism. In hypothyroidism, the CK is often elevated and, if there is clinical suspicion, other signs suggestive of the diagnosis should be sought. In the case of thyrotoxicosis, CK is ofen normal. In both conditions, symptoms usually resolve on treating the underlying disorder. 4 Patients with Cushing s syndrome commonly have symptomatic myopathy at presentation. Weakness is proximal and symmetrical, and there is ofen muscle pain. Other features suggestive of the diagnosis should be sought including truncal obesity, purple striae, moon face and supraclavicular fat pads. 10 Patients with a steroid-induced Cushing s syndrome are most at risk of developing muscular symptoms. In these patients, CK levels may be normal and EMG studies are usually non-specific. A muscle biopsy may help in distinguishing a steroid-induced myopathy from an inflammatory illness and treatment involves removal of the offending drug. 4 Disease processes involving the utilisation and metabolism of vitamin D and calcium are also common amongst the elderly and can similarly affect muscle strength. In patients with osteomalacia, there will be difficulty rising from a chair due to proximal muscle weakness. Patients have waddling gait and ofen bone pain. Patients with osteomalacia are likely to have hypocalcaemia and hypophosphataemia but CK levels may be normal and EMG studies are of little benefit. Recovery of muscle strength may take some weeks or months following treatment with vitamin D3. Conversely patients with
3 32 Musculoskeletal hypercalcaemia as a result of primary hyperparathyroidism can also present with myopathies although these will often be late in the illness. The mechanism of weakness is not known, although CK is usually normal and treatment of the disease process will provide symptomatic improvement. Other endocrine causes of muscle weakness in the elderly include Addison s disease as well as a small number of other disorders of carbohydrate metabolism presenting in late adulthood, such as maltase deficiency, although these are exceedingly rare. Inflammatory muscle disorders Te idiopathic inflammatory muscle disorders occurring most commonly in older people are inclusion body myositis, dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Inclusion body myositis Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is a relatively rare disorder with a prevalence of 51.3 per million population in those over 50 years of age. 7 However it is a disease predominantly affecting the elderly. IBM presents with a combination of proximal and distal weakness characteristically affecting the quadriceps and long flexors of the fingers, and a profound weakness of the forearms can occur. Te weakness is usually asymmetrical and can also affect flexion of the neck. Dysphagia associated with the condition is the main cause of morbidity and mortality in IBM. 8 It is not clear what causes IBM but there is evidence that a T-cell mediated response may be involved along with accelerated degeneration in the muscle. 2 Diagnosis is by means of nerve conduction studies, measurement of CK and muscle biopsy, which is ofen diagnostic. Steroids do not alter the progress of this condition and loss of mobility is usual within 10 years of diagnosis. 8 Dermatomyositis Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune disorder which has two peak incidences: one in childhood and a second in later life. It presents with a symmetrical proximal muscle weakness, pain, dysphagia and often characteristic skin rashes. Tese include a scaly eruption over the metacarpophalangeal joints known as Gottrons papules and a purple or heliotrope rash over the eye lids. There is often a V
4 34 Musculoskeletal shaped photosensitive rash over the anterior chest wall. Dermatomyositis may be associated with internal malignancy in as many as 20% of cases and this is particularly common in the elderly. 4 Terefore, it is vital to examine the patient thoroughly, and consideration should be given to further investigation of specific malignancies depending on the history given. The gold standard investigation is muscle biopsy although CK can help with disease monitoring. High-dose steroids, as well as steroid-sparing agents, are employed in the treatment of this disorder. Immunoglobulins and monoclonal antibodies have also been used successfully. 9 Polymyositis Polymyositis holds many similarities with dermatomyositis, and these may be considered overlapping disorders. Polymyositis is also thought to be an autoimmune disorder which presents with proximal muscle weakness but unlike dermatomyositis, no link with malignancy has been identified. It is thought the disorder may be triggered by certain infections, including human T-cell leukaemia virus 1 (HTLV1) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or by certain drugs such as D penicillamine. 10 Polymyositis causes weakness in the pelvic and shoulder girdles and may limit functionality, particularly for elderly people. Dysphagia is common, occurring in up to one third of patients and patients may have signs of associated connective tissue disorders such as Sjogren s syndrome. 4 Diagnosis and treatment is as for dermatomyositis, discussed above. Inherited disorders of the muscle Myotonic dystrophy Myotonic dystrophy is a common autosomal dominant disorder which presents most ofen in late adolescence and middle age. 11 Despite this, milder forms of the illness have been recognised in more elderly patients. There are a number of characteristic features on clinical examination which help to identify the disorder, namely ptosis and frontal balding. Tere is a generalised weakness of the facial muscles which may progress to involve other muscle groups and there is a risk of respiratory muscle weakness. Patients are unable to quickly open and close their hands and thus their grip is commonly affected. Particularly in the case of older patients, there is a risk of cardiomyopathy and associated cardiac arrhythmias, which can lead to sudden death. 2 Other systemic complications include diabetes and cataracts as well as hepatic and gastrointestinal complications. Diagnosis is based on isolation of the DM1 gene in families with a known history of the disorder. Where there is no documented history, identification of this disorder relies on recognition of the clinical features. CK is often normal. Tere is no treatment that is known to alter the progression of the illness but appropriate treatment of cardiac and other complications is likely to increase longevity. It is important to establish a diagnosis even in an elderly person who may be only mildly affected. This is because the disease demonstrates anticipation and therefore future generations are likely to be more severely affected at an earlier age. 3 Oculopharyngeal dystrophy Oculopharyngeal dystrophy is a late-onset disorder commonly affecting adults in their fifies or older. Presentation is with ptosis or dysphagia and there may be mild weakness of the proximal muscles of the shoulder and pelvic girdle. There is usually a positive family history. The disorder is autosomal dominant and identification of the PABPN1 gene confirms the diagnosis in affected individuals. 2 Life expectancy is normal although the patient may eventually be wheelchair bound. Treatment is aimed at relieving problematic dysphagia and, where appropriate, surgery for ptosis. Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy Patients with facioscapulohumeral dystrophy occasionally present in old age; however, more commonly the disease presents in early adult life. Te disorder affects the muscles of the face, scapula and the upper arm. CK levels may be increased or normal and diagnosis is based on identification of a deletion on the FSHMD1A gene. 2 Treatment is supportive. Becker s muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a widely recognised disorder in the paediatric population and death occurs in late teens. However,
5 36 Musculoskeletal a milder form of the disorder namely Becker s muscular dystrophy presents in adolescence with muscle weakness of the limb girdle. Calf pseudohypertrophy is a common finding on examination and there may be contractures as well as significant muscle wasting. 4 In some cases where females have been affected more mildly, symptoms may not present until middle age. 12 In these cases the heart is often affected and a cardiomyopathy can occur. In patients presenting in late middle age, CK levels may be normal although in younger patients CK is usually elevated. EMG, muscle biopsy and genetic testing will help to confirm the diagnosis and treatment is supportive. Myasthenia gravis Tis disorder is a neuromuscular condition rather than a muscular disorder; it is relatively uncommon with a prevalence of one in 17, As well as its classical presentation affecting young women under the age of 40, there is a second peak in incidence in men over 60 years. Te disorder is characterised by fatigable muscle weakness commonly affecting the ocular and bulbar muscles, although the proximal limb girdle and respiratory muscles are also ofen involved. Diagnosis is based on clinical demonstration of muscle fatigability combined with a history of diplopia, ptosis, dysphagia, speech disturbance or weakness affecting other muscle groups. A history of other associated autoimmune conditions particularly hypothyroidism may also be present in the patient or relatives. There is a recognised familial predisposition in about 5% of cases. 13 Anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies should be measured in all patients suspected of having the disorder and where the result is negative, antibodies against muscle specific kinase (MuSK) should be requested. 2 A tensilon test should be performed to help aid the diagnosis and repetitive nerve stimulation/ electromyogram (EMG) studies should also be performed. It is also vital to obtain a computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the neck to look for thymomas, which are commonly found in association with myasthenia gravis. Where thymomas are identified, surgery should be offered to the patient. 2 Treatment of the disorder is lifelong, particularly in older patients, and will include cholinesterase inhibitors in combination with immunosuppressant. In a myasthenic crisis, intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange have been shown to produce rapid clinical improvement. Patients should be regularly followed-up to allow early identification of possible deterioration and intervention. Tere is no conflict of interest References 1. Laguno M, Miró O, Perea M et al. Muscle diseases in elders: a 10-year retrospective study, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2002; 57: Roberts M E. Neuromuscular diseases including myasthenic disorders In: Taltis R C, Fillit M, Brocklehurst s Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 6th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone. 2003, pg Young A. Muscle disease. In: Grimely Evans J, Franklin Williams T, Lynn Beattie B. Oxford textbook of Geriatric Medicine. 2nd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press pg Hilton-Jones D. Muscle disorders. In Pathy JMS, Sinclair JA, MorleyJ E. Principles and Practice of Geriatric Medicine. 4th ed. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons pg Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ, Wilson JD. In: Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine. 14th ed. McGraw-Hill. New York. 1998: Bromberg MB. Drug-induced myopathies, J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2005; 7: Greenberg SA. Inclusion body myositis: review of recent literature, Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2009; 9: Needham M, Corbett A, Day T et al.dysphagia in inclusion body myositis: clinical features, management, and clinical outcome. J Clin Neurosci 2008; 15: Basta M, Dalakas MC. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin exerts its beneficial effect in patients with dermatomyositis by blocking endomysial deposition of activated complement fragments. J Clin Invest 1994; 94: Kumar P, Clark M. Clinical Medicine. 4th ed. Edinburgh. W.B. Saunders: pg Longman C, Myotonic dystrophy. J R Coll Physicians Edinb 2006; 36: Angelini C, Fanin M, Pegoraro E. Clinical- molecular correlation in 104 mild X-linked muscular dystrophy patients: characterisation of sub-clinical phenotypes. Neuromuscul Disord 1994: 4: Grob D. Natural history of myasthenia gravis. In Engel Ag (ed): Myasthenia Gravis and Myasthenic disorders. Oxford University Press, Oxford pg
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction
 Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Disorders of Muscle. Disorders of Muscle. Muscle Groups Involved in Myopathy. Needle Examination of EMG. History. Muscle Biopsy
 Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Myasthenia gravis. Page 1 of 7
 Myasthenia gravis What is myasthenia gravis? Myasthenia gravis (sometimes abbreviated to MG) is a chronic, autoimmune condition that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is rare, affecting
Myasthenia gravis What is myasthenia gravis? Myasthenia gravis (sometimes abbreviated to MG) is a chronic, autoimmune condition that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is rare, affecting
Myasthenia gravis. David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre
 Myasthenia gravis David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre SWIM, Taunton, 2018 Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of thymus Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of
Myasthenia gravis David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre SWIM, Taunton, 2018 Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of thymus Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of
Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Who is at risk of developing MG? Is MG hereditary? What are the symptoms of MG? What causes MG?
 Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is uncommon, affecting about 15 in every
Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is uncommon, affecting about 15 in every
Myasthenia Gravis. Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06
 Myasthenia Gravis Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06 Overview Background Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment Associated Conditions Background Severe muscle disease Most common disorder of neuromuscular
Myasthenia Gravis Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06 Overview Background Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment Associated Conditions Background Severe muscle disease Most common disorder of neuromuscular
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Case 1: History of J.H. Outside Evaluation. Outside Labs. Question #1
 Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Muscular Dystrophies. Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018
 Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
The many faces of myositis. Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Centre Dept of Neurology Amsterdam The Netherlands
 The many faces of myositis Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Centre Dept of Neurology Amsterdam The Netherlands Outline of the presentation Classification Diagnosis Therapy Prognosis Diagnostic criteria
The many faces of myositis Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Centre Dept of Neurology Amsterdam The Netherlands Outline of the presentation Classification Diagnosis Therapy Prognosis Diagnostic criteria
Muscular System. Disorders & Conditions
 Muscular System Disorders & Conditions Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. Often is described
Muscular System Disorders & Conditions Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. Often is described
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer OUTLINE Background Anatomy Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Treatment BACKGROUND Acquired autoimmune disorder Clinically characterized by: Weakness
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer OUTLINE Background Anatomy Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Treatment BACKGROUND Acquired autoimmune disorder Clinically characterized by: Weakness
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM. Andrzej Sladkowski
 Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
IMMUNE MEDIATED NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES FRONTIERS OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE HEREDITARY NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES P.
 IMMUNE MEDIATED NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES FRONTIERS OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE IMMUNE MEDIATED NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES PDF HEREDITARY NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES P. PARIZEL AND JOHAN (PDF) PLASMA EXCHANGE AND
IMMUNE MEDIATED NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES FRONTIERS OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE IMMUNE MEDIATED NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES PDF HEREDITARY NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES P. PARIZEL AND JOHAN (PDF) PLASMA EXCHANGE AND
1/28/2019. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team. Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team: Who are we?
 Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Title. CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
4/16/2018. Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis. Objectives. Disclosures. Off-label uses for medications will be discussed
 Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis Jemima Albayda, MD Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins Myositis center Disclosures Off-label uses for medications will be discussed Objectives To
Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis Jemima Albayda, MD Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins Myositis center Disclosures Off-label uses for medications will be discussed Objectives To
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference. November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D.
 Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
L. Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 2012
 L. Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 2012 L Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 09 17 yo Ashkenazi male with proximal muscle pain and weakness, mild malar erythema and erythema over knees and dorsal aspect of PIPs Mild tenderness
L. Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 2012 L Nandini Moorthy, MD MS 09 17 yo Ashkenazi male with proximal muscle pain and weakness, mild malar erythema and erythema over knees and dorsal aspect of PIPs Mild tenderness
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
Rheumatology E-learning. University of Szeged Department of Rheumatology and Immunology
 Rheumatology E-learning University of Szeged Department of Rheumatology and Immunology Introduction Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of systemic diseases characterized by an immune
Rheumatology E-learning University of Szeged Department of Rheumatology and Immunology Introduction Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of systemic diseases characterized by an immune
Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 Pedss Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Juvenile Dermatomyositis. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
Pedss Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Juvenile Dermatomyositis. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 myopathies and muscle diseases handbook of clinical neurology myopathies and muscle diseases
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 myopathies and muscle diseases handbook of clinical neurology myopathies and muscle diseases
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral
 Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
 Page 1 of 6 Title Authored By Course No Contact Hour 1 An Overview of Myasthenia Gravis Ray Lengel RN, FNP, MS MG2061208 Purpose The goal of this course is to provide an understanding about myasthenia
Page 1 of 6 Title Authored By Course No Contact Hour 1 An Overview of Myasthenia Gravis Ray Lengel RN, FNP, MS MG2061208 Purpose The goal of this course is to provide an understanding about myasthenia
Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis
 Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis Thomas Lloyd, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Neurology and Neuroscience Co-director, Johns Hopkins Myositis Center Sporadic IBM (IBM) Age at onset usually > 50 Prevalence
Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis Thomas Lloyd, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Neurology and Neuroscience Co-director, Johns Hopkins Myositis Center Sporadic IBM (IBM) Age at onset usually > 50 Prevalence
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 MYASTHENIA GRAVIS INTRODUCTION Most common primary disorder of neuromuscular transmission Usually due to acquired immunological abnormality Also due to genetic abnormalities at neuromuscular junction.
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS INTRODUCTION Most common primary disorder of neuromuscular transmission Usually due to acquired immunological abnormality Also due to genetic abnormalities at neuromuscular junction.
Neonatal Hypotonia. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy. Neurology Chapter of IAP
 The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of
 Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Idiopathic inflammatory muscle diseases. Dr. Paul Etau Ekwom MBChB, MMED Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi-Kenya
 Idiopathic inflammatory muscle diseases. Dr. Paul Etau Ekwom MBChB, MMED Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi-Kenya I.W, 28 YRS, FEMALE SHOP STEWARD Referred to KNH on 16/06/09 from Thika Nursing Home Weakness
Idiopathic inflammatory muscle diseases. Dr. Paul Etau Ekwom MBChB, MMED Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi-Kenya I.W, 28 YRS, FEMALE SHOP STEWARD Referred to KNH on 16/06/09 from Thika Nursing Home Weakness
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS)
 Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) This fact sheet is for children and adults diagnosed with congenital myasthenic syndrome. It s a complex subject, so information has been adapted to suit all audiences.
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) This fact sheet is for children and adults diagnosed with congenital myasthenic syndrome. It s a complex subject, so information has been adapted to suit all audiences.
Global Myasthenia Gravis Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts ( ) August 2017
 Global Myasthenia Gravis Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts (2017-2021) August 2017 Global Myasthenia Gravis Market Scope of the Report The report titled Global Myasthenia Gravis Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts
Global Myasthenia Gravis Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts (2017-2021) August 2017 Global Myasthenia Gravis Market Scope of the Report The report titled Global Myasthenia Gravis Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts
Hypokalaemic periodic paralysis: In these attacks the blood potassium is low
 Periodic paralyses The ability we have to control and move the muscles in our body depends upon the passage of electrical signals along the nerves and into our muscles. The periodic paralyses are conditions
Periodic paralyses The ability we have to control and move the muscles in our body depends upon the passage of electrical signals along the nerves and into our muscles. The periodic paralyses are conditions
Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies
 Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies This leaflet provides a brief summary of the genetics of the muscular dystrophies. An understanding of their inheritance patterns makes it possible for families
Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies This leaflet provides a brief summary of the genetics of the muscular dystrophies. An understanding of their inheritance patterns makes it possible for families
Case 3. Your Diagnosis?
 Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015
 1 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015 Name: Nursing Case Study: Muscle Weakness Chief Complaint: A 26-year-old woman with muscle weakness in the face. Patient Presentation: A 26-year-old woman
1 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015 Name: Nursing Case Study: Muscle Weakness Chief Complaint: A 26-year-old woman with muscle weakness in the face. Patient Presentation: A 26-year-old woman
Patient: RG DOB: NKDA
 Patient: RG DOB: 09.26.1959 NKDA RG presented to the ED complaining of new onset generalized weakness Difficulty walking, fatigued with exertion, feeling off balance, dry mouth, and dysphasia HPI: approximately
Patient: RG DOB: 09.26.1959 NKDA RG presented to the ED complaining of new onset generalized weakness Difficulty walking, fatigued with exertion, feeling off balance, dry mouth, and dysphasia HPI: approximately
Profile, types, duration and severity of muscular dystrophy: a clinical study at a tertiary care hospital
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Viswajyothi P et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Jun;5(3):700-704 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20182126
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Viswajyothi P et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Jun;5(3):700-704 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20182126
A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies.
 1 A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies. Available on-line at: Bill Tillier Calgary Alberta September, 2008. Terminology.
1 A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies. Available on-line at: Bill Tillier Calgary Alberta September, 2008. Terminology.
5.1 Alex.
 5.1 Alex http://tinyurl.com/neuromakessense Alex is a 20-year-old full-time national serviceman. His only past medical history is asthma, presents to A&E with a 4-day history of bilateral finger weakness
5.1 Alex http://tinyurl.com/neuromakessense Alex is a 20-year-old full-time national serviceman. His only past medical history is asthma, presents to A&E with a 4-day history of bilateral finger weakness
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
M0BCore Safety Profile
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A haemagglutinin complex Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: powder for solution for injection, 300 unit and 500 unit P-RMS:
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A haemagglutinin complex Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: powder for solution for injection, 300 unit and 500 unit P-RMS:
Myopathies. Team Members: Aroob Alhuthail, Moayed Ahmad, Rema Albarrak, Ghadah Almazrou, Noura AlShabib
 Myopathies Objectives: Understanding normal muscle histology and physiology. Understanding Myopathy definition. Understanding Approach to myopathy. Knowing the most common hereditary myopathies. Knowing
Myopathies Objectives: Understanding normal muscle histology and physiology. Understanding Myopathy definition. Understanding Approach to myopathy. Knowing the most common hereditary myopathies. Knowing
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE
 MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
Inflammatory Myopathies 4 th year MBBS. Marwan Adwan MBChB, MSc, MRCPI, MRCP(rheum) Consultant Rheumatologist
 Inflammatory Myopathies 4 th year MBBS Marwan Adwan MBChB, MSc, MRCPI, MRCP(rheum) Consultant Rheumatologist Case A 64 woman presents with erythematous itchy rash over back of hands & forehead. For 1 month
Inflammatory Myopathies 4 th year MBBS Marwan Adwan MBChB, MSc, MRCPI, MRCP(rheum) Consultant Rheumatologist Case A 64 woman presents with erythematous itchy rash over back of hands & forehead. For 1 month
CONTENT ANATOMIC LOCI OF NM DISEASE ASSOCIATED FEATURES FUNCTIONAL DIFFICULTIES. CLINICAL HISTORY IN NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES Weakness 06/11/60
 CONTENT HOW TO APPROACH LIMB GIRDLE AND NON-LIMB GIRDLE WEAKNESS Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn, M.D. Professor Thammasat University Clinical approach in NM disease and phenotype Common and uncommon LGMDs Common
CONTENT HOW TO APPROACH LIMB GIRDLE AND NON-LIMB GIRDLE WEAKNESS Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn, M.D. Professor Thammasat University Clinical approach in NM disease and phenotype Common and uncommon LGMDs Common
1GENERAL INFORMATION
 1 GENERAL INFORMATION General information 11 1.1 Diagnosis Some children will have a diagnosis of their muscle-wasting condition when they begin their school life. Others will still be having investigations
1 GENERAL INFORMATION General information 11 1.1 Diagnosis Some children will have a diagnosis of their muscle-wasting condition when they begin their school life. Others will still be having investigations
Faculty Disclosure. Sanjay P. Singh, MD, FAAN. Dr. Singh has listed an affiliation with: Consultant Sun Pharma Speaker s Bureau Lundbeck, Sunovion
 Faculty Disclosure Sanjay P. Singh, MD, FAAN Dr. Singh has listed an affiliation with: Consultant Sun Pharma Speaker s Bureau Lundbeck, Sunovion however, no conflict of interest exists for this conference.
Faculty Disclosure Sanjay P. Singh, MD, FAAN Dr. Singh has listed an affiliation with: Consultant Sun Pharma Speaker s Bureau Lundbeck, Sunovion however, no conflict of interest exists for this conference.
The spectrum of elderly myopathies in an Asian population
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(2) : 177 181 The spectrum of elderly myopathies in an Asian population Shereen Ng, *Kum-Thong Wong FRCPath MD, Khean-Jin Goh FRCP Division of Neurology, Department of Medicine and
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(2) : 177 181 The spectrum of elderly myopathies in an Asian population Shereen Ng, *Kum-Thong Wong FRCPath MD, Khean-Jin Goh FRCP Division of Neurology, Department of Medicine and
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression. Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre
 Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Case Studies in Peripheral Neurophysiology. Elliot L. Dimberg Mayo Clinic Florida 2015 American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Annual Meeting
 Case Studies in Peripheral Neurophysiology Elliot L. Dimberg Mayo Clinic Florida 2015 American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Annual Meeting Disclosures None Goals and Objectives To provide a concise,
Case Studies in Peripheral Neurophysiology Elliot L. Dimberg Mayo Clinic Florida 2015 American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Annual Meeting Disclosures None Goals and Objectives To provide a concise,
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis
 Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis 1 Shannon Venance 1 and Rabi Tawil 2 1 Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada 2 University
Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis 1 Shannon Venance 1 and Rabi Tawil 2 1 Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada 2 University
MYOSITIS. A physician s guide to the
 MYOSITIS A physician s guide to the TABLE OF CONTENTS Myositis basics... 1 contents... 3 Causes... 7... 11 Affected populations... 15 Diagnosis... 17... 25... 31 PHYSICIAN S GUIDE TO MYOSITIS matory
MYOSITIS A physician s guide to the TABLE OF CONTENTS Myositis basics... 1 contents... 3 Causes... 7... 11 Affected populations... 15 Diagnosis... 17... 25... 31 PHYSICIAN S GUIDE TO MYOSITIS matory
The limb girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMDs)
 The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
POLYMYOSITIS (PM) DERMATOMYOSITIS (DM) Body myositis Eosinophilic myositis Giant cell myositis Focal / localised myositis Myopathies caused by
 POLYMYOSITIS (PM) DERMATOMYOSITIS (DM) Body myositis Eosinophilic myositis Giant cell myositis Focal / localised myositis Myopathies caused by infections, drugs, toxins Definition Epidemiology Pathogenesis
POLYMYOSITIS (PM) DERMATOMYOSITIS (DM) Body myositis Eosinophilic myositis Giant cell myositis Focal / localised myositis Myopathies caused by infections, drugs, toxins Definition Epidemiology Pathogenesis
Elements for a public summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a public summary Overview of disease epidemiology Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a public summary Overview of disease epidemiology Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
A48-year-old Hispanic woman
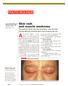 Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease. Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine
 Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Index. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
INCLUSION BODY MYOSITIS. Bill Tillier Calgary, Alberta February, 2014.
 INCLUSION BODY MYOSITIS. Bill Tillier Calgary, Alberta February, 2014. IBM classification. 2 Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis (sibm) is classified as a type of muscle disease. Idiopathic inflammatory myositis
INCLUSION BODY MYOSITIS. Bill Tillier Calgary, Alberta February, 2014. IBM classification. 2 Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis (sibm) is classified as a type of muscle disease. Idiopathic inflammatory myositis
Myasthenia: Is Medical Therapy in the Grave? Katy Marino, PGY-5
 Myasthenia: Is Medical Therapy in the Grave? Katy Marino, PGY-5 Disclosures Outline History of Thymus Anatomy of Thymus Pathophysiology of Myasthenia Gravis Medical Management of Myasthenia Gravis Surgical
Myasthenia: Is Medical Therapy in the Grave? Katy Marino, PGY-5 Disclosures Outline History of Thymus Anatomy of Thymus Pathophysiology of Myasthenia Gravis Medical Management of Myasthenia Gravis Surgical
READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES (LGMD) Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) are a heterogeneous group of genetically determined disorders with a
READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES (LGMD) Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) are a heterogeneous group of genetically determined disorders with a
Update in Neuromuscular Disorders Monday 16 th Friday 20 th June 2008 Wolfson Lecture Theatre, NHNN, Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG
 Update in Neuromuscular Disorders Monday 16 th Friday 20 th June 2008 Wolfson Lecture Theatre, NHNN, Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG Day 1 Monday 16 th June 2008 Muscular dystrophies in childhood 09:00 09:30
Update in Neuromuscular Disorders Monday 16 th Friday 20 th June 2008 Wolfson Lecture Theatre, NHNN, Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG Day 1 Monday 16 th June 2008 Muscular dystrophies in childhood 09:00 09:30
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study. Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting
 Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING
 AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY
 IMPORTANT NEW UPDATE A Summary of the Report of the DMD Care Considerations Working Group Intended for US healthcare professionals only. CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Full article
IMPORTANT NEW UPDATE A Summary of the Report of the DMD Care Considerations Working Group Intended for US healthcare professionals only. CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Full article
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20412 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Niks, E.H. Title: Myasthenia gravis with antibodies to muscle-specific kinase
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20412 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Niks, E.H. Title: Myasthenia gravis with antibodies to muscle-specific kinase
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Inclusion body myositis clinical features, diagnosis and management
 Inclusion body myositis clinical features, diagnosis and management Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Center Dept. of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands Inclusion body myositis Most frequent myopathy
Inclusion body myositis clinical features, diagnosis and management Marianne de Visser Academic Medical Center Dept. of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands Inclusion body myositis Most frequent myopathy
2/23/18. Disclosures. Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood. Making Room for Rheumatology. I have nothing to disclose. James J.
 Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Neurologic Examination
 John W. Engstrom, MD October 16, 2015 Neurologic Examination Overview The Neurologic Examination Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. Dept. of Neurology University of California, San Francisco
John W. Engstrom, MD October 16, 2015 Neurologic Examination Overview The Neurologic Examination Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. Dept. of Neurology University of California, San Francisco
What is myotonic dystrophy?
 What is myotonic dystrophy? Myotonic dystrophy is a muscle condition that falls under the umbrella term muscular dystrophy. The muscular dystrophies all have three features in common; they are hereditary,
What is myotonic dystrophy? Myotonic dystrophy is a muscle condition that falls under the umbrella term muscular dystrophy. The muscular dystrophies all have three features in common; they are hereditary,
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis
 Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis Marianne de Visser, Dept. of Neurology, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs),
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis Marianne de Visser, Dept. of Neurology, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs),
HPI. HPI (cont.) Pause for Discussion. Clinical Problem Solving Session. CC: blurry vision
 HPI CC: blurry vision Clinical Problem Solving Session Advances in Internal Medicine 2012 Discussant: Harry Hollander, MD Moderator: Nader Najafi, MD A 59 yo woman complained to her PMD of 3 months of
HPI CC: blurry vision Clinical Problem Solving Session Advances in Internal Medicine 2012 Discussant: Harry Hollander, MD Moderator: Nader Najafi, MD A 59 yo woman complained to her PMD of 3 months of
Objectives. Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies. Abnormal Muscle Signal Intensity. Inflammatory Myositis. Polymyostis / Dermatomyositis.
 Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
Diagnosis of ocular myopathy
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 97I) 55, 633 Diagnosis of ocular myopathy MARGARET BARRIE Consultant Neurologist, St. Margaret's Hospital, Epping AND KENNETH HEATHFIELD Consultant Neurologist, Oldchurch Hospital,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 97I) 55, 633 Diagnosis of ocular myopathy MARGARET BARRIE Consultant Neurologist, St. Margaret's Hospital, Epping AND KENNETH HEATHFIELD Consultant Neurologist, Oldchurch Hospital,
Two simple, reliable and valid tests of proximal muscle function, and their application to the management of idiopathic inflammatory myositis
 Rheumatology 26;45:874 879 Advance Access publication 31 January 26 Two simple, reliable and valid tests of proximal muscle function, and their application to the management of idiopathic inflammatory
Rheumatology 26;45:874 879 Advance Access publication 31 January 26 Two simple, reliable and valid tests of proximal muscle function, and their application to the management of idiopathic inflammatory
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy Disease name: Welander distal myopathy ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: late adult onset type 1 distal myopathy;
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy Disease name: Welander distal myopathy ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: late adult onset type 1 distal myopathy;
The role of plasmapheresis in Myasthenia Gravis. Ri 陳文科
 The role of plasmapheresis in Myasthenia Gravis Ri 陳文科 Myaasthenia Gravis S/S: 2/3 initial symptoms: Ocular motor disturbances, ptosis or diplopia. 1/6:Oropharyngeal muscle weakness 1/10: limb weakness
The role of plasmapheresis in Myasthenia Gravis Ri 陳文科 Myaasthenia Gravis S/S: 2/3 initial symptoms: Ocular motor disturbances, ptosis or diplopia. 1/6:Oropharyngeal muscle weakness 1/10: limb weakness
Grave s Disease. of the endocrine system known as Grave s disease. This disease condition which affects the
 Grave s Disease The proper functioning of the human body is dependant upon the normal working of the systems of the human body. The coordination of these systems is essential for maintaining all the normal
Grave s Disease The proper functioning of the human body is dependant upon the normal working of the systems of the human body. The coordination of these systems is essential for maintaining all the normal
Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies
 J.A.L.Bulcke A.L.Baert Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies CT Scanning EMG Radioisotopes With 151 Figures and 30 Tables Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Dr. JAN A. L BULCKE K. U. Leuven,
J.A.L.Bulcke A.L.Baert Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies CT Scanning EMG Radioisotopes With 151 Figures and 30 Tables Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Dr. JAN A. L BULCKE K. U. Leuven,
The Neurologic Examination. John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine
 The Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine Overview The Neurologic Examination Mental status demonstration/questions Cranial nerves demonstration/questions
The Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine Overview The Neurologic Examination Mental status demonstration/questions Cranial nerves demonstration/questions
American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum
 American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum 10/03/01 1. Introduction: Neuromuscular disorders are a significant component of the diseases of the nervous system that neurologists
American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum 10/03/01 1. Introduction: Neuromuscular disorders are a significant component of the diseases of the nervous system that neurologists
1 DOS CME Course 2011
 Statin Myopathy February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation 1 Case 1 50 y/o woman with hyperlipidemia presents with one year history of deep
Statin Myopathy February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation 1 Case 1 50 y/o woman with hyperlipidemia presents with one year history of deep
PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY. Reversible. dementias Blackwell Science Ltd
 138 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Reversible dementias JUNE 2002 139 Gunhild Waldemar Memory Disorders Research Unit, Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100
138 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Reversible dementias JUNE 2002 139 Gunhild Waldemar Memory Disorders Research Unit, Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100
Johns Hopkins Medicine - eform A
 Johns Hopkins Medicine - eform A Use the section headings to write the eform A, inserting the appropriate material in each. If a section is not applicable, leave heading in and insert N/A. When submitting
Johns Hopkins Medicine - eform A Use the section headings to write the eform A, inserting the appropriate material in each. If a section is not applicable, leave heading in and insert N/A. When submitting
Nemaline (rod) myopathies
 Nemaline (rod) myopathies Nemaline, or rod, myopathies are a group of conditions which fall under the umbrella of congenital myopathies. They are characterised by rod-like structures in the muscle cells,
Nemaline (rod) myopathies Nemaline, or rod, myopathies are a group of conditions which fall under the umbrella of congenital myopathies. They are characterised by rod-like structures in the muscle cells,
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Neurology. Brain death. Tests. EEG in Monitoring 3.B.2. Neuromuscular disorders and anaesthesia. Neurology 3.C.6.1 James Mitchell (December 24, 2003)
 Neurology Brain death Tests EEG in Monitoring 3.B.2 Neuromuscular disorders and anaesthesia Neurology 3.C.6.1 James Mitchell (December 24, 2003) Brain death Coma GCS < 8, potential for recovery Persistent
Neurology Brain death Tests EEG in Monitoring 3.B.2 Neuromuscular disorders and anaesthesia Neurology 3.C.6.1 James Mitchell (December 24, 2003) Brain death Coma GCS < 8, potential for recovery Persistent
Signs: The most common sign seen by ophthalmologists are lid droop
 Myasthenia Gravis Your doctor thinks that you have Myasthenia Gravis (MG). This is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system has damaged receptors on your muscles. This results in muscle weakness
Myasthenia Gravis Your doctor thinks that you have Myasthenia Gravis (MG). This is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system has damaged receptors on your muscles. This results in muscle weakness
Ch 6 12/19/02 8:29 AM Page CHAPTER 6
 Ch 6 12/19/02 8:29 AM Page 12 6-12 CHAPTER 6 would appear that the continued release of acetylcholine, or possibly some other transmitter, from the nerve, is the agent responsible for this trophic influence.
Ch 6 12/19/02 8:29 AM Page 12 6-12 CHAPTER 6 would appear that the continued release of acetylcholine, or possibly some other transmitter, from the nerve, is the agent responsible for this trophic influence.
Publications List. 1. General factsheets. 2. Medical conditions factsheets
 Publications List We produce a wide range of publications, from factsheets about specific medical conditions to comprehensive guides on adapting your home. To order a free publication: Call the Information
Publications List We produce a wide range of publications, from factsheets about specific medical conditions to comprehensive guides on adapting your home. To order a free publication: Call the Information
