IgG4-Related Disease
|
|
|
- Bryan Spencer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune fibroinflammatory disease that produces sclerotic, tumefactive masses containing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 þ plasma cells. Initially characterized as a form of autoimmune pancreatitis, the distinctive histopathology of IgG4-RD has now been described in almost every organ system. However, because the clinical manifestations of IgG4-RD are diverse and nonspecific, the disease may go unsuspected until a biopsy or resection specimen is obtained to diagnose a presumed malignancy. Pathologists thus play a key role in the diagnosis of IgG4-RD, and familiarity with its histopathologic features is essential to preventing the irreversible comorbidities associated with this treatable disease. This brief review outlines the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and histopathology of IgG4-RD, with the aim of furthering pathologists awareness of and ability to diagnose this disorder. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017;141: ; doi: /arpa RA) IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune disorder characterized by elevated serum immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 levels and tumorlike fibroinflammatory masses with distinctive histopathologic features that almost always include infiltrates of IgG4 þ plasma cells. Described initially as a form of sclerosing autoimmune pancreatitis (now designated as type I autoimmune pancreatitis), 1 3 the disease has since been recognized as having the capacity to affect nearly every organ system. Indeed, IgG4-RD is notable for unifying several historical and seemingly organspecific fibrosing diseases into a single process (Figure 1). The designation of IgG4-RD as a distinct disease entity was proposed in Much literature has been published since then (Figure 2), including many recommendations regarding its diagnosis and management. 4,5 Despite these advances, however, the pathophysiology of IgG4-RD Accepted for publication July 10, From the Department of Pathology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Dr Frederiksen is now with the Department of Pathology, Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, Florida. The authors have no relevant financial interest in the products or companies described in this article. Presented in part at the New Frontiers in Pathology meeting; October 13 15, 2016; Ann Arbor, Michigan. Reprints: John Karl Frederiksen, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, Jackson Memorial Hospital, Holtz 2042C, 1611 NW 12th Ave, Miami, FL ( john.frederiksen@jhsmiami.org). IgG4-Related Disease A Reminder for Practicing Pathologists Steven C. Weindorf, MD; John Karl Frederiksen, MD, PhD remains poorly understood. Moreover, as some 6,7 have observed, diagnosis of the disease suffers from a paradoxical combination of underrecognition and overrecognition underrecognition due to unfamiliarity, and overrecognition due to overeagerness to demonstrate familiarity. Accurate and timely recognition of the characteristic histopathologic features of IgG4-RD, and differentiation from its mimics, is important because it is eminently treatable, yet debilitating and potential deadly if left unchecked. Pathologists in particular play a crucial role by alerting clinicians to the possibility of a diagnosis of IgG4-RD, since it may be unsuspected clinically until a resection specimen arrives (Figure 3, A through H). This brief review will summarize the clinical features, histopathology, and differential diagnosis of IgG4-RD, with an eye toward increasing pathologists awareness of this unique disorder. EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES The incidence of IgG4-RD across all organ systems is difficult to determine, since the disease has only recently been described and global population-based data are lacking. In Japan, where the disease has been characterized extensively, one study examining the incidence of autoimmune pancreatitis reported a rate of 0.8 per individuals. 8 More recently, a rate for all forms of IgG4- RD of 0.28 to 1.08 per individuals was estimated in Japan from the number of patients with IgG4-RD who presented to 2 hospitals within a single prefecture over the course of several years. 9 These rates may rise as additional data accumulate and physicians become more familiar with and able to recognize the disease. 10 Unlike most autoimmune diseases, IgG4-RD is more prevalent in middle-aged and elderly males, although the extent of this male predominance varies with the anatomic site of involvement. At least in Japanese populations, IgG4- related autoimmune pancreatitis has a male to female ratio of 3 4:1, 11 but this ratio decreases nearly to unity in the context of head and neck disease. 12 The most common clinical manifestation is the development of a mass lesion that produces site-specific symptoms and raises suspicion for malignancy. The effects range from simple swelling of the affected organs (salivary and lacrimal glands, lymph nodes) to obstruction (pancreaticobiliary, ureteral), organ dysfunction (pituitary insufficiency secondary to hypophysitis, kidney disease), and even frank medical emergency (aortic dissection, pachymeningitis, pancreatitis). Apart from the mass effects, a small number of patients may experience constitutional symptoms such as fever and weight loss Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen
2 Figure 1. Some of the many clinical manifestations of IgG4-related disease, including the names of historic fibrosing diseases (italicized) subsequently linked to the disorder. Abbreviation: IgG4, immunoglobulin G4. Figure 2. The yearly number of PubMed citations since 2000 containing the search term IgG4-related. Abbreviation: IgG4, immunoglobulin G4. Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen 1477
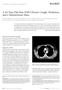
3 Figure 3. IgG4-related disease involving the submandibular gland. The specimen was taken from a 46-year-old woman with a 3-month history of a right submandibular gland mass and mild regional neck lymphadenopathy. Her medical history included Graves disease and asthma. Nineteen months earlier she underwent a lacrimal gland biopsy for periorbital swelling. Lymphoma had been suspected, but flow cytometry was negative, and the biopsy was interpreted as sclerosing inflammatory pseudotumor with numerous active lymphoid follicles. Sections of the excised right submandibular gland mass (A) show serous salivary gland tissue and adjacent nodular lymphoid tissue consisting of reactive germinal centers (B) 1478 Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen
4 Other patients are asymptomatic, and a mass lesion is only found incidentally on imaging. With such diverse clinical presentations, it is perhaps not surprising that the possibility of a systemic autoimmune disease may be overlooked in favor of alternative diagnoses during initial or even subsequent evaluations. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY The etiology of IgG4-RD remains obscure, and it is easier to describe the inflammatory response in affected patients than to identify definitive causative mechanisms. Evidence suggests that the disease is associated with both T helper 2 (Th2) and regulatory T-cell (Treg) immune responses. Th2 responses are linked to the development of allergies and bronchial asthma, conditions that are more prevalent in patients with IgG4-RD. 13,14 They are characterized by CD4 þ T cells secreting the cytokines interleukin (IL) 4, IL-5, and IL-13, and they promote class switching to IgG4, increased IgE synthesis, and eosinophilia. Regulatory CD4 þ T cells (Tregs), in contrast, secrete cytokines such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor b (TGF-b), leading to immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive effects. Serum from patients with IgG4-RD shows elevated mrna expression of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10, as well as increased concentrations of IgG4 and IgE. 15 Tissue sections of salivary glands, 16 lacrimal glands, 16 and pancreas 17 from patients with IgG4- RD show high mrna expression of Th2- and Tregassociated cytokines. Circulating Treg-type CD4 þ T cells are increased in the peripheral blood of patients with IgG4- related autoimmune pancreatitis. 18 Treg cells (as defined by immunohistochemical expression of the Treg-related transcription factor Foxp3) are also increased in liver biopsies from patients with IgG4-RD. 19 These findings suggest a possible model 10,20 in which an unknown immunologic trigger induces an aberrant Th2- type immune response leading to peripheral blood and tissue eosinophilia and increased IgE production. At the same time, Treg cells, perhaps to ameliorate the Th2 response, are stimulated to secrete IL-10, which (along with IL-4) induces class switching to IgG4, and TGF-b, a known stimulator of fibroblast activity. Repeated cycles of antigenic stimulation and cytokine secretion then produce the histopathologic findings of tissue fibrosis and a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate rich in IgG4 þ plasma cells. However, direct evidence that Th2-associated cytokines truly drive the inflammation in IgG4-RD is still lacking, and no convincing environmental trigger (infectious or otherwise) or autoantigen has been identified. Other possible predisposing conditions or contributors to IgG4-RD pathogenesis include specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles and single-nucleotide polymorphisms within some non-hla genes. 21,22 Also puzzling is the precise role of IgG4 in the disease. IgG4 is the least common IgG subtype, comprising less than 5% of total IgG, 23 and is usually viewed as an antiinflammatory molecule. IgG4 binds C1q and the Fcc receptor with relatively low affinity, 24,25 and consequently is not expected to be as effective as other IgG subclasses at activating complement or promoting phagocytosis. In addition, owing to unstable inter heavy chain disulfide bonds, 26 IgG4 can exchange its Fab arms with other IgG4 molecules, rendering it functionally monovalent. Because IL-10, a cytokine produced by Treg cells, promotes class switching to IgG4, one possibility is that the infiltrates of IgG4 þ plasma cells in IgG4-RD result from Treg cells attempting to dampen the immune response. However, whether the IgG4 þ plasma cells damage tissue directly or represent the byproduct of an exaggerated immune response remains unclear. HISTOPATHOLOGY For several reasons, histopathologic evaluation of affected tissues remains a critical component in the diagnosis of IgG4-RD. The histologic pattern is highly characteristic (with certain caveats described below), and immunohistochemistry demonstrating increased IgG4 þ plasma cells is important and necessary confirmatory evidence. Moreover, considering the diverse clinical presentations associated with IgG4-RD, histopathology can both exclude malignancy and alert clinicians to the presence of a separate (and treatable) disease that may have been unsuspected. The major histologic features associated with IgG4-RD have been well described 5,10,27,28 and include (1) a dense lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate with increased numbers of IgG4 þ plasma cells and often increased eosinophils; (2) a storiform pattern of fibrosis; and (3) obliterative vasculitis. The Inflammatory Infiltrate While IgG4-RD is usually described in terms of increased IgG4 þ plasma cells, T cells (predominantly CD4 þ ) actually comprise the bulk of the inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 4, A and B). Other components include small aggregates of B cells (which may be distributed in germinal centers, depending on anatomic location), along with interspersed macrophages and the requisite IgG4 þ plasma cells (Figure 4, C and D). These may be diffusely increased (Figure 3, E and H) or distributed in variably dense patches (Figure 4, D). Tissue eosinophilia is usually present (Figure 3, C). Not characteristic are epithelioid granulomas, multinucleated giant cells, overt necrosis, and neutrophilic infiltrates in sites other than the lung (see below). If present, these findings should prompt consideration of alternative diagnoses. The number of IgG4 þ plasma cells should be quantified in some manner, either as the number per high-power field or as the IgG4 þ :IgG þ plasma cell ratio. The absolute number of IgG4 þ plasma cells often varies with anatomic site, and many organ-specific cutoff values of IgG4 þ plasma cells per high-power field have been proposed. 5,27 These range from greater than 10 to greater than 200 IgG4 þ plasma cells, with values in most sites falling somewhere between 10 and 50. separated by thick intervening bands of sclerosis in a storiform pattern. The sclerotic areas (C) contain a lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate with frequent eosinophils. The infiltrate surrounds the ducts and glands of the salivary acinar structures without forming lymphoepithelial lesions. Immunohistochemical stains show abundant IgG þ plasma cells (D), nearly all of which are also IgG4 þ (E). Re-evaluation of the patient s prior lacrimal gland biopsy (F) and immunohistochemical stains for IgG (G) and IgG4 (H) demonstrate similar results. Following the submandibular gland biopsy, the patient was found to have a serum IgG4 concentration that exceeded 1000 mg/dl (reference range, mg/dl) (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnifications 3 20 [A and F], 3100 [B], and 3400 [C]; immunoperoxidase, original magnification 320 [D, E, G, and H]). Abbreviations: IgG, immunoglobulin G; IgG4, immunoglobulin G4. Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen 1479
5 Figure 4. A, Dense lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate in pericardial tissue taken from a patient with IgG4-related mediastinitis. B, Most of the cells in the infiltrate are T cells. C, Higher magnification view of the infiltrate showing many plasma cells. D, In this case, the IgG4 þ plasma cells exhibit a patchy distribution (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnifications 3100 [A] and 3400 [C]; CD3, immunoperoxidase, original magnification 3100 [B]; IgG4, immunoperoxidase, original magnification 3100 [D]). Abbreviation: IgG4, immunoglobulin G4. Alternatively, an elevated IgG4 þ :IgG þ plasma cell ratio may be more specific for IgG4-RD, with most authors recommending a ratio greater than 40% as characteristic. 5,27 30 The ratio may be especially useful in evaluating specimens that lack large absolute numbers of IgG4 þ plasma cells, such as small needle biopsy samples or specimens consisting predominantly of paucicellular fibrosis. Storiform Fibrosis This pattern is defined by dense, wirelike strands of fibrotic collagen deposition radiating outward from a central point (Figure 3, A and F; Figure 5, A and B). The collagen fibers contain fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, and may resemble similar arrangements associated with fibrohistiocytic malignancies. In cases of long-standing fibrosis, a sparsely cellular or acellular fibrotic pattern may predominate (Figure 5, B). Obliterative Vasculitis Inflammatory infiltrates fill both the walls and lumina of the affected vessels, producing partial or complete obliteration (Figure 6, A and B). Veins are most often involved, and fully obliterated veins may sometimes be identified by their proximity to adjacent arteries, which are usually spared. However, arteritis is sometimes observed, especially in the lung, and elastic stains may be required to highlight the residual vessel walls (Figure 6, B). Despite the dense inflammatory infiltrate, necrotizing vasculitis is not characteristic. Caveats and Differential Diagnosis While the histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings are distinctive, they are not always present to the same extent within each affected organ. Salivary and lacrimal glands, for example, may show more of a thick, collagenous pattern of fibrosis (Figure 3, A and F). These organs are also less likely to feature obliterative vasculitis, and the inflammatory infiltrates may manifest instead as many lymphoid follicles, albeit with increased numbers of IgG4 þ plasma cells. In the lung, 31 plasma cell rich infiltrates are often distributed along vessels and lymphatic channels, and may surround bronchioles concentrically. In contrast to other tissues, the infiltrates may include small neutrophilic aggregates within alveolar spaces, although abscess formation and necrosis are not characteristic. Typical storiform fibrosis may be absent, and obliterative vasculitis affects 1480 Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen
6 Figure 5. A, Storiform fibrosis from the lacrimal gland biopsy shown in Figure 3, F. B, Storiform fibrosis within periureteral tissue in a case of IgG4related retroperitoneal fibrosis. The specimen consists largely of fibrotic tissue with a sparsely cellular inflammatory infiltrate (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification [A and B]). Abbreviation: IgG4, immunoglobulin G4. Figure 6. Obliterative phlebitis in a case of IgG4-related pancreatitis (type I autoimmune pancreatitis). A, Hematoxylin-eosin stain. B, Movat pentachrome stain demonstrating residual elastic fibers (original magnification [A and B]). Abbreviation: IgG4, immunoglobulin G4. both pulmonary arteries and veins. Some of the most variable IgG4-related morphologies occur in lymph nodes, in which 5 separate patterns are recognized and typical storiform fibrosis is again often absent.7 Since not all histologic features may be present within a given specimen, core needle biopsies may not sample the most important diagnostic areas, and therefore larger specimens should be obtained whenever possible. In addition, owing to their highly variable patterns of involvement, enlarged lymph nodes may not be optimal specimens for diagnosing IgG4RD prospectively.32,33 Further complicating interpretation is the observation that increased numbers of IgG4þ plasma cells is not a finding specific to IgG4-RD. Many other benign and malignant processes may also feature increased IgG4þ plasma cells,27,34 including granulomatosis with polyangiitis,35 multicentric Castleman disease,36 Rosai-Dorfman disease,37 marginal zone lymphoma,38 41 pancreatic adenocarcinoma,42,43 and even reactive lymphadenopathy,44 to name just a few. Additionally, the histologic patterns of both these and other Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 entities sometimes overlap with that of true IgG4-RD. These mimics include lymphoproliferative/histiocytic disorders (multicentric Castleman disease, Rosai-Dorfman disease, lymphoma), autoimmune disorders (Sjo gren syndrome in salivary and lacrimal glands, primary sclerosing cholangitis in the liver), spindle cell neoplasms (inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, desmoid fibromatosis), and infections (especially within the lung). Thus, a specimen with increased IgG4þ plasma cells and IgG4-RD like histology must also be interpreted within the context of the associated clinical history. In some cases, judicious use of additional immunohistochemical or special stains may also provide important diagnostic clues. CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, AND THE ROLE OF THE PATHOLOGIST Beyond the histologic findings, the clinical diagnosis of IgG4-RD requires additional correlation with laboratory and radiologic evaluations. According to the proposed Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-RD,29 a definite IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen 1481
7 diagnosis of IgG4-RD may be made by demonstrating (1) organ involvement; (2) a serum IgG4 level exceeding 135 mg/dl; and (3) greater than 10 IgG4 þ plasma cells per highpower field and an IgG4 þ :IgG þ plasma cell ratio of at least 40% on histologic tissue sections. In contrast, if organ involvement is present along with only 1 of the remaining 2 criteria, a diagnosis of IgG4-RD is considered possible or probable. Confirmation then depends upon the radiologic appearance of the affected organ or organs, organ-specific histologic criteria, or the responsiveness of patient symptoms to a trial of steroids. An elevated serum IgG4 level (.135 mg/dl) is suggestive of IgG4-RD but is not specific, and may be found in patients with chronic sinusitis, pneumonia, other autoimmune diseases, and certain malignancies. 45 Moreover, although the negative predictive value for an elevated serum IgG4 is high (96%), 45 occasional patients will have a normal level despite characteristic IgG4- RD histology on a tissue biopsy. Once the diagnosis of IgG4-RD has been established, most patients symptoms respond within several weeks to an initial course of glucocorticoids. For IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis, both retrospective 46,47 and prospective 48 studies have demonstrated the efficacy of glucocorticoids at inducing an initial remission. Subsequent management may include observation or maintenance therapy with either steroids or steroid-sparing immunomodulatory agents. For nonresponders or for patients unable to tolerate steroids, B-cell depletion with rituximab has shown efficacy in retrospective studies The availability and efficacy of therapy for IgG4-RD, along with its myriad clinical presentations, further highlight the pathologist s critical role as both caregiver and guide to treatment. Patients with symptomatic, active IgG4-RD require treatment. 4 Some those with aortitis, retroperitoneal fibrosis, proximal biliary strictures, hypertrophic pachymeningitis, pancreatic enlargement, or pericarditis require treatment urgently to prevent irreversible disease-related complications or death. Accurate and timely diagnosis of this condition opens the door to treatment and helps to avoid both complications and unnecessary surgical procedures (such as the Whipple resections that furnished so many autoimmune pancreatitis specimens before IgG4-RD was recognized). The chief responsibilities of the pathologist are awareness of the disease, recognition of its characteristic histology, and appropriate communication with the clinical team. Because histology constitutes only a part of the diagnostic criteria (albeit a major one), one consensus statement recommends a 3-tiered approach to reporting on suspected IgG4-RD specimens. 5,27 Cases histologically highly suggestive of IgG4-RD show, in addition to increased IgG4 þ plasma cells, at least 2 of the following: a dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, fibrosis (usually storiform), and obliterative vasculitis (usually phlebitis). Cases showing probable histologic features of IgG4-RD may show only 1 of these features, may be insufficiently large (needle cores), or may derive from an anatomic site not typically associated with IgG4-RD. The remaining cases may be described as having insufficient histopathologic evidence of IgG4-RD, with the caveat that the diagnosis is not excluded. While not providing a definitive diagnosis, these designations at a minimum alert the clinical team to the possibility of IgG4-RD, which may prompt further diagnostic laboratory and radiologic evaluations. CONCLUSIONS IgG4-RD is a systemic autoimmune disease with distinctive histopathology and protean clinical implications. Histopathologic examination of affected tissues is crucial for diagnosis, partly because the pattern is so distinctive, but also because the disease may be unsuspected owing to its diverse and nonspecific clinical presentations. Pathologists familiarity with and prompt recognition of the features of IgG4-RD allows clinicians to institute proper treatment and avoid unnecessary comorbidities. References 1. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(10): Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet. 2002;359(9315): Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(10): Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(7): Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(9): Fox RI, Fox CM. IgG4 levels and plasmablasts as a marker for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1): Cheuk W, Chan JK. Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related disease: an underdiagnosed and overdiagnosed entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012;29(4): Nishimori I, Tamakoshi A, Otsuki M; Research Committee on Intractable Diseases of the Pancreas Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan. Prevalence of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan from a nationwide survey in J Gastroenterol. 2007;42(suppl 18): Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4- related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22(1): Mahajan VS, Mattoo H, Deshpande V, Pillai SS, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9: Kanno A, Nishimori I, Masamune A, et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan. Pancreas. 2012;41(6): Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(12): Kuruma S, Kamisawa T, Tabata T, et al. Allergen-specific IgE antibody serologic assays in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern Med. 2014; 53(6): Kamisawa T, Anjiki H, Egawa N, Kubota N. Allergic manifestations in autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21(10): Kanari H, Kagami S, Kashiwakuma D, et al. Role of Th2 cells in IgG4- related lacrimal gland enlargement. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010;152(suppl 1): Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and the initiation of Mikulicz disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(1): Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology. 2007;45(6): Miyoshi H, Uchida K, Taniguchi T, et al. Circulating naive and CD4þCD25high regulatory T cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2008;36(2): Koyabu M, Uchida K, Miyoshi H, et al. Analysis of regulatory T cells and IgG4-positive plasma cells among patients of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and autoimmune liver diseases. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45(7): Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366(6): Islam AD, Selmi C, Datta-Mitra A, et al. The changing faces of IgG4-related disease: clinical manifestations and pathogenesis. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(10): Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. Pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(1): Aalberse RC, Stapel SO, Schuurman J, Rispens T. Immunoglobulin G4: an odd antibody. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39(4): Tao MH, Smith RI, Morrison SL. Structural features of human immunoglobulin G that determine isotype-specific differences in complement activation. J Exp Med. 1993;178(2): Canfield SM, Morrison SL. The binding affinity of human IgG for its high affinity Fc receptor is determined by multiple amino acids in the CH2 domain and is modulated by the hinge region. J Exp Med. 1991;173(6): Schuurman J, Perdok GJ, Gorter AD, Aalberse RC. The inter-heavy chain disulfide bonds of IgG4 are in equilibrium with intra-chain disulfide bonds. Mol Immunol. 2001;38(1): Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen
8 27. Deshpande V. The pathology of IgG4-related disease: critical issues and challenges. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012;29(4): Cheuk W, Chan JK. IgG4-related sclerosing disease: a critical appraisal of an evolving clinicopathologic entity. Adv Anat Pathol. 2010;17(5): Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22(1): Zen Y, Kitagawa S, Minato H, et al. IgG4-positive plasma cells in inflammatory pseudotumor (plasma cell granuloma) of the lung. Hum Pathol. 2005;36(7): Yi ES, Sekiguchi H, Peikert T, Ryu JH, Colby TV. Pathologic manifestations of Immunoglobulin(Ig)G4-related lung disease. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012;29(4): Stone JH. IgG4-related disease: nomenclature, clinical features, and treatment. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012;29(4): Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015; 385(9976): Strehl JD, Hartmann A, Agaimy A. Numerous IgG4-positive plasma cells are ubiquitous in diverse localised non-specific chronic inflammatory conditions and need to be distinguished from IgG4-related systemic disorders. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64(3): Chang SY, Keogh K, Lewis JE, Ryu JH, Yi ES. Increased IgG4-positive plasma cells in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a diagnostic pitfall of IgG4- related disease. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012: Sato Y, Kojima M, Takata K, et al. Multicentric Castleman s disease with abundant IgG4-positive cells: a clinical and pathological analysis of six cases. J Clin Pathol. 2010;63(12): Menon MP, Evbuomwan MO, Rosai J, Jaffe ES, Pittaluga S. A subset of Rosai-Dorfman disease cases show increased IgG4-positive plasma cells: another red herring or a true association with IgG4-related disease? Histopathology. 2014; 64(3): De Souza A, Ferry JA, Burghart DR, et al. IgG4 expression in primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma: a multicenter study [published online ahead of print February 1, 2017]. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. doi: /PAI Igawa T, Hayashi T, Ishiguro K, et al. IgG4-producing lymphoma arising in a patient with IgG4-related disease. Med Mol Morphol. 2016;49(4): Sato Y, Ohshima K, Takata K, et al. Ocular adnexal IgG4-producing mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related disease. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2012;52(1): Sato Y, Takata K, Ichimura K, et al. IgG4-producing marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2008;88(4): Zhang L, Notohara K, Levy MJ, Chari ST, Smyrk TC. IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Mod Pathol. 2007; 20(1): Deshpande V, Chicano S, Finkelberg D, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: a systemic immune complex mediated disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30(12): Martinez LL, Friedlander E, van der Laak JA, Hebeda KM. Abundance of IgG4þ plasma cells in isolated reactive lymphadenopathy is no indication of IgG4-related disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 2014;142(4): Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone JH. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1): Hart PA, Topazian MD, Witzig TE, et al. Treatment of relapsing autoimmune pancreatitis with immunomodulators and rituximab: the Mayo Clinic experience. Gut. 2013;62(11): Ebbo M, Daniel L, Pavic M, et al. IgG4-related systemic disease: features and treatment response in a French cohort: results of a multicenter registry. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012;91(1): Sandanayake NS, Church NI, Chapman MH, et al. Presentation and management of post-treatment relapse in autoimmune pancreatitis/immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(10): Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, Unizony S, Bloch DB, Stone JH. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012;91(1): Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. Treatment approaches to IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(1): Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(6): Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, November 2017 IgG4-Related Disease Weindorf & Frederiksen 1483
How 5 Diseases Became One. Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University
 How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease
 Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
IgG4 Disease. General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman
 IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore
 IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
Overview of the Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Spectrum
 Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis of Other Etiology
 94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci
 CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY. Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
 Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin G4-related Lymphadenopathy Mimicking Sjögren s Syndrome
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08. Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
 CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
IgG4-related sclerosing disease
 IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
Renal Pathology Case Conference. Case 2
 Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
Key words: diagnosis, immunoglobulin G4, immunoglobulin G4-related diseases, immunohistochemistry, pseudolymphoma. CASE HISTORY
 doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma
 Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
CME/SAM. Increased Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 Positive Plasma Cell Density and IgG4/IgG Ratio Are Not Specific for IgG4- Related Disease in the Skin
 Increased Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 Positive Plasma Cell Density and IgG4/IgG Ratio Are Not Specific for IgG4- Related Disease in the Skin Julia S. Lehman, MD, 1,2 Thomas C. Smyrk, MD, 1 and Mark R. Pittelkow,
Increased Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 Positive Plasma Cell Density and IgG4/IgG Ratio Are Not Specific for IgG4- Related Disease in the Skin Julia S. Lehman, MD, 1,2 Thomas C. Smyrk, MD, 1 and Mark R. Pittelkow,
The newly recognized fibroinflammatory condition. An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases
 case report J Neurosurg Spine 25:790 794, 2016 An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases Bishan D. Radotra, MD, 1 Ashish Aggarwal, DNB, MCh, 2 Ankur Kapoor, MS, MCh, 2 Navneet
case report J Neurosurg Spine 25:790 794, 2016 An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases Bishan D. Radotra, MD, 1 Ashish Aggarwal, DNB, MCh, 2 Ankur Kapoor, MS, MCh, 2 Navneet
Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
 Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Thomas C. Smyrk, MD Associate Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN 55902 smyrk.thomas@mayo.edu Summary Retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated
Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Thomas C. Smyrk, MD Associate Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN 55902 smyrk.thomas@mayo.edu Summary Retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease, a systemic,
 IgG4-Related Disease of the Gastrointestinal Tract A 21st Century Chameleon Vikram Deshpande, MD Context. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related disease is a systemic fibroinflammatory disease capable of affecting
IgG4-Related Disease of the Gastrointestinal Tract A 21st Century Chameleon Vikram Deshpande, MD Context. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related disease is a systemic fibroinflammatory disease capable of affecting
Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone Phenomenon in Patients With IgG4-Related Disease
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 213 217 DOI 10.1002/art.38193 2014, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 213 217 DOI 10.1002/art.38193 2014, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone
A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy
 Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
Pulmonary function tests findings and their diagnostic value in patients with IgG4-related disease
 Original Article Pulmonary function tests findings and their diagnostic value in patients with IgG4-related disease Lu Cao, Yi-Bing Chen, Da-Hui Zhao, Wen-Fang Shi, Song Meng, Li-Xin Xie Department of
Original Article Pulmonary function tests findings and their diagnostic value in patients with IgG4-related disease Lu Cao, Yi-Bing Chen, Da-Hui Zhao, Wen-Fang Shi, Song Meng, Li-Xin Xie Department of
Consensus Statement on the Pathology of IgG4-Related Disease
 Consensus Statement on the Pathology of IgG4-Related Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Deshpande,
Consensus Statement on the Pathology of IgG4-Related Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Deshpande,
IgG4-Related Disease: Puzzles and Pitfalls
 IgG4-Related Disease: Puzzles and Pitfalls Roberto Novoa, MD Section of Dermatopathology Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University Medical Center Stanford, CA Disclosures I have no relevant
IgG4-Related Disease: Puzzles and Pitfalls Roberto Novoa, MD Section of Dermatopathology Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University Medical Center Stanford, CA Disclosures I have no relevant
Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis without IgG4 tissue infiltration or serum IgG4 elevation: IgG4-related disease without IgG4
 238 & 2015 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/15 $32.00 Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis without IgG4 tissue infiltration or serum IgG4 elevation: IgG4-related disease without IgG4 Phil
238 & 2015 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/15 $32.00 Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis without IgG4 tissue infiltration or serum IgG4 elevation: IgG4-related disease without IgG4 Phil
Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
 Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related Disease
 Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
Clinical Study Spectrum of Disorders Associated with Elevated Serum IgG4 Levels Encountered in Clinical Practice
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 232960, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/232960 Clinical Study Spectrum of Disorders Associated with Elevated Serum IgG4 Levels Encountered in Clinical Practice
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 232960, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/232960 Clinical Study Spectrum of Disorders Associated with Elevated Serum IgG4 Levels Encountered in Clinical Practice
A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion and Thrombophlebitis
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.76.4.179 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;76:179-183 A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.76.4.179 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;76:179-183 A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion
IgG-4 related disease: A mini-review
 www.rarediseasesjournal.com Journal of Rare Diseases Research & Treatment Mini review Open Access IgG-4 related disease: A mini-review Ramy Sedhom 1*, Daniel Sedhom 1 and Roger Strair 2 1 Department of
www.rarediseasesjournal.com Journal of Rare Diseases Research & Treatment Mini review Open Access IgG-4 related disease: A mini-review Ramy Sedhom 1*, Daniel Sedhom 1 and Roger Strair 2 1 Department of
A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass
 [ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
[ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease
 Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc. Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz
 Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) was described more than a
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1229 1234 The Use of Immunoglobulin G4 Immunostaining in Diagnosing Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Involvement in Autoimmune Pancreatitis MAESHA G. DEHERAGODA,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1229 1234 The Use of Immunoglobulin G4 Immunostaining in Diagnosing Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Involvement in Autoimmune Pancreatitis MAESHA G. DEHERAGODA,*
Nozomu Kurose. Key Words: IgG4-related disease, comprehensive diagnostic criteria, fibrosis grade, IL-6. J Kanazawa Med Univ , 2016
 J Kanazawa Med Univ 41 76 85, 2016 Clinicopathological Analysis between IgG4-related and Non-IgG4-related Diseases Occurring in Various Organs and Tissues: Re-evaluation of Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria
J Kanazawa Med Univ 41 76 85, 2016 Clinicopathological Analysis between IgG4-related and Non-IgG4-related Diseases Occurring in Various Organs and Tissues: Re-evaluation of Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) can be defined as a
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1010 1016 Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: The Mayo Clinic Experience SURESH T. CHARI,* THOMAS C. SMYRK, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* MARK D. TOPAZIAN,* NAOKI
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1010 1016 Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: The Mayo Clinic Experience SURESH T. CHARI,* THOMAS C. SMYRK, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* MARK D. TOPAZIAN,* NAOKI
Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis
 Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) Reference: NHS England A13X07/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) Reference: NHS England A13X07/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
A Case of IgG4-Related Disease with Bronchial Asthma and Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Korea
 CSE REPORT Immunology, llergic Disorders & Rheumatology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.599 J Korean Med Sci 2014; 29: 599-603 Case of IgG4-Related Disease with ronchial sthma and Chronic Rhinosinusitis
CSE REPORT Immunology, llergic Disorders & Rheumatology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.599 J Korean Med Sci 2014; 29: 599-603 Case of IgG4-Related Disease with ronchial sthma and Chronic Rhinosinusitis
IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma with systemic disease
 Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with
 A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with IgG4-related disease 1)*, Yasuharu Sato 1) 2)*, Koh-ichi Ohshima 3), Katsuyoshi Takata 1), Tomoko Miyata-Takata 1), Mai
A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with IgG4-related disease 1)*, Yasuharu Sato 1) 2)*, Koh-ichi Ohshima 3), Katsuyoshi Takata 1), Tomoko Miyata-Takata 1), Mai
Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator
 Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation
 ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease
 International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
Clinical Study Development of an IgG4-RD Responder Index
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 259408, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/259408 Clinical Study Development of an IgG4-RD Responder Index Mollie N. Carruthers, 1 John H. Stone, 1 Vikram Deshpande,
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 259408, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/259408 Clinical Study Development of an IgG4-RD Responder Index Mollie N. Carruthers, 1 John H. Stone, 1 Vikram Deshpande,
Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis
 J Hematopathol (2011) 4:207 214 DOI 10.1007/s12308-011-0117-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis Imran
J Hematopathol (2011) 4:207 214 DOI 10.1007/s12308-011-0117-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis Imran
Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4-
 Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4- related disease: a case report and literature review Authors: María Isabel Ortuño Moreno,
Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4- related disease: a case report and literature review Authors: María Isabel Ortuño Moreno,
Dermatopathology. Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia
 Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
Case report: IgG4-related mass-forming thyroiditis accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy
 Sakai and Imamura Diagnostic Pathology (2018) 13:3 DOI 10.1186/s13000-017-0681-9 CASE REPORT Case report: IgG4-related mass-forming thyroiditis accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy Yasuhiro Sakai 1,2*
Sakai and Imamura Diagnostic Pathology (2018) 13:3 DOI 10.1186/s13000-017-0681-9 CASE REPORT Case report: IgG4-related mass-forming thyroiditis accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy Yasuhiro Sakai 1,2*
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3): /ISSN: /IJCEP Sun Young Choi 1, Sanghui Park 2
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
Recovery of renal function after glucocorticoid therapy for IgG4-related kidney disease with renal dysfunction
 Clin Exp Nephrol (2016) 20:87 93 DOI 10.1007/s10157-015-1140-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recovery of renal function after glucocorticoid therapy for IgG4-related kidney disease with renal dysfunction Takako Saeki
Clin Exp Nephrol (2016) 20:87 93 DOI 10.1007/s10157-015-1140-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recovery of renal function after glucocorticoid therapy for IgG4-related kidney disease with renal dysfunction Takako Saeki
IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT
 J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 129-133 IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT Han-Jui Lee 1 Yi-Chen Yeh 2,3 Chun-Ku Chen 1,3 Rheun-Chuan Lee 1,3
J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 129-133 IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT Han-Jui Lee 1 Yi-Chen Yeh 2,3 Chun-Ku Chen 1,3 Rheun-Chuan Lee 1,3
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Orbital Inflammation With IgG4-Positive Plasma Cells
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Orbital Inflammation With IgG4-Positive Plasma Cells Manifestation of IgG4 Systemic Disease José Antonio Plaza, MD; James A. Garrity, MD; Ahmet Dogan, MD, PhD; Anuradha Ananthamurthy,
CLINICAL SCIENCES Orbital Inflammation With IgG4-Positive Plasma Cells Manifestation of IgG4 Systemic Disease José Antonio Plaza, MD; James A. Garrity, MD; Ahmet Dogan, MD, PhD; Anuradha Ananthamurthy,
Overlap of IgG4-related Disease and Multicentric Castleman s Disease in a Patient with Skin Lesions
 CASE REPORT Overlap of IgG4-related Disease and Multicentric Castleman s Disease in a Patient with Skin Lesions Hiroki Mochizuki 1, Manako Kato 1, Takakazu Higuchi 2, Ryosuke Koyamada 2, Satoru Arai 3,
CASE REPORT Overlap of IgG4-related Disease and Multicentric Castleman s Disease in a Patient with Skin Lesions Hiroki Mochizuki 1, Manako Kato 1, Takakazu Higuchi 2, Ryosuke Koyamada 2, Satoru Arai 3,
IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal
 CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Lymphadenopathy after Therapy for Malignant Lymphoma
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Lymphadenopathy after Therapy for Malignant Lymphoma Yasuko Oshima 1, Ryosuke Usui 1, Shun Manabe 1, Naoki Hasegawa 2, Yukio Kakuta 2, Kosaku Nitta
CASE REPORT IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Lymphadenopathy after Therapy for Malignant Lymphoma Yasuko Oshima 1, Ryosuke Usui 1, Shun Manabe 1, Naoki Hasegawa 2, Yukio Kakuta 2, Kosaku Nitta
A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease
 CASE REPORT A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease Hirofumi Takei 1, Hayato Nagasawa 1, Ryota Sakai 1, Koji Nishimura 1, Takahiko
CASE REPORT A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease Hirofumi Takei 1, Hayato Nagasawa 1, Ryota Sakai 1, Koji Nishimura 1, Takahiko
Cerebral involvement in IgG4-related disease
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Clinical Medicine 2015 Vol 15, No 2: 130 4 Cerebral involvement in IgG4-related disease Authors: Deepak Joshi, A Rolf Jager, B Steven Hurel, C Stephen P Pereira, D Gavin J Johnson, E
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Clinical Medicine 2015 Vol 15, No 2: 130 4 Cerebral involvement in IgG4-related disease Authors: Deepak Joshi, A Rolf Jager, B Steven Hurel, C Stephen P Pereira, D Gavin J Johnson, E
International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 7, July 2015, pp 1688 1699 DOI 10.1002/art.39132 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology SPECIAL ARTICLE International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 7, July 2015, pp 1688 1699 DOI 10.1002/art.39132 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology SPECIAL ARTICLE International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management
IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis
 REVIEW IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Emma L. Culver, B.Sc., M.B.Ch.B., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.,* and Eleanor Barnes, M.B.B.S., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.*,, BACKGROUND IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC)
REVIEW IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Emma L. Culver, B.Sc., M.B.Ch.B., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.,* and Eleanor Barnes, M.B.B.S., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.*,, BACKGROUND IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC)
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Case Report
 CASE REPORT Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas Involving Type 1 Localized Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Normal Serum IgG4 Levels Successfully Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided
CASE REPORT Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas Involving Type 1 Localized Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Normal Serum IgG4 Levels Successfully Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided
IgG4-related systemic disease (ISD) is a multisystem
 Utility of Serum Immunoglobulin G4 in Distinguishing Immunoglobulin G4-Associated Cholangitis from Cholangiocarcinoma Abdul M. Oseini, 1 * Roongruedee Chaiteerakij, 1 * Abdirashid M. Shire, 1 Amaar Ghazale,
Utility of Serum Immunoglobulin G4 in Distinguishing Immunoglobulin G4-Associated Cholangitis from Cholangiocarcinoma Abdul M. Oseini, 1 * Roongruedee Chaiteerakij, 1 * Abdirashid M. Shire, 1 Amaar Ghazale,
Immunoglobulin G4 related Disease in Genitourinary Organs: An Emerging Fibroinflammatory Entity Often Misdiagnosed Preoperatively as Cancer
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) 865 872 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Opinion Editorial Immunoglobulin G4 related Disease in Genitourinary Organs: An
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) 865 872 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Opinion Editorial Immunoglobulin G4 related Disease in Genitourinary Organs: An
J. Zwicker, J. Michaud, C. Torres
 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Copyright 2014 the Canadian Journal of neurological SCienCeS inc. IgG4-related Disease Presenting as Dural Thickening A Rare Cause of Myelopathy J. Zwicker, J. Michaud, C. Torres Can
BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Copyright 2014 the Canadian Journal of neurological SCienCeS inc. IgG4-related Disease Presenting as Dural Thickening A Rare Cause of Myelopathy J. Zwicker, J. Michaud, C. Torres Can
IgG4 cholangitis Case Report: Joanne Verheij, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam.
 IgG4 cholangitis New Perspectives on Biliary Tract Disease Case Report: male, 64 yrs, truck driver and car industry worker Joanne Verheij, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam
IgG4 cholangitis New Perspectives on Biliary Tract Disease Case Report: male, 64 yrs, truck driver and car industry worker Joanne Verheij, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam
The Pathology of IgG4-Related Disease in the Bile Duct and Pancreas
 242 The Pathology of IgG4-Related Disease in the Bile Duct and Pancreas Yoh Zen, MD, PhD, FRCPath 1 1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan Semin
242 The Pathology of IgG4-Related Disease in the Bile Duct and Pancreas Yoh Zen, MD, PhD, FRCPath 1 1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan Semin
Kazuichi Okazaki 1 and Hisanori Umehara Introduction. 2. The Concept of IgG4-Related Disease
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 357071, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/357071 Review Article Are Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD Now Possible?
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 357071, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/357071 Review Article Are Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD Now Possible?
Histopathological findings in 29 lymph node biopsies with increased IgG4 plasma cells
 480 & 2012 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/12 $32.00 Histopathological findings in 29 lymph node biopsies with increased IgG4 plasma cells Kate E Grimm 1, Todd S Barry 1, Vladislav Chizhevsky
480 & 2012 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/12 $32.00 Histopathological findings in 29 lymph node biopsies with increased IgG4 plasma cells Kate E Grimm 1, Todd S Barry 1, Vladislav Chizhevsky
Ulcerative Colitis and Immunoglobulin G4
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 1, January 2014, pp. 29-4 ORiginal Article Ulcerative Colitis and Immunoglobulin G4 Go Kuwata*, Terumi Kamisawa*, Koichi Koizumi*, Taku Tabata*, Seiichi Hara*, Sawako Kuruma*,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 1, January 2014, pp. 29-4 ORiginal Article Ulcerative Colitis and Immunoglobulin G4 Go Kuwata*, Terumi Kamisawa*, Koichi Koizumi*, Taku Tabata*, Seiichi Hara*, Sawako Kuruma*,
A case of marginal zone B cell lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis
 Ohta et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:67 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0459-z WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A case of marginal zone B cell lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related
Ohta et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:67 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0459-z WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A case of marginal zone B cell lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Ocular Adnexal IgG4-Related Lymphoplasmacytic Infiltrative Disorder
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Ocular Adnexal IgG4-Related Lymphoplasmacytic Infiltrative Disorder Toshinobu Kubota, MD; Suzuko Moritani, MD; Masao Katayama, MD; Hiroko Terasaki, MD, PhD Objective: To determine the
CLINICAL SCIENCES Ocular Adnexal IgG4-Related Lymphoplasmacytic Infiltrative Disorder Toshinobu Kubota, MD; Suzuko Moritani, MD; Masao Katayama, MD; Hiroko Terasaki, MD, PhD Objective: To determine the
Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy Takayoshi Nishino 1, Fumitake Toki 2,HiroyasuOyama 3, Kyoko Shimizu 1 and Keiko Shiratori 1 Abstract Objective
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy Takayoshi Nishino 1, Fumitake Toki 2,HiroyasuOyama 3, Kyoko Shimizu 1 and Keiko Shiratori 1 Abstract Objective
The most common presentation of autoimmune pancreatitis. A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1097 1103 A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer SURESH T. CHARI,* NAOKI TAKAHASHI, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* THOMAS
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1097 1103 A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer SURESH T. CHARI,* NAOKI TAKAHASHI, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* THOMAS
Contents. vii. Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii
 Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus
 Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis in Korea
 Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2014;19(1):7-12 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 한국에서자가면역췌장염의진단전략 성균관대학교의과대학삼성서울병원내과학교실 이종균 Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2014;19(1):7-12 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 한국에서자가면역췌장염의진단전략 성균관대학교의과대학삼성서울병원내과학교실 이종균 Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Overview of Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
 2007 년도대한췌담도학회추계학술대회 Session II: Comparison of Diagnostic Criteria for AIP: Japan, USA & Korea Overview of Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Pancreatitis Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National
2007 년도대한췌담도학회추계학술대회 Session II: Comparison of Diagnostic Criteria for AIP: Japan, USA & Korea Overview of Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Pancreatitis Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National
Immunoglobulin G4 related disease (IgG4-RD) is an. Immunoglobulin G4 related disease mimicking an epidural spinal cord tumor: case report
 case report J Neurosurg Spine 26:76 80, 2017 Immunoglobulin G4 related disease mimicking an epidural spinal cord tumor: case report Michelle M. Williams, MD, 1 Hazem Mashaly, MD, 2,5 Vinay K. Puduvalli,
case report J Neurosurg Spine 26:76 80, 2017 Immunoglobulin G4 related disease mimicking an epidural spinal cord tumor: case report Michelle M. Williams, MD, 1 Hazem Mashaly, MD, 2,5 Vinay K. Puduvalli,
Case Report IgG4-Seronegative Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Sclerosing Cholangitis
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 591360, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/591360 Case Report IgG4-Seronegative Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Sclerosing Cholangitis
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 591360, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/591360 Case Report IgG4-Seronegative Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Sclerosing Cholangitis
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Affiliazione autori0. Riccardo Ricci Journal Club GIPAD, settore GIST Anatomia Patologica, Università Cattolica, Roma
 GIST Manifesting as a Retroperitoneal Tumor: Clinicopathologic Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Genetic Study of 112 Cases American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 2017, 41:577-585 Miettinen M*; Felisiak-Golabek
GIST Manifesting as a Retroperitoneal Tumor: Clinicopathologic Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Genetic Study of 112 Cases American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 2017, 41:577-585 Miettinen M*; Felisiak-Golabek
Case year old Chinese female. Radiological echo-distortion in the right breast at o clock. Core biopsy of the o clock lesion.
 Case 3 64 year old Chinese female. Radiological echo-distortion in the right breast at 10-12 o clock. Core biopsy of the 11-12 o clock lesion. Division of Pathology Courtesty of Dr Lester Leong ill-defined,
Case 3 64 year old Chinese female. Radiological echo-distortion in the right breast at 10-12 o clock. Core biopsy of the 11-12 o clock lesion. Division of Pathology Courtesty of Dr Lester Leong ill-defined,
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease
 CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
IgG4-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients
 IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
IgG4 ᛶ ᝈ䛸 ᶫᮏ ᕫච ᛶ ⅖ ḷᒣ Ꮫ య Ꮫ ぬ㐨
 IgG4 Autoimmune pancreatitis Histopathological features: Diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration Stromal fibrosis Acinar atrophy Obliterative phlebitis 1. Hamano et al reported that serum IgG4 levels were
IgG4 Autoimmune pancreatitis Histopathological features: Diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration Stromal fibrosis Acinar atrophy Obliterative phlebitis 1. Hamano et al reported that serum IgG4 levels were
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-
 review article Oman Medical Journal [2018], Vol. 33, No. 2: 97-103 ARTICLE INFO Article history: Received: 12 April 2017 Accepted: 14 August 2017 Online: DOI 10.5001/omj.2018.20 Keywords: Immunoglobulin
review article Oman Medical Journal [2018], Vol. 33, No. 2: 97-103 ARTICLE INFO Article history: Received: 12 April 2017 Accepted: 14 August 2017 Online: DOI 10.5001/omj.2018.20 Keywords: Immunoglobulin
Objectives. Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System. Role of Salivary Gland FNA 04/26/2018
 Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
ANCA associated vasculitis in China
 ANCA associated vasculitis in China Min Chen Renal Division, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, P. R. China 1 General introduction of AAV in China Disease spectrum and ANCA type Clinical
ANCA associated vasculitis in China Min Chen Renal Division, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, P. R. China 1 General introduction of AAV in China Disease spectrum and ANCA type Clinical
Review Article IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: a potentially under- and over-diagnosed entity
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10153-10166 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026563 Review Article IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: a potentially under- and over-diagnosed entity Zenggang Pan 1, Jiehao
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10153-10166 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026563 Review Article IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: a potentially under- and over-diagnosed entity Zenggang Pan 1, Jiehao
Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels Keiichi Torimoto, Yosuke Okada, Akira Kurozumi, Manabu Narisawa, Tadashi Arao and Yoshiya Tanaka Abstract
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels Keiichi Torimoto, Yosuke Okada, Akira Kurozumi, Manabu Narisawa, Tadashi Arao and Yoshiya Tanaka Abstract
