Intercellular communication
|
|
|
- Debra Alaina Norton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endocrine system
2 Intercellular communication Blood Neurocrine Endocrine Blood Distant Paracrine Tissue Autocrine Local Synaptic Synapsis Contact
3 General properties of endocrine organs Endocrine organs (e.g. pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal) Endocrine tissue within other organs (pancreas, gonads, kidneys, placenta) Isolated endocrine cells (DNES, APUD) Neuroendocrine cells Common developmental scheme - invagination of epithelia, losing contact with the original tissue - ducts absents
4 General properties of endocrine organs c.t. capsule + septs Trabecules of glandular epithelium, follicles or clusters of glandular cells or Neurosecretory cells Capillary network - Fenestrated capillaries - Sinusoids Merocrine secretion - not only hormones endocrine gland is sensu lato also liver
5 General properties of hormones steroids hydrophobic, intracytoplasmic or nuclear receptors (sex hormones, corticoids) proteins and polypeptides hydrophilic, plasma membrane receptors (insulin, pituitary hormones, PTH, ) aminoacids and their derivatives (adrenalin, noradrenalin, thyroxin)
6 v
7 Pituitary gland (gl. pituitaria)
8 Pituitary gland (gl. pituitaria) sphenoid bone sella turcica fossa hypophysialis
9 Pituitary gland (gl. pituitaria)
10 Pituitary gland (gl. pituitaria) adenohypophysis (pars distalis, pars tuberalis, pars intermedia) neurohypophysis (pars nervosa) infundibulum, eminentia mediana
11 Pituitary gland (gl. pituitaria) adenohypophysis - glandotropic hormones, prolactin, GH neurohypophysis - hypothalamic hormones - ADH, oxytocin anatomical and functional association with hypothalamus capillary systems and neuroendocrine secretion
12 Hypothalamus NC CC Th GP Pu small region of diencephalon complex neuroarchitecture core of the limbic system complex functions - regulation of temperature, emotions, eating behavior, circadian rythms - hormonal regulation controlled by various stimuli (osmoreception, concentration of nutrients, electrolytes, systemic functions - pain) hypothalamic nuclei - n. supraopticus, n. paraventricularis - magnocelullar neurons - tractus hypothalamo-hypophysialis - parvocelullar neurons - capillaries in eminentia mediana Hyp SI
13 Hypothalamo-hypophyseal system
14 Mechanism of neurosecretion Tractus hypothalamo-hypophysialis - axons of magnocelullar neurons in nucleus supraopticus and paraventricularis - terminating on fenestrated capillaries in neurohypophysis - synthesis of prohormones maturation during axonal transportation - capillary plexus from arteria hypophysialis inferior (branch of arteria carotis interna v. lobi posterioris Hypophyseal portal system - parvocellular neurons e.g. in nucleus arcuatus, preopticus, paraventricularis and nuclei tuberales - axonal transport onto primary capillary plexus in eminentia mediana (from anterior and posterior superior hypophyseal arteries) hypophyseal portal veins (venae portales hypophysiales) secondary capillary plexus in adenohypophysis v. lobi anterioris sinus cavernosus v. jugularis interna
15 Capillary system of hypophysis ncl. paraventricularis ncl. supraopticus hypophyseal arteries Tractus hypothalamo-hypophysialis anterior lobe secondary plexus of posterior lobe
16 Eminentia mediana elevated part of tuber cinereum, ( detachment of infundibulum p. nervosa) neurohemal area hematoencephalic barrier open fenestrated capillaries with large perivascular spaces
17
18 Embryonal development of pituitary gl. Ectoderm (Rathke s pouch) Neuroectoderm of ventral wall of diencephalon
19 Embryonal development of pituitary gl.
20 A = fossa B = hypothalamus C = eminentia mediana D = adenohypophysis
21
22 Chromophilic cells Acidophils Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe) - Somatotropic Nonglandotropic (STH, somatotropin), 50% - direct effect on target tissues - Mammotropic (LTH, prolactin), 10-25% Bazophils Glandotropic - Thyrotropic - regulation (TSH), of other 3-5% endocrine glands - Gonadotropic (FSH, LH), 10-15% - Corticotropic (POMC, ACTH, MSH), 15-25% Chromophobic cells undifferentiated cells degranulated ( empty ) chromophils stromal cells
23 Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe)
24 Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe)
25 FLAT PEG FSH LH ACTH TSH Prolactin Endorphins Growth hormone
26 Pro-opio-melanocortin (POMC) rough ER pre-prohormon produced by various tissues cleavage to ACTH (target: adrenal cortex kortisol) MSH (target: melanocytes - mostly in paracrine way) lipotropin (lipolysis, steroidogenesis) endorphins
27 FSH (folitropin), LH (lutropin) gonadotropic cells of adenohypophysis stimulated by GnRH glycoproteins, 30kDa heterodimer, two noncovalent bound subunits (a/ - common for - LH, FSH, TSH, hcg, b/ - specific) FSH receptor (testes, ovarium, uterus) G-protein coupled receptor - glycosylated extracellular domain of 11 leucine rich repeats specific to FSH - after ligand binding, activation of G-protein and camp signaling - alternative activation of MAPK cascade (ERK) - complex signaling response (prostaglandins, PLPc, NO) ovarium FSH follicle development (FSHR in m. granulosa cells) LH ovulation, development of corpus luteum, production of androgens in thecal cells testes spermatogenesis, FSHR in Sertoli cells production of testosterone in Leydig cells (expression of LHR) extragonadal FSHR in secretory endometrium of luteal phase uterus (endometrial functions, embryoendometrial interactions) uterus, seminal vesicles, prostate, skin... unknown function
28 TSH, thyrotropin thyrotropic cells of adenohypophysis stimulated by TRH production of T4 (thyroxin) a T3 (triiodothyronin) by thyroid gland glycoprotein, 28,5 kda, heterodimer, two noncovalent bound subunits (a, b) TSH receptor on thyroid follicular cells G-protein signaling adenylylcyklase camp - camp iodide channels (pendrin), transcription of thyreoglobulin, endo- and exocytic pathway cross-reactivity with hcg in pregnancy - alterations in synthesis of thyroid hormones (gestational hyperthyroidism)
29 GH, somatotropin, growth hormone somatotropic cells of adenohypophysis stimulated by GHRH (somatocrinin) several molecular isoforms (alternative splicing), ~20-24 kda broad spectrum of target cell types and physiological circuits - transcription of DNA, translation of RNA, proteosynthesis - lipid use (fatty acid mobilization, conversion to acetyl-coa) - inhibition of direct use of glucose, stimulation of glukoneogenesis - transmembrane transport of aminoacids - proteosynthesis in chondrocytes and osteoblasts, proliferation, osteogenesis GHR in various tissues - RTK, JAK-STAT somatomedins - small proteins (MW 7,5 kda), IGF-like - produced by liver various pathologies associated with GH
30
31 Clinical links Hypophyseal tumors compression of surrounding structures (optic chiasma) hyperfunction of endocrine component - prolactinoma - galactorrhea - hypogonadism (alterations of GnRH) - gigantism - acromegaly - nanism
32
33 Posterior hypophysis (neurohypohysis) nonmyelinated nerve fibers axons of neurosecretory cells (c.a ) of hypothalamic nuclei (n. supraopticus and paraventricularis) pituicytes (neuroglia) - astrocyte-like (intermediate fialmets, GFAP) - local control of secretion from neuroscretory termini - Herring bodies neurosecretory endings dilatation close to capillaries Hormones - oxytocin (OT) - antidiuretic hormone (ADH, vasopresin)
34
35
36 nonapeptide retention of water effective in collecting duct and distal convoluted tubule (aquaporine translocations) blood pressure regulation by affecting t. media diabetes insipidus, hypernatremia, polyuremia Oxytocin nonapeptide magno-cellular supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus OR - G-coupled receptor lactation reflex uterine contraction social behavior Vasopressin
37 Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) Anatomy Microscopic anatomy Hormones and target tissues chromophobes chromophils acidophilic nonglandotropic basophilic glandotropic small polypeptides glycoproteins small peptides trabecular epithelium in cords and clusters, reticular fibers pars distalis pars tuberalis superior hypophyseal arteries primary capillary plexus hypophyseal portal veins + inferior hypophyseal arteries secondary capillary plexus hypophyseal portal veins vv. jugulares internae undifferentiated cells degranulated chromophilic cells stromal cells mammotropic cells somatotropic cells corticotropic cells lack hormonal activity dopamin (PIH) (PRF prolactin somatostatin (GHIH) GHRH somatotropin (STH) CRH ACTH, MSH mammary gland in gravidity and lactations directly liver and growth plates other tissues via somatomedins adrenal cortex cortisol melanocytes thyrotropic cells TRH TSH thyroid thyroxin, T3 pars intermedia Rathke s cysts gonadotropic cells GnRH FSH (ICSH), LH gonads androgens, estrogens, progesterone eminentia mediana infundibulum pars nervosa anterior and posterior superior hypophyseal arteries primary capillary plexus, fenestrated capillaries nonmyelinated axons of hypothalamic neurons n. supraopticus, n. paraventricularis (tractus hypothalamohypophysialis), pituicytes ADH oxytocin tubulus reuniens, ductus colligens t.media of vessels myometrium of uterus during gravidity myoepithelium of lactating mammary gland
38 Epiphysis (c. pineale) epithalamus c.t. capsule continuous to pia mater thin c.t. septa nonmyelinated nerve fibers pinealocytes (95%, large, pale, round nuclei) interstitial neuroglia (astrocytes, dark, elongated nuclei) acervulus cerebri melatonin
39
40 pinealocytes Epiphysis (c. pineale) - star-like, modified neurons in trabecules - association with fenestrated capillaries - neurosecretory dilatations - nonvisual photoreception
41 Embryonic development of epiphysis (c. pineale) thickening of caudal part of ependyma that does not contribute to development of choroid plexus at the roof of diencephalon neuroectoderm
42 Thyroid gland (gl. thyroidea) Follicular cells thyroid hormones (T3, T4) C cells calcitonin C.t. capsule, septs Lobes lobuli - follicles Follicles (50 µm -1 mm) - separated by interstitial loose collagen c.t. - simple epithelium (flat to cubic, according to secretory activity) - colloid Capillary network from thyroid arteries
43 Thyroid gland - follicles
44 Thyroid gland - follicles C-cells Follicular cells and C-cells (parafollicular)
45 Synthesis of T3 and T4 T4 synthesis in thyroid sodium-iodide symporter transports two Na+ and one I- across the basement I is moved across the apical membrane into the colloid of the follicle. thyroperoxidase oxidises 2 I I 2. thyroperoxidase iodinates the tyrosyl residues of thyroglobulin (TSH) stimulates the endocytosis of the colloidal content endocytic vesicles + lysosomes, lysosomal enzymes cleave T 4 from the iodinated thyroglobulin exocytosis T3 synthesis from T4 T4 half-life in blood 6.5 days, T3 2.5 (T4 is a reservoir for T3) deiodination by tissue specific deiodinase enzymes generates T3
46 thyreoglobulin triiodothyronin T 3 tetraiodothyronin (thyroxin) T 4
47 Alternative T3 pathway Canonical T3 pathway
48 C cells of thyroid Neuroendocrine cells - pale staining - epithelial basis, under basal lamina no contact with colloid - derived from neural crest - associate with ultimobranchial body, (derivative of the 4th pharyngeal pouch) Calcitonin - inhibition of osteoclasts
49 Thyroid development endodermal proliferation of pharyngeal floor hypobranchial eminence and foramen caecum bilobed civerticulum ductus thyreoglossus
50 Parathyroid gland (gl. parathyreoidea) 6 mm, 130 mg c.t. capsule and septs Capillary network Cords and clusters of glandular cells - Chief - Oxyphilic - Adipose
51 Parathyroid gland (gl. parathyreoidea) Chief - most abundant - small cells (7-10µm, big nucleus - mildly acidophilic - PTH calcium metabolism Oxyphylic - large, polyhedral, - strongly acidophilic - round nucleus - glycogen
52 Parathyroid gland (gl. parathyreoidea)
53 Parathyroid hormone (PTH, parathormone, parathyrin) 84 aminoacids stimulates resorption by osteoclasts enhances resorption of calcium and magnesium in distal tubules and thick ascending limb enhances absorption in the intestine (via vd3)
54 PTH vs. calcitonin
55 Embryonic development of parathyroid gland glandulae parathyroideae superiores from endoderm of 4th pharyngeal pouch glandulae parathyroideae inferiores from dorsal process of 3th pharyngeal pouch - together with thymus descend to lower poles of thyroid ectopic PTH gland in thymus or mediastinum
56 Embryonic development of parathyroid gland
57 Adrenal gland (corpus suprarenale) c.t. capsule, septs capillary plexus
58 Adrenal development cortex - mesoderm - mesothelium, coelomic epithelium medulla - neural crest
59 Adrenal cortex
60 Adrenal cortex Zona glomerulosa (1/10) - thin layer under capsule - relatively small cells in coiled glomeruli - not abundand lipid droplets - mineralocorticoids Zona fasciculata (6/10) - radially arranged trabecules - lipid droplets in cytoplasm - glucocorticoids Zona reticularis (3/10) - branched trabecules - small, acidophilic cells - lipofuscin - androgen precursors
61 Adrenal cortex hormones Steroids produced incortex = CORTICOSTEROIDS Steroidogenic cells - SER, lipid droplets, mitochondria - mineralocorticoids - glucocorticoids Aldosteron zona glomerulosa Kortisol zona fasciculata Androgens, estrogens, progesteron zona reticularis
62 Adrenal cortex hormones
63 Adrenal medulla Clusters of glandular cells in reticular c.t. - chromaffin cells modified postganglionic neurons - ganglionic cells - capillaries, venules, nerve fibers - adrenaline and noradrenaline Neural crest origin
64
65 Adrenal vascularisation c.t. capsule cortical arteriole capsular arteriole capsular venule medullar artery arteriae suprarenales (3) arterial plexus in cortex under c.t. capsule radially oriented fenestrated sinusoid capillaries continuous with medullar capillaries medullar veins v. suprarenalis z. glomerulosa z. fasciculata capillaries of z. glomerulosa arteria perforans capillaries of z. fasciculata three arterial regions 1) c.t. capsule and superior parts of cortex 2) radial capillaries of cortex continuing to medulla 3) medullar capillaries from aa. perforantes z. reticularis medulla capillaries of z. reticularis venules of z. reticularis medullar capillaries medullar veins
66 CNS (sympaticus) STRESS Hypothalamus Pituitary gland ACTH Adrenal medulla Adrenaline - blood pressure, vasoconstriction, heart rate Adrenal cortex Kortisol - glycogen lysis - stabilization of glucose levels - suppression of immune system Fight or Flight Adaptation, regeneration
67 Langerhans islet of pancreas
68 Langerhans islets of pancreas B-cells producing insulin Ab-anti insulin Alexa Fluor A-cells producing glucagon Ab-anti glukagon Texas Red
69 Thank you for attention
Intercellular communication
 Endocrine system Intercellular communication Blood Neurocrine Endocrine Blood Distant Paracrine Tissue Autocrine Local Synaptic Synapsis Contact General properties of endocrine organs Endocrine organs
Endocrine system Intercellular communication Blood Neurocrine Endocrine Blood Distant Paracrine Tissue Autocrine Local Synaptic Synapsis Contact General properties of endocrine organs Endocrine organs
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG
 Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
The endocrine system
 The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture. Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
Endocrine System. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU
 The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System: An Overview. A system of ductless glands. Interacts closely with the nervous system Endocrinology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
ENDOCRINE GLANDS. Pituitary Gland
 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Endocrine (or internally secreting) glands are also named ductless glands, since they lack excretory ducts. Instead, the secretory cells release their products, hormones, into the extracellular
ENDOCRINE GLANDS Endocrine (or internally secreting) glands are also named ductless glands, since they lack excretory ducts. Instead, the secretory cells release their products, hormones, into the extracellular
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Endocrine System. Human Physiology Unit 3
 Endocrine System Human Physiology Unit 3 Endocrine System Various glands located throughout the body Some organs may also have endocrine functions Endocrine glands/organs synthesize and release hormones
Endocrine System Human Physiology Unit 3 Endocrine System Various glands located throughout the body Some organs may also have endocrine functions Endocrine glands/organs synthesize and release hormones
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Fig The Endocrine System The connective tissue will be very well vascularized. Due to their need to distribute their products by the blood, the
 Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
The Endocrine System. Qian XiaoJing. Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE QIAN
 The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland
 Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB
 Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Endocrine Glands. Endocrine glands
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland
 Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System
 Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
11/26/2007. The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System. NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Lecture Series
 The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline. Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
Endocrine System. Always willing to lend a helping gland
 Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
3/12/2012. Pituitary Gland (hypophysis) Anterior Pituitary. Anterior Pituitary. Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Glands Hypothalamus (Master Gland) 8 hormones produced in hypothalamus 6 regulate anterior pituitary e.g., TRH, GnRH, GHRH E.g., PIH, Somatastatin (GH TSH) Hypothalamus
Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Glands Hypothalamus (Master Gland) 8 hormones produced in hypothalamus 6 regulate anterior pituitary e.g., TRH, GnRH, GHRH E.g., PIH, Somatastatin (GH TSH) Hypothalamus
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Gross anatomy. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran
 Gross anatomy Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Glands drain ipsillaterally by superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran In the fifth week, epithelium of
Gross anatomy Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Glands drain ipsillaterally by superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran In the fifth week, epithelium of
Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones
 Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones By Adeyomoye O.I Department of Physiology Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences Ondo, Ondo City. 11/9/2017 1 Introduction The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that
Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones By Adeyomoye O.I Department of Physiology Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences Ondo, Ondo City. 11/9/2017 1 Introduction The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that
HIHIM 409. Endocrine system. Differences between systems. Hormone effects. Similarities. Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system
 The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
The endocrine system -- a brief overview.
 The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
21 Endocrine organs and cells
 21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
Chapter 11. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
Histology of the Thyroid Gland
 Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Hypophysis. Organization
 Hypophysis The hypophysis or pituitary is a complex endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, lying in the sella turcica, a small depression in the sphenoid bone. It is attached to the hypothalamic
Hypophysis The hypophysis or pituitary is a complex endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, lying in the sella turcica, a small depression in the sphenoid bone. It is attached to the hypothalamic
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Classic Endocrine Glands
 1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
Lecture 03. Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018
 Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES:
 ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES: -In a living organism there must be coordination of number of physiological activities taking place simultaneously such as: movement, respiration,
ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES: -In a living organism there must be coordination of number of physiological activities taking place simultaneously such as: movement, respiration,
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination
 I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
Art labeling Activity: Figure 16.1
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
Major Endocrine Glands
 The Endocrine System These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best screen
The Endocrine System These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best screen
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises
 A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-22
 Chapter-22 CHEMICAL COORDINATION AND INTEGRATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Endocrine glands : These are ductless glands which secrete hormones directly into the blood stream. Hormones : Non-nutrient chemicals,
Chapter-22 CHEMICAL COORDINATION AND INTEGRATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Endocrine glands : These are ductless glands which secrete hormones directly into the blood stream. Hormones : Non-nutrient chemicals,
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome)
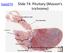 histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
The Endocrine System
 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
