Hepatobiliary Imaging Clinical Observations
|
|
|
- Joy Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CT of Cholangiocarcinoma with Pyogenic Cholangitis Hepatobiliary Imaging Clinical Observations C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Jung Hoon Kim 1 Tae Kyoung Kim 2 Hyo Won Eun 3 Jae Young yun 4 Moon-Gyu Lee 5 Hyun Kwon Ha 5 Yong Ho uh 6 Kim JH, Kim TK, Eun HW, et al. Keywords: biliary system, cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, CT, liver disease, pyogenic cholangitis DOI: /JR Received March 19, 2005; accepted after revision June 13, Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, 657 Hannam-Dong, Youngsan-Ku, Seoul, South Korea ddress correspondence to J. H. Kim (junghkim@hosp.sch.ac.kr). 2 Medical Imaging, Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada. 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, South Korea. 4 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Kangnam St. Mary s Hospital College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, South Korea. 5 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, san Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea. 6 Department of Radiology, Cornell University Weill Medical College, New York, NY. JR 2006; 187: X/06/ merican Roentgen Ray Society CT Findings of Cholangiocarcinoma ssociated with Recurrent Pyogenic Cholangitis OJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to determine the characteristic CT findings of cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis. CONCLUSION. CT findings of cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis are important in order to improve early diagnosis and proper treatment. Cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis is predominantly located in the atrophic hepatic lobes and in the hepatic lobes of biliary calculi and is associated with the narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein. ecurrent pyogenic cholangitis is R characterized clinically by recurrent attacks of fever, chills, abdominal pain, and jaundice caused by intrahepatic ductal strictures and pigment stones. This disease is endemic to Southeast sian countries, but it is being increasingly encountered in the West as a result of growing sian immigration. The cause of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis is repeated bouts of cholangitis from enteric organisms such as Escherichia coli or endemic parasites such as Opisthorchis sinensis and scaris lumbricoides. Pathogenic factors that can contribute to disease progression include malnutrition, parasitic infection, and portal bacteremia [1 4]. In general, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis is a well-known risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma. The pathogenesis is incompletely understood. Some investigators report that chronic bacterial infection, bile stasis, and mechanical irritation from biliary calculi can lead to the development of mucosal adenomatous hyperplia and chronic proliferative cholangitis, which can undergo a progressive change to atypical epithelial hyperplasia and, ultimately, to cholangiocarcinoma [5 7]. There are many clinical reports about recurrent pyogenic cholangitis associated with cholangiocarcinoma. The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis is reported to be % of patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis [5, 6, 8 21]. Cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis has a poor prognosis as a consequence of delayed diagnosis, a low diagnosis rate, and few curative resections [11 14]. It is difficult to accurately diagnosis cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis before treatment. The CT features of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis include bile duct dilation, bile duct stricture, biliary calculi, hepatic atrophy, portal vein obliteration, hepatic abscess, and biloma. These findings may lead to delayed diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis because they may obscure the underlying cholangiocarcinoma [3, 4]. lthough there are some reports of CT findings for cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis in a small number of patients [22], to our knowledge there has not been a report of a large series addressing the use of CT when these two pathologies are coincident. Thus, this study assesses the CT features of cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis in 82 patients. Materials and Methods Patients This study was approved by our institutional review board for human investigation, and informed consent was obtained from patients or their relatives. computerized search of the medical records of two institutions from January 1998 to ugust 2002, revealed 1,344 patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. Of these patients, 82 patients with pathologically proven cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis constituted the basis of this study. JR:187, December
2 TLE 1: CT Findings in 82 Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma ssociated with Recurrent Pyogenic Cholangitis CT Findings No. κ Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma 66 Contrast enhancement pattern Thin and lobulated enhancement at periphery Thick and lobulated enhancement at periphery Ill-defined homogeneous enhancement Intratumoral appearance Marked hypoattenuation Slight hyperattenuation Septum-like linear structure Morphologic change of the liver Segmental atrophy Narrowing or obliteration of portal vein iliary calculi Hilar and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 16 Ill-defined hypoattenuating mass in hilum Enhancing intraductal mass Enhancing focally thickened biliary ductal wall Narrowing or obliteration of bile duct Cholangiocarcinoma is classified into three types on the basis of anatomic location. Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma is defined as carcinoma arising from second-order or more distal branches of the intrahepatic ducts. Hilar cholangiocarcinoma is defined as carcinoma arising from one of the hepatic ducts or the bifurcation of the common hepatic duct. Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is defined as carcinoma arising from an extrahepatic bile duct distal to the hilum. There were 66 patients with peripheral cholangiocarcinoma, nine patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma, and seven patients with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. ll 82 patients had acute cholangitis with abdominal pain, fever, or jaundice at the time of admission. ll patients had been symptomatic from 4 to 30 years (mean, 9.5 years) and had had recurrent attacks of the disease on more than three occasions. Leukocytosis and hyperbilirubinemia were also present in 63 and 42 patients, respectively. Thirtyfive of the 82 patients had a history of Opisthorchis sinensis infestation and five of the 82 patients had a history of Escherichia coli in bile cultures. Thirty-six patients had previously undergone cholecystectomy because of gallbladder stone. Of these 82 patients, 53 underwent dual-phase CT and 29 underwent single-phase CT. There were 50 men and 32 women. Patient ages ranged from 30 to 72 years (mean, 56 years). The pathologic diagnoses were confirmed by surgical resection (n = 25), exploratory laparotomy (n = 7), percutaneous liver biopsy (n = 40), and percutaneous transhepatic choledochoscopy guided biopsy (n = 10). Surgical procedures included right lobectomy (n =5), left lobectomy (n = 14), and segmentectomy (n =6). Serum for tumor markers, including carcinoembryonic antigen (CE) and cancer antigen (C) 19-9, were available for 53 patients. The normal value for CE was less than 4 ng/ml; for C19-9, it was less than 37 U/mL. CE was elevated in 18 (34%) patients and C19-9 was elevated in 29 (55%) patients. CE values ranged from 6.51 to 83.1 ng/ml (mean, 41.5 ng/ml); C 19-9 values ranged from 45 to 3,500 U/mL (mean, 655 U/mL). Imaging CT was performed with a 9800 Quick System (GE Healthcare), a HiLight dvantage (GE Healthcare), or a Somatom Plus-S (Siemens Medical Solutions) scanner. Each patient received 120 ml of contrast medium ([iopamidol] Iopamiro 300, racco; or [iopromide] Ultravist, Schering) by bolus injection in a forearm vein at a rate of 3 ml/s. ll patients ingested 1,000 ml of water before scanning. Helical CT parameters included 8-mm collimation, table feed of 10 mm, and reconstruction increments of 8 mm. Unenhanced CT scans were obtained in all patients; and dual-phase CT scans, including hepatic arterial and portal venous phases, were then obtained 35 and 70 seconds, respectively, after initiation of the infusion. Single-phase CT scans were obtained 70 seconds after initiation of the infusion. nalysis CT findings were retrospectively analyzed independently by two board-certified radiologists. We used a hard-copy system. When the reviewers interpretations differed, a third opinion was obtained. The radiologists experience with abdominal CT ranged from 5 to 15 years. In cases of peripheral cholangiocarcinoma, the following imaging variables were analyzed: tumor size, number of lesions, contrast-enhancement patterns, intratumoral appearance, narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein, segmental atrophy, coincident biliary calculi, and other ancillary findings such as the presence of biloma or abscess. In hilar cholangiocarcinoma and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, imaging variables included the presence or absence of an ill-defined hypoattenuating mass in the hilum, enhancing intraductal mass, enhancing focally thickened biliary ductal wall, and narrowing or obliteration of the bile duct (Table 1). If a patient had multiple lesions, the largest mass was analyzed. In contrast-enhancement patterns, thick, lobulated contrast enhancement at the tumor periphery was diagnosed when the thickness was greater than 3 mm with a well-defined line at the margin of the mass. Ill-defined homogeneous enhancement was diagnosed when the margin of the mass could not be outlined. In intratumoral appearance, marked hypoattenuation was defined as a decreased attenuation similar to that of water but less than that of back muscle. Presence of a slightly hyperattenuated area was defined as slightly hyperattenuated area within the hypoattenuated mass. Septumlike linear structure was defined as a linear-enhanced line within the mass. Narrowing of the portal vein was defined as a decreased diameter less than one third that of the main portal vein. Obliteration of the portal vein was defined as a vein being unapparent or unenhanced. Enhancing focally thickened biliary ductal wall was diagnosed when the thickness was greater than 5 mm. For the variable CT findings in each patient, the interobserver agreement was evaluated using the kappa statistic. kappa value less than 0.20 was considered poor; , fair; , moderate; , good; and excellent. The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma was compared between atrophic lobe and nonatrophic lobes, between lobes with narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein and lobes with normal portal veins, and between lobes having biliary calculi and lobes without biliary calculi, using Fisher s exact test, after adjusting for the effect of clustering according to literature references [23, 24] JR:187, December 2006
3 CT of Cholangiocarcinoma with Pyogenic Cholangitis Results Table 1 shows the CT findings in the 82 patients with cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. Peripheral Cholangiocarcinoma Sixty-six patients had peripheral cholangiocarcinoma. The size of the masses as measured on CT was mm (mean, 51.5 mm) in the largest dimension. Five patients had multiple hepatic masses. The dominant mass was located in the left lobe (n = 36), right lobe (n = 25), or in both lobes (n =5). Thin and lobulated contrast enhancement at the tumor periphery was seen in 57 (86%) patients. The intratumoral appearance was marked hypoattenuation in 63 (95%) patients and slight hyperattenuation in 50 (75%) patients (Fig. 1). Segmental atrophy was seen in 41 (62%) patients. Segmental atrophy of the liver was seen in the lateral segment of the left lobe (n = 21), posterior segment of the right lobe (n = 11), left lobe (n = 5), and anterior segment of the right lobe (n = 4). mong these C 41 patients, 36 (88%) patients had a mass within the atrophic segment (Fig. 2). The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma was greater in the atrophic lobe (88%; 36 of 41 atrophic lobes) than in the nonatrophic lobe (33%; 30 of 91 nonatrophic lobes) (p < ). ll atrophic segments showed narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein. Radiographic changes of the portal vein, including luminal narrowing or obliteration, were seen in 60 (91%) patients. Narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein was seen in the right portal vein (n = 22) and the left portal vein (n = 38). mong these 60 patients, 50 (83%) had a mass within the lobe associated with narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein (Fig. 3). The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma was also greater in the lobe with narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein (83%; 50 of 60 lobes with narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein) than in the lobe with normal portal veins (22%; 16 of 72 lobes with a normal portal vein) (p < ). Fig. 1 Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis in 69-year-old man who complained of abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis. He has history of recurrent attacks of cholangitis and had previously undergone cholecystectomy because of gallstone., Unenhanced CT scan shows hepatolithiasis in right intrahepatic duct (arrowheads) with severe atrophy in posterior segment of right lobe., Contrast-enhanced CT scan at same level shows luminal narrowing of right portal vein (arrowheads). C, Contrast-enhanced CT scan obtained 16 mm below during hepatic artery phase shows thick and lobulated enhancement at periphery of mass during arterial phase. This mass shows markedly hypoattenuated, septumlike linear structure and slightly hyperattenuated area. Diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma was made at percutaneous liver biopsy. Intrahepatic biliary calculi were seen in 39 (59%) patients. Intrahepatic biliary calculi was seen in the right intrahepatic bile ducts (n = 14), the left intrahepatic bile duct (n =21), and both intrahepatic bile duct (n =4). mong the 39 patients with intrahepatic biliary calculi, 26 (67%) had a mass within the same lobe. The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma was also greater in lobes having biliary calculi (67%; 26 of 39 lobes having biliary calculi) than in lobes without biliary calculi (43%; 40 of 93 lobes without biliary calculi) (p < 0.02). iloma and abscess were seen in six and five patients, respectively. Three (50%) of six patients with biloma and two (40%) of five patients with abscess were correctly diagnosed. Hilar and Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Sixteen patients had hilar and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. No patient had multiple hepatic masses. Hilar cholangiocarcinoma presented as an enhancing, focally thickened biliary duct in five (55%) patients, and as narrowing or obliteration of the bile duct in all JR:187, December
4 (100%) patients (Fig. 4). Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma presented as an enhancing, focally thickened biliary duct in six (85%) patients, and narrowing or obliteration of the ductal lumen in all (100%) patients. Segmental atrophy and narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein was seen in three and five patients, respectively. Intrahepatic biliary calculi were seen in four patients. Discussion Many investigators confirm an association between cholangiocarcinoma and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis is reported to be % of patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis C Fig. 2 Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis in 65-year-old-man who complained of abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis. He has history of recurrent attacks of cholangitis and Opisthorchis sinensis infestation., Contrast-enhanced CT scan obtained during hepatic artery phase shows severe atrophy in left lobe of liver., Contrast-enhanced CT scan obtained during portal venous phase also shows severe atrophy in left lobe of liver. Masslike lesion within atrophic left lobe (arrows) has thin enhancement at periphery on both arterial phase () and portal phase. C, CT scan obtained 8 mm below shows obliteration of left portal vein (arrowheads). Diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma was made at surgical resection. [5, 6, 8 21]. In our study, 6.1% of the cases of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis were associated with cholangiocarcinoma. Su et al. [6] report that cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis had a significantly worse survival rate than that of cholangiocarcinoma without recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. The 5-year survival rate was 42% in patients with cholangiocarcinoma without recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, which was significantly better than the 6% survival rate reported in those patients with cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. These differences in survival rates may be attributed to delayed diagnosis, previous liver damage caused by long-standing cholangitis, the relatively fewer curative resections in cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, and a lower diagnostic rate of radiologic studies. The diagnostic rate of radiologic studies is reported to range from 0 42% [6, 10 14]. Various reasons are postulated for the lower diagnostic rate, including limitations of the imaging studies such as difficulty differentiating cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis from abscess or biloma, or occurrence of an infiltrative tumor, usually in a stricture segment [6, 13]. ecause the radiologic findings for cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis are not well established, accurate preoperative diagnosis is usually difficult. In most patients, 1574 JR:187, December 2006
5 CT of Cholangiocarcinoma with Pyogenic Cholangitis the diagnosis is made during surgery. Consequently, identifying established CT findings of cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis is important to improve early diagnosis and proper treatment. Fig. 3 Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis in 56-year-old-woman who complained of abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, leukocytosis, and hyperbilirubinemia. She has a history of recurrent attacks of cholangitis., Initial contrast-enhanced CT scan performed at another institution shows large, peripheral, enhanced, hypoattenuated mass in right lobe (arrows). spiration confirmed mass as abscess. trophied left lobe shows enhancement with intrahepatic duct dilatation but no definite mass., Five-month follow-up contrast-enhanced CT scan shows complete resolution of hepatic abscess in right lobe and newly developed hypoattenuated mass (arrowheads) and slightly hyperattenuated area in left lobe. Note severe atrophy of lateral segment of left lobe and concomitant narrowing of left portal vein (arrow). Diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma was made at surgical resection. Fig. 4 Hilar cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis in 61-year-old-man who complained of abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, leukocytosis, and hyperbilirubinemia. He has history of recurrent attacks of cholangitis and Opisthorchis sinensis infestation., Contrast-enhanced CT scan of superior part of liver shows severe atrophy in lateral segment of left lobe of liver and obliteration of left portal vein (arrowheads)., CT scan 24 mm below shows narrowing and enhanced, focal, thickened wall of right main bile duct (arrows) with dilation of intrahepatic duct. Hilar cholangiocarcinoma was confirmed at percutaneous transhepatic choledochoscopy guided biopsy. In our study, cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis predominantly localizes in segments with atrophy and with narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein. Segmental atrophy was seen in 54% (44 of 82 patients), and narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein in 79% (65 of 82 patients). Segmental atrophy of the liver was predominantly located in the lateral segment of the left lobe (n = 21) and the posterior JR:187, December
6 segment of the right lobe (n = 11), where intrahepatic ductal calculi usually occurred. This may be related to the more acute angulation of these ducts, resulting in less efficient drainage on this side of the biliary system. ll atrophic segments showed narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein. The pathogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis is incompletely understood. Some investigators report that chronic proliferative cholangitis in the presence of biliary calculi can undergo progressive changes to atypical epithelial hyperplasia, which may progress to cholangiocarcinoma [5 9]. In our study, the coincident rate of peripheral cholangiocarcinoma in hepatic atrophy was 88% (36 of 41 cases), and that of peripheral cholangiocarcinoma in portal vein narrowing or obliteration was 83% (50 of 60 cases). Kubo et al. report [11] that portography might be useful for diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis. In their report, the portal vein in the hepatic lobe with cholangiocarcinoma could not be seen in any of the five patients with cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. Therefore, they insist that portal vein obstruction indicates deterioration of the hepatic tissue and strongly suggests the existence of cholangiocarcinoma. lthough we do not have a pathologic correlation, portal vein obliteration and subsequent parenchymal atrophy can be a result of involvement of the portal vein by the tumor instead of occurring before the development of the tumor. In any event, there is high frequency of coexistence of the two events cholangiocarcinoma and portal vein or parenchymal change and one should look for the tumor carefully in the hepatic segment or lobe with portal vein obliteration and parenchymal atrophy. In our study, intrahepatic biliary calculi were seen in 52% (43 of 82) of patients. Twenty-six (32%) patients had a mass within the same lobe. Su et al. [6] report that tumor and biliary calculi were closely related in 26 (96%) of 27 patients with cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. In previous reports, biliary calculi were present in approximately 75 80% of cases of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis; in the remaining cases, the biliary tree was recurrently infected in the absence of calculi [1 4]. Complications of hepatolithiasis include abscess and biloma. It is also often difficult to differentiate between these benign lesions and cholangiocarcinoma [11, 13]. Kubo et al. [11] report that 50% (five of 10) of their patients with cholangiocarcinoma associated with hepatolithiasis were initially diagnosed as having hepatolithiasis with liver abscess or cholangitis. These findings may lead to delayed diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma associated with hepatolithiasis. In our study, 50% (three of six) patients with biloma and 40% (two of five) patients with abscess were correctly diagnosed. ecause of the difficulty differentiating between these benign lesions and cholangiocarcinoma, further prospective study is required to establish the differences between these lesions. Our study has some limitations. First, the study was performed retrospectively without a control group. We did not evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of the observed CT findings to establish the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis. Second, surgical correlation of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis with cholangiocarcinoma was not available for all patients. prospective study with pathologic correlation is required to elucidate the pathogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma from recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. Third, we used thick collimation by using helical CT; if we had used thinner collimation by using MDCT, we would have increased the number of good results. Despite these limitations, our study suggests several unique CT findings of cholangiocarcinoma cholangitis. We analyzed the relationship of cholangiocarcinoma, hepatic atrophy, and portal vein obliteration. The interrelationship of hepatic atrophy, portal vein obliteration, and cholangiocarcinoma in patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, as evaluated by CT, is unknown. This significant correlation of cholangiocarcinoma, hepatic atrophy, and portal vein obliteration should be recognized because doing so improves the early diagnosis and proper treatment of patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. In conclusion, cholangiocarcinoma associated with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis is predominantly located in atrophic hepatic segments or lobes and is associated with narrowing or obliteration of the portal vein. In peripheral cholangiocarcinoma, it is almost always a markedly hypoattenuating mass with thin, lobulated contrast enhancement at the tumor periphery. Hilar and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma are most often accompanied by narrowing or obliteration of the bile duct with enhancing focal thickening. Correlation with clinical and laboratory findings is warranted because benign inflammatory processes can mimic malignancy. cknowledgments We thank onnie Hami, University Hospitals of Cleveland, Cleveland, Ohio, for her editorial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript and Jeong Kon Kim, san Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, for his assistance with statistical analysis. References 1. Carmona RH, Crass R, Lim RC Jr, Trunkey DD. Oriental cholangitis. m J Surg 1984; 148: Seel DJ, Park YK. Oriental infestational cholangitis. m J Surg 1983; 146: Chan FL, Man SW, Leong LL, Fan ST. Evaluation of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis with CT: analysis of 50 patients. Radiology 1989; 170: Lim JH. Oriental cholangiohepatitis: pathologic, clinical, and radiologic features. JR 1991; 157: Chijiiwa K, Ichimiya H, Kuroki S, Koga, Nakayama F. Late development of cholangiocarcinoma after the treatment of hepatolithiasis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1993; 177: Su CH, Shyr YM, Lui WY, P Eng FK. Hepatolithiasis associated with cholangiocarcinoma. r J Surg 1997; 84: Ohta T, Nagakawa T, Ueda N, et al. Mucosal dysplasia of the liver and the intraductal variant of peripheral cholangiocarcinoma in hepatolithiasis. Cancer 1991; 68: Koga, Ichimiya H, Yamaguchi K, Miyazaki K, Nakayama F. Hepatolithiasis associated with cholangiocarcinoma. Possible etiologic significance. Cancer 1985; 55: Nakanuma Y, Terada T, Tanaka Y, Ohta G. re hepatolithiasis and cholangiocarcinoma etiologically related? morphological study of 12 cases of hepatolithiasis associated with cholangiocarcinoma. Virchows rch Pathol nat Histopathol 1985; 406: Sanes S, MacCallum JD. Primary carcinoma of the liver: cholangiocarcinoma in hepatolithiasis. m J Pathol 1942; 18: Kubo S, Kinoshita H, Hirohashi K, Hamba H. Hepatolithiasis associated with cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg 1995; 19: Chen MF, Jan YY, Wang CS, et al. reappraisal of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with hepatolithiasis. Cancer 1993; 71: Chen MF, Jan YY, Wang CS, Jeng L, Hwang TL, Chen SC. Intrahepatic stones associated with cholangiocarcinoma. m J Gastroenterol 1989; 1576 JR:187, December 2006
7 CT of Cholangiocarcinoma with Pyogenic Cholangitis 84: Sheen-Chen SM, Chou FF, Eng HL. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in hepatolithiasis: a frequently overlooked disease. J Surg Oncol 1991; 37: Chen MF, Jan YY, Hwang TL, Jeng L, Yeh TS. Impact of concomitant hepatolithiasis on patients with peripheral cholangiocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 2000; 45: Chen PH, Lo HW, Wang CS, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma in hepatolithiasis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1984; 6: Lesurtel M, Regimbeau JM, Farges O, Colombat M, FOR YOUR INFORMTION Sauvanet, elghiti J. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatolithiasis: an unusual association in Western countries. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002; 14: Sato M, Watanabe Y, Ueda S, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with hepatolithiasis. Hepatogastroenterology 1998; 45: Kim YT, yun JS, Kim J, et al. Factors predicting concurrent cholangiocarcinomas associated with hepatolithiasis. Hepatogastroenterology 2003; 50: Lee CC, Wu CY, Chen GH. What is the impact of coexistence of hepatolithiasis on cholangiocarcinoma? J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002; 17: Chu KM, Lo CM, Liu CL, Fan ST. Malignancy associated with hepatolithiasis. Hepatogastroenterology 1997; 44: Radin DR, Ray MJ, Ralls PW, oswell WD Jr, Halls JM. Hepatolithiasis complicated by cholangiocarcinoma. J Comput Tomogr 1987; 11: Rao JNK, Scott J. simple method for the analysis of clustered binary data. iometrics 1992; 48: Zhou XH, Obuchowski N, McClish DK. Statistical methods in diagnostic medicine, 1st ed. New York, NY: Wiley, 2002: , The JR has made getting the articles you really want really easy with a new online tool, Really Simple Syndication, available at It s simple. Click the yellow RSS button located in the menu on the left of the page. You ll be on your way to syndicating your JR content in no time. JR:187, December
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Associated with Intrahepatic Duct Stones
 Original Article Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Associated with Intrahepatic Duct Stones Hoon Hur, Il-Young Park, Gi-Young Sung, Do-Sang Lee, Wook Kim and Jong-Man Won, Department of Surgery, Holy Family
Original Article Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Associated with Intrahepatic Duct Stones Hoon Hur, Il-Young Park, Gi-Young Sung, Do-Sang Lee, Wook Kim and Jong-Man Won, Department of Surgery, Holy Family
Hepatobiliary Imaging Original Research
 CT Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma Versus Periductal Fibrosis Hepatobiliary Imaging Original Research C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G CT Differentiation of Cholangiocarcinoma from Periductal
CT Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma Versus Periductal Fibrosis Hepatobiliary Imaging Original Research C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G CT Differentiation of Cholangiocarcinoma from Periductal
Cholangiocarcinoma: appearances and mimics
 Cholangiocarcinoma: appearances and mimics Poster No.: C-1572 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cardenas Valencia, J. Fernandez Jara, J. Cubero Carralero, B. Corral Ramos, P. Perez
Cholangiocarcinoma: appearances and mimics Poster No.: C-1572 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cardenas Valencia, J. Fernandez Jara, J. Cubero Carralero, B. Corral Ramos, P. Perez
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht
 Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct
 Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct Pages with reference to book, From 94 To 96 Tanveer ul Haq, Mohammed Younus Sheikh, Changes Khan Jadun, M.N. Ahmad, Yousuf H. Husen
Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct Pages with reference to book, From 94 To 96 Tanveer ul Haq, Mohammed Younus Sheikh, Changes Khan Jadun, M.N. Ahmad, Yousuf H. Husen
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1
 Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrabiliary Growth of Colorectal Liver Metastasis: Spectrum of Imaging Findings and Implications for Surgical Management
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Peungjesada et al. Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Silanath Peungjesada 1 Thomas. loia 2 Harmeet Kaur 1 Leonardo Marcal 1 Haesun Choi 1 Jean-Nicolas Vauthey
Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Peungjesada et al. Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Silanath Peungjesada 1 Thomas. loia 2 Harmeet Kaur 1 Leonardo Marcal 1 Haesun Choi 1 Jean-Nicolas Vauthey
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma
 Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
A Local Experience in the Management of Recurrent Pyogenic Cholangitis (Oriental Cholangitis)
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.1, March 2002 A Local Experience in the Management of Recurrent Pyogenic Cholangitis (Oriental Cholangitis) Suhair Khalifa Al-Saad, CABS, FRCSI* Mohammed Khurshid Alam,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.1, March 2002 A Local Experience in the Management of Recurrent Pyogenic Cholangitis (Oriental Cholangitis) Suhair Khalifa Al-Saad, CABS, FRCSI* Mohammed Khurshid Alam,
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Sparing of Fatty Infiltration Around Focal Hepatic Lesions in Patients with Hepatic Steatosis: Sonographic Appearance with CT and MRI Correlation
 Hepatobiliary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kim et al. Sonography of Hepatic Steatosis Hepatobiliary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kyoung Won Kim 1 Min Ju Kim 2 Seung Soo Lee 1 Hyoung Jung Kim 3 Yong Moon Shin 1 Pyo-Nyun
Hepatobiliary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kim et al. Sonography of Hepatic Steatosis Hepatobiliary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kyoung Won Kim 1 Min Ju Kim 2 Seung Soo Lee 1 Hyoung Jung Kim 3 Yong Moon Shin 1 Pyo-Nyun
CT Differentiation of Mucin- Producing Cystic Neoplasms of the Liver From Solitary Bile Duct Cysts
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Kim et al. CT of Hepatic Cystic Neoplasms and Cysts Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Hyoung Jung Kim 1 Eun Sil Yu 2 Jae Ho Byun 1 Seung-Mo Hong 2 Kyoung
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Kim et al. CT of Hepatic Cystic Neoplasms and Cysts Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Hyoung Jung Kim 1 Eun Sil Yu 2 Jae Ho Byun 1 Seung-Mo Hong 2 Kyoung
pitfall Table 1 4 disorientation pitfall pitfall Table 1 Tel:
 11 687 692 2002 pitfall 1078 29 17 9 1 2 3 dislocation outflow block 11 1 2 3 9 1 2 3 4 disorientation pitfall 11 687 692 2002 Tel: 075-751-3606 606-8507 54 2001 8 27 2002 10 31 29 4 pitfall 16 1078 Table
11 687 692 2002 pitfall 1078 29 17 9 1 2 3 dislocation outflow block 11 1 2 3 9 1 2 3 4 disorientation pitfall 11 687 692 2002 Tel: 075-751-3606 606-8507 54 2001 8 27 2002 10 31 29 4 pitfall 16 1078 Table
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Original article: new surgical approaches to the Klatskin tumour
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Original article: new surgical approaches to the Klatskin tumour T. M. VAN GULIK*, S. DINANT*, O. R. C. BUSCH*, E. A. J. RAUWS, H. OBERTOP* & D. J. GOUMA Departments
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Original article: new surgical approaches to the Klatskin tumour T. M. VAN GULIK*, S. DINANT*, O. R. C. BUSCH*, E. A. J. RAUWS, H. OBERTOP* & D. J. GOUMA Departments
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: CT Findings in Patients with Hepatic Lobar or Segmental Involvement
 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: CT Findings in Patients with Hepatic Lobar or Segmental Involvement Jae Hoon Lim, MD 1 Won Jae Lee, MD 1 Dong Ho Lee, MD 2 Kyung Jin Nam, MD 3 Index words: Liver, CT Liver,
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: CT Findings in Patients with Hepatic Lobar or Segmental Involvement Jae Hoon Lim, MD 1 Won Jae Lee, MD 1 Dong Ho Lee, MD 2 Kyung Jin Nam, MD 3 Index words: Liver, CT Liver,
Laparoscopic left hepatectomy in patients with intrahepatic duct stones and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 212;16:15-19 Original Article Laparoscopic left hepatectomy in patients with intrahepatic duct stones and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis Sunjong Han, Insang Song, and
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 212;16:15-19 Original Article Laparoscopic left hepatectomy in patients with intrahepatic duct stones and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis Sunjong Han, Insang Song, and
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Ibukuro et al. Hepatic rtery natomy of the Left Hemiliver Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Kenji Ibukuro 1 Takaya Takeguchi
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Ibukuro et al. Hepatic rtery natomy of the Left Hemiliver Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Kenji Ibukuro 1 Takaya Takeguchi
Focal Eosinophilic Necrosis of the Liver in Patients with Underlying Gastric or Colorectal Cancer: CT Differentiation from Metastasis
 Focal Eosinophilic Necrosis of the Liver in Patients with Underlying Gastric or Colorectal Cancer: CT Differentiation from Metastasis Hyun-Jung Jang, MD 1,2 Won Jae Lee, MD 1 Soon Jin Lee, MD 1 Seung Hoon
Focal Eosinophilic Necrosis of the Liver in Patients with Underlying Gastric or Colorectal Cancer: CT Differentiation from Metastasis Hyun-Jung Jang, MD 1,2 Won Jae Lee, MD 1 Soon Jin Lee, MD 1 Seung Hoon
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst
 Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Intraductal papillary neoplasms in the bile ducts
 Intraductal papillary neoplasms in the bile ducts Seok Hwa Youn Myunghee Yoon Dong Hoon Shin Kosin University Gospel Hospital Department of general surgery Hepato-biliary-pancreatic division Introduction
Intraductal papillary neoplasms in the bile ducts Seok Hwa Youn Myunghee Yoon Dong Hoon Shin Kosin University Gospel Hospital Department of general surgery Hepato-biliary-pancreatic division Introduction
OCCULT COLON CANCER IN A PATIENT WITH DIABETES AND RECURRENT KLEBSIELLA
 OCCULT COLON CANCER IN A PATIENT WITH DIABETES AND RECURRENT KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE LIVER ABSCESS Wen-Hung Hsu, 1 Fang-Jung Yu, 1 Chien-Han Chuang, 2 Chin-Fan Chen, 3 Chien-Ting Lee, 4 and Chien-Yu Lu 1,5
OCCULT COLON CANCER IN A PATIENT WITH DIABETES AND RECURRENT KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE LIVER ABSCESS Wen-Hung Hsu, 1 Fang-Jung Yu, 1 Chien-Han Chuang, 2 Chin-Fan Chen, 3 Chien-Ting Lee, 4 and Chien-Yu Lu 1,5
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment
 State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Intramural Hypoattenuated Nodules in Thickened Wall of the Gallbladder: CT Features According to Their Primary Causes 1
 Intramural Hypoattenuated Nodules in Thickened Wall of the Gallbladder: CT Features ccording to Their Primary Causes 1 Jun Hyung Lee, M.D., Hyun Kwon Ha, M.D., Jeong Hyun Lee, M.D., Jean Hwa Lee, M.D.,
Intramural Hypoattenuated Nodules in Thickened Wall of the Gallbladder: CT Features ccording to Their Primary Causes 1 Jun Hyung Lee, M.D., Hyun Kwon Ha, M.D., Jeong Hyun Lee, M.D., Jean Hwa Lee, M.D.,
Imaging diagnosis of clonorchiasis
 Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 45, No. 2: 77-85, June 2007 Mini-Review Imaging diagnosis of clonorchiasis Dongil CHOI 1) and Sung-Tae HONG 2) * 1) Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan
Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 45, No. 2: 77-85, June 2007 Mini-Review Imaging diagnosis of clonorchiasis Dongil CHOI 1) and Sung-Tae HONG 2) * 1) Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Bronchobiliary fistula treated with histoacryl embolization under bronchoscopic guidance: A case report
 Respiratory Medicine CME (2008) 1, 164 168 respiratory MEDICINE CME CASE REPORT Bronchobiliary fistula treated with histoacryl embolization under bronchoscopic guidance: A case report Jung Hyun Kim a,
Respiratory Medicine CME (2008) 1, 164 168 respiratory MEDICINE CME CASE REPORT Bronchobiliary fistula treated with histoacryl embolization under bronchoscopic guidance: A case report Jung Hyun Kim a,
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Multiple Primary Quiz
 Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Spectrum of Cholangiocarcinoma
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2013; 1(6):695-699 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2013; 1(6):695-699 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
RECURRENT PYOGENIC CHOLANGITIS
 RECURRENT PYOGENIC CHOLANGITIS Resident(s): Evan Raff, MD MHA Attending(s): Narasimham Dasika, MD Program/Dept(s): University of Michigan Health System, Department of Radiology CHIEF COMPLAINT & HPI Chief
RECURRENT PYOGENIC CHOLANGITIS Resident(s): Evan Raff, MD MHA Attending(s): Narasimham Dasika, MD Program/Dept(s): University of Michigan Health System, Department of Radiology CHIEF COMPLAINT & HPI Chief
Case Report pissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2012;67(4): INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 Focal Fat Deposition Developed in the Segment IV of the Liver Following Gastrectomy Mimicking a Hepatic Metastasis: Two Case Reports 1 위절제술후에간의제 4 분절에서발생한간전이를닮은국소지방침윤 : 두증례보고
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 Focal Fat Deposition Developed in the Segment IV of the Liver Following Gastrectomy Mimicking a Hepatic Metastasis: Two Case Reports 1 위절제술후에간의제 4 분절에서발생한간전이를닮은국소지방침윤 : 두증례보고
Trans-abdominal ultrasound features of the newly named intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct
 Original Article on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Trans-abdominal ultrasound features of the newly named intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct Xian-Shui Fu 1 *, Meng-Na He 2 *,
Original Article on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Trans-abdominal ultrasound features of the newly named intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct Xian-Shui Fu 1 *, Meng-Na He 2 *,
Personal Profile. Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history. Hepatitis B carrier
 Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Index terms: Liver, CT Liver neoplasm, CT. Korean J Radiol 2005;6: Received February 21, 2005; accepted after revision May 24, 2005.
 Depiction of Viable Tumor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization: Multiphasic Helical CT with Review of the Previous Serial CT Images Kyung Mi Jang, MD 1 Dongil Choi,
Depiction of Viable Tumor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization: Multiphasic Helical CT with Review of the Previous Serial CT Images Kyung Mi Jang, MD 1 Dongil Choi,
Gastrointestinal Metastasis From Primary Lung Cancer: CT Findings and Clinicopathologic Features
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Kim et al. Gastrointestinal Metastasis of Lung Cancer Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations So Yeon Kim 1,2 Hyun Kwon Ha 1 Sung Won Park 1 Jun Kang
Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Kim et al. Gastrointestinal Metastasis of Lung Cancer Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations So Yeon Kim 1,2 Hyun Kwon Ha 1 Sung Won Park 1 Jun Kang
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA
 MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
Abdominal Imaging. Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings
 Abdom Imaging 27:47 50 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00261-001-0048-1 Abdominal Imaging Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2002 Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings K. Konno, 1 H. Ishida, 1 M. Sato, 1 H.
Abdom Imaging 27:47 50 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00261-001-0048-1 Abdominal Imaging Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2002 Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings K. Konno, 1 H. Ishida, 1 M. Sato, 1 H.
Incidence of underlying biliary neoplasm in patients after major hepatectomy for preoperative benign hepatolithiasis
 Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2016;20:173-179 https://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2016.20.4.173 Original Article Incidence of underlying biliary neoplasm in patients after major hepatectomy for preoperative
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2016;20:173-179 https://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2016.20.4.173 Original Article Incidence of underlying biliary neoplasm in patients after major hepatectomy for preoperative
Current Treatment Strategies for Hilar and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
 Current Treatment Strategies for Hilar and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Jean-Nicolas Vauthey, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery Chief Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Section Department of Surgical Oncology Crescent
Current Treatment Strategies for Hilar and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Jean-Nicolas Vauthey, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery Chief Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Section Department of Surgical Oncology Crescent
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
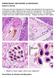 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
Common and unusual CT and MRI manifestations of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a pictorial review
 Review Article Common and unusual CT and MRI manifestations of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a pictorial review Min-Jie Yang, Su Li, Yong-Guang Liu, Na Jiao, Jing-Shan Gong Department of Radiology, Shenzhen
Review Article Common and unusual CT and MRI manifestations of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a pictorial review Min-Jie Yang, Su Li, Yong-Guang Liu, Na Jiao, Jing-Shan Gong Department of Radiology, Shenzhen
Current status of hepatic surgery in Korea
 Korean J Hepatol. 2009 Dec; 15(Suppl 6):S60 - S64. DOI: 10.3350/kjhep.2009.15.S6.S60 Current status of hepatic surgery in Korea Kyung Sik Kim Department of Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University
Korean J Hepatol. 2009 Dec; 15(Suppl 6):S60 - S64. DOI: 10.3350/kjhep.2009.15.S6.S60 Current status of hepatic surgery in Korea Kyung Sik Kim Department of Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University
Biliary Papillomatosis: case report
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 407-412 407 Biliary Papillomatosis: case report CHUN-LIN HUANG WEN-PIN CHEN YU-BUN NG JOSEPH HANG LEUNG Department of Medical Imaging, Chiayi Christian Hospital Biliary papillomatosis
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 407-412 407 Biliary Papillomatosis: case report CHUN-LIN HUANG WEN-PIN CHEN YU-BUN NG JOSEPH HANG LEUNG Department of Medical Imaging, Chiayi Christian Hospital Biliary papillomatosis
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options
 Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
Fig. 1. Ileal and jejunal metastases from adenocarcinoma of the lung in 62-year-old male with a clinical history of bloody stool. A.
 507 A B Fig. 1. Ileal and jejunal metastases from adenocarcinoma of the lung in 62-year-old male with a clinical history of bloody stool. A. An intraluminal polypoid mass (arrow) is seen in the dilated
507 A B Fig. 1. Ileal and jejunal metastases from adenocarcinoma of the lung in 62-year-old male with a clinical history of bloody stool. A. An intraluminal polypoid mass (arrow) is seen in the dilated
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) Detected by Sonography
 661245JDMXXX10.1177/8756479316661245Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyHamer research-article2016 Case Study Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) Detected by Sonography Journal of Diagnostic Medical
661245JDMXXX10.1177/8756479316661245Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyHamer research-article2016 Case Study Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) Detected by Sonography Journal of Diagnostic Medical
Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center.
 Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in 2011 Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center Introduction Biliary emergencies are: Common Come in many flavors Deceiving: frequent
Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in 2011 Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center Introduction Biliary emergencies are: Common Come in many flavors Deceiving: frequent
An Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct at the Duodenal Papilla
 Published online: July 2, 2014 1662 6575/14/0072 0417$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: July 2, 2014 1662 6575/14/0072 0417$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice
 Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
KAHBPS-O-PL-01 KAHBPS-O-PL-02
 KAHBPS-O-PL-01 Proposal of future remnant liver-indocyanine green clearance rate for risk assessment of major hepatectomy - What is its cutoff? Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of
KAHBPS-O-PL-01 Proposal of future remnant liver-indocyanine green clearance rate for risk assessment of major hepatectomy - What is its cutoff? Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Contemporary Imaging of Biliary Malignancy and Preoperative Evaluation
 Contemporary Imaging of Biliary Malignancy and Preoperative Evaluation Linda Pantongrag-Brown, MD Advanced Diagnostic Imaging, Ramathibodi Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Malignancy of biliary tract Cholangiocarcinoma
Contemporary Imaging of Biliary Malignancy and Preoperative Evaluation Linda Pantongrag-Brown, MD Advanced Diagnostic Imaging, Ramathibodi Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Malignancy of biliary tract Cholangiocarcinoma
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
R.Sotoudehmanesh, MD Professor of Gastroenterology Digestive Disease Research Institute Tehran University of Medical Sciences Pancreatobiliary
 R.Sotoudehmanesh, MD Professor of Gastroenterology Digestive Disease Research Institute Tehran University of Medical Sciences Pancreatobiliary /Advanced Endoscopy group Most common biliary malignancy and
R.Sotoudehmanesh, MD Professor of Gastroenterology Digestive Disease Research Institute Tehran University of Medical Sciences Pancreatobiliary /Advanced Endoscopy group Most common biliary malignancy and
Pictorial Essay. Multidetector CT of the Pancreas and Bile Duct System: Value of Curved Planar Reformations
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.229 on 02/03/18 from IP address 46.3.207.229. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved n important feature distinguishing multidetector CT
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.229 on 02/03/18 from IP address 46.3.207.229. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved n important feature distinguishing multidetector CT
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA ASSOCIATED WITH LIVER ABSCESS
 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA ASSOCIATED WITH LIVER ABSCESS Ching-I Huang, 1 Liang-Yen Wang, 1,4 Ming-Lun Yeh, 1 Ming-Yen Hsieh, 1,3 Jee-Fu Huang, 2,3 Zu-Yau Lin, 1,4 and Wan-Long Chuang 1,4 1 Division of Hepatobiliary
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA ASSOCIATED WITH LIVER ABSCESS Ching-I Huang, 1 Liang-Yen Wang, 1,4 Ming-Lun Yeh, 1 Ming-Yen Hsieh, 1,3 Jee-Fu Huang, 2,3 Zu-Yau Lin, 1,4 and Wan-Long Chuang 1,4 1 Division of Hepatobiliary
With recent advances in diagnostic imaging technologies,
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Management of Ground-Glass Opacity Lesions Detected in Patients with Otherwise Operable Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Hong Kwan Kim, MD,* Yong Soo Choi, MD,* Kwhanmien Kim, MD,* Young Mog
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Management of Ground-Glass Opacity Lesions Detected in Patients with Otherwise Operable Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Hong Kwan Kim, MD,* Yong Soo Choi, MD,* Kwhanmien Kim, MD,* Young Mog
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma or HCC) Overview
 Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma or HCC) Overview Recent advances in liver cancer care seek to address the rising incidence of liver cancer, which has steadily increased over the past three decades.
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma or HCC) Overview Recent advances in liver cancer care seek to address the rising incidence of liver cancer, which has steadily increased over the past three decades.
Endoscopic stenting in bile duct cancer increases liver volume
 Endoscopic stenting in bile duct cancer increases liver volume Chang Hun Lee 1,3, Seung Young Seo 1,3, Seong Hun Kim 1,3, In Hee Kim 1,3, Sang Wook Kim 1,3, Soo Teik Lee 1,3, Dae Ghon Kim 1,3, Jae Do Yang
Endoscopic stenting in bile duct cancer increases liver volume Chang Hun Lee 1,3, Seung Young Seo 1,3, Seong Hun Kim 1,3, In Hee Kim 1,3, Sang Wook Kim 1,3, Soo Teik Lee 1,3, Dae Ghon Kim 1,3, Jae Do Yang
General summary GENERAL SUMMARY
 General summary GENERAL SUMMARY In Chapter 2.1 the long-term results and prognostic factors of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for unresectable colorectal liver metastases (CRLM) in a single center with
General summary GENERAL SUMMARY In Chapter 2.1 the long-term results and prognostic factors of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for unresectable colorectal liver metastases (CRLM) in a single center with
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Proximal Bile Duct Cancer: Contemporary Management. William R. Jarnagin, MD, FACS
 Proximal Bile Duct Cancer: Contemporary Management William R. Jarnagin, MD, FACS Biliary Tract Adenocarcinoma Spectrum of disease Intrahepatic (IHC) Hilar EH Gallbladder GB CBD Distal D PD Biliary Tract
Proximal Bile Duct Cancer: Contemporary Management William R. Jarnagin, MD, FACS Biliary Tract Adenocarcinoma Spectrum of disease Intrahepatic (IHC) Hilar EH Gallbladder GB CBD Distal D PD Biliary Tract
ACUTE CHOLANGITIS AS a result of an occluded
 Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract
 HPB, 2008; 10: 7276 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract DENIS CASTAING Centre hépato-biliaire, Hôpital Paul Brousse, Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Paris XI, Paris,
HPB, 2008; 10: 7276 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract DENIS CASTAING Centre hépato-biliaire, Hôpital Paul Brousse, Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Paris XI, Paris,
The Frequency and Significance of Small (15 mm) Hepatic Lesions Detected by CT
 535 Elizabeth C. Jones1 Judith L. Chezmar Rendon C. Nelson Michael E. Bernardino Received July 22, 1991 ; accepted after revision October 16, 1991. Presented atthe annual meeting ofthe American Aoentgen
535 Elizabeth C. Jones1 Judith L. Chezmar Rendon C. Nelson Michael E. Bernardino Received July 22, 1991 ; accepted after revision October 16, 1991. Presented atthe annual meeting ofthe American Aoentgen
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Review. Computed tomography in the diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma and pancreatic carcinoma
 Annals of Oncology 10 Suppl. 4: S12-S17, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Review Computed tomography in the diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma and pancreatic
Annals of Oncology 10 Suppl. 4: S12-S17, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Review Computed tomography in the diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma and pancreatic
Gum O Jung and Dong Eun Park. Department of Surgery, Wonkwang University Hospital, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2012;16:110-114 Case Report Successful percutaneous management of bronchobiliary fistula after radiofrequency ablation of metastatic cholangiocarcinoma in a patient
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2012;16:110-114 Case Report Successful percutaneous management of bronchobiliary fistula after radiofrequency ablation of metastatic cholangiocarcinoma in a patient
Malignant Focal Liver Lesions
 Malignant Focal Liver Lesions Other Than HCC Pablo R. Ros, MD, MPH, PhD Departments of Radiology and Pathology University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Case Western Reserve University Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org
Malignant Focal Liver Lesions Other Than HCC Pablo R. Ros, MD, MPH, PhD Departments of Radiology and Pathology University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Case Western Reserve University Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org
Interventional Radiology in Liver Cancer. Nakarin Inmutto MD
 Interventional Radiology in Liver Cancer Nakarin Inmutto MD Liver cancer Primary liver cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Cholangiocarcinoma Metastasis Interventional Radiologist Diagnosis Imaging US / CT
Interventional Radiology in Liver Cancer Nakarin Inmutto MD Liver cancer Primary liver cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Cholangiocarcinoma Metastasis Interventional Radiologist Diagnosis Imaging US / CT
Hepatobiliary Malignancies Retrospective Study at Truman Medical Center
 Hepatobiliary Malignancies 206-207 Retrospective Study at Truman Medical Center Brandon Weckbaugh MD, Prarthana Patel & Sheshadri Madhusudhana MD Introduction: Hepatobiliary malignancies are cancers which
Hepatobiliary Malignancies 206-207 Retrospective Study at Truman Medical Center Brandon Weckbaugh MD, Prarthana Patel & Sheshadri Madhusudhana MD Introduction: Hepatobiliary malignancies are cancers which
Lobar and segmental liver atrophy associated with hilar cholangiocarcinoma and the impact of hilar biliary anatomical variants: a pictorial essay
 Insights Imaging (2011) 2:525 531 DOI 10.1007/s13244-011-0100-9 PICTORIAL REVIEW Lobar and segmental liver atrophy associated with hilar cholangiocarcinoma and the impact of hilar biliary anatomical variants:
Insights Imaging (2011) 2:525 531 DOI 10.1007/s13244-011-0100-9 PICTORIAL REVIEW Lobar and segmental liver atrophy associated with hilar cholangiocarcinoma and the impact of hilar biliary anatomical variants:
BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II
 CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Detection of Small Pancreatic Tumors with Multiphasic Helical CT
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.203.121 on 11/24/17 from IP address 37.44.203.121. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Yulia Lisenko ronstein 1 Evelyne M. Loyer 2 Harmeet
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.203.121 on 11/24/17 from IP address 37.44.203.121. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Yulia Lisenko ronstein 1 Evelyne M. Loyer 2 Harmeet
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Is Hepatic Resection Needed in the Patients with Peritoneal Side T2 Gallbladder Cancer?
 Is Hepatic Resection Needed in the Patients with Peritoneal Side T2 Gallbladder Cancer? Lee H, Park JY, Youn S, Kwon W, Heo JS, Choi SH, Choi DW Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan
Is Hepatic Resection Needed in the Patients with Peritoneal Side T2 Gallbladder Cancer? Lee H, Park JY, Youn S, Kwon W, Heo JS, Choi SH, Choi DW Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan
Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumors of the Pancreas: MR Cholangiopancreatography
 Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumors of the Pancreas: MR Cholangiopancreatography and MR Angiography Byung Se Choi, MD 1 Tae Kyoung Kim, MD 1 Ah Young Kim,
Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumors of the Pancreas: MR Cholangiopancreatography and MR Angiography Byung Se Choi, MD 1 Tae Kyoung Kim, MD 1 Ah Young Kim,
Original Research. Jung Hoon Kim, MD, Tae Kyoung Kim, MD,* Hyo Won Eun, MD, Bong Soo Kim, MD, Moon-Gyu Lee, MD, Pyo Nyun Kim, MD, and Hyun Kwon Ha, MD
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:676 684 (2002) Original Research Preoperative Evaluation of Gallbladder Carcinoma: Efficacy of Combined Use of MR Imaging, MR Cholangiography, and Contrast-Enhanced
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:676 684 (2002) Original Research Preoperative Evaluation of Gallbladder Carcinoma: Efficacy of Combined Use of MR Imaging, MR Cholangiography, and Contrast-Enhanced
Virtual Cystoscopy of the Contrast Material Filled Bladder in Patients with Gross Hematuria
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.49 on 11/20/17 from IP address 46.3.195.49. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Jeong Kon Kim 1 Jae Hong hn 1 Taehan Park 2 Han Jong
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.49 on 11/20/17 from IP address 46.3.195.49. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Jeong Kon Kim 1 Jae Hong hn 1 Taehan Park 2 Han Jong
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Morphological Classification of Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct with Survival Correlation
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.207 RESEARCH ARTICLE Morphological Classification of Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct with Survival Correlation Vor Luvira 1 *, Kulyada Somsap 2, Ake Pugkhem
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.207 RESEARCH ARTICLE Morphological Classification of Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct with Survival Correlation Vor Luvira 1 *, Kulyada Somsap 2, Ake Pugkhem
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury
 The Liver Week 2014, Jeju, Korea Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Soon Chun Hyang University School of Medicine Bucheon/Seoul, KOREA
The Liver Week 2014, Jeju, Korea Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Soon Chun Hyang University School of Medicine Bucheon/Seoul, KOREA
Percutaneous Transhepatic Stent Placement in the Management of Portal Venous Stenosis After Curative Surgery for Pancreatic and Biliary Neoplasms
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Kim et al. Transhepatic Stent Placement for Postsurgical Stenosis Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Kyung Rae Kim 1 Gi-Young
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Kim et al. Transhepatic Stent Placement for Postsurgical Stenosis Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Kyung Rae Kim 1 Gi-Young
Differentiation of Subtypes of Renal Cell Carcinoma on Helical CT Scans
 Jeong Kon Kim 1 Tae Kyoung Kim 1 Han Jong hn 2 hung Soo Kim 2 Kyu-Rae Kim 3 Kyoung-Sik ho 1 Received September 21, 2001; accepted after revision December 28, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, san Medical
Jeong Kon Kim 1 Tae Kyoung Kim 1 Han Jong hn 2 hung Soo Kim 2 Kyu-Rae Kim 3 Kyoung-Sik ho 1 Received September 21, 2001; accepted after revision December 28, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, san Medical
- Increased incidence? - Poor prognosis?
 Imaging of Cholangiocarcinoma Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of medical sciences Definitions Tumors that arise from the bile duct epithelium. Accounts 10-20%
Imaging of Cholangiocarcinoma Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of medical sciences Definitions Tumors that arise from the bile duct epithelium. Accounts 10-20%
Case Reports. Intraductal Papillary Cholangiocarcinoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Reports Kongkam K, Rerknimitr R 45 Case Report and Review of the Literature Pradermchai Kongkam, M.D. Rungsun Rerknimitr, M.D. ABSTRACT A case of papillary cholangiocarcinoma is presented. A 64-year-old
Case Reports Kongkam K, Rerknimitr R 45 Case Report and Review of the Literature Pradermchai Kongkam, M.D. Rungsun Rerknimitr, M.D. ABSTRACT A case of papillary cholangiocarcinoma is presented. A 64-year-old
The nontraumatic acute abdomen
 CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures. Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center
 Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Malignant Biliary Strictures Etiologies: Pancreatic
Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Malignant Biliary Strictures Etiologies: Pancreatic
Biliary Anatomy in Living-related Liver Transplantation
 The 5th IHPBA Congress - Istanbul Biliary Anatomy in Living-related Liver Transplantation biliary trees hilar plate Assessment for Vascular Anatomy 1. 3DCT portal vein hepatic vein hepatic artery 2. No
The 5th IHPBA Congress - Istanbul Biliary Anatomy in Living-related Liver Transplantation biliary trees hilar plate Assessment for Vascular Anatomy 1. 3DCT portal vein hepatic vein hepatic artery 2. No
Min Jung Park, MD, PhD 2 Young Kon Kim, MD, PhD Sanghyeok Lim, MD Hyunchul Rhim, MD, PhD Won Jae Lee, MD, PhD. Purpose: Materials and Methods:
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
