For more information about how to cite these materials visit
|
|
|
- Rosamund Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Author: A. Kent Christensen, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit Any medical information in this material is intended to inform and educate and is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a replacement for medical evaluation, advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional. Please speak to your physician if you have questions about your medical condition. Viewer discretion is advised: Some medical content is graphic and may not be suitable for all viewers.
2 Citation Key for more information see: Use + Share + Adapt { Content the copyright holder, author, or law permits you to use, share and adapt. } Public Domain Government: Works that are produced by the U.S. Government. (17 USC 105) Public Domain Expired: Works that are no longer protected due to an expired copyright term. Public Domain Self Dedicated: Works that a copyright holder has dedicated to the public domain. Creative Commons Zero Waiver Creative Commons Attribution License Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike License GNU Free Documentation License Make Your Own Assessment { Content Open.Michigan believes can be used, shared, and adapted because it is ineligible for copyright. } Public Domain Ineligible: Works that are ineligible for copyright protection in the U.S. (17 USC 102(b)) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ { Content Open.Michigan has used under a Fair Use determination. } Fair Use: Use of works that is determined to be Fair consistent with the U.S. Copyright Act. (17 USC 107) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ Our determination DOES NOT mean that all uses of this 3rd-party content are Fair Uses and we DO NOT guarantee that your use of the content is Fair. To use this content you should do your own independent analysis to determine whether or not your use will be Fair.
3 Histology of the Endocrine System M1 - Endocrine/Reproduction Sequence A. Kent Christensen Department of Cell and Developmental Biology University of Michigan Medical School Winter, 2009
4 (receptors) Hormone delivery Synapse (Neurosecretion) O'Riordan et al., 2nd ed, page 5
5 Endocrine system Pituitary (hypophysis) Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary Adrenal gland (suprarenal) Adrenal cortex Adrenal medulla Thyroid gland Follicles Parafollicular cells Parathyroid gland Considered in other lectures: Endocrine pancreas Male Female Enteroendocrine
6 PITUITARY
7 US Federal Government Location of pituitary
8 Pituitary development Ross and Pawlina. Histology: Text and Atlas, 5th ed, 2006, fig 21.4, pg 690
9 Pituitary nomenclature Pituitary nomenclature Gray s Anatomy, wikimedia commons Please also see Ross and Pawlina. Histology: Text and Atlas, 5th ed, 2006, fig 21.3b, pg 689
10 LM staining Cells and hormones of the anterior pituitary Cell type Hormone Releasing (+) or Acidophil Somatotrope Acidophil Mammotrope = lactotrope Growth hormone (GH) = somatotropin Basophil Thyrotrope Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Basophil Basophil (human) A.K. Christensen inhibiting (-) horm. GHRH (+) Somatostatin (-) Prolactin (PRL) [Dopamine (-) = thyrotropin Gonadotrope Luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH); both = gonadotropin Corticotrope Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) = corticotropin estrogen (+)] TRH (+) GnRH (+) CRH (+)
11 Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 515 Pituitary, low power LM
12 Anterior pituitary, LM drawing Image of cords of cells in anterior pituitary removed. Original here: Bailey's textbook of histology. 72(700)6
13 Anterior pituitary, LM, trichrome stain Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/B/4
14 Anterior pituitary, LM, H&E stain Basophil Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH-9B3
15 Immunocytochemical localization of growth hormone, LM A.K. Christensen
16 Immunocytochemical localization of luteinizing hormone in gonadotropes, fluorescence Nucleus LH granules Nucleus A.K. Christensen
17 Anterior pituitary, EM Larry Kahn
18 Pathway of hormone secretion Fawcett. Histology, ed 11, p 486
19 Cytoplasm of prolactin-secreting cell (lactotrope), EM Golgi Secretory granule Rough ER Marilyn Farquhar in Memoirs of the Society for Endocrinology
20 Golgi and secretory granules, EM Mitochondrion Nucleus Golgi Granule Marilyn Farquhar in Memoirs of the Society for Endocrinology
21 Exocytosis of prolactin granules, EM Marilyn Farquhar in Memoirs of the Society for Endocrinology
22 LM staining Cells and hormones of the anterior pituitary Cell type Hormone Releasing (+) or Acidophil Somatotrope Acidophil Mammotrope = lactotrope Growth hormone (GH) = somatotropin Basophil Thyrotrope Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Basophil Basophil (human) A.K. Christensen inhibiting (-) horm. GHRH (+) Somatostatin (-) Prolactin (PRL) [Dopamine (-) = thyrotropin Gonadotrope Luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH); both = gonadotropin Corticotrope Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) = corticotropin estrogen (+)] TRH (+) GnRH (+) CRH (+)
23 Hedges, 1987 Regulation of the anterior pituitary
24 Regulation of anterior pituitary, detail O'Riordan et al 1988, p 47
25 SEM of pituitary: portal veins, capillaries, corrosion vascular cast Murakami T, 1975, Archivum Histologicum Japanicum 38:
26 Posterior pituitary Hormones Antidiuretic hormone (ADH = arginine vasopressin) Oxytocin Neurosecretion Hormones synthesized as part of larger proteins (neurophysins) in neuron cell bodies of hypothalamus. Transported in axons to pars nervosa (hormone cleaved from neurophysin). Hormone secreted from axon terminals into capillaries. Pituicytes Specialized glia of pars nervosa.
27 Posterior pituitary, diagram O'Riordan et al 1988, p 47
28 Posterior pituitary, LM Axon cross sections? A.K. Christensen
29 Endings Capillary Nerve endings for hormone release, posterior pituitary Pituicyte Weiss Histology, ed 5
30 Pars intermedia, between anterior and posterior pituitary, human, LM. Anterior Posterior Poorly developed and of doubtful function in humans. Intermedia Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 516
31 Pars intermedia, rat pituitary, LM Rathke's pouch A.K. Christensen
32 ADRENAL GLAND
33 Source Undetermined Adrenal (suprarenal) gland
34 Location of the adrenal (suprarenal) gland, human US Federal Government
35 Bailey s Histology Human adrenal, low power LM
36 Adrenal cortex Zona glomerulosa Main hormone: Aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid). General function: Maintain blood electrolyte balance. Main control: Angiotensin II. Zona fasciculata Main hormone: Cortisol (a glucocorticoid). General function: Includes regulating glucose and fatty acid metabolism, and response to stress. Main control: Pituitary ACTH. Zona reticularis Hormones: Some cortisol and androgens. Function and control: Similar to zona fasciculata.
37 Hadley Kirkman slide collection, slide K285 Adrenal cortex, human, LM
38 Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 547 Adrenal cortex, human, H&E, LM
39 Adrenal blood vessels Image of adrenal gland vasculature removed. Original here: Junqueira and Carneiro, 10th ed., 2003, page 414, fig 21-2.
40 Adrenal blood vessels, corrosion vascular cast, SEM Virginia Black chapter, in Weiss Histology, 6th ed
41 Zona glomerulosa (source of aldosterone), LM Fasciculata Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 548
42 Zona fasciculata (source of cortisol), LM Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 549
43 Zona fasciculata, EM SER Endothelium Capillary lumen Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/F/4
44 Smooth ER in the cytoplasm of a zona fasciculata cell, EM Long and Jones 1967
45 Zona reticularis, LM Medulla Zona fasciculata Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 550
46 Hormones Adrenal medulla Epinephrine (adrenalin) and norepinephrine (noradrenalin), both catecholamines. Two cell types, one for E and one for N. General function: Acute response to stress. Main control: Preganglionic sympathetic innervation. Embryonic source From neural crest cells, same as postganglionic sympathetic neurons. Although adrenal medulla cells do not have dendrites or axons, they behave like postganglionic sympathetic neurons, releasing norepinephrine/epinephrine in response to preganglionic sympathetic stimulation. Also called "chromaffin cells" Cells of the adrenal medulla are examples of "chromaffin cells," containing catecholamine granules that stain brown with potassium dichromate. Neurons of sympathetic ganglia are also chromaffin cells. The term is used in pathology.
47 Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 565 Adrenal medulla, LM
48 EM of adrenal medulla: norepinephrine and epinephrine cells Nucleus Norepinephrine Epinephrine Nucleus Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology Slide Collection, slide MH 9/G/2-P Nucleus
49 Production of norepinephrine and epinephrine in the cytosol Regents of the University of Michigan
50 THYROID GLAND
51 Location of thyroid gland US Federal Government, wikimedia commons
52 Thyroid follicles Thyroid gland Thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3). Synthesis: A very large protein, thyroglobulin (660 kda), is synthesized and then secreted into the follicle lumen. It is later taken up and broken down (with lysosomes) to yield T4 and T3. General function: To increase the body's metabolic rate. Main control: Pituitary TSH. Parafollicular cells (= C-cells) Hormone: Calcitonin. General function: Lower serum calcium. Main control: Serum calcium level.
53 Modified from Hedge 1987 Thyroid follicle
54 Thyroid, low power LM Blood vessel Hadley Kirkman (Stanford) slide collection, slide 18
55 Thyroid follicles, LM Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/D/6
56 Hadley Kirkman (Stanford) slide collection, slide K27 Thyroid follicles, LM
57 Thyroid capillary beds, corrosion vascular cast, SEM Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide set, slide MH 9/D/5
58 Production of thyroid hormones by a follicular cell Synthesize thyroglobulin and then secrete it into the colloid. Iodinate tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin. When stimulated by pituitary TSH, take up the thyroglobulin and break it down in lysosomes to release thyroid hormones T3 and T4. Colloid Modified from Junqueira and Carneiro, 10th ed., 2003, page 426, fig by R. Mortensen
59 Thyroid follicular cell, EM Golgi Colloid Nucleus Lysosome Porter and Bonneville, 1968, Fine structure of cells and tissues, 3rd ed
60 (increase in thyroid size) Causes of goiter Rugh and Patton 1965, Physiology and biophysics, 19th ed
61 Normal Functional states of thyroid follicles Normal Underactive = hypoactive Overactive = hyperactive Image of thyroid follicles removed. Original here: 0'Riordan, 2nd ed, p 160.
62 A.K. Christensen Underactive (hypoactive) thyroid follicles, LM
63 Overactive (hyperactive) thyroid follicles Medical Histology atlas by Stanley L. Erlandsen and Jean E. Magney
64 Thyroid gland Parafollicular cells (= C-cells) Hormone: Calcitonin. General function: Lowers serum calcium. Main control: Serum calcium level.
65 Hedge 1987 C cell location in thyroid
66 C-cell in thyroid follicular epithelium, LM C-cell A.K. Christensen
67 Immunocytochemical localization of calcitonin in C cells, LM C cell Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/D/8
68 Parafollicular cell (C cell), EM Junqueira histology textbook
69 Regulation of serum calcium Parathyroid hormone (from parathyroid) Ca ++ Calcitonin (thyroid parafollicular cells) Ca ++
70 PARATHYROID GLAND
71 Location of the four parathyroid glands on the back of the thyroid US Federal Government
72 Parathyroid gland Chief (or principal) cells Hormone: Parathyroid hormone (PTH). Main function: Raises serum calcium, lowers serum phosphate. Main control: Serum calcium level. Oxyphil cells Occasional cells or small clusters. Function unknown. Name means "acid [stain] loving" (Greek).
73 Parathyroid gland (mostly chief cells), low power LM Blood vessel Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 542
74 Parathyroid, chief cells, one oxyphil (arrow), LM Fat cell Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med
75 Parathyroid capillary bed, corrosion vascular cast, SEM Murakami et al 1987, Arch Hist Jap 50:495, fig 2
76 Oxyphil cell cluster, LM Fat cell A.K. Christensen
77 Oxyphil cell, EM diagram Nucleus Mitochondrion Thomas Lentz atlas
78 Additional Source Information for more information see: Slide 4: O'Riordan et al., 2nd ed, page 5 Slide 7: National Institutes of Health, Wikimedia Commons, Slide 8: Ross and Pawlina. Histology: Text and Atlas, 5th ed, 2006, fig 21.4, pg 690 Slide 9: Gray s Anatomy, Wikimedia Commons, Slide 10: A. Kent Christensen Slide 11: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 515 Slide 13: Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/B/4 Slide 14: Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH-9B3 Slide 15: A. Kent Christensen Slide 16: A. Kent Christensen Slide 17: EM taken by Larry Kahn, in AKC lab, in 1980 Slide 18: Fawcett. Histology, ed 11, p 486 Slide 19: Marilyn Farquhar in Memoirs of the Society for Endocrinology, number 19, fig 2, p 86. Slide 20: Marilyn Farquhar in Memoirs of the Society for Endocrinology, number 19, figs 2 and 3, p 88. Slide 21: Marilyn Farquhar in Memoirs of the Society for Endocrinology, number 19, fig 5, p 89. Slide 22: A. Kent Christensen Slide 23: Hedges, 1987, p. 86 Slide 24. O'Riordan et al 1988, p 47 Slide 25: Murakami T, 1975, Archivum Histologicum Japanicum 38: Slide 27. O'Riordan et al 1988, p 47 Slide 28: A. Kent Christensen Slide 29: Weiss Histology, ed 5, p Slide 30: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 516 Slide 31: A. Kent Christensen Slide 33: Source Undetermined Slide 34: Wikimedia Commons, Slide 35: Bailey s Histology Slide 37: Hadley Kirkman slide collection, slide K285 Slide 38: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 547 Slide 40: Virginia Black chapter, in Weiss Histology, 6th ed, p Slide 41: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 548 Slide 42: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 549 Slide 43: Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/F/4 Slide 44: Long and Jones 1967 Slide 45: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 550 Slide 47: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 565 Slide 48: Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology Slide Collection, slide MH 9/G/2-P
79 Slide 49: Regents of the University of Michigan Slide 51: US Federal Government, Wikimedia Commons, Slide 53: Modified from Hedge 1987, p. 102 Slide 54: Hadley Kirkman (Stanford) slide collection, slide 18 Slide 55: Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/D/6 Slide 56: Hadley Kirkman (Stanford) slide collection, slide K27 Slide 57: Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide set, slide MH 9/D/5 Slide 58: Modified from Junqueira and Carneiro, 10th ed., 2003, page 426, fig by R. Mortensen Slide 59: Porter and Bonneville, 1968, Fine structure of cells and tissues, 3rd ed, p. 83 Slide 60: Rugh and Patton 1965, Physiology and biophysics, 19th ed, p Slide 61: Regents of the University of Michigan, images from Virtual Histology slide collection Slide 62: A. Kent Christensen Slide 63: Medical Histology atlas by Stanley L. Erlandsen and Jean E. Magney Slide 65: Hedge 1987, p. 102 Slide 66: A. Kent Christensen Slide 67: Stan Erlandsen Medical Histology slide collection, slide MH 9/D/8 Slide 68: Junqueira histology textbook Slide 71: Wikimedia Commons, Slide 73: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med, slide 542 Slide 74: Humio Mizoguti, Kobe Univ Sch Med Slide 75: Murakami et al 1987, Arch Hist Jap 50:495, fig 2 Slide 76: A. Kent Christensen Slide 77: Thomas Lentz atlas
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
The endocrine system
 The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome)
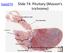 histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
21 Endocrine organs and cells
 21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU
 The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
Endocrine System. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Lab Exercise Endocrine System
 Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture. Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
The Endocrine System
 Collin College! BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Adeno-hypophesis contains mostly glandular tissue ( 75 % of APG is glandular tissue)
Collin College! BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Adeno-hypophesis contains mostly glandular tissue ( 75 % of APG is glandular tissue)
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland
 Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB
 Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
The endocrine system -- a brief overview.
 The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System: An Overview. A system of ductless glands. Interacts closely with the nervous system Endocrinology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG
 Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
The Endocrine System. Qian XiaoJing. Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE QIAN
 The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Endocrine Glands. Endocrine glands
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
The reproductive system
 The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES:
 ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES: -In a living organism there must be coordination of number of physiological activities taking place simultaneously such as: movement, respiration,
ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES: -In a living organism there must be coordination of number of physiological activities taking place simultaneously such as: movement, respiration,
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
8/26/13. Announcements
 Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
CHAPTER 41: Animal Hormones
 CHAPTER 41: Animal Hormones 1. List a few similarities and differences comparing: a. endocrine system b. nervous system 2. What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands? 3. What is the difference
CHAPTER 41: Animal Hormones 1. List a few similarities and differences comparing: a. endocrine system b. nervous system 2. What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands? 3. What is the difference
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
3/12/2012. Pituitary Gland (hypophysis) Anterior Pituitary. Anterior Pituitary. Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Glands Hypothalamus (Master Gland) 8 hormones produced in hypothalamus 6 regulate anterior pituitary e.g., TRH, GnRH, GHRH E.g., PIH, Somatastatin (GH TSH) Hypothalamus
Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Glands Hypothalamus (Master Gland) 8 hormones produced in hypothalamus 6 regulate anterior pituitary e.g., TRH, GnRH, GHRH E.g., PIH, Somatastatin (GH TSH) Hypothalamus
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview The Adrenal Glands The Pancreas Other Endocrine Tissues Stress and its effects
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview The Adrenal Glands The Pancreas Other Endocrine Tissues Stress and its effects
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
The Endocrine System
 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Endocrine System. Human Physiology Unit 3
 Endocrine System Human Physiology Unit 3 Endocrine System Various glands located throughout the body Some organs may also have endocrine functions Endocrine glands/organs synthesize and release hormones
Endocrine System Human Physiology Unit 3 Endocrine System Various glands located throughout the body Some organs may also have endocrine functions Endocrine glands/organs synthesize and release hormones
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Histology. Dr.shatarat
 Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
The Hypothalamo-Pituitary- Adrenal Axis
 The Hypothalamo-Pituitary- Adrenal Axis Table 10.1 Factors Influencing Evaluation of Endocrine Function in Aging Physiologic Metabolism Body Composition Nutrition Exercise Stress Inter-endocrine Relations
The Hypothalamo-Pituitary- Adrenal Axis Table 10.1 Factors Influencing Evaluation of Endocrine Function in Aging Physiologic Metabolism Body Composition Nutrition Exercise Stress Inter-endocrine Relations
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Thyroid Gland. Chapter 18 Part 2. Thyroid gland. Thyroid Gland. Thyroid Gland. Parathyroid Gland. Adrenal Gland. Pancreas
 Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
-Ahmad Rawajbeh. -Dania alkouz. -Saleem Khresha. 1 P a g e
 -2 -Ahmad Rawajbeh -Dania alkouz -Saleem Khresha 1 P a g e The information marked with "(+)" has not been mentioned during the lectures. I added them to clarify and explain. The pituitary gland (+) From
-2 -Ahmad Rawajbeh -Dania alkouz -Saleem Khresha 1 P a g e The information marked with "(+)" has not been mentioned during the lectures. I added them to clarify and explain. The pituitary gland (+) From
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Chapter 11. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Classic Endocrine Glands
 1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
11/26/2007. The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System. NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Lecture Series
 The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises
 A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 3 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Major Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland or Hyp op hysis TextBook Readings Pages 612 through 624. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 3 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Major Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland or Hyp op hysis TextBook Readings Pages 612 through 624. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture
