IDGH RESOLUTION UNENHANCED COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH SWOLLEN LEGS
|
|
|
- Eleanor Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 121 Lymphology 35 (2002) IDGH RESOLUTION UNENHANCED COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH SWOLLEN LEGS E.D. Monnin-Delhom, B.P. Gallix, C. Achard, J.M. Bruel, C. Janbon Service d'imagerie Medicale (EDM-D,BPG,CA,JMB) and Service de Medecine Interne (CJ), Saint Eloi Hospital, Montpellier, France ABSTRACT Purpose: To evaluate the accuracy of computed tomography (CT) scan imaging in distinguishing lymphedema from deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and lipodystrophy (lipedema) in patients with swollen legs. Material and Methods: CT scans ofthe lower limbs were performed in 55 patients with 76 swollen legs (44Iymphedemas, 12 DVT and 20 lipedemas). Thirty-four normal contralateral legs were also similarly evaluated. Primary lymphedema was verified by lymphography or lymphoscintigraphy, whereas secondary lymphedema was documented by a typical clinical history. DVT was established by ultrasound Doppler imaging. The diagnosis oflipedema was made with bilateral swollen legs where lymphoscintigraphy and Doppler examination were both unremarkable. Qualitative CT analysis was based on skin thickening, subcutaneous edema accumulation with a honeycombed pattern, and muscle compartment enlargement. Results: Sensitivity and specificity ofct scan for the diagnosis oflymphedema was 93 and 100%, respectively; for lipedema it was 95 and 100%, respectively; and for DVT it was 91 and 99%, respectively. Skin thickening was found in 42lymphedemas (95%), in 9 DVT (75%), and in 2 lipedemas (16%). Subcutaneous edema accumulation was demonstrated in 42 legs (95%) with lymphedema and in 5 (42%) with DVT but in none with lipedema. A honeycombed pattern was present only in lymphedema (18 legs or 41%); muscle enlargement was present in all patients with DVT, in no patient with lipedema, and in 4 (9%) with lymphedema. Conclusion: Edema accumulation is readily demonstrated with plain CT scan and is not present in lipedema. Specific CT features ofthe subcutaneous fat and muscle compartments allow accurate differentiation between lymphedema and DVT. Lymphedema, lipodystrophy (lipedema), and deep venous thrombosis (DVT) are common causes of swelling of the lower limb. Because treatment differs among these entities, differential diagnostic distinction is important. Clinical assessment alone to distinguish among these etiologies can be difficult and especially between lymphedema and lipedema. CT is a non-invasive method which potentially can define the patterns and localize edema to the different compartments of a limb. Lymphedema relates to insufficiency or obstruction of the lymphatic system, and is typically classified as primary or secondary. Primary lymphedema is a congenital maldevelopment of the lymphatic system whereas secondary lymphedema is the aftermath of damage or obstruction to the lymphatic drainage system. Invasive procedures such as direct lymphography
2 122 (incision) or lymphoscintigraphy (puncture) are generally considered the gold standard diagnostic methods for investigation of lymphatic transport disorders (1). Lipedema is a term often used for an abnormal deposit of subcutaneous fat (lipodystrophy). The pathogenesis is still unclear, but lipedema is not the consequence of venous or lymphatic insufficiency (2). The clinical diagnosis can be confusing and it is frequently mistaken for other causes of lower limb swelling including lymphedema. Deep venous thrombosis is a common cause of acute leg swelling and the diagnosis is nowadays usually confirmed by venography or Doppler sonography which substantiates venous blockage. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the accuracy of plain CT imaging for differentiating lymphedema, lipedema, and DVT in patients with a swollen lower limb. MATERIALS AND METHODS Fifty-five consecutive patients undergoing CT imaging to evaluate unilateral or bilateral swollen legs (from September 1996 to March 1999). There were 15 males and 40 females with an average age of 49 years (range years). The swelling was unilateral in 34 patients and bilateral in 21. A total of 110 legs was divided into two groups: group A comprised 76 swollen legs and group B comprised 34 normal contralateral legs. Group A patients included 44 with lymphedema, 12 with deep venous thrombosis, and 20 with lipedema. Primary lymphedema (33 limbs in 23 patients) was confirmed by bilateral direct lymphography (2 patients) or bilaterallymphoscintigraphy (21 patients); lymphatic insufficiency was bilateral in 10 and unilateral in 13 patients. Secondary lymphedema (11 legs) was based on a typical clinical history; that is, surgical resection of malignant tumors with or without radiotherapy in six patients (two melanomas, two cervix epitheliomas, one testicular and one bladder cancer) and surgery for a benign mass in four patients (one ovarian teratoma, two inguinal adenitis, and one lipoma); secondary lymphedema was bilateral in one patient (bladder cancer). The diagnosis of DVT was established by Doppler sonography. The diagnosis of lipedema was based on clinical findings of obesity, normallymphoscintigraphy and normal sonographic assessment of the deep and superficial venous systems. The control legs were considered normal on the basis of the clinical history, physical examination, and the normal results of both ultrasound and lymphoscintigraphic examinations. Patients were examined in a Somatom DRH CT unit (Siemens Medical Systems, Erlangen, Germany). High resolution millimetric axial slices (240Mas, 120KV) at 30 mm intervals were obtained from the top of the thigh to the ankle (20 slices) without intravenous contrast medium. The patients did not wear compression bandages during the scan. The CT scans were blindly reviewed by the same radiologist. First, a qualitative analysis of the CT scan was performed, based on assessment of the skin, the subcutaneous fat, and the muscle compartment. The following criteria, based on our experience and literature data, were studied: skin thickening, subcutaneous edema, and muscle compartment enlargement. Skin thickening was defined as direct visualization of a hyperdense line at the level of the skin. Subcutaneous edema was defined as "infiltration" of the subcutis by soft-tissue densities bands, trabeculae or collection. The dependent or non-dependent location of the edema was noted. A "honeycombed sign" was defined as subcutaneous fat stranding with trabeculae both parallel and perpendicular to the dermis. The muscle compartment was considered enlarged as compared with the contralateral leg. Second, in order to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of CT for assessing the cause of a swollen limb, the CT diagnosis was assessed as following: lymphedema was
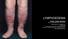
3 123 TABLE I CT Features in Lymphedema, DVT, and Lipedema Subcutaneous Edema Clinical Skin Non- Honeycombed Muscle State n Thickening Dependent Dependent Pattern Enlargement Lymphedema (95)* 0 42 (95) 18 (41) 4 (9) Deep Venous 12 9 (75) (100) Thrombosis Upedema 20 2 (16) Normal *Numbers in parenthesis=% diagnosed when skin thickening and subcutaneous edema were noted; DVT was diagnosed when there was prominent muscle enlargement, with or without skin thickening and subcutaneous edema but without a honeycombed pattern. Lipedema (obesity) was diagnosed with symmetrical bilateral soft tissue enlargement but without either skin thickening or subcutaneous edema. Calculations were based on the findings in each leg. RESULTS CT features are summarized in Table 1. Subcutaneous edema in lymphedema was uniformly in the non-dependent position (Fig. 1). A honeycombed pattern seen in lymphedema was not present in DVT or lipedema (Fig. 2). No subcutaneous or muscle edema was seen in lipedema (Fig. 3). There was enlargement of the muscle compartment in all DVT related leg edema (Fig. 4). The sensitivity and specificity of CT were respectively 97% and 100% for the diagnosis of lymphedema, 98% and 100% for the diagnosis of DVT, 100% and 95% for the diagnosis of lipedema. The two false negatives in lymphedema were related to misdiagnoses of "normal" leg (one patient) and "lipedema" (one patient). Two DVT related edemas were misdiagnosed as "normal." DISCUSSION Chronic swelling of a lower limb is a common condition. Distinguishing lymphedema, "lipedema," or obesity, and DVT-related edema can be clinically difficult. Nonetheless, the distinctions are critical for treatment. For example, a patient with DVT needs prompt anticoagulation, one with lymphedema can be improved with operation or non-operative physiotherapy (3). On the other hand, bandaging and manual drainage are inappropriate for a patient with lipedema. The three conditions each have a different pathogenesis and the distribution of the fluid/fat in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and muscle compartment is different. Axial CT slices analyze separately these 3 compartments allowing qualitative evaluation and localizing of the site of edema if present. For the diagnosis of lymphedema, based on CT demonstration of skin thickening and
4 124 Fig. 1. unenhanced CTscan ofunilateral lymphedema ofthe right lower limb. Skin thickening (large solid arrow) with subcutaneous fat infiltration (trabeculae underlying parallel to the dermis and perimuscular collection in a non-dependent location) (small solid arrow). Fig. 2. Unenhanced CT scan of bilateral lymphedema of the lower limb. Skin thickening (large solid arrow) with honeycombedpattern (small solid arrow) and collections (open arrow).
5 125 Fig. 3. Unenhanced CT scan of bilateral lipodystrophy of the lower limbs. Bilateral subcutaneous enlargement without skin thickening nor subcutaneous fat infiltration. Fig. 4. CT scan of the thighs with left femoral thrombosis. Enlargement of the left muscle compartment (large solid arrow). subcutaneous non-dependent edema, the CT sensitivity was 97% with two false negatives. One false negative related to a minimally developed lymphedema with clinical involvement limited to the foot. This patient was misdiagnosed as normal. A second false negative occurred in a young woman with congenital hemitorso dysmorphia who
6 126 developed secondary lymphedema in the hypertrophic leg related to ovarian mass compression. On initial analysis, skin and fat edema were not identified and the patient was wrongly diagnosed as "lipedema." Retrospective examination of the CT images led to the correct diagnosis and a lymphoscintigram showed minimal delay in lymphatic transport. A CT scan specificity for lymphedema is high: 100%. Thus, a nondependent honeycombed pattern was found only in lymphedema. Previous studies in patients with lymphedema have also described skin thickening (4-8) and subcutaneous fat hypertrophy (9). A major role of lymphatics is to drain extracellular fluid and macromolecules away from the interstitium (10,11). In normal limbs, these entities can drain unimpeded but with lymphatic insufficiency they accumulate in the extracellular space (12). Skin thickening has been also described with sonography and MR imaging. Using a 20 MHz transducer, high resolution sonography has demonstrated an overload of fluid in the superficial and deep dermis in patients with lymphedema (13). A precise analysis of intact skin can also be performed with high resolution MR imaging depicting the epidermis, the dermis and the subcutis (14). MR imaging shows skin thickening, an increased volume of subcutaneous fat lobules (15), and a circumferential, diffuse or reticular pattern of the subcutaneous edema. The constant non-dependent location of the subcutaneous edema we have documented (see Fig. 1) has not been described previously. Edema due to lymph stasis is rich in high weight macromolecular proteins and is distinctly different from a subcutaneous edema related to increased hydrostatic pressure (e.g., heart failure). This difference probably explains why edema from lymph stasis can coagulate as a gel, and in a short time examination in the decubitus position in our scanning protocol (10-15 min) favors a nondependent location for the edema. A honeycombed subcutaneous edema pattern is often considered as specific to lymphedema (see Fig. 2). It is not found in lipodystrophy (lipedema) or in edema of venous origin. Several hypotheses may explain this peculiar trabeculae formation (16). It is unlikely related to normal or dilated lymphatic vessels (17,18) because a honeycombed pattern is present in primary lymphedema with hypoplastic lymphatics. According to Vaughan, it may relate to chronic inflammation with an influx of macrophages and collagen laid down by fibroblasts (19). Whereas this explanation is feasible, these fluid densities can be reversed as we previously observed after complex physiotherapy (20). Thus, a honeycombed pattern is not predictive of lymphatic drainage efficacy and does not signify lack of response to treatment (21). This finding is in agreement with the MR T2-weighted images demonstrating an edematogenic hyperintense signal of honeycomb trabeculae from fluid retention in the fat interlobar spaces (5). The honeycombed pattern does not enhance after Lv. iodinated contrast injection and does not correlate to age of lymphedema, ongoing onset, or intercurrent infection (lymphangitis) (4,22). The edema in lymphedema was primarily localized to the skin and subcutaneous fat, but in four patients there was enlargement in the muscle compartment. CT and MRI studies are not uniformly concordant and in several studies, there has been no statistical difference in CT cross-sectional measurement of the subfascial compartment between the lymphedematous limb and the normal contralateral one (23). Conversely, MRI can show muscle edema with a significant T2 weighted sequence hyperintensity from lymph stasis around deep veins (24). Other studies, however, fail to show muscle involvement except for possible infiltration by adipose tissue (25). Intraluminal valves are rare in dermal initial lymphatics but are much more numerous in lymphatics of the muscle. Those lymphatics that contain both valves and
7 127 smooth muscle cells generate lymph propulsion. Accordingly, lymph stasis is less prominent in muscle than in dermis or hypodermis; moreover, during exercise, the contraction of the adjacent muscles raises interstitial pressure and favors drainage of tissue lymph fluid (26). On the other hand, the increased weight of a lymphedematous limb can lead to muscular work hypertrophy (12). In our study, the sensitivity of CT scan for the diagnosis of lipodystrophy (lipedema) was 100%. There is no skin, subcutaneous fat or muscle edema because this condition represents an excess only of fat (see Fig. 3). Upedema is a common cause of bilateral leg enlargement particularly of women. Previously considered as an abnormal deposition of subcutaneous fat with associated edema (27), this disorder is more accurately considered as lipodystrophy without venous or lymph stasis. An edema pattern was not seen in our patients on CT, ultrasound, or MR images. Ultrasound shows homogeneous hypertrophy of subcutaneous fat without fluid or fibrous elements; there is no significant difference in signal intensity between normal limb and lipedema in T1, T2, and post Gadolinium T1-weighted sequences but only a subcutis size increase from a lipid hypertrophy (22). In our study, sensitivity and specificity of CT for the diagnosis of DVT related edema was respectively 98% and 100%. We found an enlarged muscle compartment in all patients with DVT; in two false negative scans, the muscle hypertrophy was the only alteration and was not prominent enough to allow a radiological distinction between DVT and normal limb. The primary abnormalities in DVT are located within the muscle compartment. Skin thickening and moderate dependent edema of the subcutis is seen, but never in a honeycombed pattern and there is no fibrosis (See Fig. 4). CT scan is rarely needed for the diagnosis of DVT, and currently sonography is favored over phlebography. DVT occurs in deep intramuscular veins, explaining edema and enlargement of both subfascial and epifascial compartments. In an acutely swollen leg, a 10% increase of cross-sectional measurement of the muscle compartment suggests deep venous thrombosis if there is no previous trauma with muscle hematoma (19). In conclusion, a plain CT scan is a useful non-invasive method to distinguish among lymphedema, DVT related edema, and lipodystrophy (lipedema) of the legs. REFERENCES 1. Proby, CM: Investigation of the swollen limb with isotopic lymphography. Br. J. Dermatol 12 (1990), Harwood, CA, RH Bull, H Evans, et al: Lymphatic and venous function in lipoedema. Br. J. Dermatol134 (1996), Campisi, C: Lymphedema: Modern diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. IntI. Angiology 18 (1999), Hadjis, NS, DH Carr, L Banks, et al: The role of CT in the diagnosis of primary lymphedema of the lower limb. Am. J. Roentgenol, 144 (1985), Haaverstad, R, G Nilsen, PA Rinck, et at: The use of MRI in the diagnosis of chronic lymphedema of the lower extremity. IntI. Angiology 13 (1994), Cox, NH, WD Paterson, AW Popple: A reticulate vascular abnormality in patients with lymphedema: observations in eight patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 135 (1996), Mortimer, PS, GW Cherry, RL Jones, et al: The importance of elastic fibres in skin lymphatics. Br. J. Dermatoi. 108 (1983), Schneider, I, F Czako: Histologic studies on the skin of patients with recurrent erysipelas. Dermatol. Monasschrift 15 (1972), Marotel, M, R Cluzan, M Pascot, et al: Tomodensitometrie de 150 cas de lymphoedemes des membres inferieurs. J. Radiol 79 (1998), Daroczy, J: Pathology oflymphedema. Clinics in Dermatology 13 (1995), Casley-Smith, JR: The fine structure and functioning of tissue channels and lymphatics. Lymphology 13 (1980), Szuba A, SG Rockson: Lymphedema: Anatomy, physiology and pathogenesis. Vase. Med. 2 (1997), Gniadecka, M, P Copenhagen: Localization of dermal edema in lipodermatosclerosis,
8
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND CLINICAL FINDINGS IN LOWER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA (LO): TOWARD A COMPREHENSIVE STAGING
 1 Lymphology 41 (2008) 1-10 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND CLINICAL FINDINGS IN LOWER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA (LO): TOWARD A COMPREHENSIVE STAGING A.P. Pecking, J.L. Albérini, M. Wartski, V. Edeline,
1 Lymphology 41 (2008) 1-10 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND CLINICAL FINDINGS IN LOWER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA (LO): TOWARD A COMPREHENSIVE STAGING A.P. Pecking, J.L. Albérini, M. Wartski, V. Edeline,
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers. Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities. Evidence of healed ulcers. Dermatitis. Normal ABI.
 Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
MR IMAGING, PROTON MR SPECTROSCOPY, ULTRASONOGRAPHIC, HISTOLOGIC FINDINGS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LYMPHEDEMA
 157 Lymphology 40 (2007) 157-162 MR IMAGING, PROTON MR SPECTROSCOPY, ULTRASONOGRAPHIC, HISTOLOGIC FINDINGS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LYMPHEDEMA E. Fumiere, O. Leduc, S. Fourcade, C. Becker, C. Garbar, R.
157 Lymphology 40 (2007) 157-162 MR IMAGING, PROTON MR SPECTROSCOPY, ULTRASONOGRAPHIC, HISTOLOGIC FINDINGS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LYMPHEDEMA E. Fumiere, O. Leduc, S. Fourcade, C. Becker, C. Garbar, R.
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure
 When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE
 LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
Microvascular Research
 Microvascular Research 77 (2009) 335 339 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Microvascular Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ymvre Regular Article MR imaging of the lymphatic system
Microvascular Research 77 (2009) 335 339 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Microvascular Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ymvre Regular Article MR imaging of the lymphatic system
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Subcutaneous Tissue Ultrasonography in Legs with Dependent Edema and Secondary Lymphedema
 Ann Vasc Dis Vol. 7, No. 1; 2014; pp 21 27 Online February 4, 2014 2014 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.13-00107 Original Article Subcutaneous Tissue Ultrasonography in Legs with Dependent
Ann Vasc Dis Vol. 7, No. 1; 2014; pp 21 27 Online February 4, 2014 2014 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.13-00107 Original Article Subcutaneous Tissue Ultrasonography in Legs with Dependent
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA. John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA
 When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography for the Study of Lymphatic System in Lymphedema
 66 Invited Review Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography for the Study of Lymphatic System in Lymphedema NingFei Liu, MD, PhD 1 Yixin Zhang, MD, PhD 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai
66 Invited Review Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography for the Study of Lymphatic System in Lymphedema NingFei Liu, MD, PhD 1 Yixin Zhang, MD, PhD 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai
The Lymphatic System. Oedema (Edema) Lymphoedema (Lymphedema)
 The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
Differentiation of High and Low Output Lymphatic Failure Using Qualitative Lymphangioscintigraphy
 2015 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.15-00034 Original Article Differentiation of High and Low Output Lymphatic Failure Using Qualitative Lymphangioscintigraphy Kotaro Suehiro, MD, Noriyasu
2015 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.15-00034 Original Article Differentiation of High and Low Output Lymphatic Failure Using Qualitative Lymphangioscintigraphy Kotaro Suehiro, MD, Noriyasu
Controversies & updates in Vascular Surgery
 Controversies & updates in Vascular Surgery Paris - january 24 2018 Venous session VENOUS ODDITIES DUPLEX IMAGE Philippe LEMASLE Le Chesnay - France I have no financial relationship to disclose Case n
Controversies & updates in Vascular Surgery Paris - january 24 2018 Venous session VENOUS ODDITIES DUPLEX IMAGE Philippe LEMASLE Le Chesnay - France I have no financial relationship to disclose Case n
Lipedema COMMON CLINICAL ENTITY RARELY DIAGNOSED FVS 2018
 1 Lipedema COMMON CLINICAL ENTITY RARELY DIAGNOSED FVS 2018 No disclosures 2 Lipedema 3 Bilateral symmetrical fat deposition from hips to ankles Trunk is spared, chest small Not obesity, note waist/hip
1 Lipedema COMMON CLINICAL ENTITY RARELY DIAGNOSED FVS 2018 No disclosures 2 Lipedema 3 Bilateral symmetrical fat deposition from hips to ankles Trunk is spared, chest small Not obesity, note waist/hip
LYMPHATIC CLEARANCE OF THE HUMAN SKIN IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS USING A NOVEL FLUORESCENT TECHNIQUE
 127 Lymphology 39 (2006) 127-131 LYMPHATIC CLEARANCE OF THE HUMAN SKIN IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS USING A NOVEL FLUORESCENT TECHNIQUE M.J. Husmann, R. Simon. T. Kovacevic, G. Gitzelmann,
127 Lymphology 39 (2006) 127-131 LYMPHATIC CLEARANCE OF THE HUMAN SKIN IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS USING A NOVEL FLUORESCENT TECHNIQUE M.J. Husmann, R. Simon. T. Kovacevic, G. Gitzelmann,
Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound. Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons)
 Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons) Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Venous Deep System Common Iliac External/Internal Iliac Common Femoral Femoral
Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons) Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Venous Deep System Common Iliac External/Internal Iliac Common Femoral Femoral
2007 ICL SHANGHAI 24/03/2013
 Background Intradermal Lymphoscintigraphy: Technical Improvement and an Interpretation of the Pathological Patterns on Clinical Management of Severe Stage Lymphoedema. Girolamo Tartaglione, MD Department
Background Intradermal Lymphoscintigraphy: Technical Improvement and an Interpretation of the Pathological Patterns on Clinical Management of Severe Stage Lymphoedema. Girolamo Tartaglione, MD Department
4. WHY a Lymphovenous anastomosis can be indicated in Lymphedema?
 LYMPHOVENOUS ANASTOMOSIS TECHNIQUE ( LVA / MLVA / MLVLA ). Alessandro Busetto Wolfsberg March 20-21, 2018 1. Speaer s agreement 2. Title. The aim of our communication is to describe and compare the various
LYMPHOVENOUS ANASTOMOSIS TECHNIQUE ( LVA / MLVA / MLVLA ). Alessandro Busetto Wolfsberg March 20-21, 2018 1. Speaer s agreement 2. Title. The aim of our communication is to describe and compare the various
Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence
 What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence North of England Cancer Network Lymphoedema Conference - A problem shared 8 March 2013 Dr Andrew Hughes Consultant in Palliative Medicine Outline 1) What is
What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence North of England Cancer Network Lymphoedema Conference - A problem shared 8 March 2013 Dr Andrew Hughes Consultant in Palliative Medicine Outline 1) What is
According to the etiology, edema may be:
 What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION
 JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
Management of Lower Limb Lymphoedema in the United Kingdom
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 31, 311 315 (6) doi:1.116/j.ejvs.5.9.17, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on Management of Lower Limb Lymphoedema in the United Kingdom A. Tiwari, F. Myint and
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 31, 311 315 (6) doi:1.116/j.ejvs.5.9.17, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on Management of Lower Limb Lymphoedema in the United Kingdom A. Tiwari, F. Myint and
High-Resolution MR Lymphangiography in Patients with Primary and Secondary Lymphedema
 Lohrmann et al. MR Lymphangiog raphy of Patients with Lymphedem a Vascular Imaging Technical Innovation C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:556 561 0361 803X/06/1872 556 merican Roentgen Ray
Lohrmann et al. MR Lymphangiog raphy of Patients with Lymphedem a Vascular Imaging Technical Innovation C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:556 561 0361 803X/06/1872 556 merican Roentgen Ray
CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema
 CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema Hisako Hara, MD, and Makoto Mihara, MD Department of Lymphatic and Reconstructive Surgery, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Saitama, Japan
CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema Hisako Hara, MD, and Makoto Mihara, MD Department of Lymphatic and Reconstructive Surgery, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Saitama, Japan
Painful fat syndrome in a male patient q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 282 286 CASE REPORT Painful fat syndrome in a male patient q Shyi-Gen Chen a, *, Shih-Dar Hsu b, Tim-Mo Chen a, Hsian-Jenn Wang a a Division of Plastic
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 282 286 CASE REPORT Painful fat syndrome in a male patient q Shyi-Gen Chen a, *, Shih-Dar Hsu b, Tim-Mo Chen a, Hsian-Jenn Wang a a Division of Plastic
Popliteal Node Visualization During Standard Pedal Lymphoscintigraphy for a Swollen Limb Indicates Impaired Lymph Drainage
 Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Burnand et al. Popliteal Nodes in Lymphoscintigraphy Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Katherine M. Burnand 1 Daphne M. Glass
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Burnand et al. Popliteal Nodes in Lymphoscintigraphy Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Katherine M. Burnand 1 Daphne M. Glass
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond
 Disclosure of Conflict of Interest Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond Shawn Amyot, MD, CCFP Fellow of the Canadian Society of Phlebology Ottawa Vein Centre I do not have relevant financial
Disclosure of Conflict of Interest Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond Shawn Amyot, MD, CCFP Fellow of the Canadian Society of Phlebology Ottawa Vein Centre I do not have relevant financial
Coding Companion for Podiatry. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Podiatry comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2016 Contents Contents Foot and Toes 28043-28045 [28039, 28041] 28043 28039 28045 28041 Excision, tumor, soft tissue
Coding Companion for Podiatry comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2016 Contents Contents Foot and Toes 28043-28045 [28039, 28041] 28043 28039 28045 28041 Excision, tumor, soft tissue
DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS
 TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
Interactive Learning Session
 Chronic Venous Disease - Part I Interactive Learning Session 2011 Ali Sabbour Prof of Vascular Surgery http://mic.shams.edu.eg/moodle6 Login as a guest Surgery 2 Ali Sabbour - Chronic Venous Disease Intended
Chronic Venous Disease - Part I Interactive Learning Session 2011 Ali Sabbour Prof of Vascular Surgery http://mic.shams.edu.eg/moodle6 Login as a guest Surgery 2 Ali Sabbour - Chronic Venous Disease Intended
PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY
 PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY CONTENTS 1.0. PRESSURE THERAPY 1.1. The physiological effects of pressure therapy 1.2. When pressure therapy is indicated 2.0.
PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY CONTENTS 1.0. PRESSURE THERAPY 1.1. The physiological effects of pressure therapy 1.2. When pressure therapy is indicated 2.0.
High resolution ultrasound scanner for skin imaging
 High resolution ultrasound scanner for skin imaging Christine Turlat Sales Director Atys medical 17 Parc d Arbora 69510 SOUCIEU EN JARREST Atys company Principle of ultrasound imaging DERMCUP Normal image
High resolution ultrasound scanner for skin imaging Christine Turlat Sales Director Atys medical 17 Parc d Arbora 69510 SOUCIEU EN JARREST Atys company Principle of ultrasound imaging DERMCUP Normal image
Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh
 Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
REPEATED INTRANODAL LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHATIC LEAKAGE
 59 Lymphology 48 (2015) 59-63 REPEATED INTRANODAL LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHATIC LEAKAGE S. Kariya, M. Nakatani, R. Yoshida, Y. Ueno, A. Komemushi, N. Tanigawa Department of Radiology,
59 Lymphology 48 (2015) 59-63 REPEATED INTRANODAL LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHATIC LEAKAGE S. Kariya, M. Nakatani, R. Yoshida, Y. Ueno, A. Komemushi, N. Tanigawa Department of Radiology,
MEASUREMENT OF SOFT TISSUE COMPLIANCE WITH PRESSURE USING ULTRASONOGRAPHY
 167 Lymphology 41 (2008) 167-177 MEASUREMENT OF SOFT TISSUE COMPLIANCE WITH PRESSURE USING ULTRASONOGRAPHY W. Kim, S.-G. Chung, T.-W. Kim, K.-S. Seo Department of Rehabilitation Medicine (WK, S-GC, K-SS),
167 Lymphology 41 (2008) 167-177 MEASUREMENT OF SOFT TISSUE COMPLIANCE WITH PRESSURE USING ULTRASONOGRAPHY W. Kim, S.-G. Chung, T.-W. Kim, K.-S. Seo Department of Rehabilitation Medicine (WK, S-GC, K-SS),
Color duplex-doppler ultrasonography of lower extremities veins - types of findings
 Color duplex-doppler ultrasonography of lower extremities veins - types of findings Boris Brkljačić 1, Božidar Šebečić 2, Ante Grga 2, Leonardo Patrlj 2, Andrija Hebrang 1 1 Department of Radiology and
Color duplex-doppler ultrasonography of lower extremities veins - types of findings Boris Brkljačić 1, Božidar Šebečić 2, Ante Grga 2, Leonardo Patrlj 2, Andrija Hebrang 1 1 Department of Radiology and
CASE STUDY. Potential conflict of interest:
 CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth
 Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: 01/23/2019
 Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
Noncontrast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging vs lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymph circulation disorders: A comparative study
 Noncontrast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging vs lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymph circulation disorders: A comparative study Ningfei Liu, MD, PhD, a Chenguang Wang, MD, PhD, b and
Noncontrast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging vs lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymph circulation disorders: A comparative study Ningfei Liu, MD, PhD, a Chenguang Wang, MD, PhD, b and
Appearance And Visibility Of The Thoracic Duct On Computed Tomography Of The Chest
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 Appearance And Visibility Of The Thoracic Duct On Computed Tomography Of The Chest J Gossner Citation J Gossner. Appearance And Visibility
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 Appearance And Visibility Of The Thoracic Duct On Computed Tomography Of The Chest J Gossner Citation J Gossner. Appearance And Visibility
Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries. Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA
 Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries Pat Archer ATC, LMP Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA Lymphatic Facilitation A specific lymphatic technique proven as an easy
Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries Pat Archer ATC, LMP Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA Lymphatic Facilitation A specific lymphatic technique proven as an easy
Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression
 The Vascular Center : A model to improve patient care Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression F. Vin C. Gardon-Mollard Compression Therapy is an efficient treatment for the management
The Vascular Center : A model to improve patient care Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression F. Vin C. Gardon-Mollard Compression Therapy is an efficient treatment for the management
Additional Information S-55
 Additional Information S-55 Network providers are encouraged, but not required to participate in the on-line American Venous Forum Registry (AVR) - The First National Registry for the Treatment of Varicose
Additional Information S-55 Network providers are encouraged, but not required to participate in the on-line American Venous Forum Registry (AVR) - The First National Registry for the Treatment of Varicose
Saphenous Vein Wall Thickness in Age and Venous Reflux-Associated Remodeling in Adults
 Saphenous Vein Wall Thickness in Age and Venous Reflux-Associated Remodeling in Adults Nicos Labropoulos Professor of Surgery Director, Vascular Laboratory Division of Vascular Surgery Stony Brook Medicine
Saphenous Vein Wall Thickness in Age and Venous Reflux-Associated Remodeling in Adults Nicos Labropoulos Professor of Surgery Director, Vascular Laboratory Division of Vascular Surgery Stony Brook Medicine
ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED
 ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED Ralph Wang UCSF Department of Emergency Medicine 53 yo f c/o left leg swelling recent cholecystectomy its midnight how do you manage this patient?
ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED Ralph Wang UCSF Department of Emergency Medicine 53 yo f c/o left leg swelling recent cholecystectomy its midnight how do you manage this patient?
Ultrasound With SHU 508A In The Diagnosis Of Suspected Lower Limbs Deep Vein Thrombosis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 2 Ultrasound With SHU 508A In The Diagnosis Of Suspected Lower Limbs Deep Vein Thrombosis A Kotis, P Brestas, L Guidaglia, O Dafni, E
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 2 Ultrasound With SHU 508A In The Diagnosis Of Suspected Lower Limbs Deep Vein Thrombosis A Kotis, P Brestas, L Guidaglia, O Dafni, E
A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management.
 A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management. Poster No.: C-1030 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. J. Ley, E.
A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management. Poster No.: C-1030 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. J. Ley, E.
Ning-Fei Liu, MD, PhD, a Qing Lu, MD, b Zhao-Hua Jiang, MD, PhD, a Chen-Guang Wang, MD, PhD, c and Jian-Guo Zhou, MD, a Shanghai, China
 Anatomic and functional evaluation of the lymphatics and lymph nodes in diagnosis of lymphatic circulation disorders with contrast magnetic resonance lymphangiography Ning-Fei Liu, MD, PhD, a Qing Lu,
Anatomic and functional evaluation of the lymphatics and lymph nodes in diagnosis of lymphatic circulation disorders with contrast magnetic resonance lymphangiography Ning-Fei Liu, MD, PhD, a Qing Lu,
The Incidental Renal lesion
 The Incidental Renal lesion BACKGROUND Increase in abdominal CT/US in last 15 years Resulted in detection of many (small) renal lesions 50% > 50yrs has at least 1 lesion majority simple cysts Renal lesions
The Incidental Renal lesion BACKGROUND Increase in abdominal CT/US in last 15 years Resulted in detection of many (small) renal lesions 50% > 50yrs has at least 1 lesion majority simple cysts Renal lesions
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Complete Evaluation of the Chronic Venous Patient: Recognizing deep venous obstruction. Erin H. Murphy, MD Rane Center
 Complete Evaluation of the Chronic Venous Patient: Recognizing deep venous obstruction Erin H. Murphy, MD Rane Center Disclosure Speaker name: Erin H. Murphy... I have the following potential conflicts
Complete Evaluation of the Chronic Venous Patient: Recognizing deep venous obstruction Erin H. Murphy, MD Rane Center Disclosure Speaker name: Erin H. Murphy... I have the following potential conflicts
Catherine Holley, RN Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital
 Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital March 13, 2019 What is Lymphedema? Swelling (edema) that occurs due to injury or impairment of the lymphatic system Causes: Anything that disrupts the
Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital March 13, 2019 What is Lymphedema? Swelling (edema) that occurs due to injury or impairment of the lymphatic system Causes: Anything that disrupts the
Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review
 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0102-7 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review F. Muratori M. Esposito F. Rosa F. Liuzza N. Magarelli B. Rossi H.M. Folath F. Pacelli G. Maccauro
DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0102-7 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review F. Muratori M. Esposito F. Rosa F. Liuzza N. Magarelli B. Rossi H.M. Folath F. Pacelli G. Maccauro
An Arteriovenous Malformation in the Suprapatellar Fat Pad of the Knee associated with Klippel-Trenaunay- Weber Syndrome: A Case Report 1
 n rteriovenous Malformation in the Suprapatellar Fat Pad of the Knee associated with Klippel-Trenaunay- Weber Syndrome: Case Report 1 Mi Hyun Park, M.D., Soon Tae Kwon, M.D., yung Seok Shin, M.D., Young
n rteriovenous Malformation in the Suprapatellar Fat Pad of the Knee associated with Klippel-Trenaunay- Weber Syndrome: Case Report 1 Mi Hyun Park, M.D., Soon Tae Kwon, M.D., yung Seok Shin, M.D., Young
Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Ultrasound of soft-tissue vascular anomalies
 Ultrasound of soft-tissue vascular anomalies Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Ultrasound of soft-tissue vascular anomalies Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Starting with deep venous treatment
 Starting with deep venous treatment Carsten Arnoldussen, MD Interventional Radiologist Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht VieCuri Medical Centre, Venlo The Netherlands Background Maastricht
Starting with deep venous treatment Carsten Arnoldussen, MD Interventional Radiologist Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht VieCuri Medical Centre, Venlo The Netherlands Background Maastricht
Training Outline. History of medi. Circulation in the body. Medical Conditions. Athletic Conditions. Compression in Sports. Compression for recovery
 Compression 101 1 Training Outline History of medi Circulation in the body Medical Conditions Athletic Conditions Compression in Sports Compression for recovery Tips 2 History of medi medi began in the
Compression 101 1 Training Outline History of medi Circulation in the body Medical Conditions Athletic Conditions Compression in Sports Compression for recovery Tips 2 History of medi medi began in the
Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches
 Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches Nina Linnitt RN Clinical Manager medi UK Current Chair British Lymphology Society (BLS) What is lymphoedema? International Societie de Lymphologue
Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches Nina Linnitt RN Clinical Manager medi UK Current Chair British Lymphology Society (BLS) What is lymphoedema? International Societie de Lymphologue
THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS IN ELECTIVE FOOT AND ANKLE SURGERY
 THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS IN ELECTIVE FOOT AND ANKLE SURGERY Andy Molloy University Hospital Aintree BMI Sefton Hospital 1 Pathology /signs / investigation (brief!) What is the evidence? What do people do? What
THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS IN ELECTIVE FOOT AND ANKLE SURGERY Andy Molloy University Hospital Aintree BMI Sefton Hospital 1 Pathology /signs / investigation (brief!) What is the evidence? What do people do? What
Selection and work up for the right patients suspected of deep venous disease
 Selection and work up for the right patients suspected of deep venous disease R A G H U K O L L U R I, M S, M D, R V T S Y S T E M M E D I C A L D I R E C T O R V A S C U L A R M E D I C I N E / V A S
Selection and work up for the right patients suspected of deep venous disease R A G H U K O L L U R I, M S, M D, R V T S Y S T E M M E D I C A L D I R E C T O R V A S C U L A R M E D I C I N E / V A S
THE MANAGEMENT OF THE SWOLLEN ARM IN CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST
 THE MANAGEMENT OF THE SWOLLEN ARM IN CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST NORMAN TREVES, M.D. The terms "brawny arm" and "lymphedema" have been given to the swollen arm which may complicate the inoperable, recurrent,
THE MANAGEMENT OF THE SWOLLEN ARM IN CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST NORMAN TREVES, M.D. The terms "brawny arm" and "lymphedema" have been given to the swollen arm which may complicate the inoperable, recurrent,
Deep Vein Thrombosis: Can a Second Sonographic Examination Be Avoided?
 Alfonsa Friera 1 Nuria R. Giménez 2 Paloma Caballero 1 Pilar S. Moliní 2 Carmen Suárez 2 Received August 15, 2001; accepted after revision October 16, 2001. 1 Radiology Department, Hospital de la Princesa,
Alfonsa Friera 1 Nuria R. Giménez 2 Paloma Caballero 1 Pilar S. Moliní 2 Carmen Suárez 2 Received August 15, 2001; accepted after revision October 16, 2001. 1 Radiology Department, Hospital de la Princesa,
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions
 Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Lymphoscintigraphy of the Upper Extremities
 Lymphoscintigraphy of the Upper Extremities MJ de Haas, Meander Medical Centre Amersfoort (Retired) 1. Introduction Lymphoedema is a chronic, progressive, and often debilitating condition. Primary lymphoedema
Lymphoscintigraphy of the Upper Extremities MJ de Haas, Meander Medical Centre Amersfoort (Retired) 1. Introduction Lymphoedema is a chronic, progressive, and often debilitating condition. Primary lymphoedema
Priorities Forum Statement
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 9 Subject Varicose Vein Surgery Date of decision September 2014 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review September 2018 Relevant OPCS codes: L841-46, L848-49, L851-53,
Priorities Forum Statement Number 9 Subject Varicose Vein Surgery Date of decision September 2014 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review September 2018 Relevant OPCS codes: L841-46, L848-49, L851-53,
9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!
 1 9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!) On-Line COURSE OUTLINE/Overview of Topics (62.5hrs): Lymphatics
1 9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!) On-Line COURSE OUTLINE/Overview of Topics (62.5hrs): Lymphatics
Diagnostic investigations for oedema of the upper limb. Helen Young
 Diagnostic investigations for oedema of the upper limb Helen Young Oedema of the upper limb may be attributable to several factors, including malignancy, venous or lymphatic abnormality. This article illustrates
Diagnostic investigations for oedema of the upper limb Helen Young Oedema of the upper limb may be attributable to several factors, including malignancy, venous or lymphatic abnormality. This article illustrates
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy Number: MP.066.MH Last Review Date: 11/08/2018 Effective Date: 01/01/2019
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar CareFirst PPO MedStar Health considers the treatment of Varicose
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar CareFirst PPO MedStar Health considers the treatment of Varicose
Venous drainage of the lower limb
 Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
COLORECTAL CANCER STAGING in 2010
 COLORECTAL CANCER STAGING in 2010 Robert A. Halvorsen, MD, FACR MCV Hospitals / VCU Medical Center Richmond, Virginia I do not have any relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests COLON
COLORECTAL CANCER STAGING in 2010 Robert A. Halvorsen, MD, FACR MCV Hospitals / VCU Medical Center Richmond, Virginia I do not have any relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests COLON
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis
 Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION DEVICES IN THE HOME SETTING
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Medicine Policy Number: II-60 Effective Date: 05/19/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Medicine Policy Number: II-60 Effective Date: 05/19/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Determine the patients relative risk of thrombosis. Be confident that you have had a meaningful discussion with the patient.
 Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
LYMPHEDEMA GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT. the more you know TEDS. Diuretics. Prescribe compression garments without first reducing edema
 LYMPHEDEMA the more you know GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT TEDS Recognize full Continuum of Lymphedema stages Identify Range of Lymphedema Diagnoses Differentiate Effective Treatment Options from
LYMPHEDEMA the more you know GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT TEDS Recognize full Continuum of Lymphedema stages Identify Range of Lymphedema Diagnoses Differentiate Effective Treatment Options from
Gastric Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma: Unilateral Lower Extremity Lymphoedema as the Presenting Feature
 Clinical Image TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 1189 1192 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.199 Gastric Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma: Unilateral Lower Extremity Lymphoedema as the Presenting Feature
Clinical Image TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 1189 1192 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.199 Gastric Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma: Unilateral Lower Extremity Lymphoedema as the Presenting Feature
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa
 Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Suspected Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis EVIDENCE TABLE
 . Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
. Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment
 Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu Lymphedema Physiology
Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu Lymphedema Physiology
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
OHTAC Recommendation. Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins. Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009
 OHTAC Recommendation Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009 April 2010 Issue Background The Ontario Health Technology
OHTAC Recommendation Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009 April 2010 Issue Background The Ontario Health Technology
What is Lymphedema? Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels are not formed completely or malformed
 Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
chronic venous disorders, varicose vein, CEAP classification, lipodermatosclerosis, Klippel- Trenaunay syndrome DVT CVD
 Online publication August 27, 2009 chronic venous disorders: CVD CEAP 4 CEAP CVD J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 201 205 chronic venous disorders, varicose vein, CEAP classification, lipodermatosclerosis,
Online publication August 27, 2009 chronic venous disorders: CVD CEAP 4 CEAP CVD J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 201 205 chronic venous disorders, varicose vein, CEAP classification, lipodermatosclerosis,
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Lymphoedema in bariatric patients
 Lymphoedema in bariatric patients Lymfødemseminar 27. oktober 2016 Mungo Park, Kolding, Denmark Mieke Flour, Leuven, Belgium Morbid obesity and lymphedema Morbid obesity: definition and co-morbidities
Lymphoedema in bariatric patients Lymfødemseminar 27. oktober 2016 Mungo Park, Kolding, Denmark Mieke Flour, Leuven, Belgium Morbid obesity and lymphedema Morbid obesity: definition and co-morbidities
Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012
 Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt of a new version. Date Approved: March 2011 reissued April
Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt of a new version. Date Approved: March 2011 reissued April
