Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography for the Study of Lymphatic System in Lymphedema
|
|
|
- Milton Newman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 66 Invited Review Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography for the Study of Lymphatic System in Lymphedema NingFei Liu, MD, PhD 1 Yixin Zhang, MD, PhD 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai 9th People s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China J Reconstr Microsurg 2016;32: Address for correspondence NingFei Liu, MD, PhD, Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai 9th People s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, 639 Zhi Zao Ju Road, Shanghai , China ( liuningfei@126.com). Abstract Background Imaging of the lymphatic system is difficult because of its structural and anatomical characteristics, and the conventional diagnostic method, radionuclidebased imaging, has the disadvantage of poor resolution. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging has been shown the capability of depicting lymphatic channels in lymphedema recently. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the imaging of MR lymphangiography (MRL) in diagnosis of limb lymphedema and its possible role in the microsurgical management of lymphedema. Methods A total of 710 patients with primary lymphedema (n ¼ 378), secondary lymphedema (n ¼ 332), were enrolled in the study. Contrast-enhanced lymphangiography was performed with 3.0 T MR unit (Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands) after intracutaneously injection of gadobenate dimeglumine. Kinetic of enhanced lymph flow within lymphatics and lymph nodes as well as the morphological abnormalities of lymphatic system were evaluated. Results MRL was able to display the detailed anatomical changes in the vessels and nodes. In primary lymphedema, there are three major types of lymphatic system malformation: (1) only lymph nodes affected, (2) only lymph vessels affected, and (3) both lymph vessels and lymph nodes affected. In secondary lymphedema MRL clearly demonstrated tortuous and dilated collecting lymphatics in lymphedemtous limbs. MRL also provided information concerning the functional status of lymph transport in Keywords lymphedema MR lymphangiography lymphatic lymph node lymphatic vessels and nodes by real-time visualization of enhanced lymph flow in lymphatic channels and within lymph nodes. Conclusion Contrast MRL was capable of evaluating the anatomical and functional status of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes in lymphedematous limb. This new imaging shows good potential for use in the diagnosis and surgical management of lymphedema. Impairments of lymph circulation can occur either because of congenital defects leading to malformation of the lymphatic system, or because of secondary damage to lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes. These impairments can cause accumulation of macromolecules and fluid in the tissue, resulting in lymphedema. 1 Clinical diagnosis of lymphedema in an extremity is typically not difficult, particularly during the late stages of the disease. However, the history and clinical examination do not always indicate the nature or extent of the underlying abnormality (i.e., the anatomical extent, pathology, and cause). The development of clinical lymphology was slow for a long time. This was largely due to the lack of optimal diagnostic methods, including methods for lymphatic system received April 12, 2014 accepted after revision June 1, 2014 published online July 15, 2014 Copyright 2016 by Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc., 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA. Tel: +1(212) DOI /s ISSN X.
2 Lymphedema Treatment MR Lymphangiography Lymphatic System Liu, Zhang 67 imaging. The commonly used lymphoscintigraphy, with an isotopic contrast agent, has insufficient resolution to accurately outline the internal anatomy of the lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels. The measurement of tracer clearance at the injection point and accumulation of the tracer in the inguinal lymph nodes may be valuable in functional evaluation but are limited in accuracy. 2 Direct lymphangiography using iodine oil as the contrast agent, which is capable of visualizing the lymphatics, is no longer routinely performed because it is highly invasive and difficult to perform, and also can lead to life-threatening complications. 3 Neither of the above methods is able to dynamically visualize lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes. It is, therefore essential to use a combination of imaging modalities that, in addition to mapping the anatomical distribution of the affected lymphatic system, is capable of defining its function. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has recently emerged as a new method for diagnosing lymphostatic diseases. 4 7 Since 2007 we have adopted three-dimensional (3D) dynamic magnetic resonance lymphangiography (MRL) using the paramagnetic contrast agent Gd-BOPTA (gadolinium benzyloxypropionictetraacetate) to assess the lymphatic system architecture and lymph drainage in extremities affected by lymphedema. 8 MRL is currently the routine diagnostic modality for lymphedema in the authors clinic. This article presents the results of MRL in the diagnosis of lymphedema based on the examination of 710 patients for the purpose of leading to a better understanding of this relatively new technique. Materials and Methods The present study included 710 patients (335 men, 375 women; mean age 35 years, range: 5 78 years). Among them, 378 were diagnosed with primary extremity lymphedema and 332 with secondary lymphedema after lymph node dissection, surgery and/or radiation therapy, lymph node metastasis, injury or lymphadenitis. The mean durationofdiseaseacrossallpatients was 8 years, and ranged from 1 month to 55 years. MRL was performed as described previously 8 with a 3.0 T MR unit (Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands). First, 3D heavily T2-weighted MRI was performed. After intradermal injection of Gd-BOPTA into the first and second digital web space of bilateral hand/feet ( ml per point; MultiHance; Bracco, Milan, Italy), 3D fast spoiled gradientrecalled echo T1-weighted images were acquired with a fat saturation technique at consecutive time points for dynamic observation. Images were reconstructed using maximum intensity projection to map the lymphatic vessels. In addition to mapping lymphatic distribution patterns, the lymph flow speed in lymphatic collectors was recorded to calculate the length of the enhancement of the lymphatic vessels per minute of testing time using the formula: Speed (cm/min) = Total length of visualized lymph vessel (cm) Inspection time (min). Images of regional lymph nodes were acquired before and after injection of contrast agent. The contrast enhancement in regional lymph nodes was recorded and measured as the node to muscle signal intensity ratio for direct comparison between bilateral inguinal lymph nodes. Results Imaging of the Lymphatic System in Primary Lymphedema After intracutaneous injection, the contrast agent was quickly taken up by the primary lymph vessels and transported with the lymph. The enhancement of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes was inspected accordingly during the dynamic MRL. The drainage patterns of lymphatic vessels and nodes were clearly demonstrated. In most contralateral healthy limbs no enhanced or only a few light lymph vessels were visualized ( Fig. 1a), and the inguinal nodes enhanced quickly and completely ( Fig. 1b). The changes in the lymphatic system in primary lymphedema may occur in the lymph vessels, in the nodes, or in both. The number of lymphatic vessels was from none or one to many, and the diameter was from 0.5 to 8 mm in lymphedematous limbs. The lymphatic abnormalities fell into two major categories: aplasia/hypoplasia or hyperplasia. In aplasia/hypoplasia the peripheral vessels could be absent or severely hypoplastic in number and size. In hyperplasia, varicose lymphatic vessels that were numerous, tortuous, and dilated were found in the limb and trunk ( Fig. 1a). Common pathological features of the affected lymph nodes included: significant enlargement, smaller in size and number, absent, irregular in outline, heterogeneous in texture, and partial (marginal or central region) contrast enhancement ( Fig. 1b). Combining the lymphatic and lymph node anomalies seen on MRL, the malformation of the lymph system in primary lymphedema included three major types: 1. Only lymph nodes affected with abnormal nodal structural (17%) 2. Only lymph vessels affected (32%) with three subtypes (lymphatic aplasia, hypoplasia, and hyperplasia) 3. Both lymph vessels and lymph nodes affected (51%) The speed of enhanced lymph flow ranged from to 1.48 cm/min ( Fig. 2a). The speed of lymph transport seems largely individual in primary lymphedema. However, the transport of lymph was significantly delayed in varicose lymphatic vessels compared with that in the contralateral nonedematous limb. The contrast-enhanced MR images showed marked asymmetrical accumulation of contrast agent between the nodes of the edematous limb and contralateral limb of patients with unilateral lymphedema ( Fig. 2b), and the contrast enhancement measured as the node to muscle signal intensity ratio in lymphedematous limbs was significantly lower than in the contralateral limbs. Imaging of the Lymphatic System in Secondary Lymphedema In acute secondary lymphedema, for example, resulting from a tumor in the inguinal lymph node, the afferent lymphatic vessel might be extremely dilated (diameter > 1
3 68 Lymphedema Treatment MR Lymphangiography Lymphatic System Liu, Zhang Fig. 1 (a) A 36-year-old woman with primary lymphedema of left lower limb, numerous tortuous and dilated lymph vessels (arrowheads) were demonstrated in contrast with contralateral no edema right limb with a few light lymphatic vessels (arrows) on postcontrast MRL imaging. (b) Enlarged inguinal lymph node with heterogeneous appearance and inhomogeneous enhancement in edema limb (arrows) in contrast with the contralateral nodes that were evenly enhanced (arrowheads). (c) Axial section of T2-weighted MR image shows the thickness and edema of the subcutis (high signal intensity) of the left lower limb. MRL, magnetic resonance lymphangiography. cm) and/or even disrupted ( Fig. 3a). Tortuous and dilated collecting lymphatics were also clearly seen in the lymphedematous arms after mastectomy in contrast with a single lymphatic in the contralateral no edema arm ( Fig. 3b). Dilated lymph collectors were seen in the distal third of the lower leg without visualization of proximal channels in a considerable number of patients ( Fig. 3c), which indicated obliteration of the lymphatic channels in the proximal part of the limb. In patients with secondary lymphedema of a lower extremity after surgery and/or radiation, the inguinal lymph nodes were found to be smaller, decreased in number, irregular in shape, and with poor contrast enhancement. In patients with lymph node metastasis, the inguinal and iliac nodes were found to be enlarged and partial or totally without contrast enhancement. In general, edema was more extensive and tissue fibrosis progressed during the course of the disease in both types of lymphedema. On cross-sectional MRI it was possible to localize the water and observe other pathological changes such as fat deposition in the subcutaneous layer ( Fig. 1c), and it was therefore possible to recognize the disease stage in affected limbs. Discussion Although, all lymphostatic diseases result in lymphedema, the pathogenesis of lymphatic disorders is quite complicated. The anatomical changes in the lymphatic system (lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes) are closely related to its function, so that localization of the involved parts and characterization and functional analysis of the interrupted lymph flow are equally valuable in the diagnosis of lymphatic circulation disorders. In this clinical study, MRL with Gd-BOPTA as a contrast agent quickly and sufficiently visualized the lymphatic pathway and lymph nodes draining from the intracutaneous injection sites in lymphedematous limbs, and enabled both morphological and functional assessments of the lymphatic system. Contrast-enhanced MR images specifically depicted the lymphatic vessels in the limb with disturbance of lymph back flow but not the lymphatic vessels in healthy limbs. Contrast-enhanced lymphatic channels in affected limbs were visualized together with accumulation of edema fluid in the tissue. 9 Therefore, a lymph circulation disorder should be highly suspected when contrast-enhanced lymphatic vessels are visualized with this test. The specificity of the absorption and transportation of the contrast agent by the lymphatic system made possible visualization of the finely detailed morphological changes in lymphatic vessels as well as regional lymph nodes by high-resolution MR imaging. MRL clearly depicted lymph vessels with various morphological abnormalities, in both small solitary vessels (1 mm in diameter), and in networks of tortuous and dilated lymphatic trunks (10 mm in diameter). The quality of MRL imaging for mapping lymphatic patterns was comparable to that of direct
4 Lymphedema Treatment MR Lymphangiography Lymphatic System Liu, Zhang 69 Fig. 2 Dynamic images of enhanced lymph flow. (a) Observation of movement of contrast-enhanced flow (arrows) in a lymphedema limb. (b, c) Coronal postcontrast images of real-time record of comparison of nodal enhancement in edematous (right) and nonedematous (left) limbs in a series images. The wash-in curve was prolonged in the affected limb in contrast with quick wash-out curve in unaffected limb. lymphangiography with the use of an iodine oil contrast agent. The detection rate of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes with MRL was much higher than that found with lymphoscintigraphy. 10 MRL imaging was able to display distinct morphological changes in regional lymph nodes, and more structural abnormalities could be displayed by evaluating intranodal contrast-filling patterns. Intranodal pathology was indicated by a heterogeneous appearance, partial nodal enhancement, or irregularity in nodal outline, which could be the distinct characteristics in some types of primary 8,11 and secondary lymphedema. 12 Previous diagnostic approaches such as direct lymphangiography and lymphoscintigraphy may indicate the functional status of the lymphatic system and allow assessment of patency, but none of these techniques are capable of realtime lymph flow monitoring. Neither iodized oil contrast agents nor isotopically labeled tracers are able to measure enhanced lymph flow velocities in lymphatic vessels, because of the slow movement and slow absorption of the contrast agent, and the prolonged time (hours or days) involved in imaging. The present study showed that the rapid transportation of contrast agent by draining lymphatic vessels and regional lymph nodes during MRL allows consecutive and real-time evaluation of the transport function of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes within a reasonable length of time. Tracing the movement of enhanced flow within lymphatic vessels allowed quantitative assessment of abnormal lymph flow kinetics. Comparison of dynamic nodal enhancement between the edematous and contralateral limbs and analysis of the time signal intensity curves could clarify the delayed or decreased transport of lymph in individual nodes and
5 70 Lymphedema Treatment MR Lymphangiography Lymphatic System Liu, Zhang Fig. 3 (a) Postcontrast MR lymphangiogram displays significantly dilated lymphatic vessels (arrowheads) of the left lower limb in a patient with inguinal lymph nodal occupation. (b) Contrast-enhanced lymphatic vessels (arrowheads) of the right upper limb in contrast with single lymphatic (arrow) in the contralateral no edema arm on the MRL imaging in a woman after mastectomy. (c) Contrast-enhanced lymphatics ended at the distal third of the right lower leg (arrows) without visualized proximal channels in a patient with lymphedema after surgical treatment of endometrial carcinoma. Dilated lymphatic collectors were visualized in the left leg (arrowheads). MRL, magnetic resonance lymphangiography. allow quantitative assessment of abnormal nodal lymph flow kinetics. The combination of lymphatic vessel and lymph node images may then offer an integrated picture of an affected lymphatic system. Taking together the morphological observation of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes by MRL imaging made possible the classification of lymphatic anatomical abnormalities in primary lymphedema. 11 By accurately localizing the damage to the lymphatic system in secondary lymphedema, MRL could help in choosing the appropriate surgical (e.g., selecting a suitable vessel for lymphovenous anastomosis) or conservative treatment, and could also be used during follow-up for the evaluation of outcome after therapy. Contrast-enhanced 3D MRL not only demonstrated the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes, but also identified extralymphatic abnormalities such as the location of edema and other pathological changes resulting from stagnant lymph such as fat deposition and tissue fibrosis, and was also able to differentiate lymphedema from other types of edema. MRI has several potential advantages compared with lymphoscintigraphy, including higher spatial resolution enabling depiction of lymphatic channels, higher temporal resolution, 3D images, and the absence of ionizing radiation. MRL as currently used is safe and repeatable. No side effects have yet been found during or after the examination. It is suitable for diagnosis and the differential diagnosis of various types of chronic peripheral lymphedema, malignant lymphedema, venous edema, lymphovenous edema, lipedema, and other lymphatic vascular diseases. Like routine MRI examination, MRL should not be performed in patients with any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implants. The MRL technique still has limitations. Except for extremely dilated vessels in patients with lymphatic hyperplasia, MRL with Gd-BOPTA is unable to depict deep lymphatic system structures such as lumbar trunks, the cistern, and the thoracic duct. In conclusion, MRL is much more sensitive and accurate for detecting anatomical and functional abnormalities of the lymphatic system in contrast to the previous and currently used diagnostic methods. This new lymphatic system imaging test shows good application prospect in the microsurgical management of lymphedema. Funding Chinese Nature Science Foundation (Grant no , ); Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (Grant no ). References 1 Foldi E, Foldi M. Lymphostatic diseases. In: Foldi M, Foldi E, Kubik S. eds. Textbook of Lymphology. München: Elsevier GmbH; 2003: Szuba A, Shin WS, Strauss HW, Rockson S. The third circulation: radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymphedema. J Nucl Med 2003;44(1): Silvestri RC, Huseby JS, Rughani I, Thorning D, Culver BH. Respiratory distress syndrome from lymphangiography contrast medium. Am Rev Respir Dis 1980;122(4): Liu N, Wang C, Sun M. Noncontrast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging vs lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymph circulation disorders: A comparative study. J Vasc Surg 2005;41(1): Barrett T, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Imaging of the lymphatic system: new horizons. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2006;1(6): Liu NF, Lu Q, Wang CG, Zhou JG. Magnetic resonance imaging as a new method to diagnose protein losing enteropathy. Lymphology 2008;41(3): Dayan JH, Dayan E, Kagen A, et al. The use of magnetic resonance angiography in vascularized groin lymph node transfer: an anatomic study. J Reconstr Microsurg 2014;30(1): Liu NF, Lu Q, Jiang ZH, Wang CG, Zhou JG. Anatomic and functional evaluation of the lymphatics and lymph nodes in
6 Lymphedema Treatment MR Lymphangiography Lymphatic System Liu, Zhang 71 diagnosis of lymphatic circulation disorders with contrast magnetic resonance lymphangiography. J Vasc Surg 2009;49(4): Liu NF, Lu Q, Yan ZX. Lymphatic malformation is a common component of Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome. J Vasc Surg 2010; 52(6): Liu NF, Lu Q, Liu PA, Wu XF, Wang BS. Comparison of radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy and dynamic magnetic resonance lymphangiography for investigating extremity lymphoedema. Br J Surg 2010;97(3): Liu NF, Yan ZX, Wu XF. Classification of lymphatic-system malformations in primary lymphoedema based on MR lymphangiography. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2012;44(3): Liu N, Yan Z, Lu Q, Wang C. Diagnosis of inguinal lymph node metastases using contrast enhanced high resolution MR lymphangiography. Acad Radiol 2013;20(2):
European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
 European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery 44 (2012) 345e349 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery journal homepage: www.ejves.com
European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery 44 (2012) 345e349 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery journal homepage: www.ejves.com
Ning-Fei Liu, MD, PhD, a Qing Lu, MD, b Zhao-Hua Jiang, MD, PhD, a Chen-Guang Wang, MD, PhD, c and Jian-Guo Zhou, MD, a Shanghai, China
 Anatomic and functional evaluation of the lymphatics and lymph nodes in diagnosis of lymphatic circulation disorders with contrast magnetic resonance lymphangiography Ning-Fei Liu, MD, PhD, a Qing Lu,
Anatomic and functional evaluation of the lymphatics and lymph nodes in diagnosis of lymphatic circulation disorders with contrast magnetic resonance lymphangiography Ning-Fei Liu, MD, PhD, a Qing Lu,
Noncontrast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging vs lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymph circulation disorders: A comparative study
 Noncontrast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging vs lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymph circulation disorders: A comparative study Ningfei Liu, MD, PhD, a Chenguang Wang, MD, PhD, b and
Noncontrast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging vs lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymph circulation disorders: A comparative study Ningfei Liu, MD, PhD, a Chenguang Wang, MD, PhD, b and
Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
High-Resolution MR Lymphangiography in Patients with Primary and Secondary Lymphedema
 Lohrmann et al. MR Lymphangiog raphy of Patients with Lymphedem a Vascular Imaging Technical Innovation C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:556 561 0361 803X/06/1872 556 merican Roentgen Ray
Lohrmann et al. MR Lymphangiog raphy of Patients with Lymphedem a Vascular Imaging Technical Innovation C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:556 561 0361 803X/06/1872 556 merican Roentgen Ray
Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance Lymphography
 80 Invited Review Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance Lymphography Lionel Arrivé, MD 1 Sarah Derhy, MD 1 Sanaâ El Mouhadi, MD 1 Laurence Monnier-Cholley, MD 1 Yves Menu, MD 1 Corinne Becker, MD 2 1 Department
80 Invited Review Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance Lymphography Lionel Arrivé, MD 1 Sarah Derhy, MD 1 Sanaâ El Mouhadi, MD 1 Laurence Monnier-Cholley, MD 1 Yves Menu, MD 1 Corinne Becker, MD 2 1 Department
Dynamic MR Lymphangiography
 Dynamic MR Lymphangiography Rajesh Krishnamurthy, MD EB Singleton Department of Radiology, Texas Children s Hospital, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX Acknowledgement: Dr. Sheena Pimpalwar, MD Interventional
Dynamic MR Lymphangiography Rajesh Krishnamurthy, MD EB Singleton Department of Radiology, Texas Children s Hospital, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX Acknowledgement: Dr. Sheena Pimpalwar, MD Interventional
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND CLINICAL FINDINGS IN LOWER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA (LO): TOWARD A COMPREHENSIVE STAGING
 1 Lymphology 41 (2008) 1-10 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND CLINICAL FINDINGS IN LOWER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA (LO): TOWARD A COMPREHENSIVE STAGING A.P. Pecking, J.L. Albérini, M. Wartski, V. Edeline,
1 Lymphology 41 (2008) 1-10 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND CLINICAL FINDINGS IN LOWER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA (LO): TOWARD A COMPREHENSIVE STAGING A.P. Pecking, J.L. Albérini, M. Wartski, V. Edeline,
THE ROLE OF LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF LYMPHEDEMA IN TURNER SYNDROME
 123 Lymphology 42 (2009) 123-129 THE ROLE OF LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF LYMPHEDEMA IN TURNER SYNDROME C. Bellini, E. Di Battista, F. Boccardo, C. Campisi, G. Villa, G. Taddei, C. Traggiai,
123 Lymphology 42 (2009) 123-129 THE ROLE OF LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF LYMPHEDEMA IN TURNER SYNDROME C. Bellini, E. Di Battista, F. Boccardo, C. Campisi, G. Villa, G. Taddei, C. Traggiai,
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE
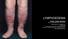 LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA. John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA
 When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
MICROSURGERY. Predictive Lymphatic Mapping
 MICROSURGERY A Method for Mapping Lymphatic Channels in Patients With Advanced Unilateral Lymphedema Using Indocyanine Green Lymphography Makoto Mihara, MD,* Yukio Seki, MD,* Hisako Hara, MD,* Takuya Iida,
MICROSURGERY A Method for Mapping Lymphatic Channels in Patients With Advanced Unilateral Lymphedema Using Indocyanine Green Lymphography Makoto Mihara, MD,* Yukio Seki, MD,* Hisako Hara, MD,* Takuya Iida,
2007 ICL SHANGHAI 24/03/2013
 Background Intradermal Lymphoscintigraphy: Technical Improvement and an Interpretation of the Pathological Patterns on Clinical Management of Severe Stage Lymphoedema. Girolamo Tartaglione, MD Department
Background Intradermal Lymphoscintigraphy: Technical Improvement and an Interpretation of the Pathological Patterns on Clinical Management of Severe Stage Lymphoedema. Girolamo Tartaglione, MD Department
Course Objectives. Circulatory system. Understand the basic design of the lymphatic system
 Lymphedema: What Every Healthcare Practitioner Needs to Know Debbie Chasse DPT, WCS, CLT-LANA www.functionabilitypt.com Understand the basic design of the lymphatic system Course Objectives Circulatory
Lymphedema: What Every Healthcare Practitioner Needs to Know Debbie Chasse DPT, WCS, CLT-LANA www.functionabilitypt.com Understand the basic design of the lymphatic system Course Objectives Circulatory
Appearance And Visibility Of The Thoracic Duct On Computed Tomography Of The Chest
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 Appearance And Visibility Of The Thoracic Duct On Computed Tomography Of The Chest J Gossner Citation J Gossner. Appearance And Visibility
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 Appearance And Visibility Of The Thoracic Duct On Computed Tomography Of The Chest J Gossner Citation J Gossner. Appearance And Visibility
The Lymphatic System. Oedema (Edema) Lymphoedema (Lymphedema)
 The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
Lymphoscintigraphy of the Upper Extremities
 Lymphoscintigraphy of the Upper Extremities MJ de Haas, Meander Medical Centre Amersfoort (Retired) 1. Introduction Lymphoedema is a chronic, progressive, and often debilitating condition. Primary lymphoedema
Lymphoscintigraphy of the Upper Extremities MJ de Haas, Meander Medical Centre Amersfoort (Retired) 1. Introduction Lymphoedema is a chronic, progressive, and often debilitating condition. Primary lymphoedema
MR Lymphography of Lymphatic Vessels in Lower Extremity with Gynecologic Oncology-Related Lymphedema
 MR Lymphography of Lymphatic Vessels in Lower Extremity with Gynecologic Oncology-Related Lymphedema Qing Lu 1, Zachary Delproposto 2, Alice Hu 3, Christine Tran 4, Ningfei Liu 5, Yulai Li 1, Jianrong
MR Lymphography of Lymphatic Vessels in Lower Extremity with Gynecologic Oncology-Related Lymphedema Qing Lu 1, Zachary Delproposto 2, Alice Hu 3, Christine Tran 4, Ningfei Liu 5, Yulai Li 1, Jianrong
Differentiation of High and Low Output Lymphatic Failure Using Qualitative Lymphangioscintigraphy
 2015 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.15-00034 Original Article Differentiation of High and Low Output Lymphatic Failure Using Qualitative Lymphangioscintigraphy Kotaro Suehiro, MD, Noriyasu
2015 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.15-00034 Original Article Differentiation of High and Low Output Lymphatic Failure Using Qualitative Lymphangioscintigraphy Kotaro Suehiro, MD, Noriyasu
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Postoperative Chylothorax: the Use of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography and Thoracic Duct Embolization
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:182-186 Postoperative Chylothorax: the Use of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography and Thoracic Duct Embolization Chae Woon Lee, Hyun Jung Koo, Ji Hoon
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:182-186 Postoperative Chylothorax: the Use of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography and Thoracic Duct Embolization Chae Woon Lee, Hyun Jung Koo, Ji Hoon
Lymphoscintigraphy to confirm the diagnosis of lymphedema
 Lymphoscintigraphy to confirm the diagnosis of lymphedema clinical Peter J. Golueke, MD, Robert A. Montgomery, MD, John D. Petronis, MD,* Stanley L. Minken, MD, Bruce A. Perler, MD, and G. Melville Williams,
Lymphoscintigraphy to confirm the diagnosis of lymphedema clinical Peter J. Golueke, MD, Robert A. Montgomery, MD, John D. Petronis, MD,* Stanley L. Minken, MD, Bruce A. Perler, MD, and G. Melville Williams,
Popliteal Node Visualization During Standard Pedal Lymphoscintigraphy for a Swollen Limb Indicates Impaired Lymph Drainage
 Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Burnand et al. Popliteal Nodes in Lymphoscintigraphy Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Katherine M. Burnand 1 Daphne M. Glass
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Burnand et al. Popliteal Nodes in Lymphoscintigraphy Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Katherine M. Burnand 1 Daphne M. Glass
CHARACTERIZATION OF CONGENITAL VASCULAR MALFORMATION IN THE EXTREMITIES USING WHOLE BODY BLOOD POOL SCINTIGRAPHY AND LYMPHSCINTIGRAPHY
 77 Lymphology 42 (2009) 77-84 CHARACTERIZATION OF CONGENITAL VASCULAR MALFORMATION IN THE EXTREMITIES USING WHOLE BODY BLOOD POOL SCINTIGRAPHY AND LYMPHSCINTIGRAPHY Y.H. Kim, J.Y. Choi, Y.W. Kim, D.I.
77 Lymphology 42 (2009) 77-84 CHARACTERIZATION OF CONGENITAL VASCULAR MALFORMATION IN THE EXTREMITIES USING WHOLE BODY BLOOD POOL SCINTIGRAPHY AND LYMPHSCINTIGRAPHY Y.H. Kim, J.Y. Choi, Y.W. Kim, D.I.
REPEATED INTRANODAL LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHATIC LEAKAGE
 59 Lymphology 48 (2015) 59-63 REPEATED INTRANODAL LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHATIC LEAKAGE S. Kariya, M. Nakatani, R. Yoshida, Y. Ueno, A. Komemushi, N. Tanigawa Department of Radiology,
59 Lymphology 48 (2015) 59-63 REPEATED INTRANODAL LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHATIC LEAKAGE S. Kariya, M. Nakatani, R. Yoshida, Y. Ueno, A. Komemushi, N. Tanigawa Department of Radiology,
Primary lower limb lymphoedema: classification with non-contrast MR lymphography
 Primary lower limb lymphoedema: classification with non-contrast MR lymphography Lionel Arrivé, S. Derhy, B. Dahan, S. El Mouhadi, L. Monnier-Cholley, Y. Menu, C. Becker To cite this version: Lionel Arrivé,
Primary lower limb lymphoedema: classification with non-contrast MR lymphography Lionel Arrivé, S. Derhy, B. Dahan, S. El Mouhadi, L. Monnier-Cholley, Y. Menu, C. Becker To cite this version: Lionel Arrivé,
LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY IN CHILDREN*
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 177. LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY IN CHILDREN* BY MALCOLM H. GOUGH From the Department of Surgery, St. Thomas's Hospital Medical School, London Lymphangiography was first introduced by
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 177. LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY IN CHILDREN* BY MALCOLM H. GOUGH From the Department of Surgery, St. Thomas's Hospital Medical School, London Lymphangiography was first introduced by
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad
 CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
The Role of Radionuclide Lymphoscintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Lymphedema of the Extremities
 The Role of Radionuclide Lymphoscintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Lymphedema of the Extremities Poster No.: C-1229 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Osher 1, A. Pallas
The Role of Radionuclide Lymphoscintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Lymphedema of the Extremities Poster No.: C-1229 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Osher 1, A. Pallas
An Arteriovenous Malformation in the Suprapatellar Fat Pad of the Knee associated with Klippel-Trenaunay- Weber Syndrome: A Case Report 1
 n rteriovenous Malformation in the Suprapatellar Fat Pad of the Knee associated with Klippel-Trenaunay- Weber Syndrome: Case Report 1 Mi Hyun Park, M.D., Soon Tae Kwon, M.D., yung Seok Shin, M.D., Young
n rteriovenous Malformation in the Suprapatellar Fat Pad of the Knee associated with Klippel-Trenaunay- Weber Syndrome: Case Report 1 Mi Hyun Park, M.D., Soon Tae Kwon, M.D., yung Seok Shin, M.D., Young
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Kentaro Tanaka, 1 Hiroki Mori, 1 Mutsumi Okazaki, 1 Aya Nishizawa, 2 and Hiroo Yokozeki Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 259326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/259326 Case Report Long-Term Treatment Outcome after Only Popliteal Lymph Node Dissection for
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 259326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/259326 Case Report Long-Term Treatment Outcome after Only Popliteal Lymph Node Dissection for
IDGH RESOLUTION UNENHANCED COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH SWOLLEN LEGS
 121 Lymphology 35 (2002) 121-128 IDGH RESOLUTION UNENHANCED COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH SWOLLEN LEGS E.D. Monnin-Delhom, B.P. Gallix, C. Achard, J.M. Bruel, C. Janbon Service d'imagerie Medicale
121 Lymphology 35 (2002) 121-128 IDGH RESOLUTION UNENHANCED COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH SWOLLEN LEGS E.D. Monnin-Delhom, B.P. Gallix, C. Achard, J.M. Bruel, C. Janbon Service d'imagerie Medicale
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: 01/23/2019
 Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L.
 Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure
 When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
Radionuclide detection of sentinel lymph node
 Radionuclide detection of sentinel lymph node Sophia I. Koukouraki Assoc. Professor Department of Nuclear Medicine Medicine School, University of Crete 1 BACKGROUND The prognosis of malignant disease is
Radionuclide detection of sentinel lymph node Sophia I. Koukouraki Assoc. Professor Department of Nuclear Medicine Medicine School, University of Crete 1 BACKGROUND The prognosis of malignant disease is
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University
 Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure Comments The speaker Alice Fung, MD Has relevant financial relationships to disclose. Received honorarium from (Guerbet). This individual
Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure Comments The speaker Alice Fung, MD Has relevant financial relationships to disclose. Received honorarium from (Guerbet). This individual
Microvascular Research
 Microvascular Research 77 (2009) 335 339 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Microvascular Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ymvre Regular Article MR imaging of the lymphatic system
Microvascular Research 77 (2009) 335 339 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Microvascular Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ymvre Regular Article MR imaging of the lymphatic system
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy
 Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: Zhanghq58@126.com Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308 Mobile:13761809799
Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: Zhanghq58@126.com Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308 Mobile:13761809799
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
QUESTIONS for the examination in surgery for 4 th -year students of the Faculty of foreign students
 QUESTIONS for the examination in surgery for 4 th -year students of the Faculty of foreign students 1. The main principles of surgical deontology and its founders. 2. Acute appendicitis. Anatomico-physiological
QUESTIONS for the examination in surgery for 4 th -year students of the Faculty of foreign students 1. The main principles of surgical deontology and its founders. 2. Acute appendicitis. Anatomico-physiological
From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift
 Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging
 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema
 Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema Nathalie Johnson,MD,FACS Medical Director, Legacy Cancer Institute and Breast Health Centers Portland,Oregon Objectives for Learning Understand
Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema Nathalie Johnson,MD,FACS Medical Director, Legacy Cancer Institute and Breast Health Centers Portland,Oregon Objectives for Learning Understand
CASE STUDY. Potential conflict of interest:
 CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
Vascularized Lymph Node Transfer From Thoracodorsal Axis for Congenital and Post Filarial Lymphedema of the Lower Limb
 CASE REPORT Vascularized Lymph Node Transfer From Thoracodorsal Axis for Congenital and Post Filarial Lymphedema of the Lower Limb HARI VENKATRAMANI, MCh, DNB, EDHS,* SENTHIL KUMARAN, MCh, SHIVANNAIAH
CASE REPORT Vascularized Lymph Node Transfer From Thoracodorsal Axis for Congenital and Post Filarial Lymphedema of the Lower Limb HARI VENKATRAMANI, MCh, DNB, EDHS,* SENTHIL KUMARAN, MCh, SHIVANNAIAH
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
FDG PET/CT STAGING OF LUNG CANCER. Dr Shakher Ramdave
 FDG PET/CT STAGING OF LUNG CANCER Dr Shakher Ramdave FDG PET/CT STAGING OF LUNG CANCER FDG PET/CT is used in all patients with lung cancer who are considered for curative treatment to exclude occult disease.
FDG PET/CT STAGING OF LUNG CANCER Dr Shakher Ramdave FDG PET/CT STAGING OF LUNG CANCER FDG PET/CT is used in all patients with lung cancer who are considered for curative treatment to exclude occult disease.
IPC Use in Lymphedema: Physiological Considerations
 IPC Use in Lymphedema: Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD, Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences, Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale Florida mayrovit@nova.edu ICC
IPC Use in Lymphedema: Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD, Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences, Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale Florida mayrovit@nova.edu ICC
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012. Lymph Nodes. John McGrath
 Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Emerging Referral Patterns for Whole-Body Diffusion Weighted Imaging (WB-DWI) in an Oncology Center
 Emerging Referral Patterns for Whole-Body Diffusion Weighted Imaging (WB-DWI) in an Oncology Center Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Petralia 1, G. Conte 1, S.
Emerging Referral Patterns for Whole-Body Diffusion Weighted Imaging (WB-DWI) in an Oncology Center Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Petralia 1, G. Conte 1, S.
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours. Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany
 PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
Noninvasive evaluation of the swollen extremity: Experiences with 190 lymphoscintigraphic examinations.
 Noninvasive evaluation of the swollen extremity: Experiences with 190 lymphoscintigraphic examinations. Peter Gloviczki, M_D, David Calcagno, MD, Alexander Schirger, MD, Peter C. Pairolero, MD, Kenneth
Noninvasive evaluation of the swollen extremity: Experiences with 190 lymphoscintigraphic examinations. Peter Gloviczki, M_D, David Calcagno, MD, Alexander Schirger, MD, Peter C. Pairolero, MD, Kenneth
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth
 Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Management of Lower Limb Lymphoedema in the United Kingdom
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 31, 311 315 (6) doi:1.116/j.ejvs.5.9.17, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on Management of Lower Limb Lymphoedema in the United Kingdom A. Tiwari, F. Myint and
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 31, 311 315 (6) doi:1.116/j.ejvs.5.9.17, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on Management of Lower Limb Lymphoedema in the United Kingdom A. Tiwari, F. Myint and
What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence
 What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence North of England Cancer Network Lymphoedema Conference - A problem shared 8 March 2013 Dr Andrew Hughes Consultant in Palliative Medicine Outline 1) What is
What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence North of England Cancer Network Lymphoedema Conference - A problem shared 8 March 2013 Dr Andrew Hughes Consultant in Palliative Medicine Outline 1) What is
Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions
 Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Malignancy is a life-threatening condition in which tumor cells are of a highly invasive character and penetrate normal organs and exhibit an obstinate resistance against cancer
Chapter 1 Introduction Malignancy is a life-threatening condition in which tumor cells are of a highly invasive character and penetrate normal organs and exhibit an obstinate resistance against cancer
A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management.
 A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management. Poster No.: C-1030 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. J. Ley, E.
A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management. Poster No.: C-1030 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. J. Ley, E.
Prenatal and Postnatal Evaluation of Lymphatic Disorders
 Prenatal and Postnatal Evaluation of Lymphatic Disorders David M Biko, MD Director, Section of Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Imaging Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Assistant Professor of Radiology
Prenatal and Postnatal Evaluation of Lymphatic Disorders David M Biko, MD Director, Section of Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Imaging Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Assistant Professor of Radiology
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
What is Lymphedema? Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels are not formed completely or malformed
 Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
CaresiaTM. Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners
 CaresiaTM M A N U F A C T U R E D B Y S O L A R I S Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners Table of Contents 2 3 4 6 8 10 11 Contact Information About Caresia Upper Extremity Garments Lower Extremity Garments Donning
CaresiaTM M A N U F A C T U R E D B Y S O L A R I S Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners Table of Contents 2 3 4 6 8 10 11 Contact Information About Caresia Upper Extremity Garments Lower Extremity Garments Donning
Melanoma. Kaushik Mukherjee MD A. Scott Pearson MD
 Melanoma Kaushik Mukherjee MD A. Scott Pearson MD Disclosures You still have to study Not all inclusive No Western blots Extensive use of Google Image Search and Sabiston Melanoma Basics 8 th most common
Melanoma Kaushik Mukherjee MD A. Scott Pearson MD Disclosures You still have to study Not all inclusive No Western blots Extensive use of Google Image Search and Sabiston Melanoma Basics 8 th most common
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D20 Statement on Peripheral Venous Ultrasound
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D20 Statement on Peripheral Venous Ultrasound Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D20 Statement on Peripheral Venous Ultrasound Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Imaging of the cisterna chyli on PET-CT in patients with known malignancy: Report of two cases
 Imaging of the cisterna chyli on PET-CT in patients with known malignancy: Report of two cases Natalie Burns, B.S., Jason Barksdale, M.D., Linh Ho, M.D., and Patrick M. Colletti, M.D. Citation: Burns N,
Imaging of the cisterna chyli on PET-CT in patients with known malignancy: Report of two cases Natalie Burns, B.S., Jason Barksdale, M.D., Linh Ho, M.D., and Patrick M. Colletti, M.D. Citation: Burns N,
4. WHY a Lymphovenous anastomosis can be indicated in Lymphedema?
 LYMPHOVENOUS ANASTOMOSIS TECHNIQUE ( LVA / MLVA / MLVLA ). Alessandro Busetto Wolfsberg March 20-21, 2018 1. Speaer s agreement 2. Title. The aim of our communication is to describe and compare the various
LYMPHOVENOUS ANASTOMOSIS TECHNIQUE ( LVA / MLVA / MLVLA ). Alessandro Busetto Wolfsberg March 20-21, 2018 1. Speaer s agreement 2. Title. The aim of our communication is to describe and compare the various
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema
 CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema Hisako Hara, MD, and Makoto Mihara, MD Department of Lymphatic and Reconstructive Surgery, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Saitama, Japan
CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema Hisako Hara, MD, and Makoto Mihara, MD Department of Lymphatic and Reconstructive Surgery, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Saitama, Japan
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 65. Benign Hepatic Masses
 65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll.
 Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll. For the Department of Vascular Surgery and Kidney Transplantation University Hospital of Strasbourg, FRANCE Popliteal artery entrapment: misdiagnosed Epidemiology Prevalence:
Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll. For the Department of Vascular Surgery and Kidney Transplantation University Hospital of Strasbourg, FRANCE Popliteal artery entrapment: misdiagnosed Epidemiology Prevalence:
Imaging of Hearing Loss
 Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks
 Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Vol. 28 No Best New Investigator Award: Development Update: A Promising Surgical Procedure For Treating Secondary Lymphedema
 Vol. 28 No.1-2014 Best New Investigator Award: Development Update: A Promising Surgical Procedure For Treating Secondary Lymphedema By: Michael Paukshto, PhD; Catarina Hadamitzky, MD, Hannover Medical
Vol. 28 No.1-2014 Best New Investigator Award: Development Update: A Promising Surgical Procedure For Treating Secondary Lymphedema By: Michael Paukshto, PhD; Catarina Hadamitzky, MD, Hannover Medical
The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations
 The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu
The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings
 Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
RECTAL CARCINOMA: A DISTANCE APPROACH. Stephanie Nougaret
 RECTAL CARCINOMA: A DISTANCE APPROACH Stephanie Nougaret stephanienougaret@free.fr Despite the major improvements that have been made due to total mesorectal excision (TME) management of rectal cancer
RECTAL CARCINOMA: A DISTANCE APPROACH Stephanie Nougaret stephanienougaret@free.fr Despite the major improvements that have been made due to total mesorectal excision (TME) management of rectal cancer
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
CLASSIFICATION OF LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND RELEVANCE TO SURGICAL INDICATION FOR LYMPHATICOVENOUS ANASTOMOSIS IN UPPER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA
 155 Lymphology 44 (2011) 155-167 CLASSIFICATION OF LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND RELEVANCE TO SURGICAL INDICATION FOR LYMPHATICOVENOUS ANASTOMOSIS IN UPPER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA T. Mikami, M. Hosono, Y. Yabuki, Y.
155 Lymphology 44 (2011) 155-167 CLASSIFICATION OF LYMPHOSCINTIGRAPHY AND RELEVANCE TO SURGICAL INDICATION FOR LYMPHATICOVENOUS ANASTOMOSIS IN UPPER LIMB LYMPHEDEMA T. Mikami, M. Hosono, Y. Yabuki, Y.
SPECT/CT in Endocrine Diseases and Dosimetry
 SPECT/CT in Endocrine Diseases and Dosimetry Heather A. Jacene, MD Division of Nuclear Medicine Russell H. Morgan Dept. of Radiology and Radiological Science Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD Disclosures
SPECT/CT in Endocrine Diseases and Dosimetry Heather A. Jacene, MD Division of Nuclear Medicine Russell H. Morgan Dept. of Radiology and Radiological Science Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD Disclosures
Gynecologic Oncology
 Gynecologic Oncology 127 (2012) 638 642 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Gynecologic Oncology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno Would complex decongestive therapy reveal
Gynecologic Oncology 127 (2012) 638 642 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Gynecologic Oncology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno Would complex decongestive therapy reveal
VENOUS DRAINAGE O US F UPPER UPPER LIM B BY dr.fahad Ullah
 VENOUS DRAINAGE OF UPPER LIMB BY dr.fahad Ullah Venous drainage of the supper limb The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm, forearm and hand It can anatomically be divided
VENOUS DRAINAGE OF UPPER LIMB BY dr.fahad Ullah Venous drainage of the supper limb The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm, forearm and hand It can anatomically be divided
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Sentinel Node Localisation of Melanoma
 Sentinel Node Localisation of Melanoma V Bongers, Diakonessenhuis, Utrecht 1. Introduction A melanoma is mostly a malignancy of the skin. The sentinel lymph node (SLN) concept of sequential progression
Sentinel Node Localisation of Melanoma V Bongers, Diakonessenhuis, Utrecht 1. Introduction A melanoma is mostly a malignancy of the skin. The sentinel lymph node (SLN) concept of sequential progression
Venous drainage of the lower limb
 Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
ADVANCED IMAGING TECHNOLOGIES FOR MAPPING CADAVERIC LYMPHATIC ANATOMY: MAGNETIC RESONANCE AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY
 126 Lymphology 41 (2008) 126-130 ADVANCED IMAGING TECHNOLOGIES FOR MAPPING CADAVERIC LYMPHATIC ANATOMY: MAGNETIC RESONANCE AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY W.R. Pan, W.M. Rozen, J. Stretch, B.
126 Lymphology 41 (2008) 126-130 ADVANCED IMAGING TECHNOLOGIES FOR MAPPING CADAVERIC LYMPHATIC ANATOMY: MAGNETIC RESONANCE AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY W.R. Pan, W.M. Rozen, J. Stretch, B.
Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
Melanoma Surgery Update James R. Ouellette, DO FACS Premier Health Cancer Institute Wright State University Chief, Surgical Oncology Division
 Melanoma Surgery Update 2018 James R. Ouellette, DO FACS Premier Health Cancer Institute Wright State University Chief, Surgical Oncology Division Surgery for Melanoma Mainstay of treatment for potentially
Melanoma Surgery Update 2018 James R. Ouellette, DO FACS Premier Health Cancer Institute Wright State University Chief, Surgical Oncology Division Surgery for Melanoma Mainstay of treatment for potentially
