Title Management of Inoculation Injuries Policy
|
|
|
- Laurence Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Document Control Title Author Directorate Nursing Date Version Issued 1.0 March April May May Sept October Nov 2008 Status Revision Revision Final Revision Revision Revision Author s job title Lead Nurse Infection Prevention and Control Department Infection Prevention & Control Comment / Changes / Approval Approved by Infection Prevention and Control Committee. Revised in line with NHS Litigation Authority Inspection. Approved by Infection Prevention and Control Committee , Health and Safety Committee and final Approval by Clinical Services Executive Committee. Ratified by Trust Board. Published on Tarkanet following Board ratification. Final amends to ensure corporate identity requirements. Change of PEP medication. Insertion of quick reference guide to Appendix B of the policy, this is already present in the Inoculation Injury Boxes out in clinical departments. 2.4 Jan 2010 Revision Amendments for clarity of compliance with NHSLA requirements to 12.1 approved at Team meeting of Hyperlinks and books marks to Appendices added. 2.5 March May Dec 2011 Revision Revision Revision Addition of PEP to definitions list. Approved at team meeting 4/3/2010. Minor amendments by Corporate Affairs to document control report, formatting for document map navigation. Harmonisation of policy for Northern and Eastern localities of NDHT inc. Community services in Exeter East and Mid Devon. Harmonised policy as a result of the merging of Northern Devon Healthcare NHS Trust and NHS Devon community services. Approved by Northern Infection Prevention & Control Committee on following consultation. A summary of key issues and differences is on page 3. The monitoring section has been strengthened as a result of revised NHSLA requirements. Also added a training section (7). 3.0 Feb 2012 Final Approved by Northern Infection Prevention & Control Committee (NIPCC) on 07/02/12 following consultation at NIPCC 06/12/11 and EIPCC 13/12/11. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 1 of 26
2 3.1 June June August Dec March 2015 Revision Revision Revision Revision Revision Minor revisions only. Approval at Infection Prevention and Control Team meeting on 14/6/12 Minor revisions only. Approval at Infection Prevention and Control Team meeting on 4 th June Minor amendments by Corporate Governance to document control report and preparation for publishing. Amendment to post exposure prophylaxis Appendix C. Link to consent policy added. Blood bottles to be used for staff in Eastern areas added. Approval at Infection Prevention and Control Committee meeting on 6 th January Update of format to new trust template Out-dated NHSLA standard removed 4.0 Sept Final Update of format to new Trust template. Updates to contact 2017 details Main Contact Infection Prevention& Control Team Tel: Direct Dial North Devon District Hospital Raleigh Park Barnstaple, EX31 4JB Lead Director Director of Nursing Superseded Documents v3.5 Issue Date Review Date September 2017 September 2020 Consulted with the following stakeholders: Infection Prevention & Control Committee Approval and Review Process Infection Prevention & Control Committee Review Cycle Three years Local Archive Reference G:\ Local Path \IC Manual-Policies\New Templates from 2015\Management of Inoculation Injuries Policy Filename Management of Inoculation Policy v4.0 September 2017 Policy categories for Trust s internal website (Bob) Infection Prevention & Control Occupational Health Tags for Trust s internal website (Bob) injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 2 of 26
3 CONTENTS Document Control Purpose Definitions... 4 Inoculation injury... 4 Donor 5 Recipient 5 Sharps 5 Body fluids 5 Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)... 5 High risk injury... 5 Low risk injury Responsibilities... 6 Role of the Director of Nursing... 6 The Infection Prevention and Control Committee... 6 Ward/ Departmental Managers... 6 Infection Prevention and Control Team... 6 Clinical Staff 6 Role of Link Practitioners (ICLPs)/ Nurses... 7 Role of Assistant Directors of Operations... 7 Role of Divisional Nurses... 7 Role of Occupational Health (OH)... 7 Role of Emergency Department (ED)... 8 Role of the Consultant Medical Microbiologist... 8 Role of the employee Contacting the Infection Prevention and Control Team Staff Injury - Inoculation Injury Advice Line... 8 Staff Injury - Immediate Action following Injury or Splash... 8 Patient or Visitor Injury Immediate Action following Injury or Splash... 9 Human Bites... 9 Major trauma/bomb blast victims The Person to Whom the Incident has been reported Post Exposure Treatment / Prophylaxis of HIV (PEP) and Hepatitis B Follow up of Injured Person Training requirements Monitoring Compliance with and the Effectiveness of the Policy Standards/ Key Performance Indicators Equality Impact Assessment References Associated Documentation Appendix A: Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids Assessment Appendix B: Inoculation Quick Reference Guide injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 3 of 26
4 Appendix C: Post Exposure Prophylaxis Appendix D: Checklist for Northern Locality: Occupational Health and Emergency Department: Purpose This document sets out Northern Devon Healthcare NHS Trust s system for the immediate attention and management of inoculation injuries, whether caused by a percutaneous or splash exposure injury. It provides a robust framework to ensure a consistent approach across the whole organisation, and supports our statutory duties as set out in the NHS Constitution. The purpose of this document is to guide staff, both the injured person and their manager, on what to do in the event of an inoculation injury. Guidance is also given on correct management of patients, including personnel of public and voluntary services, who have received inoculation injuries and present to emergency departments or are already under in-patient healthcare. The policy applies to all Trust, Locum, Agency and Sodexo staff working within the Trust. Implementation of this policy will ensure that: The risk of acquisition of a blood borne virus is assessed rapidly. Post exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is initiated as rapidly as possible following the injury with the aim of that being within the first hour, following an informed consenting process. The need for Hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccination is assessed and given for the unvaccinated or vaccine non-responders. Staff are directed to the Prevention of Inoculation Injury Policy for advice on prevention of needlestick and sharps injuries, also available on BOB in the intranet pages 2. Definitions Inoculation injury Inoculation injury describes all incidents in which any of the following occur and where there is exposure to blood/ body fluids resulting from Percutaneous injury (from needles, instruments, bone fragments, bites which break the skin). Splash exposure injury via broken skin (e.g. abrasions, cuts, eczema) or via mucous membranes, including the eye. Exposure to blood/bodily fluids following decontamination failure of invasive equipment e.g. instruments, needles, scopes etc. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 4 of 26
5 Donor Refers to the person whose blood or body fluids may have been transferred to another person Recipient Refers to the person who may have been contaminated with blood or body fluids from another person Sharps Are needles, blades, scalpels, knives, lancets and other sharp instruments contaminated with blood or body fluids Body fluids High risk body fluids: blood, amniotic fluids, vaginal secretions, semen, human breast milk, cerebrospinal fluid, peritoneal fluid, pleural fluid, synovial fluid, saliva in association with dentistry, unfixed tissues or organs, pericardial fluid, wound or tissue fluids, saliva in association with dentristy, any low risk body fluids visibly contaminated with blood. Low risk body fluids: urine, vomit, faeces, sputum, saliva; unless visibly contaminated with blood. If blood stained it should be considered as a high risk. Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) is the drug treatment given following an inoculation injury with blood suspected to contain a blood borne virus (BBV), notably Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). High risk injury An injury involving blood or high risk body fluid known or suspected to carry blood borne virus (BBV) or from an individual from a high risk group where the chance of BBV carriage is elevated. Low risk injury An injury involving blood or high risk body fluid not known or suspected to carry a BBV. This Trustwide policy ratified by the Trust Board is a corporate framework document that enables staff to adopt safe and effective working practice. Any local policy must reflect the main policy document. All other Infection Prevention and Control policies in the Manual on BOB fall under this framework document injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 5 of 26
6 3. Responsibilities Role of the Director of Nursing The Director or Nursing is responsible for: Acting as a second point of contact to support Ensuring that a replacement main contact is identified should the original author be re-deployed or leave the organisation The Infection Prevention and Control Committee Monitoring compliance with the policy Ensuring that the policy is approved after review and prior to publishing Ward/ Departmental Managers The Ward/ Department Manager is responsible for implementation of this policy in their area. In particular, for ensuring that Inoculation Quick Reference Guide is available for staff in the event of injury, and for ensuring that immediate on ward/department management of the case is carried out. Normal practice will be to ensure that all inoculation incidents are assessed with immediate action taken on the ward/dept and any high risk incidents (where the donor blood is known or suspected to be carrying HIV,) are sent for immediate management in Emergency Department (ED), having pre-alerted ED by telephone. In incidents where Hepatitis B or another blood borne infection e.g. malaria is known or suspected to be involved, the manager will ensure prompt attention (within 24 hours) is given to the member of staff by the ED, Occupational Health or MIU. In all cases the manager is responsible for informing Occupational Health. Infection Prevention and Control Team The Infection Prevention and Control Team undertake to provide education and clarification to support the utilisation of this policy when requested to do so by Clinical or Facilities staff and managers. Clinical Staff It is the responsibility of all Trust Clinical Staff to follow the guidance contained in this Policy and report any problems with compliance to their line manager. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 6 of 26
7 Role of Link Practitioners (ICLPs)/ Nurses The role of ICLPs is to provide a focus on wards, other clinical settings and for community teams working in patient s homes forwarding key aspects of the Infection Prevention and Control programme. In particular they are responsible for undertaking monthly hand hygiene audits and other relevant audit work as identified and agreed through the Infection Prevention & Control Committees Role of Assistant Directors of Operations Assistant directors of operations will ensure that infection prevention & control objectives from the Infection Prevention & Control annual plan are incorporated into Divisional action plans. Assistant directors of operations are responsible for ensuring that systems are in place to ensure that Infection Prevention and Control policies, practices and guidance are carried out reliably within their area of responsibility; local investigation of healthcare associated infections and highlighting areas of practice or the environment which present a risk to patient safety. They are also responsible for setting a good example of infection prevention practice, and challenging poor practice. Role of Divisional Nurses Are accountable for Infection Prevention and Control in wards, departments and community teams, are key role models for good infection prevention practice and have responsibility for maintaining standards of Infection Prevention and Control practice. Also for the implementation and communication of Infection Prevention and Control initiatives and surveillance results; ensuring the clinical environment is safe and maintained to a high standard of cleanliness. Role of Occupational Health (OH) The Occupational Health Team based at Barnstaple Health Centre for the Northern Locality will, staffing permitting, provide assessment, management and follow up of each injured member of staff injury during office hours. The Occupational Health Team based at RD&E for the Eastern Locality will during opening hours be the first point of contact for management of inoculation injury cases. The OH Teams will provide a hotline with answerphone message for guidance out of hours and when the OH advisors are unable to answer the phone. The OH teams will provide on request to staff advice and clarification by phone on any inoculation injury policy or procedural issue. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 7 of 26
8 Role of Emergency Department (ED) ED will provide immediate assessment and management for patients (including personnel of public and voluntary services) who have sustained inoculation injury. Follow up will be undertaken by the patient s GP on receipt of relevant details from ED. ED at NDDH and in RD&E will provide HIV PEP following a risk factor assessment. ED will ensure that a consent process equivalent to that outlined in this policy is completed prior to initiation of HIV PEP. Role of the Consultant Medical Microbiologist The Consultant Medical Microbiologist on call will support ED when cases of particular uncertainty occur following their risk assessment of inoculation injured staff or patients. They will provide advice to Occupational Health and ED staff on the need to administer HIV PEP and Hepatitis B vaccination courses when requested. Role of the employee To report any inoculation injury or unsafe systems that could endanger staff, patients or visitors. To co-operate with employer and other relevant healthcare professional should an injury occur 4. Contacting the Infection Prevention and Control Team The Infection Prevention and Control Team can be contacted in hours on (ext 2680 internal at North Devon District Hospital), via bleep 011 or out of hours by contacting the on-call Medical Microbiologist via North Devon District Hospital switchboard. 5. Staff Injury - Inoculation Injury Advice Line An Inoculation Injury Advice Line with a recorded message outlining what happens following an injury is available on the following numbers: Northern Locality Occupational Health Team Eastern Locality Occupational Health Team Staff Injury - Immediate Action following Injury or Splash Any recipient of a percutaneous or exposure inoculation injury must immediately: Allow the area to bleed if relevant. Do not suck or squeeze affected area. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 8 of 26
9 Wash the affected area with soap and running water or rinse the area with copious amounts of water whichever is most appropriate. Cover affected area with waterproof plaster, if appropriate. Report the incident to the person in charge of you at that time. Contact Inoculation Injury Advice line (see 5.1). Complete an incident report (Datixweb or Incident Report Form) within the remaining period of the shift in which the injury occurs. Patient or Visitor Injury Immediate Action following Injury or Splash Where a patient or visitor is the recipient, the person in charge of that area must immediately: Follow advice in section 5.2 If the recipient is a patient inform the patient s medical team (or GP if injury has occurred in the patient s home). Undertake an assessment of risk factors for blood borne viruses and if any factors present contact the Consultant Medical Microbiologist on-call for advice on next step. Complete an incident report (Datixweb or Incident Report Form). Human Bites See Appendix A All recipients of a percutaneous bite (i.e. where skin is broken) should: Follow advice in section 5.2 Injured staff and hospital visitors must go to Emergency Department (ED) or Minor Injuries Unit (MIU) for assessment and treatment of wound. All human bites where skin penetration has occurred are recommended to have antibiotic prophylaxis (see local antibiotic policy), especially in cases where: The wound is on the face, hand or foot. The recipient has lowered immunity (e.g. receiving chemotherapy, has diabetes, is immune-compromised). injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 9 of 26
10 Injured in-patients will be assessed and treated by their medical teams on the ward. Major trauma/bomb blast victims There is a risk of transmission of bloodborne viruses when: Multiple people have presented with significant blast injuries Incidents where body parts may have created human tissue projectile injuries to other people Rescuers and responders at such scenes may have skin penetration injuries from presence at such scenes Public Health England guidance for these scenarios can be found at: The Person to Whom the Incident has been reported The person to whom the incident has been reported must: Inform the Occupational Health Department (staff injuries) (see 5.1 for phone numbers). Listen to Advice Line message or where available utilize Inoculation Quick Reference Guide Assess injury (percutaneous including bites, and splash inoculations) for high risk or low risk injury status using Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids Form in Appendix A. Staff, patient or visitor low risk injury manage on ward/dept. Staff, visitor or out-patient high risk injury (see Appendix A) - donor blood is known or suspected BBV positive Inform Emergency Dept by phone of incident and need for urgent triage and then take or send to ED for immediate assessment and management. Donor blood is known or suspected to be HBV positive ensure injured person attends ED or MIU promptly and preferably within 24 hours (or for Staff cases contact Occupational Health within this time frame). injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 10 of 26
11 Inform Occupational Health of any high risk staff injury so that follow up can be co-ordinated. In-patient high risk injury manage on ward without delay. Brief blood sampling guidance can be found on Appendix B The recipient s blood sample should be collected in a yellow top bottle This sample should be sent with a Microbiology request form stating Storage post inoculation injury to the Microbiology Laboratory Contact donor s medical team to arrange consent for testing blood from the donor as per Consent Policy. This should not be undertaken by the recipient of the inoculation injury The donor s blood sample should be collected in a yellow top bottle The sample of the donor s blood should be tested for HBV and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and HIV. This should be clearly requested on a Microbiology request form and sent to the Microbiology Laboratory Take steps to ensure prevention of reoccurrence of the incident. Ensure an incident form is completed (NB. may be reportable under RIDDOR). Post Exposure Treatment / Prophylaxis of HIV (PEP) and Hepatitis B See appendix A and appendix C for treatment details for HIV and Hepatitis B exposure. Emergency Department (ED) doctor working in concert with ED Consultant and if necessary the on call Consultant Medical Microbiologist will provide post exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for those inoculated with known or suspected HIV blood. Individuals requiring HIV PEP should preferably provide written consent to treatment (See the consent policy) Follow up of Injured Person Follow up of Recipient In the case of a staff member (including Sodexo) being the recipient, the Occupational Health Team will be responsible for providing follow up care. Emergency Services personnel injured whilst at work will be referred by ED to their own Occupational Health Service for follow up care. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 11 of 26
12 In the case of a patient being the recipient the patient s consultant will be responsible for the co-ordination of blood samples and appropriate follow up. In the case of a member of the public, visitor or an on-site contractor being the recipient, the ED Team will take blood samples and communicate with the recipient s GP who will be responsible for appropriate follow up. The Microbiology Department will be responsible for ensuring the OH Dept or GP is sent results of blood tests and provided with advice, if required, regarding follow-up blood tests or treatment/ vaccination schedules. ED or the MIU should preferably complete a copy of the checklist at Appendix D: following inoculation injury, and forward it to the Occupational Health Department along with a copy of the casualty records, if the recipient is a healthcare worker. Additional advice is available to staff in the Supporting Staff Policy, which covers staff involved in an incident, investigation or claim Donor Follow Up It is the responsibility of the clinical team caring for the patient to undertake any relevant follow up including providing blood test results directly or via the GP where appropriate. Training requirements All staff who are required to undertake Inoculation Incident management training will be identified through the Trust s training matrix available via BOB under What training do I need?. The training matrix will detail: Staff groups requiring training. Frequency of training. Mode of deliver taught. Titles of courses incorporating this training Trust Induction mandatory annual IC updates, Venepuncture and Cannulation, and Parenteral Drugs courses it is also supported by ad hoc enquiries to. Booking for all training that incorporates inoculation injury training will be undertaken through Workforce Development via the Electronic Staff Record. Signed records must be kept of all training undertaken in the Trust. These records will be held centrally and reported Trust wide through ESR records. Individuals are encouraged to keep a copy of this in their portfolio. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 12 of 26
13 On updating the Electronic Staff Record, line managers will be notified of all nonattenders, further detail on booking and reporting processes are contained within Risk Management (Statutory and Mandatory) Training Policy. 6. Monitoring Compliance with and the Effectiveness of the Policy Standards/ Key Performance Indicators KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS COMPRISE: Time from HIV high risk body fluid injury to healthcare workers to the administration of PEP (as recorded in Appendix D and Emergency Department notes) The annual reduction of avoidable inoculation injuries (reported in annual report). Process for Implementation and Monitoring Compliance and Effectiveness After final approval, the author will arrange for a copy of the policy to be placed on the Trust s intranet. The policy will be referenced on the home page as a latest news release. Information will also be included in the Chief Executive s Bulletin which is circulated electronically to all staff. Line managers are responsible for ensuring this policy is implemented across their area of work. Responsibility The Director of Infection Prevention and Control (DIPC) will be responsible for monitoring and reporting to the Infection Prevention and Control Committee, and the Trustwide position to the Trust Board. The Lead Nurse for Infection Prevention and Control will be responsible for reporting information to the DIPC and to the Infection Prevention and Control Committee. Methodology Weekly review of all inoculation injury incident reports/datixweb reports received by the Infection Prevention and Control Team. The IPCT will ensure that Occupational Health have been involved with all high risk body fluid injuries and alert them immediately when this appears to have been missed. All inoculation injury incidents will be explored to determine if the incident was avoidable, either through safer equipment or safer clinical practice. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 13 of 26
14 Incidents where details are insufficient to determine if correct procedures have been followed will be investigated by the Infection Prevention and Control Team Where non-compliance is identified, support and advice will be provided to improve practice. Reporting Arrangements Incident data and learning themes identified will presented monthly to the IPCC in the Incident Report, a standard agenda item. Relevant staff including the IP&C Team will be actioned where appropriate through the IPCC minutes to explore safer devices or implementation of safer practice to prevent future injuries. 7. Equality Impact Assessment The author must include the Equality Impact Assessment Table and identify whether the policy has a positive or negative impact on any of the groups listed. The Author must make comment on how the policy makes this impact. Table 1: Equality impact Assessment Age Disability Group Positive Impact Negative Impact No Impact X X Comment Gender X Gender Reassignment X Human Rights (rights to privacy, dignity, liberty and non-degrading treatment), marriage and civil partnership Pregnancy X X Maternity and Breastfeeding Race (ethnic origin) X X Religion (or belief) X Sexual Orientation X injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 14 of 26
15 8. References References - Legislation The Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 The Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992 SI 1992/2966 The Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations 1995 SI 1995/3163 The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 SI 1999/3242 Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) Regulations 2002 (as amended) SI 2002/2677 References - General The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) website provides further information on managing the risks associated with inoculation incidents: Needlestick Injuries. HSE website page Management and Prevention of Sharps Injuries: Inspection of NHS Trusts 2010/2011 by Occupational Health Inspectors. HSE website page Health and safety regulation: A short guide. (2003) A guide to the Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations (2008) Working with substances hazardous to health: What you need to know about COSHH. (2009) Department of Health. (1998). Guidance for Clinical Health Care Workers - Protection against Infection with Blood-borne Viruses. London: Department of Health. Available at: Department of Health. (2006). Health Technical Memorandum 07-01: Safe management of healthcare waste. London: Department of Health. Available at: Department of Health (2008) HIV post exposure prophylaxis: Guidance from the UK Chief Medical Officers Expert Advisory Group on AIDS. Available at: PolicyAndGuidance/DH_ Department of Health. (2010). The Health and Social Care Act 2008 Code of Practice on the prevention and control of infections and related guidance. London: Department of Health. Available at: Department of Health (2011) (letter from Prof Matthew Cooke National Clinical Director for Urgent and Emergency Care) Management of bloodexposure in personnel of public and voluntary services. Gateway Reference injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 15 of 26
16 Health and Safety Executive 2001 Blood borne viruses in the workplace: Guidance for employers and employees. Available at: Health Protection Agency (HPA). (2008). Eye of the Needle - United Kingdom Surveillance of Significant Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Viruses in Healthcare Workers. London: HPA. Available at: Health Protection Agency (HPA). (2010). Examples of good and bad practice to avoid sharps injuries. HPA website page. London: HPA. Available at: Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. (2005). Medical device alert: Pen Injection Devices and Pen Needles. MHRA. Available at: National Audit Office (NAO). (2003). A Safer Place to Work: Improving the management of health and safety risks to staff in NHS trusts. London: The Stationery Office. Available at: NHS Employers. (2010). Health and safety essential guide. NHS Employers website pages. NHS Employers. Available at: NHSLA Risk Management Standards NHSLA Risk Management Handbook Plymouth Teaching PCT (2009) management of inoculation injuries v8.2 RD&E Inoculation Injury Policy (approval date at IP&C Group October 2011) Royal College of Nursing (RCN). (2007). Safe Management of Healthcare Waste: RCN Guidance. London: RCN. Available at: Expert Advisory Group on AIDS. (2014). Change to recommended regimen for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP). Available at: hange_to_recommended_regimen_for_pep_starter_pack_final.pdf 9. Associated Documentation Health and Safety Policy Incident reporting Policy Prevention of Inoculation Injuries Policy Risk Management Policy Staff Screening and Immunisation Policy Standard Precautions Policy Consent policy - Appendix A adults, Appendix B paediatrics injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 16 of 26
17 Appendix A: Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids Assessment An inoculation injury has occurred: Percutaneous (from needles, sharps, bone fragments, scratches, bites which break the skin). Splash exposure via broken or disrupted skin (abrasions, cuts, eczema) or mucous membrane (eyes, mouth). Was there exposure to high risk body fluid?: Blood; Amniotic fluids; Vaginal secretions; Semen; Human breast milk; Cerebrospinal fluid; peritoneal fluid; pleural fluid; synovial fluid; pericardial fluid; wound or tissue fluids; saliva in association with dentistry; unfixed organs or tissues; any low risk fluid visibly contaminated with blood. No Exposure to low risk body fluid occurred: Urine; Vomit; Faeces; Sputum; Saliva unless visibly contaminated with blood which means it is counted as a high risk fluid. Actions: Manage incident in own department Low risk body fluid injuries do not need Occupational Health follow-up First aid o Allow to bleed, do not squeeze or suck o Wash and dress injury or rinse out eye/mouth o If bite, send injured staff member or visitor to ED or MIU for examination dressing and antibiotics; treat inpatients on ward Complete incident report form or datixweb Yes Was high risk body fluid from a known BBV carrier or from an individual in a high BBV carriage risk group?: Men who have sex with men; High risk sexual practice; Commercial sex workers; Intravenous drug users; People from countries with high BBV populations (e.g. Sub Saharan Africa); Sexual partners of any of the above. No Actions: Manage incident in own department Use Occupational Health Advice Line (North = ; East = OR Inoculation Injury Box for guidance on blood sampling (record donor consent given to blood sampling on Specimen Request form) First aid: o Allow to bleed, do not squeeze or suck o Wash and dress injury o If bite, send injured staff member or visitor to ED or MIU for examination dressing and antibiotics; treat in-patients on ward Phone details to Occupational Health for follow up (North = ; East = Complete incident form or datixweb. Yes URGENT ACTION REQUIRED (see urgent action algorithms below). injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 17 of 26
18 URGENT ACTION ALGORITHM - HIV Is Donor known or suspected HIV positive? Known HIV positive Take/send (community hospitals use taxi) to: Northern locality NDHT Emergency Dept (ED) phone ahead to ensure urgent triage. Eastern locality in hours RD&E Occupational Health; out of hours RD&E Emergency dept (phone triage desk ) Suspected HIV only (there are identified risk factors for HIV carriage). Counsel and consent for PEP: Give within 1 hour if possible Consent donor for bloods (record consent given on Specimen Request form): EDTA for viral load (purple top tube for staff in Northern areas & red top tube for staff in Eastern areas). Clotted blood for serology (yellow topped tube for staff in Northern areas and brown topped tube for staff in Eastern areas). Counsel PEP is rarely indicated for injuries involving these patients. In exceptional circumstances the risk of HIV may be higher e.g. Injuries from sharps in the vicinity (same bed space or bay) of a known HIV patient. It is important to take into account the views of the member of staff, for example they may wish to consider starting PEP until further information/test results are available on the donor. Follow up responsibilities: NDHT Staff - Contact Occupational Health relevant to locality (North = ; East = ) and leave contact details Visitors GP (ED to contact GP to provide details) ED out-patient GP (ED to contact GP to provide details - if unregistered follow up by ED) In-Patients Medical team (inform GP in discharge letter) Personnel of public and voluntary services own Occupational Health Service (ED to contact own OH dept to provide details) injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 18 of 26
19 URGENT ACTION ALGORITHM - Hepatitis Donor is known or suspected to carry Hepatitis B take advice from Occupational Health (in hours), or Emergency Dept, MIU or on-call Medical Microbiologist (out of hours) preferably within 24 hours of injury Consent donor for bloods (record consent given on Specimen Request form): EDTA for viral load (purple top tube for staff in Northern areas & red top tube for staff in Eastern areas ) & Clotted blood for serology (yellow topped tube for staff in Northern areas and brown topped tube for staff in Eastern areas). Hepatitis C Urgent action is not required there is no prophylactic treatment - see notes. Status of recipient Not vaccinated (or 1 dose only) 2 (or more) doses vaccine and immune status unknown Known vaccine responder (anti- HBs > 10 mix/ml) Non responder to vaccine(anti- HBs < 10 mix/ml, 2-4 months post vaccination) Hepatitis B status of source patient Unknown HBsAg Pos HBsAg Nag Accelerated course of Hepatitis B vaccine* One dose of Hepatitis B vaccine Consider booster dose of Hepatitis B vaccine HBIG 1 dose** + one dose of Hepatitis B vaccine Discuss further vaccination and HBIG with Microbiologist during working hours Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG) + Accelerated course of Hepatitis B vaccine* One dose of Hepatitis B vaccine followed by second dose 1 month later One dose of Hepatitis B vaccine if more than one year since last tested & shown to have >100 units of antibody. If uncertain, the recipients antibody level can be tested the following day and interpretation sought from on call microbiologist. HBIG 1 dose** + one dose of Hepatitis B vaccine Discuss further vaccination and HBIG with Microbiologist during working hours * Accelerated schedule: months, fourth dose at 12 months if continued risk of exposure to hepatitis B ** HBIG should be given as soon as possible but can be given up to 1 week following injury Start or complete Hepatitis B vaccine course Complete Hepatitis B vaccine course or give booster if 4 or more years since last booster or course Consider booster dose of Hepatitis B vaccine No action but refer recipient to Occupational Health for further advice. Consider booster dose of Hepatitis B vaccine. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 19 of 26
20 NOTES: Risk of transmission from a known or suspected source HIV HBV HCV The risk of transmission of HIV from a penetrating injury with a sharp object contaminated with blood containing HIV is 1 in 300 (0.3%). The risk from a mucocutaneous exposure is less than 1 in The risk of infection from patients with hepatitis B depends upon the presence of virus in the blood. The chance of becoming infected with HBV from an inoculation injury involving surface antigen (HBsAg) positive blood is greatest (1 in 3) during the acute illness and in cases with a high HBV viral load (note that HbeAgnegative disease can be associated with high levels of viraemia and ready transmission). After full recovery, when neither HBeAg nor HBsAg is present, and anti-e and anti-s antibodies have appeared, there is no longer a risk of transmission of hepatitis B. Approximately 95% of adults who acquire HBV will make a full recovery. The risk of infection with HCV from a penetrating inoculation injury is around 1 in 30. Transmission from a human bite has been documented. The risk from mucous membrane contamination (eye, mouth) is much less. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 20 of 26
21 Appendix B: Inoculation Quick Reference Guide Inoculation Quick Reference Guide Inoculation / Needlestick Injury? A scratch or bite that breaks the skin. A used needle or sharp object that pierces your skin. A splash of blood/body fluid into your mouth, eyes, broken skin, wound. Carry out First Aid: Allow to bleed, do not squeeze or suck Wash and dress injury or rinse out eye/mouth Contact Occupational Health Advice Line for more guidance if needed NDDH RD&E Report to line manager / nurse in charge of shift Complete an Incident Report Form/Datix web An assessment must be made to see if it is likely that the injured person has been exposed to a blood borne virus (BBV). Risk factors: Known carrier of BBV High risk sexual practice Commercial sex worker Multiple sexual partners IV drug user People from countries with high rates of BBV s e.g. Sub- Saharan Africa If yes urgent action is required contact Consultant Medical Microbiologist on call Recipient (Injured person) blood test. Take blood for storage: 1 clotted sample (yellow-top blood bottle for staff in Northern areas and brown topped tube for staff in Eastern areas), sent with a Microbiology Form labelled recipient bloods post inoculation injury. This blood sample will be stored. Donor (the person whose blood or bodily fluids you have been in contact with) blood test. Consent the donor for blood tests: Hepatitis B antigen Hepatitis C antibody HIV antibody 1 clotted sample (yellow top bottle for staff in Northern areas and brown topped tube for staff in Eastern areas)) sent on a microbiology form labelled donor bloods post inoculation injury. Consent must be obtained for these tests and documented in patient s notes. Consent not to be done by the injured person An inoculation injuries Reporting and Advice Line is available for Northern locality on and Eastern locality on By listening to the whole message it will give you information on what to do following an injury. You must also leave a message giving your name, where you work and a contact number so Occupational Health can contact you for follow up. Prevention and Management of Inoculation Injuries Policies are available on BOB in the Infection Control section. It is your professional responsibility to familiarise yourself with these policies and to act accordingly. The policy is there to protect and guide you. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 21 of 26
22 Appendix C: Post Exposure Prophylaxis Guidance notes for use of PEP for HIV These notes are to guide those who have experienced a needle-stick or percutaneous injury and are thought to be at risk of acquiring HIV infection. What is PEP? Post exposure prophylaxis is the term used to describe the combination of anti-viral drugs given to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV after a percutaneous injury. PEP reduces the probability of acquiring HIV infection by about 80% but the drugs need to be taken exactly as advised to achieve maximal benefit. Who should take PEP? PEP should only be taken by individuals following discussion with staff in either Occupational Health or the Emergency Department, and following discussion with a Consultant Microbiologist. PEP would only be offered to those who have sustained an injury from a donor who is known or clinically suspected of being HIV positive. When to start PEP? PEP should be started as soon as possible following the injury. Ideally this should be within one hour Sometimes it is best to take the initial doses of PEP immediately whilst waiting for more information about the exact risk. How to take PEP? Follow the directions on the labels. It is important to take all the doses at the correct interval. If you vomit within an hour after taking PEP then you should take it again as soon as possible. The drugs used for PEP Anti-viral drugs used are:- One Truvada tablet (245mg tenofovir and 200mg emtricitabine (FTC)) once a day plus One Raltegravir (400mg) tablet twice a day Duration of PEP treatments is 28 days. When to stop PEP The duration of PEP is based on clinical review of each case although you may decide to stop taking PEP after consultation with Occupational Health if more information about the risk of acquiring HIV becomes available. If you are taking other medicines (including the oral contraceptive pill) Some medicines can interact with the drugs used for PEP so if you are taking any other medicines, including the oral contraceptive pill, any regular over the counter medications, herbal preparations or recreational drugs you should mention these to the person advising you about PEP. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 22 of 26
23 Pregnancy and sex If you are pregnant, or think that you may be pregnant, you should tell the prescribing Doctor. It is important that you should not become pregnant whilst taking PEP as the drugs can affect the developing baby. You should use a barrier form of contraception whilst on treatment. For further advice on safer sex please contact the Health Advisor at your local sexual health clinic (GUM) Reducing risk to others During the six month follow-up period, if you are well, there is no need to modify your working practices, for example by avoiding exposure prone procedures. However, it is important to practice safer sex, particularly the use of condoms for penetrative sex and to avoid blood donation during the follow-up period. Side effects PEP like any medicine can have side effects. The most likely side effects that you may experience taking PEP are nausea, headaches, tiredness and diarrhoea. These side effects commonly appear in the first few days of taking PEP and usually diminish or disappear with time. If you experience any side effects it is important to continue the treatment but do contact the Occupational Health Team or your GP for advice. It is not unusual to need time off work at the beginning of treatment. Support and advice Northern Locality staff During working hours: The Occupational Health Team: Outside normal working hours: NDDH Emergency Department Doctors Ext 2480 Support and advice Eastern locality staff During working hours: The Occupational Health Team: Outside normal working hours: RD&E Emergency Department Doctors (via ED reception) Support and advice Patients Following your initial consultation in ED, support and advice can be obtained from: Your GP please make contact with your GP on the next working day. Reference Department of Health (2007) Update to Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) guidance from the Expert Advisory Group on AIDS (EAGA) following the recent recall of Viracept. (information accessed 20/02/2008) injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 23 of 26
24 Appendix D: Checklist for Northern Locality: Occupational Health and Emergency Department: Date: Following Inoculation and Needlestick Injuries Name of Recipient:..D.O.B Name of Donor:...D.O.B Recipient blood taken *YES/NO Donor blood taken *YES/NO Recipient given: Hep B vaccine *YES/NO Hep B Immunoglobulin *YES/NO H.I.V post exposure prophylaxis *YES/NO Decision Made by: Name Signature: Job title:.. Reason:. NDDH Emergency Dept for Northern Locality or Devon Partnership Trust (N Devon Section) staff injury cases see in the E.D. - send this form and copy of E.D notes to OH Dept at Barnstaple HC RD&E Emergency Dept for Eastern Locality Staff Injury cases: - Inform OH Dept at RD&E of relevant case details to enable follow up. Recipient Hep B status following vaccination: (Please tick relevant response) injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 24 of 26
25 Immune Low Positive Negative Previous doses of Hep B vaccine: 1..Date 2 Date 3..Date 4..Date 5 Date 6...Date Blood Borne Virus results of Donor: Hep B Hep C HIV Date Results Follow up in Occupational Health: HIV Markers Serological Testing for Hep B Date/Results Hep C Date/Results Date/Results 3/12 6/12 PTO Please give account of how injury occurred. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 25 of 26
26 Action taken by Occupational Health / Emergency Department. Signature: Name:.. Date:. injuries mgmt\ v4.0 Sept 2017.docx Page 26 of 26
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions
 Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis).
 LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP:
 Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
PROTECTION FROM OCCUPATIONAL ACQUIRED/TRANSMITTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Policy
 PROTECTION FROM OCCUPATIONAL ACQUIRED/TRANSMITTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Policy 1 Policy title Protection from Occupational Acquired /Transmitted Communicable Diseases Policy COR 60 reference Policy category
PROTECTION FROM OCCUPATIONAL ACQUIRED/TRANSMITTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Policy 1 Policy title Protection from Occupational Acquired /Transmitted Communicable Diseases Policy COR 60 reference Policy category
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines
 Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses
 Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy
 Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
making a referral for breast imaging Standard Operating Procedure
 Document Control Title Reporting Radiographer Author Directorate Surgery Date Version Issued 0.1 May 2016 Status Draft Author s job title Reporting Radiographer Department Breast Imaging Comment / Changes
Document Control Title Reporting Radiographer Author Directorate Surgery Date Version Issued 0.1 May 2016 Status Draft Author s job title Reporting Radiographer Department Breast Imaging Comment / Changes
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS
 TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure
 Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions
 Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Inoculation Incidents and Blood Borne Viruses Version 1.0 Date approved: October 2013 Approved by: The Board Review due: March 2016 Contents Section Topic Page
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Inoculation Incidents and Blood Borne Viruses Version 1.0 Date approved: October 2013 Approved by: The Board Review due: March 2016 Contents Section Topic Page
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens. Exposure Control Plan
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS.
 SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy
 Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
SHARPS MANAGEMENT AND INOCULATION INJURIES
 Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Sharps Management and Inoculation Injuries Version 1.01 May 15 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Sharps Management
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Sharps Management and Inoculation Injuries Version 1.01 May 15 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Sharps Management
Infection Control Standard Precautions. CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients
 Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES
 NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
BAY-ARENAC BEHAVIORAL HEALTH AUTHORITY POLICIES AND PROCEDURES MANUAL
 Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
HEPATITIS B VIRUS: PROTECTING EMPLOYEES AND PATIENTS
 HUMAN RESOURCES (WITH OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH) HEPATITIS B VIRUS: PROTECTING EMPLOYEES AND PATIENTS DOCUMENT REF: PHRMHEPAB (Version No. 5.0) Name and designation of policy author(s) Approved by (committee,
HUMAN RESOURCES (WITH OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH) HEPATITIS B VIRUS: PROTECTING EMPLOYEES AND PATIENTS DOCUMENT REF: PHRMHEPAB (Version No. 5.0) Name and designation of policy author(s) Approved by (committee,
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection
 Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
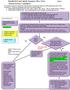 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure. Marsh Gelbart 2010
 HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
Colgate University. Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
 Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES
 Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts)
 SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
Sharps Injuries Management
 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust)
 A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC20 VACCINATION PROGRAMME FOR STAFF AND
A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC20 VACCINATION PROGRAMME FOR STAFF AND
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS. All clinical areas of the Trust. Prevent spread of Hepatitis B virus
 Trust Policy and Procedure PP(15)027 Document Ref No: HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS For use in: For use by: For use for: Document owner: Status: All clinical
Trust Policy and Procedure PP(15)027 Document Ref No: HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS For use in: For use by: For use for: Document owner: Status: All clinical
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1
 PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses
 Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] 2014 Aim To raise awareness of the key information and procedures in NHS Lanarkshire's Control of Infection
Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] 2014 Aim To raise awareness of the key information and procedures in NHS Lanarkshire's Control of Infection
B. Tasks and Procedures where employees, students or contractors can be exposed to bloodborne pathogens:
 Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005
 Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005 Version Date Date of Next Reason for Change (eg. full rewrite, No. Ratified/ Implementation Review amendment
Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005 Version Date Date of Next Reason for Change (eg. full rewrite, No. Ratified/ Implementation Review amendment
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy. Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011
 HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy
 Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE
 Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting
 Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV]
![The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV]](/thumbs/93/112976583.jpg) The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] Control of Infection Manual Section G Study Morning 25 th November 2014 Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] Aim To raise awareness
The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] Control of Infection Manual Section G Study Morning 25 th November 2014 Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] Aim To raise awareness
Drew University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan and Procedures
 PURPOSE To provide a written plan for preventing and/or minimizing exposure to bloodborne pathogens for those Drew University personnel who may be involved in the handling of human blood, blood products,
PURPOSE To provide a written plan for preventing and/or minimizing exposure to bloodborne pathogens for those Drew University personnel who may be involved in the handling of human blood, blood products,
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Greater Glasgow and Clyde. Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts
 Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus disease Updated 17 Oct 2014
 Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus This guidance is aimed at clinical staff undertaking direct patient care in primary care, including GP surgeries,
Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus This guidance is aimed at clinical staff undertaking direct patient care in primary care, including GP surgeries,
BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of transmission for school staff. for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood
 BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of transmission for school staff for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood MASSACHUSETTS DIVISION OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY Robert Prezioso,
BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of transmission for school staff for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood MASSACHUSETTS DIVISION OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY Robert Prezioso,
3/23/2016. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures
 This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
EU Directive for Safer Sharps. Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant
 EU Directive for Safer Sharps Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant Regulation and Legislation Health and Social Care Act 2008 Occupier s Liability Act 1957 Health and Safety at Work Act
EU Directive for Safer Sharps Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant Regulation and Legislation Health and Social Care Act 2008 Occupier s Liability Act 1957 Health and Safety at Work Act
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post-Exposure Chemophrophylaxis
 Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Management of Healthcare Workers Infected With A Blood-borne Virus (HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C)
 Management of Healthcare Workers Infected With A Blood-borne Virus (HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
Management of Healthcare Workers Infected With A Blood-borne Virus (HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURE TO HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS (HCAI) AND INOCULATION INCIDENTS (INCLUDING SAFE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS)
 MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURE TO HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS (HCAI) AND INOCULATION INCIDENTS (INCLUDING SAFE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS) INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY NO. 4 Applies to: Staff employed
MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURE TO HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS (HCAI) AND INOCULATION INCIDENTS (INCLUDING SAFE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS) INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY NO. 4 Applies to: Staff employed
Title Management of Impetigo Protocol in MIUs and WICs. Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate
 Document Control Title Management of Impetigo Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Department MIU Version Date Issued Status Comment /
Document Control Title Management of Impetigo Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Department MIU Version Date Issued Status Comment /
Equality of Opportunity Committee
 Equality of Opportunity Committee EOC(3)-12-09 (p8) Inquiry into Discrimination against People Living with HIV by Healthcare Professionals and Providers Written evidence from Abertawe Bro Morgannwg University
Equality of Opportunity Committee EOC(3)-12-09 (p8) Inquiry into Discrimination against People Living with HIV by Healthcare Professionals and Providers Written evidence from Abertawe Bro Morgannwg University
Author and Designation Equality Impact Assessment Associated Documents. Supporting References
 Title Policy for the prevention and Management of Needlestick and Sharps Injuries (Inoculation Incidents) Description of document This policy promotes sharps safety with the aim to prevent needlestick
Title Policy for the prevention and Management of Needlestick and Sharps Injuries (Inoculation Incidents) Description of document This policy promotes sharps safety with the aim to prevent needlestick
QUALITY LIFE CONCEPTS Policy on Bloodborne Pathogens
 QUALITY LIFE CONCEPTS Policy on Bloodborne Pathogens A24 TUBERCULOSIS TESTING Quality Life Concepts is committed to protecting its employees and individuals who will be served by vigilance and regular
QUALITY LIFE CONCEPTS Policy on Bloodborne Pathogens A24 TUBERCULOSIS TESTING Quality Life Concepts is committed to protecting its employees and individuals who will be served by vigilance and regular
Ward/Unit/Team managers to carry out an occupational skin disease risk assessment for their area
 Policy Title: Prevention and Management of Occupational Skin Disease Reference and Version No: RM26 Version 3 Author and Job Title: Jude Cooper Head of Occupational Health and Wellbeing Executive Lead
Policy Title: Prevention and Management of Occupational Skin Disease Reference and Version No: RM26 Version 3 Author and Job Title: Jude Cooper Head of Occupational Health and Wellbeing Executive Lead
patients with blood borne viruses Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled Document Lead:
 CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: F:
 University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
UK Standards for Microbiology Investigations
 UK Standards for Microbiology Investigations Blood Borne Virus Testing in Dialysis Patients Issued by the Standards Unit, Microbiology Services, PHE Virology V 10 Issue no: 2 Issue date: 27.04.15 Page:
UK Standards for Microbiology Investigations Blood Borne Virus Testing in Dialysis Patients Issued by the Standards Unit, Microbiology Services, PHE Virology V 10 Issue no: 2 Issue date: 27.04.15 Page:
Goldenrod Hills Community Action. Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR
 Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
Infection Control Program (ICP) ICP Components 1. Exposure Determination 2. Control Methods A. Universal Precautions
 Compliance Assistance Guideline for the February 27, 1990, OSHA Instruction CPL 2 2.44B Enforcement Procedures for Occupational Exposure to Hepatitis B Virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus from the U.S.
Compliance Assistance Guideline for the February 27, 1990, OSHA Instruction CPL 2 2.44B Enforcement Procedures for Occupational Exposure to Hepatitis B Virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus from the U.S.
What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS. They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids.
 What are Universal Precautions? What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids. Universal precautions are:
What are Universal Precautions? What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids. Universal precautions are:
Staff Immunisation Policy
 Policy No: IC05 Version: 8.0 Name of Policy: Staff Immunisation Policy Effective From: 18/08/2015 Date Ratified 15/07/2015 Ratified Infection Prevention & Control Committee Review Date 01/07/2017 Sponsor
Policy No: IC05 Version: 8.0 Name of Policy: Staff Immunisation Policy Effective From: 18/08/2015 Date Ratified 15/07/2015 Ratified Infection Prevention & Control Committee Review Date 01/07/2017 Sponsor
This SOP applies to all staff employed by NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde and locum staff on fixed term contracts and volunteer staff.
 Page 1 of 8 SOP Objective To ensure that Healthcare Workers (HCWs) are aware of the actions and precautions necessary to minimise the risk of outbreaks and the importance of diagnosing patients clinical
Page 1 of 8 SOP Objective To ensure that Healthcare Workers (HCWs) are aware of the actions and precautions necessary to minimise the risk of outbreaks and the importance of diagnosing patients clinical
Blood and Body Fluid Spillage Procedure
 Blood and Body Fluid Spillage Procedure (IPC Manual) DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: v1.1 Ratified by: Clinical Policies Review and Approval Group Date ratified: 8 January 2019 Name of originator/author: Senior
Blood and Body Fluid Spillage Procedure (IPC Manual) DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: v1.1 Ratified by: Clinical Policies Review and Approval Group Date ratified: 8 January 2019 Name of originator/author: Senior
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training
 Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
Bloodborne Pathogens. Montclair Kimberley Academy 1
 Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
School Hearing Screening Policy
 School Hearing Screening Policy V2.1 1st August 2017 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions / Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
School Hearing Screening Policy V2.1 1st August 2017 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions / Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
Safety Services Guidance. Guidance on working with blood and body fluids
 Guidance on working with blood and body fluids Key word(s): Blood, body fluids, sputum, blood borne viruses, BBV Target audience: Laboratory personnel Contents Introduction... 2 Assessing the risks...
Guidance on working with blood and body fluids Key word(s): Blood, body fluids, sputum, blood borne viruses, BBV Target audience: Laboratory personnel Contents Introduction... 2 Assessing the risks...
Primary Care Services for blood borne viral hepatitis prevention, treatment and care
 Primary Care Services for blood borne viral hepatitis prevention, treatment and care Author: Josie Smith, Marion Lyons Page 1 of 13 October 2006 Status : Final Contents: Page: Executive Summary 3 Introduction
Primary Care Services for blood borne viral hepatitis prevention, treatment and care Author: Josie Smith, Marion Lyons Page 1 of 13 October 2006 Status : Final Contents: Page: Executive Summary 3 Introduction
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE HEPATITIS B
 DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses. HIV and AIDS Hepatitis B Hepatitis C
 A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses HIV and AIDS Hepatitis B Hepatitis C A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses This question and answer tool kit has been designed by the Children in Care Team (Integrated
A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses HIV and AIDS Hepatitis B Hepatitis C A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses This question and answer tool kit has been designed by the Children in Care Team (Integrated
SHARPS POLICY: SAFE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF SHARPS
 SHARPS POLICY: SAFE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF SHARPS Version 10. Feb 2017 First issued Oct 2008 Reviewed Feb 2017 Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps
SHARPS POLICY: SAFE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF SHARPS Version 10. Feb 2017 First issued Oct 2008 Reviewed Feb 2017 Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps
Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps
 Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Version: 8 Status: Owner: In review Infection Prevention
Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Version: 8 Status: Owner: In review Infection Prevention
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training.
 You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
Bloodborne Pathogens Training
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training OSHA S Bloodborne Pathogen Standard 29CFR 1910.1030 Employers must: Develop an Exposure Control Plan (ECP) that details their Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Program Provide employees
Bloodborne Pathogens Training OSHA S Bloodborne Pathogen Standard 29CFR 1910.1030 Employers must: Develop an Exposure Control Plan (ECP) that details their Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Program Provide employees
ADMINISTRATIVE SERVICES MANUAL
 1 of 10 Purpose Scope University of Alaska Anchorage departments will develop plans and procedures to limit occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (PIM) in compliance
1 of 10 Purpose Scope University of Alaska Anchorage departments will develop plans and procedures to limit occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (PIM) in compliance
Document Control Report
 Document Control Report Title Recording Clinical Evaluation and Dose - IR(ME)R 2000 Standard Operating Procedure Author Gill Kite Author s job title Senior Radiographer Directorate Sub-directorate Department
Document Control Report Title Recording Clinical Evaluation and Dose - IR(ME)R 2000 Standard Operating Procedure Author Gill Kite Author s job title Senior Radiographer Directorate Sub-directorate Department
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure STUDENT. Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure. Student. Rev:
 Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Revised April WGH ER #5 Hospital Rd. Whitehorse Phone: (867) Outside of Whitehorse: Local Community Health Centre/Clinic/ER
 Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Module 1: HIV epidemiology, transmission and prevention
 Session 2 Module goals Module 1 Participants will be able to: -offer an insight into the epidemiological situation in the country and worldwide -present the HIV transmission modes and the broad approaches
Session 2 Module goals Module 1 Participants will be able to: -offer an insight into the epidemiological situation in the country and worldwide -present the HIV transmission modes and the broad approaches
June 4, Page 1 of 5 POLICY STATEMENT
 POLICY STATEMENT This policy has been written to inform all staff, clients, relatives and other visitors to the homes of service users about the risks associated with MRSA, AIDS and HIV hazards in the
POLICY STATEMENT This policy has been written to inform all staff, clients, relatives and other visitors to the homes of service users about the risks associated with MRSA, AIDS and HIV hazards in the
NHS PREPAREDNESS FOR A MAJOR INCIDENT
 NHS PREPAREDNESS FOR A MAJOR INCIDENT In light of the recent tragic events in Paris, NHS England has asked that the Trust reviews the following, and that assurance is provided in the form of a Statement
NHS PREPAREDNESS FOR A MAJOR INCIDENT In light of the recent tragic events in Paris, NHS England has asked that the Trust reviews the following, and that assurance is provided in the form of a Statement
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury
 43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
Trust Guideline for the Prevention of Tuberculosis and Management of Tuberculosis Exposure in Health Care Workers
 A Clinical Guideline For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job title of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by: Assessed
A Clinical Guideline For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job title of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by: Assessed
