Bladder Malignancies on CT: The Underrated Role of CT in Diagnosis
|
|
|
- Clarissa Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Genitourinary Imaging Clinical Perspective Raman and Fishman CT of ladder Malignancies Genitourinary Imaging Clinical Perspective Siva P. Raman 1 Elliot K. Fishman Raman SP, Fishman EK Keywords: bladder cancer, CT urography, transitional cell carcinoma DOI: /JR Received October 1, 2013; accepted after revision October 31, oth authors: Department of Radiology, Johns Hopkins University, JHOC 3251, 601 N Caroline St, altimore, MD ddress correspondence to S. P. Raman (srsraman3@gmail.com). JR 2014; 203: X/14/ merican Roentgen Ray Society ladder Malignancies on CT: The Underrated Role of CT in Diagnosis OJECTIVE. The purpose of this article is to review the utility of CT in diagnosing bladder malignancies, CT protocol options that may improve the conspicuity of bladder tumors, suggestive imaging features, and potential mimics. CONCLUSION. lthough evaluation of the bladder has traditionally been considered purely the realm of cystoscopy, many bladder tumors can be identified with CT. However, diagnosis requires optimization of CT technique and close attention to a number of potentially subtle findings. T he role of CT, CT urography in particular, has been well described in the literature with regard to the diagnosis of upper urinary tract tumors (i.e., tumors of the ureters and pelvicalyceal system) [1]. The role of CT in the imaging of patients with hematuria has become well established, and CT urography is regularly used in both the outpatient and emergency settings. ecause cystoscopy is considered the reference standard examination for evaluation of the bladder and diagnosis of bladder malignancies, the bladder has been a largely ignored and disregarded structure during routine CT interpretation [2]. This is a potentially dangerous perspective on the part of radiologists, because bladder malignancies can often be incidentally appreciated at screening CT examinations in the emergency department, particularly when patients are imaged with a full bladder and arterial phase technique is used [3 5]. Moreover, even in individuals being imaged with CT urography for hematuria, particularly in the emergency setting, it is far from certain that patients will ultimately undergo diagnostic cystoscopy, placing the onus on the radiologist for diagnosis. In this article, we discuss the pathophysiology and background of bladder malignancies, CT urography protocol considerations that may improve the visualization of subtle tumors, the imaging findings that should raise suspicion of these lesions, and some potential imaging mimics. ackground ladder cancer is quite common; 2.7 million patients either receive a diagnosis of or are treated for bladder cancer each year worldwide. ladder cancer is the fourth leading cause of malignant disease in the United States [6, 7]. Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) of the bladder is approximately 50 times as common as TCC of the upper urinary tract [6]. lthough most of the tumors are TCC, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma account for a small minority of lesions [6]. Like those for TCC of the upper urinary tract, the primary risk factors for bladder TCC include male sex, advancing age (typically older than 60 years), smoking, several specific chemical carcinogens, and pelvic radiation [6]. The most common (> 80%) clinical symptom of bladder cancer is gross hematuria, which confers a four times higher risk of malignancy compared with microscopic hematuria. Most patients with macroscopic hematuria, particularly those older than 50 years, should undergo both cystoscopy and CT urography [2]. Microscopic hematuria carries a much lower risk of malignancy and may be present in a sizeable percentage of persons without symptoms, making the decision to perform further investigation (CT urography or cystoscopy) largely dependent on a patient s underlying risk factors [8]. Other than hematuria, potential patient symptoms include urinary frequency, urgency, repeated urinary tract infections, and urinary obstruction secondary to an advanced mass [2]. JR:203, ugust
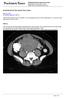
2 Raman and Fishman Protocol Considerations and Technique Three primary CT urography protocols have been described, including the single-bolus technique, split-bolus technique, and triple-bolus technique. The single-bolus technique, the most commonly used of the three options, involves administration of a fullstrength bolus of contrast material, followed by the acquisition of separate arterial, venous, and excretory phase images [1]. In the splitbolus technique, the total contrast material dose is divided into two separate administrations, and images are acquired in a combined excretory and nephrographic phase [9, 10]. The triple-bolus technique splits a full dose of contrast material into three separate small boluses, and acquisition is a combined corticomedullary-nephrographic-excretory phase [1]. Given that a smaller amount of IV contrast material is ultimately excreted in the latter two protocol options, it is not surprising that use of the split-bolus and triple-bolus techniques ultimately reduces the degree of urinary bladder distention on delayed phase images and may limit identification of a subtle filling defect. However and most important, both the split-bolus and the triple-bolus techniques were designed primarily to reduce radiation dose by combining the different phases of acquisition. s a result, each of these two protocols may markedly limit sensitivity for bladder malignancies if early phase images with unopacified urine distending the bladder are not acquired [1, 10 12]. In the performance of CT urography, a number of ancillary techniques have been described, including oral hydration, IV hydration, IV administration of diuretics, abdominal compression, and prone positioning [11, 13 16]. For the most part, these techniques have been described in the literature with regard to improving the efficacy of upper urinary tract distention, and their effect on the detection of bladder malignancies has not been specifically discussed. lthough some of these techniques are unlikely to have a substantial effect on bladder distention, three of these techniques are likely to improve detection of a bladder malignancy: oral hydration, IV hydration, and IV administration of diuretics. These techniques can improve excretion into and distention of the collecting system and ultimately improve bladder distention. Moreover, all three result in dilution of the excreted contrast material, potentially improving the ability to identify subtle lesions. t our institution, we use oral hydration as a component of our standard CT urography protocol to improve distention not only of the upper urinary tract but also of the bladder. Moreover, we routinely ask patients not Fig year-old man undergoing CT in preparation for transcatheter aortic valve replacement. xial arterial phase image shows hypervascular wall thickening (arrow) along right bladder wall, confirmed at cystoscopy to represent transitional cell carcinoma. to urinate for at least 1 hour before the study so as to improve bladder distention. Notably, all three of these techniques increase not only the excretion of opacified contrast medium into the collecting system and bladder on delayed phase images but also the excretion of unopacified, low-density urine into the collecting system and bladder on early phase images. The result is improved juxtaposition of subtle bladder wall thickening or hyperenhancement compared with low-density fluid within the bladder lumen [11, 14]. Diagnostic Performance lthough there is little doubt that cystoscopy is the most sensitive, specific, and reproducible method for identification of bladder malignancies, the diagnostic performance of CT is better than is commonly thought: In a study by Turney et al. [8], 200 patients with hematuria underwent both cystoscopy Fig year-old woman with gross hematuria. and, rterial phase CT image () shows nodular hypervascular wall thickening along posterior bladder wall (arrow) more clearly than does delayed phase image (). Finding was found to represent transitional cell carcinoma. 348 JR:203, ugust 2014
3 CT of ladder Malignancies and CT urography. ladder malignancy was found in 24% of the patients, and the sensitivity and specificity of CT urography were 0.93 and 0.99 (positive predictive value, 0.98; negative predictive value, 0.97). Similarly, Sadow et al. [17] conducted a study that included 838 patients who had undergone CT urography and cystoscopy within 6 months of each another and found that CT urography had a sensitivity and specificity of 79% and Fig year-old man with hematuria. xial arterial phase CT image shows nodular wall thickening (arrow) along right anterior bladder that was proved at subsequent cystoscopy to represent transitional cell carcinoma. Fig year-old man with dysuria and suprapubic pain. and, xial () and coronal () volumerendered CT images show extensive polyploid nodular thickening (arrow, ) of bladder wall, in keeping with multifocal transitional cell carcinoma. Coronal image nicely shows extensive vascularity and enhancement associated with malignancy. 94% (positive predictive value, 75%; negative predictive value, 95%). In another study, Kim et al. [18] found CT urography effective in the diagnosis of recurrent tumors in patients who had previously undergone transurethral resection of a bladder tumor. It is undoubtedly true that the diagnostic performance of CT will vary dramatically depending on the technique used and degree of bladder distention, thus explaining the variable diagnostic performance from one study to another. dedicated CT urography technique with multiphase protocol will clearly be more sensitive for a subtle tumor than a routine screening examination performed in the emergency department for suspected abdominal pain. Nevertheless, the results of these studies suggest that if technique is optimized, subtle malignancies can be identified reasonably accurately at imaging. Fig year-old woman with hematuria and incontinence. xial arterial phase axial CT image shows multiple sites of focal urothelial thickening (arrows) and abnormal hyperenhancement, ultimately proven to represent multifocal transitional cell carcinoma. JR:203, ugust
4 Raman and Fishman Fig year-old man with history of multiple sclerosis. CT image shows multifocal bladder wall thickening and hyperenhancement. Given young age of patient and presence of multiple sclerosis and multifocal thickening of bladder, finding was originally thought to represent either cystitis or neurogenic bladder but was ultimately proved to represent diffuse infiltrating transitional cell carcinoma. Fig year-old man with abdominal pain. and, rterial () and delayed () phase CT images show focal nodular thickening (arrow) along posterior bladder wall. Given vascularity and enhancement of this nodularity, abnormality is more apparent on arterial phase images and was proved to represent transitional cell carcinoma. Fig year-old man with 2-year history of hematuria. and, rterial phase CT image () shows nodular thickening (arrow) along posterior bladder wall more clearly than does delayed image (). Finding was ultimately proved to represent transitional cell carcinoma. 350 JR:203, ugust 2014
5 CT of ladder Malignancies Imaging Findings ladder Wall Thickening In a well-distended bladder, focal bladder wall thickening, particularly when nodular or irregular, should be considered suspicious for malignancy (Figs. 1 10). Nevertheless, one should be hesitant to overinterpret bladder abnormalities in an underdistended bladder, because the anterior bladder can often look spuriously thickened in such cases [19]. Moreover, diffuse bladder wall thickening rarely represents malignancy, except in cases of irregular or nodular wall thickening: In a study by McPartlin et al. [20], in which bladder wall thickening was further evaluated with cystoscopy, there were no cases of malignancy in patients with diffuse wall thickening. In many cases, subtle focal thickening may be difficult to appreciate on delayed images, particularly along the dependent posterior wall of the bladder, because it can be obscured by contrast Fig year-old man with hematuria. and, lthough bladder is decompressed, arterial phase image () shows subtle foci of urothelial hyperenhancement (arrows), whereas delayed phase image () does not. Finding was proved to represent transitional cell carcinoma. material in the bladder lumen and associated beam-hardening artifact. ladder Nodule or Mass The presence of a discrete bladder mass or nodule should be considered suspicious for malignancy (Fig ). In many cases, such lesions may be better appreciated on early phase images when surrounded by low-attenuation urine, particularly when the lesion is avidly enhancing, although a discrete filling defect may not be difficult to appreciate on delayed images when the nodule is large. bnormal Urothelial Enhancement In a study by Kim et al. [3], the attenuation of 20 bladder tumors was measured on arterial, venous, and delayed images. The investigators found that the enhancement of bladder TCC peaked at approximately 105 HU, usually at approximately 60 seconds, before washing out slowly over time. In other words, although TCC has typically been regarded as a hypovascular tumor, these lesions have considerable urothelial hypervascularity and are typically most conspicuous on early phase images. s a result, any focal hyperenhancement of the bladder urothelium must be considered suspicious for malignancy. This also emphasizes the point that although the delayed phase has typically been considered the most important for identifying bladder tumors, early phase images (whether arterial or venous) are likely more important for lesion conspicuity, particularly because subtle lesion enhancement may be more difficult to appreciate once contrast material has been excreted into the bladder (as a result of beam hardening artifact and washout of enhancement) (Figs. 1, 2, 4 11). s a result, for any patient presenting with hematuria, it is critical to obtain at least one early phase image (arterial or venous) through the bladder before contrast excretion occurs. Fig year-old man with hematuria. CT image shows focal hypervascular thickening along left posterolateral bladder wall (arrow) that was confirmed to represent transitional cell carcinoma. JR:203, ugust
6 Raman and Fishman Calcification lthough calcification is seen in rare instances as a sequela of previous infections, schistosomiasis, previously treated malignancy, and even intravesical bacille Calmette- Guérin therapy, the presence of any calcification along the bladder wall, particularly in association with bladder wall thickening, should prompt further evaluation with cystoscopy [19] (Fig. 13). Imaging Mimics Inflammatory or Infectious Cystitis Diffuse bladder wall thickening in the absence of focal nodularity or a discrete mass is rarely a manifestation of malignancy and Fig year-old man with 1-year history of macroscopic hematuria. rterial phase CT image shows multiple hypervascular nodules (arrows) throughout bladder in keeping with multifocal transitional cell carcinoma. Fig year-old woman with incidentally discovered bladder tumor. and, rterial phase image () does not clearly show small tumor nodule (arrow) along left posterior wall of bladder, but delayed excretory phase image () does. Fig year-old man with incidentally diagnosed bladder mass. xial arterial phase CT image shows polyploid lesion (arrow) along right lateral bladder wall with subtle calcification. Finding was confirmed to represent transitional cell carcinoma at cystoscopy. Fig year-old man with gross hematuria. rterial phase CT image shows small hypervascular polyploid nodule (arrow) clearly accentuated by surrounding low-attenuation urine. 352 JR:203, ugust 2014
7 CT of ladder Malignancies Fig year-old man with incidentally diagnosed transitional cell carcinoma. xial arterial phase CT image shows polyploid mass (arrow) in right posterior aspect of bladder. Fig year-old man with cystitis based on positive urinalysis result. Coronal phase CT image shows bladder appears thickened and hyperemic with surrounding fat stranding. usually reflects either underdistention or cystitis. In most cases, it is secondary to bladder infection, although hemorrhagic and radiation cystitis are other possibilities (Fig. 17). ladder Hematoma or lood Clot In many cases, hematoma can be difficult to differentiate from an underlying malignancy, appearing as a discrete mass (Fig. 18). Whereas a hematoma would be expected to have no change in attenuation over the different phases of the study and no clear attachment to the mucosa of the bladder, such subtle distinctions can be difficult to make reliably, and the presence of an underlying tumor can be difficult to exclude. Ultimately, cystoscopy may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis [19]. Enlarged Prostate n enlarged prostate, whether secondary to benign prostatic hypertrophy or to prostate cancer, does not infrequently have a focal nodular component that extends upward to abut the base of the bladder. In most cases, careful appraisal of the sagittal multiplanar reformatted images can help differentiate an enlarged prostate from a true polyploid bladder mass, although in the most concerning cases, cystoscopy may ultimately be necessary [19]. Fig year-old man undergoing evaluation of liver mass. CT image shows incidentally identified bladder mass (arrow) that was ultimately proved to represent transitional cell carcinoma. Fig year-old man with hematuria after renal biopsy. CT image shows large mass (arrow) in bladder that was concluded to represent large hematoma because of its morphologic features and patient s history. ladder Leiomyoma benign bladder mass arising from the smooth muscle layer of the bladder wall, leiomyoma is the most common of a number of benign bladder neoplasms (e.g., adenoma, leiomyoma, hemangiomas, neurofibroma) [2]. lthough the presence of any bladder mass on images should prompt cystoscopy, these lesions are characteristically very well circumscribed and smoothly marginated, in keeping with their mural smooth muscle origin. ladder Lymphoma lthough extraordinarily rare, lymphomatous involvement of the bladder is much more often secondary rather than primary, and evidence of extensive lymphadenopathy is typically found in the abdomen and pelvis. From an imaging standpoint alone, bladder lymphoma cannot be differentiated from other primary bladder masses [2]. JR:203, ugust
8 Raman and Fishman Conclusion Evaluation of the bladder has been largely considered the domain of cystoscopy, and the bladder regularly goes ignored by the radiologist. However, several imaging findings should strongly suggest the presence of malignancy whether CT is performed as CT urography for hematuria or routinely in the emergency setting. The cases in this article illustrate the importance of early phase imaging through the bladder, which is often the most sensitive technique for detecting subtle urothelial thickening, nodularity, and hyperenhancement that may suggest the presence of an underlying tumor. References 1. Raman SP, Horton KM, Fishman EK. Transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: optimizing image interpretation with 3D reconstructions. bdom Imaging 2012; 37: Dighe MK, hargava P, Wright J. Urinary bladder masses: techniques, imaging spectrum, and staging. J Comput ssist Tomogr 2011; 35: Kim JK, Park SY, hn HJ, Kim CS, Cho KS. ladder cancer: analysis of multi-detector row helical CT enhancement pattern and accuracy in tumor detection and perivesical staging. Radiology 2004; 231: Xie Q, Zhang J, Wu PH, et al. ladder transitional cell carcinoma: correlation of contrast enhancement on computed tomography with histological grade and tumour angiogenesis. Clin Radiol 2005; 60: Gufler H, Schulze CG, Wagner S. Incidental findings in computed tomographic angiography for planning percutaneous aortic valve replacement: advanced age, increased cancer prevalence? cta Radiol 2014; 55: O Connor OJ, McSweeney SE, Maher MM. Imaging of hematuria. Radiol Clin North m 2008; 46: Rouprêt MM. Tumours of the bladder: what does the urologist expect from imaging? Diagn Interv Imaging 2012; 93: Turney W, Willatt JM, Nixon D, Crew JP, Cowan NC. Computed tomography urography for diagnosing bladder cancer. JU Int 2006; 98: Dillman JR, Caoili EM, Cohan RH, et al. Comparison of urinary tract distension and opacification using single-bolus 3-phase vs split-bolus 2-phase multidetector row CT urography. J Comput ssist Tomogr 2007; 31: Chow LC, Kwan SW, Olcott EW, Sommer G. Split-bolus MDCT urography with synchronous nephrographic and excretory phase enhancement. JR 2007; 189: Johnson PT, Horton KM, Fishman EK. Optimizing detectability of renal pathology with MDCT: protocols, pearls, and pitfalls. JR 2010; 194: Maheshwari E, O Malley ME, Ghai S, Staunton M, Massey C. Split-bolus MDCT urography: upper tract opacification and performance for upper tract tumors in patients with hematuria. JR 2010; 194: Caoili EM, Inampudi P, Cohan RH, Ellis JH. Optimization of multi-detector row CT urography: effect of compression, saline administration, and prolongation of acquisition delay. Radiology 2005; 235: Kawamoto S, Horton KM, Fishman EK. Opacification of the collecting system and ureters on excretory-phase CT using oral water as contrast medium. JR 2006; 186: Mueller-Lisse UL, Coppenrath EM, Meindl T, et al. Delineation of upper urinary tract segments at MDCT urography in patients with extra-urinary mass lesions: retrospective comparison of standard and low-dose protocols for the excretory phase of imaging. Eur Radiol 2011; 21: Silverman SG, kbar S, Mortele KJ, Tuncali K, hagwat JG, Seifter JL. Multi-detector row CT urography of normal urinary collecting system: furosemide versus saline as adjunct to contrast medium. Radiology 2006; 240: Sadow C, Silverman SG, O Leary MP, Signorovitch JE. ladder cancer detection with CT urography in an academic medical center. Radiology 2008; 249: Kim CS, Kim SH, Lee HJ, Kim YW. Clinical significance of bladder urothelial thickening and enhancement revealed on MDCT urography after transurethral resection of tumor. J Comput ssist Tomogr 2012; 36: Shinagare, Sadow C, Sahni V, Silverman SG. Urinary bladder: normal appearance and mimics of malignancy at CT urography. Cancer Imaging 2011; 11: McPartlin DS, Klausner P, Nottingham CU, et al. Is cystoscopy indicated for incidentally identified bladder wall thickening? Can J Urol 2013; 20: JR:203, ugust 2014
MDCT Evaluation of Ureteral Tumors: Advantages of 3D Reconstruction and Volume Visualization
 Genitourinary Imaging Review Raman et al. MDCT of Ureteral Tumors Genitourinary Imaging Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.206.31 on 02/16/18 from IP address 37.44.206.31. Copyright RRS.
Genitourinary Imaging Review Raman et al. MDCT of Ureteral Tumors Genitourinary Imaging Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.206.31 on 02/16/18 from IP address 37.44.206.31. Copyright RRS.
CT Urography. Bladder. Stuart G. Silverman, M.D.
 CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman, M.D. Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Bladder Boston, MA CT Urography Stuart G.
CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman, M.D. Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Bladder Boston, MA CT Urography Stuart G.
Residents Section Structured Review Article
 Residents Section Structured Review rticle O Connor et al. CT Urography Residents Section Structured Review rticle Residents inradiology Owen J. O Connor 1 Michael M. Maher O Connor OJ, Maher MM Keywords:
Residents Section Structured Review rticle O Connor et al. CT Urography Residents Section Structured Review rticle Residents inradiology Owen J. O Connor 1 Michael M. Maher O Connor OJ, Maher MM Keywords:
Audit of split-bolus CT urography for the investigation of haematuria over a 12 month period at two district general hospitals
 Audit of split-bolus CT urography for the investigation of haematuria over a 12 month period at two district general hospitals Poster No.: C-1349 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary
Audit of split-bolus CT urography for the investigation of haematuria over a 12 month period at two district general hospitals Poster No.: C-1349 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary
IMAGING OF UPPER UT TCC
 IMAGING OF UPPER UT TCC IS THERE AN EVIDENCE BASED STRATEGY? S A MOUSSA FRCS Ed, FRCR WESTERN GENERAL HOSPITAL EDINBURGH UPPER TRACT TCC 0.7-4% of patients with primary bladder cancer develops UT-TCC.
IMAGING OF UPPER UT TCC IS THERE AN EVIDENCE BASED STRATEGY? S A MOUSSA FRCS Ed, FRCR WESTERN GENERAL HOSPITAL EDINBURGH UPPER TRACT TCC 0.7-4% of patients with primary bladder cancer develops UT-TCC.
Yield of Urinary Tract Cancer Diagnosis With Repeat CT Urography in Patients With Hematuria
 Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Mullen et al. CT Urography in Urinary Tract Cancer Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Katherine M. Mullen 1 V. nik Sahni Cheryl. Sadow Stuart G. Silverman Mullen
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Mullen et al. CT Urography in Urinary Tract Cancer Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Katherine M. Mullen 1 V. nik Sahni Cheryl. Sadow Stuart G. Silverman Mullen
CT urography: Saline infusion vs furosemide
 CT urography: Saline infusion vs furosemide Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: C. M. Rodríguez Paz, M. Otero García, P. Rodríguez Fernández, A.
CT urography: Saline infusion vs furosemide Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: C. M. Rodríguez Paz, M. Otero García, P. Rodríguez Fernández, A.
UROGENITAL. Abstract Objective To assess the effect of oral hydration and contrastmedium
 Eur Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00330-010-1785-8 UROGENITAL Dieter H. Szolar Manfred Tillich Klaus W. Preidler Multi-detector CT urography: effect of oral hydration and contrast medium volume on renal parenchymal
Eur Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00330-010-1785-8 UROGENITAL Dieter H. Szolar Manfred Tillich Klaus W. Preidler Multi-detector CT urography: effect of oral hydration and contrast medium volume on renal parenchymal
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research
 Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Patel et al. MDCT Urography With High-Volume Low-Concentration Contrast Agent Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Sohil H. Patel 1 James S. Babb 1 Nicole Hindman
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Patel et al. MDCT Urography With High-Volume Low-Concentration Contrast Agent Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Sohil H. Patel 1 James S. Babb 1 Nicole Hindman
The Queen Alexandra Hospital PORTSMOUTH, UK
 DR NIGEL COWAN DM FRCP FRCR The Queen Alexandra Hospital PORTSMOUTH, UK The development of diagnostic strategies for investigating haematuria with special focus on disease prevalence diagnostic accuracy
DR NIGEL COWAN DM FRCP FRCR The Queen Alexandra Hospital PORTSMOUTH, UK The development of diagnostic strategies for investigating haematuria with special focus on disease prevalence diagnostic accuracy
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay
 Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Patil et al. PET/CT of Transitional Cell Carcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.193.45 on 01/04/18 from IP address
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Patil et al. PET/CT of Transitional Cell Carcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.193.45 on 01/04/18 from IP address
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey
 September 2006 Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey Amsalu Dabela, Harvard Medical School III Outline Overview: Renal Anatomy Our Patient s Story Diagnostic Imaging Studies Appearance
September 2006 Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey Amsalu Dabela, Harvard Medical School III Outline Overview: Renal Anatomy Our Patient s Story Diagnostic Imaging Studies Appearance
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Citation for published version (APA): Leliveld-Kors, A. (2014). Urothelial Cell Carcinoma: Patterns of care and contemporary urography [S.n.
 University of Groningen Urothelial Cell Carcinoma Leliveld, Anna M. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Urothelial Cell Carcinoma Leliveld, Anna M. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
STANDARDIZED MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADRENAL NODULES: EVIDENCE-BASED CONSENSUS POWERSCRIBE MACROS FROM AN ACADEMIC/PRIVATE PRACTICE
 STANDARDIZED MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADRENAL NODULES: EVIDENCE-BASED CONSENSUS POWERSCRIBE MACROS FROM AN ACADEMIC/PRIVATE PRACTICE COLLABORATIVE Pamela Johnson 1, Darcy Wolfman 2, Upma Rawal 3,
STANDARDIZED MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADRENAL NODULES: EVIDENCE-BASED CONSENSUS POWERSCRIBE MACROS FROM AN ACADEMIC/PRIVATE PRACTICE COLLABORATIVE Pamela Johnson 1, Darcy Wolfman 2, Upma Rawal 3,
PICTORIAL ESSAY. Experiences of using a single post-contrast CT scan of the urinary tract after triphasic contrast injection
 Experiences of using a single post-contrast CT scan of the urinary tract after triphasic contrast injection P C Pretorius, FCRad (Diag) SA Drs Visser, Erasmus, Vawda & Partners, Port Elizabeth Corresponding
Experiences of using a single post-contrast CT scan of the urinary tract after triphasic contrast injection P C Pretorius, FCRad (Diag) SA Drs Visser, Erasmus, Vawda & Partners, Port Elizabeth Corresponding
Ask EuroSafe Imaging. Tips & Tricks. CT Working Group
 Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group The use of bi-phase injection protocols to reduce the number of acquisition phases and radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Medical Imaging Department, HIA
Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group The use of bi-phase injection protocols to reduce the number of acquisition phases and radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Medical Imaging Department, HIA
CT Urography. Ureter. Stuart G. Silverman, M.D.
 CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman, M.D. Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Ureter Boston, MA CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman,
CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman, M.D. Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Ureter Boston, MA CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman,
Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma: Multiphase MDCT Enhancement Patterns and Morphologic Features
 Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Raman et al. Enhancement Patterns and Morphologic Features of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Siva P. Raman 1 Pamela T.
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Raman et al. Enhancement Patterns and Morphologic Features of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Siva P. Raman 1 Pamela T.
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules URINARY. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Urinary Site Specific Coding Rules
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules URINARY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules URINARY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
Split-Bolus MDCT Urography with Synchronous Nephrographic and Excretory Phase Enhancement
 Split-olus MDCT Urography Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Lawrence C. Chow 1,2 Sharon W. Kwan 1 Eric W. Olcott 1,3 Graham Sommer 1 Chow LC, Kwan SW, Olcott EW, Sommer G Keywords: bladder, CT, kidney,
Split-olus MDCT Urography Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Lawrence C. Chow 1,2 Sharon W. Kwan 1 Eric W. Olcott 1,3 Graham Sommer 1 Chow LC, Kwan SW, Olcott EW, Sommer G Keywords: bladder, CT, kidney,
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
To explain why image-guided biopsy of upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinoma (UUTUCC) found by CT urography is recommended before surgery.
 An innovative technique for image-guided biopsy of upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinoma detected by CT urography for histopathological confirmation of diagnosis and elimination of false-positive
An innovative technique for image-guided biopsy of upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinoma detected by CT urography for histopathological confirmation of diagnosis and elimination of false-positive
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
ESUR 2018, Sept. 13 th.-16 th., 2018 Barcelona, Spain
 ESUR 2018, Sept. 13 th.-16 th., 2018 Barcelona, Spain OUR APPROACH Incidental adrenal nodule/mass Isaac R Francis, M.B;B.S University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan Disclosures None (in memory) M Korobkin,
ESUR 2018, Sept. 13 th.-16 th., 2018 Barcelona, Spain OUR APPROACH Incidental adrenal nodule/mass Isaac R Francis, M.B;B.S University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan Disclosures None (in memory) M Korobkin,
Urological Science. Imaging diagnosis of ketamine-induced uropathy * Shu-Huei Shen a, b, *, Jia-Hwia Wang b, c. Review article.
 Urological Science 26 (2015) 160e164 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Urological Science journal homepage: www.urol-sci.com Review article Imaging diagnosis of ketamine-induced uropathy * Shu-Huei
Urological Science 26 (2015) 160e164 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Urological Science journal homepage: www.urol-sci.com Review article Imaging diagnosis of ketamine-induced uropathy * Shu-Huei
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6
 Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how clinical presentation drives the diagnostic workup 2. Recognize how patient education is
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how clinical presentation drives the diagnostic workup 2. Recognize how patient education is
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay
 rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
Cystitis cystica is a rare chronic reactive inflammatory
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
4,3,2,1...How Many Phases are Needed? Balancing Diagnostic Efficacy and Radiation Modulation for MDCT Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma
 4,3,2,1...How Many Phases are Needed? Balancing Diagnostic Efficacy and Radiation Modulation for MDCT Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma Jeremy Hackworth, MD, MS Steven P Rowe, MD, PhD Satomi Kawamoto, MD
4,3,2,1...How Many Phases are Needed? Balancing Diagnostic Efficacy and Radiation Modulation for MDCT Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma Jeremy Hackworth, MD, MS Steven P Rowe, MD, PhD Satomi Kawamoto, MD
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO) syndrome: imaging with Multidetector CT (MDCT) prior to minimally invasive treatment
 Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO) syndrome: imaging with Multidetector CT (MDCT) prior to minimally invasive treatment Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E.
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO) syndrome: imaging with Multidetector CT (MDCT) prior to minimally invasive treatment Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E.
ROLE OF MULTIDETECTOR CT UROGRAPHY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH HAEMATURIA
 ROLE OF MULTIDETECTOR CT UROGRAPHY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH HAEMATURIA Varsha Rathi 1, Swenil Shah, Chaitali Nimbalkar 3, Kalyani Patankar 4 1Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Indira
ROLE OF MULTIDETECTOR CT UROGRAPHY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH HAEMATURIA Varsha Rathi 1, Swenil Shah, Chaitali Nimbalkar 3, Kalyani Patankar 4 1Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Indira
Imaging Features of Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients
 Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Ti et al. Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in CPD Patients Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Joanna P. Ti 1 li l-radi 2 Peter J. Conlon 2 Michael J. Lee 1 Martina
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Ti et al. Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in CPD Patients Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Joanna P. Ti 1 li l-radi 2 Peter J. Conlon 2 Michael J. Lee 1 Martina
Incidental Esophageal Findings on Chest CT. Amira Hussien, MD, Elliot Fishman, MD, Bouchra Younes, MD, Ahmed Hatw. Johns Hopkins Medical Institution
 Incidental Esophageal Findings on Chest CT Amira Hussien, MD, Elliot Fishman, MD, ouchra Younes, MD, Ahmed Hatw. Johns Hopkins Medical Institution I have nothing to disclose. DISCLOSURE INTRODUCTION Although
Incidental Esophageal Findings on Chest CT Amira Hussien, MD, Elliot Fishman, MD, ouchra Younes, MD, Ahmed Hatw. Johns Hopkins Medical Institution I have nothing to disclose. DISCLOSURE INTRODUCTION Although
Bladder Cancer Guidelines
 Bladder Cancer Guidelines Agreed by Urology CSG: October 2011 Review Date: September 2013 Bladder Cancer 1. Referral Guidelines The following patients should be considered as potentially having bladder
Bladder Cancer Guidelines Agreed by Urology CSG: October 2011 Review Date: September 2013 Bladder Cancer 1. Referral Guidelines The following patients should be considered as potentially having bladder
Correlation and comparison of CT Urography and non contrast MR Urography in evaluation of malignant urinary tract lesions- A study of 54 patients
 Original Article Correlation and comparison of CT Urography and non contrast MR Urography in evaluation of malignant urinary tract lesions- A study of 54 patients Makada MT 1, Thummar KK 1 1 Department
Original Article Correlation and comparison of CT Urography and non contrast MR Urography in evaluation of malignant urinary tract lesions- A study of 54 patients Makada MT 1, Thummar KK 1 1 Department
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis
 INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION
 BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
11/1/2014. Radiologic incidentalomas Ordering pitfalls Newer technology and applications
 Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
Traumatic and Non Traumatic Adrenal Emergencies
 Traumatic and Non Traumatic Adrenal Emergencies Michael N. Patlas, MD, FRCPC (1), Christine O. Menias, MD (2), Douglas S. Katz, MD, FACR (3), Ania Z. Kielar, MD, FRCPC (4), Alla M. Rozenblit, MD (5), Jorge
Traumatic and Non Traumatic Adrenal Emergencies Michael N. Patlas, MD, FRCPC (1), Christine O. Menias, MD (2), Douglas S. Katz, MD, FACR (3), Ania Z. Kielar, MD, FRCPC (4), Alla M. Rozenblit, MD (5), Jorge
Pancreatic Imaging Mimics: Part 2, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Their Mimics
 Integrative Imaging Pictorial Essay Raman et al. Mimics of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Integrative Imaging Pictorial Essay CME SM Pancreatic Imaging Mimics Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.193
Integrative Imaging Pictorial Essay Raman et al. Mimics of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Integrative Imaging Pictorial Essay CME SM Pancreatic Imaging Mimics Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.193
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 24/June 16, 2014 Page 6628
 ADENOCARCINOMA OF BLADDER-SIGNET RING CELL MUCINOUS VARIANT S. Senthil Kumar 1, D. Prem Charles 2, B. Krishnaswamy 3, P. Viswanathan 4, S. Sarath Chandran 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. Senthil Kumar,
ADENOCARCINOMA OF BLADDER-SIGNET RING CELL MUCINOUS VARIANT S. Senthil Kumar 1, D. Prem Charles 2, B. Krishnaswamy 3, P. Viswanathan 4, S. Sarath Chandran 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. Senthil Kumar,
A patient with recurrent bladder cancer presents with the following history:
 MP/H Quiz A patient with recurrent bladder cancer presents with the following history: 9/23/06 TURB 1/12/07 TURB 4/1/07 TURB 7/12/07 TURB 11/14/07 Non-invasive papillary transitional cell carcinoma from
MP/H Quiz A patient with recurrent bladder cancer presents with the following history: 9/23/06 TURB 1/12/07 TURB 4/1/07 TURB 7/12/07 TURB 11/14/07 Non-invasive papillary transitional cell carcinoma from
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Staging and Grading Last Updated Friday, 14 November 2008
 Staging and Grading Last Updated Friday, 14 November 2008 There is a staging graph below Blood in the urine is the most common indication that something is wrong. Often one will experience pain or difficulty
Staging and Grading Last Updated Friday, 14 November 2008 There is a staging graph below Blood in the urine is the most common indication that something is wrong. Often one will experience pain or difficulty
Virtual Cystoscopy of the Contrast Material Filled Bladder in Patients with Gross Hematuria
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.49 on 11/20/17 from IP address 46.3.195.49. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Jeong Kon Kim 1 Jae Hong hn 1 Taehan Park 2 Han Jong
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.49 on 11/20/17 from IP address 46.3.195.49. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Jeong Kon Kim 1 Jae Hong hn 1 Taehan Park 2 Han Jong
Bladder Case # 1. Principal Diagnosis: Bladder Tumor, Suspect Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Secondary Diagnoses: 1. Hypertension. 2. Hyperlipidemia.
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY Bladder Case # 1 Date: 04/22/2010 Principal Diagnosis: Bladder Tumor, Suspect Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Secondary Diagnoses: 1. Hypertension. 2. Hyperlipidemia. Hospital Course: Mr.
DISCHARGE SUMMARY Bladder Case # 1 Date: 04/22/2010 Principal Diagnosis: Bladder Tumor, Suspect Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Secondary Diagnoses: 1. Hypertension. 2. Hyperlipidemia. Hospital Course: Mr.
How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review
 How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Financial Disclosure This presentation
How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Financial Disclosure This presentation
The Focal Hepatic Lesion: Radiologic Assessment
 The Focal Hepatic Lesion: Radiologic Assessment Kevin Kuo, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient: PS 67 y/o female w/ long history of alcohol use Drinking since age 18, up to one bottle of wine/day
The Focal Hepatic Lesion: Radiologic Assessment Kevin Kuo, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient: PS 67 y/o female w/ long history of alcohol use Drinking since age 18, up to one bottle of wine/day
Diagnostic value of 64 slice spiral computed tomography imaging of the urinary tract during the excretory phase for urinary tract obstruction
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 4761-4766, 2017 Diagnostic value of 64 slice spiral computed tomography imaging of the urinary tract during the excretory phase for urinary tract obstruction DE
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 4761-4766, 2017 Diagnostic value of 64 slice spiral computed tomography imaging of the urinary tract during the excretory phase for urinary tract obstruction DE
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Renal and adrenal tumours Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Renal cell carcinoma 3 Clinical
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Renal and adrenal tumours Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Renal cell carcinoma 3 Clinical
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples. VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė
 Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
MDCT Findings of Renal Trauma
 MDT of Renal Trauma Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/06/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
MDT of Renal Trauma Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/06/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(2): 87-94 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of Multidetector Computed Tomography in Haematuria Ranjan KUMAR a, Raj KUMAR
MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(2): 87-94 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of Multidetector Computed Tomography in Haematuria Ranjan KUMAR a, Raj KUMAR
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
CT Findings of Rupture, Impending Rupture, and Contained Rupture of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Schwartz et al. CT of bdominal ortic neurysms bdominal Imaging Pictorial Essay W57.FM 12/7/06 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.182 on 01/02/18 from IP address 46.3.194.182. Copyright RRS.
Schwartz et al. CT of bdominal ortic neurysms bdominal Imaging Pictorial Essay W57.FM 12/7/06 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.182 on 01/02/18 from IP address 46.3.194.182. Copyright RRS.
Patient Information. Age: 8 y/o Sex: Female. Date of Admission: Date of Discharge:
 Patient Information Age: 8 y/o Sex: Female Date of Admission: 92-10-08 Date of Discharge: 92-10-18 Chief Complaint Severe admominal pain and vomiting with dysuria since last afternoon Present Illness Lower
Patient Information Age: 8 y/o Sex: Female Date of Admission: 92-10-08 Date of Discharge: 92-10-18 Chief Complaint Severe admominal pain and vomiting with dysuria since last afternoon Present Illness Lower
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors
 CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis
 GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
MDCT Enteroclysis Urography With Split-Bolus Technique Provides Information on Ureteral Involvement in Patients With Suspected Bowel Endometriosis
 Women s Imaging Original Research Biscaldi et al. MDCT Enteroclysis Urography of Endometriosis Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING MDCT Enteroclysis Urography With Split-Bolus Technique Provides
Women s Imaging Original Research Biscaldi et al. MDCT Enteroclysis Urography of Endometriosis Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING MDCT Enteroclysis Urography With Split-Bolus Technique Provides
Multitechnique Imaging Findings of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair
 Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Cronin et al. Imaging of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Carmel G. Cronin 1 Mukesh G. Harisinghani Onofrio Catalano Michael. lake
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Cronin et al. Imaging of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Carmel G. Cronin 1 Mukesh G. Harisinghani Onofrio Catalano Michael. lake
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Multidetector CT Urography with Abdominal Compression and Three-Dimensional Reconstruction
 Pictorial Essay Multidetector T Urography with bdominal ompression and Three-imensional Reconstruction ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/28/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright
Pictorial Essay Multidetector T Urography with bdominal ompression and Three-imensional Reconstruction ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/28/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Bladder:
 Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Bladder: Report of Two Cases 1 Hanna Kim, M.D., Soon Nam Oh, M.D., Sung Eun Rha, M.D., Seung Eun Jung, M.D., Young Joon Lee, M.D., Jae Young Byun, M.D., Chan-Kwon
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Bladder: Report of Two Cases 1 Hanna Kim, M.D., Soon Nam Oh, M.D., Sung Eun Rha, M.D., Seung Eun Jung, M.D., Young Joon Lee, M.D., Jae Young Byun, M.D., Chan-Kwon
National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
 CONGENITAL SEMINAL VESICLE CYST ASSOCIATED WITH IPSILATERAL RENAL AGENESIS MIMICKING BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Chien-Chang Kao, 1 Ching-Jiunn Wu, 2 Guang-Huan
CONGENITAL SEMINAL VESICLE CYST ASSOCIATED WITH IPSILATERAL RENAL AGENESIS MIMICKING BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Chien-Chang Kao, 1 Ching-Jiunn Wu, 2 Guang-Huan
Role of imaging in evaluation of genitourinary i trauma Spectrum of GU injuries Relevance of imaging findings in determining management Focus on MDCT
 Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
KEYWORDS Bladder cancer, Transitional cell carcinoma, Magnetic resonance imaging, staging, Tumor node metastasis
 DIAGNOSTIC ACCURACY OF MRI IN DIFFERENTIATING NON-MUSCLE INVASIVE FROM MUSCLE INVASIVE BLADDER CARCINOMA TAKING HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STAGING AS A STANDARD. Syed Muhammad Faiq 1,Khujasta Mehtab 1,Nazish Naz
DIAGNOSTIC ACCURACY OF MRI IN DIFFERENTIATING NON-MUSCLE INVASIVE FROM MUSCLE INVASIVE BLADDER CARCINOMA TAKING HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STAGING AS A STANDARD. Syed Muhammad Faiq 1,Khujasta Mehtab 1,Nazish Naz
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Plasmacytoid Variant Urothelial Carcinoma: Diagnostic and Grossing Challenges. Kailyn Gibson MS, PA-ASCP, Congli Wang, MD
 1 Plasmacytoid Variant Urothelial Carcinoma: Diagnostic and Grossing Challenges Kailyn Gibson MS, PA-ASCP, Congli Wang, MD Johns Hopkins Hospital Department of Surgical Pathology 2 Plasmacytoid Variant
1 Plasmacytoid Variant Urothelial Carcinoma: Diagnostic and Grossing Challenges Kailyn Gibson MS, PA-ASCP, Congli Wang, MD Johns Hopkins Hospital Department of Surgical Pathology 2 Plasmacytoid Variant
Citation International journal of urology (2. Right which has been published in final f
 Title Novel constant-pressure irrigation of renal pelvic tumors after ipsila Nakamura, Kenji; Terada, Naoki; Sug Author(s) Toshinori; Matsui, Yoshiyuki; Imamu Kazutoshi; Kamba, Tomomi; Yoshimura Citation
Title Novel constant-pressure irrigation of renal pelvic tumors after ipsila Nakamura, Kenji; Terada, Naoki; Sug Author(s) Toshinori; Matsui, Yoshiyuki; Imamu Kazutoshi; Kamba, Tomomi; Yoshimura Citation
Reviewer's report. Version:1Date:31 January Reviewer:IOANNIS LEOTSAKOS. Reviewer's report:
 Reviewer's report Title:A segregation index combining phenotypic (clinical characteristics) and genotypic (gene expression) biomarkers from a urine sample to triage out patients presenting with hematuria
Reviewer's report Title:A segregation index combining phenotypic (clinical characteristics) and genotypic (gene expression) biomarkers from a urine sample to triage out patients presenting with hematuria
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach
 Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Bladder Cancer in Primary Care. Dr Penny Kehagioglou Consultant Clinical Oncologist
 Bladder Cancer in Primary Care Dr Penny Kehagioglou Consultant Clinical Oncologist Objectives Patient presentation in primary care Investigating bladder cancer Management of bladder cancer Differential
Bladder Cancer in Primary Care Dr Penny Kehagioglou Consultant Clinical Oncologist Objectives Patient presentation in primary care Investigating bladder cancer Management of bladder cancer Differential
Imaging characterization of renal clear cell carcinoma
 Imaging characterization of renal clear cell carcinoma Poster No.: C-0327 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ballester 1, A. Gaser 2, M. Dotta 1, M. F. CAPPA 1, F. Hammar 1 ; 1 2
Imaging characterization of renal clear cell carcinoma Poster No.: C-0327 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ballester 1, A. Gaser 2, M. Dotta 1, M. F. CAPPA 1, F. Hammar 1 ; 1 2
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Some prostatic diseases
 Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
Life Science Journal 2015;12(6)
 Evaluation of the Role of Computer Tomography Virtual Cystoscopy in Diagnosis of Carcinoma of the Bladder RababShimy¹, Ahmed Mehena 2, Mohamed Wishahi 2, HossamElganzoury 2,Ahmed M. Kamal 2, Mohamed Badawy
Evaluation of the Role of Computer Tomography Virtual Cystoscopy in Diagnosis of Carcinoma of the Bladder RababShimy¹, Ahmed Mehena 2, Mohamed Wishahi 2, HossamElganzoury 2,Ahmed M. Kamal 2, Mohamed Badawy
1/25/13 Right partial nephrectomy followed by completion right radical nephrectomy.
 History and Physical Case Scenario 1 45 year old white male presents with complaints of nausea, weight loss, and back pain. A CT of the chest, abdomen and pelvis was done on 12/8/12 that revealed a 12
History and Physical Case Scenario 1 45 year old white male presents with complaints of nausea, weight loss, and back pain. A CT of the chest, abdomen and pelvis was done on 12/8/12 that revealed a 12
Learning Objectives. 1. Identify which patients meet criteria for annual lung cancer screening
 Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Common Blind Spots on Chest CT: Where Are They All Hiding? Part 1 Airways, Lungs, and Pleura
 Residents Section Structured Review Wu et al. Common lind Spots on Chest CT Residents Section Structured Review Carol C. Wu 1 Leila Khorashadi 2 Gerald F. bbott 1 Matthew D. Gilman 1 Wu CC, Khorashadi
Residents Section Structured Review Wu et al. Common lind Spots on Chest CT Residents Section Structured Review Carol C. Wu 1 Leila Khorashadi 2 Gerald F. bbott 1 Matthew D. Gilman 1 Wu CC, Khorashadi
3/16/2015 VCUG. T2-weighted MRI of lower pelvis
 1 Reference: Grayson DE, Abbot RM, Levy AD, Sherman PM (2002) Emphysematous infections of the abdomen and pelvis: a pictorial review. RadioGraphics 22: 543-561. 2 VCUG T2-weighted MRI of lower pelvis Reference:
1 Reference: Grayson DE, Abbot RM, Levy AD, Sherman PM (2002) Emphysematous infections of the abdomen and pelvis: a pictorial review. RadioGraphics 22: 543-561. 2 VCUG T2-weighted MRI of lower pelvis Reference:
Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
 May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
The Incidental Renal lesion
 The Incidental Renal lesion BACKGROUND Increase in abdominal CT/US in last 15 years Resulted in detection of many (small) renal lesions 50% > 50yrs has at least 1 lesion majority simple cysts Renal lesions
The Incidental Renal lesion BACKGROUND Increase in abdominal CT/US in last 15 years Resulted in detection of many (small) renal lesions 50% > 50yrs has at least 1 lesion majority simple cysts Renal lesions
How To Approach Renal Masses? - Differential Diagnosis On Image
 How To Approach Renal Masses? - Differential Diagnosis On Image Poster No.: C-1646 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. E. A. G. Costa, A. Gomes, A. Duarte, I. Távora; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
How To Approach Renal Masses? - Differential Diagnosis On Image Poster No.: C-1646 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. E. A. G. Costa, A. Gomes, A. Duarte, I. Távora; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
10/23/2012 CASE STUDIES: RENAL AND UROLOGIC IMPAIRMENTS. 1) Are there any clues from this history that suggest a particular diagnosis?
 Case # 1 An underwriter enters your office, hands you a sheet of paper, and asks What do you think? Can we make an offer? You look at the paper and see it s lab results on a 60 year male looking for $500,000
Case # 1 An underwriter enters your office, hands you a sheet of paper, and asks What do you think? Can we make an offer? You look at the paper and see it s lab results on a 60 year male looking for $500,000
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
Gadolinium-Enhanced Fat- Suppressed T1-Weighted Imaging for Staging Ureteral Carcinoma: Correlation with Histopathology
 Obuchi et al. T1-Weighted Imaging for Staging Ureteral Carcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Clinical Observations Masao Obuchi 1,2 Kousei Ishigami 3 Koji Takahashi 4 Minoru Honda 5 Toshiyuki Mitsuya 6 David
Obuchi et al. T1-Weighted Imaging for Staging Ureteral Carcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Clinical Observations Masao Obuchi 1,2 Kousei Ishigami 3 Koji Takahashi 4 Minoru Honda 5 Toshiyuki Mitsuya 6 David
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22
 Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
