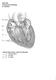
Using Figure 14.1, match the following: 1) Myelin sheath. 1) 2) Cell body of ANS preganglionic neuron. 2)
|
|
|
- Emory Earl Richardson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Practice Exam 1 AP 2 chapters 14 and 18 Name MATCHING: Match labeled areas with the appropriate terminology from the list below. Figure 14.1 Using Figure 14.1, match the following: 1) Myelin sheath. 1) 2) Cell body of ANS preganglionic neuron. 2) 3) Cell body of ANS postganglionic neuron. 3) 4) Cell body of the somatic neuron. 4) TRUE/FALSE. Answer "A" if the statement is true or "B" if it is false. 5) Because the ANS is a visceral motor system, afferent pathways are of no importance and actually are rarely found. 5) 6) The autonomic nervous system may cause activation or inhibition, depending on the division that is active and the target that is affected. 6) 7) Thermoregulatory responses to increased heat are mediated by the sympathetic nervous division. 7) 8) The adrenal medulla is considered a "misplaced" sympathetic ganglion by some. 8) 1
2 9) Most disorders of the autonomic nervous system reflect abnormalities of smooth muscle control. 9) 10) Acetylcholine is the substance released by the axonal endings of the somatic efferent fibers and by the parasympathetic nerve fiber endings. 10) 11) Most body organs are innervated by only the sympathetic division of the nervous system. 11) 12) Through direct neural stimulation, the sympathetic division promotes many metabolic effects via hormone release. 12) 13) Alpha-adrenergic effects are usually stimulatory and mediatory. 13) 14) Cranial nerves VII, IX, and X contain postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system. 14) 15) The ANS stimulates smooth and skeletal muscles and glands, whereas the somatic nervous system innervates cardiac muscles only. 15) 16) Norepinephrine-releasing fibers are called cholinergic fibers. 16) 17) Autonomic ganglia are motor ganglia only. 17) 18) The craniosacral division is another name for the parasympathetic division. 18) 19) Most blood vessels are innervated by the sympathetic division alone. 19) 20) The structures that specifically exhibit vasomotor tone are mostly under sympathetic control. 20) 21) Because many of the same cardiac cells are innervated by both parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers, the influence of the two divisions on the heart is synergistic. 21) 22) -adrenergic receptors are the only receptors found on the heart. 22) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 23) The secretions of the adrenal medulla act to supplement the effects of. 23) A) neurosecretory substances B) vagus nerve activity C) parasympathetic innervation D) sympathetic stimulation 24) Which of the following does not describe the ANS? 24) A) a system of motor neurons that innervates all muscle cells B) a system of motor neurons that innervates smooth and cardiac muscle and glands C) general visceral motor system D) involuntary nervous system 2
3 25) The somatic and autonomic nervous systems differ in all of the following except. 25) A) their efferent pathways B) their effectors C) to some degree in target responses to their neurotransmitters D) all of the neurotransmitters 26) A drug that might be used specifically to reduce heart rate in cardiac patients could be. A) anticholinesterase B) norepinephrine C) epinephrine D) a beta-blocker 26) 27) Cardiovascular effects of the sympathetic division include all except. 27) A) dilation of the blood vessels serving the skin and digestive viscera B) constriction of most blood vessels C) dilation of the vessels serving the skeletal muscles D) increase of heart rate and force 28) Over 90% of all parasympathetic fibers are derived from cranial nerve number. 28) A) VII B) X C) XII D) V 29) The "resting and digesting" division of the autonomic nervous system is the. 29) A) parasympathetic division B) peripheral nervous system C) sympathetic division D) somatic division 30) Control of temperature, endocrine activity, and thirst are functions associated with the. A) medulla B) hypothalamus C) cerebellum D) thalamus 30) 31) Which of these effectors is not directly controlled by the autonomic nervous system? 31) A) smooth muscle B) cardiac muscle C) most glands D) skeletal muscle 32) Which of the following is not a result of parasympathetic stimulation? 32) A) increased peristalsis of the digestive viscera B) elimination of urine C) salivation D) dilation of the pupils 33) Which of the following statements is not true? 33) A) Sympathetic ganglia are within a few centimeters of the CNS; parasympathetic are close to visceral organs served. B) Sympathetic origin is craniosacral; parasympathetic is thoracolumbar. C) Sympathetic division has short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers; parasympathetic has long preganglionic and short postganglionic fibers. D) Sympathetic has extensive branching of preganglionic fibers; parasympathetic has minimal branching of preganglionic fibers. 3
4 34) Sympathetic responses generally are widespread because. 34) A) preganglionic fibers are short B) NE and epinephrine are secreted into the blood as part of the sympathetic response C) inactivation of ACh is fairly slow D) preganglionic fibers are long 35) Autonomic ganglia contain. 35) A) the cell bodies of motor neurons B) synapses between postganglionic fibers and their effectors C) an outer connective tissue capsule around the cell bodies of preganglionic motor neurons D) both somatic afferent and efferent neurons 36) The parasympathetic fibers of the nerves innervate smooth muscles of the eye that cause the lenses to bulge to accommodate close vision. A) abducens B) trochlear C) oculomotor D) optic 36) 37) The parasympathetic tone. 37) A) determines normal activity of the urinary tract B) prevents unnecessary heart deceleration C) accelerates activity of the digestive tract D) causes blood pressure to rise 38) Beta-blockers. 38) A) have widespread sympathetic effects B) are potent antidepressants C) increase a dangerously low heart rate D) decrease heart rate and blood pressure 39) Which is a uniquely sympathetic function? 39) A) regulation of body temperature B) regulation of cardiac rate C) regulation of respiratory rate D) regulation of pupil size 40) Sympathetic division stimulation causes. 40) A) increased blood glucose, increased GI peristalsis, and decreased heart rate and blood pressure B) increased blood glucose, decreased GI peristalsis, and increased heart rate and blood pressure C) decreased blood glucose, increased GI peristalsis, and increased heart rate and blood pressure D) decreased blood glucose, increased GI peristalsis, and decreased heart rate and blood pressure 41) The smooth muscle of the digestive viscera is served largely by the. 41) A) pelvic nerves B) lumbar splanchnic nerves C) tenth cranial nerve D) cephalic plexus 42) The route of major parasympathetic outflow from the head is via the. 42) A) phrenic nerve B) sacral nerve C) vagus nerve D) sympathetic trunk 4
5 43) Parasympathetic functions include. 43) A) allowing the body to cope with an external threat B) lens accommodation for close vision C) a stimulation of heart rate and force of contraction D) mobilizing storage energy sources 44) Emotions influence autonomic reactions primarily through integration in the. 44) A) inferior colliculus B) lateral horn of the spinal cord C) hypothalamus D) lateral geniculate of the thalamus MATCHING: Match labeled areas with the appropriate terminology from the list below. Figure 18.1 Using Figure 18.1, match the following: 45) Purkinje fibers. 45) 46) SA node. 46) 47) AV bundle. 47) 48) AV node. 48) 49) Bundle branches. 49) 5
6 Figure 18.2 Using Figure 18.2, match the following: 50) Atrial depolarization. 50) 51) Point after which pressure begins to rise in the aorta. 51) 52) Ventricular repolarization. 52) 53) Point that represents the "dup" sound made by the heart. 53) 6
7 Figure 18.3 Using Figure 18.3, match the following: 54) Ventricular fibrillation. 54) 55) Second-degree heart block. 55) 56) Junctional rhythm. 56) 57) Normal sinus rhythm. 57) 7
8 MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Match the following: 58) The pacemaker of the heart. A) Purkinje fibers 58) 59) Found in the interventricular septum. 60) Network found in the ventricular myocardium. B) AV node C) AV bundle D) SA node 59) 60) 61) The point in the conduction system of the heart where the impulse is temporarily delayed. 61) Match the following: 62) Prevents backflow into the left ventricle. 63) Prevents backflow into the right atrium. A) Aortic valve B) Pulmonary valves C) Mitral valve 62) 63) 64) Prevents backflow into the left atrium. D) Tricuspid valve 64) 65) Prevents backflow into the right ventricle. 65) 66) AV valve with two flaps. 66) 67) AV valve with three flaps. 67) 8
9 MATCHING: Match labeled areas with the appropriate terminology from the list below. Figure 18.4 Using Figure 18.4, match the following: 68) Tricuspid valve. 68) 69) Mitral valve. 69) 70) Right atrium. 70) 71) Left ventricle. 71) 72) Pulmonary veins. 72) TRUE/FALSE. Answer "A" if the statement is true or "B" if it is false. 73) Anastomoses among coronary arterial branches provide collateral routes for blood delivery to the heart muscle. 73) 74) Tissues damaged by myocardial infarction are replaced by connective tissue. 74) 75) The left side of the heart pumps the same volume of blood as the right. 75) 76) Chronic release of excess thyroxine can cause a sustained increase in heart rate and a weakened heart. 76) 9
10 77) Cardiac muscle has more mitochondria and depends less on a continual supply of oxygen than does skeletal muscle. 77) 78) Arterial blood supply to heart muscle is continuous whether the heart is in systole or diastole. 78) 79) The "lub" sounds of the heart are valuable in diagnosis because they provide information about the function of the heart's pulmonary and aortic valves. 79) 80) An ECG provides direct information about valve function. 80) 81) As pressure in the aorta rises due to atherosclerosis, more ventricular pressure is required to open the aortic valve. 81) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 82) Normal heart sounds are caused by which of the following events? 82) A) friction of blood against the chamber walls B) opening and closing of the heart valves C) closure of the heart valves D) excitation of the SA node 83) Which of the events below does not occur when the semilunar valves are open? 83) A) Ventricles are in systole. B) Blood enters pulmonary arteries and the aorta. C) AV valves are closed. D) Ventricles are in diastole. 84) The left ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right wall in order to. 84) A) accommodate a greater volume of blood B) expand the thoracic cage during diastole C) pump blood through a smaller valve D) pump blood with greater pressure 85) The P wave of a normal electrocardiogram indicates. 85) A) atrial depolarization B) ventricular depolarization C) ventricular repolarization D) atrial repolarization 86) Small muscle masses attached to the chordae tendineae are the. 86) A) venae cavae B) trabeculae carneae C) papillary muscles D) pectinate muscles 87) The term for pain associated with deficient blood delivery to the heart that may be caused by the transient spasm of coronary arteries is. A) pericarditis B) ischemia C) myocardial infarct D) angina pectoris 87) 10
11 88) To auscultate the aortic semilunar valve, you would place your stethoscope in the. 88) A) second intercostal space to the right of the sternum B) fifth intercostal space inferior to the left nipple C) fifth right intercostal space D) second intercostal space to the left of the sternum 89) The fact that the left ventricle of the heart is thicker than the right ventricle reveals that it. A) pumps blood against a greater resistance B) expands the thoracic cage C) sends blood through a smaller valve D) pumps a greater volume of blood 89) 90) Norepinephrine acts on the heart by. 90) A) blocking the action of calcium B) causing threshold to be reached more quickly C) causing a decrease in stroke volume D) decreasing heart contractility 91) Which of these vessels receives blood during ventricular systole? 91) A) aorta only B) both the aorta and pulmonary trunk C) pulmonary arteries only D) pulmonary veins only 92) Which of the following is not part of the conduction system of the heart? 92) A) bundle of His B) AV node C) SA node D) AV valve 93) The tricuspid valve is closed. 93) A) by the movement of blood from atrium to ventricle B) when the ventricle is in systole C) while the ventricle is in diastole D) while the atrium is contracting 94) Select the correct statement about the heart valves. 94) A) Aortic and pulmonary valves control the flow of blood into the heart. B) The tricuspid valve divides the left atrium from the left ventricle. C) The mitral valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle. D) The AV valves are supported by chordae tendineae so that regurgitation of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction does not occur. 95) Select the correct statement about the function of myocardial cells. 95) A) Each cardiac muscle cell is innervated by a sympathetic nerve ending so that the nervous system can increase heart rate. B) The influx of potassium ions from extracellular sources is the initiating event in cardiac muscle contraction. C) The refractory period in skeletal muscle is much longer than that in cardiac muscle. D) The entire heart contracts as a unit or it does not contract at all. 11
12 96) Compared to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle. 96) A) has gap junctions that allow it to act as a functional syncytium B) lacks striations C) cells are larger than skeletal muscle cells D) has more nuclei per cell 97) During the period of ventricular filling. 97) A) pressure in the heart is at its peak B) it is represented by the P wave on the ECG C) blood flows passively through the atria and the open AV valves into the ventricles D) the atria remain in diastole 98) The second heart sound is heard during which phase of the cardiac cycle? 98) A) isovolumetric relaxation B) ventricular filling C) isovolumetric contraction D) ventricular ejection 99) Select the correct statement about cardiac output. 99) A) A slow heart rate increases end diastolic volume, stroke volume, and force of contraction. B) Stroke volume increases if end diastolic volume decreases. C) If a semilunar valve were partially obstructed, the end systolic volume in the affected ventricle would be decreased. D) Decreased venous return will result in increased end diastolic volume. 100) Isovolumetric contraction. 100) A) occurs immediately after the aortic and pulmonary valves close B) refers to the short period during ventricular systole when the ventricles are completely closed chambers C) occurs while the AV valves are open D) occurs only in people with heart valve defects 12
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Approximately the size of your fist Location. Pericardial physiology
 Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
IP: Regulation of Cardiac Output
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
The Heart. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Autonomic Division of NS
 Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates. *Ensuring one-way blood. *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction
 *Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton. Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node.
 BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
Neuropsychiatry Block
 Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS)
 Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS) ANS Pharmacology Lecture 1 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy, University of Sulaimani 2018-2019 AUTOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) The ANS is the major
Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS) ANS Pharmacology Lecture 1 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy, University of Sulaimani 2018-2019 AUTOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) The ANS is the major
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
The Autonomic Nervous
 Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 18 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part A Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of a fist Location In the mediastinum
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 18 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part A Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of a fist Location In the mediastinum
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 12 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter 12 Learning Outcomes 12-1 12-2 Describe the anatomy of the heart,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 12 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter 12 Learning Outcomes 12-1 12-2 Describe the anatomy of the heart,
Collin County Community College. ! BIOL Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5. The Heart
 Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
Cardiovascular Physiology. Heart Physiology. Introduction. The heart. Electrophysiology of the heart
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
The Nervous System. Autonomic Division. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology
 The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices. Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY]](/thumbs/96/126998162.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Describe the ionic basis of action potentials in cardiac contractile and autorhythmic cells Explain the relationship
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Describe the ionic basis of action potentials in cardiac contractile and autorhythmic cells Explain the relationship
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Lujain Hamdan. Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem. Mohammed khatatbeh
 12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 13 Done by Tamara Wahbeh Corrected by Doctor Omar Shaheen In this sheet the following concepts will be covered: 1. Divisions of the nervous system 2. Anatomy of the ANS. 3. ANS innervations. 4.
number 13 Done by Tamara Wahbeh Corrected by Doctor Omar Shaheen In this sheet the following concepts will be covered: 1. Divisions of the nervous system 2. Anatomy of the ANS. 3. ANS innervations. 4.
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
4/8/2015. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS. Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Ch 9. The Autonomic Nervous System
 Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
Do Now pg What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in.
 Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 2 Nervous, Muscle, Cardiovascular
 AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 2 Nervous, Muscle, Cardiovascular Select the best answer choice in the questions below. 1) On the electrocardiogram, repolarization of the atria is represented by the: A) P wave
AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 2 Nervous, Muscle, Cardiovascular Select the best answer choice in the questions below. 1) On the electrocardiogram, repolarization of the atria is represented by the: A) P wave
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System
 Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions
 The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
4/9/2019. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni
 Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Introduction. Circulation
 Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
The Heart. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System Learning Outcomes Describe the superficial anatomy of
20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System Learning Outcomes Describe the superficial anatomy of
The Autonomic Nervous System
 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully integrate text
14 The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully integrate text
Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions
 16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
Chapter 11. The Cardiovascular System. Clicker Questions Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
The Cardiovascular System. anatom.ua 1
 The Cardiovascular System anatom.ua 1 The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial
The Cardiovascular System anatom.ua 1 The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Storage is accomplished through the following mechanisms:
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 13, 2017 Examples of Coordinated Autonomic and Motor Responses and Return to the Cardiovascular System 1) Micturition Micturition, or the process of emptying
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 13, 2017 Examples of Coordinated Autonomic and Motor Responses and Return to the Cardiovascular System 1) Micturition Micturition, or the process of emptying
