The Muscular System. Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move.
|
|
|
- Amberly Annabelle Gray
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Muscular System Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move.
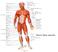
2 Anterior View
3 Posterior View
4 TRIVIA! How many muscles are there in the human body? Answer: 640 Muscles The muscles make up about 40 % of the body mass. What is the longest muscle in the body? Answer: The Sartorius The Sartorius runs from the outside of the hip, down and across to the inside of the knee. It twists and pulls the thigh outwards. What is the smallest muscle in the body? Answer: The Stapedius The Stapedius is located deep in the ear. It is only 5mm long and thinner than cotton thread. It is involved in hearing. What is the biggest muscle in the body? Answer: The Gluteus Maximus The Gluteus Maximus is located in the buttock. It pulls the leg backwards powerfully for walking and running.
5 Functions of the Muscles Movement Maintenance of posture and muscle tone Heat production Protects the bones and internal organs.
6 Muscle Classification Functionally Voluntarily can be moved at will Involuntarily can t be moved intentionally Structurally Striated have stripes across the fiber Smooth no striations
7 The 3 Types of Muscles 3 Types of Muscles Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle Cardiac Muscle
8 Smooth Muscle Fibers are thin and spindle shaped. No striations Single nuclei Involuntary Contracts slowly
9 Smooth Muscle They fatigue but very slowly Found in the circulatory system Lining of the blood vessels Helps in the circulation of the blood Found in the digestive system Esophagus, stomach, intestine Controls digestion Found in the respiratory system Controls breathing Found in the urinary system Urinary bladder Controls urination
10 Cardiac Muscle Cells are branched and appear fused with one another Has striations Each cell has a central nuclei Involuntary
11 Cardiac Muscle Found ONLY in the heart Contractions of the heart muscles pump blood throughout the body and account for the heartbeat. Healthy cardiac muscle NEVER fatigues or else
12 Skeletal Muscle Fibers are long and cylindrical Has many nuclei Has striations Have alternating dark and light bands Voluntary
13 Skeletal Muscle Attached to skeleton by tendons Causes movement of bones at the joints. And yes they do fatigue Muscle fatigue activity what substance forms causing muscle fatigue??? Lactic Acid
14 Functions of Skeletal Muscle Movement muscle move bones by pulling not pushing. Synergists any movement is generally accomplished by more than one muscle. All of the muscles responsible for the movement are synergists. The one that is most responsible for the movement is the Prime Mover (agonist).
15 Functions of Skeletal Muscle Movement Antagonists muscles and muscle groups usually work in pairs example the biceps flex your arm and its partner the triceps extend your arm. The two muscles are antagonists, i.e. cause opposite actions. when one contracts the other relaxes. Levators muscle that raise a body part.
16 Anatomy of the Muscular System Origin Insertion Action Muscle attachment that remains fixed Muscle attachment that moves What joint movement a muscle produces i.e. flexion, extension, abduction, etc.
17 For muscles to create a movement, they can only pull, not push Muscles in the body rarely work alone, & are usually arranged in groups surrounding a joint A muscle that contracts to create the desired action is known as an agonist or prime mover A muscle that helps the agonist is a synergist A muscle that opposes the action of the agonist, therefore undoing the desired action is an antagonist
18 Categories of skeletal muscle actions Categories Actions Extensor Increases the angle at a joint Flexor Decreases the angle at a joint Abductor Moves limb away from long axis of body Adductor Moves limb toward long axis of body Levator Moves insertion upward Depressor Moves insertion downward Rotator Rotates a bone along its axis Sphincter Constricts an opening
19
20
21 Functions of Skeletal Muscle Maintenance of posture or muscle tone We are able to maintain our body position because of tonic contractions in our skeletal muscles. These contractions don t produce movement yet hold our muscles in position. Heat production contraction of muscles produces most of the heat required to maintain body temperature.
22 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composed of striated muscle cells (=muscle fibers) and connective tissue. Most muscles attach to 2 bones that have a moveable joint between them. The attachment to the bone that does not move is the origin. The attachment to the bone that moves is the insertion. Tendons anchor muscle firmly to bones. Tendons are made of dense fibrous connective tissue. Ligaments connect bone to bone at a joint.
23 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Bursae small fluid filled sacs that lie between some tendons and the bones beneath them. They are made of connective tissue and are lined with synovial membrane that secretes synovial fluid.
24 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Contribution of the nervous system Electrochemical impulses travel from the frontal lobes of the cerebrum via motor nerves to the muscle fibers and cause them to contract. Sensation is a function of the brain impulses are integrated in the parietal lobes of the cerebrum (conscious muscle sense) and in the cerebellum (unconscious). These activities promote coordination.
25 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Microscopic anatomy Muscle cells (fibers) are grouped in a highly organized way in the muscle. The membrane that surrounds the muscle cell is called the sarcolemma. Muscle cells are filled with 2 types of fine threadlike proteins called myofilaments: myosin (thick) and actin (thin). These structures slide past each other causing the muscle cell to contract or shorten. The myofilaments are arranged in the cells in small units called sarcomeres.
26 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Neuromuscular junction Spot where the axon of a motor nerve nears the muscle fiber. The axon terminal does not touch the muscle but comes close. The space between the axon and the muscle cell is called the synapse. Within the terminal end of the axon are small sacs filled with a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine.
27 Muscle Contraction Sequence Electrical impulse travels down a motor neuron. When it reaches the end, acetylcholine (chemical) is released into the synapse. Acetylcholine bind to special receptors on the muscle cell and causes an electrical impulse to spread over the cell. The sarcomeres shorten and the muscle cell contracts.
28 Anatomy of skeletal muscles tendon epimysium perimysium Muscle Fascicle Surrounded by perimysium Skeletal muscle Surrounded by epimysium endomysium Skeletal muscle fiber (cell) Surrounded by endomysium
29 Microanatomy of a Muscle Fiber (cell)
30 Microanatomy of a Muscle Fiber (Cell) transverse (T) tubules sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae sarcolemma myoglobin mitochondria thick myofilament thin myofilament myofibril nuclei triad Play IP Anatomy of Skeletal muscles (IP p. 7)
31 Muscle fiber Myofibril Z-line sarcomere Sarcomere Thin filaments Thin myofilament Myosin molecule of thick myofilament Thick filaments
32 Thin Myofilament (myosin binding site)
33 Thick myofilament (has ATP & actin binding site)
34 Sarcomere Z line A band H zone Z line Thin myofilaments I band Zone of overlap Thick myofilaments M line Zone of overlap
35 Sliding Filament Theory Myosin heads attach to actin molecules (at binding (active) site) Myosin pulls on actin, causing thin myofilaments to slide across thick myofilaments, towards the center of the sarcomere Sarcomere shortens, I bands get smaller, H zone gets smaller, & zone of overlap increases
36 As sarcomeres shorten, myofibril shortens. As myofibrils shorten, so does muscle fiber Once a muscle fiber begins to contract, it will contract maximally This is known as the all or none principle
37
38 Sarcomere Z A Z A Z I Z Z Z
39 Physiology of skeletal muscle contraction Skeletal muscles require stimulation from the nervous system in order to contract Motor neurons are the cells that cause muscle fibers to contract cell body dendrites axon hillock axon telodendria Synaptic terminals (synaptic end bulbs) (motor neuron)
40 Neuromuscular junction telodendria Synaptic terminal (end bulb) Synaptic vessicles containing Ach Synaptic cleft Neuromuscular junction Motor end plate of sarcolemma
41 Overview of Events at the neuromuscular junction An action potential (AP), an electrical impulse, travels down the axon of the motor neuron to the end bulbs (synaptic terminals) The AP causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the end bulb membrane, resulting in the release of Acetylcholine (Ach) into the synaptic cleft Ach diffuses across the synaptic cleft & binds to Ach receptors on the motor end plate The binding of Ach to its receptors causes a new AP to be generated along the muscle cell membrane Immediately after it binds to its receptors, Ach will be broken down by Acetylcholinesterase (AchE) an enzyme present in the synaptic cleft
42 Arrival of an action potential at the synaptic terminal Arriving action potential Action potential Synaptic terminal Axon Sarcolemma Synaptic cleft Sarcolemma of motor end plate Vesicles ACh AChE molecules ACh receptor site Muscle fiber An action potential (AP), an electrical impulse, travels down the axon of the motor neuron to the end bulbs (synaptic terminals) Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 7-4(b-c) 2 of 5
43 Arrival of an action potential at the synaptic terminal Arriving action potential Action potential Synaptic terminal Axon Sarcolemma Synaptic cleft Sarcolemma of motor end plate Vesicles ACh AChE molecules ACh receptor site Muscle fiber Release of acetylcholine Vesicles in the synaptic terminal fuse with the neuronal membrane and dump their contents into the synaptic cleft. The AP causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the end bulb membrane, resulting in the release of Acetylcholine (Ach) into the synaptic cleft Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 7-4(b-c) 3 of 5
44 Arrival of an action potential at the synaptic terminal Arriving action potential Action potential Synaptic terminal Axon Sarcolemma Synaptic cleft Sarcolemma of motor end plate Vesicles ACh AChE molecules ACh receptor site Muscle fiber Release of acetylcholine Vesicles in the synaptic terminal fuse with the neuronal membrane and dump their contents into the synaptic cleft. ACh binding at the motor and plate The binding of ACh to the receptors increases the membrane permeability to sodium ions. Sodium ions then rush into the cell. Na + Ach diffuses across the synaptic cleft & binds to Ach receptors on the motor end plate Na + Na + Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 7-4(b-c) 4 of 5
45 The binding of Ach to its receptors causes a new AP to be generated along the muscle cell membrane Immediately after it binds to its receptors, Ach will be broken down by Acetylcholinesterase (AchE) an enzyme present in the synaptic cleft
46 Physiology of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Table 7-1 Once an action potential (AP) is generated at the motor end plate it will spread like an electrical current along the sarcolemma of the muscle fiber The AP will also spread into the T-tubules, exciting the terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticula This will cause Calcium (Ca +2 ) gates in the SR to open, allowing Ca +2 to diffuse into the sarcoplasm Calcium will bind to troponin (on the thin myofilament), causing it to change its shape. This then pulls tropomyosin away from the active sites of actin molecules. The exposure of the active sites allow the sliding of the filaments
47 Physiology of skeletal muscle contraction events at the myofilaments Resting sarcomere Active-site exposure + P Myosin head Troponin + P Sarcoplasm Tropomyosin Actin P + Active site P + Calcium (Ca +2 ) gates in the SR open, allowing Ca +2 to diffuse into the sarcoplasm Calcium will bind to troponin (on the thin myofilament), causing it to change its shape. This then pulls tropomyosin away from the active sites of actin molecules. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure of 7
48 Physiology of skeletal muscle contraction events at the myofilaments Resting sarcomere Active-site exposure Cross-bridge formation + P Troponin Myosin head + P Sarcoplasm + P Tropomyosin Actin P + Active site P + + P Myosin heads are energized by the presence of + PO 4 3- at the ATP binding site (energy is released as phosphate bond of ATP breaks) Once the active sites are exposed, the energized myosin heads hook into actin molecules forming cross-bridges Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure of 7
49 Physiology of skeletal muscle contraction events at the myofilaments Resting sarcomere Active-site exposure Cross-bridge formation + P Troponin Myosin head + P Sarcoplasm + P Tropomyosin Actin P + Active site P + + P Using the stored energy, the attached myosin heads pivot toward the center of the sarcomere The & phosphate group are released from the myosin head Pivoting of myosin head + P + P Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure of 7
50 Physiology of skeletal muscle contraction events at the myofilaments Resting sarcomere Active-site exposure Cross-bridge formation + P Troponin Myosin head + P Sarcoplasm + P Tropomyosin Actin P + Active site P + + P A new molecule of ATP binds to the myosin head, causing the cross bridge to detach from the actin strand The myosin head will get re-energized as the ATP +P Cross bridge detachment ATP ATP Pivoting of myosin head + P + P As long as the active sites are still exposed, the myosin head can bind again to the next active site
51 Physiology of skeletal muscle contraction events at the myofilaments Resting sarcomere Active-site exposure Cross-bridge formation + P Troponin Myosin head + P Sarcoplasm + P Tropomyosin Actin P + Active site P + + P Myosin reactivation Cross bridge detachment Pivoting of myosin head + P ATP + P P + ATP + P - animation animation with Taylor Swift song
52 Physiology of Skeletal Muscle Contraction If there are no longer APs generated on the motor neuron, no more Ach will be released AchE will remove Ach from the motor end plate, and AP transmission on the muscle fiber will end Ca +2 gates in the SR will close & Ca +2 will be actively transported back into the SR With Ca +2 removed from the sarcoplasm (& from troponin), tropomyosin will re-cover the active sites of actin No more cross-bridge interactions can form Thin myofilaments slide back to their resting state Table 7-1
53 RJq4w
54 Muscle Fiber Contraction These physiological processes describe what happen at the cellular level how skeletal muscle fibers contract But what about at the organ level? How do skeletal muscles (like your biceps brachii) contract to create useful movement?
55 Muscle Fiber Contraction Skeletal muscles are made up of thousands of muscle fibers A single motor neuron may directly control a few fibers within a muscle, or hundreds to thousands of muscle fibers All of the muscle fibers controlled by a single motor neuron constitute a motor unit
56 The size of the motor unit determines how fine the control of movement can be small motor units precise control (e.g. eye muscles large motor units gross control (e.g. leg muscles)
57 Recruitment is the ability to activate more motor units as more force (tension) needs to be generated Hypertrophy stressing a muscle (i.e. exercise) causes more myofilaments/myofibrils to be produced within muscle fibers; allows for more cross bridges resulting in more force (strength) as well as larger size There are always some motor units active, even when at rest. This creates a resting tension known as muscle tone, which helps stabilize bones & joints, & prevents atrophy PLAY Play IP Contraction of motor units p. 3-7
58 MUSCLE MYOFIBRIL MUSCLE FIBER SARCOMERE
59 Movement of skeletal muscle These muscles move when the brain sends messages to the muscle Always work in pairs 2 movements of skeletal muscle Contraction (shorten) Extension (lengthen)
The Muscular System. Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move.
 The Muscular System Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move. Anterior View Posterior View TRIVIA! How many muscles are there in the human body? Answer: 640 Muscles The muscles make
The Muscular System Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move. Anterior View Posterior View TRIVIA! How many muscles are there in the human body? Answer: 640 Muscles The muscles make
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
Functions of Muscle Tissue
 The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology)
 Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
MUSCULAR TISSUE. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Bio 103 Muscular System 61
 61 Lecture Outline: MUSCULAR SYSTEM [Chapter 9] A. Functions of Skeletal Muscle 1. Movement 2. Maintain posture 3. Support 4. Guard openings 5. Maintain body temperature (thermogenesis) B. Muscle Tissue
61 Lecture Outline: MUSCULAR SYSTEM [Chapter 9] A. Functions of Skeletal Muscle 1. Movement 2. Maintain posture 3. Support 4. Guard openings 5. Maintain body temperature (thermogenesis) B. Muscle Tissue
Energy for Muscle Contractions: Direct phosphorylation. Creatine phosphate loses a phosphate to ADP to create ATP
 Energy for Muscle Contractions: Direct phosphorylation Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration (lactic acid fermentation) Creatine phosphate loses a phosphate to ADP to create ATP Requires oxygen to
Energy for Muscle Contractions: Direct phosphorylation Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration (lactic acid fermentation) Creatine phosphate loses a phosphate to ADP to create ATP Requires oxygen to
Muscle Tissue. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: Skeletal muscle
10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: Skeletal muscle
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law).
 The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular System STUDY GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscles & Muscle Tissue
 Muscles & Muscle Tissue Chapter 6 I. Overview of Muscle 1 A. MUSCLE TYPES SKELETAL: striated, voluntary CARDIAC: only in heart involuntary striated SMOOTH: walls of organs involuntary nonstriated All Muscle
Muscles & Muscle Tissue Chapter 6 I. Overview of Muscle 1 A. MUSCLE TYPES SKELETAL: striated, voluntary CARDIAC: only in heart involuntary striated SMOOTH: walls of organs involuntary nonstriated All Muscle
1/4/2017. Introduction. Connective Tissue Coverings. 9.1: Structure of a Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Fibers. Connective Tissue Coverings
 Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
The Muscular System PART A
 6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function
 Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle
 Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Chapter 8 Notes. Muscles
 Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 9 Muscular System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts
 Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Skeletal Muscle. Cardiac Muscle. Smooth Muscle. II. Muscular System. The Muscular System
 Chapter CHAPTER 8 8 The Muscular System College Prep NOTES Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
Chapter CHAPTER 8 8 The Muscular System College Prep NOTES Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
Chapter 10: Muscles. Vocabulary: aponeurosis, fatigue
 Chapter 10: Muscles 37. Describe the structural components of skeletal muscle tissue from the molecular to the organ level. 38. Describe the structure, function, and importance of sarcomeres. 39. Identify
Chapter 10: Muscles 37. Describe the structural components of skeletal muscle tissue from the molecular to the organ level. 38. Describe the structure, function, and importance of sarcomeres. 39. Identify
Types of Muscle. Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart
 Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscular System. This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions:
 Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle. I. 3 Types of Muscle Tissue. 1. Smooth 2. Cardiac 3. Skeletal
 I. 3 Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Smooth 2. Cardiac 3. Skeletal Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
I. 3 Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Smooth 2. Cardiac 3. Skeletal Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP
 The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
Muscle Tissue. Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells. Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy
 Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function
 Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Anatomy & Physiology. Unit Two. Muscular System URLs Frog Dissection
 Anatomy & Physiology 9 Muscular System URLs Frog Dissection http://curry.edschool.virginia.edu/go/frog/home.html Cat Dissection http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/cat_dissect/index.htm List of Muscles http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/meded/
Anatomy & Physiology 9 Muscular System URLs Frog Dissection http://curry.edschool.virginia.edu/go/frog/home.html Cat Dissection http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/cat_dissect/index.htm List of Muscles http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/meded/
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle cells have unique characteristics which allow for body movement.
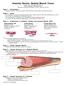 Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Tissue Outline. General Function of Muscle Tissue
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Outline General Functions of Muscle Tissue Characteristics of Muscle Tissue Classification of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Muscle Energetics Muscle Mechanics
Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Outline General Functions of Muscle Tissue Characteristics of Muscle Tissue Classification of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Muscle Energetics Muscle Mechanics
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
10/30/2014 APPEARANCE
 APPEARANCE Striated: has a striped appearance due to the thickness of the protein fibers Smooth: protein fibers (which are arranged the same in striated muscle) is not as thick so you cannot see the pattern
APPEARANCE Striated: has a striped appearance due to the thickness of the protein fibers Smooth: protein fibers (which are arranged the same in striated muscle) is not as thick so you cannot see the pattern
7/10/18. Introduction. Muscular System. Anatomy. Physiology. Skeletal Muscle Anatomy. Muscle Fiber
 Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
2/28/18. Muscular System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Physiology. Anatomy. Muscle Fiber
 Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
2/28/18. Muscular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 20
 Muscular System Chapter 20 1 Introduction Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Muscular System Chapter 20 1 Introduction Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
(c) sarcolemma with acethylcholine (protein) receptors
 (slide 1) Lecture Notes: Muscular System I. (slide 2) Introduction to Muscular System A) Tissues of the Muscular System: 1) Connective Tissues (a) dense fibrous (tendons and ligaments) 2) Nervous Tissue
(slide 1) Lecture Notes: Muscular System I. (slide 2) Introduction to Muscular System A) Tissues of the Muscular System: 1) Connective Tissues (a) dense fibrous (tendons and ligaments) 2) Nervous Tissue
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Skeletal Muscle. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The best-known feature of skeletal muscle is its ability to contract and cause movement. Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The best-known feature of skeletal muscle is its ability to contract and cause movement. Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
A and P CH 8 Lecture Notes.notebook. February 10, Table of Contents # Date Title Page # /30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 2. 1 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. i 1 Turnitin.com Class #: 13551662 Password: GoViks 2 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System Objective: Students will
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 2. 1 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. i 1 Turnitin.com Class #: 13551662 Password: GoViks 2 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System Objective: Students will
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle
 Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Muscle. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscular Tissue. Functions of Muscular Tissue. Types of Muscular Tissue. Skeletal Muscular Tissue. Properties of Muscular Tissue
 Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Fig Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Nucleus. Muscle fiber. Endomysium. Striations.
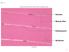 Fig. 11.1 Nucleus Muscle fiber Endomysium Striations Ed Reschke 1 Fig. 11.2 Muscle fiber Nucleus I band A band Z disc Mitochondria Openings into transverse tubules Sarcoplasmic reticulum Triad: Terminal
Fig. 11.1 Nucleus Muscle fiber Endomysium Striations Ed Reschke 1 Fig. 11.2 Muscle fiber Nucleus I band A band Z disc Mitochondria Openings into transverse tubules Sarcoplasmic reticulum Triad: Terminal
Page 1. Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue. Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle. Characteristics of Muscle:
 1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Muscle little mouse Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics:
1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Muscle little mouse Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics:
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA (
 Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz. Remember, you need to know the structure and the function!
 Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz Remember, you need to know the structure and the function! What is this called? What is this? Schwann cell What is this called? Basal lamina
Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz Remember, you need to know the structure and the function! What is this called? What is this? Schwann cell What is this called? Basal lamina
Lecture Overview. Muscular System. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview Types, characteristics, functions of muscle Structure of skeletal muscle Mechanism of
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview Types, characteristics, functions of muscle Structure of skeletal muscle Mechanism of
Chapter 9. The Muscular System. Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Muscle Organization. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 9 The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Muscle Organization Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction Humans rely on muscles for: Many of our physiological
Chapter 9 The Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Muscle Organization Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction Humans rely on muscles for: Many of our physiological
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Differ in their microscopic anatomy, location and how they are controlled by the endocrine and nervous system. 3 Types of Muscle
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Differ in their microscopic anatomy, location and how they are controlled by the endocrine and nervous system. 3 Types of Muscle
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Nerve Cell (aka neuron)
 Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
11.2 Muscles and Movement
 11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
10/4/18. Muscular System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
 Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Page 1. Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue. Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle. Gross Anatomy of Muscle:
 1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics: Composes
1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics: Composes
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
Muscle Physiology. Introduction. Four Characteristics of Muscle tissue. Skeletal Muscle
 Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscle Tissue. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An Introduction
C h a p t e r 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An Introduction
Muscular system MOVE ME!
 Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
Organismic Biology Bio 207. Lecture 6. Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics. Prof.
 Organismic Biology Bio 207 Lecture 6 Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics Prof. Simchon Today s Agenda Skeletal muscle Neuro Muscular Junction
Organismic Biology Bio 207 Lecture 6 Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics Prof. Simchon Today s Agenda Skeletal muscle Neuro Muscular Junction
Types of Muscle. Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart
 Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
Muscular System. Human A & P
 Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 9 Part A Muscles and Muscle Tissue Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Why This Matters Understanding skeletal
Chapter 9 Part A Muscles and Muscle Tissue Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Why This Matters Understanding skeletal
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 Chapter 9 The Muscular System Introduction Skeletal muscles - movement in environment Smooth muscles - intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle - pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Chapter 9 The Muscular System Introduction Skeletal muscles - movement in environment Smooth muscles - intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle - pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Muscle Physiology. Dr. Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue Muscle is one of the 4 primary types of tissue. It is subdivided into skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle. I. Skeletal Muscle Tissue and the Muscular System, p. 284 Objective
Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue Muscle is one of the 4 primary types of tissue. It is subdivided into skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle. I. Skeletal Muscle Tissue and the Muscular System, p. 284 Objective
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Muscular System. Honors Anatomy & Physiology. Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
NOTES MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 NOTES for the MUSCULAR SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson I. Muscular System A. Specialized tissue that does one thing: shorten. B. Functions: 1. Movement (of body, blood, food, etc.). 2. Stabilize
NOTES for the MUSCULAR SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson I. Muscular System A. Specialized tissue that does one thing: shorten. B. Functions: 1. Movement (of body, blood, food, etc.). 2. Stabilize
Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
2/19/2018. Learn and Understand:
 Muscular System with Special Emphasis on Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Physiology Learn and Understand: The definition of cell changes again The contractile unit of muscle is the sarcomere. ATP and Ca 2+
Muscular System with Special Emphasis on Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Physiology Learn and Understand: The definition of cell changes again The contractile unit of muscle is the sarcomere. ATP and Ca 2+
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Class XI Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Biology
 Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline Module 10.1 Overview of muscle tissue (Figures 10.1 10.2) A. Types of Muscle Tissue (Figure 10.1) 1. The three types of cells in muscle tissue are,,
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline Module 10.1 Overview of muscle tissue (Figures 10.1 10.2) A. Types of Muscle Tissue (Figure 10.1) 1. The three types of cells in muscle tissue are,,
I. Overview of Muscle Tissues
 I. Overview of Muscle Tissues A. Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Terminology 1. Muscle fibers = muscle cells are greatly elongated therefore known as fibers; true for skeletal and smooth muscles only 2. Myo
I. Overview of Muscle Tissues A. Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Terminology 1. Muscle fibers = muscle cells are greatly elongated therefore known as fibers; true for skeletal and smooth muscles only 2. Myo
Warm-Up. 2. What structure connects muscle to bone?
 Warm-Up 1. Based on what you know about Latin root words, what do you think these terms refer to? Sarcomere Sarcoplasm Myofibril Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium 2. What structure connects muscle to bone?
Warm-Up 1. Based on what you know about Latin root words, what do you think these terms refer to? Sarcomere Sarcoplasm Myofibril Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium 2. What structure connects muscle to bone?
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
