Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin
|
|
|
- Anabel McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C Vogt, John Ruud, Kho D Nguyen, Sestin Theurich, A Christine Husen, Joel Schmitz,,, Hell S Brönneke,, Emm Estevez 7, Tmr L Allen 7, Andre Mesros, Lind Prtridge, Mrk A Ferio 7, Ajy Chwl, F Thoms Wunderlich & Jens C Brüning,, Oesity nd resistnce to insulin re closely ssocited with the development of low-grde inflmmtion. Interleukin () is linked to oesity-ssocited inflmmtion; however, its role in this context remins controversil. Here we found tht mice with n inctivted gene encoding the R chin of the receptor for in myeloid cells ( mice) developed exggerted deteriortion of glucose homeostsis during diet-induced oesity, due to enhnced resistnce to insulin. Tissues trgeted y insulin showed incresed inflmmtion nd shift in mcrophge polriztion. induced expression of the receptor for nd ugmented the response to in mcrophges in cell-utonomous mnner. mice were resistnt to -medited lterntive polriztion of mcrophges nd exhiited enhnced susceptiility to lipopolyscchride (LPS)-induced endotoxemi. Our results identify signling vi s n importnt determinnt of the lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges nd ssign n unexpected homeosttic role to in limiting inflmmtion. Western societies hve experienced lifestyle shift towrd less physicl ctivity nd more consumption of energy-dense food; those chnges hve led to sustntil increse in overweight nd oese people. Oesity is ssocited with chronic, low-grde inflmmtory stte, reflected y infiltrtion nd ctivtion of cells of the immune system in dipose tissue, s well s systemiclly greter undnce of proinflmmtory cytokines. Those cytokines in turn ctivte intrcellulr stress-signling cscdes ssocited with the trnscription fctor NF-κB nd the kinse Jnk, which susequently inhiit the ction of insulin in trget tissues such s dipose tissue, liver, skeletl muscle nd even the centrl nervous system 7. Prolonged inhiition of insulin signling eventully leds to the development of resistnce to insulin nd, ultimtely, progression to overt type dietes mellitus,9. Interleukin () is cytokine linked to oesity nd resistnce to insulin; however, it is still uncler whether serves hrmful role or protective role in this context. increses in undnce in the circultion with the degree of oesity, nd cute infusion of impirs sensitivity to insulin in mice. However, deficiency in leds to dult-onset oesity, nd heptic disruption of signling cuses resistnce to insulin. Becuse mcrophges re centrl meditors of oesityssocited inflmmtion, we imed to directly investigte signling y in these cells. We found tht primed mcrophges for -dependent M polriztion y inducing expression of the receptor for (R). In mice with conditionl inctivtion of the gene encoding the Rα chin of the receptor for (Ilr) in myeloid cells, we oserved greter propensity to develop oesity-induced inflmmtion nd intolernce for glucose, s well s n exggerted response to lipopolyscchride (LPS)-induced endotoxemi. Our results identify s regultor of the lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges during inflmmtory conditions such s oesity nd endotoxemi. RESULTS Signling y in myeloid cells regultes glucose homeostsis To investigte the role of signling y in mcrophges in oesity, we conditionlly inctivted Ilr in myeloid cells in mice. For this, we generted mice heterozygous for trnsgene encoding Cre recominse expressed vi the gene encoding LysM (LysM-Cre), which is expressed specificlly in cells of the myeloid linege, nd homozygous for loxp-flnked Ilr lleles ( LysM-Cre Tg/wt ; Deprtment of Mouse Genetics nd Metolism, Institute for Genetics, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germny. Mx Plnck Institute for Neurologicl Reserch, Cologne, Germny. Cologne Excellence Cluster on Cellulr Stress Responses in Aging Associted Diseses, Cologne, Germny. Crdiovsculr Reserch Institute, Deprtments of Physiology nd Medicine, University of Cliforni, Sn Frncisco, Cliforni, USA. Center for Endocrinology, Dietes nd Preventive Medicine, University Hospitl Cologne, Cologne, Germny. Center for Moleculr Medicine Cologne, Cologne, Germny. 7 Cellulr nd Moleculr Metolism Lortory, Bker IDI Hert nd Dietes Institute, Melourne, Austrli. Mx Plnck Institute for Biology of Ageing, Cologne, Germny. 9 These uthors contriuted eqully to this study. Correspondence should e ddressed to J.C.B. (ruening@nf.mpg.de). Received Jnury; ccepted Mrch; pulished online Mrch ; doi:./ni. nture immunology DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION
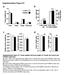
2 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Figure Signling y in myeloid cells regultes glucose homeostsis. () Body weight of nd mice fed NCD (n = ( ) or ( )) or HFD (n = ( ) or ( )). (,c) Concentrtion of glucose in the lood of HFD-fed mice (n = () or 7 (c)) nd mice (n = () or 7 (c)) fter glucose-tolernce test (GTT; ) or insulintolernce test (ITT; c); results re presented reltive to initil lood glucose concentrtion. (d,e) Fsting serum insulin concentrtion (d) nd HOMA-IR indices (e) in HFD-fed nd mice (n = 9 per group in ech). (f,g) Glucose-infusion rte (f) nd glucoseuptke rte in skeletl muscle (SM), nd (g) during euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clmp nlysis of HFD-fed mice (n = in ech) nd mice (n = 7 in ech). (h) Suppression of the relese of free ftty cid (FFA) in the serum of HFD-fed mice (n = ) nd mice (n = 7) during clmp nlysis. (i) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of the gene encoding hormone-sensitive lipse (Lipe) in from mice (n = ) nd mice (n = 7) t the end of clmp nlysis; results re presented reltive to those of mice, set s %. (j) Suppression of heptic glucose production (HGP) during clmp nlysis of HFD-fed mice clled here). littermtes without the LysM-Cre trnsgene served s controls. To verify efficient disruption of signling in these mice, we isolted one mrrow derived mcrophges (BMDMs) from nd mice nd stimulted them with. Immunolot nlysis reveled roust phosphoryltion of STAT in BMDMs derived from mice (clled control BMDMs here) upon stimultion with, wheres phosphorylted STAT ws undetectle in lystes of -stimulted BMDMs derived from mice (clled Ilr / BMDMs here) (Supplementry Fig. ). Next we exposed nd mice to either norml chow diet (NCD) or high-ft diet (HFD) nd monitored ody weight from weeks of ge to 9 weeks of ge. The HFD induced more weight gin thn did the NCD; however, ody weight ws similr for mice nd their counterprts for ech diet (Fig. ). In line with their unltered development of oesity, nd mice fed NCD or HFD exhiited similr ody composition, ft-pd weight nd, s n indirect mesure of ody ft content, serum leptin concentrtions (Supplementry Fig. d). Moreover, mice showed no difference in oxygen consumption or dily cloric intke compred with tht of mice (Supplementry Fig. e,f). To nlyze possile ltertions in glucose homeostsis, we sujected nd mice to glucose-tolernce tests. Wheres nd mice fed NCD hd comprle lood glucose concentrtions during the glucose-tolernce test (Supplementry Fig. ), mice fed HFD were significntly more intolernt to glucose thn were their counterprts (Fig. ). Similrly, wheres mice fed NCD showed no genotype-relted difference in their response to n insulin-tolernce test (Supplementry Fig. ), mice fed HFD were more resistnt to insulin thn were Body weight (g) d Insulin (ng/ml) h Serum FFA suppression (%) HFD HFD NCD NCD Age (weeks) e HOMA-IR (mg/dl mu/i) i Lipe expression (%) Blood glucose (mg/dl) GTT f Glucose-infusion rte (mg/kg min) j HGP suppression (%) HFD HFD k their counterprts (Fig. c). Moreover, the deteriortion in glucose homeostsis in fed HFD ws lso reflected y the higher fsting serum insulin concentrtions nd enhnced HOMA-IR indices ( homeosttic model ssessment index of insulin resistnce ) in fed HFD compred with tht of their counterprts (Fig. d,e). Insulin exerts its lood glucose lowering effects y promoting the uptke of glucose in skeletl muscle nd dipose tissue nd through the suppression of de novo gluconeogenesis, predominntly in liver. To determine which of those processes ws impired in mice fed HFD, we used euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clmps. mice hd % lower glucose-infusion rte in the stedy stte (Fig. f nd Supplementry Fig. c,d), which further supported the proposl tht these mice developed profound degree of resistnce to insulin. Moreover, we ssessed insulin-stimulted uptke of glucose in skeletl muscle, rown dipose tissue () nd white dipose tissue (). While we oserved no difference etween mice fed HFD nd their counterprts in terms of insulin-induced uptke of glucose in the skeletl muscle, insulinstimulted uptke of glucose ws % lower in nd % lower in of mice thn in their counterprts (Fig. g). Moreover, the ility of insulin to suppress lipolysis nd limit expression of the gene encoding hormone-sensitive lipse in ws significntly impired in mice reltive to its ility to do so in their counterprts (Fig. h,i); this indicted resistnce to insulin in the nd of mice fed HFD. Finlly, insulin-medited suppression of heptic glucose production in mice fed HFD ws % tht of their counterprts (Fig. j). Consistent with tht finding, expression of the gene encoding glucose--phosphtse, rte-limiting enzyme of Time (min) c Blood glucose (%) g Glucose-uptke rte (nmol/g min) 9 ITT SM Gpc expression (%) HFD HFD Time (min) (n = ) nd mice (n = 7); results re presented reltive to sl heptic glucose production. (k) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of the gene encoding glucose--phosphtse (Gpc) in livers from mice (n = ) nd mice (n = 7) t the end of clmp nlysis (presented s in i). NS, not significnt (P =. in g); P. nd P. (two-wy nlysis of vrince (ANOVA) followed y Bonferroni s post-test (,c) or two-tiled unpired Student s t-test (d k)). Dt re pooled from three (,c e), four () or five (f k) independent experiments (men nd s.e.m.). DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION nture immunology
3 µm A rt i c l e s Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Figure mice fed HFD hve enhnced systemic inflmmtion. () Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of gene expression in from HFD-fed nd mice (n = 9 per genotype); results re presented reltive to those of mice, set s %. () Immunohistochemicl stining of F/ cells in from HFD-fed nd mice (left) nd quntifiction of F/ crown-like structures (CLS) in from those mice (n = 7 per genotype), presented s the frequency of crown-like structures of dipocytes (right). Scle rs (left), µm. (c,d) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of gene expression in (c) or liver (d) from HFD-fed nd mice (n = 9 per genotype in ech), presented s in. (e) Jnk ctivity in the, nd liver of HFD-fed nd mice (n = 9 per genotype), ssessed y immunoprecipittion (IP) of phosphorylted (p-) Jnk nd susequent in vitro kinse ssy with recominnt c-jun fusion protein nd immunolot nlysis (IB) of recominnt c-jun (top), followed y quntifiction of Jnk ctivity s the rtio of phosphorylted c-jun to clnexin, presented in ritrry units (AU) reltive to results for mice, set s % (ottom). Immunolot nlysis of totl gluconeogenesis, ws significntly higher in livers of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts during clmping nd in the fsted stte (Fig. k nd Supplementry Fig. e). Furthermore, heptic resistnce to insulin ws ccompnied y greter undnce of liver triglycerides nd higher concentrtion of triglycerides in serum of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Supplementry Fig. f,g). Thus, signling y in myeloid cells limited oesity-ssocited deteriortion of glucose metolism y promoting sensitivity to insulin in, nd the liver. Enhnced systemic inflmmtion in mice fed HFD Oesity induces proinflmmtory stte nd the ccumultion of mcrophges in the dipose tissue,. To investigte possile inflmmtory chnges in fed HFD, we nlyzed gene expression in y quntittive rel-time PCR. These nlyses reveled higher expression of genes encoding molecules typiclly linked to the development of resistnce to insulin (tumor-necrosis fctor (Tnf), IL-β (Il), (Il), IL-p (Il) nd inducile nitric oxide synthse (Nos)) in the of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Fig. ). We lso oserved higher expression of the gene encoding the minerlocorticoid receptor (Nrc), which is mrker of M mcrophges, together with lower expression of the genes encoding the R α-chin (Ilr), mnnose receptor (Mrc) nd resistin-like-α (Retnl), which re ll M mcrophge ssocited genes, in mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Fig. ). Additionlly, immunohistochemicl nlysis of the mcrophge mrkers F/ nd Mc- reveled twofold more crown-like structures in the dipose tissue of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Fig. nd Supplementry Fig. ), which indicted greter undnce of ctivted mcrophges in the mice. Similrly, the expression of genes encoding proinflmmtory molecules nd M-polriztion mrkers ws Expression (%) c Expression (%) d Expression (%) Tnf Tnf Tnf ll ll ll ll ll ll ll ll Ccl Ccl Nrc Nos llr Mrc ll ll Ccl Ccl Nrc Nos llr ll ll Ccl Ccl Nrc Nos llr Mrc llr myel Mrc Retnl Chil Arg llr myel Retnl Chil Arg llr myel Retnl Chil Arg e IP: p-jnk IB: p-c-jun IB: Jnk IB: Clnexin IP: p-jnk IB: p-c-jun IB: Jnk IB: Clnexin IP: p-jnk IB: p-c-jun IB: Jnk IB: Clnexin llr myel higher in the of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts, while the expression of genes encoding mrkers of M mcrophges ws significntly lower in the of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Fig. c). Becuse mice fed HFD displyed sustntil heptic resistnce to insulin, we next ssessed the expression of genes encoding inflmmtory molecules in liver. Consistent with the oserved inflmmtory chnges in nd, the livers of mice fed HFD hd higher expression of Il, Il, Ccl, Nrc nd Nos (Fig. d). We did not oserve ny ltertion in the expression of genes encoding proinflmmtory cytokines or M- or M-polriztion mrkers in ny of the tissues nlyzed from mice fed NCD reltive to tht in their counterprts (Supplementry Fig. d). Moreover, Il / mice fed HFD, which show greter propensity to develop diet-induced resistnce to insulin 7, hd chnges similr to those of their counterprts in the expression of genes encoding proinflmmtory molecules nd M-polriztion mrkers in the nd liver (Supplementry Fig.,). We oserved no difference etween LysM-Cre Tg/wt mice fed HFD nd wild-type mice fed HFD in their expression of genes encoding inflmmtory molecules in the, or liver (Supplementry Fig. c e), which excluded the possiility tht the oserved ltertions in mice might hve een dependent on the expression of Cre lone. To further ssess how chnges in the expression of genes encoding proinflmmtory molecules might promote resistnce to insulin, we ssessed ctivtion of the kinse Jnk, criticl regultor of oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin, in the, nd liver of nd mice fed HFD. Immunoprecipittion of phosphorylted Jnk nd susequent in vitro kinse ssy with recominnt c-jun fusion protein reveled six- to tenfold greter ctivtion of Jnk in the, nd liver of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Fig. e). These experiments llr myel p-c-jun/clnexin (%AU),, F/ CLS (%) llr myel µm Jnk nd clnexin (without immunoprecipittion) serve s input control. P., P. nd P. (two-tiled unpired Student s t-test). Dt re pooled from three independent experiments (men nd s.e.m.). Ilrfl/fl llr myel nture immunology DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION
4 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Figure Signling y promotes R expression in mcrophges. () Het mp of trnscripts regulted differently in control BMDMs derived from mice (Ctrl) versus Ilr / BMDMs (n = mice per group) fter h of stimultion with, ssessed with cut-off of chnge in expression of.-fold. () Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of Ilr nd Ilr in control nd Ilr / BMDMs (n = mice per group) left untreted () or stimulted for h with (); results re presented reltive to those of untreted control BMDMs, set s. (c) Men fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Rα in wild-type BMDMs (n = mice per group) left untreted or stimulted for h with, ssessed y flow cytometry. (fr left), flow cytometry of untreted wild-type BMDMs with. (d) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of Ilr in wild-type BMDMs left untreted or stimulted for h with in the presence of indicted tht cted in cells of the myeloid linege to promote M polriztion nd to limit the expression of genes encoding proinflmmtory molecules, ctivtion of Jnk nd resistnce to insulin in the, nd liver of oese mice. signling promotes R expression in mcrophges Becuse mice fed HFD exhiited shift towrd the M polriztion of mcrophges in the, nd liver, we next investigted the underlying mcrophge-utonomous chnges tht depended on signling y. For this, we stimulted control BMDMs (derived from mice) nd Ilr / BMDMs with nd nlyzed gene expression y microrry hyridiztion. Of, nnotted trnscripts,,7 were regulted differently in -stimulted control BMDMs versus Ilr / BMDMs (P.). Ingenuity pthwy nlysis of gene-expression ptterns reveled differences in the regultion of signling cscdes dependent on the products of the genes Nos, Il, Il nd Pprg (which encodes the trnscription fctor PPAR-γ), mong other pthwys (Supplementry Fig. f). The ppliction of the cut-off of chnge in expression (upregultion or downregultion) of.-fold yielded 9 trnscripts tht were regulted, with upregulted nd downregulted in Ilr / BMDMs reltive to their expression in control BMDMs (Fig. ). Along with Ilr, one of the trnscripts whose expression ws diminished the most in the sence of functionl signling y ws Ilr (Fig. ). To verify those findings, we did quntittive RT-PCR nlysis nd oserved tht stimultion with incresed Ilr mrna expression in control BMDMs (Fig. nd Supplementry Fig. g) nd tht this response ws lunted in Ilr / BMDMs, which exhiited ~9% lower Ilr mrna expression thn tht of control BMDMs (Fig. ); this indicted efficient disruption of Ilr. We next nlyzed -stimulted wild-type BMDMs y flow cytometry nd oserved they hd greter undnce of Rα thn did unstimulted wild-type cells (Fig. c nd Supplementry Fig. h). Becuse IL- cn directly induce Ilr expression in mcrophges 9 nd cn stimulte the expression nd relese of IL-, we next investigted whether the -medited modultory effects BMDM Ctrl IIr / IIr IIr z-score e Expression (fold) Rα Clnexin Ctrl IIr / IIr IIr IIr IIr lgg α-ll- f Expression (fold) c Rα MFI ( )... Ctrl sirna Stt sirna IIr sirna on Ilr expression were medited vi relese of IL-. Anlysis of gene expression showed roust -induced increse in Il mrna in control BMDMs (Supplementry Fig. i). While Ilr / BMDMs hd slightly lower undnce of Il mrna thn did control BMDMs in the sl stte, the -induced upregultion of Il ws lunted in Ilr / BMDMs compred with tht in control BMDMs (Supplementry Fig. i), which suggested tht the oserved -medited increse in Ilr expression might hve een dependent on utocrine IL- signling. To further pursue tht possile mode of ction, we next treted wild-type BMDMs with in the presence or sence of neutrlizing ntiody to IL-, which efficiently locked IL--medited phosphoryltion of STAT (Supplementry Fig. j). However, induced the expression of Ilr mrna nd Rα protein to the sme extent in BMDMs in which IL- ws locked nd those treted with control immunogloulin G () (Fig. d,e), which indicted tht -dependent upregultion of Rα expression occurred independently of expression nd signling of IL-. We next determined whether the -medited expression of Rα ws dependent on STAT. Knockdown of Stt (nd, s positive control, Ilr) medited y smll interfering RNA (sirna) diminished expression of Stt nd Ilr y ~% compred with tht of BMDMs trnsfected with control sirna with nontrgeting sequence (Fig. f). Knockdown of Stt or Ilr in BMDMs potently lunted the -stimulted induction of Ilr mrna y ~7% or ~%, respectively (Fig. g). The expression of Socs (which encodes the inhiitor SOCS) showed reduction similr to tht of Ilr fter knockdown of Stt or Ilr (Supplementry Fig. k). In summry, we demonstrted tht signling y promoted Rα expression in mcrophges in n IL--independent mnner nd tht the trnscription fctor STAT ws essentil in mediting this effect. STAT inds to distinct motifs in the Ilr promoter To further investigte the role of signling vi STAT in the regultion of Rα expression, we looked for STAT-inding sites in the Ilr promoter. Anlysis with the JASPAR dtse of trnscription lgg g IIr expression (fold) d IIr expression (fold) lgg α-il- sirna: Ctrl Stt IIr or IL--neutrlizing ntiody (α-il-), presented s in. (e) Immunolot nlysis of Rα nd clnexin (loding control) in BMDMs s in d (n = iologicl replictes per group). (f) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of Stt nd Ilr in wild-type BMDMs trnsfected with Stt- or Ilr-specific sirna (key); results re presented reltive to those of BMDMs trnsfected with control sirna, set s. (g) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of Ilr in wild-type BMDMs trnsfected s in f nd left untreted or stimulted for h with ; results re presented reltive to those of untreted BMDMs trnsfected with control sirna, set s. P. nd P. (two-tiled unpired Student s t-test (,f), two-wy ANOVA followed y Bonferroni s post-test (,g) or one-wy ANOVA followed y Tukey s post-test (c)). Dt re from four (), three (,d g) or five (c) independent experiments (men nd s.e.m. in d nd men nd s.e.m. of duplictes in f,g). DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION nture immunology
5 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Figure -induced STAT inds to distinct motifs in the Ilr promoter. () Luciferse ctivity (right) of vrious reporter constructs (left) in immortlized wild-type mcrophges trnsfected with those constructs nd left untreted or stimulted for h with. () Occupncy of vrious sites of the Ilr promoter (top) y phosphorylted STAT in control BMDMs (derived from mice) nd Ilr / BMDMs left untreted or stimulted for, or min (horizontl xis) with, ssessed y ChIP followed y quntittive RT-PCR nd presented reltive to the results of untreted control BMDMs, set s. P. nd P. (two-wy ANOVA followed y Bonferroni s post-test). Dt re representtive of three experiments (men nd s.e.m. of triplictes in ; men nd s.e.m. in ). fctor inding profiles reveled four puttive STAT-inding sites locted within. kiloses upstrem of the first exon of (min) the Ilr promoter, nd two puttive STAT- inding sites in the Socs promoter (Supplementry Fig. ). To determine which of those sites were necessry for Rα expression medited y STAT, we cloned vrious segments of the Ilr promoter upstrem of Ilr exon into firefly luciferse reporter nd trnsfected those constructs into immortlized mcrophges (Fig. ). Only the full-length frgment contining the two distl sites (STAT_ nd STAT_) resulted in roust luciferse expression, nd tht expression incresed sustntilly fter stimultion with (Fig. ). Deletion of those sites lmost completely olished luciferse expression, wheres deletion of the two proximl STAT-inding sites (STAT_ nd STAT_) did not further diminish luciferse ctivity (Fig. ); this indicted tht those sites (STAT_ nd STAT_) seemed to e dispensle for -dependent expression of Rα. To determine whether STAT regulted Ilr expression directly, we used n ntiody to phosphorylted STAT for chromtinimmunoprecipittion (ChIP) nlysis. We oserved trnsient ut roust occuption of the Socs promoter y STAT fter stimultion with in control BMDMs (derived from mice) ut not in Ilr / BMDMs (Supplementry Fig.,c). Additionlly, neither control BMDMs nor Ilr / BMDMs showed enrichment for STAT in regions tht were not open reding frmes, s ssessed y ChIP with ntiody to phosphorylted STAT (negtive control region mplified with IGXA primers) (Supplementry Fig.,c). Thus, we investigted whether the puttive STAT-inding sites we hd identified showed specific enrichment for STAT in BMDMs fter exposure to. In line with the luciferse-expression pttern, the two distl STAT-inding sites (STAT_ nd STAT_) in the Ilr promoter showed specific enrichment for STAT in control BMDMs fter stimultion with, ut the two proximl STAT-inding sites (STAT_ nd STAT_) did not, s ssessed y ChIP with ntiody to phosphorylted STAT (Fig. nd Supplementry Fig. c). We detected no -induced enrichment for STAT t those sites in Ilr / BMDMs (Fig. nd Supplementry Fig. c). Thus, induced inding of STAT to the Ilr promoter. Signling y in myeloid cells ugments the response We next investigted if upregultion of Rα expression rendered mcrophges more sensitive to stimultion with. Immunolot nlysis showed tht stimultion with potently incresed the phosphoryltion of STAT nd expression Rα in control BMDMs, p STAT_ STAT_ Luciferse ctivity (%) STAT_ STAT_ Exon IIr STAT_ Enrichment (fold), p STAT_ STAT_ p STAT_ Enrichment (fold) STAT_ STAT_ STAT_ STAT_ p (min) IIr exon STAT_ Enrichment (fold) (min) (derived from mice) ut not in Ilr / BMDMs (Fig. ). When we ssessed -stimulted phosphoryltion of STAT, we found tht preincution with ugmented the response of control BMDMs to, n effect we did not see in Ilr / BMDM (Fig. ). Tht suggested tht not only promoted Rα expression in mcrophges ut lso ugmented the -medited phosphoryltion of STAT. Becuse nd STAT regulte mcrophge polriztion y inducing M-ssocited genes such s Mrc (which encodes the mnnose receptor CD (MR-)), Arg (which encodes the ureohydrolse rginse), Il (which encodes IL-) nd Retnl (which encodes the cytokine Fizz), we sought to determine whether modulted the expression of M mcrophge ssocited genes in BMDMs. induced the expression of Mrc nd Arg in control BMDMs ut not in Ilr / BMDMs, wheres the expression of Socs (which encodes the signling inhiitor SOCS) or Retnl ws not modulted y (Supplementry Fig. ). Tretment with lone induced similr expression of Socs, Mrc, Arg, Il nd Retnl in control BMDMs nd Ilr / BMDMs (Fig. ), while plus synergisticlly enhnced the expression of genes encoding M mcrophge ssocited mrkers in control BMDMs ut not in Ilr / BMDMs (Fig. ). nd cted synergisticlly to induce expression of the proteins CD (MRC) nd rginse, s ssessed y flow cytometry of wild-type BMDMs (Fig. c nd Supplementry Fig. ). Moreover, in control BMDMs ut not in Ilr / BMDMs, cted synergisticlly with to inhiit the expression of Nrc nd Tnf, which oth encode clssic mrkers of M mcrophges (Supplementry Fig. c). We next ssessed whether cted synergisticlly with to induce the M polriztion of mcrophges in vivo. We treted wild-type mice with or lone or plus together nd ssessed expression of the M mrker CD y flow cytometry in vrious mcrophge comprtments. In line with the results otined for BMDMs in vitro, enhnced the -induced M polriztion of mcrophges from the,, lood nd peritoneum in vivo (Fig. d,e nd Supplementry Fig. d,e). regultes the onset of diet-induced oesity nd resistnce to insulin. Four weeks of exposure to resulted in significntly improved glucose tolernce in mice fed HFD ut not in their counterprts (Fig. f nd Supplementry Fig. 7). Enrichment (fold) STAT_ Ctrl IIr / (min) nture immunology DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION
6 µm µm µm µm A rt i c l e s Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Ctrl Ilr / Pretretment: None None (ng/ml) e CD ( MFI) p-stat Blood STAT Hsc7 Rα Clnexin p-stat STAT Clnexin Peritoneum CD ( MFI) Socs expression (fold) f Il expression (fold) GTT ( AUC) Mrc expression (fold) Retnl expression (fold) g Mrc expression (fold) Arg expression (fold ) Ctrl Ilr / Retnl expression (fold ) d CD ( MFI) c CD ( MFI) Arg expression (fold) h ARG ( MFI) CD ( MFI) CD Figure Signling y in myeloid cells ugments the response. () Immunolot nlysis of control BMDMs (derived from mice) nd Ilr / BMDMs given no pretretment (None) or preincuted for h with, nd then stimulted for min with vrious concentrtions (ove lnes). () Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of control nd Ilr / BMDMs (n = mice per group) given no pretretment (None ) or preincuted with ( ) for h, then stimulted for h with ; results re presented reltive to those of untreted control BMDMs set s. (c) Expression of CD nd rginine (ARG) in wild-type BMDMs (n = mice per group) left untreted or treted with or lone or with plus, ssessed y flow cytometry (, s in Fig. c). (d,e) Expression of CD in nd (d) or lood nd peritoneum (e) of wild-type mice (n = per group) treted s in c, ssessed y flow cytometry (, s in Fig. c). (f) Results of glucose-tolernce tests for HFD-fed mice (n = ) nd mice (n = 7) efore () nd fter () weeks of tretment with, presented s the re under the curve (AUC) for lood glucose concentrtion during the test. (g) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of gene expression in the, nd liver of HFD-fed mice (n = 7) nd mice (n = ) treted for weeks with ; results re presented reltive to those of untreted mice, set s. (h) Immunohistochemicl stining of CD in livers from HFD-fed nd mice (n= per group) left untreted or treted for week with. Scle rs, µm. P., P. nd P. (two-wy ANOVA followed y Bonferroni s post-test (,f), one-wy ANOVA followed y Tukey s post-test (c e) or two-tiled unpired Student s t-test (g)). Dt re from three (,,f h) or five (c e) independent experiments (men nd s.e.m. in g). In ddition, tretment with diminished the HOMA-IR indices to greter extent in mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Supplementry Fig. 7). Furthermore, quntittive RT-PCR nlysis reveled significntly lower -induced expression of Mrc, Retnl nd Arg in vivo in the, nd liver of mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Fig. g). Furthermore, in line with the mrna expression dt, we oserved less stining of CD in the livers of -treted mice fed HFD thn in their counterprts (Fig. h). Thus, myeloid cell restricted deficiency in Rα led to resistnce to the eneficil effects of on glucose homeostsis nd sensitivity to insulin in oesity. Furthermore, the ctivity of in mcrophges ws necessry prerequisite for -induced lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges in vivo. signling in myeloid cells limits LPS-induced endotoxemi Next we imed to determine whether, in ddition to ugmenting the STAT xis, lso exhiits nti-inflmmtory properties in conditions tht promote oth clssic M ctivtion of mcrophges nd lterntive M ctivtion of mcrophges independently of metolic inflmmtion. Therefore, we stimulted control BMDMs (derived from mice) nd Ilr / BMDMs (derived from mice) with cteril LPS nd ssessed the expression of genes encoding typicl M mrkers nd inflmmtory cytokines. LPS lone induced expression of Nos, Tnf, Il nd Il to the sme extent cells of in oth genotypes in vitro (Fig. ). However, costimultion with lunted the LPS-induced expression of genes encoding inflmmtory cytokines y pproximtely % in control BMDMs ut not in Ilr / BMDMs (Fig. ). Thus, the trnscription of clssic LPS-induced cytokines ws lunted y nd tht response ws not present in BMDMs derived from mice. To ssess whether signling in mcrophges lso regultes the inflmmtory response to LPS in vivo, we treted nd mice with sulethl dose of LPS ( mg per kg ody weight). While tretment with LPS significntly diminished the ody weight, food intke nd respirtory exchnge rtio of mice of oth genotypes, those responses were significntly greter in mice (Fig. d). Tht ws prlleled y significntly greter undnce of the proinflmmtory cytokines TNF, IL-β nd IL- in the circultion DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION nture immunology
7 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Nos expression (%) LPS LPS Tnf expression (%) Figure Signling y in myeloid cells limits LPS-induced endotoxemi. () Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of control BMDMs (derived from mice) nd d Respirtory exchnge rtio..9. fter injection of LPS in mice thn in mice (Fig. e). Additionlly, LPS-treted mice hd higher concentrtion of in the circultion thn did LPS-treted mice (Fig. e), which indicted possile compenstory upregultion of protein in the circultion due to resistnce to in mice. Anlysis of gene expression in the liver nd t h fter injection of LPS reveled significntly higher expression of genes encoding inflmmtory cytokines in mice thn in mice, while expression of Ilr nd Retnl ws significntly lower in the of mice (Fig. f). Collectively, these experiments reveled tht signling in mcrophges limited not only dietinduced inflmmtion nd resistnce to insulin ut lso LPS-induced inflmmtory responses (Supplementry Fig. 7c). DISCUSSION In the present study we hve, through disruption of the gene encoding Rα in myeloid cells, identified s n dditionl determinnt of mcrophge polriztion oth upon feeding of HFD nd during endotoxemi. Mice with myeloid cell specific deficiency in Ilr tht were fed HFD hd greter propensity for disruption of glucose homeostsis nd hd higher expression of M mcrophge mrkers nd lower expression of M mcrophge mrkers thn tht of their Ilr-sufficient counterprts, concomitnt with enhnced ctivtion of Jnk in the, nd liver. Activtion of the expression of genes encoding inflmmtory cytokines induces ctivtion of Jnk, which is well-chrcterized effector of oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin,. Proinflmmtory M mcrophges re centrl meditors of oesity-induced inflmmtion nd resistnce to insulin, nd specific ltion of these cells normlizes sensitivity to insulin in oese, insulin-resistnt mice. Conversely, deletion of genes encoding trnscription fctors such s PPAR-γ tht promote the lterntive ctivtion of M mcrophges predisposes len mice to the development of glucose intolernce nd resistnce to insulin 7. Hence, M mcrophges re criticl for metolic control nd, upon the development of oesity, n incresed undnce of M mcrophges leds to the disruption of glucose homeostsis. LPS LPS Il expression (%).7 Bsl LPS Ilr / BMDMs (n = mice per group) left untreted nd then exposed to LPS LPS LPS e Plsm cytokines (ng/ml) TNF IL-β Il expression (%) IL- NS LPS LPS LPS LPS Ctrl Ilr / f Expression (%) Tnf Weight loss (g) Il Il Nos Ilr Mrc Retnl Arg Our results hve identified s criticl instigtor of the M polriztion of mcrophges nd hve ssigned it eneficil role in the prevention of oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin. Tht finding my seem unexpected, given the generl ssumption tht cts s proinflmmtory cytokine. In fct, lockde of signling hs proven vlule clinicl pproch for the tretment of rheumtoid rthritis 9. However, the role of in oesity-ssocited inflmmtion hd remined controversil until now. Tht stemmed predominntly from clmp experiments indicting tht infusion of cuses resistnce to insulin nd from the positive correltion etween oesity nd the mount of in the circultion. Nevertheless, studies tht hve tken lterntive pproches hve indicted tht my insted exert eneficil metolic effects, s -deficient mice develop lte-onset oesity nd resistnce to insulin. Moreover, HFD-induced inflmmtion nd deteriortion of glucose metolism is enhnced in -deficient mice 7, heptic inctivtion of signling promotes resistnce to insulin, trnsgenic overexpression of humn in mice improves energy nd glucose homeostsis nd enhnces insulin secretion vi the production of GLP-, glucgon-like peptide. On cell-utonomous level, we found tht directly induced expression of R nd therefore primed mcrophges for - dependent ctivtion of STAT. Notly, the STAT xis is the most potent inducer of the M polriztion of mcrophges, nd ltion of the genes encoding Rα or STAT strongly inhiits the lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges in vitro nd in vivo,. A pulished study hs demonstrted tht during inflmmtory conditions, Rα expression is upregulted specificlly in myeloid effector cells. Tht upregultion is dependent on solule protein, which (given our findings here) is proly. In ddition, evidence from the tumor-immunology field indictes tht signling y is involved in the polriztion of tumorssocited mcrophges, which re mcrophge sutypes similr to oesity-ssocited M mcrophges. However, those studies did not demonstrte the potent -sensitizing effect of tht we hve documented here. Tnf c Food intke (g/dy) Il Il Nos Bsl LPS Ctrl LPS LPS Ilr Mrc Retnl Arg lone for h (LPS) or stimulted for h with nd then exposed to LPS plus for h; results re presented reltive to those of LPS-stimulted control BMDMs, set s %. () Body-weight loss of mice (n = 7) nd mice (n = ) h fter exposure to LPS ( mg per kg ody weight). (c) Food intke of mice (n = 7) nd mice (n = ) in sl conditions nd h fter exposure to LPS. (d) Respirtory exchnge rtio of mice (n = 7) nd mice (n = ) in sl conditions nd h fter exposure to LPS s in. (e) Concentrtion of vrious cytokines (horizontl xis) in the circultion of mice (n = 7) nd mice (n = 7) t h fter exposure to LPS s in. (f) Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of gene expression in the liver nd of mice (n = 7) nd mice (n = ) t h fter exposure to LPS s in ; results re presented reltive to those of control mice, set s %. NS, P =. (e); P. nd P. (two-wy ANOVA followed y Bonferroni s post-test (,c,d) or two-tiled unpired Student s t-test (,e,f). Dt re from three experiments (men nd s.e.m.). nture immunology DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION
8 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Our oservtions tht cted not only to prime myeloid cells for signling y during oesity ut lso to limit LPS-induced endotoxemi indicte tht generlly functions s n ntiinflmmtory cytokine. Tht role ws ssigned to more thn decde go ; however, our results hve further extended tht conclusion nd hve demonstrted tht such nti-inflmmtory properties depend on direct signling y in myeloid cells. In further support of our findings, it hs een demonstrted tht myeloid cell specific disruption of SOCS, the negtive regultor of the STAT xis, skews mcrophges towrd n M phenotype nd renders mice more resistnt to LPS-induced endotoxemi 7 ; this emphsizes the importnce of intct signling y in this context. Given those oservtions, we propose tht during inflmmtory conditions (i.e., in the presence of greter undnce of free ftty cids nd/or cteril LPS), limits the expression of genes encoding inflmmtory cytokines nd ugments the responsiveness of mcrophges to. It thus cts to prtilly counterlnce the typicl shift of mcrophge popultions towrd proinflmmtory M phenotype nd ultimtely diminishes inflmmtion nd the ssocited resistnce to insulin. Together our dt hve demonstrted homeosttic role for in limiting oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin nd oesity-ssocited inflmmtion nd hve defined previously unknown mechnism for the control of mcrophge polriztion. This my set the sis for investigtion of the role of signling in mcrophges in conditions in which lterntive ctivtion is lso of criticl importnce, such s firosis, wound heling nd crcinogenesis. Methods Methods nd ny ssocited references re ville in the online version of the pper. Accession codes. GEO : microrry dt, nd re ccessile through GEO Series ccession numer GSE7. Note: Any Supplementry Informtion nd Source Dt files re ville in the online version of the pper. Acknowledgments We thnk G. Schmll nd T. Ryle for secretril ssistnce, nd B. Hmpel nd D. Kutyniok for technicl ssistnce. Supported y the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschft (SFB nd SFB 7 to J.C.B.), the Leiniz Preis (BR 9/7- to J.C.B.), the Cologne Excellence Cluster on Cellulr Stress Responses in Aging Associted Diseses (funded y the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschft within the Excellence Inititive y Germn Federl nd Stte Governments), the US Ntionl Institutes of Helth (DPAR, HL77 nd DK9 to A.C.) nd the Ntionl Helth nd Medicl Reserch Council of Austrli (APP7, APP nd SPRF APP to M.A.F.). AHOR CONTRIBIONS J.M., J.R., A.C., F.T.W. nd J.C.B. designed the experiments; J.M., B.C., J.G., M.C.V., J.R. nd K.D.N. did the experiments; S.T. helped with the flow cytometry; A.C.H. did the clmp opertions; J.S. ssisted during the ChIP nlyses; H.S.B. did the indirect clorimetry; E.E., T.L.A., A.M., L.P. nd M.A.F. supplied regents; nd J.M. nd J.C.B. wrote the mnuscript. COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS The uthors declre no competing finncil interests. Reprints nd permissions informtion is ville online t reprints/index.html.. Swinurn, B.A. et l. The glol oesity pndemic: shped y glol drivers nd locl environments. Lncet 7, ().. Xu, H. Chronic inflmmtion in ft plys crucil role in the development of oesity-relted insulin resistnce. J. Clin. Invest., ().. Wellen, K.E. Oesity-induced inflmmtory chnges in dipose tissue. J. Clin. Invest., 7 7 ().. Lumeng, C.N. & Sltiel, A.R. Inflmmtory links etween oesity nd metolic disese. J. Clin. Invest., 7 ().. Arkn, M.C. et l. IKK-β links inflmmtion to oesity-induced insulin resistnce. Nt. Med., 9 9 ().. Ci, D. et l. Locl nd systemic insulin resistnce resulting from heptic ctivtion of IKK-β nd NF-κB. Nt. Med., 9 (). 7. Kleinridders, A. et l. MyD signling in the CNS is required for development of ftty cid-induced leptin resistnce nd diet-induced oesity. Cell Met., 9 9 (9).. Donth, M.Y. & Shoelson, S.E. Type dietes s n inflmmtory disese. Nt. Rev. Immunol., 9 7 (). 9. Khn, S.E., Hull, R.L. & Utzschneider, K.M. Mechnisms linking oesity to insulin resistnce nd type dietes. Nture, ().. Pedersen, B.K. & Ferio, M.A. Point: Interleukin- does hve eneficil role in insulin sensitivity nd glucose homeostsis. J. Appl. Physiol., (7).. Weiss, R. et l. Oesity nd the metolic syndrome in children nd dolescents. N. Engl. J. Med., 7 ().. Kim, H.-J. et l. Differentil effects of interleukin- nd - on skeletl muscle nd liver insulin ction in vivo. Dietes, 7 ().. Wllenius, V. et l. Interleukin--deficient mice develop mture-onset oesity. Nt. Med., 7 79 ().. Wunderlich, F.T. et l. Interleukin- signling in liver-prenchyml cells suppresses heptic inflmmtion nd improves systemic insulin ction. Cell Met., 7 9 ().. Clusen, B.E., Burkhrdt, C., Reith, W., Renkwitz, R. & Förster, I. Conditionl gene trgeting in mcrophges nd grnulocytes using LysMcre mice. Trnsgenic Res., 77 (999).. Vogt, M.C. & Brüning, J.C. CNS insulin signling in the control of energy homeostsis nd glucose metolism from emryo to old ge. Trends Endocrinol. Met., 7 (). 7. Mtthews, V.B. et l. Interleukin--deficient mice develop heptic inflmmtion nd systemic insulin resistnce. Dietologi, ().. Belgrdt, B.F. et l. Hypothlmic nd pituitry c-jun N-terminl kinse signling coordintely regultes glucose metolism. Proc. Ntl. Acd. Sci. USA 7, (). 9. Hutchins, A.P., Poulin, S. & Mirnd-Svedr, D. Genome-wide nlysis of STAT inding in vivo predicts effectors of the nti-inflmmtory response in mcrophges. Blood 9, e e9 ().. Portles-Csmr, E. et l. JASPAR : the gretly expnded open-ccess dtse of trnscription fctor inding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res., D D ().. Bumgrtl, J. et l. Myeloid linege cell-restricted insulin resistnce protects polipoproteine-deficient mice ginst therosclerosis. Cell Met., 7 ().. Mosser, D.M. & Edwrds, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of mcrophge ctivtion. Nt. Rev. Immunol., 9 99 ().. Ricrdo-Gonzlez, R.R. et l. /STAT immune xis regultes peripherl nutrient metolism nd insulin sensitivity. Proc. Ntl. Acd. Sci. USA 7, 7 ().. Hirosumi, J. et l. A centrl role for JNK in oesity nd insulin resistnce. Nture, ().. Lumeng, C.N., Bodzin, J.L. & Sltiel, A.R. Oesity induces phenotypic switch in dipose tissue mcrophge polriztion. J. Clin. Invest. 7, 7 (7).. Ptsouris, D. et l. Altion of CDc-positive cells normlizes insulin sensitivity in oese insulin resistnt nimls. Cell Met., 9 (). 7. Odegrd, J.I. et l. Mcrophge-specific PPARγ controls lterntive ctivtion nd improves insulin resistnce. Nture 7, (7).. Ouchi, N., Prker, J.L., Lugus, J.J. & Wlsh, K. Adipokines in inflmmtion nd metolic disese. Nt. Rev. Immunol., 97 (). 9. Scheller, J., Chlris, A., Schmidt-Arrs, D. & Rose-John, S. The pro- nd ntiinflmmtory properties of the cytokine interleukin-. Biochim. Biophys. Act, 7 ().. Sdgurski, M. et l. Humn IL enhnces leptin ction in mice. Dietologi, (9).. Ellingsgrd, H. et l. Interleukin- enhnces insulin secretion y incresing glucgon-like peptide- secretion from L cells nd lph cells. Nt. Med. 7, 9 ().. Herert, D.R. et l. Alterntive mcrophge ctivtion is essentil for survivl during schistosomisis nd downmodultes T helper responses nd immunopthology. Immunity, ().. Vts, D. et l. Oxidtive metolism nd PGC-et ttenute mcrophge-medited inflmmtion. Cell Met., ().. Wermeling, F., Anthony, R.M., Bromcher, F. & Rvetch, J.V. Acute inflmmtion primes myeloid effector cells for nti-inflmmtory STAT signling. Proc. Nt. Acd. Sci., 7 9 ().. Duluc, D. et l. Tumor-ssocited leukemi inhiitory fctor nd skew monocyte differentition into tumor-ssocited mcrophge-like cells. Blood, 9 (7).. Xing, Z. et l. is n ntiinflmmtory cytokine required for controlling locl or systemic cute inflmmtory responses. J. Clin. Invest., (99). 7. Spence, S. et l. Suppressors of cytokine signling nd dimetriclly control mcrophge polriztion. Immunity, 7 ().. Edgr, R., Domrchev, M. & Lsh, A.E. Gene Expression Omnius: NCBI gene expression nd hyridiztion rry dt repository. Nucleic Acids Res., 7 (). DVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION nture immunology
9 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. ONLINE METHODS Animls. All niml procedures were in complince with protocols pproved y locl government uthorities (Bezirksregierung, Cologne, Germny; Alfred Medicl Reserch nd Eduction Precinct Animl Ethics Committee, Melourne, Austrli; Institutionl Animl Cre nd Use Committee of the University of Cliforni, Sn Frncisco) nd were in ccordnce with guidelines of the US Ntionl Institutes of Helth. Mice were housed in groups of three to five t C in -hour -hour light-drk cycle (with lights on t : AM). Mice were fed NCD (Tekld Glol Rodent T..R; Hrln) contining.% crohydrtes,.% protein nd.% ft (% of clories from ft) or, from weeks of ge, were fed HFD (C7; Altromin) contining.7% crohydrtes, % protein nd.% ft (.% of clories from ft). Wter ws ville d liitum nd food ws withdrwn only if required for n experiment. Body weight ws mesured once week. Experiments on mice were done t weeks of ge. Genertion of Ilr myel mice. Mice ering lleles were generted s descried. LysM-Cre mice were mted with mice, nd reeding colony ws mintined y the mting of mice with LysM- Cre Tg/wt ( ) mice s descried 9. Those lines hd een ckcrossed to C7BL/J mice for t lest ten genertions. LysM-Cre mice were genotyped y PCR s descried ; were genotyped y PCR with primers crossing the loxp site s descried. LysM-Cre Tg/wt mice nd wild-type control mice were killed t the ge of weeks, nd tissues were isolted for RNA extrction. Tissues were collected s descried 7 from -deficient mice nd wild-type (control) mice fed HFD. Anlysis of ody composition. Body composition ws determined in vivo with minispec mq7. nucler mgnetic resonnce nlyzer (Bruker Optik). Indirect clorimetry. A PhenoMster System (TSE Systems) ws used for clorimetry mesurements. Mice were mintined t C in 7.-liter chmers of PhenoMster open-circuit clorimetry system. Before ech -hour mesurement period egn, mice were llowed to dpt to the chmers for h. Food nd wter were provided d liitum nd intke of food nd wter ws mesured y the integrted utomtic instruments. Glucose- nd insulin-tolernce tests, injection of nd clcultion of HOMA-IR. Glucose-tolernce tests were done with - to -week-old mice fter they underwent fsting period of h. Glucose concentrtions in lood were mesured fter the fsting period, then ech mouse received n intrperitonel injection of % glucose ( ml per kg ody weight; DeltSelect) nd glucose concentrtions in lood were mesured fter,, nd min. Insulin-tolernce tests were done with -week-old mice fed d liitum. After sl glucose concentrtions in lood were mesured, ech mouse received n intrperitonel injection of insulin (.7 units per kg ody weight; Actrpid; Novo Nordisk) nd glucose concentrtions in lood were mesured fter, nd min. Mice were treted with s descried. -week-old control nd mice fed HFD were given intrperitonel injection twice per week of µg (PeproTech) in complex with rt ntiody to mouse (purified, no zide nd low endotoxin; ; B; BD Phrmingen). HOMA-IR ws clculted s descried. For promotion of the lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges in vivo, mice were given single injection of in sterile PBS ( µg per kg ody weight). (R&D Systems) ws used t dose of µg per kg ody weight for in vivo studies. efore the clmping ( µci priming t rte of. µci/min; PerkinElmer). After -minute sl period, lood smple ( µl) ws collected from the til tip for determintion of sl prmeters. To minimize lood loss, red lood cells were collected y centrifugtion, resuspended in sline nd reinfused. The clmping egn with primed-continuous insulin infusion ( µu prime per g ody weight, t rte of µu per g ody weight per min; INSUMAN rpid; Snofi-Aventis) nd glucose concentrtions in lood were mesured every min (B-Glucose Anlyzer; Hemocue). Physiologicl concentrtions of glucose in lood ( mg/dl) were mintined y djustment of % glucose infusion (DeltSelect). Approximtely min efore the end of the experiment, -[- C]-deoxy-d-glucose ( µci; Americn Rdioleled Chemicls) ws infused, nd lood smples ( µl) were collected until stedy stte ws reched. The stedy stte ws considered to hve een chieved when fixed glucose-infusion rte mintined the glucose concentrtion in lood constnt for min. During the stedy stte, lood smples ( µl) were collected for the mesurement of stedystte prmeters. At the end of the experiment, mice were killed y cervicl disloction, nd liver, dipose tissue nd skeletl muscle were dissected nd stored t C. The [- H]glucose rdioctivity of plsm in sl conditions nd t stedy stte ws mesured s descried. The rdioctivity of -[- C]-deoxy-dglucose in plsm ws mesured directly in liquid scintilltion counter. Lystes of dipose tissue nd skeletl muscle were processed through ionexchnge chromtogrphy columns (AG R -X formte resin, mesh dry; Poly-Prep Prefilled Chromtogrphy Columns; Bio Rd Lortories) for the seprtion of -[- C]-deoxy-d-glucose from -[- C]-deoxy-d-glucose- -phosphte, -[- C] (DGP). The glucose-turnover rte (mg kg min ) ws clculted s descried. The uptke of glucose in dipose tissue nd skeletl muscle in vivo (nmol g min ) ws clculted on the sis of the ccumultion of -[- C]-deoxy-d-glucose--phosphte, -[- C] in the respective tissue nd the disppernce rte of -[- C]-deoxy-d-glucose from plsm, s descried. LPS-induced endotoxemi. 9- to -week-old control nd mice were cclimtized to the PhenoMster System cges for d, then ll mice were chllenged y intrperitonel injection of LPS (Escherichi coli serotype O: B; L; Sigm-Aldrich) in.9% sline, t dose of mg per kg ody weight, nd mesurement of food intke (NCD) nd energy expenditure ws resumed. Whole lood ws collected into heprinized tues t h fter injection nd ws spun t 7,g ( C) for 7 min to otin plsm. The LPS serotype nd preprtion, s well s the dministrtion route, were chosen on the sis of pulished studies,. Cytokines were quntified in plsm (diluted :) with Multiplex Bed Immunossys (Life Technologies) nd Bio-Plex system (Bio-Rd) ccording to the mnufcturer s instructions. Anlyticl procedures. Glucose concentrtions in whole venous lood were mesured with n utomtic glucose monitor (Byer Contour; Byer). The concentrtions of leptin nd insulin in serum were mesured y enzymelinked immunosorent ssy, with mouse stndrds, ccording to mnufcturer s guidelines (Mouse Leptin ELISA nd Mouse Insulin ELISA; Crystl Chem). Serum nonesterified free ftty cids were quntified with FilterMx F multiplte reder (Moleculr Devices) ccording to the mnufcturer s instructions (WAKO Chemicls). The concentrtions of triglycerides in liver nd serum were determined in mice tht hd een mde to fst for h. Triglycerides were extrcted from liver s descried. Triglycerides in liver nd serum were quntified with FilterMx F multiplte reder (Moleculr Devices) ccording to the mnufcturer s instructions (Sigm). Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clmp studies in wke mice. Surgicl implnttion of ctheters into the jugulr vein ws chieved s descried. After d of recovery, only mice tht hd lost less thn % of their preopertive weight were included. Ech niml ws mde to fst for h on the morning of the experiment nd then ws plced in restriner for the durtion of the clmp experiment. All infustes used in the experiment were prepred with % plsm solution otined from donor mice tht hd een mde to fst. A primed-continuous infusion of trcer d-[- H]-glucose ws egun min Genertion of BMDMs. Mice were killed y overexposure to CO nesthesi, then were rinsed in 7% (vol/vol) ethnol, nd one mrrow ws isolted from femurs nd tiis. Bone mrrow cells were plted t density of to cells per ml in RPMI- medium (supplemented with % FCS, % glutmine, % penicillin-streptomycin nd ng/ml mcrophge colonystimulting fctor (PeproTech)) on -cm petridishes nd were llowed to differentite for d. At h efore ll experiments, mcrophge colony-stimulting fctor ws removed nd cells were wshed two times with sterile PBS. doi:./ni. nture immunology
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
 Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ameliorates lipid and glucose accumulation in C57BL/6J mice via activation of PPAR-α and AMPK
 3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 regulates the immune response to infection by a unique inhibition of type I interferon activity
 5 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology Suppressor of cytokine signling 1 regultes the immune response to infection y unique inhiition of type I interferon ctivity Jennifer E Fenner
5 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology Suppressor of cytokine signling 1 regultes the immune response to infection y unique inhiition of type I interferon ctivity Jennifer E Fenner
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated β-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling
 Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Interleukin-4 Restores Insulin Sensitivity in Lipid-Induced Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes
 ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
Critical role of c-kit in beta cell function: increased insulin secretion and protection against diabetes in a mouse model
 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 DOI 1.17/s15-1-5-5 ARTICLE Criticl role of c-kit in et cell function: incresed insulin secretion nd protection ginst dietes in mouse model Z. C. Feng & J. Li & B. A. Turco & M. Riopel
Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 DOI 1.17/s15-1-5-5 ARTICLE Criticl role of c-kit in et cell function: incresed insulin secretion nd protection ginst dietes in mouse model Z. C. Feng & J. Li & B. A. Turco & M. Riopel
Combined deletion of SCD1 from adipose tissue and liver does not protect
 Comined deletion of SCD1 from dipose tissue nd liver does not protect mice from oesity Mtthew T. Flowers 1, Lcmouh de 1, Mggie S. Strle 2 nd Jmes M. Ntmi 1,2,* Deprtments of 1 Biochemistry nd 2 Nutritionl
Comined deletion of SCD1 from dipose tissue nd liver does not protect mice from oesity Mtthew T. Flowers 1, Lcmouh de 1, Mggie S. Strle 2 nd Jmes M. Ntmi 1,2,* Deprtments of 1 Biochemistry nd 2 Nutritionl
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
AMPK maintains energy homeostasis and survival in cancer cells via. regulating p38/pgc-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION AMPK mintins energy homeostsis nd survivl in cncer cells vi regulting p38/pgc-1α-medited mitochondril iogenesis Blkrishn Chue 1, Prmnnd Mlvi 1, Shivendr Vikrm Singh 1, Noshd Mohmmd
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION AMPK mintins energy homeostsis nd survivl in cncer cells vi regulting p38/pgc-1α-medited mitochondril iogenesis Blkrishn Chue 1, Prmnnd Mlvi 1, Shivendr Vikrm Singh 1, Noshd Mohmmd
IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulating sodium transport via the PI-3 kinase/sgk1 pathway in a cortical collecting duct cell line
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Type II monocytes modulate T cell-mediated central nervous system autoimmunity
 Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
Supplementary Information. SAMHD1 Restricts HIV-1 Infection in Resting CD4 + T Cells
 Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
T cell intrinsic role of Nod2 in promoting type 1 immunity to Toxoplasma gondii
 T cell intrinsic role of Nod in promoting type 1 immunity to Toxoplsm gondii Michel H Shw 1, Thornik Reimer 1, Crmen Sánchez-Vldepeñs, Neil Wrner 1, Yun-Gi Kim 1, Mnuel Fresno & Griel Nuñez 1 Nod elongs
T cell intrinsic role of Nod in promoting type 1 immunity to Toxoplsm gondii Michel H Shw 1, Thornik Reimer 1, Crmen Sánchez-Vldepeñs, Neil Wrner 1, Yun-Gi Kim 1, Mnuel Fresno & Griel Nuñez 1 Nod elongs
A. Kinoshita 1, L. Locher 2, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S. Dänicke 3, J. Rehage 4, K. Huber 5
 Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
Northern blot analysis
 Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
Ndfip-mediated degradation of Jak1 tunes cytokine signalling to limit expansion of CD4 þ effector T cells
 Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
CD160 inhibits activation of human CD4 + T cells through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator
 CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
Synergistic effects of metformin, resveratrol, and hydroxymethylbutyrate on insulin sensitivity
 Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Effects of Recombinant Bovine Somatotropin Administration at Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus and Subsequent Offspring Performance of Beef Cattle
 Effects of Recominnt Bovine Somtotropin Administrtion t Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus nd Susequent Offspring Performnce of Beef Cttle V. R. G. Mercdnte 1, F. M. Cirico 1, D. D. Henry 1, P. L. P. Fontes
Effects of Recominnt Bovine Somtotropin Administrtion t Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus nd Susequent Offspring Performnce of Beef Cttle V. R. G. Mercdnte 1, F. M. Cirico 1, D. D. Henry 1, P. L. P. Fontes
GDF11 Protects against Endothelial Injury and Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Formation in Apolipoprotein E-Null Mice
 originl rticle The Americn Society of Gene & Cell Therpy Protects ginst Endothelil Injury nd Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Formtion in Apolipoprotein E-Null Mice Wen Mei, Gungd Xing, Yixing Li 2, Hun
originl rticle The Americn Society of Gene & Cell Therpy Protects ginst Endothelil Injury nd Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Formtion in Apolipoprotein E-Null Mice Wen Mei, Gungd Xing, Yixing Li 2, Hun
Chapter 5: The peripheral nervous system Learning activity suggested answers
 Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Cytochrome P450-2E1 promotes fast food-mediated hepatic fibrosis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INRMATION Cytochrome P-E1 promotes fst food-medited heptic fibrosis Mohmed A. Abdelmegeed, Youngshim Choi, Grzegorz Godlewski b, Seung-Kwon H, Atryee Bnerjee, Sehwn Jng, nd Byoung-Joon Song
SUPPLEMENTARY INRMATION Cytochrome P-E1 promotes fst food-medited heptic fibrosis Mohmed A. Abdelmegeed, Youngshim Choi, Grzegorz Godlewski b, Seung-Kwon H, Atryee Bnerjee, Sehwn Jng, nd Byoung-Joon Song
IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 and STAT6
 ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE
 THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
Chromium Alleviates Glucose Intolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic ER Stress in Obese Mice
 nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
Not for Citation or Publication Without Consent of the Author
 Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Chronic high-sodium diet intake after weaning lead to neurogenic hypertension in adult Wistar rats
 Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY
 METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 4010 is procedure for screening solids such s soils, sludges, nd queous medi such s wste wter nd lechtes
METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 4010 is procedure for screening solids such s soils, sludges, nd queous medi such s wste wter nd lechtes
A critical role for interleukin 4 in activating alloreactive CD4 T cells
 A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
A Specific Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis of Type 2 Diabetic Mice Induces GLP-1 Resistance through an Enteric NO-Dependent and Gut-Brain Axis Mechanism
 Article A Specific Gut Microiot Dysiosis of Type 2 Dietic Mice Induces GLP-1 Resistnce through n Enteric NO-Dependent nd Gut-Brin Axis Mechnism Grphicl Astrct Authors Estelle Grsset, Anthony Puel, Julie
Article A Specific Gut Microiot Dysiosis of Type 2 Dietic Mice Induces GLP-1 Resistnce through n Enteric NO-Dependent nd Gut-Brin Axis Mechnism Grphicl Astrct Authors Estelle Grsset, Anthony Puel, Julie
TREM-1 regulates macrophage polarization in ureteral obstruction
 sic reserch http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology regultes mcrophge polriztion in ureterl ostruction Tzu-Hn Lo 1,1, Ki-Yu Tseng,1, Wen-Shn Tso, Chih-Y Yng,3, Shie-Ling
sic reserch http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology regultes mcrophge polriztion in ureterl ostruction Tzu-Hn Lo 1,1, Ki-Yu Tseng,1, Wen-Shn Tso, Chih-Y Yng,3, Shie-Ling
Effect of environmental stress on biochemical and physiological features in cultured fish
 Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-b and metabolic health
 Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Brown adipose tissue activity controls triglyceride clearance
 Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Platelet-derived growth factor-a receptor activation is required for human cytomegalovirus infection
 Vol 455 18 Septemer 28 doi:1.138/nture729 LETTERS Pltelet-derived growth fctor- receptor ctivtion is required for humn cytomeglovirus infection Lilin Sorocenu 1, Armin Akhvn 1 & Chrles S. Cos 1,2 Humn
Vol 455 18 Septemer 28 doi:1.138/nture729 LETTERS Pltelet-derived growth fctor- receptor ctivtion is required for humn cytomeglovirus infection Lilin Sorocenu 1, Armin Akhvn 1 & Chrles S. Cos 1,2 Humn
