Arteriohepatic Dysplasia (Alagille s Syndrome): A Common Cause of Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia
|
|
|
- Kathleen Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANNALS O F CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 14, No. 6 Copyright 1984, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Arteriohepatic Dysplasia (Alagille s Syndrome): A Common Cause of Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia ELLEN KAHN, M.D.* and FREDRIC DAUM, M.D.f *D epartm ent o f Laboratories and Departm ent o f Pediatrics, f Division o f Pediatric Gastroenterology, Departm ent o f Pediatrics, North Shore University Hospital, Manhasset, NY Cornell University Medical College, New York, NY ABSTRACT Syndromatic paucity of interlobular bile ducts is a common cause of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia in children. The clinical presentation is not always obvious. Therefore, the liver biopsy may be a useful diagnostic tool in the definition of this entity. The hepatic and biliary morphology of five children with arteriohepatic dysplasia (Alagille s syndrome) is described. Prior to diagnosis, four underwent Kasai procedures after intraoperative cholangiograms failed to demonstrate patency of the extrahepatic bile ducts. In three patients, a focal proximal hypoplasia of the common hepatic duct was demonstrated. Hypoplasia of the gallbladder occurred in two patients. Hepatic features of sequential liver biopsies obtained in the five patient^ were divided into early and late changes. From birth to four months of age, the pathology consisted of cholestasis and bile duct destruction. After four months of age, there was persistent cholestasis, paucity of interlobular bile ducts and portal fibrosis. The etiology of arteriohepatic dysplasia is unclear. The main pathogenic mechanisms are discussed. It is felt that the syndromatic duct paucity represents an acquired primary ductal defect resulting from a genetically determined immune response to as yet undefined agent or agents. Introduction Paucity of interlobular bile ducts is the most common cause of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.3 6,8 It may present as an isolated defect (nonsyndromatic paucity of interlobular bile ducts) or may be associated with other extrahepatic anomalies (structural syndromatic, Alagille s syndrome, arteriohepatic dysplasia).3 These anomalies are variable and may not be obvious in the newborn. The liver biopsy has provided the clinician with perhaps a more objective means of characterizing this group of syndromatic children.9,14 In this report, the hepatic morphology of five patients with arteriohepatic dysplasia is described. The clinical data are summarized in tables I and II. Prior to the diagnosis of arteriohepatic dysplasia, four of five pa /84/ $01.20 Institute for Clinical Science, Inc.
2 TABLE I C lin ica l Data Hepatic Visualiza ti on Conjugated Excretion of Intrahepatic Porto- Hyperbili- of Radio- B.T. by enter- Patieut rubinemia nuclide Cholangiogram ostomy #1 3d + #2 3d + #3 2m + #4 lm + #5 2m + B.T. = Biliary tree d = Days ARTERIOHEPATIC DYSPLASIA * = Not performed m = Months tients had undergone Kasai procedures after intraoperative cholangiograms had failed to demonstrate patency of the extrahepatic biliary tree. Pathology Microscopic examination of the extrahepatic biliary tree in three patients revealed a common bile duct of normal calibre and hypoplasia of the proximal hepatic duct (150 to 308 microns; normal = 900 microns (figure 1). The gallbladder was also hypoplastic in two patients (table III), hypoplasia being defined as a narrow but patent lumen.112,20 Atresia denotes complete obliteration of the structure.10,19 Two to five sequential liver biopsies were obtained between 19 days and 27 months of age (table IV). Detailed microscopic findings have been recently reported.9 The features of these biopsies can be divided into early (birth to four months) and later stages (older than four months). Early hepatic morphology consists primarily of cholestasis associated with giant cell transformation. A decrease in the number of interlobular bile ducts is not apparent at this stage, although there is early duct destruction. This is reflected by pyknosis of the ductal epithelium, focal destruction of the basement membrane, luminal collapse, asymmetrical cellular infiltration of the portal spaces contiguous to interlobular bile ducts, periductal fibrosis, and focal ductal obliteration by cellular fibrous connective tissue (figure 2). Large bile ducts are either hypoplastic or completely obliterated by cellular fibrous connective tissue (figure 3). Portal spaces are of normal size and there is no ductular proliferation. The late changes consist of persistent cholestasis, a decreased number of interlobular bile ducts, and a lack of ductular proliferation. Portal fibrosis is present. Hepatocellular and canalicular cholestasis is moderate to severe and centrilobular or diffuse. A paucity of interlobular bile ducts is apparent after four months. Most portal spaces do not contain bile ducts (figure 4). Discussion Arteriohepatic dysplasia is an autosomal dominant16 or recessive2 disease. It is characterized by a distinctive facies and specific extrahepatic anomalies, including cardiovascular (peripheral pulmonic stenosis, coarction of the aorta), ocular (prominent Schwalbe s line, retinal pigmentary changes), and vertebral (butterfly vertebrae) changes.3,7,1617 Delayed mental and sexual development as well as growth retardation have also been described. The disease is nonprogressive in the majority of the patients and its etiology remains unclear. Because the diagnosis of arteriohepatic dysplasia may not be obvious, patients TABLE C lin ic a l F e a tu re s o f A rte r io h e p a tic D y sp la sia Peripheral Abnormal Typical Pulmonic Butterfly Oph thalmol ogi c Patient Facies Stenosis Vertebrae Findings # # # #4 + + #5 + + I I
3 482 KAHN AND DAUM Figure 1. A. Serial sections of the extrahepatic biliary system. Patent common bile duct (c.b.) and cystic duct (c.d.) Hypoplasia of the gallbladder (g.b.) and of the common hepatic duct (h.d.) is apparent, (p.h.) porta hepatis. B. Higher magnification of the bracketed area depicting a hypoplastic 150 micron hepatic duct. Hematoxylin-eosin x 50.
4 ARTERIOHEPATIC DYSPLASIA «y ** «'' *# 4 -ç,*» %**> : x-* *!* *Vy«#T x& h Vi.1«* * V *-v*1«''v "!', v 6 _ sj ->w< v -. ÿ - i i '; ««; «Vi'Hrl?- f '* "t t ~ y «> TJ», - Vs. * '.*» «* Ÿ * i r * * *? - i* >; ** 1* 483 V V\ j * - >'\xu r,\ 4 *A 1. <' : v - * *-? ^ ~ >, Figure 2. Composite of progressive destruction of interlobular bile ducts. A. Portal space with asym m etrical m ononuclear in filtration adjacent to an in terlobular bile duct. H ematoxylin-eosin X 120. B. Bile duct seen as solid cluster of epithelial cells (arrow s). H em atoxylineosin X300. C. H ig her magnification of figure 2a; o bliterated in terlob ular bile duct (arrow). Hem atoxylin-eosin X300.
5 4 8 4 KAHN AND DAUM T A BLE III Hypoplasia of the Extrahepatic Biliary Tree #1 P a tie n ts #2 #3 #4 #5 Gallbladder NL NL + + * Common Hepatic Duct + * + + * Common Bile Duct NL NL NL NL NL The common hepatic ducts in patients 3 and 4 were serially sectioned. Patency persists throughout. *Not examined NL - Normal +Hypoplasia present may be subjected to laparotomy and intraoperative cholangiography. Intraoperative cholangiograms may be indistinguishable from those seen in children with extrahepatic biliary atresia. Hypoplasia of the common hepatic duct, observed in three of the infants, most likely accounted for the nonvisualization of the intrahepatic radicles. Indeed, hypoplasia of the extrahepatic biliary tree may be common in patients with arteriohepatic dysplasia. The hepatic morphology of the portal spaces seems to be quite characteristic. Before four months of age, the portal spaces are not increased in size and contain a normal number of interlobular bile ducts with the ratio of interlobular bile ducts to portal spaces being 0.9 to Bile duct destruction is associated with a mononuclear cell infiltration. Three main theories have been proposed to explain paucity of interlobular bile ducts: failure of development, atrophy, and ductal destruction. The consensus is that arteriohepatic dysplasia is not a developmental anomaly but rather an acquired disease.4,918 The actual destruction of interlobular bile ducts in the early stage with eventual disappearance of these structures mitigates against a developmental anomaly. Some15 have proposed a primary hepatocellular defect resulting in atrophy and subsequent ductal paucity. This is based on ultrastructural signs of hepatocellular bile retention not associated with biliary canalicular changes seen with cholestasis of other etiologies. Electron microscopic examination was not performed in our patients prior to portoenterostomy. The autosomal dominant or recessive inheritance of arteriohepatic dysplasia implies a possible genetic predisposition among certain individuals.16 What triggers the destruction of the interlobular bile ducts and whether this process begins distally or proximally in the biliary system is unclear. Toxins and infectious agents have been implicated.3,6'11 Our observations seem to suggest that ductal destruction begins in the larger and intermediate size bile ducts, while small interlobular bile ducts are affected later in the course of the disease. On purely morphologic criteria, the ductal destruction seen in our patients, including the basement membrane destruction and disappearance of ducts without scarring, bears strong resemblance to that seen in primary biliary cirrhosis, an autoimmune process observed in adults. In primary biliary cirrhosis, there is also a periductal mononuclear response followed by disappearance of intermediate bile ducts without subsequent ductal fibrosis.13 Paucity of interlobular bile ducts has also been described in graft versus host disease and in liver transplant,5,18 further supporting an immune etiology for the duct destruction. Hypoplasia of the extrahepatic biliary tree might be interpreted either as a manifestation of disuse or perhaps, inasmuch as it was present early in the course, a less severe involvement by the same basic pathogenic process. T A B L E I V Nature of Material and Time of Liver Biopsies Pt. 1 P t. 2 P t. 3 Pt. 4 Pt. 1 5W J.4M 27M 19D 7W 3M 8M 17M 3M 7M 6W 3M 5M J.J.W 7M 27M WB NB Autopsy + Pt. = Patient W = Week M - Months D = Days WB = Wedge biopsy NB = Needle biopsy
6 ARTERIOHEPATIC DYSPLASIA 485 Figure 3. L arge bile du ct o b lite rated by fibrous connective tissue. R em nants o f cuboidal ep ith eliu m are indicated by arrow s. H em atoxylin-eosin X500. '* v Figure 4. Portal space w ith o u t in terlo b u lar bile ducts. H em atoxylin-eosin X 50
7 4 8 6 KAHN AND DAUM References 1. A l a g i l l e, D.: C h o lestasis in th e first th re e m onths of life. Prog. L iver D is. 6: , A l a g i l l e, D. and O d i e v r e, M.: Cholestasis in children. L iver and Biliary Tract in C h ildren. N ew York, John W iley and Sons, 1978, pp A l a g i l l e, D., O d i e v r e, M., G a u t i e r, M., et al: H ep atic d u c tu la r h y p o p lasia associated w ith characteristic facies, vertebral malformations, retarded physical, m ental and sexual developm ent and cardiac murm ur. J. Pediatr. 86:63-71, D a h m s, B. B., P e t r e l l i, M., W y l l i e, R., et al: A rteriohepatic dysplasia in infancy and childhood: a longitudinal study of six patients. H epatology 2: , F e n n e l l, R. H., S h i k e s, R. H., and V i e r l i n g, J. M.: Relationship of pretransplant hepatobiliary disease to bile duct dam age occuring in the liver allograft. Hepatology 3 :84-89, H e a t h c o t e, J., D e o d h a r, K. P., S c h e u e r, P. J., et al: Intrahepatic cholestasis in childhood. N. Engl. J. M ed. 295: , H e n r i k s e n, N. T., L a n g m a r k, F., S 0 r l a n d, S. J., e t a l: H e r e d i t a r y c h o l e s t a s i s c o m b i n e d w i t h p e r i p h e r a l p u l m o n a r y s t e n o s i s a n d o t h e r a n o m a l i e s. A c t a P a e d i a t r. S c a n d. 66:7 15, H y a m s, J. S., B e r m a n, M. M., and D a v i s, B. H. : T ubulointerstitial n ep h ro p ath y associated w ith a rte rio h e p a tic d y sp lasia. G a stro e n te ro lo g y 85: , K a h n, E., D a u m, F., M a r k o w i t z, J., et al: Arteriohepatic dysplasia. II. H epatobiliary m orphology. Hepatology 3 :77-83, K a s a i, M.: Treatm ent o f biliary atresia w ith special reference to hepatic porto-enterostom y and its m odifications. Prog. Pediatr. Surg. 6 :5-52, L e v i n, S. E., Z a r b o s, P., M i l n e r, S., e t al: Arteriohepatic dysplasia: association of liver disease w ith pulm onary arterial stenosis as well as facial and skeletal anom alies. Pediatrics 66: , L i l l y, K. R. : T he surgery of biliary hypoplasia. J. Pediatr. Surg. ii: , M a c S w e e n, R. N. M., A n t h o n y, P. W., and S c h e u e r, P. J. : Pathology of th e Liver. E d in b urgh, C h u rch ill L ivingston, 1979, pp M a r k o w i t z, J., D a u m, F., K a h n, E., e t al: Arteriohepatic dysplasia. I. Pitfalls in diagnosis and management. Hepatology 3:74 76, P h i l l i p s, M. J., C u t z, E., M a y o r a, P. V., et al: D istinctive ultrastructural pathology in Alagille syndrom e. Lab. Invest. 4S:67A-68A, R i e l y, C. A., C o t l i e r, E., J e n s e n, P. S., e t al: A rteriohepatic dysplasia a benign syndrom e of intrahepatic cholestasis w ith m ultiple organ inv o lv em ent. A nn. In te rn. M ed. 9 i: , W a t s o n, G. H., and M i l l e r, V.: A rteriohepatic dysplasia. Fam ilial pulm onary arterial stenosis w ith neonatal liver disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 48: , W i t z l e b e n, C. L. : Bile duct paucity ( intrahepatic atresia ). Perspect. Pediatr. Path. 7: , W i t z l e b e n, C. L.: E xtrahepatic biliary atresia: concepts o f cause, diagnosis and m anagem ent. Perspect. Pediatr. Path. 5:41-62, W i t z l e b e n, C. L.: T he pathogenesis of biliary atresia. N eonatal H epatitis and Biliary Atresia. Javitt, N. B., ed. B ethesda, U.S. Public H ealth Service Publications, No. (N IH ) : , 1977.
Biliary Atresia. Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s
 Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Current Management of Biliary Atresia. Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007
 Current Management of Biliary Atresia Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007 Overview Etiology and diagnosis Work-up and management History of Kasai Portoenterostomy Studies Advances
Current Management of Biliary Atresia Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007 Overview Etiology and diagnosis Work-up and management History of Kasai Portoenterostomy Studies Advances
Neonatal Cholestasis. What is Cholestasis? Congenital and Pediatric liver diseases 4/26/18
 Congenital and Pediatric liver diseases Nitika Gupta, M.D. Personal/Professional Financial Relationships with Industry in the past year External Industry Relationships * Equity, stock, or options in biomedical
Congenital and Pediatric liver diseases Nitika Gupta, M.D. Personal/Professional Financial Relationships with Industry in the past year External Industry Relationships * Equity, stock, or options in biomedical
Approach to a case of Neonatal Cholestasis
 Approach to a case of Neonatal Cholestasis Ira Shah (Co-Incharge, Consultant Pediatrician, Pediatric Liver Clinic) Gunjan Narkhede (Resident in Pediatric Liver Clinic) Pediatric Hepatobiliary Clinic, B.J.Wadia
Approach to a case of Neonatal Cholestasis Ira Shah (Co-Incharge, Consultant Pediatrician, Pediatric Liver Clinic) Gunjan Narkhede (Resident in Pediatric Liver Clinic) Pediatric Hepatobiliary Clinic, B.J.Wadia
4/7/2015. Conflicts of Interest. None Heather Rush
 Heather Rush, APRN, CDE Wendy L Novak Diabetes Care Center Louisville, KY Conflicts of Interest None Heather Rush A conflict of interest exists when an individual is in a position to profit directly or
Heather Rush, APRN, CDE Wendy L Novak Diabetes Care Center Louisville, KY Conflicts of Interest None Heather Rush A conflict of interest exists when an individual is in a position to profit directly or
BILIARY ATRESIA. What is biliary atresia?
 The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
NEONATAL CHOLESTASIS AND BILIARY ATRESIA: PERSPECTIVE FROM MALAYSIA
 NEONATAL CHOLESTASIS AND BILIARY ATRESIA: PERSPECTIVE FROM MALAYSIA Lee WS Department of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. ABSTRACT: The liver is an important
NEONATAL CHOLESTASIS AND BILIARY ATRESIA: PERSPECTIVE FROM MALAYSIA Lee WS Department of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. ABSTRACT: The liver is an important
Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 761326-1332, 1979 Histometric and Serial Section Observations of the Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis YASUNI NAKANUMA and GOROKU OHTA Second Department of Pathology,
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice
 Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice Ahmed Laving KPA Annual Scientific Conference 2018 Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Case Presentation
Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice Ahmed Laving KPA Annual Scientific Conference 2018 Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Case Presentation
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
CD56-immunostaining of the extrahepatic biliary tree as an indicator of clinical outcome in biliary atresia: a preliminary report
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 8; 5: 54-548 Original CD56-immunostaining of the extrahepatic as an indicator of clinical outcome in atresia: a preliminary report Tadao Okada, Tomoo Itoh, Fumiaki Sasaki,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 8; 5: 54-548 Original CD56-immunostaining of the extrahepatic as an indicator of clinical outcome in atresia: a preliminary report Tadao Okada, Tomoo Itoh, Fumiaki Sasaki,
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Case Report Two Rare Cases of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Kasai Procedure for Biliary Atresia: A Recommendation for Close Follow-Up
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2015, Article ID 982679, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/982679 Case Report Two Rare Cases of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Kasai Procedure for Biliary Atresia:
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2015, Article ID 982679, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/982679 Case Report Two Rare Cases of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Kasai Procedure for Biliary Atresia:
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
Outcome of liver disease in children with Alagille syndrome: a study of 163 patients
 Gut 2001;49:431 435 431 Service d Hépatologie Pédiatrique, Hôpital de Bicêtre, 94275 Le Kremlin Bicêtre Cedex, France P Lykavieris M Hadchouel O Bernard Unité INSERM 347, 94276 Le Kremlin Bicêtre Cedex,
Gut 2001;49:431 435 431 Service d Hépatologie Pédiatrique, Hôpital de Bicêtre, 94275 Le Kremlin Bicêtre Cedex, France P Lykavieris M Hadchouel O Bernard Unité INSERM 347, 94276 Le Kremlin Bicêtre Cedex,
Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Paucity of Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Neonates: the First Case Series from Iran
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Feb 2013; Vol 23 (No 1), Pp: 65-70 Paucity of Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Neonates: the First Case Series from Iran Zahmatkeshan, Mozhgan*, MD; Geramizadeh, Bita, MD; Haghighat,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Feb 2013; Vol 23 (No 1), Pp: 65-70 Paucity of Intrahepatic Bile Ducts in Neonates: the First Case Series from Iran Zahmatkeshan, Mozhgan*, MD; Geramizadeh, Bita, MD; Haghighat,
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target
 Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Biliary Atresia. Greg Tiao, MD. 3 rd Annual Pediatric Surgery Update Course GlobalCastMD
 Biliary Atresia Greg Tiao, MD GlobalCastMD 3 rd Annual Pediatric Surgery Update Course 2015 Case Pediatrician calls you about a 60 day old full term male who is otherwise healthy but is noted to have persistent
Biliary Atresia Greg Tiao, MD GlobalCastMD 3 rd Annual Pediatric Surgery Update Course 2015 Case Pediatrician calls you about a 60 day old full term male who is otherwise healthy but is noted to have persistent
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Title: Alagille syndrome: an uncommon cause of intrahepatic cholestasis in adults
 Title: Alagille syndrome: an uncommon cause of intrahepatic cholestasis in adults Authors: Wei Zhang, Xinyan Zhao, Jian Huang, Xiaojuan Ou, Jidong Jia DOI: 10.17235/reed.2019.5679/2018 Link: PubMed (Epub
Title: Alagille syndrome: an uncommon cause of intrahepatic cholestasis in adults Authors: Wei Zhang, Xinyan Zhao, Jian Huang, Xiaojuan Ou, Jidong Jia DOI: 10.17235/reed.2019.5679/2018 Link: PubMed (Epub
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Outcomes of Liver Transplant for Biliary Atresia: A Ten Year Single Centre Experience
 Outcomes of Liver Transplant for Biliary Atresia: A Ten Year Single Centre Experience Dr Yentl van Heerden; Dr Andrew Grieve, Professor Jerome Loveland For Paediatric Hepatobiliary and Liver Transplant
Outcomes of Liver Transplant for Biliary Atresia: A Ten Year Single Centre Experience Dr Yentl van Heerden; Dr Andrew Grieve, Professor Jerome Loveland For Paediatric Hepatobiliary and Liver Transplant
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08. Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
 CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 primary sclerosing cholangitis primary sclerosing cholangitis pdf primary sclerosing cholangitis Diagnosis and Management
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 primary sclerosing cholangitis primary sclerosing cholangitis pdf primary sclerosing cholangitis Diagnosis and Management
Chronic Pancreatitis
 Falk Symposium 161 October 12, 2007 Chronic Pancreatitis David C Whitcomb MD PhD Giant Eagle Foundation Professor of Cancer Genetics. Professor of Medicine, Cell biology & Physiology, and Human Genetics
Falk Symposium 161 October 12, 2007 Chronic Pancreatitis David C Whitcomb MD PhD Giant Eagle Foundation Professor of Cancer Genetics. Professor of Medicine, Cell biology & Physiology, and Human Genetics
Table 1. Results of Sonography, Tc-99m DISIDA Scan and MR Cholangiography in 22 Patients with Neonatal Cholestasis
 337 Table 1. Results of Sonography, Tc-99m DISIDA Scan and MR Cholangiography in 22 Patients with Neonatal Cholestasis No. Sex Age (days) Final Dx Sonography Tc-99m DISIDA scan MR cholangiography Dx GB;
337 Table 1. Results of Sonography, Tc-99m DISIDA Scan and MR Cholangiography in 22 Patients with Neonatal Cholestasis No. Sex Age (days) Final Dx Sonography Tc-99m DISIDA scan MR cholangiography Dx GB;
Ultrasonographic Triangular Cord Sign and Gallbladder Abnormality in Diagnosis of Biliary Atresia
 Iranian Journal of Neonatology 14 Ultrasonographic Triangular Cord Sign and Gallbladder Abnormality in Diagnosis of Biliary Atresia Seyed Ali Jafari*, MD,1 Mehrzad Mehdizadeh, MD,2 Fatemeh Farahmand, MD,
Iranian Journal of Neonatology 14 Ultrasonographic Triangular Cord Sign and Gallbladder Abnormality in Diagnosis of Biliary Atresia Seyed Ali Jafari*, MD,1 Mehrzad Mehdizadeh, MD,2 Fatemeh Farahmand, MD,
Jaundice in children - Imaging features
 Jaundice in children - Imaging features Poster No.: C-2340 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. R. Matos, A. T. Ferreira, A. V. Nunes ; Lisbon/PT, 1 2 2 1 1 Oeiras/PT Keywords: Ultrasound,
Jaundice in children - Imaging features Poster No.: C-2340 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. R. Matos, A. T. Ferreira, A. V. Nunes ; Lisbon/PT, 1 2 2 1 1 Oeiras/PT Keywords: Ultrasound,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013
 Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Diagnostic Paediatric Pathology
 Annals of Diagnostic Paediatric Pathology 2006, 10(1 2):37 42 Copyright by Polish Paediatric Pathology Society Annals of Comparison of histological changes in liver biopsy specimens in patients with biliary
Annals of Diagnostic Paediatric Pathology 2006, 10(1 2):37 42 Copyright by Polish Paediatric Pathology Society Annals of Comparison of histological changes in liver biopsy specimens in patients with biliary
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis
 Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Cholestatic Syndromes in Infancy: Diagnostic Value of Serum Bile Acid Pattern and Cholestyramine Administration
 Pediat. Res. 7: 119-5 (1973) Bile cholestatic syndromes biliary atresia, extrahepatic cholestyramine Cholestatic Syndromes in Infancy: Diagnostic Value of Serum Bile Acid Pattern and Cholestyramine Administration
Pediat. Res. 7: 119-5 (1973) Bile cholestatic syndromes biliary atresia, extrahepatic cholestyramine Cholestatic Syndromes in Infancy: Diagnostic Value of Serum Bile Acid Pattern and Cholestyramine Administration
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
Biliary Atresia. Who is at risk for biliary atresia?
 Biliary Atresia Biliary atresia is a life-threatening condition in infants in which the bile ducts inside or outside the liver do not have normal openings. Bile ducts in the liver, also called hepatic
Biliary Atresia Biliary atresia is a life-threatening condition in infants in which the bile ducts inside or outside the liver do not have normal openings. Bile ducts in the liver, also called hepatic
Jaundice in children - Imaging features
 Jaundice in children - Imaging features Poster No.: C-2340 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. R. Matos, A. T. Ferreira, A. V. Nunes ; Lisboa/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 3 Oeiras/PT, 1800-348/PT
Jaundice in children - Imaging features Poster No.: C-2340 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. R. Matos, A. T. Ferreira, A. V. Nunes ; Lisboa/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 3 Oeiras/PT, 1800-348/PT
Pathogenesis and Outcome of Biliary Atresia: Current Concepts
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 37:4 21 July 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Invited Review Pathogenesis and Outcome of Biliary Atresia: Current Concepts * Ronald
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 37:4 21 July 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Invited Review Pathogenesis and Outcome of Biliary Atresia: Current Concepts * Ronald
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Neonatal Liver Disease. Khoula Al Said, FRCPC, FAAP Senior consultant Pediatric Gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition Royal Hospital
 Neonatal Liver Disease Khoula Al Said, FRCPC, FAAP Senior consultant Pediatric Gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition Royal Hospital Outline Embryology Etiologies of neonatal liver disease Approach
Neonatal Liver Disease Khoula Al Said, FRCPC, FAAP Senior consultant Pediatric Gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition Royal Hospital Outline Embryology Etiologies of neonatal liver disease Approach
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management
 Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Cholangiocarcinoma: appearances and mimics
 Cholangiocarcinoma: appearances and mimics Poster No.: C-1572 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cardenas Valencia, J. Fernandez Jara, J. Cubero Carralero, B. Corral Ramos, P. Perez
Cholangiocarcinoma: appearances and mimics Poster No.: C-1572 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cardenas Valencia, J. Fernandez Jara, J. Cubero Carralero, B. Corral Ramos, P. Perez
EVALUATION & LISTING. Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation. What is the Liver?
 EVALUATION & LISTING Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation The University of Michigan is a national leader in liver transplantation, as well as the surgical and medical management of patients with liver
EVALUATION & LISTING Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation The University of Michigan is a national leader in liver transplantation, as well as the surgical and medical management of patients with liver
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
Features of Alagille Syndrome in 92 Patients: Frequency and Relation to Prognosis
 Features of Alagille Syndrome in 92 Patients: Frequency and Relation to Prognosis KARAN M. EMERICK, 1 ELIZABETH B. RAND, 1 ELIZABETH GOLDMUNTZ, 2 IAN D. KRANTZ, 3 NANCY B. SPINNER, 3 AND DAVID A. PICCOLI
Features of Alagille Syndrome in 92 Patients: Frequency and Relation to Prognosis KARAN M. EMERICK, 1 ELIZABETH B. RAND, 1 ELIZABETH GOLDMUNTZ, 2 IAN D. KRANTZ, 3 NANCY B. SPINNER, 3 AND DAVID A. PICCOLI
USCAP PEDIATRIC PATHOLOGY Slide Session
 USCAP PEDIATRIC PATHOLOGY Slide Session CASE 4 Milton J. Finegold Patient 1 Slide B Twin A: 27 4/7 wk gestation; 1090 gm Maternal gestational DM, ITP - Rx IVIG Ventilatory support for 3 months Multiple
USCAP PEDIATRIC PATHOLOGY Slide Session CASE 4 Milton J. Finegold Patient 1 Slide B Twin A: 27 4/7 wk gestation; 1090 gm Maternal gestational DM, ITP - Rx IVIG Ventilatory support for 3 months Multiple
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst
 Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children
 Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children David A. Mong, MD SUNDAY Andrew Mong MD Beyond the interstitium (path includes airways/airspace) Radiographic diffuse disease Adult Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children David A. Mong, MD SUNDAY Andrew Mong MD Beyond the interstitium (path includes airways/airspace) Radiographic diffuse disease Adult Interstitial Lung Disease
Research Article Mortality of Biliary Atresia in Children Not Undergoing Liver Transplantation in Egypt (Single Institutional Study)
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Yasser K Rashed 1 *, Behairy E Behairy 1, Magdy A Saber 1, Taha E Yassein 2 and Eman Z Soliman 1 1 Department of Pediatric Hepatology, National Liver Institute, Menoufiya University,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Yasser K Rashed 1 *, Behairy E Behairy 1, Magdy A Saber 1, Taha E Yassein 2 and Eman Z Soliman 1 1 Department of Pediatric Hepatology, National Liver Institute, Menoufiya University,
Biliary Atresia. Objectives After completing this article, readers should be able to:
 Article gastroenterology Biliary Atresia Garret S. Zallen, MD,* David W. Bliss, MD,* Thomas J. Curran, MD, Marvin W. Harrison, MD,* Mark L. Silen, MD, MBA* Objectives After completing this article, readers
Article gastroenterology Biliary Atresia Garret S. Zallen, MD,* David W. Bliss, MD,* Thomas J. Curran, MD, Marvin W. Harrison, MD,* Mark L. Silen, MD, MBA* Objectives After completing this article, readers
Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking a Mass: Report of Three Cases
 Case Report Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):54-60 Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking
Case Report Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):54-60 Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
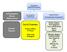 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen. Jonathan Swanson, MD
 Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree
 Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions. American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course
 Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico
 Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
Paediatric Liver Transplant Programme Wits Donald Gordon Medical Centre
 Paediatric Liver Transplant Programme Wits Donald Gordon Medical Centre J Loveland, J Botha, R Britz, B Strobele, S Rambarran, A Terblanche, C Kock, P Walabh, M Beretta, M Duncan et al 1817 reveal the
Paediatric Liver Transplant Programme Wits Donald Gordon Medical Centre J Loveland, J Botha, R Britz, B Strobele, S Rambarran, A Terblanche, C Kock, P Walabh, M Beretta, M Duncan et al 1817 reveal the
Natural history of α-1-atd in children
 Natural history of α-1-atd in children Agnieszka Bakuła Dpt of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Nutrition Disorders and Paediatrics The Children s Memorial Health Institute Warsaw, Poland Topics to be discussed
Natural history of α-1-atd in children Agnieszka Bakuła Dpt of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Nutrition Disorders and Paediatrics The Children s Memorial Health Institute Warsaw, Poland Topics to be discussed
Biliary Atresia and Its Complications*
 ANNALS O F CLIN ICAL AN D LABORATORY SCIEN CE, Vol. 20, No. 2 Copyright 1990, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Biliary Atresia and Its Complications* A. S. K n is e l y, M.D. Departments of Hematology
ANNALS O F CLIN ICAL AN D LABORATORY SCIEN CE, Vol. 20, No. 2 Copyright 1990, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Biliary Atresia and Its Complications* A. S. K n is e l y, M.D. Departments of Hematology
Biliary Anatomy in Living-related Liver Transplantation
 The 5th IHPBA Congress - Istanbul Biliary Anatomy in Living-related Liver Transplantation biliary trees hilar plate Assessment for Vascular Anatomy 1. 3DCT portal vein hepatic vein hepatic artery 2. No
The 5th IHPBA Congress - Istanbul Biliary Anatomy in Living-related Liver Transplantation biliary trees hilar plate Assessment for Vascular Anatomy 1. 3DCT portal vein hepatic vein hepatic artery 2. No
Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 725-730 Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants with mucoviscidosis J. R. OLSON AND D. K. WEAVER From the Department ofpathology, The University of Michigan Medical Center,
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 725-730 Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants with mucoviscidosis J. R. OLSON AND D. K. WEAVER From the Department ofpathology, The University of Michigan Medical Center,
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice
 Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
A review of histological parameters and CMV serology in Biliary atresia, and its relationship to long-term outcomes
 A review of histological parameters and CMV serology in Biliary atresia, and its relationship to long-term outcomes DR A. WITHERS, DR A. GRIEVE DEPARTMENT OF PAEDIATRIC SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
A review of histological parameters and CMV serology in Biliary atresia, and its relationship to long-term outcomes DR A. WITHERS, DR A. GRIEVE DEPARTMENT OF PAEDIATRIC SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis. Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K.
 Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. Citation Pediatric Surgery International, 28
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Partial internal biliary diversion intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. Mochizuki, Kyoko; Obatake, Masayuki Akiko; Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Okudaira Citation Pediatric
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Partial internal biliary diversion intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. Mochizuki, Kyoko; Obatake, Masayuki Akiko; Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Okudaira Citation Pediatric
Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction
 Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht
 Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
SURGICAL BILIARY TREE PATHOLOGIES IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SURGICAL BILIARY TREE PATHOLOGIES IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS JAMSHED AKHTAR, SOOFIA AHMED, M AQIL SOOMRO, NAIMA ZAMIR, AHMED SHARIF ABSTRACT Objective Study design Place & Duration of study
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SURGICAL BILIARY TREE PATHOLOGIES IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS JAMSHED AKHTAR, SOOFIA AHMED, M AQIL SOOMRO, NAIMA ZAMIR, AHMED SHARIF ABSTRACT Objective Study design Place & Duration of study
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Analysis of Cardiovascular Phenotype and Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Individuals With a JAG1 Mutation and/or Alagille Syndrome
 Analysis of Cardiovascular Phenotype and Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Individuals With a Mutation and/or Alagille Syndrome Doff B. McElhinney, MD; Ian D. Krantz, MD; Lynn Bason, MS; David A. Piccoli,
Analysis of Cardiovascular Phenotype and Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Individuals With a Mutation and/or Alagille Syndrome Doff B. McElhinney, MD; Ian D. Krantz, MD; Lynn Bason, MS; David A. Piccoli,
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA
 MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
Liver Tumors. Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy
 Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Color Doppler imaging of the liver in neonates with biliary atresia
 Color Doppler imaging of the liver in neonates with biliary atresia Mu Sook Lee Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University Color Doppler imaging of the liver in neonates with biliary
Color Doppler imaging of the liver in neonates with biliary atresia Mu Sook Lee Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University Color Doppler imaging of the liver in neonates with biliary
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Interpreting Liver Function Tests
 PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
Unique Aspects of the Neonatal Immune System Provide Clues to the Pathogenesis of Biliary Atresia. Disclosures. Objectives
 Unique Aspects of the Neonatal Immune System Provide Clues to the Pathogenesis of Biliary Atresia Cara L. Mack, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Pediatric GI, Hepatology & Nutrition Children s Hospital
Unique Aspects of the Neonatal Immune System Provide Clues to the Pathogenesis of Biliary Atresia Cara L. Mack, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Pediatric GI, Hepatology & Nutrition Children s Hospital
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids. Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada
 Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Pathology of the Sinusoids Ian R. Wanless Department of Pathology Dalhousie University Halifax, Canada Non cirrhotic portal hypertension Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Jaundice in Infants and Children
 431 Jaundice in Infants and Children Marilyn J. Siegel, MD ULTRASOUND CLINICS Ultrasound Clin 1 (2006) 431 441 - Sonographic examination - Overview of cholestatic diseases - Neonatal jaundice Biliary atresia
431 Jaundice in Infants and Children Marilyn J. Siegel, MD ULTRASOUND CLINICS Ultrasound Clin 1 (2006) 431 441 - Sonographic examination - Overview of cholestatic diseases - Neonatal jaundice Biliary atresia
Liver Disease in Cystic Fibrosis
 Liver Disease in Cystic Fibrosis Basic Overview Clinical Aspects Management What Is Cystic Fibrosis? Autosomal recessive disease W-1:3000, H-1:10,000, AA-1:15,000 Mutations of CFTR defective Cl - transport
Liver Disease in Cystic Fibrosis Basic Overview Clinical Aspects Management What Is Cystic Fibrosis? Autosomal recessive disease W-1:3000, H-1:10,000, AA-1:15,000 Mutations of CFTR defective Cl - transport
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
