Chapter 14. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
|
|
|
- Jeffery French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
2 Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal cord Integrates and processes information Can function with the brain Can function independently of the brain The brain Integrates and processes information Can function with the spinal cord Can function independently of the spinal cord
3 Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Features of the Spinal Cord 45 cm in length Passes through the foramen magnum Extends from the brain to L 1 Consists of: Cervical region Thoracic region Lumbar region Sacral region Coccygeal region
4 Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Features of the Spinal Cord Consists of (continued): Cervical enlargement Lumbosacral enlargement Conus medullaris Cauda equina Filum terminale: becomes a component of the coccygeal ligament Posterior and anterior median sulci
5 Figure 14.1a Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord C 1 Cervical spinal nerves C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 T 5 T 6 Cervical enlargement T 7 Thoracic spinal nerves T 8 T 9 Posterior median sulcus T 10 T 11 T 12 Lumbosacral enlargement L 1 Conus medullaris L 2 Lumbar spinal nerves L 3 L 4 L 5 Inferior tip of spinal cord Cauda equina Sacral spinal nerves S 1 S 2 S 3 Coccygeal nerve (Co 1 ) S 4 S 5 Filum terminale (in coccygeal ligament) a Superficial anatomy and orientation of the adult spinal cord. The numbers to the left identify the spinal nerves and indicate where the nerve roots leave the vertebral canal. The spinal cord, however, extends from the brain only to the level of vertebrae L 1 L 2.
6 Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Features of the Spinal Cord Consists of (continued): 31 spinal segments Each segment consists of: Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglia Ventral root Spinal nerve
7 Figure 14.1a Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord C 1 Cervical spinal nerves C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 T 5 T 6 Cervical enlargement T 7 Thoracic spinal nerves T 8 T 9 Posterior median sulcus T 10 T 11 T 12 Lumbosacral enlargement L 1 Conus medullaris L 2 Lumbar spinal nerves L 3 L 4 L 5 Inferior tip of spinal cord Cauda equina Sacral spinal nerves S 1 S 2 S 3 Coccygeal nerve (Co 1 ) S 4 S 5 Filum terminale (in coccygeal ligament) a Superficial anatomy and orientation of the adult spinal cord. The numbers to the left identify the spinal nerves and indicate where the nerve roots leave the vertebral canal. The spinal cord, however, extends from the brain only to the level of vertebrae L 1 L 2.
8 Figure 14.1d Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Posterior median sulcus White matter Central canal Gray matter Spinal nerve Ventral root Anterior median fissure C 3 T 3 L 1 S 2 d Inferior views of cross sections through representative segments of the spinal cord showing the arrangement of gray and white matter.
9 Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Features of the Spinal Cord Transverse view White matter Gray matter Central canal Anterior median fissure Posterior median sulcus
10 Figure 14.1a Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord C 1 Cervical spinal nerves C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 T 5 T 6 Cervical enlargement T 7 Thoracic spinal nerves T 8 T 9 Posterior median sulcus T 10 T 11 T 12 Lumbosacral enlargement L 1 Conus medullaris L 2 Lumbar spinal nerves L 3 L 4 L 5 Inferior tip of spinal cord Cauda equina Sacral spinal nerves S 1 S 2 S 3 Coccygeal nerve (Co 1 ) S 4 S 5 Filum terminale (in coccygeal ligament) a Superficial anatomy and orientation of the adult spinal cord. The numbers to the left identify the spinal nerves and indicate where the nerve roots leave the vertebral canal. The spinal cord, however, extends from the brain only to the level of vertebrae L 1 L 2.
11 Figure 14.1d Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Posterior median sulcus White matter Central canal Gray matter Spinal nerve Ventral root Anterior median fissure C 3 T 3 L 1 S 2 d Inferior views of cross sections through representative segments of the spinal cord showing the arrangement of gray and white matter.
12 Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Features of the Spinal Nerves Classified as mixed nerves Sensory nerves (afferent nerves) Transmit impulses toward the spinal cord Motor nerves (efferent nerves) Transmit impulses away from the spinal cord
13 Spinal Meninges Features of Spinal Meninges Specialized membranes that provide protection, physical stability, and shock absorption Continuous with the cranial (cerebral) meninges Denticulate ligaments help anchor the spinal cord in position
14 Figure 14.2c The Spinal Cord and Spinal Meninges Spinal cord Anterior median fissure Pia mater Denticulate ligaments Arachnoid mater (reflected) Dura mater (reflected) Spinal blood vessel Dorsal root of sixth cervical nerve Ventral root of sixth cervical nerve c Anterior view of spinal cord shows meninges and spinal nerves. For this view, the dura and arachnoid membranes have been cut longitudinally and retracted (pulled aside); notice the blood vessels that run in the subarachnoid space bound to the outer surface of the delicate pia mater.
15 Spinal Meninges Features of Spinal Meninges Made of three layers Dura mater Tough, fibrous outermost layer Arachnoid mater Middle layer Pia mater Innermost layer
16 Figure 14.2a The Spinal Cord and Spinal Meninges White matter Ventral root Dorsal root Gray matter Dorsal root ganglion Spinal nerve Meninges Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater a Posterior view of the spinal cord shows the meningeal layers, superficial landmarks, and distribution of gray and white matter.
17 Spinal Meninges The Dura Mater Tough fibrous outermost layer of the meninges Stabilizes the spinal cord within the vertebral canal Cranial and sacral attachments stabilize the longitudinal axis of the spinal cord
18 Spinal Meninges The Arachnoid Mater Middle meningeal layer Separated from the pia mater by the subarachnoid space Cerebrospinal fluid flows within this space Arachnoid trabeculae extend from the arachnoid to the outer layer of the pia mater
19 Spinal Meninges The Pia Mater Deepest meningeal layer Blood vessels are found in this layer Firmly bound to the brain tissue and the spinal cord tissue
20 Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Gray Matter Central canal Consists of somas (cell bodies) surrounding the central canal Consists of glial cells White Matter Consists of axons Nerves are organized into tracts or columns Located outside the gray matter area
21 Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Organization of Gray Matter Somas are organized into groups called nuclei Sensory nuclei Motor nuclei Transverse view shows: Posterior gray horns Lateral gray horns Anterior gray horns Gray commissure
22 Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Organization of Gray Matter Posterior gray horns Somatic sensory and visceral nuclei Lateral gray horns Visceral motor nuclei Anterior gray horns Somatic motor nuclei Gray commissure Consists of axons crossing from one side to the other
23 Figure 14.4b Sectional Organization of the Spinal Cord Posterior gray horn Posterior median sulcus From dorsal root Posterior gray commissure Somatic Visceral Sensory nuclei Lateral gray horn Anterior gray horn Anterior gray commissure To ventral root Visceral Somatic Motor nuclei Anterior median fissure b The left half of this sectional view shows important anatomical landmarks; the right half indicates the functional organization of the gray matter in the anterior, lateral, and posterior gray horns.
24 Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Organization of White Matter Consists of columns of nerves (funiculi) Posterior white column Anterior white column Lateral white column Columns convey either: Sensory tracts (ascending tracts) Motor tracts (descending tracts)
25 Figure 14.4c Sectional Organization of the Spinal Cord Posterior white column (funiculus) Leg Hip Trunk Arm Lateral white column (funiculus) Flexors Extensors Hand Forearm Arm Shoulder Trunk Anterior white column (funiculus) Anterior white commissure c The left half of this sectional view shows the major columns of white matter. The right half indicates the anatomical organization of sensory tracts in the posterior white column for comparison with the organization of motor nuclei in the anterior gray horn. Note that both sensory and motor components of the spinal cord have a definite regional organization.
26 Spinal Nerves There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves 8 cervical nerves 12 thoracic nerves 5 lumbar nerves 5 sacral nerves 1 coccygeal nerve
27 Figure 14.1a Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord C 1 Cervical spinal nerves C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 T 5 T 6 Cervical enlargement T 7 Thoracic spinal nerves T 8 T 9 Posterior median sulcus T 10 T 11 T 12 Lumbosacral enlargement L 1 Conus medullaris L 2 Lumbar spinal nerves L 3 L 4 L 5 Inferior tip of spinal cord Cauda equina Sacral spinal nerves S 1 S 2 S 3 Coccygeal nerve (Co 1 ) S 4 S 5 Filum terminale (in coccygeal ligament) a Superficial anatomy and orientation of the adult spinal cord. The numbers to the left identify the spinal nerves and indicate where the nerve roots leave the vertebral canal. The spinal cord, however, extends from the brain only to the level of vertebrae L 1 L 2.
28 Spinal Nerves Spinal Nerves Each peripheral nerve consists of: Epineurium Outer layer becomes continuous with the dura mater Perineurium Layer surrounding a fascicle a fascicle is a bundle of axons Endoneurium Layer surrounding a single axon
29 Figure 14.5a Anatomy of a Peripheral Nerve Blood vessels Connective Tissue Layers Epineurium covering peripheral nerve Perineurium (around one fascicle) Endoneurium Fascicle Schwann cell Myelinated axon a A typical peripheral nerve and its connective tissue wrappings
30 Spinal Nerves Peripheral Distribution of Spinal Nerves Spinal nerves from two branches Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus Spinal nerves T 1 to L 2 have two additional branches White ramus Gray ramus White and gray rami are collectively called rami communicantes
31 Spinal Nerves Peripheral Distribution of Spinal Nerves Motor impulses leave the spinal cord via the ventral root Sensory information enters the spinal cord via the dorsal root Rami communicantes (white and gray rami) Innervates smooth muscles, glands, and organs Dorsal ramus Innervates skeletal muscles of the neck and back Ventral ramus Innervates skeletal muscles of the limbs
32 Figure 14.6a Peripheral Distribution of Spinal Nerves Motor Commands Postganglionic fibers to smooth muscles, glands, etc., of back To skeletal muscles of back Dorsal root ganglion Dorsal root Visceral motor Somatic motor Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus To skeletal muscles of body wall, limbs Ventral root Postganglionic fibers to smooth muscles, glands, etc., of body wall, limbs Spinal nerve Rami communicantes KEY Somatic motor commands Visceral motor commands White ramus (preganglionic) Gray ramus (postganglionic) Sympathetic nerve Sympathetic ganglion Postganglionic fibers to smooth muscles, glands, visceral organs in thoracic cavity Preganglionic fibers to sympathetic ganglia innervating aboominopelvic viscera a The distribution of motor neurons in the spinal cord and motor fibers within the spinal nerve and its branches
33 Figure 14.6b Peripheral Distribution of Spinal Nerves Sensory Information From interoceptors of back From exteroceptors, proprioceptors of back Dorsal root Somatic sensory Visceral sensory Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus From exteroceptors, proprioceptors of body wall, limbs From interoceptors of body wall, limbs Dorsal root ganglion Rami communicantes KEY Ventral root Somatic sensations Visceral sensations From interoceptors of visceral organs b A comparable view detailing the distribution of sensory neurons and sensory fibers
34 Spinal Nerves Dermatomes Each pair of spinal nerves monitors specific surface areas These are clinically important areas regarding surgery
35 Figure 14.7 Dermatomes C 2 C 3 N V C 2 C 3 C 2 C 3 C 3 T 2 C 6 L 1 C 4 T C 2 5 T T 3 1 T T 4 2 T T 5 3 T T 6 4 T 7 T 5 T 6 T 7 T 8 T 9 T 10 T 11 T 12 T 8 T 9 T 10 T 11 T 12 L 1 L 2L3 L 4L5 C 4 T 2 C 5 C 6 C 7 T1 L 2 S 2 S 4 S 3 C7 T1 L 3 L 4 C 8 C 8 L 1 S 5 S 1 L 5 L S 2 2 L 5 L 3 S 1 L 4 ANTERIOR POSTERIOR
36 Nerve Plexuses There are four nerve plexuses Cervical plexus Brachial plexus Lumbar plexus Sacral plexus Sometimes the lumbar and sacral are combined to form the lumbosacral plexus
37 Figure 14.8 Peripheral Nerves and Nerve Plexuses Cervical plexus Brachial plexus C 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 T 5 T 6 T 7 T 8 T 9 T 10 Lesser occipital nerve Great auricular nerve Transverse cervical nerve Supraclavicular nerve Phrenic nerve Axillary nerve Musculocutaneous nerve Thoracic nerves T 11 Lumbar plexus T 12 L 1 L 2 L 3 L 4 Radial nerve Ulnar nerve Median nerve Sacral plexus L 5 S 1 S 2 S 3 S 4 S 5 Co 1 Iliohypogastric nerve Ilioinguinal nerve Genitofemoral nerve Femoral nerve Obturator nerve Superior Inferior Gluteal nerves Pudendal nerve Sciatic nerve Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve Saphenous nerve Common fibular nerve Tibial nerve Medial sural cutaneous nerve
38 Nerve Plexuses The Cervical Plexus (C 1 C 5 ) Consists of cutaneous and muscular branches Cutaneous branch innervates: Head Neck Chest
39 Nerve Plexus The Cervical Plexus Consists of cutaneous and muscular branches Muscular branch innervates: Omohyoid, sternohyoid, geniohyoid, thyrohyoid, sternothyroid Rhomboids Serratus anterior Sternocleidomastoid Diaphragm (controlled by the phrenic nerve of the cervical plexus)
40 Figure 14.9 The Cervical and Brachial Plexuses
41 Nerve Plexus The Brachial Plexus (C 5 T 1 ) Innervates the pectoral girdle and upper limbs The ventral rami emerging from C 5 to T 1 form the trunks Superior trunk Middle trunk Inferior trunk
42 Nerve Plexus The Brachial Plexus (C 5 T 1 ) The trunks form the divisions Anterior Posterior The divisions form the cords Posterior Lateral Medial The cords form the spinal nerves
43 Figure 14.9 The Cervical and Brachial Plexuses
44 Figure 14.10a The Brachial Plexus BRACHIAL PLEXUS Dorsal scapular nerve Suprascapular nerve Superior trunk Middle trunk Inferior trunk C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 T 1 Musculocutaneous nerve Median nerve Ulnar nerve Radial nerve Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve Superficial branch of radial nerve Palmar digital nerves Anterior antebrachial interosseous nerve Ulnar nerve Median nerve Anterior interosseous nerve Deep branch of ulnar nerve Superficial branch of ulnar nerve Radial nerve a In this anterior view of the brachial plexus and upper limb, the distribution of major peripheral nerves can be seen. Ulnar nerve Median nerve Anterior
45 Figure 14.10b The Brachial Plexus b This posterior view of the brachial plexus shows the location and distribution of the nerves. Musculocutaneous nerve Axillary nerve Branches of axillary nerve Radial nerve Ulnar nerve Median nerve Posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve Deep branch of radial nerve Radial nerve Ulnar nerve Superficial branch of radial nerve Dorsal digital nerves Median nerve Posterior
46 Nerve Plexus The Cords of the Brachial Plexus (details) Lateral cord: extends to form the musculocutaneous nerve The lateral cord and medial cord extend to form the median nerve Medial cord extends to form the ulnar nerve Posterior cord: branches to form the radial nerve and axillary nerve
47 Figure 14.9 The Cervical and Brachial Plexuses
48 Figure 14.10a The Brachial Plexus BRACHIAL PLEXUS Dorsal scapular nerve Suprascapular nerve Superior trunk Middle trunk Inferior trunk C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 T 1 Musculocutaneous nerve Median nerve Ulnar nerve Radial nerve Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve Superficial branch of radial nerve Palmar digital nerves Anterior antebrachial interosseous nerve Ulnar nerve Median nerve Anterior interosseous nerve Deep branch of ulnar nerve Superficial branch of ulnar nerve Radial nerve a In this anterior view of the brachial plexus and upper limb, the distribution of major peripheral nerves can be seen. Ulnar nerve Median nerve Anterior
49 Figure 14.10c The Brachial Plexus Clavicle, cut and removed Deltoid muscle Musculocutaneous nerve Right axillary artery over axillary nerve Median nerve Radial nerve Biceps brachii, long and short heads Ulnar nerve Coracobrachialis muscle Skin Right brachial artery Cervical plexus Right common carotid artery Brachial plexus (C 5 T 1 ) Sternocleidomastoid muscle, sternal head Sternocleidomastoid muscle, clavicular head Right subclavian artery Retractor holding pectoralis major muscle (cut and reflected) Median nerve c This dissection shows the major nerves arising from the cervical and brachial plexuses.
50 Nerve Plexus The Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses (T 12 S 4 ) Also called the lumbosacral plexus Lumbar plexus arises from L 1 to L 4 Sacral plexus arises from L 4 to S 4
51 Figure The Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses
52 Figure The Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses
53 Nerve Plexus The Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses (T 12 S 4 ) Lumbar plexus nerves L 1 to L 4 Genitofemoral nerve Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve Femoral nerve Iliohypogastric nerve Ilioinguinal nerve Obturator nerve
54 Nerve Plexus The Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses (T 12 S 4 ) Sacral plexus nerves L 4 to S 4 Sciatic nerve (branches to form the common fibular nerve and the tibial nerve) Pudendal nerve Superior gluteal nerve Inferior gluteal nerve Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
55 Figure 14.12a Peripheral Nerves Originating from the Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Nerves Originating from the Lumbar Plexus Iliohypogastric nerve Illioinguinal nerve Genitofemoral nerve Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve Femoral nerve Obturator nerve Subcostal nerve Nerves Originating from the Sacral Plexus Superior gluteal nerve Inferior gluteal nerve Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve Pudendal nerve Sciatic nerve Saphenous nerve Common Fibular Nerve and Its Branches Common fibular nerve Superficial fibular nerve Deep fibular nerve a The lumbar and sacral plexuses, anterior view
56 Figure 14.12b Peripheral Nerves Originating from the Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Nerves Originating from the Sacral Plexus Superior gluteal nerve Inferior gluteal nerve Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve Pudendal nerve Sciatic nerve Branches of the Sciatic Nerve Tibial nerve Common fibular nerve Medial sural cutaneous nerve Lateral sural cutaneous nerve Sural nerve Medial plantar nerve Lateral plantar nerve b The sacral plexus, posterior view
57 Nerve Plexus Summary of the Spinal Nerves Cervical spinal nerves emerge from C 1 C 8 Thoracic spinal nerves emerge from T 1 T 12 Lumbar spinal nerves emerge from L 1 L 5 Sacral spinal nerves emerge from S 1 S 5 Coccygeal spinal nerves emerge from Co 1
58 Nerve Plexus Summary of the Nerve Plexuses Cervical plexus nerves emerge from C 1 C 5 Brachial plexus nerves emerge from C 5 T 1 There is not a thoracic plexus Lumbar plexus nerves emerge from T 12 L 4 Sacral plexus nerves emerge from L 4 S 4 There is not a coccygeal plexus
59 Figure 14.3 Posterior View of Vertebral Column and Spinal Nerves Occipital bone Spinal cord emerging from foramen magnum Cervical plexus (C 1 C 5 ) Cervical spinal nerves (C 1 C 8 ) Brachial plexus (C 5 T 1 ) Thoracic spinal nerves (T 1 T 12 ) Lumbar plexus (T 12 L 4 ) Sacral plexus (L 4 S 4 ) Lumbar spinal nerves (L 1 L 5 ) Sciatic nerve Coccygeal nerves (Co 1 ) Sacral spinal nerves (S 1 S 5 ) emerging from sacral foramina
60 Reflexes Reflex An immediate involuntary motor response Reflex Arc The neural wiring of a single reflex Begins at a sensory receptor and ends at a peripheral receptor
61 Reflexes Pathway of a Reflex Arc 1. Activation of a sensory receptor 2. Relay of information to the CNS 3. Information processing 4. Activation of a motor neuron 5. Response by the effector
62 Reflexes Classification of Reflexes Reflexes are classified according to: Their development Innate or acquired The site where information is processed Spinal or cranial (cerebral) The nature of the resulting motor response Somatic, visceral, or autonomic The complexity of the neural circuit Monosynaptic or polysynaptic
63 Figure A Reflex Arc 1 Arrival of 2 Activation of a Dorsal stimulus and sensory neuron root activation of receptor Sensation relayed to the brain by collateral Stimulus Receptor REFLEX ARC Effector Ventral root 3 Information processing in CNS 5 Response by effector 4 Activation of a motor neuron KEY Sensory neuron (stimulated) Excitatory interneuron Motor neuron (stimulated)
64 Figure The Classification of Reflexes Reflexes can be classified by Development Response Complexity of Circuit Processing Site Innate Reflexes Somatic Reflexes Monosynaptic Spinal Reflexes Genetically determined Control skeletal muscle contractions Include superficial and stretch reflexes One synapse Processing in the spinal cord Acquired Reflexes Visceral (Autonomic) Reflexes Polysynaptic Cranial Reflexes Learned Control actions of smooth and cardiac muscles, glands Multiple synapses (two to several hundred) Processing in the brain
65 Reflexes Classification of Reflexes Spinal reflexes can be: Monosynaptic Involves a single segment of the spinal cord Polysynaptic Integrates motor output from several spinal segments
66 Figure Neural Organization and Simple Reflexes Ganglion Sensory neuron CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Ganglion Sensory neuron CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Motor neuron Sensory receptor Circuit 2 Interneurons Circuit 1 Motor neurons Sensory receptor (muscle spindle) Skeletal muscle 1 Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle 2 a A monosynaptic reflex circuit involves a peripheral sensory neuron and a central motor neuron. In this example, stimulation of the receptor will lead to a reflexive contraction in a skeletal muscle. b A polysynaptic reflex circuit involves a sensory neuron, interneurons, and motor neurons. In this example, the stimulation of the receptor leads to the coordinated contractions of two different skeletal muscles.
67 Reflexes Spinal Reflexes Stretch reflex 1. Stimulus stretches a muscle 2. Activates a sensory neuron 3. Information is processed in the spinal cord 4. Motor neurons are activated 5. Muscle (effector) contracts
68 Figure 14.16a Stretch Reflexes 1 Stimulus. Stretching of muscle stimulates muscle spindles 2 Activation of a sensory neuron 3 Information processing at motor neuron 4 Activation of motor neuron 5 Response. Contraction of muscle a Steps 1 5 are common to all stretch reflexes.
69 Figure 14.16b Stretch Reflexes Stretch Receptor (muscle spindle) Stimulus Spinal cord REFLEX ARC Contraction Effector KEY Sensory neuron (stimulated) Motor neuron (stimulated) Response b The patellar reflex is controlled by muscle spindles in the quadriceps muscle group. The stimulus is a reflex hammer striking the muscle tendon, stretching the spindle fibers. This results in a sudden increase in the activity of the sensory neurons, which synapse on spinal motor neurons. The response occurs upon the activation of motor units in the quadriceps group, which produces an immediate increase in muscle tone and a reflexive kick.
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13! Chapter 13 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Chapter 12
 Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
 Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
The Nervous System: The
 C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Lab Activity 13. Spinal Cord. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 12 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Spinal Cord Learning Outcomes 12.1 Describe how the spinal cord can
12 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Spinal Cord Learning Outcomes 12.1 Describe how the spinal cord can
Spinal Cord Protection. Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. External Anatomy of Spinal Cord. Structures Covering the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
With other members of your lab group, discuss the following questions: - The spinal cord connects directly to which part of the brain?
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD
 THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System. DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy
 The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. C1. Cervical spinal ner ves. Thor acic. T12 Spinal nerve rootlets
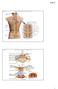 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Spinal nerves. Aygul Shafigullina. Department of Morphology and General Pathology
 Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD. Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes The Nervous System Coordinates the activity of muscles, organs, senses, and actions Made
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes The Nervous System Coordinates the activity of muscles, organs, senses, and actions Made
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 14 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Chapter 12. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 12 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 12 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses. A & P II Spring, 2014
 Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
Nervous System. Overview, Tissues and Spinal Nerves
 Nervous System Overview, Tissues and Spinal Nerves neurology - study of the nervous system - nervous system and endocrine system work together to maintain homeostasis - More than 80 major nerves and billions
Nervous System Overview, Tissues and Spinal Nerves neurology - study of the nervous system - nervous system and endocrine system work together to maintain homeostasis - More than 80 major nerves and billions
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes
 Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
Classification of the nervous system. Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 2
 1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint
 Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13)
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Part 1: Communication between CNS & PNS
 Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus.
 *Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity
 Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Laboratory 08 Peripheral Nervous System
 Laboratory 08 Peripheral Nervous System Goals: Structure and function of the cranial nerves. 1. List the cranial nerves by name and number. 2. Describe the specific functions of each of the cranial nerves
Laboratory 08 Peripheral Nervous System Goals: Structure and function of the cranial nerves. 1. List the cranial nerves by name and number. 2. Describe the specific functions of each of the cranial nerves
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System
 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:"
50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:"
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni
 Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Nervous System. Basic Divisions of the Nervous System C H A P T E R 12.
 C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System
 Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Define peripheral nervous system and list its components. 2. Classify general sensory receptors by structure, stimulus detected, and body location.
Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Define peripheral nervous system and list its components. 2. Classify general sensory receptors by structure, stimulus detected, and body location.
4/5/2015. Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
 Peripheral Nervous System Learn and Understand: Peripheral nerves connect the edges of the body and outside world to the CNS. Most nerves carry specific types of information to/from specific locations.
Peripheral Nervous System Learn and Understand: Peripheral nerves connect the edges of the body and outside world to the CNS. Most nerves carry specific types of information to/from specific locations.
Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Structure of Spinal Nerves: Somatic Pathways dorsal root CNS interneuron spinal nerve dorsal ramus somatic sensory
Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Structure of Spinal Nerves: Somatic Pathways dorsal root CNS interneuron spinal nerve dorsal ramus somatic sensory
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
