Chapter 12. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
|
|
|
- Lynne Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 12 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 12-1
2 Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 12-2
3 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Nerves 31 pairs Spinal cord
4 12.1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform in diameter throughout length Cervical enlargement: supplies upper limbs Lumbar enlargement: supplies lower limbs Conus medullaris: tapered inferior end. Cauda equina: origins of spinal nerves extending inferiorly from lumbosacral enlargement and conus medullaris. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Lumbosacral enlargement Cervical enlargement Level of second lumbar vertebra Brain Level of foramen magnum Roots of spinal nerves Spinal nerves Spinal cord Conus medullaris Cauda equina Filum terminale Posterior view 12-4
5 Spinal Cord Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccygeal
6 Cervical & Lumbosacral Enlargements
7 Medullary Cone & Cauda Equina
8 Spinal Cord Conus medullaris Filum terminale Cauda equina 8
9 Meninges of the Spinal Cord Connective tissue membranes surrounding spinal cord and brain Dura mater: continuous with epineurium of the spinal nerves Arachnoid mater: thin and wispy Pia mater: bound tightly to surface of brain and spinal cord. Forms the filum terminale, which anchors spinal cord to coccyx and the denticulate ligaments that attach the spinal cord to the dura mater Spaces Epidural: anesthesia injected. Contains blood vessels, areolar connective tissue and fat. Subdural: serous fluid Subarachnoid: CSF and blood vessels within web-like strands of arachnoid tissue Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. (a) Anterolateral view Duramater Subdural space Denticulate ligament Arachnoid mater Subarachnoid space Pia mater Epineurium of spinal nerve Dorsal root ganglion Spinal nerve Ventral root 12-9
10 Meninges of Spinal Cord
11 Meninges of the Spinal Cord Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Posterior Spinous process of vertebra Transverse process of vertebra Spinal cord Denticulate ligament Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Spinal nerve Ventral root Pia mater Body of vertebra Subarachnoid space Periosteum Arachnoid mater Subdural space Dura mater Epidural space filled with adipose tissue Anterior (b) Superior view 12-11
12 Cross Section of Spinal Cord Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Central canal White matter Dorsal (posterior) column Ventral (anterior) column Lateral column Spinal nerve Posterior median sulcus Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Central canal Ventral root Gray matter Posterior (dorsal) horn Lateral horn Anterior (ventral) horn Rootlets (a) Anterolateral view Ventral root Gray commissure White commissure Anterior median fissure Ascending nerve tracts Descending nerve tracts (c) Anterolateral view 12-12
13 Spinal Cord Gray matter White matter
14 Cross Section of Spinal Cord Anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus: deep clefts partially separating left and right halves White matter: myelinated axons forming tracts Three columns (funiculi): ventral, dorsal, lateral Each of these divided into tracts (fasciculi; pathways) Gray matter: neuron, cell, cell bodies, dendrites, axons Horns Posterior (dorsal) Anterior (ventral) Lateral (associated with ANS) 12-14
15 Cross Section of Spinal Cord Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Central canal White matter Dorsal (posterior) column Ventral (anterior) column Lateral column Spinal nerve Posterior median sulcus Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Central canal Ventral root Gray matter Posterior (dorsal) horn Lateral horn Anterior (ventral) horn White matter Dorsal (posterior) column Ventral (anterior) column Lateral column Dorsal root Rootlets (a) Anterolateral view Ventral root Gray commissure White commissure Anterior median fissure (b) Dorsal root ganglion Ascending nerve tracts Descending nerve tracts (c) Anterolateral view b: Ed Reschke/Peter Arnold, Inc./Getty Images 12-15
16 Cross Section of Spinal Cord Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Commissures: connections between left and right halves Gray with central canal in the center White Roots: spinal nerves arise as rootlets then combine to form roots Dorsal (posterior) root has a ganglion Ventral (anterior) Two roots merge laterally and form the spinal nerve Central canal White matter Dorsal (posterior) column Ventral (anterior) column Lateral column Spinal nerve Rootlets (a) Anterolateral view (c) Anterolateral view Posterior median sulcus Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Central canal Ventral root Gray matter Posterior (dorsal) horn Lateral horn Anterior (ventral) horn Ventral root Gray commissure White commissure Ascending nerve tracts Descending nerve tracts Anterior median fissure 12-16
17 Dorsal rootlets Spinal Nerve Ventral rootlets Dorsal root Ventral root Dorsal root gangion Spinal nerve
18 Organization of Neurons in the Spinal Dorsal root ganglion: collections of cell bodies of unipolar sensory neurons forming dorsal roots. Cord and Spinal Nerves Lateral horn Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Posterior horn Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Anterior horn Superior view Ventral root Interneuron Sensory neuron Spinal nerve Autonomic neuron Somatic motor neuron Motor neuron cell bodies are in anterior and lateral horns of spinal cord gray matter. Multipolar somatic motor neurons in anterior (motor) horn Autonomic neurons in lateral horn Axons of motor neurons form ventral roots and pass into spinal nerves 12-18
19 12.2 Reflexes Basic functional unit of nervous system and simplest portion capable of receiving a stimulus and producing a response Automatic response to a stimulus that occurs without conscious thought. Homeostatic. Components Action potentials produced in sensory receptors transmitted to Sensory neuron. To-Interneurons. To-Motor neuron. To- Effector organ which responds with a reflex 12-19
20 Reflex Arc Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 3 Interneuron Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion 2 Sensory neuron 1 Sensory receptor Spinal cord Skin 4 Motor neuron Spinal nerve A sensory receptor detects a stimulus. Ventral root 5 Effector organ A sensory neuron conducts action potentials through the nerve and dorsal root to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the sensory neuron synapses with an interneuron. (An interneuron is not involved in a monosynaptic reflex arc.) The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron. A motor neuron axon conducts action potentials through the ventral root and spinal nerve to an effector organ. Skeletal muscle 12-20
21 Variety of Reflexes Some integrated within spinal cord; some within brain Some involve excitatory neurons yielding a response; some involve inhibitory neurons that prevent an action Higher brain centers can influence, suppress, or exaggerate reflex responses 12-21
22 Stretch Reflex Muscles contract in response to a stretching force applied to them. Unique because no interneuron. Muscle spindle: specialized muscle cells that respond to stretch. Innervated by specific motor neurons: gamma motor neurons (small diameter neurons). Control sensitivity of muscle spindle. Sensory neurons innervate the noncontractile centers of the muscle spindle cells. These sensory neurons synapse with motor neurons of the spinal cord called alpha motor neurons which in turn innervate the muscle in which the muscle spindle is embedded
23 Stretch Reflex Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Sudden stretch of a muscle results in: From brain 1 Muscle spindles detect stretch of the muscle. To brain 2 Sensory neurons conduct action potentials to the spinal cord. 3 4 Sensory neurons synapse directly with alpha motor neurons. Alpha motor neurons conduct action potentials to the muscle, causing it to contract and resist being stretched. Note: The muscle that contracts is the muscle that is stretched. Quadriceps femoris muscle (extensor) Sensory neuron Muscle spindle Alpha motor neuron Gamma motor neuron endings Sensory neuron endings Gamma motor neuron Sensory neuron Patellar tendon Hammer tap Patellar ligament Muscle fiber of muscle spindle Hamstring muscles (flexor) Muscle fiber of muscle St r et c h Stretch reflex Muscle spindle 12-23
24 Golgi Tendon Reflex Prevents contracting muscles from applying excessive tension to tendons Golgi tendon organ. Encapsulated nerve endings that have at their ends numerous terminal branches with small swellings associated with bundles of collagen fibers in tendon. Located in tendon near muscle Prevent damage to tendons that could be caused by excessive tension Produces sudden relaxation of the muscles Example: weight lifter suddenly drops heavy weight. Sudden movements of clean and jerk put so much tension on tendons like Achilles, they could break. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Intense stretch of a skeletal muscle results in: 1 Golgi tendon organs detect tension applied to a tendon. 2 Sensory neurons conduct action potentials to the spinal cord. 3 4 Sensory neurons synapse with inhibitory interneurons that synapse with alpha motor neurons. Inhibition of the alpha motor neurons causes muscle relaxation, relieving the tension applied to the tendon. Note: The muscle that relaxes is attached to the tendon to which tension is applied. Muscle contraction increases tension applied to tendons. In response, action potentials are conducted to the spinal cord. Sensory neuron Tendon Golgi tendon organ Muscle Golgi tendon organ Sensory neuron Alpha motor neuron Hamstring muscles (fexor) Golgi tendon refex To brain Inhibitory interneuron 12-24
25 Withdrawal Reflex Function is to remove a body limb or other part from a painful stimulus. Reciprocal innervation: causes relaxation of extensor muscle when flexor muscle contracts. Also involved in stretch reflex. Crossed extensor reflex: when a withdrawal reflex is initiated in one lower limb, the crossed extensor reflex causes extension of opposite lower limb
26 Withdrawal Reflex Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Stimulation of pain receptors results in: To brain 1 Pain receptors detect a painful stimulus. Sensory neuron Sensory neurons conduct action potentials to the spinal cord. Sensory neurons synapse with excitatory Interneurons that synapse with alpha motor neurons. Excitation of the alpha motor neurons results in contraction of the flexor muscles and withdrawal of the limb from the painful stimulus. Quadriceps femoris muscle (extensor) Hamstring muscles (fexor) 4 3 Alpha motor neuron Excitatory interneuron Sensory neuron 1 Stimulus Pain receptor Withdrawal reflex 12-26
27 Withdrawal Reflex with Reciprocal Innervation Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Reciprocal innervation 1 2 During the withdrawal reflex, sensory neurons conduct action potentials from pain receptors to the spinal cord. Sensory neurons synapse with excitatory interneurons that are part of the withdrawal reflex. Quadriceps femoris muscle (extensor) Reciprocal innervation Inhibitory interneuron Collateral branch from sensory neuron 3 Collateral branches of the sensory neurons also synapse with inhibitory interneurons that are part of reciprocal innervation. Hamstring muscles (flexor) Sensory neuron To brain 4 The inhibitory interneurons synapse with alpha motor neurons supplying the extensor muscles, causing them to relax and not oppose the flexor muscles of the withdrawal reflex, which are contracting. Withdrawal reflex Alpha motor neuron 2 Excitatory interneuron 12-27
28 Withdrawal Reflex with Crossed Extensor Reflex Crossed extensor reflex Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. During the withdrawal reflex, sensory neurons from pain receptors conduct action potentials to the spinal cord. Sensory neurons synapse with excitatory interneurons that are part of the withdrawal reflex. The excitatory interneurons that are part of the withdrawal reflex stimulate alpha motor neurons that innervate flexor muscles, causing withdrawal of the limb from the painful stimulus. 4 5 Collateral branches of the sensory neurons also synapse with excitatory interneurons that cross to the opposite side of the spinal cord as part of the crossed extensor reflex. The excitatory interneurons that cross the spinal cord stimulate alpha motor neurons supplying extensor muscles in the opposite limb, causing them to contract and support body weight during the withdrawal reflex. 1 Sensory neuron To brain Quadriceps femoris muscle (extensor) Alpha motor neuron Hamstring muscles (flexor) Alpha motor neuron Excitatory interneuron Withdrawal reflex Crossed extensor reflex 12-28
29 Interactions with Spinal Cord Reflexes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Ascending axon Ascending tract Interneuron To brain Site of divergence From brain Descending axon Descending tract Sensory neuron Site of convergence Motor neuron Effector organ Sensory receptor Skin Skeletal muscle Sensory information goes to brain; e.g., pain. Descending tracts from brain carry info to reflexes. Neurotransmitters produce either EPSPs or IPSPs modifying the reflex
30 12.3 Spinal Nerves Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Consist of Axon bundles Schwann cells Connective tissue Endoneurium: surrounds individual neurons Perineurium: surrounds axon groups to form fascicles Epineurium: surrounds the entire nerve Epineurium Perineurium Endoneurium Schwann cell Fascicle Axon Adipose tissue Artery and vein Loose connective tissue 12-30
31 31 Pair of Spinal Nerves
32 Posterior (Dorsal) & Anterior (Ventral) Roots
33 Posterior (Dorsal) Root Ganglia
34 Posterior (Dorsal) and Anterior (Ventral) Rootlets
35 Spinal nerves Posterior root ganglia Posterior rami Anterior rami
36 Organization of Spinal Nerves Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves First pair exit vertebral column between skull and atlas Last four pair exit via the sacral foramina Others exit through intervertebral foramina Eight pair cervical, twelve pair thoracic, five pair lumbar, five pair sacral, one pair coccygeal Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cervical nerves Thoracic nerves Lumbar nerves Sacral nerves Coccygeal nerves C T L Posterior view Duramater Cervical plexus (C1 C4) Brachial plexus (C5 T1) Cauda equina S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 Co Lumbar plexus (L1 L4) Sacral plexus (L4 S4) Coccygeal plexus (S5 Co) Lumbosacral plexus (L1 S4) 12-36
37 Dermatomal Map Spinal nerves indicated by capital letter and number Dermatomal map: skin area supplied with sensory innervation by spinal nerves Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Functions Cervical nerves Thoracic nerves C T Head movement Diaphragm movement Neck and shoulder movement Upper limb movement Rib movement inbreathing, vertebral column movement, and tone in postural back muscles C5 C6 T1 C4 T1 C7 C8 L1 L2 S3 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 S4 C2 C3 T10 T 1 1 T12 S3 C4 C5 T1 C6 C7 T1 C8 L2 T2 C6 T1 L2 C6 C8 C7 C2 S3 C3 C4 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 T10 T 1 1 T12 L1 S4 T1 T2 S2 S5 Co L2 C5 C6 C7 C L1 Hip movement L3 L3 S2 L3 S2 Lumbar nerves 2 3 L4 L4 L4 L4 L5 4 5 Lower limb movement S1 L5 S1 L5 S1 L5 S1 L5 S1 Sacral nerves Coccygeal nerves (a) Posterior view
38 Branches of Spinal Nerves Dorsal Ramus: innervate deep muscles of the trunk responsible for movements of the vertebral column and the C.T. and skin near the midline of the back. Ventral Ramus: what they innervate depends upon which part of the spinal cord is considered. Thoracic region: form intercostal nerves that innervate the intercostal muscles and the skin over the thorax Remaining spinal nerve ventral rami (roots of the plexus): form five plexuses (intermingling of nerves). Ventral rami of C1-C4= cervical plexus Ventral rami of C5-T1= brachial plexus Ventral rami of L1-L4= lumbar plexus Ventral rami of L4-S4= sacral plexus Ventral rami of S4 and S5= coccygeal plexus Communicating Rami: communicate with sympathetic chain of ganglia
39 Branches of Spinal Nerves Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dorsal root (spinal) ganglion Spinal nerve Dorsal root of spinal nerve Ventral root of spinal nerve Rootlets Communicating rami Ganglion of sympathetic chain Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve Ventral ramus of spinal nerve (intercostal nerve) Roots of Splanchnic nerve (a) Anterolateral view Dorsal rootlets Intervertebral foramen (b) Posterior view Dorsal root ganglion Spinal nerve Transverse process of vertebra (cut) b: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, Inc./Rebecca Gray, photographer/don Kincaid, dissections 12-39
40 Posterior ramus Rami Anterior ramus Gray ramus Sympathetic ganglion White ramus
41 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cervical Plexus Roots (ventral rami): C1, C2, C3, C4 Branches Other nerves (not part of cervical plexus) Hypoglossal nerve (XII) Accessory nerve (XI) Lesser occipital nerve Greater auricular nerve Nerve to sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior root of ansa cervicalis Branch to infrahyoid muscles Transverse cervical nerve Ansa cervicalis Nerve to trapezius muscle Branches to infrahyoid muscles Inferior root of ansa cervicalis C1 C4 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C1-C4 Innervates superficial neck structures, skin of neck, posterior portion of head Ansa cervicalis: loop between C1 and C3 Phrenic nerve From C3-C5 (cervical and brachial plexuses) Innervate diaphragm Supraclavicular nerves Phrenic nerve Anterior view
42 Cervical Plexus Phrenic Nerve
43 Phrenic Nerve
44 Brachial Plexus Roots (ventral rami): C5, C6, C7, C8, T1 Trunks: upper, middle, lower Anterior divisions Posterior divisions Cords: posterior, lateral, medial Major branches: Axillary nerve Radial nerve Musculocutaneous nerve Median nerve Ulnar nerve Dorsal scapular nerve Sub clavian nerve Suprascapular nerve Posterior cord Axillary nerve Lateral cord Radial nerve Musculocutaneous nerve Medial and lateral pectoral nerves Median nerve Thoracodorsal nerve Upper and lower subscapular nerves Ulnar nerve Anterior view Medial cord Medial brachial cutaneous nerve Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve T1 C6 C5 C7 C5 T1 Upper trunk Middle trunk Long thoracic nerve C8 Lower trunk C4 from cervical plus C5-T1 Five ventral rami form three trunks that separate into six divisions then form cords that give rise to: Branches/nerves Axillary Radial Musculocutaneous Ulnar Median Smaller nerves such as pectoral, long thoracic, thoracodorsal, subscapular, suprascapular 12-44
45 Brachial Plexus
46 Axillary n. Brachial Plexus Median n. Musculocutaneous n. Superior, Middle, and Inferior Trunks of Brachial Plexus Radial n. Ulnar n.
47 Axillary Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Origin Axillary Nerve Posterior cord of brachial plexus, C5 C6 Movements/Muscles Innervated Laterally rotates arm Teres minor Abducts arm Deltoid Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Inferior lateral shoulder Posterior cord Lateral cord Medial cord Axillary nerve Teres minor Deltoid Posterior views
48 Axillary Nerve 12-48
49 Radial Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Origin Radial Nerve Posterior cord of brachial plexus, C5 T1 Movements/Muscles Innervated Extends elbow Triceps brachii Anconeus Flexes elbow Brachialis (part; sensory only) Brachioradialis Extends and abducts wrist Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Supinates forearm and hand Supinator Extends fingers Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Extensor indicis Extends and adducts wrist Extensor carpi ulnaris Abducts thumb Abductor pollicis longus Extends thumb Extensor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Posterior surface of arm and forearm, lateral two-thirds of dorsum of hand Posterior cord Lateral cord Medial cord Long head of triceps brachii Medial head of triceps brachii Anconeus Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor indicis Radial nerve Lateral head of triceps brachii Brachioradialis Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialisbrevis Supinator Adductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis and longus Posterior view Posterior view Anterior view
50 Radial Nerve 12-50
51 Musculocutaneous Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Musculocutaneous Nerve Origin Lateral cord of brachial plexus, C5 C7 Movements/Muscles Innervated Flexes shoulder Biceps brachii Coracobrachialis Flexes elbow and supinates forearm and hand Biceps brachii Flexes elbow Brachialis (also small amount of innervation from radial nerve) Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Lateral surface of forearm Musculocutaneous nerve Biceps brachii Brachialis Posterior cord Lateral cord Medial cord Coracobrachialis Anterior views Posterior view 12-51
52 Musculocutaneous Nerve 12-52
53 Ulnar Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Origin Ulnar Nerve Medial cord of brachial plexus, C8 T1 Movements/Muscles Innervated Flexes and adducts wrist Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexes fingers Part of the flexor digitorum profundus controlling the distal phalanges of little and ring fingers Adducts thumb Adductor pollicis Controls hypothenar muscles Flexor digiti minimi brevis Abductor digiti minimi Opponens digiti minimi Flexes metacarpophalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal joints Two medial (ulnar) lumbricales Abducts and adducts fingers Interossei Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Medial third of hand, little finger, and medial half of ring finger Adductor pollicis Posterior view Anterior view Flex or digitorum profundus Ulnar nerve Flexor carpi ulnaris Posterior cord Lateral cord Medial cord All dorsal and palmar interossei Hypothenar muscles The two medial (ulnar) lumbricales Anterior view
54 Ulnar Nerve 12-54
55 Median Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Origin Median Nerve Medial and lateral cords of brachial plexus, C5 T1 Movements/Muscles Innervated Pronates forearm and hand Pronator teres Pronator quadratus Flexes and abducts wrist Flexor carpiradialis Flexes wrist Palmaris longus Flexes fingers Part of flexor digitorum profundus controlling the distal phalanx of the middle and index fingers Flexor digitorum superficialis Controls thumb muscle Flexor pollicis longus Controls thenar muscles Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis Flexes metacarpophalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal joints Two lateral (radial) lumbricales Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Lateral two-thirds of palm of hand, thumb, index and middle fingers, and the lateral half of ring finger and dorsal tips of the same fingers Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Thenar muscles The two lateral (radial) lumbricales Posterior view Anterior view Carpal tunnel deep to flexor retinaculum Palmaris longus Pronator teres Median nerve Flexor carpi radialis Posterior cord Lateral cord Medial cord Flexor digitorum superficialis Anterior view
56 Brachial Plexus - Median Nerve
57 Other Nerves of the Brachial Plexus Small nerves that innervate muscles acting on scapula and arm Pectoral Long thoracic Thoracodorsal Subscapular Suprascapular Innervate the skin of the medial arm and forearm 12-57
58 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses L1 Lumbar plexus: ventral rami of L1-L4 Sacral plexus: ventral rami of L4-S4 Usually considered together because of their close relationship Four major nerves exit and enter lower limb Obturator Femoral Tibial Common fibular (peroneal) Superior gluteal Tibial Iliohypogastric Ilioinguinal Lateral femoral cutaneous Genitofemoral Femoral Obturator Lumbosacral trunk Inferior gluteal Sciatic Common fibular (peroneal) Posterior femoral cutaneous L4 S4 Roots ( ventral rami) Posterior divisions Anterior divisions Nerves L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 Pudendal Anterior view
59 Lumbar Plexus Femoral n. Obturator n. Lumbosacral trunk
60 Sacral Plexus Sciatic n. Tibial n. Common Fibular n. Superficial Fibular n. Deep Fibular n. Tibial n. Fibular n. 60
61 Obturator Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Origin Obturator Nerve Lumbosacral plexus, L2 L4 Movements/Muscles Innervated Rotates thigh laterally Obturator externus Adducts thigh Adductor magnus (adductor part) Adductor longus Adductor brevis Gracilis Adducts thigh and flexes knee Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Superior medial side of thigh Obturator externus Adductor magnus L2 L3 L4 Obturator nerve Adductor brevis Adductor longus Gracilis Medial view Anterior view 12-61
62 Obturator Nerve 12-62
63 Femoral Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Femoral Nerve Origin Lumbosacral plexus, L2 L4 Movements/Muscles Innervated Flexes hip Psoas major Iliacus Pectineus Flexes hip and flexes knee Sartorius Extends knee Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Vastus medialis Extends knee and flexes hip Rectus femoris Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Anterior and lateral branches supply the anterior and lateral thigh; saphenous branch supplies the medial leg and foot Psoas major Iliacus Sartorius Vastus lateralis Rectus femoris Vastus intermedius L2 L3 L4 Femoral nerve Pectineus Vastus medialis Anterior view Medial view Anterior view
64 Femoral Nerve 12-64
65 Tibial and Common Fibular Nerves The two nerves together referred to as the sciatic (ischiadic) nerve 12-65
66 Sciatic Nerve 12-66
67 Tibial Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Tibial Nerve Origin Lumbosacral plexus, L4 S3 Movements/Muscles Innervated Extends hip and flexes knee Biceps femoris (long head) Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Extends hip and adducts thigh Adductor magnus (hamstring part) Plantar flexes foot Plantaris Gastrocnemius Soleus Tibialis posterior Flexes knee Popliteus Flexes toes Flexor digitorum longus Flexor hallucis longus Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation None L4 L5 S1 S2 S3 Biceps femoris long head Semimembranosus Semitendinosus Tibial nerve Adductor magnus Gastrocnemius Medial and Lateral Plantar Nerves Origin Tibial nerve Movements/Muscles Innervated Flex and adduct toes Plantar muscles of foot Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Sole of foot Popliteus Flexor digitorum longus Tibialis posterior Soleus Flexor hallucis longus Sural Nerve (Not Shown) Origin Tibial nerve Movements/Muscles Innervated None Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Lateral and posterior one-third of leg and lateral side of foot Anterior view Posterior view Medial plantar nerve to plantar muscles Lateral plantar nerve to plantar muscles Posterior view
68 Tibial Nerve 12-68
69 Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Origin Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve Lumbosacral plexus, L4 S2 Movements/Muscles Innervated Extends hip and flexes knee Biceps femoris (short head) Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Lateral surface of knee L4 L5 S1 S2 Common fibular (peroneal) nerve Deep Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve Biceps femoris short head Origin Common fibular (peroneal) nerve Movements/Muscles Innervated Dorsiflexes foot Tibialis anterior Fibularis tertius Extends toes Extensor digitorum longus Extensor hallucis longus Extensor digitorum brevis Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Great and second toe Fibularis longus Fibularis brevis Tibialis anterior Extensor digitorum longus Extensor hallucis longus Origin Superficial Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve Common fibular (peroneal) nerve Movements/Muscles Innervated Plantar flexes and everts foot Fibularis longus Fibularis brevis Cutaneous (Sensory) Innervation Dorsal anterior third of leg and dorsum of foot Anterior view Lateral view Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve Fibularis tertius Extensor digitorum brevis Anterior view Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve 12-69
70 Common Fibular Nerve 12-70
71 Other Lumbosacral Plexus Nerves Nerves that innervate the skin of the suprapubic area, external genitalia, superior medial thigh, posterior thigh Gluteal nerves Pudendal nerve Iliohypogastric nerve Ilioingual nerve Genitofemoral nerve Cutaneous femoral 12-71
72 Coccygeal Plexus S5; coccygeal nerve Muscles of pelvic floor Sensory information from skin over coccyx 12-72
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Chapter 12
 Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 14. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Lab Activity 13. Spinal Cord. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Chapter 13! Chapter 13 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
 Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
Part 1: Communication between CNS & PNS
 Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Spinal Cord Protection. Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. External Anatomy of Spinal Cord. Structures Covering the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
With other members of your lab group, discuss the following questions: - The spinal cord connects directly to which part of the brain?
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses. A & P II Spring, 2014
 Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. C1. Cervical spinal ner ves. Thor acic. T12 Spinal nerve rootlets
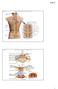 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
Peripheral Nervous System: Lower Body
 Peripheral Nervous System: Lower Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 11 Department of Myotherapy Lumbar Plexus Iliohypogastric nerve (T12-L1) Motor: Transverse abdominis and internal obliques Sensory:
Peripheral Nervous System: Lower Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 11 Department of Myotherapy Lumbar Plexus Iliohypogastric nerve (T12-L1) Motor: Transverse abdominis and internal obliques Sensory:
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves. Clinical Anatomy
 Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Organization of the Lower Limb Audrone Biknevicius, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences, OU HCOM at Dublin Clinical Anatomy Immersion 2014
 Organization of the Lower Limb Audrone Biknevicius, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences, OU HCOM at Dublin Clinical Anatomy Immersion 2014 www.thestudio1.co.za LIMB FUNCTION choco-locate.com blog.coolibar.com
Organization of the Lower Limb Audrone Biknevicius, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences, OU HCOM at Dublin Clinical Anatomy Immersion 2014 www.thestudio1.co.za LIMB FUNCTION choco-locate.com blog.coolibar.com
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Spinal nerves. Aygul Shafigullina. Department of Morphology and General Pathology
 Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 14 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System. DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy
 The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
- Pelvic activities speed up good time for urination and defecation. - Pelvic parasympathetic nerves = Sacral nerves (soothing sacral nerves)
 1 Ch 6: PNS 1. Intro slide with objectives 2. Communication between CNS & PNS. > sensory info from receptors ascends the spinal cord to part of brain where interopreted > motor commands descend brain,
1 Ch 6: PNS 1. Intro slide with objectives 2. Communication between CNS & PNS. > sensory info from receptors ascends the spinal cord to part of brain where interopreted > motor commands descend brain,
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS
 TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 12 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Spinal Cord Learning Outcomes 12.1 Describe how the spinal cord can
12 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Spinal Cord Learning Outcomes 12.1 Describe how the spinal cord can
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB
 MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
The Hay is in the Barn
 Anatomy 1 Practical 1 Review Made by Forrest Allen (nerd) Edited by TJ Williamson (not nerd) The Hay is in the Barn 2019 Thunderbringers Too much to handle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glii-kaza d8
Anatomy 1 Practical 1 Review Made by Forrest Allen (nerd) Edited by TJ Williamson (not nerd) The Hay is in the Barn 2019 Thunderbringers Too much to handle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glii-kaza d8
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS
 HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint
 Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
Chapter 13. The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD
 THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13)
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
