Implications of a Dynamic Causal Modeling Analysis of fmri Data. Andrea Stocco University of Washington, Seattle
|
|
|
- Junior Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Implications of a Dynamic Causal Modeling Analysis of fmri Data Andrea Stocco University of Washington, Seattle
2 Production Rules and Basal Ganglia Buffer Buffer Buffer Thalamus Striatum Matching Striatum Selection Pallidum Substantia Nigra Pallidum Execution Thalamus Procedural Module
3 Production Rules Transfer Variables Respond-if-asked IF.. Request About. Status Movie Status THEN Raise Hand Imitation Stranger Game Things Seen Imitation Stranger Game Things Seen Do. Raise Hand
4 Exchanging information across buffers Question 1: Can we experimentally test it? Question 2: Are we missing something crucial from basal ganglia anatomy
5 Exchanging information across buffers Question 1: Can we experimentally test it? Question 2: Are we missing something crucial from basal ganglia anatomy
6 How Do We Measure Information Transfer? Functional connectivity
7 Increased Correlation Functional connectivity
8 Bidirectional Measures Functional connectivity
9 How do we test it? Effective connectivity
10 Dynamic Causal Modeling b 1 b 2 A 1,2 B 2,3 C 2,1 D 1,2 y 2 y 1 y 3 y 2 y 1 y 3 x 1 x 2 y = S i b i *x i x 1 x 2 dy/dt = Ay + S i x i B(i)y + S j y j D(j)y + Cx
11 Do the Basal Ganglia Modulate Connectivity? Direct Model Modulatory Model Prat, Stocco et al., submitted
12 They Do! Prat, Stocco et al., submitted
13 L Caudate L PFC Motor ACC Visual R Caudate R Prefrontal Empirical Connectivity Matrix Modulatory Model Connectivity Matrix R PFC R Caudate Visual ACC LBG Motor LCaudate
14 ACT-R s Connectivity Matrix PROCEDURAL CONFLICT-RESOLUTION PROCEDURAL PRODUCTION-FIRED PREPARE-FOR-ENCODING PROCEDURAL CLEAR-BUFFER RETRIEVAL PROCEDURAL CONFLICT-RESOLUTION PROCEDURAL PRODUCTION-FIRED NEXT-POSITION PROCEDURAL CLEAR-BUFFER GOAL GOAL SET-BUFFER-CHUNK GOAL OPERATION PROCEDURAL CONFLICT-RESOLUTION IMAGINAL MOD-BUFFER-CHUNK IMAGINAL PROCEDURAL CONFLICT-RESOLUTION PROCEDURAL PRODUCTION-FIRED RETRIEVE-OPERATION (p prepare-for-encoding =visual> =TASK ==> +imaginal> task =TASK +visual-location> PROCEDURAL CLEAR-BUFFER RETRIEVAL DECLARATIVE START-RETRIEVAL PROCEDURAL CONFLICT-RESOLUTION DECLARATIVE RETRIEVED-CHUNK OPERATION DECLARATIVE SET-BUFFER-CHUNK RETRIEVAL OPERATION PROCEDURAL CONFLICT-RESOLUTION +t
15 L Caudate Motor L PFC ACC Visual R Caudate R PFC L Caudate Motor L PFC ACC Visual R Caudate R PFC The Connectivity Matrix Model Experimental Data R PFC R Caudate Visual ACC L PFC Motor L Caudate R PFC R Caudate Visual ACC L PFC Motor L Caudate
16 Negative Values Are Important Prat, Stocco et al., submitted
17 Summary, part 1 The effect of production rules can be measured through effective connectivity Effective connectivity patterns can be used to test ACT-R models However: Negative values pose a problem Suggest inhibitory production rules
18 Exchanging information across buffers Question 1: Is it compatible with basal ganglia anatomy? Question 2: Are we missing something crucial from basal ganglia anatomy
19 Basal Ganglia physiology and ACT-R Buffer Buffer Buffer Thalamus Striatum Matching Striatum Selection Pallidum Substantia Nigra Pallidum Execution Thalamus Procedural Module
20 Basal Ganglia physiology and ACT-R Thalamus Substantia Nigra Pallidum + + D2(-) Indirect Pathway (NO GO) Striatum D1(+) Direct Pathway (GO) + To Frontal Cortex
21 Probabilistic Stimulus Selection (PSS) Choose Accuracy Avoid Accuracy まみ Correct! Feedback Choice タ 70% ま 80% と 60% み 20% の 30% れ 40% まと No Feedback Choice タ 70% ま 80% と 60% み 20% の 30% れ 40% Training Phase Test Phase Frank, Seeberger, & O Reilly, 2004, Science
22 Influence of Dopamine on Choose and Avoid Accuracies Accuracy (%) Frank, Seeberger, O Reilly, Controls Controls 50 Choose Decision Strategy Avoid
23 Dopamine in Parkinson Disease HO OH NH 2 Dopamine Dopamine gap Healthy control -1 Parkinson Excess Dopamine -1 Parkinson, on meds
24 Accuracy (%) Influence of Dopamine on Go & No-Go 100 Frank, Seeberger, O Reilly, Controls PD, Off 50 Choose Decision Strategy Avoid
25 Accuracy (%) Influence of Dopamine on Go & No-Go 100 Frank, Seeberger, O Reilly, Controls PD, On PD, Off 50 Choose Decision Strategy Avoid
26 Straightforward model まみ PSS Task Visual Module Left: A Right: B Object Choose A ACT-R Choose B Choose C Choose D Visual Module Left Location Choose E Respond Choose F Motor Module Index Left Press Manual Procedural Module
27 Learning rate α? Expected noise s? Alpha = 0.20, Noise = 0.10 Alpha = 0.18, Noise = 0.10 Alpha = 0.15, Noise = 0.10 Alpha = 0.13, Noise = 0.10 Alpha = 0.10, Noise = Alpha = 0.20, Noise = 0.10 Alpha = 0.20, Noise = 0.08 Alpha = 0.20, Noise = 0.06 Alpha = 0.20, Noise = 0.04 Alpha = 0.20, Noise = Choose A Avoid B 0.5 Choose A Avoid B
28 A Dual-Pathway Model まみ PSS Task まみ PSS Task Visual Module Left: A Right: B Object Standard ACT-R Choose A Choose B Visual Module Left: A Right: B Object ACT-R With Competitive Pathways Choose A Avoid A Choose B Avoid B Choose C Choose D Choose C Avoid C Choose D Avoid D Choose E Choose F Choose E Avoid E Choose F Avoid F Visual Module Left Location Visual Module Left Location Respond Respond Motor Module Index Left Press Manual Procedural Module Motor Module Index Left Press Manual Procedural Module
29 Results D1 = 1.00, D2 = 1.00 D1 = 1.00, D2 = 0.75 D1 = 1.00, D2 = 0.50 D1 = 1.00, D2 = 0.25 D1 = 1.00, D2 = D1 = 1.00, D2 = D1 = 0.75, D2 = 1.00 D1 = 0.50, D2 = 1.00 D1 = 0.25, D2 = 1.00 D1 = 0.10, D2 = Choose A Avoid B 0.5 Choose A Avoid B
30 Results (Default parameters) Comtrol PD, On PD, Off 0.5 Choose A Avoid B Stocco, submitted
31 Implications for Executive Functions Press left if you see a square or or Congruent Trials Incongruent Trials
32 Experimental Results
33 Simon Task Model Task Model Visual Buffer Circle Left Process Shape Don t Process Shape Process Position Don t Process Position Working Memory Module Circle --- Motor Module Spreading Activation Respond Long-Term Memory Module Task Rule 1 Square Left Task Rule 2 Circle Right
34 Model predictions Stocco et al., submitted
35 Fluid Intelligence: Raven s Advanced Progressive Matrices (RAPM)
36 Raven's Score Raven's Score Results: Experiment 1 (N = 95) Correlation between Avoid and Intelligence Correlation between Choose and Intelligence R = 0.34 R = Avoid Accuracy Choose Accuracy
37 Abbreviated Raven's Score Raven's Score Replication: Experiment 2 (N = 83) Correlation between Avoid and Intelligence Correlation between Choose and Intelligence R = 0.24 R = Avoid Accuracy Choose Accuracy
38 Model Strategy Start Retrieve solution Found? Select feature Find pattern Select rule Time from last rule > Criterion? Uses time from last successful rule identification to decide when no progress can be made Done? End
39 Crucial Steps Start Retrieve solution Pick Feature Found? Select feature Pick F1 Don t Pick F1 Pick F2 Don t Pick F2 Pick FN Don t Pick FN Find pattern Select rule Pick Rule Done? End Pick Rule 1 Don t Pick Rule 1 Pick Rule 2 Don t Pick Rule 2 Pick Rule N Don t Pick Rule N
40 Model Predictions 0.8 % RAPM Problems Solved D2 = 1.00 D2 = 0.75 D2 = 0.50 D2 = 0.25 D2 = 0.10
41 Mean brain activity during problems p < 0.05, FWE-corrected
42 Negative correlation with Accuracy Bilateral Basal Ganglia
43 Mean Problem Accuracy Negative correlations in the BG Striatum R = Mean Problem Related Activity
44 Dynamic Causal Modeling Imaginal Retrieval Visual Caudate
45 Accuracy Dynamic Causal Modeling Modulatory Effect of BG on Negative Connectivity Value (Visual to Prefrontal) R = 0.35, p = Parameter Value
46 Summary, part 2 The effect of production rules can be measured through effective connectivity Effective connectivity patterns can be used to test ACT-R models Anatomically, we are missing the functional distinction between two pathways It seems to play an important functional role across multiple domains.
47 Thank You! The Basal UW Chantel Prat Lauren Graham Brianna Yamasaki Jose Ceballos Patrick Rice Michael McDonald Nicole Murray
48 After the talk EXTRA SLIDES
49 Plausibility of BG as Production Rules D C B A Cortex, Layer 2/3 from D from C from B from A A B C D Striatal Interneurons Cortex, Layer 4 from D Striatum from C from B from A from D from C from B from A to A to B to C to D GPi/SNr from D from C from B from A to A to B to C to D Thalamus from D from C from B from A to A to B to C to D from D from C from B from A to A B C D A B C D from D from C from B from A STN from D from C from B from A to A to B to C to D GPe SNc Interneurons Stewart, Berkolay, & SNc Eliasmith, 2012, Front Neurosci. Stocco, Lebiere, & Anderson, 2010, Psych Review. O Reilly & Frank, 2006, Neural Netw. Terrence Stewart Randy O Reilly
50 % BOLD Change A Few Empirical Verifications Anderson, 2005: Basal ganglia activity varies with number of rules Left Caudate Nucleus Stocco & Anderson, 2008: Basal Scan ganglia activity varies with number of variables in a rule Stocco & Prat, 2014: Basal ganglia activity varies with bilingualism (larger set of rules!)
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia
 Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre
Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function. NS201c
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND
 THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD How did I get here? What did I do? Start driving home after work Aware when you left
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD How did I get here? What did I do? Start driving home after work Aware when you left
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale
 Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
Neural Cognitive Modelling: A Biologically Constrained Spiking Neuron Model of the Tower of Hanoi Task
 Neural Cognitive Modelling: A Biologically Constrained Spiking Neuron Model of the Tower of Hanoi Task Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre for Theoretical
Neural Cognitive Modelling: A Biologically Constrained Spiking Neuron Model of the Tower of Hanoi Task Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre for Theoretical
On the nature of Rhythm, Time & Memory. Sundeep Teki Auditory Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging University College London
 On the nature of Rhythm, Time & Memory Sundeep Teki Auditory Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging University College London Timing substrates Timing mechanisms Rhythm and Timing Unified timing
On the nature of Rhythm, Time & Memory Sundeep Teki Auditory Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging University College London Timing substrates Timing mechanisms Rhythm and Timing Unified timing
Neural Cognitive Modelling: A Biologically Constrained Spiking Neuron Model of the Tower of Hanoi Task
 Neural Cognitive Modelling: A Biologically Constrained Spiking Neuron Model of the Tower of Hanoi Task Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre for Theoretical
Neural Cognitive Modelling: A Biologically Constrained Spiking Neuron Model of the Tower of Hanoi Task Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre for Theoretical
Symbolic Reasoning in Spiking Neurons: A Model of the Cortex/Basal Ganglia/Thalamus Loop
 Symbolic Reasoning in Spiking Neurons: A Model of the Cortex/Basal Ganglia/Thalamus Loop Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca)
Symbolic Reasoning in Spiking Neurons: A Model of the Cortex/Basal Ganglia/Thalamus Loop Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca)
Learning Working Memory Tasks by Reward Prediction in the Basal Ganglia
 Learning Working Memory Tasks by Reward Prediction in the Basal Ganglia Bryan Loughry Department of Computer Science University of Colorado Boulder 345 UCB Boulder, CO, 80309 loughry@colorado.edu Michael
Learning Working Memory Tasks by Reward Prediction in the Basal Ganglia Bryan Loughry Department of Computer Science University of Colorado Boulder 345 UCB Boulder, CO, 80309 loughry@colorado.edu Michael
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
The Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes 3/2/2011. Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions. Readings: KW Ch.
 The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
Connections of basal ganglia
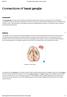 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Research Article A Biologically Inspired Computational Model of Basal Ganglia in Action Selection
 Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Volume 25, Article ID 8747, 24 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/25/8747 Research Article A Biologically Inspired Computational Model of Basal Ganglia in Action Selection
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Volume 25, Article ID 8747, 24 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/25/8747 Research Article A Biologically Inspired Computational Model of Basal Ganglia in Action Selection
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Cortico-Striatal Connections Predict Control over Speed and Accuracy in Perceptual Decision Making
 Cortico-Striatal Connections Predict Control over Speed and Accuracy in Perceptual Decision Making Birte U. Forstmann 1,*, Andreas Schäfer 2, Alfred Anwander 2, Jane Neumann 2, Scott Brown 3, Eric-Jan
Cortico-Striatal Connections Predict Control over Speed and Accuracy in Perceptual Decision Making Birte U. Forstmann 1,*, Andreas Schäfer 2, Alfred Anwander 2, Jane Neumann 2, Scott Brown 3, Eric-Jan
Huntington s Disease COGS 172
 Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Reinforcement Learning, Conflict Monitoring, and Cognitive Control: An Integrative Model of Cingulate-Striatal Interactions and the ERN
 17 Reinforcement Learning, Conflict Monitoring, and Cognitive Control: An Integrative Model of Cingulate-Striatal Interactions and the ERN Jeffrey Cockburn and Michael Frank Fortune favors those who are
17 Reinforcement Learning, Conflict Monitoring, and Cognitive Control: An Integrative Model of Cingulate-Striatal Interactions and the ERN Jeffrey Cockburn and Michael Frank Fortune favors those who are
Page # Perception and Action. Lecture 3: Perception & Action. ACT-R Cognitive Architecture. Another (older) view
 Perception and Action Lecture 3: Perception & Action Cognition is a lot, but not enough! We want models to perceive stimuli in the outside world respond by acting in the outside world This gives us a more
Perception and Action Lecture 3: Perception & Action Cognition is a lot, but not enough! We want models to perceive stimuli in the outside world respond by acting in the outside world This gives us a more
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
A model of dual control mechanisms through anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex interactions
 Neurocomputing 69 (2006) 1322 1326 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom A model of dual control mechanisms through anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex interactions Nicola De Pisapia, Todd S. Braver Cognitive
Neurocomputing 69 (2006) 1322 1326 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom A model of dual control mechanisms through anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex interactions Nicola De Pisapia, Todd S. Braver Cognitive
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
A Grey Box Neural Network Model of Basal Ganglia for Gait Signal of Patients with Huntington Disease
 Basic and Clinical April 2016. Volume 7. Number 2 A Grey Box Neural Network Model of Basal Ganglia for Gait Signal of Patients with Huntington Disease Abbas Pourhedayat 1, Yashar Sarbaz 1* 1. Department
Basic and Clinical April 2016. Volume 7. Number 2 A Grey Box Neural Network Model of Basal Ganglia for Gait Signal of Patients with Huntington Disease Abbas Pourhedayat 1, Yashar Sarbaz 1* 1. Department
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease
 Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease Alexander Hui Department of Bioengineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 alexhui@ucsd.edu Abstract Parkinson s disease is a slowly progressing
Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease Alexander Hui Department of Bioengineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 alexhui@ucsd.edu Abstract Parkinson s disease is a slowly progressing
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
A Computational Model of Complex Skill Learning in Varied-Priority Training
 A Computational Model of Complex Skill Learning in Varied-Priority Training 1 Wai-Tat Fu (wfu@illinois.edu), 1 Panying Rong, 1 Hyunkyu Lee, 1 Arthur F. Kramer, & 2 Ann M. Graybiel 1 Beckman Institute of
A Computational Model of Complex Skill Learning in Varied-Priority Training 1 Wai-Tat Fu (wfu@illinois.edu), 1 Panying Rong, 1 Hyunkyu Lee, 1 Arthur F. Kramer, & 2 Ann M. Graybiel 1 Beckman Institute of
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Linking thought and movement simultaneously! Forebrain Basal ganglia Midbrain and
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Linking thought and movement simultaneously! Forebrain Basal ganglia Midbrain and
Organization of the nervous system 2
 Organization of the nervous system 2 Raghav Rajan Bio 334 Neurobiology I August 22nd 2013 1 Orienting within the brain absolute axes and relative axes SUPERIOR (above) ANTERIOR (in front) Anterior/Posterior,
Organization of the nervous system 2 Raghav Rajan Bio 334 Neurobiology I August 22nd 2013 1 Orienting within the brain absolute axes and relative axes SUPERIOR (above) ANTERIOR (in front) Anterior/Posterior,
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease
 Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
BUILDING A BEHAVING BRAIN
 BUILDING A BEHAVING BRAIN Chris Eliasmith One of the grand challenges that the National Academy of Engineers identified is to reverse engineer the brain. Neuroscientists and psychologists would no doubt
BUILDING A BEHAVING BRAIN Chris Eliasmith One of the grand challenges that the National Academy of Engineers identified is to reverse engineer the brain. Neuroscientists and psychologists would no doubt
The Neurobiology of Attention
 The Neurobiology of Attention by Nadia Fike, MD/PhD Pediatric Neurology Center for Neurosciences Disclosures Nadia Fike, MD/PhD No relevant financial or nonfinancial relationships to disclose. Objectives
The Neurobiology of Attention by Nadia Fike, MD/PhD Pediatric Neurology Center for Neurosciences Disclosures Nadia Fike, MD/PhD No relevant financial or nonfinancial relationships to disclose. Objectives
Reinforcement learning and the brain: the problems we face all day. Reinforcement Learning in the brain
 Reinforcement learning and the brain: the problems we face all day Reinforcement Learning in the brain Reading: Y Niv, Reinforcement learning in the brain, 2009. Decision making at all levels Reinforcement
Reinforcement learning and the brain: the problems we face all day Reinforcement Learning in the brain Reading: Y Niv, Reinforcement learning in the brain, 2009. Decision making at all levels Reinforcement
Brain Dynamics, Reward, & Mocap
 Brain Dynamics, Reward, & Mocap Howard Poizner and David Peterson I. MC/BDL Developments II. Project 2.1.3 Update A. Science meets Art (With Scott Makeig & Terry Sejnowski) B. VR System Development a.
Brain Dynamics, Reward, & Mocap Howard Poizner and David Peterson I. MC/BDL Developments II. Project 2.1.3 Update A. Science meets Art (With Scott Makeig & Terry Sejnowski) B. VR System Development a.
Allen Newell December 4, 1991 Great Questions of Science
 Allen Newell December 4, 1991 Great Questions of Science You need to realize if you haven t before that there is this collection of ultimate scientific questions and if you are lucky to get grabbed by
Allen Newell December 4, 1991 Great Questions of Science You need to realize if you haven t before that there is this collection of ultimate scientific questions and if you are lucky to get grabbed by
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review
 The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
THE FORMATION OF HABITS The implicit supervision of the basal ganglia
 THE FORMATION OF HABITS The implicit supervision of the basal ganglia MEROPI TOPALIDOU 12e Colloque de Société des Neurosciences Montpellier May 1922, 2015 THE FORMATION OF HABITS The implicit supervision
THE FORMATION OF HABITS The implicit supervision of the basal ganglia MEROPI TOPALIDOU 12e Colloque de Société des Neurosciences Montpellier May 1922, 2015 THE FORMATION OF HABITS The implicit supervision
Evaluating the roles of the basal ganglia and the cerebellum in time perception
 Sundeep Teki Evaluating the roles of the basal ganglia and the cerebellum in time perception Auditory Cognition Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging SENSORY CORTEX SMA/PRE-SMA HIPPOCAMPUS BASAL
Sundeep Teki Evaluating the roles of the basal ganglia and the cerebellum in time perception Auditory Cognition Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging SENSORY CORTEX SMA/PRE-SMA HIPPOCAMPUS BASAL
Geography of the Forehead
 5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
By Carrot or by Stick: Cognitive Reinforcement Learning in Parkinsonism
 By Carrot or by Stick: Cognitive Reinforcement Learning in Parkinsonism Michael J. Frank, 1* Lauren C. Seeberger, 2 Randall C. O Reilly 1* 1 Department of Psychology and Center for Neuroscience, University
By Carrot or by Stick: Cognitive Reinforcement Learning in Parkinsonism Michael J. Frank, 1* Lauren C. Seeberger, 2 Randall C. O Reilly 1* 1 Department of Psychology and Center for Neuroscience, University
Prefrontal cortex. Executive functions. Models of prefrontal cortex function. Overview of Lecture. Executive Functions. Prefrontal cortex (PFC)
 Neural Computation Overview of Lecture Models of prefrontal cortex function Dr. Sam Gilbert Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience University College London E-mail: sam.gilbert@ucl.ac.uk Prefrontal cortex
Neural Computation Overview of Lecture Models of prefrontal cortex function Dr. Sam Gilbert Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience University College London E-mail: sam.gilbert@ucl.ac.uk Prefrontal cortex
Cognitive Control as Alternation of Activation and Suppression in the Stroop Task
 Cognitive Control as Alternation of Activation and Suppression in the Stroop Task Ion Juvina (ijuvina@andrew.cmu.edu) Niels A. Taatgen (taatgen@cmu.edu) Daniel Dickison (danieldickison@cmu.edu) Department
Cognitive Control as Alternation of Activation and Suppression in the Stroop Task Ion Juvina (ijuvina@andrew.cmu.edu) Niels A. Taatgen (taatgen@cmu.edu) Daniel Dickison (danieldickison@cmu.edu) Department
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
A Neurocomputational Model of Dopamine and Prefrontal Striatal Interactions during Multicue Category Learning by Parkinson Patients
 A Neurocomputational Model of Dopamine and Prefrontal Striatal Interactions during Multicue Category Learning by Parkinson Patients Ahmed A. Moustafa and Mark A. Gluck Abstract Most existing models of
A Neurocomputational Model of Dopamine and Prefrontal Striatal Interactions during Multicue Category Learning by Parkinson Patients Ahmed A. Moustafa and Mark A. Gluck Abstract Most existing models of
Conditional Routing of Information to the Neocortex: A Network Model of Basal Ganglia Function
 Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Department of Psychology Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences November 2008 Conditional Routing of Information to the Neocortex: A Network
Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Department of Psychology Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences November 2008 Conditional Routing of Information to the Neocortex: A Network
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Dysfunctional and compensatory synaptic plasticity in Parkinson s disease
 European Journal of Neuroscience European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 39, pp. 688 702, 2014 doi:10.1111/ejn.12434 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Dysfunctional and compensatory synaptic plasticity in
European Journal of Neuroscience European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 39, pp. 688 702, 2014 doi:10.1111/ejn.12434 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Dysfunctional and compensatory synaptic plasticity in
COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN PARKINSON S DISEASE
 1 GENERAL INTRODUCTION GENERAL INTRODUCTION PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative movement disorder, named after James Parkinson who described some of its characteristic
1 GENERAL INTRODUCTION GENERAL INTRODUCTION PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative movement disorder, named after James Parkinson who described some of its characteristic
Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps
 Training course: Real-time fmri: Fundamental Principles for Clinical Applications Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps David Linden Cardiff University 1) What is your clinical
Training course: Real-time fmri: Fundamental Principles for Clinical Applications Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps David Linden Cardiff University 1) What is your clinical
Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing
 Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk
 Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk... and corresponding risk prediction errors Peter Bossaerts 1 Contents 1. Reward Encoding And The Dopaminergic System 2. Reward Prediction Errors And TD (Temporal
Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk... and corresponding risk prediction errors Peter Bossaerts 1 Contents 1. Reward Encoding And The Dopaminergic System 2. Reward Prediction Errors And TD (Temporal
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cognitive change in Parkinson's disease Broeders, M. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cognitive change in Parkinson's disease Broeders, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Broeders, M. (2015). Cognitive change in Parkinson's
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cognitive change in Parkinson's disease Broeders, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Broeders, M. (2015). Cognitive change in Parkinson's
Study of Verbal Working Memory in Patients with Parkinson s Disease
 Study of Verbal Working Memory in Patients with Parkinson s Disease Gilbert, Belleville, Bherer, & Chouinard, 2005 presented by Jonathan Reinharth May 2, 2005 Parkinson s Disease Symptoms: resting tremors,
Study of Verbal Working Memory in Patients with Parkinson s Disease Gilbert, Belleville, Bherer, & Chouinard, 2005 presented by Jonathan Reinharth May 2, 2005 Parkinson s Disease Symptoms: resting tremors,
2 Summary of Part I: Basic Mechanisms. 4 Dedicated & Content-Specific
 1 Large Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 2 Summary of Part I: Basic Mechanisms 2. Distributed Representations 5. Error driven Learning 1. Biological realism w = δ j ai+ aia j w = δ j ai+ aia j
1 Large Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 2 Summary of Part I: Basic Mechanisms 2. Distributed Representations 5. Error driven Learning 1. Biological realism w = δ j ai+ aia j w = δ j ai+ aia j
Effort, Reward, and Behavior: The Role of A2a receptors on Effort Guided Decision Making
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2013 Effort, Reward, and Behavior: The Role of A2a receptors on Effort Guided Decision Making Heidi Guenther
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2013 Effort, Reward, and Behavior: The Role of A2a receptors on Effort Guided Decision Making Heidi Guenther
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
3 A Tripartite Cognitive Architecture. 4 Broad Points
 1 Prefrontal-Hippocampal Interactions: Computational Perspective Randall C. O Reilly Department of Psychology Center for Neuroscience Institute of Cognitive Science University of Colorado Boulder 2 Tripartite
1 Prefrontal-Hippocampal Interactions: Computational Perspective Randall C. O Reilly Department of Psychology Center for Neuroscience Institute of Cognitive Science University of Colorado Boulder 2 Tripartite
How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics
 How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics Hecke CNS Seminar WS 2006/07 Motivation Motivation Ferdinand Porsche "Wir wollen Autos bauen, die keiner braucht aber jeder haben will." Outline 1 Introduction
How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics Hecke CNS Seminar WS 2006/07 Motivation Motivation Ferdinand Porsche "Wir wollen Autos bauen, die keiner braucht aber jeder haben will." Outline 1 Introduction
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Research Article A Functional Model of Sensemaking in a Neurocognitive Architecture
 Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Volume 213, Article ID 921695, 29 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/921695 Research Article A Functional Model of Sensemaking in a Neurocognitive Architecture
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Volume 213, Article ID 921695, 29 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/921695 Research Article A Functional Model of Sensemaking in a Neurocognitive Architecture
Effects of nicotine on neuronal firing patterns in human subthalamic nucleus. Kim Scott Mentor: Henry Lester SURF seminar, January 15, 2009
 Effects of nicotine on neuronal firing patterns in human subthalamic nucleus Kim Scott Mentor: Henry Lester SURF seminar, January 15, 2009 Smoking tobacco protects against Parkinson s Disease (PD). Identical
Effects of nicotine on neuronal firing patterns in human subthalamic nucleus Kim Scott Mentor: Henry Lester SURF seminar, January 15, 2009 Smoking tobacco protects against Parkinson s Disease (PD). Identical
 Passport control a bit carried away. appreciated the advice forgot to talk to the manager, next thing I know my fmri thankfully, when aroused things back to normal Inattentive impaired children and adolescents:
Passport control a bit carried away. appreciated the advice forgot to talk to the manager, next thing I know my fmri thankfully, when aroused things back to normal Inattentive impaired children and adolescents:
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura Avanzino
 Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Biomedical Technology Research Center 2011 Workshop San Francisco, CA
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes
 Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes Poster No.: C-0851 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Onu, L. Badea,
Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes Poster No.: C-0851 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Onu, L. Badea,
Myeong-Ho Sohn 1. Curriculum Vitae. Correspondence Myeong-Ho Sohn Phone : (202) BH 345E Fax : (202) Pittsburgh, PA 15213
 Myeong-Ho Sohn 1 Curriculum Vitae Correspondence Myeong-Ho Sohn Phone : (202) 994-6322 BH 345E Fax : (202) 994-1602 Department of Psychology e-mail : mhsohn@gwu.edu Carnegie-Mellon University http://home.gwu.edu/~mhsohn/
Myeong-Ho Sohn 1 Curriculum Vitae Correspondence Myeong-Ho Sohn Phone : (202) 994-6322 BH 345E Fax : (202) 994-1602 Department of Psychology e-mail : mhsohn@gwu.edu Carnegie-Mellon University http://home.gwu.edu/~mhsohn/
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
Study of habit learning impairments in Tourette syndrome and obsessive-compulsive disorder using reinforcement learning models
 Study of habit learning impairments in Tourette syndrome and obsessive-compulsive disorder using reinforcement learning models Vasco Conceição Instituto Superior Técnico Instituto de Medicina Molecular
Study of habit learning impairments in Tourette syndrome and obsessive-compulsive disorder using reinforcement learning models Vasco Conceição Instituto Superior Técnico Instituto de Medicina Molecular
Time Perception: Beyond Simple Interval Estimation
 Time Perception: Beyond Simple Interval Estimation Niels Taatgen 12 (taatgen@cmu.edu), Hedderik van Rijn 12 (hedderik@ai.rug.nl) and John Anderson 1 (ja@cmu.edu) 1 Carnegie Mellon University, Department
Time Perception: Beyond Simple Interval Estimation Niels Taatgen 12 (taatgen@cmu.edu), Hedderik van Rijn 12 (hedderik@ai.rug.nl) and John Anderson 1 (ja@cmu.edu) 1 Carnegie Mellon University, Department
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS. specifications
 NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
What goes wrong with balance in Parkinson s Disease? Fay B Horak, PhD, PT Professor of Neurology Oregon Health and Science. CoM
 What goes wrong with balance in Parkinson s Disease? Fay B Horak, PhD, PT Professor of Neurology Oregon Health and Science CoM CoM Course Objectives Understand different types of balance systems affected
What goes wrong with balance in Parkinson s Disease? Fay B Horak, PhD, PT Professor of Neurology Oregon Health and Science CoM CoM Course Objectives Understand different types of balance systems affected
9/13/2018. Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
 DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Neil P. Jones 7th Annual Conference on ADHD and Executive Function September 14, 218 Diagnosis Child
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Neil P. Jones 7th Annual Conference on ADHD and Executive Function September 14, 218 Diagnosis Child
Computational Psychiatry and Neurology. Michael J. Frank Laboratory for Neural Computation and Cognition Brown University
 Computational Psychiatry and Neurology Michael J. Frank Laboratory for Neural Computation and Cognition Brown University Computation as a link between brain, mind, and pathology Computation as a link
Computational Psychiatry and Neurology Michael J. Frank Laboratory for Neural Computation and Cognition Brown University Computation as a link between brain, mind, and pathology Computation as a link
A Neural Model of Context Dependent Decision Making in the Prefrontal Cortex
 A Neural Model of Context Dependent Decision Making in the Prefrontal Cortex Sugandha Sharma (s72sharm@uwaterloo.ca) Brent J. Komer (bjkomer@uwaterloo.ca) Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Chris
A Neural Model of Context Dependent Decision Making in the Prefrontal Cortex Sugandha Sharma (s72sharm@uwaterloo.ca) Brent J. Komer (bjkomer@uwaterloo.ca) Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Chris
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
CAREGIVER SUMMIT. The PD You Can't See: Dealing with Non-Motor Symptoms. Kaitlyn Roland, PhD. Sponsored by:
 CAREGIVER SUMMIT The PD You Can't See: Dealing with Non-Motor Symptoms Kaitlyn Roland, PhD Sponsored by: Cognition VS Dementia Memory Executive Function Attention Bradyphrenia Visuospatial Language Hallucinations
CAREGIVER SUMMIT The PD You Can't See: Dealing with Non-Motor Symptoms Kaitlyn Roland, PhD Sponsored by: Cognition VS Dementia Memory Executive Function Attention Bradyphrenia Visuospatial Language Hallucinations
